Label: RHOGAM ULTRA-FILTERED PLUS (human rho- d immune globulin injection, solution
MICRHOGAM ULTRA-FILTERED PLUS (human rho- d immune globulin injection, solution
-
NDC Code(s):
0562-7805-00,
0562-7805-01,
0562-7805-05,
0562-7805-25, view more0562-7806-00, 0562-7806-01, 0562-7806-05, 0562-7806-25
- Packager: Kedrion Biopharma Inc
- Category: PLASMA DERIVATIVE
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Biologic Licensing Application
Drug Label Information
Updated December 17, 2024
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use RhoGAM Ultra-Filtered PLUS (RhoGAM) safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for RhoGAM.
RhoGAM® Ultra-Filtered PLUS [Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human)] (300 μg) (1500 IU), prefilled syringe, for intramuscular use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1968RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Dosage and Administration (2) Dosage forms and Strength (3) Description (11) Clinical Studies (14) References (15) How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16) 04/2024 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
RhoGAM is an immune globulin indicated for use in preventing Rh immunization for:
- Pregnancy and other obstetrical conditions in Rh-negative women unless the father or baby are conclusively Rh-negative, e.g. delivery of an Rh-positive baby irrespective of the ABO groups of the mother and baby, any antepartum fetal-maternal hemorrhage (suspected or proven), actual or threatened pregnancy loss at any stage of gestation and ectopic pregnancy. (1.1)
- Prevention of Rh immunization in any Rh-negative person after incompatible transfusion of Rh-positive blood or blood products. (1.2)
- Limitation of use
Pregnancy and other obstetrical conditions: In the case of postpartum use, RhoGAM is intended for maternal administration. Do not inject the newborn infant. (1.3)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For intramuscular use only. (2)
Pregnancy and other obstetrical conditions (2.1)
Dose Indication Notes* - *
- After delivery, obstetric complications, and/or invasive procedures, the volume of the fetal-maternal hemorrhage must be determined to calculate the exact dose of RhoGAM required.
RhoGAM
(300 µg)
(1500 IU)Postpartum (if the newborn is Rh-positive)
Administer within 72 hours of deliveryAdditional doses of RhoGAM are indicated when the patient has been exposed to > 15 mL of Rh-positive red blood cells. Antepartum: - Prophylaxis at 26 to 28 weeks gestation
Administer within 72 hours of suspected or proven exposure to Rh-positive red blood cells - Obstetric complications/ invasive procedures beyond 13 weeks gestation
If antepartum prophylaxis is indicated, it is essential that the mother receive a postpartum dose if the infant is Rh-positive. RhoGAM
(300 µg)
(1500 IU)Actual or threatened termination of pregnancy (spontaneous or induced) up to and including 12 weeks gestation
Administer within 72 hoursTransfusion of Rh-incompatible blood or blood products (2.1)
Administer within 72 hours of suspected or proven exposure to Rh-positive red blood cells. (2.1)
Dose Indication Notes RhoGAM
(300 µg)
(1500 IU)≥ 2.5 mL Rh-positive red blood cells Administer 20 µg of RhoGAM per mL of Rh-positive red blood cell exposure, rounding up to the next whole syringe. DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human)
- RhoGAM® Ultra-Filtered PLUS - 300 μg (1500 IU) – Prefilled Syringes (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Severe hypersensitivity reactions may occur with the use of RhoGAM. (5.1)
- RhoGAM should be administered in a setting where appropriate equipment, medications such as epinephrine, and personnel trained in the management of hypersensitivity, anaphylaxis, and shock are available. (5.1)
- Products made from human blood may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents e.g., viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent. (5.2)
- After administration of Rho(D) immune globulin, a transitory increase of various passively transferred antibodies in the patient's blood may yield positive serological testing results. (5.3)
Incompatible blood transfusion
- Patients treated for Rh-incompatible transfusion should be monitored by clinical and laboratory means for signs and symptoms of a hemolytic reaction. (5.4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- The most frequently reported adverse reactions in patients receiving Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human) products are injection site reactions, such as swelling, induration, redness and mild pain or warmth. Possible systemic reactions are skin rash, body aches or a slight elevation in temperature. (6)
- Severe systemic reactions include allergic reactions and hemolytic reactions. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Kedrion Biopharma Inc. at 1-855-3KDRION (1-855-353-7466) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. Outside of the United States, the company distributing these products should be contacted.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- May impair the efficacy of live vaccines such as measles, mumps and varicella. Administration of live vaccines should generally be delayed until 12 weeks after the final dose of immune globulin. If administered within 14 days after administration of a live vaccine, the efficacy of the vaccination may be impaired. (7)
- The postpartum vaccination of rubella-susceptible women with rubella or MMR vaccine should not be delayed because of the receipt of Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human). (7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 12/2024
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Pregnancy and other obstetrical conditions
1.2 Transfusion of Rh-incompatible blood or blood products
1.3 Limitation of use
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dose
2.2 Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity
5.2 Transmissible Infectious Agents
5.3 Interference with Laboratory Tests
5.4 Hemolysis
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Live Virus Vaccines
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED / STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Pregnancy and other obstetrical conditions
RhoGAM is indicated for administration to Rh-negative women not previously sensitized to the Rho(D) factor, unless the father or baby are conclusively Rh-negative, in case of:
- Delivery of an Rh-positive baby irrespective of the ABO groups of the mother and baby
- Antepartum prophylaxis at 26 to 28 weeks gestation
- Antepartum fetal-maternal hemorrhage (suspected or proven) as a result of placenta previa, amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling, percutaneous umbilical blood sampling, other obstetrical manipulative procedure (e.g., version) or abdominal trauma
- Actual or threatened pregnancy loss at any stage of gestation
- Ectopic pregnancy
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For intramuscular use only.
2.1 Dose
Pregnancy and other obstetrical conditions
Dose Indication Notes* - *
- : After delivery, obstetric complications, and/or invasive procedures, the volume of the fetal-maternal hemorrhage must be determined to calculate the exact dose of RhoGAM required.
RhoGAM
(300 µg)
(1500 IU)Postpartum (if the newborn is Rh-positive)
Administer within 72 hours of delivery.Additional doses of RhoGAM are indicated when the patient has been exposed to > 15 mL of Rh-positive red blood cells. This may be determined by use of qualitative or quantitative tests for fetal-maternal hemorrhage. Antepartum: - Prophylaxis at 26 to 28 weeks gestation
Administer within 72 hours of suspected or proven exposure to Rh-positive red blood cells resulting from: - Amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling (CVS) and percutaneous umbilical blood sampling (PUBS)
- Abdominal trauma or obstetrical manipulation
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Threatened pregnancy loss after 12 weeks gestation with continuation of pregnancy
- Pregnancy termination (spontaneous or induced) beyond 12 weeks gestation
If antepartum prophylaxis is indicated, it is essential that the mother receive a postpartum dose if the infant is Rh-positive.
If RhoGAM is administered early in pregnancy (before 26 to 28 weeks), there is an obligation to maintain a level of passively acquired anti-D by administration of RhoGAM at 12-week intervals.RhoGAM
(300 µg)
(1500 IU)Actual or threatened termination of pregnancy (spontaneous or induced) up to and including 12 weeks gestation
Administer within 72 hours- Administer RhoGAM every 12 weeks starting from first injection to maintain a level of passively acquired anti-D.
- If delivery occurs within three weeks after the last antepartum dose, the postpartum dose may be withheld, but a test for fetal-maternal hemorrhage should be performed to determine if exposure to > 15 mL of red blood cells has occurred.
- If delivery of the baby does not occur 12 weeks after the administration of the standard antepartum dose (at 26 to 28 weeks), a second dose is recommended to maximize protection antepartum.
RhoGAM dosage
Each single dose prefilled syringe of RhoGAM contains 300 μg (1500 IU) of Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human). This is the dose for the indications associated with pregnancy at or beyond 13 weeks unless there is clinical or laboratory evidence of a fetal-maternal hemorrhage (FMH) in excess of 15 mL of Rh-positive red blood cells.
This dose will suppress the immune response to up to 2.5 mL of Rh-positive red blood cells. RhoGAM is indicated within 72 hours after termination of pregnancy up to and including 12 weeks gestation.
Multiple Dosage
Multiple doses of RhoGAM are required if a FMH exceeds 15 mL, an event that is possible but unlikely prior to the third trimester of pregnancy and is most likely at delivery. Patients known or suspected to be at increased risk of FMH should be tested for FMH by qualitative or quantitative methods.3 In efficacy studies, RhoGAM was shown to suppress Rh immunization in all subjects when given at a dose of > 20 μg per mL of Rh-positive red blood cells. Thus, a single dose of RhoGAM will suppress the immune response after exposure to < 15 mL of Rh-positive red blood cells. However, in clinical practice, laboratory methods used to determine the amount of exposure (volume of transfusion or FMH) to Rh-positive red blood cells are imprecise. Therefore, administration of more than 20 μg of RhoGAM per mL of Rh-positive red blood cells should be considered whenever a large FMH or red blood cell exposure is suspected or documented. Multiple doses may be administered at the same time or at spaced intervals, as long as the total dose is administered within three days of exposure.1
Transfusion of Rh-incompatible blood or blood products
Administer within 72 hours of suspected or proven exposure to Rh-positive red blood cells.
Dose Indication Notes RhoGAM
(300 µg)
(1500 IU)2.5 - 15.0 mL Rh-positive red blood cells RhoGAM
(300 µg)
(1500 IU)
(multiple syringes)> 15.0 mL Rh-positive red blood cells Additional doses of RhoGAM are indicated when the patient has been exposed to > 15 mL of Rh-positive red blood cells.
Administer 20 µg of RhoGAM per mL of Rh-positive red blood cell exposure, rounding up to the next whole syringe.
Multiple doses may be administered at the same time or at spaced intervals, as long as the total dose is administered within three days of exposure.2.2 Administration
- Visually inspect RhoGAM for particulate matter, discoloration and syringe damage prior to administration.
- Do not use if particulate matter is observed.
- RhoGAM is clear or slightly opalescent. Do not use if discolored.
- Administer injection per standard protocol.
Note: When administering RhoGAM intramuscularly, place fingers in contact with glass syringe barrel through windows in shield to prevent possible premature activation of safety guard. 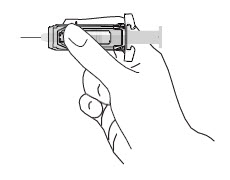
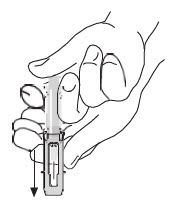
After injection, to engage the safety guard, use free hand to slide safety guard over needle. An audible "click" indicates proper activation. Keep hands behind needle at all times. Dispose of the syringe in accordance with local regulations. As with all blood products, patients should be observed for at least 20 minutes following administration of RhoGAM.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity
Severe hypersensitivity reactions may occur with the use of RhoGAM, even in patients who have tolerated previous administrations.
RhoGAM contains a small quantity of IgA3. There is a potential risk of hypersensitivity in IgA deficient individuals. Although high doses of intravenous immune globulin containing IgA at levels of 270-720 μg/mL have been given without incident during treatment of patients with high-titer antibodies to IgA4, the attending physician must weigh the benefit against the potential risks of hypersensitivity reactions.
RhoGAM should be administered in a setting where appropriate equipment, medications such as epinephrine, and personnel trained in the management of hypersensitivity, anaphylaxis, and shock are available.
5.2 Transmissible Infectious Agents
Because RhoGAM is made from human blood, it may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, e.g., viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent.
All infections thought by a physician possibly to have been transmitted by these products should be reported by the physician or other healthcare provider in the United States to Kedrion Biopharma Inc. at 1-855-3KDRION (1-855-353-7466). Outside the United States, the company distributing these products should be contacted. The physician should discuss the risks and benefits of these products with the patient.
5.3 Interference with Laboratory Tests
After administration of Rho(D) immune globulin, a transitory increase of various passively transferred antibodies in the patient's blood may yield positive serological testing results, with the potential for misleading interpretation. Passive transmission of antibodies to erythrocyte antigens (e.g., A, B, C and E) and other blood group antibodies may cause a positive direct or indirect antiglobulin (Coombs') test.
Recovery of anti-D in plasma or serum after injection of RhoGAM or other Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human) products is highly variable among individuals. Anti-D detection in a patient's plasma is dependent on assay sensitivity and time of sample collection post-injection. Currently there are no requirements or practice standards to test for the presence of anti-D in order to determine adequacy or efficacy of dose following an injection of RhoGAM.
The presence of passively acquired anti-D antibodies in the maternal serum may cause a positive antibody screening test. This does not preclude further antepartum or postpartum prophylaxis.
A large fetomaternal hemorrhage late in pregnancy or following delivery may cause a weak mixed field positive Du test result. Assess such an individual for a large fetomaternal hemorrhage and adjust the dose of Rho(D) immune globulin accordingly. The presence of passively administered anti Rho(D) in maternal or fetal blood can lead to a positive direct antiglobulin (Coombs') test. If there is an uncertainty about the father's Rh group or immune status, administer Rho(D) immune globulin to the mother.
5.4 Hemolysis
Incompatible blood transfusion
Administration of RhoGAM to patients who are Rh-positive or have received Rh-positive red blood cells may result in signs and symptoms of a hemolytic reaction, including fever, back pain, nausea and vomiting, hypo- or hypertension, hemoglobinuria/emia, elevated bilirubin and creatinine and decreased haptoglobin. Therefore, patients treated for Rh-incompatible transfusion should be monitored by clinical and laboratory means for signs and symptoms of a hemolytic reaction. Alert patients to, and monitor them for, the signs and symptoms of intravascular hemolysis, including back pain, shaking chills, fever, and discolored urine or hematuria. Absence of these signs and/or symptoms of intravascular hemolysis within 8 hours do not indicate intravascular hemolysis cannot occur subsequently.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequently reported adverse reactions in patients receiving Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human) products are injection site reactions, such as swelling, induration, redness and mild pain or warmth. Possible systemic reactions are skin rash, body aches or a slight elevation in temperature. Severe systemic reactions include allergic reactions and hemolytic reactions (see Warnings and Precautions [5.2]).
There have been no reported fatalities due to anaphylaxis or any other cause related to RhoGAM administration.
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under different protocols and widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed cannot be directly compared to rates in other clinical trials and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
No clinical studies with RhoGAM have been conducted under the current Good Clinical Practices (GCP) Guidelines.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or to establish a causal relationship to Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human) products.
The following adverse reactions have been reported during post-approval use of RhoGAM: hypersensitivity reactions, including cases of anaphylactic shock or anaphylactoid reactions, skin rash, erythema, pruritus, chill, pyrexia, malaise, and back pain. Transient injection-site irritation and pain have been reported following intramuscular administration.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Live Virus Vaccines
Immune globulin preparations including Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human) may impair the efficacy of live vaccines such as measles, mumps and varicella. Administration of live vaccines should generally be delayed until 12 weeks after the final dose of immune globulin. If an immune globulin is administered within 14 days after administration of a live vaccine, the immune response to the vaccination may be inhibited.5
Because of the importance of rubella immunity among women of childbearing age, the postpartum vaccination of rubella-susceptible women with rubella or MMR vaccine should not be delayed because of the receipt of Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human) during the last trimester of pregnancy or at delivery. Vaccination should occur immediately after delivery and if possible, testing should be performed after 3 or more months to ensure immunity to rubella and if necessary, to measles.5
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
RhoGAM is used in pregnant women for the suppression or Rh isoimmunization. The available evidence suggests that Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human) does not harm the fetus or affect future pregnancies or reproduction capacity when given to pregnant Rh0(D)-negative women for suppression of Rh isoimmunization.6
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with RhoGAM.
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
RhoGAM Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human) is a sterile solution containing immunoglobulin G (IgG) anti-D (anti-Rh) for use in preventing Rh immunization. It is manufactured from human plasma containing anti-D from Rh-negative donors immunized with Rh-positive red blood cells. A single dose of RhoGAM contains sufficient anti-D (300 μg or 1500 IU) to suppress the immune response to up to 15 mL of Rh-positive red blood cells.7 The anti-D dose is measured by comparison to the RhoGAM in-house reference standard, the potency of which is established relative to the U.S./World Health Organization/European Pharmacopoeia Standard Anti-D Immunoglobulin Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human).8
Plasma for RhoGAM is typically sourced from a donor center owned and operated by KEDPlasma LLC., US Lic. No. 1876. All donors are carefully screened by history and laboratory testing to reduce the risk of transmitting blood-borne pathogens from infected donors. Each plasma donation is tested and found to be non-reactive for the presence of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and antibodies to hepatitis C (HCV) and human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) 1 and 2. Additionally, plasma is tested by FDA licensed Nucleic Acid Testing (NAT) for hepatitis B virus (HBV), HCV and HIV-1. Each plasma unit must be negative (non-reactive) in all tests. Plasma is tested by in-process NAT procedures for hepatitis A virus (HAV) and parvovirus B19 (B19) in a minipool format. Only plasma that has passed virus screening is used for production. The NAT procedure for B19 detects all three genotypes based upon sequence alignment of known virus isolates. The limit of B19 DNA in the manufacturing pool is set not to exceed 104 IU per mL.
Fractionation of the plasma is performed by a modification of the cold alcohol procedure that has been shown to significantly lower viral titers.3 Following plasma fractionation, a viral clearance filtration step and a viral inactivation step are performed. The viral filtration step removes viruses via a size-exclusion mechanism utilizing a Viresolve 180 nanofiltration membrane (ultrafiltration mode) to remove enveloped and non-enveloped viruses.
Following viral filtration, quality control tests (CorrTest and diffusion test) are performed on the Viresolve 180 nanofiltration membrane to ensure filter integrity.9 The viral inactivation step utilizes Triton X-100 and tri-n-butyl phosphate (TNBP) to inactivate enveloped viruses such as HCV, HIV and West Nile Virus (WNV).3,10
The donor selection process, the fractionation process, the viral filtration step and the viral inactivation process increase product safety by reducing the virus load and thus the risk of transmission of enveloped and non-enveloped viruses. Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human) intended for intramuscular use and prepared by cold alcohol fractionation has not been shown to transmit hepatitis or other infectious diseases.11 There have been no documented cases of infectious disease transmission by RhoGAM.
Laboratory spiking studies3,12 have shown that the cumulative viral removal and inactivation capability of the RhoGAM manufacturing process is as follows:
Virus HIV-1 BVDV PRV PPV EMC Note : Data of viral removal/inactivation capability was generated from Kedrion Biopharma Inc. RhoGAM can be manufactured at both Kedrion Biopharma Inc. and Ortho Clinical Diagnostics Inc. up to drug substance: regardless of which product is administered (manufactured at Kedrion Biopharma Inc. or Ortho Clinical Diagnostics Inc.) data of viral removal/inactivation are applicable to both processes (Ortho and Kedrion Biopharma Inc.). Units = log10 reduction HIV Human Immunodeficiency Virus, Relevant virus for HIV-1 and 2 and model virus for Human T-cell Lymphotropic Virus (HTLV) 1 and 2
BVDV Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus, Model for Hepatitis C Virus and West Nile Virus (WNV)
PRV Pseudorabies Virus, Model for large enveloped DNA viruses such as Herpes Viruses
PPV Porcine Parvovirus, Model for Parvovirus B19
EMC Encephalomyocarditis Virus, Model for Hepatitis A Virus
N/A Not Applicable- *
- The lower reduction value was used for the calculation of overall reduction factors (log10).
Lipid Enveloped Yes Yes Yes No No Size (nm) 80-120 40-70 120-200 18-24 25-30 Genome ss-RNA ss-RNA ds-DNA ss-DNA ss-RNA Step Methanol precipitation 5.16 4.46 4.95 4.02 4.57 CUNO Depth filtration ≥ 4.95 2.53 2.34 3.83 Not Significant
(<1 Log)Viral Grade Filtration
(Nanofiltration)≥ 3.35
(≥ 4.76)*≥ 3.67
(≥ 5.02)*≥ 3.09
(≥ 4.19)*4.88 4.63 Solvent/Detergent treatment ≥ 5.08 ≥ 4.47 ≥ 4.05 N/A N/A Total Viral Reduction ≥ 18.54 ≥ 15.13 ≥ 14.43 12.73 9.20 The safety of Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human) has been further shown in an empirical study of viral marker rates in female blood donors in the United States.13 This study revealed that Rh-negative donors, of whom an estimated 55-60% had received Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human) for pregnancy-related indications, had prevalence and incidence viral marker rates similar to those of Rh-positive female donors who had not received Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human).
The final product contains 5 ± 1% IgG, 2.9 mg/mL sodium chloride, 0.01% Polysorbate 80 (non-animal derived) and 15 mg/mL glycine. Small amounts of IgA, typically less than 15 μg per dose, are present.3 The pH range is 6.20 - 7.00 and IgG purity is > 98%. The product contains no added human serum albumin (HSA), no thimerosal or other preservatives and utilizes a latex-free delivery system.
RhoGAM Ultra-Filtered PLUS is manufactured for Kedrion Biopharma Inc. either by Ortho-Clinical Diagnostics, Inc. or by Kedrion Biopharma Inc. up to the bulk products, and are filled and packaged by Kedrion Biopharma Inc., 155 Duryea Road, Melville, NY 11747 USA.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
RhoGAM acts by suppressing the immune response of Rh-negative individuals to Rh-positive red blood cells. The mechanism of action is unknown. RhoGAM and other Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human) products are not effective in altering the course or consequences of Rh immunization once it has occurred.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Use after Rh-Incompatible Transfusion
An Rh-negative individual transfused with one unit of Rh-positive red blood cells has about an 80% likelihood of producing anti-D. However, Rh immunization can occur after exposure to < 1 mL of Rh-positive red blood cells. Protection from Rh immunization is accomplished by administering > 20 μg of RhoGAM per mL of Rh-positive red blood cells within 72 hours of transfusion of incompatible red blood cells.14,15,16
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetic studies after intramuscular injection were performed on sixteen Rh-negative subjects receiving a single dose of (368 μg or 1840 IU) RhoGAM.3 Plasma anti-D levels were monitored for thirteen weeks using a validated Automated Quantitative Hemagglutination method with sensitivity of approximately 1 ng/mL. The following mean pharmacokinetic parameters were obtained from data collected over the first ten weeks of a thirteen-week study:
Parameter Mean SD Units Maximum plasma concentration obtained (Cmax) 54.0 13.0 ng/mL Time to attain Cmax (Tmax) 4 days Elimination half-life (T1/2) 30.9 13.8 days Volume of distribution (Vd) 7.3 1.5 liters Clearance (CL) 150.4 53.3 mL/day -
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human) administered at 28 weeks, as well as within 72 hours of delivery, has been shown to reduce the Rh immunization rate to about 0.1-0.2%.15,16 Clinical studies demonstrated that administration of Rh immune globulin within three hours following pregnancy termination was 100% effective in preventing Rh immunization.17
Multiple studies have been performed that prove the safety and efficacy of RhoGAM in both the obstetrical and post transfusion settings.
Pollack, Gorman and colleagues18 studied the efficacy of RhoGAM in the postpartum setting in a randomized, controlled study completed in 1967. The control group received no immunoglobulin therapy after delivery, while the test group received 300 μg of RhoGAM intramuscularly within 72 hours of delivery of an Rh-positive infant. Six months after delivery, the incidence of Rh immunization in the control group was 6.4% (32/499) versus 0.13% (1/781) in the RhoGAM group (p < 0.001).
Pollack et al. performed two randomized, placebo-controlled studies in the post transfusion setting that were designed to establish the dose response relationship of RhoGAM. In the first study,7 178 (176 males, 2 females) Rh-negative volunteers received varying volumes of Rh- positive red cells; 92 subjects then received RhoGAM. A single dose of RhoGAM (1.1 mL @ 267 μg/mL) was shown to suppress anti-D formation after injection of up to 15.1 mL of Rh-positive red cells. In a companion study, Pollack administered 500 mL of Rh-positive whole blood to 44 Rh-negative male volunteers. Twenty-two (22) subjects received 20 μg RhoGAM per mL of Rh-positive red cells and 22 received no RhoGAM. None of the RhoGAM-treated subjects developed anti-D; 18/22 control arm subjects developed anti-D (p < 0.0001) 19.
A study was conducted in 1985 using the low protein formulation of RhoGAM. None of the 30 Rh negative male volunteers who received RhoGAM after injection of 15 ml of Rh positive red cells developed anti-D.
-
15 REFERENCES
- 1
- AABB Technical Manual. 19th ed. Bethesda, Maryland: AABB, October 2017.
- 2
- Gunson HH, Bowell PJ, Kirkwood TBL. Collaborative study to recalibrate the International Reference Preparation of anti-D immunoglobulin. J Clin Pathol 1980;33:249-53.
- 3
- Data on file at Kedrion Biopharma Inc.
- 4
- Cunningham-Rundles C, Zhuo Z, Mankarious S, Courter S. Long-term use of IgA- depleted intravenous immunoglobulin in immunodeficient subjects with anti-IgA antibodies. J Clin Immunol 1993;13:272-78.
- 5
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. General recommendations on immunization: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices and the American Academy of Family Physicians. MMWR 2002;51 (No. RR-2):6-7.
- 6
- Thornton JG, Page C, Foote G, Arthur GR, Tovey LAD, Scott JS. Efficacy and long term effects of antenatal propylaxis with anti-D immunoglobulin. Br Med J. 1989;298: 1671-1673
- 7
- Pollack W, Ascari WQ, Kochesky RJ, O'Connor RR, Ho TY, Tripodi D. Studies on Rh prophylaxis. I. Relationship between doses of anti-Rh and size of antigenic stimulus. Transfusion 1971;11:333-39.
- 8
- Thorpe SJ, Sands D, Fox B, Behr-Gross ME, Schaffner G, Yu MW. A global standard for anti-D immunoglobulin: international collaborative study to evaluate a candidate preparation. Vox Sang 2003;85:313-21.
- 9
- Phillips MW, DiLeo AJ. A Validatible Porosimetric Technique for verifying the integrity of virus-retentive membranes. Biologicals 1996;24:243-53.
- 10
- Horowitz B, Wiebe ME, Lippin A, Stryker MH. Inactivation of viruses in labile blood derivatives. I. Disruption of lipid-enveloped viruses by tri (n-butyl) phosphate detergent combinations. Transfusion 1985; 25(6):516-22.
- 11
- Tabor E. The epidemiology of virus transmission by plasma derivatives: clinical studies verifying the lack of transmission of hepatitis B and C viruses and HIV type 1. Transfusion 1999;39:1160-68.
- 12
- Van Holten RW, Ciavarella D, Oulundsen G, Harmon F, Riester S. Incorporation of an additional viral-clearance step into a human immunoglobulin manufacturing process. Vox Sang 2002;83:227-33.
- 13
- Watanabe KK, Busch MP, Schreiber GB, Zuck TF. Evaluation of the safety of Rh Immunoglobulin by monitoring viral markers among Rh-negative female blood donors. Vox Sang 2000;8:1-6.
- 14
- Zipursky A, Israels LG. The pathogenesis and prevention of Rh immunization. Can Med Assoc J 1967;97:1245-56.
- 15
- de Haas M, Finning K, Massey E, Roberts DJ. Anti-D prophylaxis: past, present and future. Transfus Med 2014;24:1–7. (ex 22-24)
- 16
- Bowman J. Thirty-five years of Rh prophylaxis. Transfusion 2003;43:1661–6. (ex 22-24)
- 17
- Stewart FH, Burnhill MS, Bozorgi N. Reduced dose of Rh immunoglobulin following first trimester pregnancy termination. Obstet Gynecol 1978;51:318-22.
- 18
- Pollack, W., Gorman, J.G., Freda, V.J., Ascari, W.Q., Allen, A.E. and Baker, W.J. (1968), Results of Clinical Trials of RhoGAM in Women. Transfusion, 8: 151-153.
- 19
- Pollack W, Ascari WQ, Crispen JF, O'Connor RR, Ho TY. Studies on Rh prophylaxis. II. Rh immune prophylaxis after transfusion with Rh-positive blood. Transfusion. 1971 Nov-Dec;11(6):340-4. )
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED / STORAGE AND HANDLING
The following presentations of RhoGAM are available:
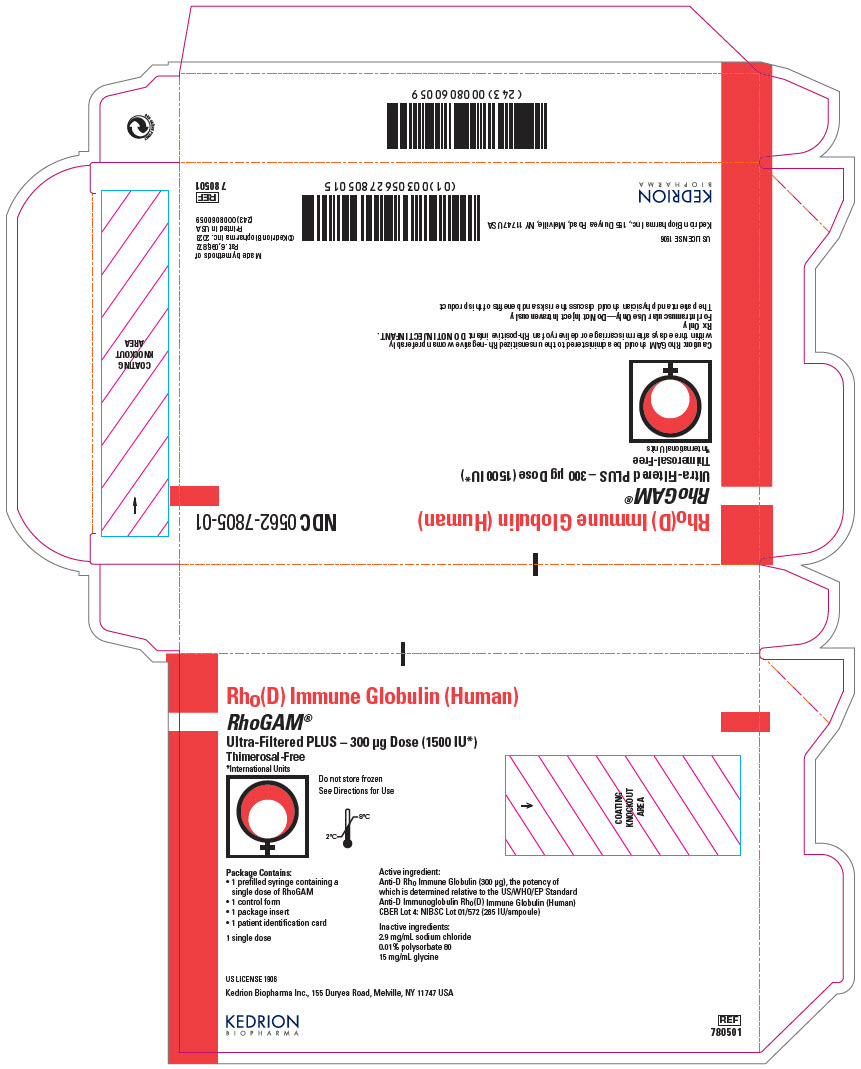
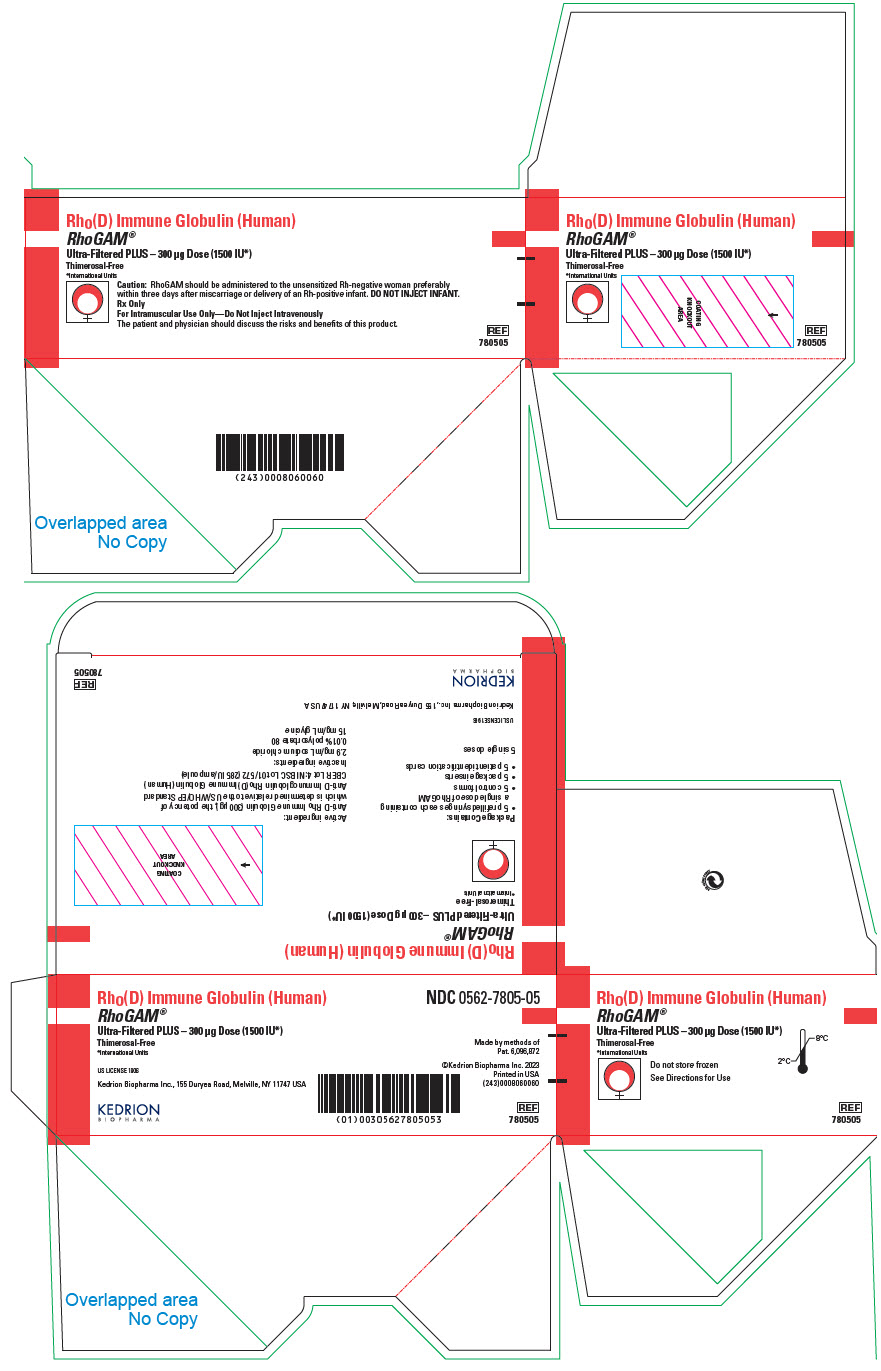
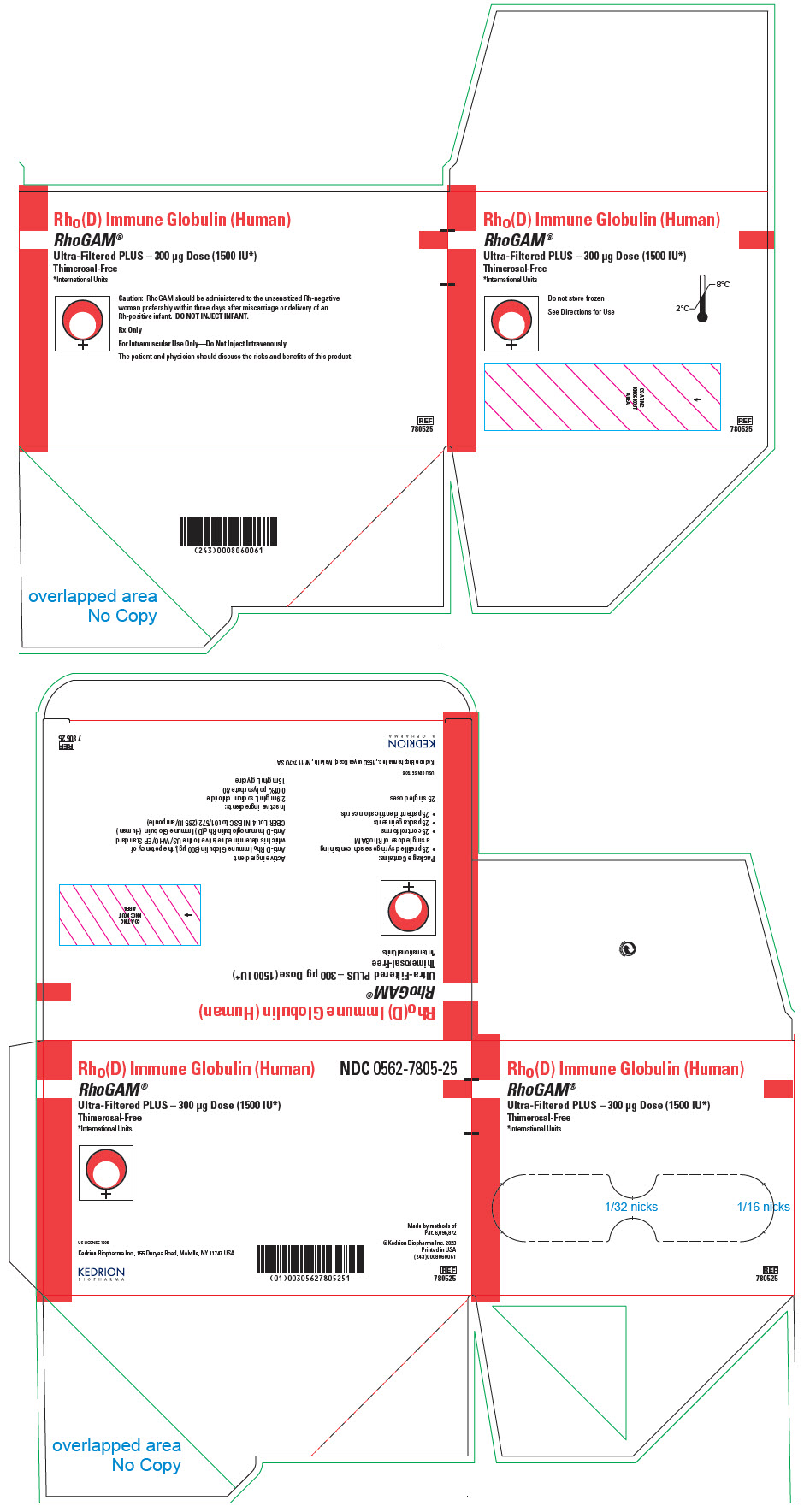
Presentation Product description/ package sizes Carton NDC number Primary container
NDC numberRhoGAM® Ultra-Filtered PLUS (300 µg) (1500 IU) – Carton of 1 syringe 1 prefilled single-dose syringe in a pouch, 1 package insert, 1 control form, 1 patient identification card NDC 0562-7805-01 prefilled single-dose syringe
NDC 0562-7805-00RhoGAM® Ultra-Filtered PLUS (300 µg) (1500 IU) – Carton of 5 syringes 5 prefilled single-dose syringe in a pouch, 5 package insert, 5 control form, 5 patient identification card NDC 0562-7805-05 RhoGAM® Ultra-Filtered PLUS (300 µg) (1500 IU) – Carton of 25 syringes 25 prefilled single-dose syringe in a pouch, 25 package insert, 25 control form, 25 patient identification card NDC 0562-7805-25 -
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Please inform patients of the following:
- The risks and benefits of RhoGAM.
- The most common adverse reactions are local reactions including swelling, induration, redness and mild pain at the site of injection, and a small number of patients have noted a slight elevation in temperature.
- Allergic reactions to RhoGAM may occur. Patients should be observed for at least 20 minutes after administration. Signs of hypersensitivity reactions include hives, generalized urticaria, tightness of the chest, wheezing, hypotension and anaphylaxis.
- RhoGAM may interfere with the response to live virus vaccines (e.g., measles, mumps, rubella, and varicella). Instruct patients to notify their healthcare professional of this potential interaction when they are receiving vaccinations.
- RhoGAM is prepared from human plasma and may contain infectious agents that can cause disease. Numerous tests have been applied in the plasma collection process and specific viral inactivation steps have been added to the manufacturing process to minimize the risk of transmission of diseases, but all risk cannot be eliminated.
- Retain the RhoGAM Patient Identification Card and advise the patient to retain the card and present it to other health care providers when appropriate.
SUMMARY OF REVISIONS
The PI was amended to eliminate the MICRhoGAM presentation. As a result, all informations related to MicRhoGAM has been deleted. All sections have undergone rewording due to the elimination of the name of the presentation. The technical-scientific information related to MicRhoGAM, has been eliminated from the following sections: Dosage and Administration (2), Dosage Form and Strength (3) Description (11) Clinical Studies (14) References (15) How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16) -
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
US LICENSE 1906
Kedrion Biopharma Inc., 155 Duryea Road, Melville, NY 11747 USA
Manufactured for Kedrion Biopharma Inc. either by Ortho-Clinical Diagnostics, Inc. or by Kedrion Biopharma Inc. up to the bulk products, filled and packaged by Kedrion Biopharma Inc.©Kedrion Biopharma Inc. 2024
Printed in U.S.A.
Made by methods of
U.S. Pat. 6,096,872
U.S. Pat. 7,655,233(243)0008060071
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
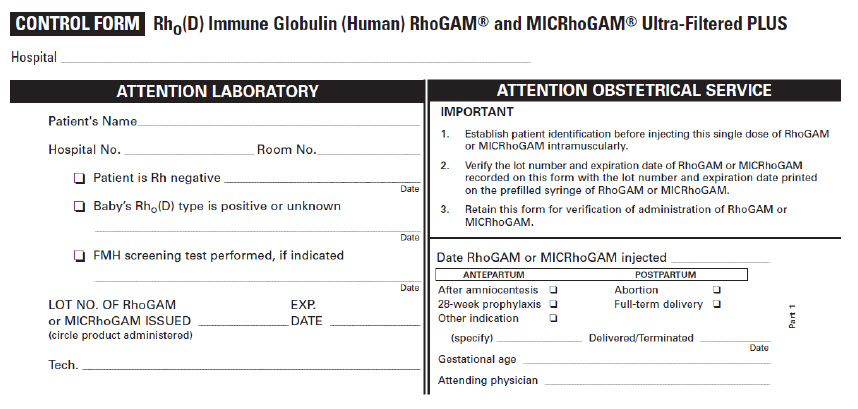
PATIENT IDENTIFICATION CARD Name Address I AM Rh NEGATIVE. I have received a protective injection of RhoGAM® Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human) Ultra-Filtered PLUS. IMPORTANT: Anti-Rh antibody (also called anti-D) will be present in my blood for several weeks after the injection, and may be detectable by laboratory testing. The presence of this passive anti-Rh antibody does not disqualify me from receiving additional injections of RhoGAM as indicated and prescribed by my physician. © Kedrion Biopharma Inc. 2024 Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human)
RhoGAM®
Ultra-Filtered PLUSThis 3-part form contains:
- Directions for Use
- Patient Control Form
- Patient Identification Card
US LICENSE 1906
Kedrion Biopharma Inc., 155 Duryea Road, Melville, NY 11747 USA
Manufactured for Kedrion Biopharma Inc. by either Ortho-Clinical Diagnostics, Inc. or by Kedrion Biopharma Inc. up to the bulk products, filled and packaged by Kedrion Biopharma Inc.(243)0008060071
Date of Injection of RhoGAM (circle product administered) Lot No. Exp. Date Injection was: ❏ at pregnancy termination ❏ during pregnancy ❏ after delivery Attending Physician Physician's Telephone Number - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 300 μg Syringe Label
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 300 μg Syringe Pouch Label
↑ TEAR HERE
Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human)
RhoGAM®
Ultra-Filtered PLUS
300 μg Dose (1500 IU*)
*International UnitsRx Only
Thimerosal-Free
Latex-Free Delivery System
Name ______________________
Room No. ___________________See Directions for Use
US LICENSE 1906
Kedrion Biopharma Inc., 155 Duryea Road, Melville, NY 11747 USA
Made by methods of
Pat. 6,096,872KEDRION
BIOPHARMANDC 0562-7805-00
©Kedrion Biopharma Inc. 2023
(243)0008060066TEAR HERE ↑
TAMPER RESISTANT:
POUCH SEALED
FOR SAFETYTO USE: Screw plunger into
stopper in syringe barrel.The patient and physician
should discuss the risks and
benefits of this product.
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 300 μg Syringe Pouch Label (Rework)
↑ TEAR HERE
Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human)
RhoGAM®
Ultra-Filtered PLUS
300 μg Dose (1500 IU*)
*International UnitsRx Only
Thimerosal-Free
Latex-Free Delivery System
Name ______________________
Room No. ___________________See Directions for Use
US LICENSE 1906
Kedrion Biopharma Inc., 155 Duryea Road, Melville, NY 11747 USA
Made by methods of
Pat. 6,096,872KEDRION
BIOPHARMANDC 0562-7805-00
©Kedrion Biopharma Inc. 2023
(243)0008060067TEAR HERE ↑
TAMPER RESISTANT:
POUCH SEALED
FOR SAFETYTO USE: Screw plunger into
stopper in syringe barrel.The patient and physician
should discuss the risks and
benefits of this product.
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 300 μg Syringe Pouch Carton - 01
Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human)
RhoGAM®
Ultra-Filtered PLUS – 300 μg Dose (1500 IU*)
Thimerosal-Free
*International UnitsDo not store frozen
See Directions for Use
Package Contains:
- 1 prefilled syringe containing a
single dose of RhoGAM - 1 control form
- 1 package insert
- 1 patient identification card
1 single dose
Active ingredient:
Anti-D Rho Immune Globulin (300 μg), the potency of
which is determined relative to the US/WHO/EP Standard
Anti-D Immunoglobulin Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human)
CBER Lot 4: NIBSC Lot 01/572 (285 IU/ampoule)Inactive ingredients:
2.9 mg/mL sodium chloride
0.01% polysorbate 80
15 mg/mL glycineUS LICENSE 1906
Kedrion Biopharma Inc., 155 Duryea Road, Melville, NY 11747 USA
KEDRION
BIOPHARMAREF
780501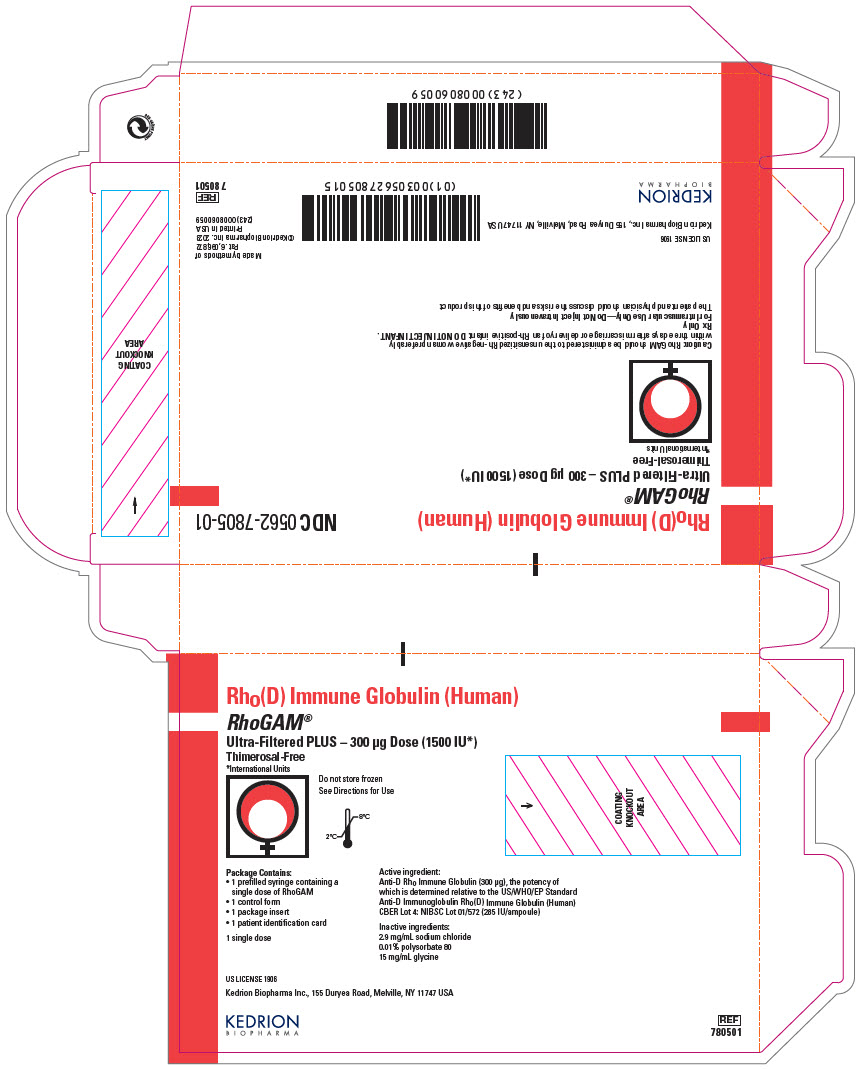
- 1 prefilled syringe containing a
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 300 μg Syringe Pouch Carton - 05
Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human)
RhoGAM®
Ultra-Filtered PLUS – 300 μg Dose (1500 IU*)
Thimerosal-Free
*International UnitsCaution: RhoGAM should be administered to the unsensitized Rh-negative woman preferably
within three days after miscarriage or delivery of an Rh-positive infant. DO NOT INJECT INFANT.Rx Only
For Intramuscular Use Only—Do Not Inject Intravenously
The patient and physician should discuss the risks and benefits of this product.
REF
780505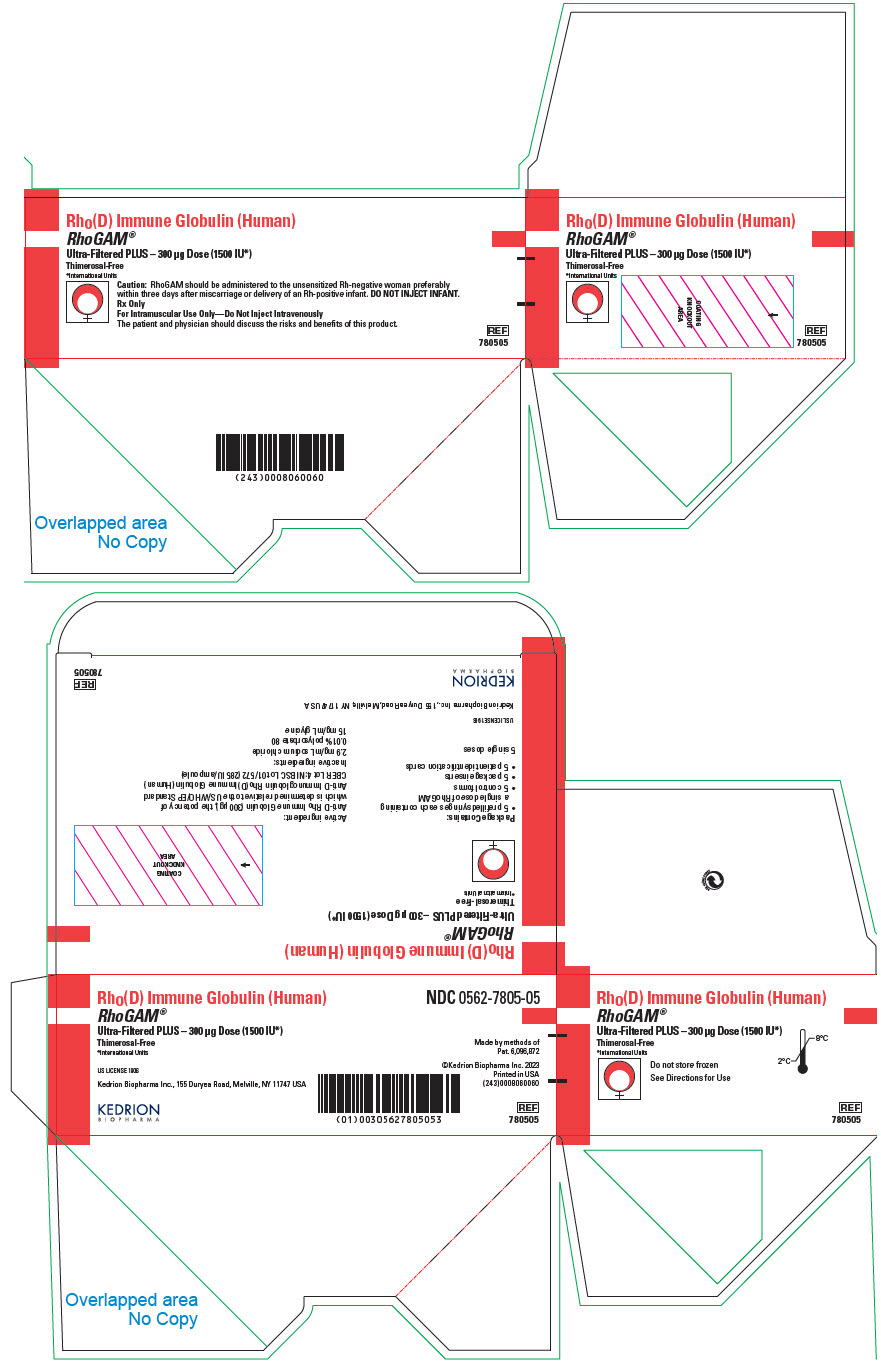
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 300 μg Syringe Pouch Carton - 25
Rho(D) Immune Globulin (Human)
RhoGAM®
Ultra-Filtered PLUS – 300 μg Dose (1500 IU*)
Thimerosal-Free
*International UnitsCaution: RhoGAM should be administered to the unsensitized Rh-negative
woman preferably within three days after miscarriage or delivery of an
Rh-positive infant. DO NOT INJECT INFANT.Rx Only
For Intramuscular Use Only—Do Not Inject Intravenously
The patient and physician should discuss the risks and benefits of this product.
REF
780525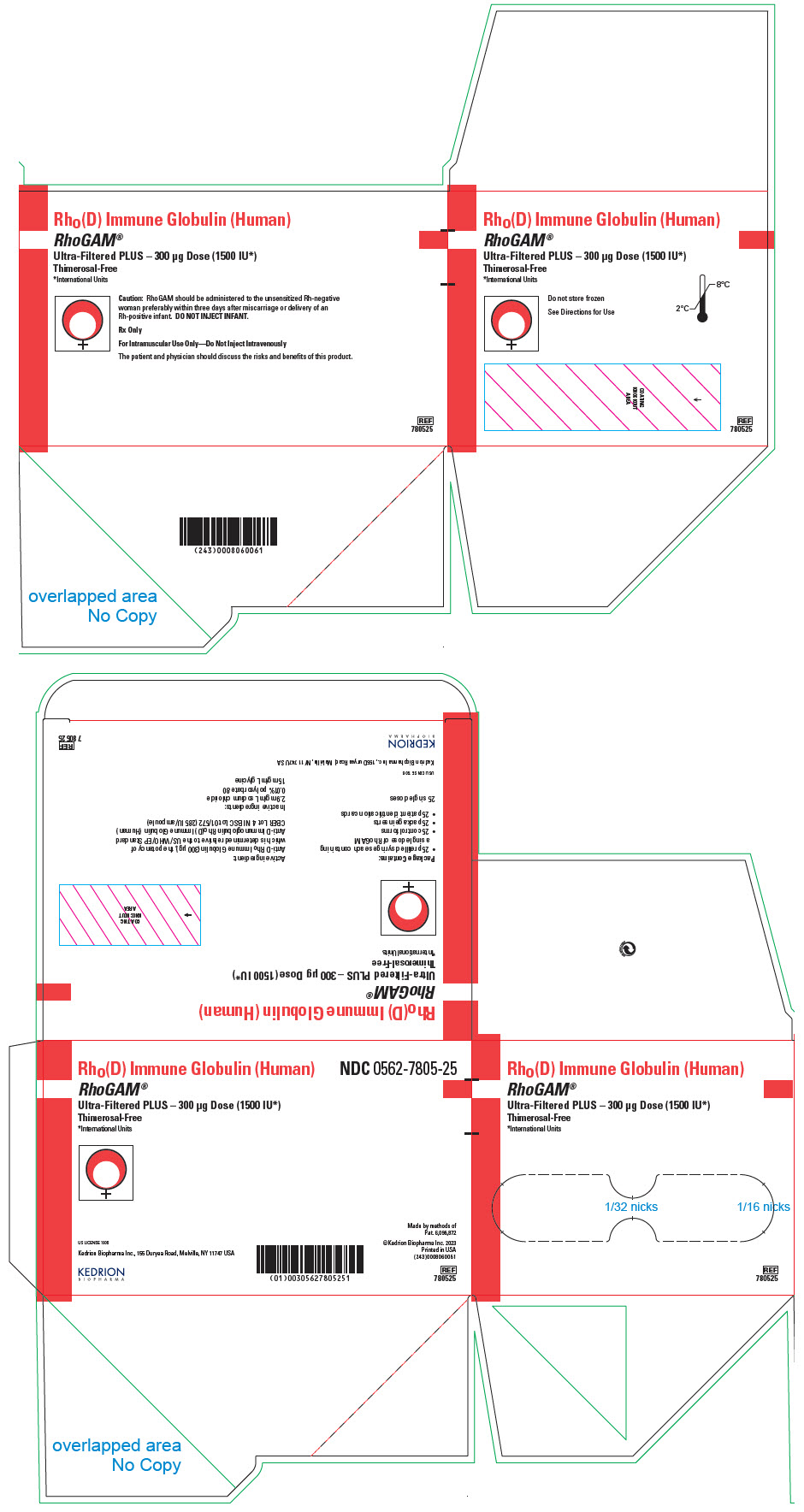
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
RHOGAM ULTRA-FILTERED PLUS
human rho(d) immune globulin injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type PLASMA DERIVATIVE Item Code (Source) NDC:0562-7805 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength HUMAN RHO(D) IMMUNE GLOBULIN (UNII: 48W7181FLP) (HUMAN RHO(D) IMMUNE GLOBULIN - UNII:48W7181FLP) HUMAN RHO(D) IMMUNE GLOBULIN 300 ug Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) GLYCINE (UNII: TE7660XO1C) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:0562-7805-01 1 in 1 CARTON 1 NDC:0562-7805-00 1 in 1 POUCH; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC:0562-7805-05 5 in 1 CARTON 2 NDC:0562-7805-00 1 in 1 POUCH; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC:0562-7805-25 25 in 1 CARTON 3 NDC:0562-7805-00 1 in 1 POUCH; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA103777 03/09/2007 MICRHOGAM ULTRA-FILTERED PLUS
human rho(d) immune globulin injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type PLASMA DERIVATIVE Item Code (Source) NDC:0562-7806 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength HUMAN RHO(D) IMMUNE GLOBULIN (UNII: 48W7181FLP) (HUMAN RHO(D) IMMUNE GLOBULIN - UNII:48W7181FLP) HUMAN RHO(D) IMMUNE GLOBULIN 50 ug Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) GLYCINE (UNII: TE7660XO1C) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:0562-7806-01 1 in 1 CARTON 1 NDC:0562-7806-00 1 in 1 POUCH; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC:0562-7806-05 5 in 1 CARTON 2 NDC:0562-7806-00 1 in 1 POUCH; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC:0562-7806-25 25 in 1 CARTON 3 NDC:0562-7806-00 1 in 1 POUCH; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA103777 03/09/2007 01/28/2024 Labeler - Kedrion Biopharma Inc (080452111) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Kedrion Biopharma Inc. 080452111 MANUFACTURE(0562-7805, 0562-7806)