Label: TRAVOPROST solution
- NDC Code(s): 51407-731-05, 51407-731-25
- Packager: Golden State Medical Supply, Inc.
- This is a repackaged label.
- Source NDC Code(s): 60505-0593
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Abbreviated New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated November 25, 2024
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
TRAVOPROST OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION. These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TRAVOPROST OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION (Ionic Buffered Solution) safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TRAVOPROST OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION (Ionic Buffered Solution) .
TRAVOPROST ophthalmic solution (Ionic Buffered Solution)
Initial U.S. Approval: 2001INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Travoprost ophthalmic solution (ionic buffered solution) 0.004% is a prostaglandin analog indicated for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
One drop in the affected eye(s) once daily in the evening. (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Ophthalmic solution containing travoprost 0.04 mg/mL (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None ( 4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reaction (30% to 50%) is conjunctival hyperemia. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Apotex Corp. at 1-800- 706-5575or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Use in pediatric patients below the age of 16 years is not recommended because of potential safety concerns related to increased pigmentation following long-term chronic use. (8.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 3/2021
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Pigmentation
5.2 Eyelash Changes
5.3 Intraocular Inflammation
5.4 Macular Edema
5.5 Angle-closure, Inflammatory or Neovascular Glaucoma
5.6 Bacterial Keratitis
5.7 Use with Contact Lenses
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic and Renal Impairment
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dosage is one drop in the affected eye(s) once daily in the evening. Travoprost ophthalmic solution (ionic buffered solution) should not be administered more than once daily since it has been shown that more frequent administration of prostaglandin analogs may decrease the IOP lowering effect.
Reduction of the IOP starts approximately 2 hours after the first administration with maximum effect reached after 12 hours.
Travoprost ophthalmic solution (ionic buffered solution) may be used concomitantly with other topical ophthalmic drug products to lower intraocular pressure (IOP). If more than one topical ophthalmic drug is being used, the drugs should be administered at least five (5) minutes apart.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Pigmentation
Travoprost ophthalmic solution has been reported to cause changes to pigmented tissues. The most frequently reported changes have been increased pigmentation of the iris, periorbital tissue (eyelid), and eyelashes. Pigmentation is expected to increase as long as travoprost is administered. The pigmentation change is due to increased melanin content in the melanocytes rather than to an increase in the number of melanocytes. After discontinuation of travoprost, pigmentation of the iris is likely to be permanent, while pigmentation of the periorbital tissue and eyelash changes have been reported to be reversible in some patients. Patients who receive treatment should be informed of the possibility of increased pigmentation. The long term effects of increased pigmentation are not known.
Iris color change may not be noticeable for several months to years. Typically, the brown pigmentation around the pupil spreads concentrically towards the periphery of the iris and the entire iris or parts of the iris become more brownish. Neither nevi nor freckles of the iris appear to be affected by treatment. While treatment with travoprost ophthalmic solution (ionic buffered solution) 0.004% can be continued in patients who develop noticeably increased iris pigmentation, these patients should be examined regularly [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.2 Eyelash Changes
Travoprost ophthalmic solution (ionic buffered solution) may gradually change eyelashes and vellus hair in the treated eye. These changes include increased length, thickness, and number of lashes. Eyelash changes are usually reversible upon discontinuation of treatment [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.3 Intraocular Inflammation
Travoprost ophthalmic solution (ionic buffered solution) should be used with caution in patients with active intraocular inflammation (e.g., uveitis) because the inflammation may be exacerbated.
5.4 Macular Edema
Macular edema, including cystoid macular edema, has been reported during treatment with travoprost ophthalmic solution. Travoprost ophthalmic solution (ionic buffered solution) should be used with caution in aphakic patients, in pseudophakic patients with a torn posterior lens capsule, or in patients with known risk factors for macular edema.
5.5 Angle-closure, Inflammatory or Neovascular Glaucoma
Travoprost ophthalmic solution (ionic buffered solution) has not been evaluated for the treatment of angle-closure, inflammatory or neovascular glaucoma.
5.6 Bacterial Keratitis
There have been reports of bacterial keratitis associated with the use of multiple-dose containers of topical ophthalmic products. These containers had been inadvertently contaminated by patients who, in most cases, had a concurrent corneal disease or a disruption of the ocular epithelial surface [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The most common adverse reaction observed in controlled clinical trials with travoprost ophthalmic solution 0.004% and travoprost ophthalmic solution (ionic buffered solution) 0.004% was ocular hyperemia, which was reported in 30% to 50% of patients. Up to 3% of patients discontinued therapy due to conjunctival hyperemia. Ocular adverse reactions reported at an incidence of 5% to 10% in these clinical trials included decreased visual acuity, eye discomfort, foreign body sensation, pain, and pruritus.
Ocular adverse reactions reported at an incidence of 1% to 4% in clinical trials with travoprost ophthalmic solution or travoprost ophthalmic solution (ionic buffered solution) included abnormal vision, blepharitis, blurred vision, cataract, conjunctivitis, corneal staining, dry eye, iris discoloration, keratitis, lid margin crusting, ocular inflammation, photophobia, subconjunctival hemorrhage, and tearing.
Non-ocular adverse reactions reported at an incidence of 1% to 5% in these clinical studies were allergy, angina pectoris, anxiety, arthritis, back pain, bradycardia, bronchitis, chest pain, cold/flu syndrome, depression, dyspepsia, gastrointestinal disorder, headache, hypercholesterolemia, hypertension, hypotension, infection, pain, prostate disorder, sinusitis, urinary incontinence, and urinary tract infections.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Additional adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of travoprost ophthalmic solution or travoprost ophthalmic solution (ionic buffered solution) in clinical practice. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made. The reactions, which have been chosen for inclusion due to either their seriousness, frequency of reporting, possible causal connection to travoprost ophthalmic solution or travoprost ophthalmic solution (ionic buffered solution), or a combination of these factors, include: arrhythmia, vomiting, epistaxis, tachycardia, and insomnia.
In postmarketing use with prostaglandin analogs, periorbital and lid changes including deepening of the eyelid sulcus have been observed.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk.
In animal reproduction studies, subcutaneous (SC) administration of travoprost to pregnant mice and rats throughout the period of organogenesis produced embryo-fetal lethality, spontaneous abortion, and premature delivery at potentially clinically relevant doses.
Advise pregnant women of a potential risk to a fetus. Because animal reproductive studies are not always predictive of human response, travoprost should be administered during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown; however, in the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects is 2% to 4% and of miscarriage is 15% to 20% of clinically recognized pregnancies.
Data
Animal Data
An embryo-fetal study was conducted in pregnant rats administered travoprost once daily by SC injection from gestation day (GD) 6 to 18, to target the period of organogenesis. At 10 mcg/kg (60 times the maximum recommended human ocular dose [MRHOD], based on estimated plasma C max), travoprost was teratogenic in rats, evidenced by an increase in the incidence of skeletal malformations as well as external and visceral malformations, including fused sternebrae, domed head and hydrocephaly. Travoprost caused post-implantation loss at 10 mcg/kg. The no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) for post-implantation loss was 3 mcg/kg (18 times the MRHOD, based on estimated plasma C max). The maternal NOAEL was 10 mcg/kg.
An embryo-fetal study was conducted in pregnant mice administered travoprost once daily by SC injection from GD 6 to 11, to target the period of organogenesis. At 1 mcg/kg (6 times the MRHOD, based on estimated plasma C max), travoprost caused post-implantation loss and decreased fetal weight. The no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) for malformations was 0.3 mcg/kg (2 times the MRHOD, based on estimated plasma C max). The maternal NOAEL was 1 mcg/kg.
Pre/postnatal studies were conducted in rats administered travoprost once daily by subcutaneous injection from GD 7 (early embryonic period) to postnatal Day 21 (end of lactation period). At doses of greater than or equal to 0.12 mcg/kg/day (0.7 times the MRHOD, based on estimated plasma C max), adverse pregnancy outcomes (embryo-fetal lethality, abortion, and early delivery), low-birth weight and developmental delays were observed. The NOAEL for adverse pregnancy outcomes, low-birth weight and developmental delay was 0.1 mcg/kg (0.6 times the MHROD, based on estimated plasma C max). The NOAEL for maternal toxicity was 0.72 mcg/kg (4 times the MHROD, based on estimated plasma C max).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the effects of travoprost on the breastfed child or milk production. It is not known if travoprost is present in human milk following ophthalmic administration. A study in lactating rats demonstrated that radio-labeled travoprost and/or its metabolites were excreted in milk following subcutaneous administration.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for travoprost ophthalmic solution 0.004% and any potential adverse effects on the breast-fed child from travoprost ophthalmic solution 0.004%.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Use in pediatric patients below the age of 16 years is not recommended because of potential safety concerns related to increased pigmentation following long-term chronic use.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Travoprost is a synthetic prostaglandin F analogue. Its chemical name is [1 R-[1α( Z),2β(1 E,3 R*),3α,5α]]-7-[3,5-Dihydroxy-2-[3-hydroxy-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl) phenoxy]-1-butenyl]cyclopentyl]-5-heptenoic acid, 1-methylethylester. It has a molecular formula of C 26H 35F 3O 6and a molecular weight of 500.55 g/mol. The chemical structure of travoprost is:
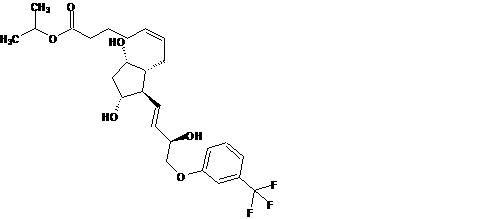
Travoprost is a clear, colorless to slightly yellow oil that is very soluble in acetonitrile, methanol, octanol, and chloroform. It is practically insoluble in water.
Travoprost ophthalmic solution, USP (ionic buffered solution) 0.004% is supplied as sterile, buffered aqueous solution of travoprost with a pH of approximately 5.7 and an osmolality of approximately 290 mOsmol/kg.
Travoprost ophthalmic solution, USP (ionic buffered solution) contains Active:travoprost 0.04 mg/mL; Inactives:polyoxyl 40 hydrogenated castor oil, ionic buffered system (boric acid, propylene glycol, sorbitol, zinc chloride), sodium hydroxide and/or hydrochloric acid (to adjust pH), and water for injection. Preserved in the bottle with an ionic buffered system.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Travoprost free acid, a prostaglandin analog is a selective FP prostanoid receptor agonist which is believed to reduce IOP by increasing uveoscleral outflow. The exact mechanism of action is unknown at this time.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Travoprost is absorbed through the cornea and is hydrolyzed to the active free acid. Data from four multiple dose pharmacokinetic studies (totaling 107 subjects) have shown that plasma concentrations of the free acid are below 0.01 ng/mL (the quantitation limit of the assay) in two-thirds of the subjects. In those individuals with quantifiable plasma concentrations (N = 38), the mean plasma C maxwas 0.018 ± 0.007 ng/mL (ranged 0.01 to 0.052 ng/mL) and was reached within 30 minutes. From these studies, travoprost is estimated to have a plasma half-life of 45 minutes. There was no difference in plasma concentrations between Days 1 and 7, indicating steady-state was reached early and that there was no significant accumulation.
Travoprost, an isopropyl ester prodrug, is hydrolyzed by esterases in the cornea to its biologically active free acid. Systemically, travoprost free acid is metabolized to inactive metabolites via beta-oxidation of the α (carboxylic acid) chain to give the 1,2-dinor and 1,2,3,4-tetranor analogs, via oxidation of the 15-hydroxyl moiety, as well as via reduction of the 13, 14 double bond.
The elimination of travoprost free acid from plasma was rapid and levels were generally below the limit of quantification within one hour after dosing. The terminal elimination half-life of travoprost free acid was estimated from fourteen subjects and ranged from 17 minutes to 86 minutes with the mean half-life of 45 minutes. Less than 2% of the topical ocular dose of travoprost was excreted in the urine within 4 hours as the travoprost free acid.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Two-year carcinogenicity studies in mice and rats at subcutaneous doses of 10, 30, or 100 mcg/kg/day did not show any evidence of carcinogenic potential. However, at 100 mcg/kg/day, male rats were only treated for 82 weeks, and the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) was not reached in the mouse study. The high dose (100 mcg/kg) corresponds to exposure levels 326 times (mouse) and 547 times (rat) the human exposure at the MRHOD of 0.04 mcg/kg, based on estimated plasma C maxfor active travoprost free acid.
Travoprost was not mutagenic in the Ames test, mouse micronucleus test or rat chromosome aberration assay. A slight increase in the mutant frequency was observed in one of two mouse lymphoma assays in the presence of rat S-9 activation enzymes.
Travoprost did not affect mating or fertility indices in male or female rats at subcutaneous doses up to 3 mcg/kg/day (18 times the MRHOD based on estimated plasma C max). At 10 mcg/kg/day (60 times the MRHOD, based on estimated plasma C max), the mean number of corpora lutea was reduced, and the post-implantation losses were increased.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
In clinical studies, patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension and baseline pressure of 25 to 27 mmHg, who were treated with travoprost ophthalmic solution 0.004% or travoprost ophthalmic solution (ionic buffered solution) 0.004% dosed once daily in the evening, demonstrated 7 to 8 mmHg reductions in IOP. In sub-group analyses of these studies, mean IOP reduction in black patients was up to 1.8 mmHg greater than in non-black patients. It is not known at this time whether this difference is attributed to race or to heavily pigmented irides.
In a multi-center, randomized, controlled trial, patients with mean baseline IOP of 24 to 26 mmHg on TIMOPTIC** 0.5% twice daily who were treated with travoprost ophthalmic solution 0.004% dosed daily adjunctively to TIMOPTIC** 0.5% twice daily demonstrated 6 to 7 mmHg reductions in IOP.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Travoprost ophthalmic solution, USP (ionic buffered solution) 0.004% is a sterile, isotonic, buffered, preserved, aqueous solution of travoprost (0.04 mg/mL).
Travoprost ophthalmic solution, USP (ionic buffered solution) 0.004% is supplied as a 2.5 mL solution and a 5 mL solution in a 5 mL translucent polypropylene ophthalmic bottle with a translucent polypropylene ophthalmic dropper and a turquoise, opaque polypropylene cap.
2.5 mL fill NDC 51407-731-25
5 mL fill NDC 51407-731-05
Storage:Store at 2°C to 25°C (36°F to 77°F).
After opening, travoprost ophthalmic solution, USP (ionic buffered solution) 0.004% can be used until the expiration date on the bottle.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Potential for Pigmentation
Advise the patient about the potential for increased brown pigmentation of the iris, which may be permanent. Inform the patient about the possibility of eyelid skin darkening, which may be reversible after discontinuation of travoprost ophthalmic solution (ionic buffered solution) 0.004% [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Potential for Eyelash Changes
Inform the patient about the possibility of eyelash and vellus hair changes in the treated eye during treatment with travoprost ophthalmic solution (ionic buffered solution). These changes may result in a disparity between eyes in length, thickness, pigmentation, number of eyelashes or vellus hairs, and/or direction of eyelash growth. Eyelash changes are usually reversible upon discontinuation of treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Handling the Container
Instruct the patient to avoid allowing the tip of the dispensing container to contact the eye, surrounding structures, fingers, or any other surface in order to avoid contamination of the solution by common bacteria known to cause ocular infections. Serious damage to the eye and subsequent loss of vision may result from using contaminated solutions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
When to Seek Physician Advice
Advise the patient that if they develop an intercurrent ocular condition (e.g., trauma or infection), have ocular surgery, or develop any ocular reactions, particularly conjunctivitis and eyelid reactions, they should immediately seek their physician's advice concerning the continued use of travoprost ophthalmic solution (ionic buffered solution) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4, 5.5)].
Use with Contact Lenses
Contact lenses should be removed prior to instillation of travoprost ophthalmic solution (ionic buffered solution) and may be reinserted 15 minutes following its administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Use with Other Ophthalmic Drugs
If more than one topical ophthalmic drug is being used, the drugs should be administered at least five (5) minutes between applications.
Rx Only
* TIMOPTIC is a registered trademark of Merck & Co., Inc.
Marketed by:
GSMS, Inc.
Camarillo, CA 93012 USA
Manufactured by: Manufactured for: Apotex Inc. Apotex Corp. Toronto, Ontario Weston, Florida Canada, M9L 1T9 33326 March 2021 - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
TRAVOPROST
travoprost solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:51407-731(NDC:60505-0593) Route of Administration OPHTHALMIC Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength TRAVOPROST (UNII: WJ68R08KX9) (TRAVOPROST - UNII:WJ68R08KX9) TRAVOPROST 0.04 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength PEG-40 CASTOR OIL (UNII: 4ERD2076EF) BORIC ACID (UNII: R57ZHV85D4) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) SORBITOL (UNII: 506T60A25R) ZINC CHLORIDE (UNII: 86Q357L16B) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:51407-731-25 1 in 1 CARTON 10/12/2022 1 2.5 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) 2 NDC:51407-731-05 1 in 1 CARTON 10/12/2022 2 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA203431 07/10/2015 Labeler - Golden State Medical Supply, Inc. (603184490) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Golden State Medical Supply, Inc. 603184490 relabel(51407-731) , repack(51407-731)




