Label: VALPROIC ACID solution
- NDC Code(s): 62559-266-16
- Packager: ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Abbreviated New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated January 2, 2024
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Medication Guide: HTML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use VALPROIC ACID ORAL SOLUTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for VALPROIC ACID ORAL SOLUTION. VALPROIC ACID ...These highlights do not include all the information needed to use VALPROIC ACID ORAL SOLUTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for VALPROIC ACID ORAL SOLUTION.
VALPROIC ACID oral solution
Initial U.S. Approval: 1978WARNING: LIFE THREATENING ADVERSE REACTIONS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- •
- Hepatotoxicity, including fatalities, usually during first 6 months of treatment. Children under the age of two years and patients with mitochondrial disorders are at higher risk. Monitor patients closely, and perform serum liver testing prior to therapy and at frequent intervals thereafter (5.1)
- •
- Fetal Risk, particularly neural tube defects, other major malformations, and decreased IQ (5.2, 5.3, 5.4)
- •
- Pancreatitis, including fatal hemorrhagic cases (5.5)
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Valproic acid oral solution is indicated for:
- •
- Monotherapy and adjunctive therapy of complex partial seizures; sole and adjunctive therapy of simple and complex absence seizures; adjunctive therapy in patients with multiple seizure types that include absence seizures (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Valproic acid oral solution is intended for oral administration. (2.1)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Oral solution: Equivalent of 250 mg valproic acid per 5 mL as the sodium salt (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- •
- Hepatic disease or significant hepatic dysfunction (4, 5.1)
- •
- Known mitochondrial disorders caused by mutations in mitochondrial DNA polymerase γ (POLG) (4, 5.1)
- •
- Suspected POLG-related disorder in children under two years of age (4, 5.1)
- •
- Known hypersensitivity to the drug (4, 5.12)
- •
- Urea cycle disorders (4, 5.6)
- •
- Prophylaxis of migraine headaches: Pregnant women, women of childbearing potential not using effective contraception (4, 8.1)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- •
- Hepatotoxicity; evaluate high risk populations and monitor serum liver tests (5.1)
- •
- Birth defects, decreased IQ, and neurodevelopmental disorders following in utero exposure; should not be used to treat women with epilepsy or bipolar disorder who are pregnant or who plan to become pregnant or to treat a woman of childbearing potential unless other medications have failed to provide adequate symptom control or are otherwise unacceptable. (5.2, 5.3, 5.4)
- •
- Pancreatitis; valproic acid should ordinarily be discontinued (5.5)
- •
- Suicidal behavior or ideation; Antiepileptic drugs, including valproic acid, increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior (5.7)
- •
- Bleeding and other hematopoietic disorders; monitor platelet counts and coagulation tests (5.8)
- •
- Hyperammonemia and hyperammonemic encephalopathy; measure ammonia level if unexplained lethargy and vomiting or changes in mental status, and also with concomitant topiramate use; consider discontinuation of valproate therapy (5.6, 5.9, 5.10)
- •
- Hypothermia; Hypothermia has been reported during valproate therapy with or without associated hyperammonemia. This adverse reaction can also occur in patients using concomitant topiramate (5.11)
- •
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)/Multiorgan hypersensitivity reaction; discontinue valproic acid (5.12)
- •
- Somnolence in the elderly can occur. Valproic acid dosage should be increased slowly and with regular monitoring for fluid and nutritional intake (5.14)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- •
- Most common adverse reactions (reported >5%) are abdominal pain, alopecia, amblyopia/blurred vision, amnesia, anorexia, asthenia, ataxia, bronchitis, constipation, depression, diarrhea, diplopia, dizziness, dyspepsia, dyspnea, ecchymosis, emotional lability, fever, flu syndrome, headache, increased appetite, infection, insomnia, nausea, nervousness, nystagmus, peripheral edema, pharyngitis, rhinitis, somnolence, thinking abnormal, thrombocytopenia, tinnitus, tremor, vomiting, weight gain, weight loss. (6.1)
- •
- The safety and tolerability of valproate in pediatric patients were shown to be comparable to those in adults (8.4).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-308-6755 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- •
- Hepatic enzyme-inducing drugs (e.g., phenytoin, carbamazepine, phenobarbital, primidone, rifampin) can increase valproate clearance, while enzyme inhibitors (e.g., felbamate) can decrease valproate clearance. Therefore increased monitoring of valproate and concomitant drug concentrations and dosage adjustment are indicated whenever enzyme- inducing or inhibiting drugs are introduced or withdrawn (7.1)
- •
- Aspirin, carbapenem antibiotics, estrogen-containing hormonal contraceptives: Monitoring of valproate concentrations is recommended (7.1)
- •
- Co-administration of valproate can affect the pharmacokinetics of other drugs (e.g. diazepam, ethosuximide, lamotrigine, phenytoin) by inhibiting their metabolism or protein binding displacement (7.2)
- •
- Patients stabilized on rufinamide should begin valproate therapy at a low dose, and titrate to clinically effective dose (7.2)
- •
- Dosage adjustment of amitriptyline/nortriptyline, propofol, warfarin, and zidovudine may be necessary if used concomitantly with valproic acid (7.2)
- •
- Topiramate: Hyperammonemia and encephalopathy (5.10, 7.3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- •
- Pregnancy: Valproic acid can cause congenital malformations including neural tube defects, decreased IQ, and neurodevelopmental disorders (5.2, 5.3, 8.1)
- •
- Pediatric: Children under the age of two years are at considerably higher risk of fatal hepatotoxicity (5.1, 8.4)
- •
- Geriatric: Reduce starting dose; increase dosage more slowly; monitor fluid and nutritional intake, and somnolence (5.14, 8.5)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 10/2023
Close -
Table of ContentsTable of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: LIFE THREATENING ADVERSE REACTIONS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Epilepsy
1.2 Important Limitations
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Epilepsy
2.2 General Dosing Advice
2.3 Dosing in Patients Taking Rufinamide
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hepatotoxicity
5.2 Structural Birth Defects
5.3 Decreased IQ Following in utero Exposure
5.4 Use in Women of Childbearing Potential
5.5 Pancreatitis
5.6 Urea Cycle Disorders
5.7 Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
5.8 Bleeding and Other Hematopoietic Disorders
5.9 Hyperammonemia
5.10 Hyperammonemia and Encephalopathy Associated with Concomitant Topiramate Use
5.11 Hypothermia
5.12 Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)/Multiorgan Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.13 Interaction with Carbapenem Antibiotics
5.14 Somnolence in the Elderly
5.15 Monitoring: Drug Plasma Concentration
5.16 Effect on Ketone and Thyroid Function Tests
5.17 Effect on HIV and CMV Viruses Replication
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Epilepsy
6.2 Mania
6.3 Migraine
6.4 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Co-Administered Drugs on Valproate Clearance
7.2 Effects of Valproate on Other Drugs
7.3 Topiramate
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Epilepsy
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: LIFE THREATENING ADVERSE REACTIONS
Hepatotoxicity
General Population: Hepatic failure resulting in fatalities has occurred in patients receiving valproate and its derivatives. These incidents usually have occurred during the first six months of treatment. Serious or fatal hepatotoxicity may be preceded by non-specific symptoms such as malaise, weakness, lethargy, facial edema, anorexia, and vomiting. In patients with epilepsy, a loss of seizure control may also occur. Patients should be monitored closely for appearance of these symptoms. Serum liver tests should be performed prior to therapy and at frequent intervals thereafter, especially during the first six months [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].Children under the age of two years are at a considerably increased risk of developing fatal hepatotoxicity, especially those on multiple anticonvulsants, those with congenital metabolic disorders, those with severe seizure disorders accompanied by mental retardation, and those with organic brain disease. When valproic acid products are used in this patient group, they should be used with extreme caution and as a sole agent. The benefits of therapy should be weighed against the risks. The incidence of fatal hepatotoxicity decreases considerably in progressively older patient groups.
Patients with Mitochondrial Disease: There is an increased risk of valproate-induced acute liver failure and resultant deaths in patients with hereditary neurometabolic syndromes caused by DNA mutations of the mitochondrial DNA Polymerase γ (POLG) gene (e.g. Alpers Huttenlocher Syndrome). Valproic acid is contraindicated in patients known to have mitochondrial disorders caused by POLG mutations and children under two years of age who are clinically suspected of having a mitochondrial disorder [see Contraindications (4)]. In patients over two years of age who are clinically suspected of having a hereditary mitochondrial disease, valproic acid should only be used after other anticonvulsants have failed. This older group of patients should be closely monitored during treatment with valproic acid for the development of acute liver injury with regular clinical assessments and serum liver testing. POLG mutation screening should be performed in accordance with current clinical practice [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Fetal Risk
Valproate can cause major congenital malformations, particularly neural tube defects (e.g., spina bifida). In addition, valproate can cause decreased IQ scores and neurodevelopmental disorders following in utero exposure.Valproate is therefore contraindicated for prophylaxis of migraine headaches in pregnant women and in women of childbearing potential who are not using effective contraception [see Contraindications (4)]. Valproate should not be used to treat women with epilepsy or bipolar disorder who are pregnant or who plan to become pregnant unless other medications have failed to provide adequate symptom control or are otherwise unacceptable.
Valproate should not be administered to a woman of childbearing potential unless other medications have failed to provide adequate symptom control or are otherwise unacceptable. In such situations, effective contraception should be used [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3, 5.4)].
A Medication Guide describing the risks of valproate is available for patients [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Pancreatitis
Close
Cases of life-threatening pancreatitis have been reported in both children and adults receiving valproate. Some of the cases have been described as hemorrhagic with a rapid progression from initial symptoms to death. Cases have been reported shortly after initial use as well as after several years of use. Patients and guardians should be warned that abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and/or anorexia can be symptoms of pancreatitis that require prompt medical evaluation. If pancreatitis is diagnosed, valproate should ordinarily be discontinued. Alternative treatment for the underlying medical condition should be initiated as clinically indicated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. -
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE1.1 Epilepsy - Valproic acid oral solution is indicated as monotherapy and adjunctive therapy in the treatment of patients with complex partial seizures that occur either in isolation or in ...
1.1 Epilepsy
Valproic acid oral solution is indicated as monotherapy and adjunctive therapy in the treatment of patients with complex partial seizures that occur either in isolation or in association with other types of seizures. Valproic acid oral solution is indicated for use as sole and adjunctive therapy in the treatment of simple and complex absence seizures, and adjunctively in patients with multiple seizure types which include absence seizures.
Simple absence is defined as very brief clouding of the sensorium or loss of consciousness accompanied by certain generalized epileptic discharges without other detectable clinical signs. Complex absence is the term used when other signs are also present.
See Warnings and Precautions (5.1) for statement regarding fatal hepatic dysfunction.
Close1.2 Important Limitations
Because of the risk to the fetus of decreased IQ, neurodevelopmental disorders, neural tube defects, and other major congenital malformations, which may occur very early in pregnancy, valproate should not be used to treat women with epilepsy or bipolar disorder who are pregnant or who plan to become pregnant unless other medications have failed to provide adequate symptom control or are otherwise unacceptable. Valproate should not be administered to a woman of childbearing potential unless other medications have failed to provide adequate symptom control or are otherwise unacceptable [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3, 5.4), Use in Specific Populations (8.1), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].
For prophylaxis of migraine headaches, valproate is contraindicated in women who are pregnant and in women of childbearing potential who are not using effective contraception [see Contraindications (4)].
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION2.1 Epilepsy - Valproic acid oral solution is intended for oral administration. Patients should be informed to take valproic acid oral solution every day as prescribed. If a dose is missed it ...
2.1 Epilepsy
Valproic acid oral solution is intended for oral administration.
Patients should be informed to take valproic acid oral solution every day as prescribed. If a dose is missed it should be taken as soon as possible, unless it is almost time for the next dose. If a dose is skipped, the patient should not double the next dose.
Valproic acid is indicated as monotherapy and adjunctive therapy in complex partial seizures in adults and pediatric patients down to the age of 10 years, and in simple and complex absence seizures. As the valproic acid dosage is titrated upward, concentrations of clonazepam, diazepam, ethosuximide, lamotrigine, tolbutamide, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, and/or phenytoin may be affected [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Complex Partial Seizures
For adults and children 10 years of age or older.
Monotherapy (Initial Therapy)
Valproic acid oral solution has not been systematically studied as initial therapy. Patients should initiate therapy at 10 to 15 mg/kg/day. The dosage should be increased by 5 to 10 mg/kg/week to achieve optimal clinical response. Ordinarily, optimal clinical response is achieved at daily doses below 60 mg/kg/day. If satisfactory clinical response has not been achieved, plasma levels should be measured to determine whether or not they are in the usually accepted therapeutic range (50 to 100 mcg/mL). No recommendation regarding the safety of valproate for use at doses above 60 mg/kg/day can be made.
The probability of thrombocytopenia increases significantly at total trough valproate plasma concentrations above 110 mcg/mL in females and 135 mcg/mL in males. The benefit of improved seizure control with higher doses should be weighed against the possibility of a greater incidence of adverse reactions.
Conversion to Monotherapy
Patients should initiate therapy at 10 to 15 mg/kg/day. The dosage should be increased by 5 to 10 mg/kg/week to achieve optimal clinical response. Ordinarily, optimal clinical response is achieved at daily doses below 60 mg/kg/day. If satisfactory clinical response has not been achieved, plasma levels should be measured to determine whether or not they are in the usually accepted therapeutic range (50 to 100 mcg/mL). No recommendation regarding the safety of valproate for use at doses above 60 mg/kg/day can be made. Concomitant antiepilepsy drug (AED) dosage can ordinarily be reduced by approximately 25% every 2 weeks. This reduction may be started at initiation of valproic acid therapy, or delayed by 1 to 2 weeks if there is a concern that seizures are likely to occur with a reduction. The speed and duration of withdrawal of the concomitant AED can be highly variable, and patients should be monitored closely during this period for increased seizure frequency.
Adjunctive Therapy
Valproic acid oral solution may be added to the patient's regimen at a dosage of 10 to 15 mg/kg/day. The dosage may be increased by 5 to 10 mg/kg/week to achieve optimal clinical response. Ordinarily, optimal clinical response is achieved at daily doses below 60 mg/kg/day. If satisfactory clinical response has not been achieved, plasma levels should be measured to determine whether or not they are in the usually accepted therapeutic range (50 to 100 mcg/mL). No recommendation regarding the safety of valproate for use at doses above 60 mg/kg/day can be made. If the total daily dose exceeds 250 mg, it should be given in divided doses.
In a study of adjunctive therapy for complex partial seizures in which patients were receiving either carbamazepine or phenytoin in addition to divalproex sodium tablets, no adjustment of carbamazepine or phenytoin dosage was needed [see Clinical Studies (14)]. However, since valproate may interact with these or other concurrently administered AEDs as well as other drugs, periodic plasma concentration determinations of concomitant AEDs are recommended during the early course of therapy [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Simple and Complex Absence Seizures
The recommended initial dose is 15 mg/kg/day, increasing at one week intervals by 5 to 10 mg/kg/day until seizures are controlled or side effects preclude further increases. The maximum recommended dosage is 60 mg/kg/day. If the total daily dose exceeds 250 mg, it should be given in divided doses.
A good correlation has not been established between daily dose, serum concentrations, and therapeutic effect. However, therapeutic valproate serum concentration for most patients with absence seizures is considered to range from 50 to 100 mcg/mL. Some patients may be controlled with lower or higher serum concentrations [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
As the valproic acid dosage is titrated upward, blood concentrations of phenobarbital and/or phenytoin may be affected [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Antiepilepsy drugs should not be abruptly discontinued in patients in whom the drug is administered to prevent major seizures because of the strong possibility of precipitating status epilepticus with attendant hypoxia and threat to life.
The following table is a guide for the initial daily dose of valproic acid oral solution (15 mg/kg/day):
Table 1. Initial Daily Dose
Weight
Total Daily Dose (mg)
Teaspoons of Oral Solution
(Kg)
(Lb)
Dose 1
Dose 2
Dose 3
10 to 24.9
22 to 54.9
250
0
0
1
25 to 39.9
55 to 87.9
500
1
0
1
40 to 59.9
88 to 131.9
750
1
1
1
60 to 74.9
132 to 164.9
1,000
1
1
2
75 to 89.9
165 to 197.9
1,250
2
1
2
2.2 General Dosing Advice
Dosing in Elderly Patients
Due to a decrease in unbound clearance of valproate and possibly a greater sensitivity to somnolence in the elderly, the starting dose should be reduced in these patients. Dosage should be increased more slowly and with regular monitoring for fluid and nutritional intake, dehydration, somnolence, and other adverse reactions. Dose reductions or discontinuation of valproate should be considered in patients with decreased food or fluid intake and in patients with excessive somnolence. The ultimate therapeutic dose should be achieved on the basis of both tolerability and clinical response [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14), Use in Specific Populations (8.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Dose-Related Adverse Reactions
The frequency of adverse effects (particularly elevated liver enzymes and thrombocytopenia) may be dose-related. The probability of thrombocytopenia appears to increase significantly at total valproate concentrations of ≥ 110 mcg/mL (females) or ≥ 135 mcg/mL (males) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]. The benefit of improved therapeutic effect with higher doses should be weighed against the possibility of a greater incidence of adverse reactions.
G.I. Irritation
Patients who experience G.I. irritation may benefit from administration of the drug with food or by slowly building up the dose from an initial low level.
Close2.3 Dosing in Patients Taking Rufinamide
Patients stabilized on rufinamide before being prescribed valproate should begin valproate therapy at a low dose and titrate to a clinically effective dose [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
-
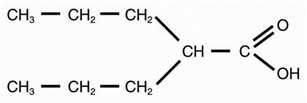
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSValproic acid oral solution USP is available as a clear, red, sour cherry flavored oral solution containing the equivalent of 250 mg valproic acid per 5 mL as the sodium salt in bottles of 16 ...
Valproic acid oral solution USP is available as a clear, red, sour cherry flavored oral solution containing the equivalent of 250 mg valproic acid per 5 mL as the sodium salt in bottles of 16 fluid ounces (473 mL).
Close -
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS• Valproic acid should not be administered to patients with hepatic disease or significant hepatic dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. • Valproic acid is contraindicated in patients ...
- •
- Valproic acid should not be administered to patients with hepatic disease or significant hepatic dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- •
- Valproic acid is contraindicated in patients known to have mitochondrial disorders caused by mutations in mitochondrial DNA polymerase γ (POLG; e.g., Alpers-Huttenlocher Syndrome) and children under two years of age who are suspected of having a POLG-related disorder [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- •
- Valproic acid is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to the drug [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
- •
- Valproic acid is contraindicated in patients with known urea cycle disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
- •
- For use in prophylaxis of migraine headaches: Valproic acid is contraindicated in women who are pregnant and in women of childbearing potential who are not using effective contraception [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3, 5.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS5.1 Hepatotoxicity - General Information on Hepatotoxicity - Hepatic failure resulting in fatalities has occurred in patients receiving valproate. These incidents usually have occurred during the ...
5.1 Hepatotoxicity
General Information on Hepatotoxicity
Hepatic failure resulting in fatalities has occurred in patients receiving valproate. These incidents usually have occurred during the first six months of treatment. Serious or fatal hepatotoxicity may be preceded by non-specific symptoms such as malaise, weakness, lethargy, facial edema, anorexia, and vomiting. In patients with epilepsy, a loss of seizure control may also occur. Patients should be monitored closely for appearance of these symptoms. Serum liver tests should be performed prior to therapy and at frequent intervals thereafter, especially during the first six months of valproate therapy. However, healthcare providers should not rely totally on serum biochemistry since these tests may not be abnormal in all instances, but should also consider the results of careful interim medical history and physical examination.
Caution should be observed when administering valproate products to patients with a prior history of hepatic disease. Patients on multiple anticonvulsants, children, those with congenital metabolic disorders, those with severe seizure disorders accompanied by mental retardation, and those with organic brain disease may be at particular risk. See below, “Patients with Known or Suspected Mitochondrial Disease.”
Experience has indicated that children under the age of two years are at a considerably increased risk of developing fatal hepatotoxicity, especially those with the aforementioned conditions. When valproic acid products are used in this patient group, they should be used with extreme caution and as a sole agent. The benefits of therapy should be weighed against the risks. In progressively older patient groups experience in epilepsy has indicated that the incidence of fatal hepatotoxicity decreases considerably.
Patients with Known or Suspected Mitochondrial Disease
Valproic acid is contraindicated in patients known to have mitochondrial disorders caused by POLG mutations and children under two years of age who are clinically suspected of having a mitochondrial disorder [see Contraindications (4)]. Valproate-induced acute liver failure and liver-related deaths have been reported in patients with hereditary neurometabolic syndromes caused by mutations in the gene for mitochondrial DNA polymerase γ (POLG) (e.g., Alpers- Huttenlocher Syndrome) at a higher rate than those without these syndromes. Most of the reported cases of liver failure in patients with these syndromes have been identified in children and adolescents.
POLG-related disorders should be suspected in patients with a family history or suggestive symptoms of a POLG-related disorder, including but not limited to unexplained encephalopathy, refractory epilepsy (focal, myoclonic), status epilepticus at presentation, developmental delays, psychomotor regression, axonal sensorimotor neuropathy, myopathy cerebellar ataxia, ophthalmoplegia, or complicated migraine with occipital aura. POLG mutation testing should be performed in accordance with current clinical practice for the diagnostic evaluation of such disorders. The A467T and W748S mutations are present in approximately 2/3 of patients with autosomal recessive POLG-related disorders.
In patients over two years of age who are clinically suspected of having a hereditary mitochondrial disease, valproic acid should only be used after other anticonvulsants have failed. This older group of patients should be closely monitored during treatment with valproic acid for the development of acute liver injury with regular clinical assessments and serum liver test monitoring.
The drug should be discontinued immediately in the presence of significant hepatic dysfunction, suspected or apparent. In some cases, hepatic dysfunction has progressed in spite of discontinuation of drug [see Boxed Warning and Contraindications (4)].
5.2 Structural Birth Defects
Valproate can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Pregnancy registry data show that maternal valproate use can cause neural tube defects and other structural abnormalities (e.g., craniofacial defects, cardiovascular malformations, hypospadias, limb malformations). The rate of congenital malformations among babies born to mothers using valproate is about four times higher than the rate among babies born to epileptic mothers using other anti-seizure monotherapies. Evidence suggests that folic acid supplementation prior to conception and during the first trimester of pregnancy decreases the risk for congenital neural tube defects in the general population [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
5.3 Decreased IQ Following in utero Exposure
Valproate can cause decreased IQ scores following in utero exposure. Published epidemiological studies have indicated that children exposed to valproate in utero have lower cognitive test scores than children exposed in utero to either another antiepileptic drug or to no antiepileptic drugs. The largest of these studies1 is a prospective cohort study conducted in the United States and United Kingdom that found that children with prenatal exposure to valproate (n=62) had lower IQ scores at age 6 (97 [95% C.I. 94-101]) than children with prenatal exposure to the other antiepileptic drug monotherapy treatments evaluated: lamotrigine (108 [95% C.I. 105-110]), carbamazepine (105 [95% C.I. 102-108]), and phenytoin (108 [95% C.I. 104-112]). It is not known when during pregnancy cognitive effects in valproate-exposed children occur. Because the women in this study were exposed to antiepileptic drugs throughout pregnancy, whether the risk for decreased IQ was related to a particular time period during pregnancy could not be assessed.
Although all of the available studies have methodological limitations, the weight of the evidence supports the conclusion that valproate exposure in utero can cause decreased IQ in children.
In animal studies, offspring with prenatal exposure to valproate had malformations similar to those seen in humans and demonstrated neurobehavioral deficits [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
5.4 Use in Women of Childbearing Potential
Because of the risk to the fetus of decreased IQ, neurodevelopmental disorders, and major congenital malformations (including neural tube defects), which may occur very early in pregnancy, valproate should not be administered to a woman of childbearing potential unless other medications have failed to provide adequate symptom control or are otherwise unacceptable. This is especially important when valproate use is considered for a condition not usually associated with permanent injury or death such as prophylaxis of migraine headaches [see Contraindications (4)]. Women should use effective contraception while using valproate.
Women of childbearing potential should be counseled regularly regarding the relative risks and benefits of valproate use during pregnancy. This is especially important for women planning a pregnancy and for girls at the onset of puberty; alternative therapeutic options should be considered for these patients [see Boxed Warning and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
To prevent major seizures, valproate should not be discontinued abruptly, as this can precipitate status epilepticus with resulting maternal and fetal hypoxia and threat to life.
Evidence suggests that folic acid supplementation prior to conception and during the first trimester of pregnancy decreases the risk for congenital neural tube defects in the general population. It is not known whether the risk of neural tube defects or decreased IQ in the offspring of women receiving valproate is reduced by folic acid supplementation. Dietary folic acid supplementation both prior to conception and during pregnancy should be routinely recommended for patients using valproate.
5.5 Pancreatitis
Cases of life-threatening pancreatitis have been reported in both children and adults receiving valproate. Some of the cases have been described as hemorrhagic with rapid progression from initial symptoms to death. Some cases have occurred shortly after initial use as well as after several years of use. The rate based upon the reported cases exceeds that expected in the general population and there have been cases in which pancreatitis recurred after rechallenge with valproate. In clinical trials, there were 2 cases of pancreatitis without alternative etiology in 2,416 patients, representing 1,044 patient-years experience. Patients and guardians should be warned that abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and/or anorexia can be symptoms of pancreatitis that require prompt medical evaluation. If pancreatitis is diagnosed, valproic acid should ordinarily be discontinued. Alternative treatment for the underlying medical condition should be initiated as clinically indicated [see Boxed Warning].
5.6 Urea Cycle Disorders
Valproic acid is contraindicated in patients with known urea cycle disorders (UCD).
Hyperammonemic encephalopathy, sometimes fatal, has been reported following initiation of valproate therapy in patients with urea cycle disorders, a group of uncommon genetic abnormalities, particularly ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. Prior to the initiation of valproic acid therapy, evaluation for UCD should be considered in the following patients: 1) those with a history of unexplained encephalopathy or coma, encephalopathy associated with a protein load, pregnancy-related or postpartum encephalopathy, unexplained mental retardation, or history of elevated plasma ammonia or glutamine; 2) those with cyclical vomiting and lethargy, episodic extreme irritability, ataxia, low BUN, or protein avoidance; 3) those with a family history of UCD or a family history of unexplained infant deaths (particularly males); 4) those with other signs or symptoms of UCD. Patients who develop symptoms of unexplained hyperammonemic encephalopathy while receiving valproate therapy should receive prompt treatment (including discontinuation of valproate therapy) and be evaluated for underlying urea cycle disorders [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
5.7 Suicidal Behavior and Ideation
Antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), including valproic acid, increase the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior in patients taking these drugs for any indication. Patients treated with any AED for any indication should be monitored for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or behavior, and/or any unusual changes in mood or behavior.
Pooled analyses of 199 placebo-controlled clinical trials (mono- and adjunctive therapy) of 11 different AEDs showed that patients randomized to one of the AEDs had approximately twice the risk (adjusted Relative Risk 1.8, 95% CI:1.2, 2.7) of suicidal thinking or behavior compared to patients randomized to placebo. In these trials, which had a median treatment duration of 12 weeks, the estimated incidence rate of suicidal behavior or ideation among 27,863 AED-treated patients was 0.43%, compared to 0.24% among 16,029 placebo-treated patients, representing an increase of approximately one case of suicidal thinking or behavior for every 530 patients treated. There were four suicides in drug-treated patients in the trials and none in placebo-treated patients, but the number is too small to allow any conclusion about drug effect on suicide.
The increased risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with AEDs was observed as early as one week after starting drug treatment with AEDs and persisted for the duration of treatment assessed. Because most trials included in the analysis did not extend beyond 24 weeks, the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior beyond 24 weeks could not be assessed.
The risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior was generally consistent among drugs in the data analyzed. The finding of increased risk with AEDs of varying mechanisms of action and across a range of indications suggests that the risk applies to all AEDs used for any indication. The risk did not vary substantially by age (5 to 100 years) in the clinical trials analyzed.
Table 2 shows absolute and relative risk by indication for all evaluated AEDs.
Table 2. Risk by Indication for Antiepileptic Drugs in the Pooled Analysis
Indication
Placebo Patients with Events Per 1,000 Patients
Drug Patients with Events Per 1,000 Patients
Relative Risk: Incidence
of Events in Drug Patients/Incidence
in Placebo PatientsRisk Difference: Additional Drug Patients with Events Per 1,000 Patients
Epilepsy
1.0
3.4
3.5
2.4
Psychiatric
5.7
8.5
1.5
2.9
Other
1.0
1.8
1.9
0.9
Total
2.4
4.3
1.8
1.9
The relative risk for suicidal thoughts or behavior was higher in clinical trials for epilepsy than in clinical trials for psychiatric or other conditions, but the absolute risk differences were similar for the epilepsy and psychiatric indications.
Anyone considering prescribing valproic acid or any other AED must balance the risk of suicidal thoughts or behavior with the risk of untreated illness. Epilepsy and many other illnesses for which AEDs are prescribed are themselves associated with morbidity and mortality and an increased risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior. Should suicidal thoughts and behavior emerge during treatment, the prescriber needs to consider whether the emergence of these symptoms in any given patient may be related to the illness being treated.
5.8 Bleeding and Other Hematopoietic Disorders
Valproate is associated with dose-related thrombocytopenia. In a clinical trial of divalproex sodium as monotherapy in patients with epilepsy, 34/126 patients (27%) receiving approximately 50 mg/kg/day on average, had at least one value of platelets ≤ 75 x 109/L. Approximately half of these patients had treatment discontinued, with return of platelet counts to normal. In the remaining patients, platelet counts normalized with continued treatment. In this study, the probability of thrombocytopenia appeared to increase significantly at total valproate concentrations of ≥ 110 mcg/mL (females) or ≥ 135 mcg/mL (males). The therapeutic benefit which may accompany the higher doses should therefore be weighed against the possibility of a greater incidence of adverse effects. Valproate use has also been associated with decreases in other cell lines and myelodysplasia.
Because of reports of cytopenias, inhibition of the secondary phase of platelet aggregation, and abnormal coagulation parameters, (e.g., low fibrinogen, coagulation factor deficiencies, acquired von Willebrand’s disease), measurements of complete blood counts and coagulation tests are recommended before initiating therapy and at periodic intervals. It is recommended that patients receiving valproic acid be monitored for blood counts and coagulation parameters prior to planned surgery and during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Evidence of hemorrhage, bruising, or a disorder of hemostasis/coagulation is an indication for reduction of the dosage or withdrawal of therapy.
5.9 Hyperammonemia
Hyperammonemia has been reported in association with valproate therapy and may be present despite normal liver function tests. In patients who develop unexplained lethargy and vomiting or changes in mental status, hyperammonemic encephalopathy should be considered and an ammonia level should be measured. Hyperammonemia should also be considered in patients who present with hypothermia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]. If ammonia is increased, valproate therapy should be discontinued. Appropriate interventions for treatment of hyperammonemia should be initiated, and such patients should undergo investigation for underlying urea cycle disorders [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.6, 5.10)].
Asymptomatic elevations of ammonia are more common and when present, require close monitoring of plasma ammonia levels. If the elevation persists, discontinuation of valproate therapy should be considered.
5.10 Hyperammonemia and Encephalopathy Associated with Concomitant Topiramate Use
Concomitant administration of topiramate and valproate has been associated with hyperammonemia with or without encephalopathy in patients who have tolerated either drug alone. Clinical symptoms of hyperammonemic encephalopathy often include acute alterations in level of consciousness and/or cognitive function with lethargy or vomiting. Hypothermia can also be a manifestation of hyperammonemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]. In most cases, symptoms and signs abated with discontinuation of either drug. This adverse reaction is not due to a pharmacokinetic interaction. Patients with inborn errors of metabolism or reduced hepatic mitochondrial activity may be at an increased risk for hyperammonemia with or without encephalopathy. Although not studied, an interaction of topiramate and valproate may exacerbate existing defects or unmask deficiencies in susceptible persons. In patients who develop unexplained lethargy, vomiting, or changes in mental status, hyperammonemic encephalopathy should be considered and an ammonia level should be measured [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.6, 5.9)].
5.11 Hypothermia
Hypothermia, defined as an unintentional drop in body core temperature to <35°C (95°F), has been reported in association with valproate therapy both in conjunction with and in the absence of hyperammonemia. This adverse reaction can also occur in patients using concomitant topiramate with valproate after starting topiramate treatment or after increasing the daily dose of topiramate [see Drug Interactions (7.3)]. Consideration should be given to stopping valproate in patients who develop hypothermia, which may be manifested by a variety of clinical abnormalities including lethargy, confusion, coma, and significant alterations in other major organ systems such as the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. Clinical management and assessment should include examination of blood ammonia levels.
5.12 Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)/Multiorgan Hypersensitivity Reactions
Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS), also known as Multiorgan Hypersensitivity, has been reported in patients taking valproate. DRESS may be fatal or life- threatening. DRESS typically, although not exclusively, presents with fever, rash, lymphadenopathy, and/or facial swelling, in association with other organ system involvement, such as hepatitis, nephritis, hematological abnormalities, myocarditis, or myositis sometimes resembling an acute viral infection. Eosinophilia is often present. Because this disorder is variable in its expression, other organ systems not noted here may be involved. It is important to note that early manifestations of hypersensitivity, such as fever or lymphadenopathy, may be present even though rash is not evident. If such signs or symptoms are present, the patient should be evaluated immediately. Valproate should be discontinued and not be resumed if an alternative etiology for the signs or symptoms cannot be established.
5.13 Interaction with Carbapenem Antibiotics
Carbapenem antibiotics (for example, ertapenem, imipenem, meropenem; this is not a complete list) may reduce serum valproate concentrations to subtherapeutic levels, resulting in loss of seizure control. Serum valproate concentrations should be monitored frequently after initiating carbapenem therapy. Alternative antibacterial or anticonvulsant therapy should be considered if serum valproate concentrations drop significantly or seizure control deteriorates [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.14 Somnolence in the Elderly
In a double-blind, multicenter trial of valproate in elderly patients with dementia (mean age = 83 years), doses were increased by 125 mg/day to a target dose of 20 mg/kg/day. A significantly higher proportion of valproate patients had somnolence compared to placebo, and although not statistically significant, there was a higher proportion of patients with dehydration. Discontinuations for somnolence were also significantly higher than with placebo. In some patients with somnolence (approximately one-half), there was associated reduced nutritional intake and weight loss. There was a trend for the patients who experienced these events to have a lower baseline albumin concentration, lower valproate clearance, and a higher BUN. In elderly patients, dosage should be increased more slowly and with regular monitoring for fluid and nutritional intake, dehydration, somnolence, and other adverse reactions. Dose reductions or discontinuation of valproate should be considered in patients with decreased food or fluid intake and in patients with excessive somnolence [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
5.15 Monitoring: Drug Plasma Concentration
Since valproate may interact with concurrently administered drugs which are capable of enzyme induction, periodic plasma concentration determinations of valproate and concomitant drugs are recommended during the early course of therapy [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.16 Effect on Ketone and Thyroid Function Tests
Valproate is partially eliminated in the urine as a keto-metabolite which may lead to a false interpretation of the urine ketone test.
There have been reports of altered thyroid function tests associated with valproate. The clinical significance of these is unknown.
Close5.17 Effect on HIV and CMV Viruses Replication
There are in vitro studies that suggest valproate stimulates the replication of the HIV and CMV viruses under certain experimental conditions. The clinical consequence, if any, is not known. Additionally, the relevance of these in vitro findings is uncertain for patients receiving maximally suppressive antiretroviral therapy. Nevertheless, these data should be borne in mind when interpreting the results from regular monitoring of the viral load in HIV infected patients receiving valproate or when following CMV infected patients clinically.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONSThe following serious adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling: • Hepatic failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] • Birth defects [see Warnings and Precautions ...
The following serious adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- •
- Hepatic failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- •
- Birth defects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- •
- Decreased IQ following in utero exposure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- •
- Pancreatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- •
- Hyperammonemic encephalopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6, 5.9, 5.10)]
- •
- Suicidal behavior and ideation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- •
- Bleeding and other hematopoietic disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- •
- Hypothermia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- •
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)/Multiorgan hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- •
- Somnolence in the elderly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
6.1 Epilepsy
The data described in the following section were obtained using divalproex sodium tablets.
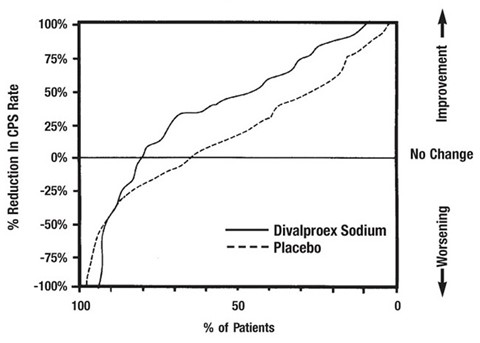
Based on a placebo-controlled trial of adjunctive therapy for treatment of complex partial seizures, divalproex sodium was generally well tolerated with most adverse reactions rated as mild to moderate in severity. Intolerance was the primary reason for discontinuation in the divalproex sodium-treated patients (6%), compared to 1% of placebo-treated patients.
Table 3 lists treatment-emergent adverse reactions which were reported by ≥ 5% of divalproex sodium-treated patients and for which the incidence was greater than in the placebo group, in a placebo-controlled trial of adjunctive therapy for treatment of complex partial seizures. Since patients were also treated with other antiepilepsy drugs, it is not possible, in most cases, to determine whether the following adverse reactions can be ascribed to divalproex sodium alone, or the combination of divalproex sodium and other antiepilepsy drugs.
Table 3. Adverse Reactions Reported by ≥ 5% of Patients Treated with Divalproex Sodium During Placebo-Controlled Trial of Adjunctive Therapy for Complex Partial Seizures
Body System/Reaction
Divalproex Sodium
(n = 77)
%Placebo
(n = 70)
%Body as a Whole
Headache
31
21
Asthenia
27
7
Fever
6
4
Gastrointestinal System
Nausea
48
14
Vomiting
27
7
Abdominal Pain
23
6
Diarrhea
13
6
Anorexia
12
0
Dyspepsia
8
4
Constipation
5
1
Nervous System
Somnolence
27
11
Tremor
25
6
Dizziness
25
13
Diplopia
16
9
Amblyopia/Blurred Vision
12
9
Ataxia
8
1
Nystagmus
8
1
Emotional Lability
6
4
Thinking Abnormal
6
0
Amnesia
5
1
Respiratory System
Flu Syndrome
12
9
Infection
12
6
Bronchitis
5
1
Rhinitis
5
4
Other
Alopecia
6
1
Weight Loss
6
0
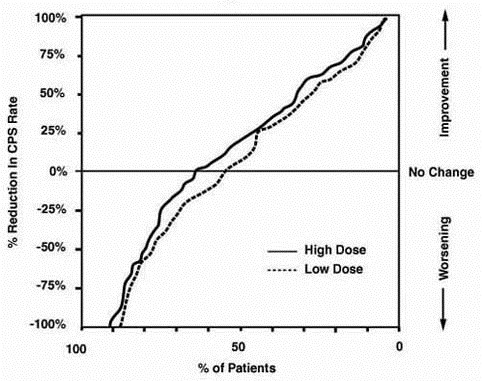
Table 4 lists treatment-emergent adverse reactions which were reported by ≥ 5% of patients in the high dose divalproex sodium group, and for which the incidence was greater than in the low dose group, in a controlled trial of divalproex sodium monotherapy treatment of complex partial seizures. Since patients were being titrated off another antiepilepsy drug during the first portion of the trial, it is not possible, in many cases, to determine whether the following adverse reactions can be ascribed to divalproex sodium alone, or the combination of divalproex sodium and other antiepilepsy drugs.
Table 4. Adverse Reactions Reported by ≥ 5% of Patients in the High Dose Group in the Controlled Trial of Divalproex Sodium Monotherapy for Complex Partial Seizures1
Body System/Reaction
High Dose
(n = 131)
%Low Dose
(n = 134)
%Body as a Whole
Asthenia
21
10
Digestive System
Nausea
34
26
Diarrhea
23
19
Vomiting
23
15
Abdominal Pain
12
9
Anorexia
11
4
Dyspepsia
11
10
Hemic/Lymphatic System
Thrombocytopenia
24
1
Ecchymosis
5
4
Metabolic/Nutritional
Weight Gain
9
4
Peripheral Edema
8
3
Nervous System
Tremor
57
19
Somnolence
30
18
Dizziness
18
13
Insomnia
15
9
Nervousness
11
7
Amnesia
7
4
Nystagmus
7
1
Depression
5
4
Respiratory System
Infection
20
13
Pharyngitis
8
2
Dyspnea
5
1
Skin and Appendages
Alopecia
24
13
Special Senses
Amblyopia/Blurred Vision
8
4
Tinnitus
7
1
1 Headache was the only adverse reaction that occurred in ≥ 5% of patients in the high dose group and at an equal or greater incidence in the low dose group.
The following additional adverse reactions were reported by greater than 1% but less than 5% of the 358 patients treated with divalproex sodium in the controlled trials of complex partial seizures:
Body as a Whole: Back pain, chest pain, malaise.
Cardiovascular System: Tachycardia, hypertension, palpitation.
Digestive System: Increased appetite, flatulence, hematemesis, eructation, pancreatitis, periodontal abscess.
Hemic and Lymphatic System: Petechia.
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders: SGOT increased, SGPT increased.
Musculoskeletal System: Myalgia, twitching, arthralgia, leg cramps, myasthenia.
Nervous System: Anxiety, confusion, abnormal gait, paresthesia, hypertonia, incoordination, abnormal dreams, personality disorder.
Respiratory System: Sinusitis, cough increased, pneumonia, epistaxis.
Skin and Appendages: Rash, pruritus, dry skin.
Special Senses: Taste perversion, abnormal vision, deafness, otitis media.
Urogenital System: Urinary incontinence, vaginitis, dysmenorrhea, amenorrhea, urinary frequency.
6.2 Mania
Although valproic acid has not been evaluated for safety and efficacy in the treatment of manic episodes associated with bipolar disorder, the following adverse reactions not listed above were reported by 1% or more of patients from two placebo-controlled clinical trials of divalproex sodium tablets.
Body as a Whole: Chills, neck pain, neck rigidity.
Cardiovascular System: Hypotension, postural hypotension, vasodilation.
Digestive System: Fecal incontinence, gastroenteritis, glossitis.
Musculoskeletal System: Arthrosis.
Nervous System: Agitation, catatonic reaction, hypokinesia, reflexes increased, tardive dyskinesia, vertigo.
Skin and Appendages: Furunculosis, maculopapular rash, seborrhea.
Special Senses: Conjunctivitis, dry eyes, eye pain.
Urogenital System: Dysuria.
6.3 Migraine
Although valproic acid has not been evaluated for safety and efficacy in the prophylactic treatment of migraine headaches, the following adverse reactions not listed above were reported by 1% or more of patients from two placebo-controlled clinical trials of divalproex sodium tablets.
Body as a Whole: Face edema.
Digestive System: Dry mouth, stomatitis.
Urogenital System: Cystitis, metrorrhagia, and vaginal hemorrhage.
Close6.4 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of divalproex sodium. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Dermatologic: Hair texture changes, hair color changes, photosensitivity, erythema multiforme, toxic epidermal necrolysis, nail and nail bed disorders, and Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
Psychiatric: Emotional upset, psychosis, aggression, psychomotor hyperactivity, hostility, disturbance in attention, learning disorder, and behavioral deterioration.
Neurologic: Paradoxical convulsion, parkinsonism
There have been several reports of acute or subacute cognitive decline and behavioral changes (apathy or irritability) with cerebral pseudoatrophy on imaging associated with valproate therapy; both the cognitive/behavioral changes and cerebral pseudoatrophy reversed partially or fully after valproate discontinuation.
There have been reports of acute or subacute encephalopathy in the absence of elevated ammonia levels, elevated valproate levels, or neuroimaging changes. The encephalopathy reversed partially or fully after valproate discontinuation.
Musculoskeletal: Fractures, decreased bone mineral density, osteopenia, osteoporosis, and weakness.
Hematologic: Relative lymphocytosis, macrocytosis, leukopenia, anemia including macrocytic with or without folate deficiency, bone marrow suppression, pancytopenia, aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, and acute intermittent porphyria.
Endocrine: Irregular menses, secondary amenorrhea, hyperandrogenism, hirsutism, elevated testosterone level, breast enlargement, galactorrhea, parotid gland swelling, polycystic ovary disease, decreased carnitine concentrations, hyponatremia, hyperglycinemia, and inappropriate ADH secretion.
There have been rare reports of Fanconi's syndrome occurring chiefly in children.
Metabolism and nutrition: Weight gain.
Reproductive: Aspermia, azoospermia, decreased sperm count, decreased spermatozoa motility, male infertility, and abnormal spermatozoa morphology.
Genitourinary: Enuresis and urinary tract infection.
Special Senses: Hearing loss.
Other: Allergic reaction, anaphylaxis, developmental delay, bone pain, bradycardia, and cutaneous vasculitis.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS7.1 Effects of Co-Administered Drugs on Valproate Clearance - Drugs that affect the level of expression of hepatic enzymes, particularly those that elevate levels of glucuronosyltransferases ...
7.1 Effects of Co-Administered Drugs on Valproate Clearance
Drugs that affect the level of expression of hepatic enzymes, particularly those that elevate levels of glucuronosyltransferases (such as ritonavir), may increase the clearance of valproate. For example, phenytoin, carbamazepine, and phenobarbital (or primidone) can double the clearance of valproate. Thus, patients on monotherapy will generally have longer half-lives and higher concentrations than patients receiving polytherapy with antiepilepsy drugs.
In contrast, drugs that are inhibitors of cytochrome P450 isozymes, e.g., antidepressants, may be expected to have little effect on valproate clearance because cytochrome P450 microsomal mediated oxidation is a relatively minor secondary metabolic pathway compared to glucuronidation and beta-oxidation.
Because of these changes in valproate clearance, monitoring of valproate and concomitant drug concentrations should be increased whenever enzyme inducing drugs are introduced or withdrawn.
The following list provides information about the potential for an influence of several commonly prescribed medications on valproate pharmacokinetics. The list is not exhaustive nor could it be, since new interactions are continuously being reported.
Drugs for which a potentially important interaction has been observed
Aspirin
A study involving the co-administration of aspirin at antipyretic doses (11 to 16 mg/kg) with valproate to pediatric patients (n = 6) revealed a decrease in protein binding and an inhibition of metabolism of valproate. Valproate free fraction was increased 4-fold in the presence of aspirin compared to valproate alone. The β-oxidation pathway consisting of 2-E-valproic acid, 3-OH-valproic acid, and 3-keto valproic acid was decreased from 25% of total metabolites excreted on valproate alone to 8.3% in the presence of aspirin. Caution should be observed if valproate and aspirin are to be co-administered.
Carbapenem Antibiotics
A clinically significant reduction in serum valproic acid concentration has been reported in patients receiving carbapenem antibiotics (for example, ertapenem, imipenem, meropenem; this is not a complete list) and may result in loss of seizure control. The mechanism of this interaction is not well understood. Serum valproic acid concentrations should be monitored frequently after initiating carbapenem therapy. Alternative antibacterial or anticonvulsant therapy should be considered if serum valproic acid concentrations drop significantly or seizure control deteriorates [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
Cholestyramine
Cholestyramine, when concurrently administered with valproic acid, led to, on average, a 14% decrease in plasma levels of valproic acid in a study conducted in 6 healthy subjects administered valproic acid and cholestyramine. Delaying the administration of cholestyramine relative to valproic acid administration by 3 hours may lessen the interaction.
Estrogen-Containing Hormonal Contraceptives
Estrogen-containing hormonal contraceptives may increase the clearance of valproate, which may result in decreased concentration of valproate and potentially increased seizure frequency. Prescribers should monitor serum valproate concentrations and clinical response when adding or discontinuing estrogen containing products.
Felbamate
A study involving the co-administration of 1,200 mg/day of felbamate with valproate to patients with epilepsy (n = 10) revealed an increase in mean valproate peak concentration by 35% (from 86 to 115 mcg/mL) compared to valproate alone. Increasing the felbamate dose to 2,400 mg/day increased the mean valproate peak concentration to 133 mcg/mL (another 16% increase). A decrease in valproate dosage may be necessary when felbamate therapy is initiated.
Rifampin
A study involving the administration of a single dose of valproate (7 mg/kg) 36 hours after 5 nights of daily dosing with rifampin (600 mg) revealed a 40% increase in the oral clearance of valproate. Valproate dosage adjustment may be necessary when it is co-administered with rifampin.
Drugs for which either no interaction or a likely clinically unimportant interaction has been observed
Antacids
A study involving the co-administration of valproate 500 mg with commonly administered antacids (Maalox, Trisogel, and Titralac - 160 mEq doses) did not reveal any effect on the extent of absorption of valproate.
Chlorpromazine
A study involving the administration of 100 to 300 mg/day of chlorpromazine to schizophrenic patients already receiving valproate (200 mg BID) revealed a 15% increase in trough plasma levels of valproate.
Haloperidol
A study involving the administration of 6 to 10 mg/day of haloperidol to schizophrenic patients already receiving valproate (200 mg BID) revealed no significant changes in valproate trough plasma levels.
Cimetidine and Ranitidine
Cimetidine and ranitidine do not affect the clearance of valproate.
7.2 Effects of Valproate on Other Drugs
Valproate has been found to be a weak inhibitor of some P450 isozymes, epoxide hydrase, and glucuronosyltransferases.
The following list provides information about the potential for an influence of valproate co- administration on the pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of several commonly prescribed medications. The list is not exhaustive, since new interactions are continuously being reported.
Drugs for which a potentially important valproate interaction has been observed
Amitriptyline/Nortriptyline
Administration of a single oral 50 mg dose of amitriptyline to 15 normal volunteers (10 males and 5 females) who received valproate (500 mg BID) resulted in a 21% decrease in plasma clearance of amitriptyline and a 34% decrease in the net clearance of nortriptyline. Rare postmarketing reports of concurrent use of valproate and amitriptyline resulting in an increased amitriptyline level have been received. Concurrent use of valproate and amitriptyline has rarely been associated with toxicity. Monitoring of amitriptyline levels should be considered for patients taking valproate concomitantly with amitriptyline. Consideration should be given to lowering the dose of amitriptyline/nortriptyline in the presence of valproate.
Carbamazepine/carbamazepine-10,11-Epoxide
Serum levels of carbamazepine (CBZ) decreased 17% while that of carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide (CBZ-E) increased by 45% upon co-administration of valproate and CBZ to epileptic patients.
Clonazepam
The concomitant use of valproate and clonazepam may induce absence status in patients with a history of absence type seizures.
Diazepam
Valproate displaces diazepam from its plasma albumin binding sites and inhibits its metabolism. Co-administration of valproate (1,500 mg daily) increased the free fraction of diazepam (10 mg) by 90% in healthy volunteers (n = 6). Plasma clearance and volume of distribution for free diazepam were reduced by 25% and 20%, respectively, in the presence of valproate. The elimination half-life of diazepam remained unchanged upon addition of valproate.
Ethosuximide
Valproate inhibits the metabolism of ethosuximide. Administration of a single ethosuximide dose of 500 mg with valproate (800 to 1,600 mg/day) to healthy volunteers (n = 6) was accompanied by a 25% increase in elimination half-life of ethosuximide and a 15% decrease in its total clearance as compared to ethosuximide alone. Patients receiving valproate and ethosuximide, especially along with other anticonvulsants, should be monitored for alterations in serum concentrations of both drugs.
Lamotrigine
In a steady-state study involving 10 healthy volunteers, the elimination half-life of lamotrigine increased from 26 to 70 hours with valproate co-administration (a 165% increase). The dose of lamotrigine should be reduced when co-administered with valproate. Serious skin reactions (such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis) have been reported with concomitant lamotrigine and valproate administration. See lamotrigine package insert for details on lamotrigine dosing with concomitant valproate administration.
Phenobarbital
Valproate was found to inhibit the metabolism of phenobarbital. Co-administration of valproate (250 mg BID for 14 days) with phenobarbital to normal subjects (n = 6) resulted in a 50% increase in half-life and a 30% decrease in plasma clearance of phenobarbital (60 mg single-dose). The fraction of phenobarbital dose excreted unchanged increased by 50% in presence of valproate.
There is evidence for severe CNS depression, with or without significant elevations of barbiturate or valproate serum concentrations. All patients receiving concomitant barbiturate therapy should be closely monitored for neurological toxicity. Serum barbiturate concentrations should be obtained, if possible, and the barbiturate dosage decreased, if appropriate.
Primidone, which is metabolized to a barbiturate, may be involved in a similar interaction with valproate.
Phenytoin
Valproate displaces phenytoin from its plasma albumin binding sites and inhibits its hepatic metabolism. Co-administration of valproate (400 mg TID) with phenytoin (250 mg) in normal volunteers (n = 7) was associated with a 60% increase in the free fraction of phenytoin. Total plasma clearance and apparent volume of distribution of phenytoin increased 30% in the presence of valproate. Both the clearance and apparent volume of distribution of free phenytoin were reduced by 25%.
In patients with epilepsy, there have been reports of breakthrough seizures occurring with the combination of valproate and phenytoin. The dosage of phenytoin should be adjusted as required by the clinical situation.
Propofol
The concomitant use of valproate and propofol may lead to increased blood levels of propofol. Reduce the dose of propofol when co-administering with valproate. Monitor patients closely for signs of increased sedation or cardiorespiratory depression.
Rufinamide
Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis, rufinamide clearance was decreased by valproate. Rufinamide concentrations were increased by <16% to 70%, dependent on concentration of valproate (with the larger increases being seen in pediatric patients at high doses or concentrations of valproate). Patients stabilized on rufinamide before being prescribed valproate should begin valproate therapy at a low dose, and titrate to a clinically effective dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Similarly, patients on valproate should begin at a rufinamide dose lower than 10 mg/kg per day (pediatric patients) or 400 mg per day (adults).
Tolbutamide
From in vitro experiments, the unbound fraction of tolbutamide was increased from 20% to 50% when added to plasma samples taken from patients treated with valproate. The clinical relevance of this displacement is unknown.
Warfarin
In an in vitro study, valproate increased the unbound fraction of warfarin by up to 32.6%. The therapeutic relevance of this is unknown; however, coagulation tests should be monitored if valproate therapy is instituted in patients taking anticoagulants.
Zidovudine
In six patients who were seropositive for HIV, the clearance of zidovudine (100 mg q8h) was decreased by 38% after administration of valproate (250 or 500 mg q8h); the half-life of zidovudine was unaffected.
Drugs for which either no interaction or a likely clinically unimportant interaction has been observed
Acetaminophen
Valproate had no effect on any of the pharmacokinetic parameters of acetaminophen when it was concurrently administered to three epileptic patients.
Clozapine
In psychotic patients (n = 11), no interaction was observed when valproate was co-administered with clozapine.
Lithium
Co-administration of valproate (500 mg BID) and lithium carbonate (300 mg TID) to normal male volunteers (n = 16) had no effect on the steady-state kinetics of lithium.
Lorazepam
Concomitant administration of valproate (500 mg BID) and lorazepam (1 mg BID) in normal male volunteers (n = 9) was accompanied by a 17% decrease in the plasma clearance of lorazepam.
Olanzapine
No dose adjustment for olanzapine is necessary when olanzapine is administered concomitantly with valproate. Co-administration of valproate (500 mg BID) and olanzapine (5 mg) to healthy adults (n=10) caused 15% reduction in Cmax and 35% reduction in AUC of olanzapine.
Oral Contraceptive Steroids
Administration of a single-dose of ethinyloestradiol (50 mcg)/levonorgestrel (250 mcg) to 6 women on valproate (200 mg BID) therapy for 2 months did not reveal any pharmacokinetic interaction.
Close7.3 Topiramate
Concomitant administration of valproate and topiramate has been associated with hyperammonemia with and without encephalopathy [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.6, 5.9, 5.10)]. Concomitant administration of topiramate with valproate has also been associated with hypothermia in patients who have tolerated either drug alone. It may be prudent to examine blood ammonia levels in patients in whom the onset of hypothermia has been reported [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9, 5.11)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS8.1 Pregnancy - Pregnancy Exposure Registry - There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), including valproic acid oral ...
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to antiepileptic drugs (AEDs), including valproic acid oral solution, during pregnancy. Encourage women who are taking valproic acid during pregnancy to enroll in the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) Pregnancy Registry by calling toll-free 1-888-233-2334 or visiting the website, http://www.aedpregnancyregistry.org/. This must be done by the patient herself.
Risk Summary
For use in prophylaxis of migraine headaches, valproate is contraindicated in women who are pregnant and in women of childbearing potential who are not using effective contraception [see Contraindications (4)].
For use in epilepsy or bipolar disorder, valproate should not be used to treat women who are pregnant or who plan to become pregnant unless other medications have failed to provide adequate symptom control or are otherwise unacceptable [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)]. Women with epilepsy who become pregnant while taking valproate should not discontinue valproate abruptly, as this can precipitate status epilepticus with resulting maternal and fetal hypoxia and threat to life.
Maternal valproate use during pregnancy for any indication increases the risk of congenital malformations, particularly neural tube defects including spina bifida, but also malformations involving other body systems (e.g., craniofacial defects including oral clefts, cardiovascular malformations, hypospadias, limb malformations). This risk is dose-dependent; however, a threshold dose below which no risk exists cannot be established. In utero exposure to valproate may also result in hearing impairment or hearing loss. Valproate polytherapy with other AEDs has been associated with an increased frequency of congenital malformations compared with AED monotherapy. The risk of major structural abnormalities is greatest during the first trimester; however, other serious developmental effects can occur with valproate use throughout pregnancy. The rate of congenital malformations among babies born to epileptic mothers who used valproate during pregnancy has been shown to be about four times higher than the rate among babies born to epileptic mothers who used other anti-seizure monotherapies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Data (Human)].
Epidemiological studies have indicated that children exposed to valproate in utero have lower IQ scores and a higher risk of neurodevelopmental disorders compared to children exposed to either another AED in utero or to no AEDs in utero [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Data (Human)].
An observational study has suggested that exposure to valproate products during pregnancy increases the risk of autism spectrum disorders [see Data (Human)].
In animal studies, valproate administration during pregnancy resulted in fetal structural malformations similar to those seen in humans and neurobehavioral deficits in the offspring at clinically relevant doses [see Data (Animal)].
There have been reports of hypoglycemia in neonates and fatal cases of hepatic failure in infants following maternal use of valproate during pregnancy.
Pregnant women taking valproate may develop hepatic failure or clotting abnormalities including thrombocytopenia, hypofibrinogenemia, and/or decrease in other coagulation factors, which may result in hemorrhagic complications in the neonate including death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.8)].
Available prenatal diagnostic testing to detect neural tube and other defects should be offered to pregnant women using valproate.
Evidence suggests that folic acid supplementation prior to conception and during the first trimester of pregnancy decreases the risk for congenital neural tube defects in the general population. It is not known whether the risk of neural tube defects or decreased IQ in the offspring of women receiving valproate is reduced by folic acid supplementation. Dietary folic acid supplementation both prior to conception and during pregnancy should be routinely recommended for patients using valproate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.4)].
All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
To prevent major seizures, women with epilepsy should not discontinue valproate abruptly, as this can precipitate status epilepticus with resulting maternal and fetal hypoxia and threat to life. Even minor seizures may pose some hazard to the developing embryo or fetus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. However, discontinuation of the drug may be considered prior to and during pregnancy in individual cases if the seizure disorder severity and frequency do not pose a serious threat to the patient.
Maternal adverse reactions
Pregnant women taking valproate may develop clotting abnormalities including thrombocytopenia, hypofibrinogenemia, and/or decrease in other coagulation factors, which may result in hemorrhagic complications in the neonate including death [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]. If valproate is used in pregnancy, the clotting parameters should be monitored carefully in the mother. If abnormal in the mother, then these parameters should also be monitored in the neonate.
Patients taking valproate may develop hepatic failure [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Fatal cases of hepatic failure in infants exposed to valproate in utero have also been reported following maternal use of valproate during pregnancy.
Hypoglycemia has been reported in neonates whose mothers have taken valproate during pregnancy.
Data
Human
Neural tube defects and other structural abnormalities
There is an extensive body of evidence demonstrating that exposure to valproate in utero increases the risk of neural tube defects and other structural abnormalities. Based on published data from the CDC’s National Birth Defects Prevention Network, the risk of spina bifida in the general population is about 0.06 to 0.07% (6 to 7 in 10,000 births) compared to the risk following in utero valproate exposure estimated to be approximately 1 to 2% (100 to 200 in 10,000 births).
The NAAED Pregnancy Registry has reported a major malformation rate of 9 to 11% in the offspring of women exposed to an average of 1,000 mg/day of valproate monotherapy during pregnancy. These data show an up to a five-fold increased risk for any major malformation following valproate exposure in utero compared to the risk following exposure in utero to other AEDs taken as monotherapy. The major congenital malformations included cases of neural tube defects, cardiovascular malformations, craniofacial defects (e.g., oral clefts, craniosynostosis), hypospadias, limb malformations (e.g., clubfoot, polydactyly), and other malformations of varying severity involving other body systems [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Effect on IQ and neurodevelopmental effects
Published epidemiological studies have indicated that children exposed to valproate in utero have lower IQ scores than children exposed to either another AED in utero or to no AEDs in utero. The largest of these studies1 is a prospective cohort study conducted in the United States and United Kingdom that found that children with prenatal exposure to valproate (n=62) had lower IQ scores at age 6 (97 [95% C.I. 94-101]) than children with prenatal exposure to the other anti-epileptic drug monotherapy treatments evaluated: lamotrigine (108 [95% C.I. 105-110]), carbamazepine (105 [95% C.I. 102-108]) and phenytoin (108 [95% C.I. 104-112]). It is not known when during pregnancy cognitive effects in valproate-exposed children occur. Because the women in this study were exposed to AEDs throughout pregnancy, whether the risk for decreased IQ was related to a particular time period during pregnancy could not be assessed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Although the available studies have methodological limitations, the weight of the evidence supports a causal association between valproate exposure in utero and subsequent adverse effects on neurodevelopment, including increases in autism spectrum disorders and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). An observational study has suggested that exposure to valproate products during pregnancy increases the risk of autism spectrum disorders. In this study, children born to mothers who had used valproate products during pregnancy had 2.9 times the risk (95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.7-4.9) of developing autism spectrum disorders compared to children born to mothers not exposed to valproate products during pregnancy. The absolute risks for autism spectrum disorders were 4.4% (95% CI: 2.6%-7.5%) in valproate-exposed children and 1.5% (95% CI: 1.5%-1.6%) in children not exposed to valproate products. Another observational study found that children who were exposed to valproate in utero had an increased risk of ADHD (adjusted HR 1.48; 95% CI, 1.09-2.00) compared with the unexposed children. Because these studies were observational in nature, conclusions regarding a causal association between in utero valproate exposure and an increased risk of autism spectrum disorder and ADHD cannot be considered definitive.
Other
There are published case reports of fatal hepatic failure in offspring of women who used valproate during pregnancy.
Animal
In developmental toxicity studies conducted in mice, rats, rabbits, and monkeys, increased rates of fetal structural abnormalities, intrauterine growth retardation, and embryo-fetal death occurred following administration of valproate to pregnant animals during organogenesis at clinically relevant doses (calculated on a body surface area [mg/m2] basis). Valproate induced malformations of multiple organ systems, including skeletal, cardiac, and urogenital defects. In mice, in addition to other malformations, fetal neural tube defects have been reported following valproate administration during critical periods of organogenesis, and the teratogenic response correlated with peak maternal drug levels. Behavioral abnormalities (including cognitive, locomotor, and social interaction deficits) and brain histopathological changes have also been reported in mice and rat offspring exposed prenatally to clinically relevant doses of valproate.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Valproate is excreted in human milk. Data in the published literature describe the presence of valproate in human milk (range: 0.4 mcg/mL to 3.9 mcg/mL), corresponding to 1% to 10% of maternal serum levels. Valproate serum concentrations collected from breastfed infants aged 3 days postnatal to 12 weeks following delivery ranged from 0.7 mcg/mL to 4 mcg/mL, which were 1% to 6% of maternal serum valproate levels. A published study in children up to six years of age did not report adverse developmental or cognitive effects following exposure to valproate via breast milk [see Data (Human)].
There are no data to assess the effects of valproic acid on milk production or excretion.
Clinical Considerations
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for valproic acid oral solution and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from valproic acid or from the underlying maternal condition.
Monitor the breastfed infant for signs of liver damage including jaundice and unusual bruising or bleeding. There have been reports of hepatic failure and clotting abnormalities in offspring of women who used valproate during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Data
Human
In a published study, breast milk and maternal blood samples were obtained from 11 epilepsy patients taking valproate at doses ranging from 300 mg/day to 2,400 mg/day on postnatal days 3 to 6. In 4 patients who were taking valproate only, breast milk contained an average valproate concentration of 1.8 mcg/mL (range: 1.1 mcg/mL to 2.2 mcg/mL), which corresponded to 4.8% of the maternal plasma concentration (range: 2.7% to 7.4%). Across all patients (7 of whom were taking other AEDs concomitantly), similar results were obtained for breast milk concentration (1.8 mcg/mL, range: 0.4 mcg/mL to 3.9 mcg/mL) and maternal plasma ratio (5.1%, range: 1.3% to 9.6%).
A published study of 6 breastfeeding mother-infant pairs measured serum valproate levels during maternal treatment for bipolar disorder (750 mg/day or 1,000 mg/day). None of the mothers received valproate during pregnancy, and infants were aged from 4 weeks to 19 weeks at the time of evaluation. Infant serum levels ranged from 0.7 mcg/mL to 1.5 mcg/mL. With maternal serum valproate levels near or within the therapeutic range, infant exposure was 0.9% to 2.3% of maternal levels. Similarly, in 2 published case reports with maternal doses of 500 mg/day or 750 mg/day during breastfeeding of infants aged 3 months and 1 month, infant exposure was 1.5% and 6% that of the mother, respectively.
A prospective observational multicenter study evaluated the long-term neurodevelopmental effects of AED use on children. Pregnant women receiving monotherapy for epilepsy were enrolled with assessments of their children at ages 3 years and 6 years. Mothers continued AED therapy during the breastfeeding period. Adjusted IQs measured at 3 years for breastfed and non- breastfed children were 93 (n=11) and 90 (n=24), respectively. At 6 years, the scores for breastfed and non-breastfed children were 106 (n=11) and 94 (n=25), respectively (p=0.04). For other cognitive domains evaluated at 6 years, no adverse cognitive effects of continued exposure to an AED (including valproate) via breast milk were observed.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Women of childbearing potential should use effective contraception while taking valproate [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Drug Interactions (7), and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. This is especially important when valproate use is considered for a condition not usually associated with permanent injury or death such as prophylaxis of migraine headaches [see Contraindications (4)].
Infertility
There have been reports of male infertility coincident with valproate therapy [see Adverse Reactions (6.4)].
In animal studies, oral administration of valproate at clinically relevant doses resulted in adverse reproductive effects in males [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
Experience has indicated that pediatric patients under the age of two years are at a considerably increased risk of developing fatal hepatotoxicity, especially those with the aforementioned conditions [see Boxed Warning]. When valproic acid is used in this patient group, it should be used with extreme caution and as a sole agent. The benefits of therapy should be weighed against the risks. Above the age of 2 years, experience in epilepsy has indicated that the incidence of fatal hepatotoxicity decreases considerably in progressively older patient groups.
Younger children, especially those receiving enzyme-inducing drugs, will require larger maintenance doses to attain targeted total and unbound valproate concentrations. Pediatric patients (i.e., between 3 months and 10 years) have 50% higher clearances expressed on weight (i.e., mL/min/kg) than do adults. Over the age of 10 years, children have pharmacokinetic parameters that approximate those of adults.
The variability in free fraction limits the clinical usefulness of monitoring total serum valproic acid concentrations. Interpretation of valproic acid concentrations in children should include consideration of factors that affect hepatic metabolism and protein binding.
Pediatric Clinical Trials
Divalproex sodium was studied in seven pediatric clinical trials.
Two of the pediatric studies were double-blinded placebo-controlled trials to evaluate the efficacy of divalproex sodium extended-release tablets for the indications of mania (150 patients aged 10 to 17 years, 76 of whom were on divalproex sodium extended-release tablets) and migraine (304 patients aged 12 to 17 years, 231 of whom were on divalproex sodium extended-release tablets). Efficacy was not established for either the treatment of migraine or the treatment of mania. The most common drug-related adverse reactions (reported >5% and twice the rate of placebo) reported in the controlled pediatric mania study were nausea, upper abdominal pain, somnolence, increased ammonia, gastritis and rash.
The remaining five trials were long term safety studies. Two six-month pediatric studies were conducted to evaluate the long-term safety of divalproex sodium extended-release tablets for the indication of mania (292 patients aged 10 to 17 years). Two twelve-month pediatric studies were conducted to evaluate the long-term safety of divalproex sodium extended-release tablets for the indication of migraine (353 patients aged 12 to 17 years). One twelve-month study was conducted to evaluate the safety of divalproex sodium sprinkle capsules in the indication of partial seizures (169 patients aged 3 to 10 years).
In these seven clinical trials, the safety and tolerability of divalproex sodium in pediatric patients were shown to be comparable to those in adults [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Juvenile Animal Toxicology
In studies of valproate in immature animals, toxic effects not observed in adult animals included retinal dysplasia in rats treated during the neonatal period (from postnatal day 4) and nephrotoxicity in rats treated during the neonatal and juvenile (from postnatal day 14) periods. The no-effect dose for these findings was less than the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis.
Close8.5 Geriatric Use
No patients above the age of 65 years were enrolled in double-blind prospective clinical trials of mania associated with bipolar illness. In a case review study of 583 patients, 72 patients (12%) were greater than 65 years of age. A higher percentage of patients above 65 years of age reported accidental injury, infection, pain, somnolence, and tremor.
Discontinuation of valproate was occasionally associated with the latter two events. It is not clear whether these events indicate additional risk or whether they result from preexisting medical illness and concomitant medication use among these patients.
A study of elderly patients with dementia revealed drug related somnolence and discontinuation for somnolence [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]. The starting dose should be reduced in these patients, and dosage reductions or discontinuation should be considered in patients with excessive somnolence [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGEOverdosage with valproate may result in somnolence, heart block, deep coma, and hypernatremia. Fatalities have been reported; however, patients have recovered from valproate levels as high as ...
Overdosage with valproate may result in somnolence, heart block, deep coma, and hypernatremia. Fatalities have been reported; however, patients have recovered from valproate levels as high as 2,120 mcg/mL.
In overdose situations, the fraction of drug not bound to protein is high and hemodialysis or tandem hemodialysis plus hemoperfusion may result in significant removal of drug. The benefit of gastric lavage or emesis will vary with the time since ingestion. General supportive measures should be applied with particular attention to the maintenance of adequate urinary output.
Naloxone has been reported to reverse the CNS depressant effects of valproate overdosage. Because naloxone could theoretically also reverse the antiepileptic effects of valproate, it should be used with caution in patients with epilepsy.
Close -
11 DESCRIPTIONValproic acid is a carboxylic acid designated as 2-propylpentanoic acid. It is also known as dipropylacetic acid. Valproic acid has the following structure: Valproic acid (pKa 4.8) has a ...
Valproic acid is a carboxylic acid designated as 2-propylpentanoic acid. It is also known as dipropylacetic acid. Valproic acid has the following structure:
Valproic acid (pKa 4.8) has a molecular weight of 144 and occurs as a colorless liquid with a characteristic odor. It is slightly soluble in water (1.3 mg/mL) and very soluble in organic solvents.
Valproic acid oral solution USP is an antiepileptic for oral administration. Valproic acid oral solution USP contains the equivalent of 250 mg valproic acid per 5 mL as the sodium salt.
Inactive Ingredients
FD&C Red No. 40, glycerin, methylparaben, propylparaben, sodium hydroxide, sorbitol, sucrose, purified water, sour cherry flavor and alcohol 0.02% (v/v).
Close -
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY12.1 Mechanism of Action - Valproic acid dissociates to the valproate ion in the gastrointestinal tract. The mechanisms by which valproate exerts its therapeutic effects have not been ...
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Valproic acid dissociates to the valproate ion in the gastrointestinal tract. The mechanisms by which valproate exerts its therapeutic effects have not been established. It has been suggested that its activity in epilepsy is related to increased brain concentrations of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA).
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The relationship between plasma concentration and clinical response is not well documented. One contributing factor is the nonlinear, concentration dependent protein binding of valproate which affects the clearance of the drug. Thus, monitoring of total serum valproate cannot provide a reliable index of the bioactive valproate species.
For example, because the plasma protein binding of valproate is concentration dependent, the free fraction increases from approximately 10% at 40 mcg/mL to 18.5% at 130 mcg/mL. Higher than expected free fractions occur in the elderly, in hyperlipidemic patients, and in patients with hepatic and renal diseases.
Epilepsy
The therapeutic range in epilepsy is commonly considered to be 50 to 100 mcg/mL of total valproate, although some patients may be controlled with lower or higher plasma concentrations.
Close12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption/Bioavailability
Equivalent oral doses of divalproex sodium products and valproic acid capsules deliver equivalent quantities of valproate ion systemically. Although the rate of valproate ion absorption may vary with the formulation administered (liquid, solid, or sprinkle), conditions of use (e.g., fasting or postprandial) and the method of administration (e.g., whether the contents of the capsule are sprinkled on food or the capsule is taken intact), these differences should be of minor clinical importance under the steady state conditions achieved in chronic use in the treatment of epilepsy.
However, it is possible that differences among the various valproate products in Tmax and Cmax could be important upon initiation of treatment. For example, in single dose studies, the effect of feeding had a greater influence on the rate of absorption of the divalproex sodium tablet (increase in Tmax from 4 to 8 hours) than on the absorption of the divalproex sodium sprinkle capsules (increase in Tmax from 3.3 to 4.8 hours).
While the absorption rate from the G.I. tract and fluctuation in valproate plasma concentrations vary with dosing regimen and formulation, the efficacy of valproate as an anticonvulsant in chronic use is unlikely to be affected. Experience employing dosing regimens from once-a-day to four-times-a-day, as well as studies in primate epilepsy models involving constant rate infusion, indicate that total daily systemic bioavailability (extent of absorption) is the primary determinant of seizure control and that differences in the ratios of plasma peak to trough concentrations between valproate formulations are inconsequential from a practical clinical standpoint.
Co-administration of oral valproate products with food and substitution among the various divalproex sodium and valproic acid formulations should cause no clinical problems in the management of patients with epilepsy [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. Nonetheless, any changes in dosage administration, or the addition or discontinuance of concomitant drugs should ordinarily be accompanied by close monitoring of clinical status and valproate plasma concentrations.
Distribution
Protein Binding
The plasma protein binding of valproate is concentration dependent and the free fraction increases from approximately 10% at 40 mcg/mL to 18.5% at 130 mcg/mL. Protein binding of valproate is reduced in the elderly, in patients with chronic hepatic diseases, in patients with renal impairment, and in the presence of other drugs (e.g., aspirin). Conversely, valproate may displace certain protein-bound drugs (e.g., phenytoin, carbamazepine, warfarin, and tolbutamide) [see Drug Interactions (7.2) for more detailed information on the pharmacokinetic interactions of valproate with other drugs].
CNS Distribution
Valproate concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) approximate unbound concentrations in plasma (about 10% of total concentration).
Metabolism
Valproate is metabolized almost entirely by the liver. In adult patients on monotherapy, 30 to 50% of an administered dose appears in urine as a glucuronide conjugate. Mitochondrial β-oxidation is the other major metabolic pathway, typically accounting for over 40% of the dose. Usually, less than 15 to 20% of the dose is eliminated by other oxidative mechanisms. Less than 3% of an administered dose is excreted unchanged in urine.
The relationship between dose and total valproate concentration is nonlinear; concentration does not increase proportionally with the dose, but rather, increases to a lesser extent due to saturable plasma protein binding. The kinetics of unbound drug are linear.
Elimination
Mean plasma clearance and volume of distribution for total valproate are 0.56 L/hr/1.73 m2 and 11 L/1.73 m2, respectively. Mean plasma clearance and volume of distribution for free valproate are 4.6 L/hr/1.73 m2 and 92 L/1.73 m2. Mean terminal half-life for valproate monotherapy ranged from 9 to 16 hours following oral dosing regimens of 250 to 1,000 mg.
The estimates cited apply primarily to patients who are not taking drugs that affect hepatic metabolizing enzyme systems. For example, patients taking enzyme-inducing antiepileptic drugs (carbamazepine, phenytoin, and phenobarbital) will clear valproate more rapidly. Because of these changes in valproate clearance, monitoring of antiepileptic concentrations should be intensified whenever concomitant antiepileptics are introduced or withdrawn.
Special Populations
Effect of Age
Neonates
Children within the first two months of life have a markedly decreased ability to eliminate valproate compared to older children and adults. This is a result of reduced clearance (perhaps due to delay in development of glucuronosyltransferase and other enzyme systems involved in valproate elimination) as well as increased volume of distribution (in part due to decreased plasma protein binding). For example, in one study, the half-life in children under 10 days ranged from 10 to 67 hours compared to a range of 7 to 13 hours in children greater than 2 months.
Children
Pediatric patients (i.e., between 3 months and 10 years) have 50% higher clearances expressed on weight (i.e., mL/min/kg) than do adults. Over the age of 10 years, children have pharmacokinetic parameters that approximate those of adults.
Elderly
The capacity of elderly patients (age range: 68 to 89 years) to eliminate valproate has been shown to be reduced compared to younger adults (age range: 22 to 26 years). Intrinsic clearance is reduced by 39%; the free fraction is increased by 44%. Accordingly, the initial dosage should be reduced in the elderly [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Effect of Sex
There are no differences in the body surface area adjusted unbound clearance between males and females (4.8 ± 0.17 and 4.7 ± 0.07 L/hr per 1.73 m2, respectively).
Effect of Race
The effects of race on the kinetics of valproate have not been studied.
Effect of Disease
Liver Disease
Liver disease impairs the capacity to eliminate valproate. In one study, the clearance of free valproate was decreased by 50% in 7 patients with cirrhosis and by 16% in 4 patients with acute hepatitis, compared with 6 healthy subjects. In that study, the half-life of valproate was increased from 12 to 18 hours. Liver disease is also associated with decreased albumin concentrations and larger unbound fractions (2 to 2.6 fold increase) of valproate. Accordingly, monitoring of total concentrations may be misleading since free concentrations may be substantially elevated in patients with hepatic disease whereas total concentrations may appear to be normal [see Boxed Warning, Contraindications (4), and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Renal Disease
A slight reduction (27%) in the unbound clearance of valproate has been reported in patients with renal failure (creatinine clearance < 10 mL/minute); however, hemodialysis typically reduces valproate concentrations by about 20%. Therefore, no dosage adjustment appears to be necessary in patients with renal failure. Protein binding in these patients is substantially reduced; thus, monitoring total concentrations may be misleading.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility - Carcinogenesis - Valproate was administered orally to rats and mice at doses of 80 and 170 mg/kg/day (less than the maximum ...Close
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Valproate was administered orally to rats and mice at doses of 80 and 170 mg/kg/day (less than the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis) for two years. The primary findings were an increase in the incidence of subcutaneous fibrosarcomas in high-dose male rats receiving valproate and a dose-related trend for benign pulmonary adenomas in male mice receiving valproate.
Mutagenesis
Valproate was not mutagenic in an in vitro bacterial assay (Ames test), did not produce dominant lethal effects in mice, and did not increase chromosome aberration frequency in an in vivo cytogenetic study in rats. Increased frequencies of sister chromatid exchange (SCE) have been reported in a study of epileptic children taking valproate; this association was not observed in another study conducted in adults.
Impairment of Fertility
In chronic toxicity studies in juvenile and adult rats and dogs, administration of valproate resulted in testicular atrophy and reduced spermatogenesis at oral doses of 400 mg/kg/day or greater in rats (approximately equal to or greater than the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) on a mg/m2 basis) and 150 mg/kg/day or greater in dogs (approximately equal to or greater than the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis). Fertility studies in rats have shown no effect on fertility at oral doses of valproate up to 350 mg/kg/day (approximately equal to the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis) for 60 days.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES The studies described in the following section were conducted using divalproex sodium tablets. 14.1 Epilepsy - The efficacy of divalproex sodium in reducing the incidence of complex partial ...
The studies described in the following section were conducted using divalproex sodium tablets.
Close14.1 Epilepsy
The efficacy of divalproex sodium in reducing the incidence of complex partial seizures (CPS) that occur in isolation or in association with other seizure types was established in two controlled trials.
In one, multi-clinic, placebo-controlled study employing an add-on design (adjunctive therapy), 144 patients who continued to suffer eight or more CPS per 8 weeks during an 8 week period of monotherapy with doses of either carbamazepine or phenytoin sufficient to assure plasma concentrations within the "therapeutic range" were randomized to receive, in addition to their original antiepilepsy drug (AED), either divalproex sodium or placebo. Randomized patients were to be followed for a total of 16 weeks. The following table presents the findings.
Table 5. Adjunctive Therapy Study Median Incidence of CPS per 8 Weeks
Add-on Treatment
Number of Patients
Baseline Incidence
Experimental Incidence
Divalproex Sodium
75
16.0
8.9*
Placebo
69
14.5
11.5
* Reduction from baseline statistically significantly greater for divalproex sodium than placebo at p ≤ 0.05 level.
Figure 1 presents the proportion of patients (X axis) whose percentage reduction from baseline in complex partial seizure rates was at least as great as that indicated on the Y axis in the adjunctive therapy study. A positive percent reduction indicates an improvement (i.e., a decrease in seizure frequency), while a negative percent reduction indicates worsening. Thus, in a display of this type, the curve for an effective treatment is shifted to the left of the curve for placebo. This figure shows that the proportion of patients achieving any particular level of improvement was consistently higher for divalproex sodium than for placebo. For example, 45% of patients treated with divalproex sodium had a ≥ 50% reduction in complex partial seizure rate compared to 23% of patients treated with placebo.
Figure 1
The second study assessed the capacity of divalproex sodium to reduce the incidence of CPS when administered as the sole AED. The study compared the incidence of CPS among patients randomized to either a high or low dose treatment arm. Patients qualified for entry into the randomized comparison phase of this study only if 1) they continued to experience 2 or more CPS per 4 weeks during an 8 to 12 week long period of monotherapy with adequate doses of an AED (i.e., phenytoin, carbamazepine, phenobarbital, or primidone) and 2) they made a successful transition over a two week interval to divalproex sodium. Patients entering the randomized phase were then brought to their assigned target dose, gradually tapered off their concomitant AED and followed for an interval as long as 22 weeks. Less than 50% of the patients randomized, however, completed the study. In patients converted to divalproex sodium monotherapy, the mean total valproate concentrations during monotherapy were 71 and 123 mcg/mL in the low dose and high dose groups, respectively.
The following table presents the findings for all patients randomized who had at least one post- randomization assessment.
Table 6. Monotherapy Study Median Incidence of CPS per 8 Weeks
Treatment
Number of Patients
Baseline Incidence
Randomized Phase Incidence
High dose divalproex sodium
131
13.2
10.7*
Low dose divalproex sodium
134
14.2
13.8
* Reduction from baseline statistically significantly greater for high dose than low dose at p ≤ 0.05 level.
Figure 2 presents the proportion of patients (X axis) whose percentage reduction from baseline in complex partial seizure rates was at least as great as that indicated on the Y axis in the monotherapy study. A positive percent reduction indicates an improvement (i.e., a decrease in seizure frequency), while a negative percent reduction indicates worsening. Thus, in a display of this type, the curve for a more effective treatment is shifted to the left of the curve for a less effective treatment. This figure shows that the proportion of patients achieving any particular level of reduction was consistently higher for high dose divalproex sodium than for low dose divalproex sodium. For example, when switching from carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital or primidone monotherapy to high dose divalproex sodium monotherapy, 63% of patients experienced no change or a reduction in complex partial seizure rates compared to 54% of patients receiving low dose divalproex sodium.
Figure 2
Information on pediatric studies is presented in section 8.
-
15 REFERENCES 1. Meador KJ, Baker GA, Browning N, et al. Fetal antiepileptic drug exposure and cognitive outcomes at age 6 years (NEAD study): a prospective observational study. Lancet Neurology 2013; 12 ...
1. Meador KJ, Baker GA, Browning N, et al. Fetal antiepileptic drug exposure and cognitive outcomes at age 6 years (NEAD study): a prospective observational study. Lancet Neurology 2013; 12 (3):244-252.
Close -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLINGValproic Acid Oral Solution USP is a clear, red, sour cherry flavored oral solution containing the equivalent of 250 mg valproic acid per 5 mL as the sodium salt and is available as follows: NDC ...
Valproic Acid Oral Solution USP is a clear, red, sour cherry flavored oral solution containing the equivalent of 250 mg valproic acid per 5 mL as the sodium salt and is available as follows:
NDC 62559-266-16: 16 fl. oz. (473 mL) bottle
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Close -
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATIONAdvise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide). Hepatotoxicity - Warn patients and guardians that nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, anorexia, diarrhea, asthenia ...
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Hepatotoxicity
Warn patients and guardians that nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, anorexia, diarrhea, asthenia, and/or jaundice can be symptoms of hepatotoxicity and, therefore, require further medical evaluation promptly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Pancreatitis
Warn patients and guardians that abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and/or anorexia can be symptoms of pancreatitis and, therefore, require further medical evaluation promptly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Birth Defects and Decreased IQ
Inform pregnant women and women of childbearing potential (including girls beginning the onset of puberty) that use of valproate during pregnancy increases the risk of birth defects, decreased IQ, and neurodevelopmental disorders in children who were exposed in utero. Advise women to use effective contraception while taking valproate. When appropriate, counsel these patients about alternative therapeutic options. This is particularly important when valproate use is considered for a condition not usually associated with permanent injury or death such as prophylaxis of migraine headache [see Contraindications (4)]. Advise patients to read the Medication Guide, which appears as the last section of the labeling [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3, 5.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Registry
Advise women of childbearing potential to discuss pregnancy planning with their doctor and to contact their doctor immediately if they think they are pregnant.
Encourage women who are taking valproic acid to enroll in the North American Antiepileptic Drug (NAAED) Pregnancy Registry if they become pregnant. This registry is collecting information about the safety of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy. To enroll, patients can call the toll free number 1-888-233- 2334 or visit the website, http://www.aedpregnancyregistry.org/ [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Suicidal Thinking and Behavior
Counsel patients, their caregivers, and families that AEDs, including valproic acid, may increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior and to be alert for the emergence or worsening of symptoms of depression, any unusual changes in mood or behavior, or the emergence of suicidal thoughts, behavior, or thoughts about self-harm. Instruct patients, caregivers, and families to report behaviors of concern immediately to the healthcare providers [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Hyperammonemia
Inform patients of the signs and symptoms associated with hyperammonemic encephalopathy and to notify the prescriber if any of these symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9, 5.10)].
CNS Depression
Since valproate products may produce CNS depression, especially when combined with another CNS depressant (e.g., alcohol), advise patients not to engage in hazardous activities, such as driving an automobile or operating dangerous machinery, until it is known that they do not become drowsy from the drug.
Multiorgan Hypersensitivity Reactions
Instruct patients that a fever associated with other organ system involvement (rash, lymphadenopathy, etc.) may be drug-related and should be reported to the physician immediately [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
Distributed by:
Close
ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Baudette, MN 56623

-
MEDICATION GUIDE Valproic (val PROE ik) Acid Oral Solution - Read this Medication Guide before you start taking valproic acid oral solution and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This ...
Valproic (val PROE ik) Acid Oral Solution
Read this Medication Guide before you start taking valproic acid oral solution and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about valproic acid oral solution?
Do not stop taking valproic acid oral solution without first talking to your healthcare provider.
Stopping valproic acid oral solution suddenly can cause serious problems.
Valproic acid oral solution can cause serious side effects, including:
- 1.
- Serious liver damage that can cause death, especially in children younger than 2 years old.
The risk of getting this serious liver damage is more likely to happen within the first 6 months of treatment.
Call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms:
- •
- nausea or vomiting that does not go away
- •
- loss of appetite
- •
- pain on the right side of your stomach (abdomen)
- •
- dark urine
- •
- swelling of your face
- •
- yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes
In some cases, liver damage may continue despite stopping the drug.
- 2.
- Valproic acid oral solution may harm your unborn baby.
- •
- If you take valproic acid oral solution during pregnancy for any medical condition, your baby is at risk for serious birth defects that affect the brain and spinal cord and are called spina bifida or neural tube defects. These defects occur in 1 to 2 out of every 100 babies born to mothers who use this medicine during pregnancy. These defects can begin in the first month, even before you know you are pregnant. Other birth defects that affect the structures of the heart, head, arms, legs, and the opening where the urine comes out (urethra) on the bottom of the penis can also happen. Decreased hearing or hearing loss can also happen.
- •
- Birth defects may occur even in children born to women who are not taking any medicines and do not have other risk factors.
- •
- Taking folic acid supplements before getting pregnant and during early pregnancy can lower the chance of having a baby with a neural tube defect.
- •
- If you take valproic acid oral solution during pregnancy for any medical condition, your child is at risk for having lower IQ and may be at risk for developing autism or attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
- •
- There may be other medicines to treat your condition that have a lower chance of causing birth defects, decreased IQ, or other disorders in your child.
- •
- Women who are pregnant must not take valproic acid oral solution to prevent migraine headaches.
- •
- All women of childbearing age (including girls from the start of puberty) should talk to their healthcare provider about using other possible treatments instead of valproic acid oral solution. If the decision is made to use valproic acid oral solution, you should use effective birth control (contraception).
- •
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant while taking valproic acid oral solution. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will continue to take valproic acid oral solution while you are pregnant.
- •
-
Pregnancy Registry: If you become pregnant while taking valproic acid oral solution, talk to your healthcare provider about registering with the North American Antiepileptic Drug Pregnancy Registry. You can enroll in this registry by calling toll-free 1-888-233-2334 or by visiting the website, http://www.aedpregnancyregistry.org/. The purpose of this registry is to collect information about the safety of antiepileptic drugs during pregnancy.
- 3.
- Inflammation of your pancreas that can cause death.
Call your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms:
- •
- severe stomach pain that you may also feel in your back
- •
- nausea or vomiting that does not go away
- 4.
- Like other antiepileptic drugs, valproic acid oral solution may cause suicidal thoughts or actions in a very small number of people, about 1 in 500.
Call a healthcare provider right away if you have any of these symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- •
- thoughts about suicide or dying
- •
- attempts to commit suicide
- •
- new or worse depression
- •
- new or worse anxiety
- •
- feeling agitated or restless
- •
- panic attacks
- •
- trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- •
- new or worse irritability
- •
- acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
- •
- acting on dangerous impulses
- •
- an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
- •
- other unusual changes in behavior or mood
How can I watch for early symptoms of suicidal thoughts and actions?
- •
- Pay attention to any changes, especially sudden changes in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings.
- •
- Keep all follow-up visits with your healthcare provider as scheduled.
Call your healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you are worried about symptoms.
Do not stop valproic acid oral solution without first talking to a healthcare provider. Stopping valproic acid oral solution suddenly can cause serious problems. Stopping a seizure medicine suddenly in a patient who has epilepsy can cause seizures that will not stop (status epilepticus).
Suicidal thoughts or actions can be caused by things other than medicines. If you have suicidal thoughts or actions, your healthcare provider may check for other causes.
What is valproic acid oral solution?
Valproic acid oral solution is a prescription medicine used alone or with other medicines, to treat:
- •
- complex partial seizures in adults and children 10 years of age and older
- •
- simple and complex absence seizures, with or without other seizure types
Who should not take valproic acid oral solution?
Do not take valproic acid oral solution if you:
- •
- have liver problems
- •
- have or think you have a genetic liver problem caused by a mitochondrial disorder (e.g. Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrome)
- •
- are allergic to divalproex sodium, valproic acid, sodium valproate, or any of the ingredients in valproic acid oral solution. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in valproic acid oral solution.
- •
- have a genetic problem called urea cycle disorder
- •
- are taking it to prevent migraine headaches and are either pregnant or may become pregnant because you are not using effective birth control (contraception)
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking valproic acid oral solution?
Before you take valproic acid oral solution, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- •
- have a genetic liver problem caused by a mitochondrial disorder (e.g. Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrome)
- •
- drink alcohol
- •
- are pregnant or breastfeeding. Valproic acid oral solution can pass into breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby if you take valproic acid oral solution.
- •
- have or have had depression, mood problems, or suicidal thoughts or behavior
- •
- have any other medical conditions
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, herbal supplements and medicines that you take for a short period of time.
Taking valproic acid oral solution with certain other medicines can cause side effects or affect how well they work. Do not start or stop other medicines without talking to your healthcare provider.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist each time you get a new medicine.
How should I take valproic acid oral solution?
- •
- Take valproic acid oral solution exactly as your healthcare provider tells you. Your healthcare provider will tell you how much valproic acid oral solution to take and when to take it.
- •
- Your healthcare provider may change your dose.
- •
- Do not change your dose of valproic acid oral solution without talking to your healthcare provider.
- •
- Do not stop taking valproic acid oral solution without first talking to your healthcare provider. Stopping valproic acid oral solution suddenly can cause serious problems.
- •
- If you take too much valproic acid oral solution, call your healthcare provider or local Poison Control Center right away.
What should I avoid while taking valproic acid oral solution?
- •
- Valproic acid oral solution can cause drowsiness and dizziness. Do not drink alcohol or take other medicines that make you sleepy or dizzy while taking valproic acid oral solution, until you talk with your doctor. Taking valproic acid oral solution with alcohol or drugs that cause sleepiness or dizziness may make your sleepiness or dizziness worse.
- •
- Do not drive a car or operate dangerous machinery until you know how valproic acid oral solution affects you. Valproic acid oral solution can slow your thinking and motor skills.
What are the possible side effects of valproic acid oral solution?
- •
- See “What is the most important information I should know about valproic acid oral solution?”
Valproic acid oral solution can cause serious side effects including:
- •
- Bleeding problems: red or purple spots on your skin, bruising, pain and swelling into your joints due to bleeding or bleeding from your mouth or nose.
- •
- High ammonia levels in your blood: feeling tired, vomiting, changes in mental status.
- •
- Low body temperature (hypothermia): drop in your body temperature to less than 95°F, feeling tired, confusion, coma.
- •
- Allergic (hypersensitivity) reactions: fever, skin rash, hives, sores in your mouth, blistering and peeling of your skin, swelling of your lymph nodes, swelling of your face, eyes, lips, tongue, or throat, trouble swallowing or breathing.
- •
- Drowsiness or sleepiness in the elderly. This extreme drowsiness may cause you to eat or drink less than you normally would. Tell your doctor if you are not able to eat or drink as you normally do. Your doctor may start you at a lower dose of valproic acid oral solution.
Call your healthcare provider right away, if you have any of the symptoms listed above.
The common side effects of valproic acid oral solution include:
- •
- nausea
- •
- headache
- •
- sleepiness
- •
- vomiting
- •
- weakness
- •
- tremor
- •
- dizziness
- •
- stomach pain
- •
- blurry vision
- •
- double vision
- •
- diarrhea
- •
- increased appetite
- •
- weight gain
- •
- hair loss
- •
- loss of appetite
- •
- problems with walking or coordination
These are not all of the possible side effects of valproic acid oral solution. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store valproic acid oral solution?
Store valproic acid oral solution at 68° to 77°F (20° to 25°C).
Keep valproic acid oral solution and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of valproic acid oral solution
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use valproic acid oral solution for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give valproic acid oral solution to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about valproic acid oral solution. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about valproic acid oral solution that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in valproic acid oral solution?
Active ingredient: valproic acid
Inactive ingredients: FD&C Red No. 40, glycerin, methylparaben, propylparaben, sodium hydroxide, sorbitol, sucrose, purified water, sour cherry flavor and alcohol 0.02% (v/v).
Distributed by:
ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Baudette, MN 56623

This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
10676 Rev 10/23
Close -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANELValproic Acid Oral Solution USP - 250 mg/5 mL - NDC 62559-266-16 - PHAMACIST: Dispense the accompanying Medication Guide to each patient. Rx only - NET CONTENTS: 16 fl. oz. (473 mL)
Valproic Acid Oral Solution USP
Close
250 mg/5 mL
NDC 62559-266-16
PHAMACIST: Dispense the accompanying Medication Guide to each patient.
Rx only
NET CONTENTS: 16 fl. oz. (473 mL)

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCEProduct Information
VALPROIC ACID valproic acid solution Product Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:62559-266 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength VALPROIC ACID (UNII: 614OI1Z5WI) (VALPROIC ACID - UNII:614OI1Z5WI) VALPROIC ACID 250 mg in 5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SORBITOL SOLUTION (UNII: 8KW3E207O2) PROPYLPARABEN (UNII: Z8IX2SC1OH) METHYLPARABEN (UNII: A2I8C7HI9T) FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) ALCOHOL (UNII: 3K9958V90M) Product Characteristics Color RED (clear) Score Shape Size Flavor CHERRY (sour) Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:62559-266-16 473 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/02/2024 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA073178 01/02/2024
CloseLabeler - ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (145588013)
Find additional resources
(also available in the left menu)Safety
Boxed Warnings, Report Adverse Events, FDA Safety Recalls, Presence in Breast Milk
Related Resources
Medline Plus, Clinical Trials, PubMed, Biochemical Data Summary
More Info on this Drug
View Labeling Archives, RxNorm, Get Label RSS Feed, View NDC Code(s)NEW!
View Labeling Archives for this drug
VALPROIC ACID solution
Number of versions: 1
| Published Date (What is this?) | Version | Files |
|---|---|---|
| Jan 4, 2024 | 1 (current) | download |
RxNorm
VALPROIC ACID solution
| RxCUI | RxNorm NAME | RxTTY | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1099687 | valproic acid 250 MG in 5 mL Oral Solution | PSN |
| 2 | 1099687 | valproic acid 50 MG/ML Oral Solution | SCD |
| 3 | 1099687 | valproate sodium 50 MG/ML Syrup | SY |
| 4 | 1099687 | valproic acid 250 MG per 5 ML Oral Solution | SY |
| 5 | 1099687 | valproic acid 500 MG per 10 ML Oral Solution | SY |
| 6 | 1099687 | VPA 50 MG/ML Oral Solution | SY |
Get Label RSS Feed for this Drug
VALPROIC ACID solution
To receive this label RSS feed
Copy the URL below and paste it into your RSS Reader application.
https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/labelrss.cfm?setid=2314af65-b928-42a9-91eb-6372909ab4f5
To receive all DailyMed Updates for the last seven days
Copy the URL below and paste it into your RSS Reader application.
https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/rss.cfm
What will I get with the DailyMed RSS feed?
DailyMed will deliver notification of updates and additions to Drug Label information currently shown on this site through its RSS feed.
DailyMed will deliver this notification to your desktop, Web browser, or e-mail depending on the RSS Reader you select to use. To view updated drug label links, paste the RSS feed address (URL) shown below into a RSS reader, or use a browser which supports RSS feeds, such as Safari for Mac OS X.
How to discontinue the RSS feed
If you no longer wish to have this DailyMed RSS service, simply delete the copied URL from your RSS Reader.
More about getting RSS News & Updates from DailyMedWhy is DailyMed no longer displaying pill images on the Search Results and Drug Info pages?
Due to inconsistencies between the drug labels on DailyMed and the pill images provided by RxImage, we no longer display the RxImage pill images associated with drug labels.
We anticipate reposting the images once we are able identify and filter out images that do not match the information provided in the drug labels.
NDC Codes
VALPROIC ACID solution
If this SPL contains inactivated NDCs listed by the FDA initiated compliance action, they will be specified as such.
| NDC | |
|---|---|
| 1 | 62559-266-16 |