Label: NORETHINDRONE ACETATE tablet
- NDC Code(s): 68462-304-05, 68462-304-50
- Packager: Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Inc., USA
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Abbreviated New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated December 6, 2018
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
DESCRIPTION
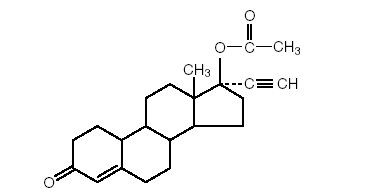
Norethindrone acetate tablets USP - 5 mg oral tablets Norethindrone acetate USP, (17-hydroxy-19-nor-17α-pregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one acetate), a synthetic, orally active progestin, is the acetic acid ester of norethindrone. It is a white, or creamy white, crystalline powder.
Norethindrone acetate tablets USP, 5 mg contain the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and talc.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Norethindrone acetate induces secretory changes in an estrogen-primed endometrium. On a weight basis, it is twice as potent as norethindrone.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption:
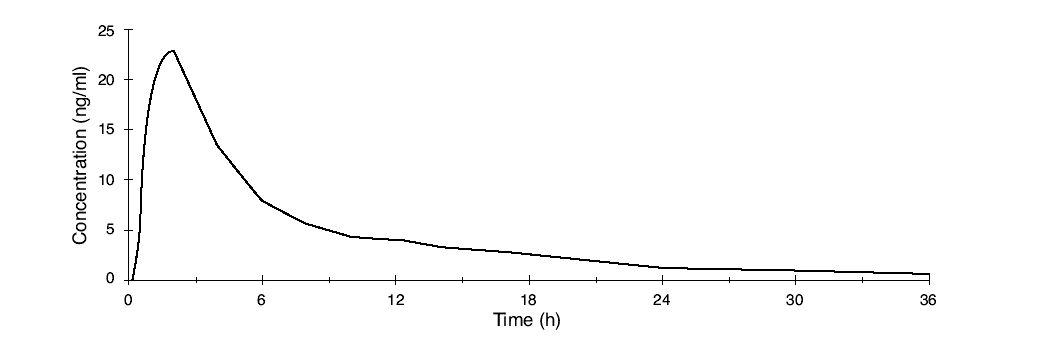
Norethindrone acetate is completely and rapidly deacetylated to norethindrone (NET) after oral administration, and the disposition of norethindrone acetate is indistinguishable from that of orally administered norethindrone. Norethindrone acetate is rapidly absorbed from norethindrone acetate tablets, with maximum plasma concentration of norethindrone generally occurring at about 2 hours post-dose. The pharmacokinetic parameters of norethindrone following single oral administration of norethindrone acetate in 29 healthy female volunteers are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1 Pharmacokinetic Parameters after a Single Dose of Norethindrone Acetate in Healthy Women Norethindrone Acetate (n=29) Arithmetic Mean ± SD
Norethindrone (NET)
AUC (0-inf) (ng/ml*h)
166.90 ± 56.28
Cmax (ng/ml)
26.19 ± 6.19
tmax (h)
1.83 ± 0.58
t1/2 (h)
8.51 ± 2.19
AUC = area under the curve,
Cmax = maximum plasma concentration,
tmax = time at maximum plasma concentration,
t1/2 = half-life,
SD = standard deviation
Effect of Food:
The effect of food administration on the pharmacokinetics of norethindrone acetate has not been studied.
Distribution:
Norethindrone is 36% bound to sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) and 61% bound to albumin. Volume of distribution of norethindrone is about 4 L/kg.
Metabolism:
Norethindrone undergoes extensive biotransformation, primarily via reduction, followed by sulfate and glucuronide conjugation. The majority of metabolites in the circulation are sulfates, with glucuronides accounting for most of the urinary metabolites.
Excretion:
Plasma clearance value for norethindrone is approximately 0.4 L/hr/kg. Norethindrone is excreted in both urine and feces, primarily as metabolites. The mean terminal elimination half- life of norethindrone following a single dose administration of norethindrone acetate is approximately 9 hours.
Special Populations
Geriatrics:
The effect of age on the pharmacokinetics of norethindrone after norethindrone acetate administration has not been evaluated.
Race:
The effect of race on the disposition of norethindrone after norethindrone acetate administration has not been evaluated.
Renal Insufficiency:
The effect of renal disease on the disposition of norethindrone after norethindrone acetate administration has not been evaluated. In pre-menopausal women with chronic renal failure undergoing peritoneal dialysis who received multiple doses of an oral contraceptive containing ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone, plasma norethindrone concentration was unchanged compared to concentrations in pre-menopausal women with normal renal function.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Norethindrone acetate is indicated for the treatment of secondary amenorrhea, endometriosis, and abnormal uterine bleeding due to hormonal imbalance in the absence of organic pathology, such as submucous fibroids or uterine cancer. Norethindrone acetate is not intended, recommended or approved to be used with concomitant estrogen therapy in postmenopausal women for endometrial protection.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- •
- Known or suspected pregnancy. There is no indication for norethindrone acetate in pregnancy. (See PRECAUTIONS ).
- •
- Undiagnosed vaginal bleeding
- •
- Known, suspected or history of cancer of the breast
- •
- Active deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism or history of these conditions
- •
- Active or recent (e.g., within the past year) arterial thromboembolic disease (e.g., stroke, myocardial infarction)
- •
- Impaired liver function or liver disease
- •
- As a diagnostic test for pregnancy
- •
- Hypersensitivity to any of the drug components
-
WARNINGS
1. Cardiovascular disorders
Patients with risk factors for arterial vascular disease (e.g., hypertension, diabetes mellitus, tobacco use, hypercholesterolemia, and obesity) and/or venous thromboembolism (e.g., personal history or family history of VTE, obesity, and systemic lupus erythematosus) should be managed appropriately.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
- •
- Because this drug may cause some degree of fluid retention, conditions which might be influenced by this factor, such as epilepsy, migraine, cardiac or renal dysfunctions, require careful observation
- •
- In cases of breakthrough bleeding, and in all cases of irregular bleeding per vagina, nonfunctional causes should be borne in mind. In cases of undiagnosed vaginal bleeding, adequate diagnostic measures are indicated
- •
- Patients who have a history of clinical depression should be carefully observed and the drug discontinued if the depression recurs to a serious degree
- •
- Data suggest that progestin therapy may have adverse effects on lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. The choice of progestin, its dose, and its regimen may be important in minimizing these adverse effects, but these issues will require further study before they are clarified. Women with hyperlipidemias and/or diabetes should be monitored closely during progestin therapy
- •
- The pathologist should be advised of progestin therapy when relevant specimens are submitted
Information for the Patient
Healthcare providers are advised to discuss the PATIENT INFORMATION leaflet with patients for whom they prescribe norethindrone acetate.
Drug/Laboratory Tests Interactions
The following laboratory test results may be altered by the use of estrogen/progestin combination drugs:
- •
- Accelerated prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time, and platelet aggregation time; increased platelet count; increased factors II, VII antigen, VIII antigen, VIII coagulant activity, IX, X, XII, VII-X complex, II-VII-X complex, and beta-thromboglobulin; decreased levels of antifactor Xa and antithrombin III, decreased antithrombin III activity; increased levels of fibrinogen and fibrinogen activity; increased plasminogen antigen and activity.
- •
- Increased thyroid-binding globulin (TBG) levels leading to increased circulating total thyroid hormone levels as measured by protein-bound iodine (PBI), T4 levels (by column or by radioimmunoassay) or T3 levels by radio immunoassay. T3 resin uptake is decreased, reflecting the elevated TBG. Free T4 and free T3 concentrations are unaltered. Patients on thyroid replacement therapy may require higher doses of thyroid hormone.
- •
- Other binding proteins may be elevated in serum (i.e., corticosteroid binding globulin (CBG), sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG)) leading to increased circulating corticosteroid and sex steroids, respectively. Free or biologically active hormone concentratios are unchanged. Other plasma proteins may be increased (angiotensinogen/renin substrate, alpha-1-antitrypsin, ceruloplasmin).
- •
- Increased plasma HDL and HDL2 cholesterol subfraction concentrations, reduced LDL cholesterol concentration, increased triglycerides levels.
- •
- Impaired glucose metabolism.
- •
- Reduced response to metyrapone test.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
Some beagle dogs treated with medroxyprogesterone acetate developed mammary nodules. Although nodules occasionally appeared in control animals, they were intermittent in nature, whereas nodules in treated animals were larger and more numerous, and persisted. There is no general agreement as to whether the nodules are benign or malignant. Their significance with respect to humans has not been established.
Pregnancy Category X
Norethindrone acetate is contraindicated during pregnancy as it may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. Several reports suggest an association between intrauterine exposure to progestational drugs in the first trimester of pregnancy and congenital abnormalities in male and female fetuses. Some progestational drugs induce mild virilization of the external genitalia of female fetuses.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
See WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS The following adverse reactions have been observed in women taking progestins:
- •
- Breakthrough bleeding
- •
- Spotting
- •
- Change in menstrual flow
- •
- Amenorrhea
- •
- Edema
- •
- Changes in weight (decreases, increases)
- •
- Changes in the cervical squamo-columnar junction and cervical secretions
- •
- Cholestatic jaundice
- •
- Rash (allergic) with and without pruritus
- •
- Melasma or chloasma
- •
- Clinical depression
- •
- Ace
- •
- Breast enlargement/tenderness
- •
- Headache/migraine
- •
- Urticaria
- •
- Abnormalities of liver tests (i.e., AST, ALT, Bilirubin)
- •
- Decreased HDL cholesterol and increased LDL/HDL ratio
- •
- Mood swings
- •
- Nausea
- •
- Insomnia
- •
- Anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions
- •
- Thrombotic and thromboembolic events (e.g., deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, retinal vascular thrombosis, cerebral thrombosis and embolism)
- •
- Optic neuritis (which may lead to partial or complete loss of vision)
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Therapy with norethindrone acetate must be adapted to the specific indications and therapeutic response of the individual patient.
Secondary amenorrhea, abnormal uterine bleeding due to hormonal imbalance in the absence of organic pathology:
2.5 to 10 mg norethindrone acetate may be given daily for 5 to 10 days to produce secretory transformation of an endometrium that has been adequately primed with either endogenous or exogenous estrogen.
Progestin withdrawal bleeding usually occurs within three to seven days after discontinuing norethindrone acetate therapy. Patients with a past history of recurrent episodes of abnormal uterine bleeding may benefit from planned menstrual cycling with norethindrone acetate.
Endometriosis:
Initial daily dosage of 5 mg norethindrone acetate for two weeks. Dosage should be increased by2.5 mg per day every two weeks until 15 mg per day of norethindrone acetate is reached. Therapy may be held at this level for six to nine months or until annoying breakthrough bleeding demands temporary termination.
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
-
PATIENT INFORMATION
Norethindrone acetate tablets USP, 5 mg
Read this PATIENT INFORMATION before you start taking norethindrone acetate tablets and read what you get each time you refill norethindrone acetate tablets. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition.
What is the most important information I should know about norethindrone acetate (A Progestin Hormone) tablets?
- •
- Do not use norethindrone acetate if you are pregnant, breast-feeding or are trying to conceive.
- •
- Do not use northindrone acetate if you have had a previous blood clot, stroke, or heart attack.
- •
- Do not use norethindrone acetate if you are postmenopausal.
What is norethindrone acetate?
Norethindrone acetate is similar to the progesterone hormones naturally produced by the body. Your healthcare provider may provide norethindrone acetate as individual tablets.
What are norethindrone acetate tablets used for?
Norethindrone acetate tablets are used for the treatment of secondary amenorrhea (absence of menstrual periods in women who have previously had a menstrual period who are not pregnant), the treatment of endometriosis, and the treatment of irregular menstrual periods due to hormone imbalance.
Who should not take norethindrone acetate tablets?
You should not tke norethindrone acetate tablets if you are postmenopausal, pregnant or breast-feeding.
You should not take norethindrone acetate tablets if you have the following conditions:
- •
- Known or suspected pregnancy. Norethindrone acetate tablets are not indicated during pregnancy as it may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. There is an increased risk of minor birth defects in children whose mothers take norethindrone acetate during the first 4 months of pregnancy (mild masculinization of the external genitalia of the female fetus, as well as hypospadias in the male fetus). If you take norethindrone acetate and later find out you were pregnant, talk with your healthcare provider right away
- •
- History of blood clots in the legs, lungs, eyes, brain, or elsewhere, or a past history of these conditions
- •
- Liver impairment or disease
- •
- Known or suspected cancer of the breast. If you have or had cancer of the breast, talk with your healthcare provider about whether you should take norethindrone acetate
- •
- Undiagnosed vaginal bleeding
- •
- Hypersensitivity to norethindrone acetate tablets. See the end of this leaflet for a list of all of the ingredients in norethindrone acetate
What are the risks associated with norethindrone acetate tablets?
- •
-
Risk to the Fetus:
Norethindrone acetate tablets should not be used if you are pregnant. Norethindrone acetate tablets are contraindicated during pregnancy as it may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. There is an increased risk of minor birth defects in children whose mothers take this drug during the first 4 months of pregnancy. Several reports suggest an association between mothers who take these drugs in the first trimester of pregnancy and congenital abnormalities in male and female babies. Although it is not clear that these events were drug related, you should check with your healthcare provider about the risks to your unborn child of any medication taken during pregnancy.
You should avoid using norethindrone acetate tablets during pregnancy. If you take norethindrone acetate tablets and later find you were pregnant when you took it, be sure to discuss this with your healthcare provider as soon as possible. - •
-
Abnormal Blood Clotting:
Use of progestational drugs, such as norethindrone acetate, has been associated with changes in the blood-clotting system. These changes allow the blood to clot more easily, possibly allowing clots to form in the bloodstream. If blood clots do form in your bloodstream, they can cut off the blood supply to vital organs, causing serious problems. These problems may include a stroke (by cutting off blood to part of the brain), a heart attack (by cutting off blood to part of the heart), a pulmonary embolus (by cutting off blood to part of the lungs), visual loss or blindness (by cutting off blood vessels in the eye), or other problems. Any of these conditions may cause death or serious long-term disability. Call your healthcare provider right away if you suspect you have any of these conditions. He or she may advise you to stop using the drug. - •
-
Eye Abnormalities:
Discontinue norethindrone acetate tablets and call your healthcare provider right away if you experience sudden partial or complete loss of vision, blurred vision, or sudden onset of bulging eyes, double vision, or migraine.
These are some of the warning signs of serious side effects with progestin therapy:
- •
- Breast lumps
- •
- Dizziness and faintness
- •
- Changes in speech
- •
- Severe headaches
- •
- Chest pain
- •
- Shortness of breath
- •
- Pain in your legs
- •
- Changes in vision
Call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of these warning signs, or any other unusual symptom that concerns you.
Common side effects include:
- •
- Headache
- •
- Breast pain
- •
- Irregular vaginal bleeding or spotting
- •
- Stomach/abdominal cramps/bloating
- •
- Nausea and vomiting
- •
- Hair loss
Other side effects include:
- •
- High blood pressure
- •
- Liver problems
- •
- High blood sugar
- •
- Fluid retention
- •
- Enlargements of benign tumors of the uterus ("fibroids")
- •
- Vaginal yeast infections
- •
- Mental depression
These are not all the possible side effects of progestin and/or estrogen therapy. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
What can I do to lower my chances of getting a serious side effect with norethindrone acetate?
- •
- Talk with your healthcare provider regularly about whether you should continue taking norethindrone acetate
- •
- Have a breast exam and mammogram (breast x-ray) every year unless your healthcare provider tells you something else. If members of your family have had breast cancer or if you have ever had breast lumps or an abnormal mammogram, you may need to have breast exams more often
- •
- If you have high blood pressure, high cholesterol (fat in the blood), diabetes, are overweight, or if you use tobacco, you may have higher chances for getting heart disease. Ask your healthcare provider for ways to lower your chances of getting heart attacks
General information about the safe and effective use of norethindrone acetate tablets:
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient information leaflets. Do not take norethindrone acetate tablets for conditions for which it was not prescribed. Do not give norethindrone acetate tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
Keep norethindrone acetate tablets out of the reach of children.
This leaflet provides a summary of the most important information about progestin and/or estrogen therapy. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider or pharmacist. You can ask for information about norethindrone acetate that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in norethindrone acetate tablets?
Norethindrone acetate tablets contain the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and talc.
Manufactured by:
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
Colvale-Bardez, Goa 403 513, IndiaManufactured for:
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Inc., USA
Mahwah, NJ 07430Questions? 1 (888)721-7115
www.glenmarkpharma.com/usaFebruary 2015
- Principal Display Panel
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
NORETHINDRONE ACETATE
norethindrone acetate tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:68462-304 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength NORETHINDRONE ACETATE (UNII: 9S44LIC7OJ) (NORETHINDRONE - UNII:T18F433X4S) NORETHINDRONE ACETATE 5 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (to off-white) Score 2 pieces Shape OVAL (flat faced beveled edged) Size 11mm Flavor Imprint Code G;304 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:68462-304-50 50 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/21/2010 2 NDC:68462-304-05 500 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/21/2010 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA091090 07/21/2010 Labeler - Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Inc., USA (130597813) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Limited 677318665 ANALYSIS(68462-304) , MANUFACTURE(68462-304)