Label: APOQUEL CHEWABLE- oclacitinib chewable tablet, chewable
-
NDC Code(s):
54771-4322-1,
54771-4322-2,
54771-4322-3,
54771-4323-1, view more54771-4323-2, 54771-4323-3, 54771-4324-1, 54771-4324-2, 54771-4324-3
- Packager: Zoetis Inc.
- Category: PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: New Animal Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated December 11, 2024
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- Caution
-
Description
APOQUEL CHEWABLE (oclacitinib chewable tablet) is a synthetic Janus Kinase (JAK) inhibitor. The chemical composition of oclacitinib maleate is N-methyl-1-[trans-4-(methyl-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-ylamino) cyclohexyl]methanesulfonamide (2Z)-2-butenedioate.
The chemical structure of oclacitinib maleate is:
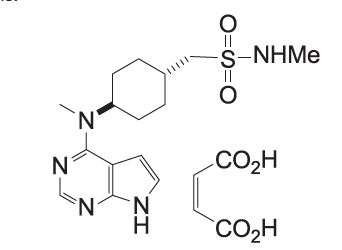
- Indications
-
Dosage and Administration
The dose of APOQUEL CHEWABLE (oclacitinib chewable tablet) is 0.18 to 0.27 mg oclacitinib/lb (0.4 to 0.6 mg oclacitinib/kg) body weight, administered orally, twice daily for up to 14 days, and then administered once daily for maintenance therapy.
Dosing Chart Weight Range
(in lb)Weight Range
(in Kg)Number of Tablets to be Administered Low High Low High 3.6 mg Tablets 5.4 mg Tablets 16 mg Tablets 6.6 9.9 3.0 4.4 0.5 - - 10.0 14.9 4.5 5.9 - 0.5 - 15.0 19.9 6.0 8.9 1 - - 20.0 29.9 9.0 13.4 - 1 - 30.0 44.9 13.5 19.9 - - 0.5 45.0 59.9 20.0 26.9 - 2 - 60.0 89.9 27.0 39.9 - - 1 90.0 129.9 40.0 54.9 - - 1.5 130.0 175.9 55.0 80.0 - - 2 -
Warnings
APOQUEL CHEWABLE is not for use in dogs less than 12 months of age (see Animal Safety).
APOQUEL CHEWABLE modulates the immune system.
APOQUEL CHEWABLE is not for use in dogs with serious infections.
APOQUEL CHEWABLE may increase susceptibility to infection, including demodicosis, and exacerbation of neoplastic conditions (see Precautions, Adverse Reactions, Post-Approval Experience and Animal Safety).New neoplastic conditions (benign and malignant) were observed in dogs treated with oclacitinib film-coated tablets (FCT) during clinical studies and have been reported in the post-approval period (see Adverse Reactions and Post-Approval Experience).
Consider the risks and benefits of treatment prior to initiating APOQUEL CHEWABLE in dogs with a history of recurrent serious infections or recurrent demodicosis or neoplasia (see Adverse Reactions, Post-Approval Experience, and Animal Safety).
Keep APOQUEL CHEWABLE in a secure location out of reach of dogs, cats, and other animals to prevent accidental ingestion or overdose. -
Human Warnings
This product is not for human use. Keep this and all drugs out of reach of children. For use in dogs only. Wash hands immediately after handling the tablets. In case of accidental eye contact, flush immediately with water or saline for at least 15 minutes and then seek medical attention. In case of accidental ingestion, seek medical attention immediately.
-
Precautions
Dogs receiving APOQUEL CHEWABLE should be monitored for the development of infections, including demodicosis, and neoplasia.
The use of APOQUEL CHEWABLE has not been evaluated in combination with glucocorticoids, cyclosporine, or other systemic immunosuppressive agents.
APOQUEL CHEWABLE is not for use in breeding dogs, or pregnant or lactating bitches. -
Adverse Reactions
The safety of APOQUEL CHEWABLE was established by pharmacokinetic data comparing oclacitinib film-coated tablets to APOQUEL CHEWABLE (see Clinical Pharmacology).
Control of Atopic Dermatitis
In a masked field study to assess the effectiveness and safety of oclacitinib for the control of atopic dermatitis in dogs, 152 dogs treated with oclacitinib FCT and 147 dogs treated with placebo (vehicle control) were evaluated for safety. The majority of dogs in the placebo group withdrew from the 112-day study by Day 16. Adverse reactions reported (and percent of dogs affected) during Days 0-16 included diarrhea (4.6% oclacitinib FCT, 3.4% placebo), vomiting (3.9% oclacitinib FCT, 4.1% placebo), anorexia (2.6% oclacitinib FCT, 0% placebo), new cutaneous or subcutaneous lump (2.6% oclacitinib FCT, 2.7% placebo), and lethargy (2.0% oclacitinib FCT, 1.4% placebo). In most cases, diarrhea, vomiting, anorexia, and lethargy spontaneously resolved with continued dosing. Dogs on oclacitinib FCT had decreased leukocytes (neutrophil, eosinophil, and monocyte counts) and serum globulin, and increased cholesterol and lipase compared to the placebo group but group means remained within the normal range. Mean lymphocyte counts were transiently increased at Day 14 in the oclacitinib FCT group.
Dogs that withdrew from the masked field study could enter an unmasked study where all dogs received oclacitinib FCT. Between the masked and unmasked study, 283 dogs received at least one dose of oclacitinib FCT. Of these 283 dogs, two dogs were withdrawn from study due to suspected treatment-related adverse reactions: one dog that had an intense flare-up of dermatitis and severe secondary pyoderma after 19 days of oclacitinib FCT administration, and one dog that developed generalized demodicosis after 28 days of oclacitinib FCT administration. Two other dogs on oclacitinib FCT were withdrawn from study due to suspected or confirmed malignant neoplasia and subsequently euthanized, including one dog that developed signs associated with a heart base mass after 21 days of oclacitinib FCT administration, and one dog that developed a Grade III mast cell tumor after 60 days of oclacitinib FCT administration.
One of the 147 dogs in the placebo group developed a Grade I mast cell tumor and was withdrawn from the masked study. Additional dogs receiving oclacitinib FCT were hospitalized for diagnosis and treatment of pneumonia (one dog), transient bloody vomiting and stool (one dog), and cystitis with urolithiasis (one dog).
In the 283 dogs that received oclacitinib FCT, the following additional clinical signs were reported after beginning oclacitinib FCT (percentage of dogs with at least one report of the clinical sign as a non-pre-existing finding): pyoderma (12.0%), non-specified dermal lumps (12.0%), otitis (9.9%), vomiting (9.2%), diarrhea (6.0%), histiocytoma (3.9%), cystitis (3.5%), anorexia (3.2%), lethargy (2.8%), yeast skin infections (2.5%), pododermatitis (2.5%), lipoma (2.1%), polydipsia (1.4%), lymphadenopathy (1.1%), nausea (1.1%), increased appetite (1.1%), aggression (1.1%), and weight loss (0.7).Control of Pruritus Associated with Allergic Dermatitis
In a masked field study to assess the effectiveness and safety of oclacitinib for the control of pruritus associated with allergic dermatitis in dogs, 216 dogs treated with oclacitinib FCT and 220 dogs treated with placebo (vehicle control) were evaluated for safety. During the 30-day study, there were no fatalities and no adverse reactions requiring hospital care. Adverse reactions reported (and percent of dogs affected) during Days 0-7 included diarrhea (2.3% oclacitinib FCT, 0.9% placebo), vomiting (2.3% oclacitinib FCT, 1.8% placebo), lethargy (1.8% oclacitinib FCT, 1.4% placebo), anorexia (1.4% oclacitinib FCT, 0% placebo), and polydipsia (1.4% oclacitinib FCT, 0% placebo). In most of these cases, signs spontaneously resolved with continued dosing. Five oclacitinib FCT group dogs were withdrawn from study because of: darkening areas of skin and fur (1 dog); diarrhea (1 dog); fever, lethargy and cystitis (1 dog); an inflamed footpad and vomiting (1 dog); and diarrhea, vomiting, and lethargy (1 dog). Dogs in the oclacitinib FCT group had a slight decrease in mean white blood cell counts (neutrophil, eosinophil, and monocyte counts) that remained within the normal reference range. Mean lymphocyte count for dogs in the oclacitinib FCT group increased at Day 7, but returned to pretreatment levels by study end without a break in oclacitinib FCT administration. Serum cholesterol increased in 25% of oclacitinib FCT group dogs, but mean cholesterol remained within the reference range.
Continuation Field Study
After completing oclacitinib FCT field studies, 239 dogs enrolled in an unmasked (no placebo control), continuation therapy study receiving oclacitinib FCT for an unrestricted period of time. Mean time on this study was 372 days (range 1 to 610 days). Of these 239 dogs, one dog developed demodicosis following 273 days of oclacitinib FCT administration. One dog developed dermal pigmented viral plaques following 266 days of oclacitinib FCT administration. One dog developed a moderately severe bronchopneumonia after 272 days of oclacitinib FCT administration; this infection resolved with antimicrobial treatment and temporary discontinuation of oclacitinib FCT. One dog was euthanized after developing abdominal ascites and pleural effusion of unknown etiology after 450 days of oclacitinib FCT administration. Six dogs were euthanized because of suspected malignant neoplasms: including thoracic metastatic, abdominal metastatic, splenic, frontal sinus, and intracranial neoplasms, and transitional cell carcinoma after 17, 120, 175, 49, 141, and 286 days of oclacitinib FCT administration, respectively. Two dogs each developed a Grade II mast cell tumor after 52 and 91 days of oclacitinib FCT administration, respectively. One dog developed low grade B-cell lymphoma after 392 days of oclacitinib FCT administration. Two dogs each developed an apocrine gland adenocarcinoma (one dermal, one anal sac) after approximately 210 and 320 days of oclacitinib FCT administration, respectively. One dog developed a low grade oral spindle cell sarcoma after 320 days of oclacitinib FCT administration.
Post-Approval Experience (2020)
The following adverse events are based on post-approval adverse drug experience reporting for oclacitinib FCT. Not all adverse events are reported to FDA/CVM. It is not always possible to reliably estimate the adverse event frequency or establish a causal relationship to product exposure using these data.
The following adverse events reported in dogs are listed in decreasing order of reporting frequency.
Vomiting, lethargy, anorexia, diarrhea, elevated liver enzymes, dermatitis (i.e. crusts, pododermatitis, pyoderma), seizures, polydipsia, and demodicosis.
Benign, malignant, and unclassified neoplasms, dermal masses (including papillomas and histiocytomas), lymphoma and other cancers have been reported.
Death (including euthanasia) has been reported.
-
Contact Information
To report suspected adverse events, for technical assistance or to obtain a copy of the Safety Data Sheet, contact Zoetis Inc. at 1-888-963-8471 or www.zoetis.com.
For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or online at www.fda.gov/reportanimalae.
-
Clinical Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
Oclacitinib inhibits the function of a variety of pruritogenic cytokines and pro-inflammatory cytokines, as well as cytokines involved in allergy that are dependent on JAK1 or JAK3 enzyme activity. It has little effect on cytokines involved in hematopoiesis that are dependent on JAK2. Oclacitinib is not a corticosteroid or an antihistamine.
Pharmacokinetics
A pharmacokinetic study was conducted to compare the bioavailability of APOQUEL CHEWABLE with oclacitinib FCT. Bioequivalence (BE) was demonstrated for the extent of exposure between APOQUEL CHEWABLE and oclacitinib FCT with the geometric mean ratio for the area under the curve from zero to the last sampling time point [AUC0-t(last)] of 1.03 and the 90% confidence interval (CI) within the acceptable range of 0.80 to 1.25. However, BE was not demonstrated for the maximum concentration (Cmax), with the geometric mean ratio of 0.86 and 90% CI of 0.78 to 0.95, outside the acceptable range of 0.8 to 1.25. Based on simulations, in accordance with the dosage regimen, the small differences in Cmax values between APOQUEL CHEWABLE and oclacitinib FCT after the first dose are likely to be minimal at steady-state.
In dogs, oclacitinib is rapidly and well absorbed following oral administration, with mean time to peak plasma concentrations (Tmax) of less than 2 hours. Following oral administration of a single 5.4 mg APOQUEL CHEWABLE to 42 dogs, the mean Cmax was 292 ng/mL and the mean area under the plasma concentration-time curve from 0 and extrapolated to infinity (AUC0-inf) was 2570 ng·hr/mL.
Oclacitinib has low protein binding with 66.3-69.7% bound in fortified canine plasma at nominal concentrations ranging from 10-1000 ng/mL. The apparent mean (95% CL)volume of distribution at steady-state was942 (870, 1014) mL/kg body weight.
Mean (95% CL) total body oclacitinib clearance from plasma was low – 316 (237, 396)mL/h/kg body weight (5.3 mL/min/kgbody weight). Following intravenous and oraladministration, the terminal half-life appearedsimilar with mean values of 3.5 (2.2, 4.7) and4.1 (3.1, 5.2) hours, respectively.
Oclacitinib is metabolized in the dog to multiple metabolites and one major oxidative metabolite was identified in plasma and urine. Overall the major clearance route is metabolism with minor contributions from renal and biliary elimination. Inhibition of canine cytochrome P450 enzymes by oclacitinib is minimal; the inhibitory concentrations (IC50s) are 50 fold greater than the observed Cmax values at the use dose. -
Effectiveness
The effectiveness of APOQUEL CHEWABLE was established by pharmacokinetic data comparing oclacitinib FCT to APOQUEL CHEWABLE (see Clinical Pharmacology).
Bioequivalence was not met for the lower 90% CI of the maximum concentration (Cmax), which may delay the speed of onset of effectiveness of APOQUEL CHEWABLE at the first dose or when transitioning from the oclacitinib FCT.Control of Atopic Dermatitis
A double-masked, 112-day, controlled study was conducted at 18 U.S. veterinary hospitals. The study enrolled 299 client-owned dogs with atopic dermatitis. Dogs were randomized to treatment with oclacitinib FCT (152 dogs: tablets administered at a dose of 0.4-0.6 mg/kg per dose twice daily for 14 days and then once daily) or placebo (147 dogs: vehicle control, tablets administered on the same schedule). During the study, dogs could not be treated with other drugs that could affect the assessment of effectiveness, such as corticosteroids, anti-histamines, or cyclosporine. Treatment success for pruritus for each dog was defined as at least a 2 cm decrease from baseline on a 10 cm visual analog scale (VAS) in pruritus, assessed by the Owner, on Day 28. Treatment success for skin lesions was defined as a 50% decrease from the baseline Canine Atopic Dermatitis Extent and Severity Index (CADESI) score, assessed by the Veterinarian, on Day 28. The estimated proportion of dogs with Treatment Success in Owner-assessed pruritus VAS score and in Veterinarian-assessed CADESI score was greater and significantly different for the oclacitinib FCT group compared to the placebo group.
Estimated Proportion of Dogs with Treatment Success, Atopic Dermatitis Effectiveness Parameter oclacitinib FCT Placebo P-value Owner-Assessed Pruritus VAS 0.66
(n = 131)0.04
(n = 133)p<0.0001 Veterinarian-Assessed CADESI 0.49
(n = 134)0.04
(n = 134)p<0.0001 Compared to the placebo group, mean Owner-assessed pruritus VAS scores (on Days 1, 2, 7, 14, and 28) and Veterinarian-assessed CADESI scores (on Days 14 and 28) were lower (improved) in dogs in the oclacitinib FCT group. By Day 30, 86% (127/147) of the placebo group dogs and 15% (23/152) of the oclacitinib FCT group dogswithdrew from the masked study because of worsening clinical signs, and had the option to enroll in an unmasked study and receive oclacitinib FCT. For dogs that continued oclacitinib FCT treatment beyond one month, the mean Owner-assessed pruritus VAS scores and Veterinarian-assessed CADESI scores continued to improve through study end at Day 112.
Control of Pruritus Associated with Allergic Dermatitis
A double-masked, 30-day, controlled study was conducted at 26 U.S. veterinary hospitals. The study enrolled 436 client-owned dogs with a history of allergic dermatitis attributed to one or more of the following conditions: atopic dermatitis, flea allergy, food allergy, contact allergy, and other/unspecified allergic dermatitis. Dogs were randomized to treatment with oclacitinib FCT (216 dogs: tablets administered at a dose of 0.4-0.6 mg/kg twice daily) or placebo (220 dogs: vehicle control, tablets administered twice daily). During the study, dogs could not be treated with other drugs that could affect the assessment of pruritus or dermal inflammation such as corticosteroids, anti-histamines, or cyclosporine. Treatment success for each dog was defined as at least a 2 cm decrease from baseline on a 10 cm visual analog scale (VAS) in pruritus, assessed by the Owner, on at least 5 of the 7 evaluation days. The estimated proportion of dogs with Treatment Success was greater and significantly different for the oclacitinib FCT group compared to the placebo group.
Owner-Assessed Pruritus VAS Treatment Success, Allergic Dermatitis Effectiveness Parameter oclacitinib FCT
(n = 203)Placebo
(n = 204)P-value Estimated Proportion of Dogs with Treatment Success 0.67 0.29 p<0.0001 After one week of treatment, 86.4% of oclacitinib FCT group dogs compared with 42.5% of placebo group dogs had achieved a 2 cm reduction on the 10 cm Owner-assessed pruritus VAS. On each of the 7 days, mean Owner-assessed pruritus VAS scores were lower in dogs in the oclacitinib FCT group (see Figure 1). Veterinarians used a 10 cm VAS scale to assess each dog’s dermatitis. After one week of treatment, the mean Veterinarian-assessed VAS dermatitis score for the dogs in the oclacitinib FCT group was lower at 2.2 cm (improved from a baseline value of 6.2 cm) compared with the placebo group mean score of 4.9 cm (from a baseline value of 6.2 cm). For dogs that continued oclacitinib FCT treatment beyond one week, the Veterinarian-assessed dermatitis scores continued to improve through study end at Day 30.
Figure 1: Owner Assessed Pruritus VAS Scores by treatment for Days 0-7
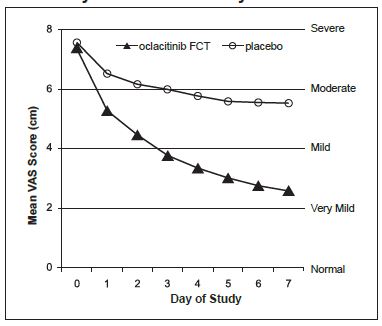
Palatability
In a well-controlled U.S. field study, in which 1,662 doses of APOQUEL CHEWABLE were administered to 120 dogs, a total of 1,522 doses (91.6%) were accepted voluntarily within 5 minutes. Of the 140 doses unconsumed after 5 minutes, 134 (8%) were consumed with assistance (with food treats or by pilling), and 6 (0.4%) doses were refused.
-
Animal Safety
Margin of Safety in 12 Month Old Dogs
Oclacitinib maleate was administered to healthy, one-year-old Beagle dogs twice daily for 6 weeks, followed by once daily for 20 weeks, at 0.6 mg/kg (1X maximum exposure dose, 8 dogs), 1.8 mg/kg (3X, 8 dogs), and 3.0 mg/kg (5X, 8 dogs) oclacitinib for 26 weeks. Eight dogs received placebo (empty gelatin capsule) at the same dosage schedule. Clinical observations that were considered likely to be related to oclacitinib maleate included papillomas and a dose-dependent increase in the number and frequency of interdigital furunculosis (cysts) on one or more feet during the study. Additional clinical observations were primarily related to the interdigital furunculosis and included dermatitis (local alopecia, erythema, abrasions, scabbing/crusts, and edema of feet) and lymphadenopathy of peripheral nodes. Microscopic findings considered to be oclacitinib maleate-related included decreased cellularity (lymphoid) in Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (GALT), spleen, thymus, cervical and mesenteric lymph node; and decreased cellularity of sternal and femoral bone marrow. Lymphoid hyperplasia and chronic active inflammation was seen in lymph nodes draining feet affected with interdigital furunculosis. Five oclacitinib maleate-treated dogs had microscopic evidence of mild interstitial pneumonia.
Clinical pathology findings considered to be oclacitinib maleate-related included mild, dose-dependent reduction in hemoglobin, hematocrit, and reticulocyte counts during the twice daily dosing period with decreases in the leukocyte subsets of lymphocytes, eosinophils, and basophils. Total proteins were decreased over time primarily due to the albumin fraction.
Vaccine Response Study
An adequate immune response (serology) to killed rabies (RV), modified live canine distemper virus (CDV), and modified live canine parvovirus (CPV) vaccination was achieved in eight 16-week old vaccine naïve puppies that were administered oclacitinib maleate at 1.8 mg/kg oclacitinib (3X maximum exposure dose) twice daily for 84 days. For modified live canine parainfluenza virus (CPI), < 80% (6 of 8) of the dogs achieved adequate serologic response. Clinical observations that were considered likely to be related to oclacitinib maleate treatment included enlarged lymph nodes, interdigital furunculosis, cysts, and pododermatitis. One oclacitinib maleate-treated dog (26-weeks-old) was euthanized on Day 74 after physical examination revealed the dog to be febrile, lethargic, with pale mucous membranes and frank blood in stool. Necropsy revealed pneumonia of short duration and evidence of chronic lymphadenitis of mesenteric lymph nodes. During the three month recovery phase to this study, one oclacitinib maleate-treated dog (32-weeks old) was euthanized on Day 28 due to clinical signs which included enlarged prescapular lymph nodes, bilateral epiphora, lethargy, mild dyspnea, and fever. The dog showed an elevated white blood cell (WBC) count. Necropsy revealed lesions consistent with sepsis secondary to immunosuppression. Bone marrow hyperplasia was consistent with response to sepsis.
Margin of Safety in 6 Month Old Dogs
A margin of safety study in 6-month-old dogs was discontinued after four months due to the development of bacterial pneumonia and generalized demodex mange infections in dogs in the high dose (3X and 5X) treatment groups, dosed at 1.8 and 3.0 mg/kg oclacitinib twice daily, for the entire study.
- Storage Conditions
-
How Supplied
APOQUEL CHEWABLE tablets contain 3.6 mg, 5.4 mg, or 16 mg of oclacitinib as oclacitinib maleate per tablet. Each strength chewable tablets are packaged in 100 and 250 count bottles and in a 100 count 10 x 10 blister pack. Each chewable tablet is pentagon shaped, scored on both sides and have a dose descriptor (S S, M M or L L) debossed on one face across the score line. The S (small), M (medium) and L (large) markings correspond to the tablet strengths of 3.6 mg, 5.4 mg and 16 mg respectively.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 3.6 mg Tablet Bottle Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5.4 mg Tablet Bottle Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 16 mg Tablet Bottle Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
APOQUEL CHEWABLE
oclacitinib chewable tablet, chewableProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:54771-4322 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength OCLACITINIB MALEATE (UNII: VON733L42A) (OCLACITINIB - UNII:99GS5XTB51) OCLACITINIB MALEATE 3.6 mg Product Characteristics Color brown (light to dark brown) Score 2 pieces Shape PENTAGON (5 sided) Size 9mm Flavor Imprint Code SS Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:54771-4322-1 100 in 1 BOTTLE 2 NDC:54771-4322-2 250 in 1 BOTTLE 3 NDC:54771-4322-3 10 in 1 CARTON 3 10 in 1 BLISTER PACK Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NADA NADA141555 07/31/2023 APOQUEL CHEWABLE
oclacitinib chewable tablet, chewableProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:54771-4323 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength OCLACITINIB MALEATE (UNII: VON733L42A) (OCLACITINIB - UNII:99GS5XTB51) OCLACITINIB MALEATE 5.4 mg Product Characteristics Color brown (light to dark brown) Score 2 pieces Shape PENTAGON (5 sided) Size 10mm Flavor Imprint Code MM Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:54771-4323-1 100 in 1 BOTTLE 2 NDC:54771-4323-2 250 in 1 BOTTLE 3 NDC:54771-4323-3 10 in 1 CARTON 3 10 in 1 BLISTER PACK Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NADA NADA141555 07/31/2023 APOQUEL CHEWABLE
oclacitinib chewable tablet, chewableProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:54771-4324 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength OCLACITINIB MALEATE (UNII: VON733L42A) (OCLACITINIB - UNII:99GS5XTB51) OCLACITINIB MALEATE 16 mg Product Characteristics Color brown (light to dark brown) Score 2 pieces Shape PENTAGON (5 sided) Size 15mm Flavor Imprint Code LL Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:54771-4324-1 100 in 1 BOTTLE 2 NDC:54771-4324-2 250 in 1 BOTTLE 3 NDC:54771-4324-3 10 in 1 CARTON 3 10 in 1 BLISTER PACK Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NADA NADA141555 07/31/2023 Labeler - Zoetis Inc. (828851555)






