Label: ZOLEDRONIC ACID injection, solution
- NDC Code(s): 55150-283-99
- Packager: Eugia US LLC
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Abbreviated New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated November 8, 2024
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Medication Guide: HTML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ZOLEDRONIC ACID INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ZOLEDRONIC ACID INJECTION.
ZOLEDRONIC ACID injection, for intravenous infusion
Initial U.S. Approval: 2001
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Zoledronic acid injection is a bisphosphonate indicated for:
- Treatment and prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis (1.1, 1.2)
- Treatment to increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis (1.3)
- Treatment and prevention of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis (1.4)
- Treatment of Paget’s disease of bone in men and women (1.5)
Limitations of Use
Optimal duration of use has not been determined. For patients at low-risk for fracture, consider drug discontinuation after 3 to 5 years of use (1.6)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Infusion given intravenously over no less than 15 minutes:
- Treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis (2.2); treatment to increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis (2.4): treatment and prevention of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis (2.5): 5 mg once a year
- Prevention of postmenopausal osteoporosis: 5 mg once every 2 years (2.3)
- Treatment of Paget’s disease of bone: a single 5 mg infusion. Patients should receive 1,500 mg elemental calcium and 800 international units vitamin D daily (2.6)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
5 mg in a 100 mL ready-to-infuse solution (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Products Containing Same Active Ingredient: Patients receiving Zometa should not receive zoledronic acid injection (5.1)
- Hypocalcemia may worsen during treatment. Patients must be adequately supplemented with calcium and vitamin D (5.2)
- Renal Impairment: A single dose should not exceed 5 mg and the duration of infusion should be no less than 15 minutes. Renal toxicity may be greater in patients with underlying renal impairment or with other risk factors, including advanced age or dehydration. Monitor creatinine clearance before each dose (2.7, 5.3)
- Osteonecrosis of the Jaw (ONJ) has been reported. All patients should have a routine oral exam by the prescriber prior to treatment (5.4)
- Atypical Femur Fractures have been reported. Patients with thigh or groin pain should be evaluated to rule out a femoral fracture (5.5)
- Severe Bone, Joint, and Muscle Pain may occur. Withhold future doses of zoledronic acid if severe symptoms occur (5.7)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (greater than 10%) were pyrexia, myalgia, headache, arthralgia, pain in extremity (6.1). Other important adverse reactions were flu-like illness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea (6.2), and eye inflammation (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Eugia US LLC at 1-866-850-2876 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Aminoglycosides: May lower serum calcium for prolonged periods (7.1)
- Loop diuretics: May increase risk of hypocalcemia (7.2)
- Nephrotoxic drugs: Use with caution (7.3)
- Drugs primarily excreted by the kidney: Exposure may be increased with renal impairment. Monitor serum creatinine in patients at risk (7.4)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 11/2024
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Treatment of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
1.2 Prevention of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
1.3 Osteoporosis in Men
1.4 Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
1.5 Paget's Disease of Bone
1.6 Important Limitations of Use
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
2.2 Treatment of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
2.3 Prevention of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
2.4 Osteoporosis in Men
2.5 Treatment and Prevention of Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
2.6 Treatment of Paget’s Disease of Bone
2.7 Laboratory Testing and Oral Examination Prior to Administration
2.8 Calcium and Vitamin D Supplementation
2.9 Method of Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Drug Products with Same Active Ingredient
5.2 Hypocalcemia and Mineral Metabolism
5.3 Renal Impairment
5.4 Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
5.5 Atypical Subtrochanteric and Diaphyseal Femoral Fractures
5.6 Musculoskeletal Pain
5.7 Patients with Asthma
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Aminoglycosides
7.2 Loop Diuretics
7.3 Nephrotoxic Drugs
7.4 Drugs Primarily Excreted by the Kidney
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Treatment of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
14.2 Prevention of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
14.3 Osteoporosis in Men
14.4 Treatment and Prevention of Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
14.5 Treatment of Paget’s Disease of Bone
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Treatment of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
Zoledronic acid injection is indicated for treatment of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. In postmenopausal women with osteoporosis, diagnosed by bone mineral density (BMD) or prevalent vertebral fracture, zoledronic acid injection reduces the incidence of fractures (hip, vertebral and non-vertebral osteoporosis-related fractures). In patients at high risk of fracture, defined as a recent low-trauma hip fracture, zoledronic acid injection reduces the incidence of new clinical fractures [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
1.2 Prevention of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
Zoledronic acid injection is indicated for prevention of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
1.3 Osteoporosis in Men
Zoledronic acid injection is indicated for treatment to increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis [see Clinical Studies (14.3)].
1.4 Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
Zoledronic acid injection is indicated for the treatment and prevention of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in men and women who are either initiating or continuing systemic glucocorticoids in a daily dosage equivalent to 7.5 mg or greater of prednisone and
who are expected to remain on glucocorticoids for at least 12 months [see Clinical Studies (14.4)].
1.5 Paget's Disease of Bone
Zoledronic acid injection is indicated for treatment of Paget’s disease of bone in men and women. Treatment is indicated in patients with Paget’s disease of bone with elevations in serum alkaline phosphatase of two times or higher than the upper limit of the age-specific normal reference range, or those who are symptomatic, or those at risk for complications from their disease [see Clinical Studies (14.5)].
1.6 Important Limitations of Use
The safety and effectiveness of zoledronic acid injection for the treatment of osteoporosis is based on clinical data of three years duration. The optimal duration of use has not been determined. All patients on bisphosphonate therapy should have the need for continued therapy re-evaluated on a periodic basis. Patients at low-risk for fracture should be considered for drug discontinuation after 3 to 5 years of use. Patients who discontinue therapy should have their risk for fracture re-evaluated periodically.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
Zoledronic acid injection must be administered as an intravenous infusion over no less than 15 minutes.
- Patients must be appropriately hydrated prior to administration of zoledronic acid injection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
- Intravenous infusion should be followed by a 10 mL normal saline flush of the intravenous line.
- Administration of acetaminophen following zoledronic acid injection administration may reduce the incidence of acute-phase reaction symptoms.
2.2 Treatment of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
The recommended regimen is a 5 mg infusion once a year given intravenously over no less than 15 minutes.
2.3 Prevention of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
The recommended regimen is a 5 mg infusion given once every 2 years intravenously over no less than 15 minutes.
2.4 Osteoporosis in Men
The recommended regimen is a 5 mg infusion once a year given intravenously over no less than 15 minutes.
2.5 Treatment and Prevention of Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
The recommended regimen is a 5 mg infusion once a year given intravenously over no less than 15 minutes.
2.6 Treatment of Paget’s Disease of Bone
The recommended dose is a 5 mg infusion. The infusion time must not be less than 15 minutes given over a constant infusion rate.
Re-treatment of Paget’s Disease
After a single treatment with zoledronic acid injection in Paget’s disease an extended remission period is observed. Specific re-treatment data are not available. However, re-treatment with zoledronic acid injection may be considered in patients who have relapsed, based on increases in serum alkaline phosphatase, or in those patients who failed to achieve normalization of their serum alkaline phosphatase, or in those patients with symptoms, as dictated by medical practice.2.7 Laboratory Testing and Oral Examination Prior to Administration
- Prior to administration of each dose of zoledronic acid injection, obtain a serum creatinine and creatinine clearance should be calculated based on actual body weight using Cockcroft-Gault formula before each zoledronic acid injection dose. Zoledronic acid injection is contraindicated in patients with creatinine clearance less than 35 mL/min and in those with evidence of acute renal impairment. A 5 mg dose of zoledronic acid injection administered intravenously is recommended for patients with creatinine clearance greater than or equal to 35 mL/min. There are no safety or efficacy data to support the adjustment of the zoledronic acid injection dose based on baseline renal function. Therefore, no dose adjustment is required in patients with CrCl greater than or equal to 35 mL/min [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- A routine oral examination should be performed by the prescriber prior to initiation of zoledronic acid injection treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
2.8 Calcium and Vitamin D Supplementation
- Instruct patients being treated for Paget’s disease of bone on the importance of calcium and vitamin D supplementation in maintaining serum calcium levels, and on the symptoms of hypocalcemia. All patients should take 1,500 mg elemental calcium daily in divided doses (750 mg two times a day, or 500 mg three times a day) and 800 international units vitamin D daily, particularly in the 2 weeks following zoledronic acid injection administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Instruct patients being treated for osteoporosis to take supplemental calcium and vitamin D if their dietary intake is inadequate. An average of at least 1,200 mg calcium and 800 to 1,000 international units vitamin D daily is recommended.
2.9 Method of Administration
The zoledronic acid infusion time must not be less than 15 minutes given over a constant infusion rate.
The i.v. infusion should be followed by a 10 mL normal saline flush of the intravenous line.
Zoledronic acid injection solution for infusion must not be allowed to come in contact with any calcium or other divalent cation-containing solutions, and should be administered as a single intravenous solution through a separate vented infusion line.
If refrigerated, allow the refrigerated solution to reach room temperature before administration. After opening, the solution is stable for 24 hours at 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F) [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)]. - 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Zoledronic acid is contraindicated in patients with the following conditions:
- Hypocalcemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Creatinine clearance less than 35 mL/min and in those with evidence of acute renal impairment due to an increased risk of renal failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Known hypersensitivity to zoledronic acid or any components of zoledronic acid injection. Hypersensitivity reactions including urticaria, angioedema, and anaphylactic reaction/shock have been reported [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Drug Products with Same Active Ingredient
Zoledronic acid injection contains the same active ingredient found in Zometa, used for oncology indications, and a patient being treated with Zometa should not be treated with zoledronic acid injection.
5.2 Hypocalcemia and Mineral Metabolism
Pre-existing hypocalcemia and disturbances of mineral metabolism (e.g., hypoparathyroidism, thyroid surgery, parathyroid surgery; malabsorption syndromes, excision of small intestine) must be effectively treated before initiating therapy with zoledronic acid. Clinical monitoring of calcium and mineral levels (phosphorus and magnesium) is highly recommended for these patients [see Contraindications (4)].
Hypocalcemia following zoledronic acid administration is a significant risk in Paget’s disease. All patients should be instructed about the symptoms of hypocalcemia and the importance of calcium and vitamin D supplementation in maintaining serum calcium levels [see Dosage and Administration (2.8), Adverse Reactions (6.1), Patient Counseling Information (17)].
All osteoporosis patients should be instructed on the importance of calcium and vitamin D supplementation in maintaining serum calcium levels [see Dosage and Administration (2.8), Adverse Reactions (6.1), Patient Counseling Information (17)].5.3 Renal Impairment
A single dose of zoledronic acid should not exceed 5 mg and the duration of infusion should be no less than 15 minutes [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Zoledronic acid is contraindicated in patients with creatinine clearance less than 35 mL/min and in those with evidence of acute renal impairment [see Contraindications (4)]. If history or physical signs suggest dehydration, zoledronic acid therapy should be withheld until normovolemic status has been achieved [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Zoledronic acid should be used with caution in patients with chronic renal impairment. Acute renal impairment, including renal failure, has been observed following the administration of zoledronic acid, especially in patients with pre-existing renal compromise, advanced age, concomitant nephrotoxic medications, concomitant diuretic therapy, or severe dehydration occurring before or after zoledronic acid administration. Acute renal failure (ARF) has been observed in patients after a single administration. Rare reports of hospitalization and/or dialysis or fatal outcome occurred in patients with underlying moderate to severe renal impairment or with any of the risk factors described in this section [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. Renal impairment may lead to increased exposure of concomitant medications and/or their metabolites that are primarily renally excreted [see Drug Interactions (7.4)].
Creatinine clearance should be calculated based on actual body weight using Cockcroft-Gault formula before each zoledronic acid dose. Transient increase in serum creatinine may be greater in patients with impaired renal function; interim monitoring of creatinine clearance should be performed in at-risk patients. Elderly patients and those receiving diuretic therapy are at increased risk of acute renal failure. These patients should have their fluid status assessed and be appropriately hydrated prior to administration of zoledronic acid. Zoledronic acid should be used with caution with other nephrotoxic drugs [see Drug Interactions (7.3)]. Consider monitoring creatinine clearance in patients at-risk for ARF who are taking concomitant medications that are primarily excreted by the kidney [see Drug Interactions (7.4)].5.4 Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) has been reported in patients treated with bisphosphonates, including zoledronic acid. Most cases have been in cancer patients treated with intravenous bisphosphonates undergoing dental procedures. Some cases have occurred in patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis treated with either oral or intravenous bisphosphonates. A routine oral examination should be performed by the prescriber prior to initiation of bisphosphonate treatment. A dental examination with appropriate preventive dentistry should be considered prior to treatment with bisphosphonates in patients with a history of concomitant risk factors (e.g., cancer, chemotherapy, angiogenesis inhibitors, radiotherapy, corticosteroids, poor oral hygiene, pre-existing dental disease or infection, anemia, coagulopathy). The risk of ONJ may increase with duration of exposure to bisphosphonates. Concomitant administration of drugs associated with ONJ may increase the risk of developing ONJ.
While on treatment, patients with concomitant risk factors should avoid invasive dental procedures if possible. For patients who develop ONJ while on bisphosphonate therapy, dental surgery may exacerbate the condition. For patients requiring dental procedures, there are no data available to suggest whether discontinuation of bisphosphonate treatment reduces the risk of ONJ. The clinical judgment of the treating physician should guide the management plan of each patient based on individual benefit/risk assessment [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.5 Atypical Subtrochanteric and Diaphyseal Femoral Fractures
Atypical, low-energy, or low trauma fractures of the femoral shaft have been reported in bisphosphonate-treated patients. These fractures can occur anywhere in the femoral shaft from just below the lesser trochanter to above the supracondylar flare and are transverse or short oblique in orientation without evidence of comminution. Causality has not been established as these fractures also occur in osteoporotic patients who have not been treated with bisphosphonates.
Atypical femur fractures most commonly occur with minimal or no trauma to the affected area. They may be bilateral and many patients report prodromal pain in the affected area, usually presenting as dull, aching thigh pain, weeks to months before a complete fracture occurs. A number of reports note that patients were also receiving treatment with glucocorticoids (e.g., prednisone) at the time of fracture.
Any patient with a history of bisphosphonate exposure who presents with thigh or groin pain should be suspected of having an atypical fracture and should be evaluated to rule out an incomplete femur fracture. Patients presenting with an atypical femur fracture should also be assessed for symptoms and signs of fracture in the contralateral limb. Interruption of bisphosphonate therapy should be considered, pending a risk/benefit assessment, on an individual basis.5.6 Musculoskeletal Pain
In post-marketing experience, severe and occasionally incapacitating bone, joint, and/or muscle pain have been infrequently reported in patients taking bisphosphonates, including zoledronic acid. The time to onset of symptoms varied from one day to several months after starting the drug. Consider withholding future zoledronic acid treatment if severe symptoms develop. Most patients had relief of symptoms after stopping. A subset had recurrence of symptoms when rechallenged with the same drug or another bisphosphonate [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Treatment of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
The safety of zoledronic acid in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis was assessed in Study 1, a large, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multinational study of 7736 postmenopausal women aged 65 to 89 years with osteoporosis, diagnosed by bone mineral density or the presence of a prevalent vertebral fracture. The duration of the trial was three years with 3862 patients exposed to zoledronic acid and 3852 patients exposed to placebo administered once annually as a single 5 mg dose in 100 mL solution infused over at least 15 minutes, for a total of three doses. All women received 1,000 to 1,500 mg of elemental calcium plus 400 to 1,200 international units of vitamin D supplementation per day.
The incidence of all-cause mortality was similar between groups: 3.4% in the zoledronic acid group and 2.9% in the placebo group. The incidence of serious adverse events was 29.2% in the zoledronic acid group and 30.1% in the placebo group. The percentage of patients who withdrew from the study due to adverse events was 5.4% and 4.8% for the zoledronic acid and placebo groups, respectively.
The safety of zoledronic acid in the treatment of osteoporosis patients with a recent (within 90 days) low-trauma hip fracture was assessed in Study 2, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multinational endpoint-driven study of 2127 men and women aged 50 to 95 years; 1065 patients were randomized to zoledronic acid and 1062 patients were randomized to placebo. Zoledronic acid was administered once annually as a single 5 mg dose in 100 mL solution infused over at least 15 minutes. The study continued until at least 211 patients had a confirmed clinical fracture in the study population who were followed for an average of approximately 2 years on study drug. Vitamin D levels were not routinely measured but a loading dose of vitamin D (50,000 to 125,000 international units orally or IM) was given to patients and they were started on 1,000 to 1,500 mg of elemental calcium plus 800 to 1,200 international units of vitamin D supplementation per day for at least 14 days prior to the study drug infusions.
The incidence of all-cause mortality was 9.6% in the zoledronic acid group and 13.3% in the placebo group. The incidence of serious adverse events was 38.3% in the zoledronic acid group and 41.3% in the placebo group. The percentage of patients who withdrew from the study due to adverse events was 5.3% and 4.7% for the zoledronic acid and placebo groups, respectively.
Adverse reactions reported in at least 2% of patients with osteoporosis and more frequently in the zoledronic acid-treated patients than placebo-treated patients in either osteoporosis trial are shown below in Table 1.
Table 1. Adverse Reactions Occurring in greater than or equal to 2.0% of Patients with Osteoporosis and More Frequently than in Placebo- Treated Patients
Study 1
Study 2
System Organ Class
5 mg IV Zoledronic acid
once per year
%
(N = 3862)
Placebo
once per year
%
(N = 3852)
5 mg IV Zoledronic acid
once per year
%
(N = 1054)
Placebo
once per year
%
(N = 1057)
Blood and the Lymphatic System Disorders
Anemia
4.4
3.6
5.3
5.2
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders
Dehydration
0.6
0.6
2.5
2.3
Anorexia
2.0
1.1
1.0
1.0
Nervous System Disorders
Headache
12.4
8.1
3.9
2.5
Dizziness
7.6
6.7
2.0
4.0
Ear and Labyrinth Disorders
Vertigo
4.3
4.0
1.3
1.7
Cardiac Disorders
Atrial Fibrillation
2.4
1.9
2.8
2.6
Vascular Disorders
Hypertension
12.7
12.4
6.8
5.4
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Nausea
8.5
5.2
4.5
4.5
Diarrhea
6.0
5.6
5.2
4.7
Vomiting
4.6
3.2
3.4
3.4
Abdominal Pain Upper
4.6
3.1
0.9
1.5
Dyspepsia
4.3
4.0
1.7
1.6
Musculoskeletal, Connective Tissue and Bone Disorders
Arthralgia
23.8
20.4
17.9
18.3
Myalgia
11.7
3.7
4.9
2.7
Pain in Extremity
11.3
9.9
5.9
4.8
Shoulder Pain
6.9
5.6
0.0
0.0
Bone Pain
5.8
2.3
3.2
1.0
Neck Pain
4.4
3.8
1.4
1.1
Muscle Spasms
3.7
3.4
1.5
1.7
Osteoarthritis
9.1
9.7
5.7
4.5
Musculoskeletal Pain
0.4
0.3
3.1
1.2
General Disorders and Administrative Site Conditions
Pyrexia
17.9
4.6
8.7
3.1
Influenza-like Illness
8.8
2.7
0.8
0.4
Fatigue
5.4
3.5
2.1
1.2
Chills
5.4
1.0
1.5
0.5
Asthenia
5.3
2.9
3.2
3.0
Peripheral Edema
4.6
4.2
5.5
5.3
Pain
3.3
1.3
1.5
0.5
Malaise
2.0
1.0
1.1
0.5
Hyperthermia
0.3
<0.1
2.3
0.3
Chest Pain
1.3
1.1
2.4
1.8
Investigations
Creatinine Renal Clearance Decreased
2.0
2.4
2.1
1.7
Renal Impairment
Treatment with intravenous bisphosphonates, including zoledronic acid, has been associated with renal impairment manifested as deterioration in renal function (i.e., increased serum creatinine) and in rare cases, acute renal failure. In the clinical trial for postmenopausal osteoporosis, patients with baseline creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min (based on actual body weight), urine dipstick greater than or equal to 2+ protein or increase in serum creatinine of greater than 0.5 mg/dL during the screening visits were excluded. The change in creatinine clearance (measured annually prior to dosing) and the incidence of renal failure and impairment was comparable for both the zoledronic acid and placebo treatment groups over 3 years, including patients with creatinine clearance between 30 to 60 mL/min at baseline. Overall, there was a transient increase in serum creatinine observed within 10 days of dosing in 1.8% of zoledronic acid-treated patients versus 0.8% of placebo-treated patients which resolved without specific therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Acute Phase Reaction
The signs and symptoms of acute phase reaction occurred in Study 1 following zoledronic acid infusion including fever (18%), myalgia (9%), flu-like symptoms (8%), headache (7%), and arthralgia (7%). The majority of these symptoms occurred within the first 3 days following the dose of zoledronic acid and usually resolved within 3 days of onset but resolution could take up to 7 to14 days. In Study 2, patients without a contraindication to acetaminophen were provided with a standard oral dose at the time of the IV infusion and instructed to use additional acetaminophen at home for the next 72 hours as needed.
Zoledronic acid was associated with fewer signs and symptoms of a transient acute phase reaction in this trial: fever (7%) and arthralgia (3%). The incidence of these symptoms decreased with subsequent doses of zoledronic acid.
Laboratory Findings
In Study 1, in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis, approximately 0.2% of patients had notable declines of serum calcium levels (less than 7.5 mg/dL) following zoledronic acid administration. No symptomatic cases of hypocalcemia were observed. In Study 2, following pre-treatment with vitamin D, no patients had treatment emergent serum calcium levels below 7.5 mg/dL.
Injection Site Reactions
In the osteoporosis trials, local reactions at the infusion site such as itching, redness and/or pain have been reported in 0% to 0.7% of patients following the administration of zoledronic acid and 0% to 0.5% of patients following administration of placebo.
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
In the postmenopausal osteoporosis trial, Study 1, in 7736 patients, after initiation of therapy, symptoms consistent with ONJ occurred in one patient treated with placebo and one patient treated with zoledronic acid. Both cases resolved after appropriate treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. No reports of osteonecrosis of the jaw were reported in either treatment group in Study 2.
Atrial Fibrillation
In the postmenopausal osteoporosis trial, Study 1, adjudicated serious adverse events of atrial fibrillation in the zoledronic acid treatment group occurred in 1.3% of patients (50 out of 3862) compared to 0.4% (17 out of 3852) in the placebo group. The overall incidence of all atrial fibrillation adverse events in the zoledronic acid treatment group was reported in 2.5% of patients (96 out of 3862) in the zoledronic acid group vs. 1.9% of patients (75 out of 3852) in the placebo group. Over 90% of these events in both treatment groups occurred more than a month after the infusion. In an ECG sub-study, ECG measurements were performed on a subset of 559 patients before and 9 to 11 days after treatment. There was no difference in the incidence of atrial fibrillation between treatment groups suggesting these events were not related to the acute infusions. In Study 2, adjudicated serious adverse events of atrial fibrillation in the zoledronic acid treatment group occurred in 1.0% of patients (11 out of 1054) compared to 1.2% (13 out of 1057) in the placebo group demonstrating no difference between treatment groups.
Ocular Adverse Events
Cases of iritis/uveitis/episcleritis/conjunctivitis have been reported in patients treated with bisphosphonates, including zoledronic acid. In the osteoporosis trials, 1 (less than 0.1%) to 9 (0.2%) patients treated with zoledronic acid and 0 (0%) to 1 (less than 0.1%) patient treated with placebo developed iritis/uveitis/episcleritis.
Prevention of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women
The safety of zoledronic acid in postmenopausal women with osteopenia (low bone mass) was assessed in a 2-year randomized, multi-center, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 581 postmenopausal women aged greater than or equal to 45 years. Patients were randomized to one of three treatment groups: (1) zoledronic acid given at randomization and Month 12 (n = 198); (2) zoledronic acid given at randomization and placebo at Month 12 (n = 181); and (3) placebo given at randomization and Month 12 (n = 202). Zoledronic acid was administered as a single 5 mg dose in 100 mL solution infused over at least 15 minutes. All women received 500 to 1,200 mg elemental calcium plus 400 to 800 international units vitamin D supplementation per day.
The incidence of serious adverse events was similar for subjects given (1) zoledronic acid at randomization and at Month 12 (10.6%), (2) zoledronic acid at randomization and placebo given at Month 12 (9.4%), and (3) placebo at randomization and at Month 12 (11.4%). The percentages of patients who withdrew from the study due to adverse events were 7.1%, 7.2%, and 3.0% in the two zoledronic acid groups and placebo group, respectively. Adverse reactions reported in at least 2% of patients with osteopenia and more frequently in the zoledronic acid-treated patients than placebo-treated patients are shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Adverse Reactions Occurring in greater than or equal to 2% of Patients with Osteopenia and More Frequently than in Placebo- Treated Patients System Organ Class
5 mg IV Zoledronic Acid Once Per Year
%
(n = 198)
5 mg IV Zoledronic Acid Once
%
(n = 181)
Placebo
once per year
%
(n = 202)
* Combined abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, and abdominal pain lower as one ADR
** Combined musculoskeletal pain and musculoskeletal chest pain as one ADR
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
Anorexia
2.0
0.6
0.0
Nervous system disorders
Headache
14.6
20.4
11.4
Dizziness
7.6
6.1
3.5
Hypoesthesia
5.6
2.2
2.0
Ear and labyrinth disorders
Vertigo
2.0
1.7
1.0
Vascular disorders
Hypertension
5.1
8.3
6.9
Gastrointestinal disorders
Nausea
17.7
11.6
7.9
Diarrhea
8.1
6.6
7.9
Vomiting
7.6
5.0
4.5
Dyspepsia
7.1
6.6
5.0
Abdominal pain*
8.6
6.6
7.9
Constipation
6.6
7.2
6.9
Abdominal discomfort
2.0
1.1
0.5
Abdominal distension
2.0
0.6
0.0
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Rash
3.0
2.2
2.5
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Arthralgia
27.3
18.8
19.3
Myalgia
19.2
22.7
6.9
Back pain
18.2
16.6
11.9
Pain in extremity
11.1
16.0
9.9
Muscle spasms
5.6
2.8
5.0
Musculoskeletal pain**
8.1
7.2
7.9
Bone pain
5.1
3.3
1.0
Neck pain
5.1
6.6
5.0
Arthritis
4.0
2.2
1.5
Joint stiffness
3.5
1.1
2.0
Joint swelling
3.0
0.6
0.0
Flank pain
2.0
0.6
0.0
Pain in jaw
2.0
3.9
2.5
General disorders and administration site conditions
Pain
24.2
14.9
3.5
Pyrexia
21.7
21.0
4.5
Chills
18.2
18.2
3.0
Fatigue
14.6
9.9
4.0
Asthenia
6.1
2.8
1.0
Peripheral edema
5.6
3.9
3.5
Non-cardiac chest pain
3.5
7.7
3.0
Influenza-like illness
1.5
3.3
2.0
Malaise
1.0
2.2
0.5
Ocular Adverse Events
Cases of iritis/uveitis/episcleritis/conjunctivitis have been reported in patients treated with bisphosphonates, including zoledronic acid. In the osteoporosis prevention trial, 4 (1.1%) patients treated with zoledronic acid and 0 (0%) patients treated with placebo developed iritis/uveitis.
Acute Phase Reaction
In patients given zoledronic acid at randomization and placebo at Month 12, zoledronic acid was associated with signs and symptoms of an acute phase reaction: myalgia (20.4%), fever (19.3%), chills (18.2%), pain (13.8%), headache (13.3%), fatigue (8.3%), arthralgia (6.1%), pain in extremity (3.9%), influenza-like illness (3.3%), and back pain (1.7%), which occurred within the first 3 days following the dose of zoledronic acid. The majority of these symptoms were mild to moderate and resolved within 3 days of the event onset but resolution could take up to 7 to 14 days.
Osteoporosis in Men
The safety of zoledronic acid in men with osteoporosis or osteoporosis secondary to hypogonadism was assessed in a two year randomized, multicenter, double-blind, active controlled group study of 302 men aged 25 to 86 years. One hundred fifty three (153) patients were exposed to zoledronic acid administered once annually with a 5 mg dose in 100 mL infused over 15 minutes for up to a total of two doses, and 148 patients were exposed to a commercially-available oral weekly bisphosphonate (active control) for up to two years. All participants received 1,000 mg of elemental calcium plus 800 to 1,000 international units of vitamin D supplementation per day.
The incidence of all-cause mortality (one in each group) and serious adverse events were similar between the zoledronic acid and active control treatment groups. The percentage of patients experiencing at least one adverse event was comparable between the zoledronic acid and active control groups, with the exception of a higher incidence of post-dose symptoms in the zoledronic acid group that occurred within 3 days after infusion. The overall safety and tolerability of zoledronic acid was similar to the active control.
Adverse reactions reported in at least 2% of men with osteoporosis and more frequently in the zoledronic acid-treated patients than the active control-treated patients and either (1) not reported in the postmenopausal osteoporosis treatment trial or (2) reported more frequently in the trial of osteoporosis in men are presented in Table 3. Therefore, Table 3 should be viewed in conjunction with Table 1.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions Occurring in greater than or equal to 2% of Men with Osteoporosis and More Frequently in the Zoledronic Acid -Treated Patients than the Active Control-Treated Patients and either (1) Not Reported in the Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Treatment Trial or (2) Reported More Frequently in this Trial System Organ Class
5 mg IV
zoledronic acid
once per year
%
(N = 153)
Active
Control
once weekly
%
(N = 148)
* Combined abdominal pain, abdominal pain upper, and abdominal pain lower as one ADR
** Combined musculoskeletal pain and musculoskeletal chest pain as one ADR
Nervous System Disorders
Headache
15.0
6.1
Lethargy
3.3
1.4
Eye Disorders
Eye pain
2.0
0.0
Cardiac Disorders
Atrial fibrillation
3.3
2.0
Palpitations
2.6
0.0
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders
Dyspnea
6.5
4.7
Abdominal pain*
7.9
4.1
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Hyperhidrosis
2.6
2.0
Musculoskeletal, Connective Tissue and Bone Disorders
Myalgia
19.6
6.8
Musculoskeletal pain**
12.4
10.8
Musculoskeletal stiffness
4.6
0.0
Renal and Urinary Disorders
Blood creatinine increased
2.0
0.7
General Disorders and Administrative Site Conditions
Fatigue
17.6
6.1
Pain
11.8
4.1
Chills
9.8
2.7
Influenza-like illness
9.2
2.0
Malaise
7.2
0.7
Acute phase reaction
3.9
0.0
Investigations
C-reactive protein increased
4.6
1.4
Renal Impairment
Creatinine clearance was measured annually prior to dosing and changes in long-term renal function over 24 months were comparable in the zoledronic acid and active control groups [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Acute Phase Reaction
Zoledronic acid was associated with signs and symptoms of an acute phase reaction: myalgia (17.1%), fever (15.7%), fatigue (12.4%), arthralgia (11.1%), pain (10.5%), chills (9.8%), headache (9.8%), influenza-like illness (8.5%), malaise (5.2%), and back pain (3.3%), which occurred within the first 3 days following the dose of zoledronic acid. The majority of these symptoms were mild to moderate and resolved within 3 days of the event onset but resolution could take up to 7 to 14 days. The incidence of these symptoms decreased with subsequent doses of zoledronic acid.
Atrial Fibrillation
The incidence of all atrial fibrillation adverse events in the zoledronic acid treatment group was 3.3% (5 out of 153) compared to 2.0% (3 out of 148) in the active control group. However, there were no patients with adjudicated serious adverse events of atrial fibrillation in the zoledronic acid treatment group.
Laboratory Findings
There were no patients who had treatment emergent serum calcium levels below 7.5 mg/dL.
Injection Site Reactions
There were 4 patients (2.6%) on zoledronic acid vs. 2 patients (1.4%) on active control with local site reactions.
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
In this trial there were no cases of osteonecrosis of the jaw [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
The safety of zoledronic acid in men and women in the treatment and prevention of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis was assessed in a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, active controlled, stratified study of 833 men and women aged 18 to 85 years treated with greater than or equal to 7.5 mg/day oral prednisone (or equivalent). Patients were stratified according to the duration of their pre-study corticosteroid therapy: less than or equal to 3 months prior to randomization (prevention subpopulation), and greater than 3 months prior to randomization (treatment subpopulation).
The duration of the trial was one year with 416 patients exposed to zoledronic acid administered once as a single 5 mg dose in 100 mL infused over 15 minutes, and 417 patients exposed to a commercially-available oral daily bisphosphonate (active control) for one year. All participants received 1,000 mg of elemental calcium plus 400 to 1,000 international units of vitamin D supplementation per day.
The incidence of all-cause mortality was similar between treatment groups: 0.9% in the zoledronic acid group and 0.7% in the active control group. The incidence of serious adverse events was similar between the zoledronic acid treatment and prevention groups, 18.4% and 18.1%, respectively, and the active control treatment and prevention groups, 19.8% and 16.0%, respectively. The percentage of subjects who withdrew from the study due to adverse events was 2.2% in the zoledronic acid group vs. 1.4% in the active control group. The overall safety and tolerability were similar between zoledronic acid and active control groups with the exception of a higher incidence of post-dose symptoms in the zoledronic acid group that occurred within 3 days after infusion. The overall safety and tolerability profile of zoledronic acid in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis was similar to the adverse events reported in the zoledronic acid postmenopausal osteoporosis clinical trial.
Adverse reactions reported in at least 2% of patients that were either not reported in the postmenopausal osteoporosis treatment trial or reported more frequently in the treatment and prevention of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis trial included the following: abdominal pain (zoledronic acid 7.5%; active control 5.0%), and musculoskeletal pain (zoledronic acid 3.1%; active control 1.7%). Other musculoskeletal events included back pain (zoledronic acid 4.3%, active control 6.2%), bone pain (zoledronic acid 3.1%, active control 2.2%), and pain in the extremity (zoledronic acid 3.1%, active control 1.2%). In addition, the following adverse events occurred more frequently than in the postmenopausal osteoporosis trial: nausea (zoledronic acid 9.6%; active control 8.4%), and dyspepsia (zoledronic acid 5.5%; active control 4.3%).
Renal Impairment
Renal function measured prior to dosing and at the end of the 12 month study was comparable in the zoledronic acid and active control groups [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Acute Phase Reaction
Zoledronic acid was associated with signs and symptoms of a transient acute phase reaction that was similar to that seen in the zoledronic acid postmenopausal osteoporosis clinical trial.
Atrial Fibrillation
The incidence of atrial fibrillation adverse events was 0.7% (3 of 416) in the zoledronic acid group compared to no adverse events in the active control group. All subjects had a prior history of atrial fibrillation and no cases were adjudicated as serious adverse events. One patient had atrial flutter in the active control group.
Laboratory Findings
There were no patients who had treatment emergent serum calcium levels below 7.5 mg/dL.
Injection Site Reactions
There were no local reactions at the infusion site.
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
In this trial there were no cases of osteonecrosis of the jaw [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Paget’s Disease of Bone
In the Paget’s disease trials, two 6-month, double-blind, comparative, multinational studies of 349 men and women aged greater than 30 years with moderate to severe disease and with confirmed Paget’s disease of bone, 177 patients were exposed to zoledronic acid and 172 patients exposed to risedronate. Zoledronic acid was administered once as a single 5 mg dose in 100 mL solution infused over at least 15 minutes. Risedronate was given as an oral daily dose of 30 mg for 2 months.
The incidence of serious adverse events was 5.1% in the zoledronic acid group and 6.4% in the risedronate group. The percentage of patients who withdrew from the study due to adverse events was 1.7% and 1.2% for the zoledronic acid and risedronate groups, respectively.
Adverse reactions occurring in at least 2% of the Paget’s patients receiving zoledronic acid (single 5 mg intravenous infusion) or risedronate (30 mg oral daily dose for 2 months) over a 6-month study period are listed by system organ class in Table 4.
Table 4. Adverse Reactions Reported in at Least 2% of Paget’s Patients Receiving Zoledronic Acid (Single 5 mg Intravenous Infusion) or Risedronate (Oral 30 mg Daily for 2 Months) Over a 6-Month Follow-up Period System Organ Class
5 mg IV
Zoledronic Acid
%
(N = 177)
30 mg/day x 2 Months risedronate
%
(N = 172)
Infections and Infestations
Influenza
7
5
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders
Hypocalcemia
3
1
Anorexia
2
2
Nervous System Disorders
Headache
11
10
Dizziness
9
4
Lethargy
5
1
Paresthesia
2
0
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders
Dyspnea
5
1
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Nausea
9
6
Diarrhea
6
6
Constipation
6
5
Dyspepsia
5
4
Abdominal Distension
2
1
Abdominal Pain
2
2
Vomiting
2
2
Abdominal Pain Upper
1
2
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Rash
3
2
Musculoskeletal, Connective Tissue and Bone Disorders
Arthralgia
9
11
Bone Pain
9
5
Myalgia
7
4
Back Pain
4
7
Musculoskeletal Stiffness
2
1
General Disorders and Administrative Site Conditions
Influenza-like Illness
11
6
Pyrexia
9
2
Fatigue
8
4
Rigors
8
1
Pain
5
4
Peripheral Edema
3
1
Asthenia
2
1
Laboratory Findings
In the Paget’s disease trials, early, transient decreases in serum calcium and phosphate levels were observed. Approximately 21% of patients had serum calcium levels less than 8.4 mg/dL 9 to 11 days following zoledronic acid administration.
Renal Impairment
In clinical trials in Paget’s disease there were no cases of renal deterioration following a single 5 mg 15-minute infusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Acute Phase Reaction
The signs and symptoms of acute phase reaction (influenza-like illness, pyrexia, myalgia, arthralgia, and bone pain) were reported in 25% of patients in the zoledronic acid-treated group compared to 8% in the risedronate-treated group. Symptoms usually occur within the first 3 days following zoledronic acid administration. The majority of these symptoms resolved within
4 days of onset.
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
Osteonecrosis of the jaw has been reported with zoledronic acid [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of zoledronic acid:
Acute Phase Reactions
Fever, headache, flu-like symptoms, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, arthralgia, and myalgia. Symptoms may be significant and lead to dehydration.
Acute Renal Failure
Acute renal failure requiring hospitalization and/or dialysis or with a fatal outcome have been rarely reported. Increased serum creatinine was reported in patients with 1) underlying renal disease, 2) dehydration secondary to fever, sepsis, gastrointestinal losses, or diuretic therapy, or 3) other risk factors such as advanced age, or concomitant nephrotoxic drugs in the post-infusion period. Transient rise in serum creatinine can be correctable with intravenous fluids.
Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions with intravenous zoledronic acid including anaphylactic reaction/shock, urticaria, angioedema, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and bronchoconstriction have been reported.
Asthma Exacerbations
Asthma exacerbations have been reported.
Hypocalcemia
Hypocalcemia has been reported.
Hypophosphatemia
Hypophosphatemia has been reported.
Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
Osteonecrosis of the jaw has been reported.
Osteonecrosis of other bones
Cases of osteonecrosis of other bones (including femur, hip, knee, ankle, wrist and humerus) have been reported; causality has not been determined in the population treated with zoledronic acid.
Ocular Adverse Events
Cases of the following events have been reported: conjunctivitis, iritis, iridocyclitis, uveitis, episcleritis, scleritis and orbital inflammation/edema.
Other
Hypotension in patients with underlying risk factors has been reported. -
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
No in vivo drug interaction studies have been performed for zoledronic acid. In vitro and ex vivo studies showed low affinity of zoledronic acid for the cellular components of human blood. In vitro mean zoledronic acid protein binding in human plasma ranged from 28% at 200 ng/mL to 53% at 50 ng/mL. In vivo studies showed that zoledronic acid is not metabolized, and is excreted into the urine as the intact drug.
7.1 Aminoglycosides
Caution is advised when bisphosphonates, including zoledronic acid, are administered with aminoglycosides, since these agents may have an additive effect to lower serum calcium level for prolonged periods. This effect has not been reported in zoledronic acid clinical trials.
7.2 Loop Diuretics
Caution should also be exercised when zoledronic acid is used in combination with loop diuretics due to an increased risk of hypocalcemia.
7.3 Nephrotoxic Drugs
Caution is indicated when zoledronic acid is used with other potentially nephrotoxic drugs such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
7.4 Drugs Primarily Excreted by the Kidney
Renal impairment has been observed following the administration of zoledronic acid in patients with pre-existing renal compromise or other risk factors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. In patients with renal impairment, the exposure to concomitant medications that are primarily renally excreted (e.g., digoxin) may increase. Consider monitoring serum creatinine in patients at risk for renal impairment who are taking concomitant medications that are primarily excreted by the kidney.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data on the use of zoledronic acid in pregnant women are insufficient to inform a drug-associated risk of adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Discontinue zoledronic acid when pregnancy is recognized.
In animal reproduction studies, daily subcutaneous administration of zoledronic acid to pregnant rats during organogenesis resulted in increases in fetal skeletal, visceral, and external malformations, decreases in postimplantation survival, and decreases in viable fetuses and fetal weight starting at doses equivalent to 2 times the recommended human 5 mg intravenous dose (based on AUC). Subcutaneous administration of zoledronic acid to rabbits during organogenesis did not cause adverse fetal effects at up to 0.4 times the human 5 mg intravenous dose (based on body surface area, mg/m2), but resulted in maternal mortality and abortion associated with hypocalcemia starting at doses equivalent to 0.04 times the human 5 mg intravenous dose. Subcutaneous dosing of female rats from before mating through gestation and lactation and allowed to deliver caused maternal dystocia and periparturient mortality, increases in stillbirths and neonatal deaths, and reduced pup body weight starting at doses equivalent to 0.1 times the human 5 mg intravenous dose (based on AUC). (see Data).
Bisphosphonates are incorporated into the bone matrix, from which they are gradually released over a period of years. The amount of bisphosphonate incorporated into adult bone, and available for release into the systemic circulation is directly related to the dose and duration of bisphosphonate use. Consequently, based on the mechanism of action of bisphosphonates, there is a potential risk of fetal harm, predominantly skeletal, if a woman becomes pregnant after completing a course of bisphosphonate therapy. The impact of variables such as time between cessation of bisphosphonate therapy to conception, the particular bisphosphonate used, and the route of administration (intravenous versus oral) on the risk has not been studied.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defects, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risks of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In pregnant rats given daily subcutaneous doses of zoledronic acid of 0.1, 0.2, or 0.4 mg/kg during organogenesis, fetal skeletal, visceral, and external malformations, increases in pre-and post-implantation loss, and decreases in viable fetuses and fetal weight were observed at 0.2 and 0.4 mg/kg/day (equivalent to 2 and 4 times the human 5 mg intravenous dose, based on AUC). Adverse fetal skeletal effects at 0.4 mg/kg/day (4 times the human 5 mg dose) included unossified or incompletely ossified bones, thickened, curved or shortened bones, wavy ribs, and shortened jaw. Other adverse fetal effects at this dose included reduced lens, rudimentary cerebellum, reduction or absence of liver lobes, reduction of lung lobes, vessel dilation, cleft palate, and edema. Skeletal variations were observed in all groups starting at 0.1 mg/kg/day (1.2 times the human 5 mg dose). Signs of maternal toxicity including reduced body weight and food consumption were observed at 0.4 mg/kg/day (4 times the human 5 mg dose).
In pregnant rabbits given daily subcutaneous doses of zoledronic acid of 0.01, 0.03, or 0.1 mg/kg during gestation no adverse fetal effects were observed up to 0.1 mg/kg/day (0.4 times the human 5 mg intravenous dose, based on body surface area, mg/m2). Maternal mortality and abortion were observed in all dose groups (starting at 0.04 times the human 5 mg dose). Adverse maternal effects were associated with drug-induced hypocalcemia.
In female rats given daily subcutaneous doses of 0.01, 0.03, or 0.1 mg/kg, beginning 15 days before mating and continuing through gestation, parturition and lactation, dystocia and periparturient mortality were observed in pregnant rats allowed to deliver starting at 0.01 mg/kg/day (0.1 times the human 5 mg intravenous dose, based on AUC). Also, there was an increase in stillbirths and a decrease in neonate survival starting at 0.03 mg/kg/day (0.3 times the human 5 mg dose), while the number of viable newborns and pup body weight on postnatal Day 7 were decreased at 0.1 mg/kg/day (equivalent to the human 5 mg dose). Maternal and neonatal deaths were considered related to drug-induced periparturient hypocalcemia.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of zoledronic acid in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breast-feeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for zoledronic acid and any potential adverse effects on the breast-fed child from zoledronic acid or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
There are no data available in humans. Female fertility may be impaired based on animal studies demonstrating adverse effects of zoledronic acid on fertility parameters [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
Zoledronic acid is not indicated for use in children.
The safety and effectiveness of zoledronic acid was studied in a one-year active controlled trial of 152 pediatric subjects (74 receiving zoledronic acid). The enrolled population was subjects with severe osteogenesis imperfecta, aged 1 to 17 years, 55% male, 84% Caucasian, with a mean lumbar spine BMD of 0.431 gm/cm2, which is 2.7 standard deviations below the mean for age-matched controls (BMD Z-score of -2.7). At one year, increases in BMD were observed in the zoledronic acid treatment group. However, changes in BMD in individual patients with severe osteogenesis imperfecta did not necessarily correlate with the risk for fracture or the incidence or severity of chronic bone pain. The adverse events observed with zoledronic acid use in children did not raise any new safety findings beyond those previously seen in adults treated for Paget’s disease of bone and treatment of osteoporosis including osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) and renal impairment. However, adverse reactions seen more commonly in pediatric patients included pyrexia (61%), arthralgia (26%), hypocalcemia (22%) and headache (22%). These reactions, excluding arthralgia, occurred most frequently within three days after the first infusion and became less common with repeat dosing. No cases of ONJ or renal impairment were observed in this study. Because of long-term retention in bone, zoledronic acid should only be used in children if the potential benefit outweighs the potential risk.
Plasma zoledronic acid concentration data was obtained from 10 patients with severe osteogenesis imperfecta (4 in the age group of 3 to 8 years and 6 in the age group of 9 to 17 years) infused with 0.05 mg/kg dose over 30 minutes. Mean Cmax and AUC(0-last) was 167 ng/mL and 220 ng.h/mL respectively. The plasma concentration time profile of zoledronic acid in pediatric patients represent a multi-exponential decline, as observed in adult cancer patients at an approximately equivalent mg/kg dose.8.5 Geriatric Use
The combined osteoporosis trials included 4863 R zoledronic acid-treated patients who were at least 65 years of age, while 2101 patients were at least 75 years old. No overall differences in efficacy or safety were observed between patients under 75 years of age with those at least 75 years of age, except that the acute phase reactions occurred less frequently in the older patients.
Of the patients receiving zoledronic acid in the osteoporosis study in men, glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis, and Paget’s disease studies, 83, 116, and 132 patients, respectively were 65 years of age or over, while 24, 29, and 68 patients, respectively were at least 75 years of age.
Because decreased renal function occurs more commonly in the elderly, special care should be taken to monitor renal function.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Zoledronic acid is contraindicated in patients with creatinine clearance less than 35 mL/min and in those with evidence of acute renal impairment. There are no safety or efficacy data to support the adjustment of the zoledronic acid dose based on baseline renal function. Therefore, no dosage adjustment is required in patients with a creatinine clearance of greater than or equal to 35 mL/min [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Risk of acute renal failure may increase with underlying renal disease and dehydration secondary to fever, sepsis, gastrointestinal losses, diuretic therapy, advanced age, etc. [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Clinical experience with acute overdosage of zoledronic acid solution for intravenous infusion is limited. Patients who have received doses higher than those recommended should be carefully monitored. Overdosage may cause clinically significant renal impairment, hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, and hypomagnesemia. Clinically relevant reductions in serum levels of calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium should be corrected by intravenous administration of calcium gluconate, potassium or sodium phosphate, and magnesium sulfate, respectively.
Single doses of zoledronic acid should not exceed 5 mg and the duration of the intravenous infusion should be no less than 15 minutes [see Dosage and Administration (2)]. -
11 DESCRIPTION
Zoledronic acid injection contains zoledronic acid, a bisphosphonic acid which is an inhibitor of osteoclastic bone resorption. Zoledronic acid is designated chemically as (1-Hydroxy-2-imidazol-1-yl-phosphonoethyl) phosphonic acid monohydrate and its structural formula is:
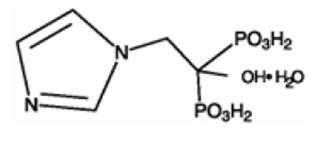
Zoledronic acid monohydrate is a white to off white crystalline powder. Its molecular formula is C5H10N2O7P2 • H2O and a molar mass of 290.1 g/Mol. Zoledronic acid monohydrate is highly soluble in 0.1N sodium hydroxide solution, sparingly soluble in water and 0.1N hydrochloric acid, and practically insoluble in organic solvents. The pH of the zoledronic acid injection solution for infusion is approximately 6.0 to 7.0.
Zoledronic acid injection is available as a sterile, clear, colorless solution in bottles for intravenous infusion. One bottle with 100 mL solution contains 5.33 mg zoledronic acid monohydrate, equivalent to 5 mg zoledronic acid on an anhydrous basis.
Inactive Ingredients: 4,950 mg of mannitol, USP; 30 mg of sodium citrate; and water for injection q.s. to 100 mL. -
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Zoledronic acid is a bisphosphonate and acts primarily on bone. It is an inhibitor of osteoclast-mediated bone resorption.
The selective action of bisphosphonates on bone is based on their high affinity for mineralized bone. Intravenously administered zoledronic acid rapidly partitions to bone and localizes preferentially at sites of high bone turnover. The main molecular target of zoledronic acid in the osteoclast is the enzyme farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase. The relatively long duration of action of zoledronic acid is attributable to its high binding affinity to bone mineral.12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In the osteoporosis treatment trial, the effect of zoledronic acid treatment on markers of bone resorption (serum beta-C-telopeptides [b-CTx]) and bone formation (bone specific alkaline phosphatase [BSAP], serum N-terminal propeptide of type I collagen [P1NP]) was evaluated in patients (subsets ranging from 517 to 1246 patients) at periodic intervals. Treatment with a 5 mg annual dose of zoledronic acid reduces bone turnover markers to the pre-menopausal range with an approximate 55% reduction in b-CTx, a 29% reduction in BSAP and a 52% reduction in P1NP over 36 months. There was no progressive reduction of bone turnover markers with repeated annual dosing.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetic data in patients with osteoporosis and Paget’s disease of bone are not available.
Distribution: Single or multiple (every 28 days) 5-minute or 15-minute infusions of 2, 4, 8 or 16 mg zoledronic acid were given to 64 patients with cancer and bone metastases. The post-infusion decline of zoledronic acid concentrations in plasma was consistent with a triphasic process showing a rapid decrease from peak concentrations at end-of-infusion to less than 1% of Cmax 24 hours post infusion with population half-lives of t1/2α 0.24 hour and t1/2β 1.87 hours for the early disposition phases of the drug. The terminal elimination phase of zoledronic acid was prolonged, with very low concentrations in plasma between Days 2 and 28 post infusion, and a terminal elimination half-life t1/2γ of 146 hours. The area under the plasma concentration versus time curve (AUC0-24h) of zoledronic acid was dose proportional from 2 to 16 mg. The accumulation of zoledronic acid measured over three cycles was low, with mean AUC0-24h ratios for cycles 2 and 3 versus 1 of 1.13 ± 0.30 and 1.16 ± 0.36, respectively.
In vitro and ex vivo studies showed low affinity of zoledronic acid for the cellular components of human blood. In vitro mean zoledronic acid protein binding in human plasma ranged from 28% at 200 ng/mL to 53% at 50 ng/mL.
Metabolism: Zoledronic acid does not inhibit human P450 enzymes in vitro. Zoledronic acid does not undergo biotransformation in vivo. In animal studies, less than 3% of the administered intravenous dose was found in the feces, with the balance either recovered in the urine or taken up by bone, indicating that the drug is eliminated intact via the kidney. Following an intravenous dose of 20 nCi 14C-zoledronic acid in a patient with cancer and bone metastases, only a single radioactive species with chromatographic properties identical to those of parent drug was recovered in urine, which suggests that zoledronic acid is not metabolized.
Excretion: In 64 patients with cancer and bone metastases on average (± SD) 39 ± 16% of the administered zoledronic acid dose was recovered in the urine within 24 hours, with only trace amounts of drug found in urine post Day 2. The cumulative percent of drug excreted in the urine over 0 to 24 hours was independent of dose. The balance of drug not recovered in urine over 0 to 24 hours, representing drug presumably bound to bone, is slowly released back into the systemic circulation, giving rise to the observed prolonged low plasma concentrations. The 0 to 24 hour renal clearance of zoledronic acid was 3.7 ± 2.0 L/h.
Zoledronic acid clearance was independent of dose but dependent upon the patient’s creatinine clearance. In a study in patients with cancer and bone metastases, increasing the infusion time of a 4 mg dose of zoledronic acid from 5 minutes (n = 5) to 15 minutes (n = 7) resulted in a 34% decrease in the zoledronic acid concentration at the end of the infusion ([mean ± SD] 403 ± 118 ng/mL vs. 264 ± 86 ng/mL) and a 10% increase in the total AUC (378 ± 116 ng x h/mL vs. 420 ± 218 ng x h/mL). The difference between the AUC means was not statistically significant.
Specific Populations
Pediatrics: Zoledronic acid is not indicated for use in children [see Pediatric Use (8.4)].
Geriatrics: The pharmacokinetics of zoledronic acid was not affected by age in patients with cancer and bone metastases whose age ranged from 38 years to 84 years.
Race: The pharmacokinetics of zoledronic acid was not affected by race in patients with cancer and bone metastases.
Hepatic Impairment: No clinical studies were conducted to evaluate the effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of zoledronic acid.
Renal Impairment: The pharmacokinetic studies conducted in 64 cancer patients represented typical clinical populations with normal to moderately-impaired renal function. Compared to patients with creatinine clearance greater than 80 mL/min (N = 37), patients with creatinine clearance = 50 to 80 mL/min (N = 15) showed an average increase in plasma AUC of 15%, whereas patients with creatinine clearance = 30 to 50 mL/min (N = 11) showed an average increase in plasma AUC of 43%. No dosage adjustment is required in patients with a creatinine clearance of greater than or equal to 35 mL/min. Zoledronic acid is contraindicated in patients with creatinine clearance less than 35 mL/min and in those with evidence of acute renal impairment due to an increased risk of renal failure [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)]. -
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis: Lifetime carcinogenicity bioassays were conducted in mice and rats. Mice were given daily oral doses of zoledronic acid of 0.1, 0.5, or 2.0 mg/kg/day for 2 years. There was an increased incidence of Harderian gland adenomas in males and females in all treatment groups (starting at doses equivalent to 0.002 times the human 5 mg intravenous dose, based on body surface area, mg/m2). Rats were given daily oral doses of zoledronic acid of 0.1, 0.5, or 2.0 mg/kg/day for 2 years. No increased incidence of tumors was observed at any dose (up to 0.1 times the human intravenous dose of 5 mg, based on body surface area, mg/m2).
Mutagenesis: Zoledronic acid was not genotoxic in the Ames bacterial mutagenicity assay, in the Chinese hamster ovary cell assay, or in the Chinese hamster gene mutation assay, with or without metabolic activation. Zoledronic acid was not genotoxic in the in vivo rat micronucleus assay.
Impairment of Fertility: Female rats were given daily subcutaneous doses of zoledronic acid of 0.01, 0.03, or 0.1 mg/kg beginning 15 days before mating and continuing through gestation. Inhibition of ovulation and a decrease in the number of pregnant rats were observed at 0.1 mg/kg/day (equivalent to the human 5 mg intravenous dose, based on AUC). An increase in preimplantation loss and a decrease in the number of implantations and live fetuses were observed at 0.03 and 1 mg/kg/day (0.3 to 1 times the human 5 mg human intravenous dose).
13.2 Animal Pharmacology
Bone Safety Studies: Zoledronic acid is a potent inhibitor of osteoclastic bone resorption. In the ovariectomized rat, single IV doses of zoledronic acid of 4 to 500 mcg/kg (0.1 to
3.5 times the human 5 mg intravenous dose, based on body surface area, mg/m2) suppressed bone turnover and protected against trabecular bone loss, cortical thinning and the reduction in vertebral and femoral bone strength in a dose-dependent manner. At a dose equivalent to human exposure at the 5 mg intravenous dose, the effect persisted for 8 months, which corresponds to approximately 8 remodeling cycles or 3 years in humans.
In ovariectomized rats and monkeys, weekly treatment with zoledronic acid dose-dependently suppressed bone turnover and prevented the decrease in cancellous and cortical BMD and bone strength, at yearly cumulative doses up to 3.5 times the human 5 mg intravenous dose, based on body surface area, mg/m2. Bone tissue was normal and there was no evidence of a mineralization defect, no accumulation of osteoid, and no woven bone.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Treatment of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
Study 1: The efficacy and safety of zoledronic acid in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis was demonstrated in Study 1, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multinational study of 7736 women aged 65 to 89 years (mean age of 73) with either: a femoral neck BMD T-score less than or equal to -1.5 and at least two mild or one moderate existing vertebral fracture(s); or a femoral neck BMD T-score less than or equal to -2.5 with or without evidence of an existing vertebral fracture(s). Women were stratified into two groups: Stratum I: no concomitant use of osteoporosis therapy or Stratum II: baseline concomitant use of osteoporosis therapies which included calcitonin, raloxifene, tamoxifen, and hormone replacement therapy, but excluded other bisphosphonates.
Women enrolled in Stratum I (n = 5661) were evaluated annually for incidence of vertebral fractures. All women (Strata I and II) were evaluated for the incidence of hip and other clinical fractures. Zoledronic acid was administered once a year for three consecutive years, as a single 5 mg dose in 100 mL solution infused over at least 15 minutes, for a total of three doses. All women received 1,000 to 1,500 mg of elemental calcium plus 400 to 1,200 international units of vitamin D supplementation per day.
The two primary efficacy variables were the incidence of morphometric vertebral fractures at 3 years and the incidence of hip fractures over a median duration of 3 years. The diagnosis of an incident vertebral fracture was based on both qualitative diagnosis by the radiologist and quantitative morphometric criterion. The morphometric criterion required the dual occurrence of 2 events: a relative height ratio or relative height reduction in a vertebral body of at least 20%, together with at least a 4 mm absolute decrease in height.
Effect on Vertebral Fractures
Zoledronic acid significantly decreased the incidence of new vertebral fractures at one, two, and three years as shown in Table 5.
Table 5. Proportion of Patients with New Morphometric Vertebral Fractures Outcome
Zoledronic acid
(%)
Placebo
(%)
Absolute Reduction
in Fracture Incidence
Relative Reduction in
Fracture Incidence
%
(95% CI)
%
(95% CI)
At least one new vertebral fracture
(0 to 1 year)
1.5
3.7
2.2
(1.4, 3.1)
60
(43, 72)*
At least one new vertebral fracture
(0 to 2 years)
2.2
7.7
5.5
(4.4, 6.6)
71
(62, 78)*
At least one new vertebral fracture
(0 to 3 years)
3.3
10.9
7.6
(6.3, 9.0)
70
(62, 76)*
* p <0.0001
The reductions in vertebral fractures over three years were consistent (including new/worsening and multiple vertebral fractures) and significantly greater than placebo regardless of age, geographical region, baseline body mass index, number of baseline vertebral fractures, femoral neck BMD T-score, or prior bisphosphonate usage.
Effect on Hip Fracture over 3 years
Zoledronic acid demonstrated a 1.1% absolute reduction and 41% relative reduction in the risk of hip fractures over a median duration of follow-up of 3 years. The hip fracture event rate was 1.4% for zoledronic acid -treated patients compared to 2.5% for placebo-treated patients.
Figure 1. Cumulative Incidence of Hip Fracture Over 3 Years
The reductions in hip fractures over three years were greater for zoledronic acid than placebo regardless of femoral neck BMD T- score.
Effect on All Clinical Fractures
Zoledronic acid demonstrated superiority to placebo in reducing the incidence of all clinical fractures, clinical (symptomatic) vertebral and non-vertebral fractures (excluding finger, toe, facial, and clinical thoracic and lumbar vertebral fractures). All clinical fractures were verified based on the radiographic and/or clinical evidence. A summary of results is presented in Table 6.
Table 6. Between–Treatment Comparisons of the Incidence of Clinical Fracture Variables Over 3 Years
Zoledronic acid
Placebo
Relative Risk
Outcome
(N= 3875)
Event Rate
n (%)+
(N= 3861)
Event Rate
n (%)+
Absolute Reduction in Fracture Incidence
%
(95% CI)+
Reduction in Fracture Incidence
%
(95% CI)
Any clinical fracture (1)
308 (8.4)
456 (12.8)
4.4
(3.0, 5.8)
33
(23, 42)**
Clinical vertebral fracture (2)
19 (0.5)
84 (2.6)
2.1
(1.5, 2.7)
77
(63, 86)**
Non-vertebral fracture (3)
292 (8.0)
388 (10.7)
2.7
(1.4, 4.0)
25
(13, 36)*
*p-value < 0.001, **p-value <0.0001
+ Event rates based on Kaplan-Meier estimates at 36 months
(1) Excluding finger, toe, and facial fractures
(2) Includes clinical thoracic and clinical lumbar vertebral fractures
(3) Excluding finger, toe, facial, and clinical thoracic and lumbar vertebral fractures
Effect on Bone Mineral Density (BMD)
Zoledronic acid significantly increased BMD at the lumbar spine, total hip and femoral neck, relative to treatment with placebo at time points 12, 24, and 36 months. Treatment with zoledronic acid resulted in a 6.7% increase in BMD at the lumbar spine, 6.0% at the total hip, and 5.1% at the femoral neck, over 3 years as compared to placebo.
Bone Histology
Bone biopsy specimens were obtained between Months 33 and 36 from 82 postmenopausal patients with osteoporosis treated with 3 annual doses of zoledronic acid. Of the biopsies obtained, 81 were adequate for qualitative histomorphometry assessment, 59 were adequate for partial quantitative histomorphometry assessment, and 38 were adequate for full quantitative histomorphometry assessment. Micro CT analysis was performed on 76 specimens. Qualitative, quantitative and micro CT assessments showed bone of normal architecture and quality without mineralization defects.
Effect on Height
In the 3-year osteoporosis study, standing height was measured annually using a stadiometer. The zoledronic acid group revealed less height loss compared to placebo (4.2 mm vs. 7.0 mm, respectively [p<0.001]).
Study 2: The efficacy and safety of zoledronic acid in the treatment of patients with osteoporosis who suffered a recent low-trauma hip fracture was demonstrated in Study 2, a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multinational endpoint study of 2127 men and women aged 50 to 95 years (mean age of 74.5). Concomitant osteoporosis therapies excluding other bisphosphonates and parathyroid hormone were allowed. Zoledronic acid was administered once a year as a single 5 mg dose in 100 mL solution, infused over at least 15 minutes. The study continued until at least 211 patients had confirmed clinical fractures in the study population. Vitamin D levels were not routinely measured but a loading dose of vitamin D (50,000 to 125,000 international units orally or IM) was given to patients and they were started on 1,000 to 1,500 mg of elemental calcium plus 800 to 1,200 international units of vitamin D supplementation per day for at least 14 days prior to the study drug infusions. The primary efficacy variable was the incidence of clinical fractures over the duration of the study.
Zoledronic acid significantly reduced the incidence of any clinical fracture by 35%. There was also a 46% reduction in the risk of a clinical vertebral fracture (Table 7).
Table 7. Between-Treatment Comparisons of the Incidence of Key Clinical Fracture Variables Outcome
Zoledronic acid
(N = 1065)
Event Rate
n (%)+
Placebo
(N = 1062)
Event Rate
n (%)+
Absolute Reduction
in
Fracture Incidence
%
(95% CI)+
Relative Risk Reduction
in
Fracture Incidence
%
(95%CI)
Any clinical fracture (1)
92 (8.6)
139 (13.9)
5.3
(2.3, 8.3)
35
(16, 50)**
Clinical vertebral fracture (2)
21 (1.7)
39 (3.8)
2.1
(0.5, 3.7)
46
(8, 68)*
*p-value <0.05, **p-value <0.005
+Event rates based on Kaplan-Meier estimates at 24 months
(1) Excluding finger, toe and facial fractures
(2) Including clinical thoracic and clinical lumbar vertebral fractures
Effect on Bone Mineral Density (BMD)
Zoledronic acid significantly increased BMD relative to placebo at the hip and femoral neck at all timepoints (12, 24, and 36 months). Treatment with zoledronic acid resulted in a 6.4% increase in BMD at the total hip and a 4.3% increase at the femoral neck over 36 months as compared to placebo.
14.2 Prevention of Postmenopausal Osteoporosis
The efficacy and safety of zoledronic acid in postmenopausal women with osteopenia (low bone mass) was assessed in a 2-year randomized, multi-center, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 581 postmenopausal women aged greater than or equal to 45 years, who were stratified by years since menopause: Stratum I women less than 5 years from menopause (n = 224); Stratum II women greater than or equal to 5 years from menopause (n = 357). Patients within Stratum I and II were randomized to one of three treatment groups: (1) zoledronic acid given at randomization and at Month 12 (n = 77) in Stratum I and (n = 121) in Stratum II; (2) zoledronic acid given at randomization and placebo at Month 12 (n = 70) in Stratum I and (n = 111) in Stratum II; and (3) Placebo given at randomization and Month 12 (n = 202). Zoledronic acid was administered as a single 5 mg dose in 100 mL solution infused over at least 15 minutes. All women received 500 to 1,200 mg elemental calcium plus 400 to 800 international units vitamin D supplementation per day. The primary efficacy variable was the percent change of BMD at 24 Months relative to baseline.
Effect on Bone Mineral Density (BMD)
Zoledronic acid significantly increased lumbar spine BMD relative to placebo at Month 24 across both strata. Zoledronic acid given once at randomization (and placebo given at Month 12) resulted in 4.0% increase in BMD in Stratum I patients and 4.8% increase in Stratum II patients over 24 months. Placebo given at randomization and at Month 12 resulted in 2.2% decrease in BMD in Stratum I patients and 0.7% decrease in BMD in Stratum II patients over 24 months. Therefore, zoledronic acid given once at randomization (and placebo given at Month 12) resulted in a 6.3% increase in BMD in Stratum I patients and 5.4% increase in Stratum II patients over 24 months as compared to placebo (both p<0.0001).
Zoledronic acid also significantly increased total hip BMD relative to placebo at Month 24 across both strata. zoledronic acid given once at randomization (and placebo given at Month 12) resulted in 2.6% increase in BMD in Stratum I patients and 2.1% in Stratum II patients over 24 months. Placebo given at randomization and at Month 12 resulted in 2.1% decrease in BMD in Stratum I patients and 1.0% decrease in BMD in Stratum II patients over 24 months. Therefore, zoledronic acid given once at randomization (and placebo given at Month 12) resulted in a 4.7% increase in BMD in Stratum I patients and 3.2% increase in Stratum II patients over 24 months as compared to placebo (both p<0.0001).
14.3 Osteoporosis in Men
The efficacy and safety of zoledronic acid in men with osteoporosis or significant osteoporosis secondary to hypogonadism, was assessed in a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, active controlled, study of 302 men aged 25 to 86 years (mean age of 64). The duration of the trial was two years. Patients were randomized to either zoledronic acid which was administered once annually as a 5 mg dose in 100 mL infused over 15 minutes for a total of up to two doses, or to an oral weekly bisphosphonate (active control) for up to two years. All participants received 1,000 mg of elemental calcium plus 800 to 1,000 international units of vitamin D supplementation per day.
Effect on Bone Mineral Density (BMD)
An annual infusion of zoledronic acid was non-inferior to the oral weekly bisphosphonate active control based on the percentage change in lumbar spine BMD at Month 24 relative to baseline (zoledronic acid: 6.1% increase; active control: 6.2% increase).
14.4 Treatment and Prevention of Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
The efficacy and safety of zoledronic acid to prevent and treat glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis (GIO) was assessed in a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, stratified, active controlled study of 833 men and women aged 18 to 85 years (mean age of 54.4 years) treated with greater than or equal to 7.5 mg/day oral prednisone (or equivalent). Patients were stratified according to the duration of their pre-study corticosteroid therapy: less than or equal to 3 months prior to randomization (prevention subpopulation), and greater than 3 months prior to randomization (treatment subpopulation). The duration of the trial was one year. Patients were randomized to either zoledronic acid which was administered once as a 5 mg dose in 100 mL infused over 15 minutes, or to an oral daily bisphosphonate (active control) for one year. All participants received 1,000 mg of elemental calcium plus 400 to 1,000 international units of vitamin D supplementation per day.
Effect on Bone Mineral Density (BMD)
In the GIO treatment subpopulation, zoledronic acid demonstrated a significant mean increase in lumbar spine BMD compared to the active control at one year (zoledronic acid 4.1%, active control 2.7%) with a treatment difference of 1.4% (p<0.001). In the GIO prevention subpopulation, zoledronic acid demonstrated a significant mean increase in lumbar spine BMD compared to active control at one year (Zoledronic acid 2.6%, active control 0.6%) with a treatment difference of 2.0% (p<0.001).
Bone Histology
Bone biopsy specimens were obtained from 23 patients (12 in the zoledronic acid treatment group and 11 in the active control treatment group) at Month 12 treated with an annual dose of zoledronic acid or daily oral active control. Qualitative assessments showed bone of normal architecture and quality without mineralization defects. Apparent reductions in activation frequency and remodeling rates were seen when compared with the histomorphometry results seen with zoledronic acid in the postmenopausal osteoporosis population. The long-term consequences of this degree of suppression of bone remodeling in glucocorticoid-treated patients is unknown.
14.5 Treatment of Paget’s Disease of Bone
Zoledronic acid was studied in male and female patients with moderate to severe Paget’s disease of bone, defined as serum alkaline phosphatase level at least twice the upper limit of the age-specific normal reference range at the time of study entry. Diagnosis was confirmed by radiographic evidence.
The efficacy of one infusion of 5 mg zoledronic acid vs. oral daily doses of 30 mg risedronate for 2 months was demonstrated in two identically designed 6-month randomized, double-blind trials. The mean age of patients in the two trials was 70. Ninety-three percent (93%) of patients were Caucasian. Therapeutic response was defined as either normalization of serum alkaline phosphatase (SAP) or a reduction of at least 75% from baseline in total SAP excess at the end of 6 months. SAP excess was defined as the difference between the measured level and midpoint of normal range.
In both trials zoledronic acid demonstrated a superior and more rapid therapeutic response compared with risedronate and returned more patients to normal levels of bone turnover, as evidenced by biochemical markers of formation (SAP, serum N-terminal propeptide of type I collagen [P1NP]) and resorption (serum CTx 1 [cross-linked C-telopeptides of type I collagen] and urine α-CTx).
The 6-month combined data from both trials showed that 96% (169/176) of zoledronic acid-treated patients achieved a therapeutic response as compared with 74% (127/171) of patients treated with risedronate. Most zoledronic acid patients achieved a therapeutic response by the Day 63 visit. In addition, at 6 months, 89% (156/176) of zoledronic acid-treated patients achieved normalization of SAP levels, compared to 58% (99/171) of patients treated with risedronate (p<0.0001) (see Figure 2).

The therapeutic response to zoledronic acid was similar across demographic and disease-severity groups defined by gender, age, previous bisphosphonate use, and disease severity. At 6 months, the percentage of zoledronic acid-treated patients who achieved therapeutic response was 97% and 95%, respectively, in each of the baseline disease severity subgroups (baseline SAP less than 3xULN, greater than or equal to 3xULN) compared to 75% and 74%, respectively, for the same disease severity subgroups of risedronate-treated patients.
In patients who had previously received treatment with oral bisphosphonates, therapeutic response rates were 96% and 55% for zoledronic acid and risedronate, respectively. The comparatively low risedronate response was due to the low response rate (7/23, 30%) in patients previously treated with risedronate. In patients naïve to previous treatment, a greater therapeutic response was also observed with zoledronic acid (98%) relative to risedronate (86%). In patients with symptomatic pain at screening, therapeutic response rates were 94% and 70% for zoledronic acid and risedronate respectively. For patients without pain at screening, therapeutic response rates were 100% and 82% for zoledronic acid and risedronate respectively.
Bone histology was evaluated in 7 patients with Paget’s disease 6 months after being treated with zoledronic acid 5 mg. Bone biopsy results showed bone of normal quality with no evidence of impaired bone remodeling and no evidence of mineralization defect. -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Zoledronic acid injection is a sterile, clear, colorless solution and is supplied as follows:
5 mg per 100 mL (0.05 mg/mL)
100 mL Bottles
packaged individually NDC 55150-283-99
Handling
After opening the solution, it is stable for 24 hours at 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F).
If refrigerated, allow the refrigerated solution to reach room temperature before administration.
Storage
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
This container closure is not made with natural rubber latex. -
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Information for Patients
Patients should be made aware that zoledronic acid injection contains the same active ingredient (zoledronic acid) found in Zometa®, and that patients being treated with Zometa should not be treated with zoledronic acid injection.
Zoledronic acid is contraindicated in patients with creatinine clearance less than 35 mL/min [see Contraindications (4)].
Before being given zoledronic acid, patients should tell their doctor if they have kidney problems and what medications they are taking.
Zoledronic acid should not be given if the patient is pregnant or plans to become pregnant, or if she is breast-feeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
There have been reports of bronchoconstriction in aspirin-sensitive patients receiving bisphosphonates, including zoledronic acid. Before being given zoledronic acid, patients should tell their doctor if they are aspirin-sensitive.
If the patient had surgery to remove some or all of the parathyroid glands in their neck, or had sections of their intestine removed, or are unable to take calcium supplements they should tell their doctor.
Zoledronic acid is given as an infusion into a vein by a nurse or a doctor, and the infusion time must not be less than 15 minutes.
On the day of treatment the patient should eat and drink normally, which includes drinking at least 2 glasses of fluid such as water within a few hours prior to the infusion, as directed by their doctor, before receiving zoledronic acid.
After getting zoledronic acid it is strongly recommended patients with Paget’s disease take calcium in divided doses (for example, 2 to 4 times a day) for a total of 1,500 mg calcium a day to prevent low blood calcium levels. This is especially important for the two weeks after getting zoledronic acid [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Adequate calcium and vitamin D intake is important in patients with osteoporosis and the current recommended daily intake of calcium is 1,200 mg and vitamin D is 800 international units – 1,000 international units daily. All patients should be instructed on the importance of calcium and vitamin D supplementation in maintaining serum calcium levels.
Patients should be aware of the most commonly associated side effects of therapy. Patients may experience one or more side effects that could include: fever, flu-like symptoms, myalgia, arthralgia, and headache. Most of these side effects occur within the first 3 days following the dose of zoledronic acid. They usually resolve within 3 days of onset but may last for up to 7 to 14 days. Patients should consult their physician if they have questions or if these symptoms persist. The incidence of these symptoms decreased markedly with subsequent doses of zoledronic acid.
Administration of acetaminophen following zoledronic acid administration may reduce the incidence of these symptoms.
Physicians should inform their patients that there have been reports of persistent pain and/or a non-healing sore of the mouth or jaw, primarily in patients treated with bisphosphonates for other illnesses. During treatment with zoledronic acid, patients should be instructed to maintain good oral hygiene and undergo routine dental check-ups. If they experience any oral symptoms, they should immediately report them to their physician or dentist.
Severe and occasionally incapacitating bone, joint, and/or muscle pain have been infrequently reported in patients taking bisphosphonates, including zoledronic acid. Consider withholding future zoledronic acid treatment if severe symptoms develop.
Atypical femur fractures in patients on bisphosphonate therapy have been reported; patients with thigh or groin pain should be evaluated to rule out a femoral fracture.
Distributed by:
Eugia US LLC
279 Princeton-Hightstown Rd.
E. Windsor, NJ 08520
Manufactured by:
Eugia Pharma Specialities Limited
Hyderabad - 500032
India -
MEDICATION GUIDE
Zoledronic Acid (zoe’’ le dron’ ik as’ id)
Injection
-
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mg per 100 mL (0.05 mg/mL) - Container Label
Rx only NDC 55150-283-99
Zoledronic
Acid Injection
5 mg per 100 mL
(0.05 mg/mL)
Solution for Intravenous Infusion
Do not mix with calcium-containing
solutions. Administer as a single
intravenous solution through a separate
vented infusion line.
Dispense the accompanying
Medication Guide to each patient.
100 mL Sterile Solution
eugia
-
PACKAGE LABEL-PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mg per 100 mL (0.05 mg/mL) - Container-Carton (1 Bottle)
Rx only NDC 55150-283-99
Zoledronic
Acid Injection
5 mg per 100 mL
(0.05 mg/mL)
Solution for Intravenous
Infusion
Do not mix with calcium-containing
solutions. Administer as a single
intravenous solution through a
separate vented infusion line.
1 bottle - Sterile Solution
Dispense the accompanying
Medication Guide to each patient.
eugia
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ZOLEDRONIC ACID
zoledronic acid injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:55150-283 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ZOLEDRONIC ACID (UNII: 6XC1PAD3KF) (ZOLEDRONIC ACID ANHYDROUS - UNII:70HZ18PH24) ZOLEDRONIC ACID ANHYDROUS 5 mg in 100 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MANNITOL (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) TRISODIUM CITRATE DIHYDRATE (UNII: B22547B95K) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:55150-283-99 1 in 1 CARTON 12/08/2017 1 100 mL in 1 BOTTLE, GLASS; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA209125 12/08/2017 Labeler - Eugia US LLC (968961354) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations EUGIA PHARMA SPECIALITIES LIMITED 650498244 ANALYSIS(55150-283) , MANUFACTURE(55150-283) , PACK(55150-283)