General
- Intravenous doses of midazolam should be decreased for elderly and for debilitated patients (see WARNINGS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). These patients will also probably take longer to ...
General
Intravenous doses of midazolam should be decreased for elderly and for debilitated patients (see WARNINGS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). These patients will also probably take longer to recover completely after midazolam administration for the induction of anesthesia.
Midazolam does not protect against the increase in intracranial pressure or against the heart rate rise and/or blood pressure rise associated with endotracheal intubation under light general anesthesia.
The efficacy and safety of midazolam in clinical use are functions of the dose administered, the clinical status of the individual patient, and the use of concomitant medications capable of depressing the CNS. Anticipated effects range from mild sedation to deep levels of sedation virtually equivalent to a state of general anesthesia where the patient may require external support of vital functions. Care must be taken to individualize and carefully titrate the dose of midazolam to the patient's underlying medical/surgical conditions, administer to the desired effect being certain to wait an adequate time for peak CNS effects of both midazolam and concomitant medications, and have the personnel and size-appropriate equipment and facilities available for monitoring and intervention (see BOXED WARNING, WARNINGS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). Practitioners administering midazolam must have the skills necessary to manage reasonably foreseeable adverse effects, particularly skills in airway management. For information regarding withdrawal (see DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE).
Information for Patients
To assure safe and effective use of benzodiazepines, the following information and instructions should be communicated to the patient when appropriate:
Inform your physician about any alcohol consumption and medicine you are now taking, especially blood pressure medication and antibiotics, including drugs you buy without a prescription. Alcohol has an increased effect when consumed with benzodiazepines; therefore, caution should be exercised regarding simultaneous ingestion of alcohol during benzodiazepine treatment.
Inform your physician if you are pregnant or are planning to become pregnant.
Inform your physician if you are nursing.
Patients should be informed of the pharmacological effects of midazolam, such as sedation and amnesia, which in some patients may be profound. The decision as to when patients who have received injectable midazolam, particularly on an outpatient basis, may again engage in activities requiring complete mental alertness, operate hazardous machinery or drive a motor vehicle must be individualized.
Patients receiving continuous infusion of midazolam in critical care settings over an extended period of time, may experience symptoms of withdrawal following abrupt discontinuation.
Effect of anesthetic and sedation drugs on early brain development: Studies conducted in young animals and children suggest repeated or prolonged use of general anesthetic or sedation drugs in children younger than 3 years may have negative effects on their developing brains. Discuss with parents and caregivers the benefits, risks, and timing and duration of surgery or procedures requiring anesthetic and sedation drugs.
Drug Interactions
Effect of Concomitant Use of Benzodiazepines and Opioids
The concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids increases the risk of respiratory depression because of actions at different receptor sites in the CNS that control respiration. Benzodiazepines interact at GABAA sites and opioids interact primarily at mu receptors. When benzodiazepines and opioids are combined, the potential for benzodiazepines to significantly worsen opioid-related respiratory depression exists. Monitor patients closely for respiratory depression and sedation.
The sedative effect of intravenous midazolam is accentuated by any concomitantly administered medication, which depresses the central nervous system, particularly opioids (e.g., morphine, meperidine and fentanyl) and also secobarbital and droperidol. Consequently, the dosage of midazolam should be adjusted according to the type and amount of concomitant medications administered and the desired clinical response (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Other Drug Interactions
Caution is advised when midazolam is administered concomitantly with drugs that are known to inhibit the P450-3A4 enzyme system such as cimetidine (not ranitidine), erythromycin, diltiazem, verapamil, ketoconazole and itraconazole. These drug interactions may result in prolonged sedation due to a decrease in plasma clearance of midazolam.
The effect of single oral doses of 800 mg cimetidine and 300 mg ranitidine on steady-state concentrations of oral midazolam was examined in a randomized crossover study (n=8). Cimetidine increased the mean midazolam steady-state concentration from 57 to 71 ng/mL. Ranitidine increased the mean steady-state concentration to 62 ng/mL. No change in choice reaction time or sedation index was detected after dosing with the H2 receptor antagonists.
In a placebo-controlled study, erythromycin administered as a 500 mg dose, three times a day, for 1 week (n=6), reduced the clearance of midazolam following a single 0.5 mg/kg intravenous dose. The half-life was approximately doubled.
Caution is advised when midazolam is administered to patients receiving erythromycin since this may result in a decrease in the plasma clearance of midazolam.
The effects of diltiazem (60 mg three times a day) and verapamil (80 mg three times day) on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of midazolam were investigated in a three-way crossover study (n=9). The half-life of midazolam increased from 5 to 7 hours when midazolam was taken in conjunction with verapamil or diltiazem. No interaction was observed in healthy subjects between midazolam and nifedipine.
In a placebo-controlled study, where saquinavir or placebo was administered orally as a 1200 mg dose, three times a day , for 5 days (n=12), a 56% reduction in the clearance of midazolam following a single 0.05 mg/kg intravenous dose was observed. The half-life was approximately doubled.
A moderate reduction in induction dosage requirements of thiopental (about 15%) has been noted following use of intramuscular midazolam for premedication in adults.
The intravenous administration of midazolam decreases the minimum alveolar concentration (MAC) of halothane required for general anesthesia. This decrease correlates with the dose of midazolam administered; no similar studies have been carried out in pediatric patients but there is no scientific reason to expect that pediatric patients would respond differently than adults.
Although the possibility of minor interactive effects has not been fully studied, midazolam and pancuronium have been used together in patients without noting clinically significant changes in dosage, onset or duration in adults. Midazolam does not protect against the characteristic circulatory changes noted after administration of succinylcholine or pancuronium and does not protect against the increased intracranial pressure noted following administration of succinylcholine. Midazolam does not cause a clinically significant change in dosage, onset or duration of a single intubating dose of succinylcholine; no similar studies have been carried out in pediatric patients but there is no scientific reason to expect that pediatric patients would respond differently than adults.
No significant adverse interactions with commonly used premedications or drugs used during anesthesia and surgery (including atropine, scopolamine, glycopyrrolate, diazepam, hydroxyzine, d-tubocurarine, succinylcholine and other nondepolarizing muscle relaxants) or topical local anesthetics (including lidocaine, dyclonine HCl and Cetacaine) have been observed in adults or pediatric patients. In neonates, however, severe hypotension has been reported with concomitant administration of fentanyl. This effect has been observed in neonates on an infusion of midazolam who received a rapid injection of fentanyl and in patients on an infusion of fentanyl who have received a rapid injection of midazolam.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Midazolam has not been shown to interfere with results obtained in clinical laboratory tests.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Midazolam maleate was administered with diet in mice and rats for 2 years at dosages of 1, 9 and 80 mg/kg/day. In female mice in the highest dose group there was a marked increase in the incidence of hepatic tumors. In high-dose male rats there was a small but statistically significant increase in benign thyroid follicular cell tumors. Dosages of 9 mg/kg/day of midazolam maleate (4 times a human induction dose of 0.35 mg/kg based on body surface area comparison) do not increase the incidence of tumors. The pathogenesis of induction of these tumors is not known. These tumors were found after chronic administration, whereas human use will ordinarily be of single or several doses.
Mutagenesis
Midazolam did not have mutagenic activity in Salmonella typhimurium (5 bacterial strains), Chinese hamster lung cells (V79), human lymphocytes or in the micronucleus test in mice.
Impairment of Fertility
Male rats were treated orally with 1, 4, or 16 mg/kg midazolam beginning 62 days prior to mating with female rats treated with the same doses for 14 days prior to mating to Gestation Day 13 or Lactation Day 21. The high dose produced an equivalent exposure (AUC) as 4 mg/kg intravenous midazolam (1.85 times the human induction dose of 0.35 mg/kg based on body surface area comparison). There were no adverse effects on either male or female fertility noted
Pregnancy:
Teratogenic Effects
(see WARNINGS).
Published studies of in pregnant primates demonstrate that the administration of anesthetic and sedation drugs that block NMDA receptors and/or potentiate GABA activity during the period of peak brain development increases neuronal apoptosis in the developing brain of the offspring when used for longer than 3 hours. There are no data on pregnancy exposures in primates corresponding to periods prior to the third trimester in humans (see DATA).
Data
Animal Data
Pregnant rats were treated with midazolam using intravenous doses of 0.2, 1, and 4 mg/kg/day (0.09, 0.46, and 1.85 times the human induction dose of 0.35 mg/kg based on body surface area comparisons) during the period of organogenesis (Gestation Day 7 through 15). Midazolam did not cause adverse effects to the fetus at doses of up to 1.85 times the human induction dose. All doses produced slight to moderate ataxia. The high dose produced a 5% decrease in maternal body weight gain compared to control.
Pregnant rabbits were treated with midazolam using intravenous doses of 0.2, 0.6, and 2 mg/kg/day (0.09, 0.46, and 1.85 times the human induction dose of 0.35 mg/kg based on body surface area comparisons) during the period of organogenesis (Gestation Day 7 to 18). Midazolam did not cause adverse effects to the fetus at doses of up to 1.85 times the human induction dose. The high dose was associated with findings of ataxia and sedation but no evidence of maternal toxicity.
Pregnant rats were administered midazolam using intravenous doses of 0.2, 1, and 4 mg/kg/day (0.09, 0.46, and 1.85 times the human induction dose of 0.35 mg/kg based on body surface area comparisons) during late gestation and through lactation (Gestation Day 15 through Lactation Day 21). All doses produced ataxia. The high dose produced a slight decrease in maternal body weight gain compared to control. There were no clear adverse effects noted in the offspring. The study included no functional assessments of the pups, such as learning and memory testing or reproductive capacity. In a published study in primates, administration of an anesthetic dose of ketamine for 24 hours on Gestation Day 122 increased neuronal apoptosis in the developing brain of the fetus. In other published studies, administration of either isoflurane or propofol for 5 hours on Gestation Day 120 resulted in increased neuronal and oligodendrocyte apoptosis in the developing brain of the offspring. With respect to brain development, this time period corresponds to the third trimester of gestation in the human. The clinical significance of these findings is not clear; however, studies in juvenile animals suggest neuroapoptosis correlates with long-term cognitive deficits (see WARNINGS/PEDIATRIC NEUROTOXICITY, PRECAUTIONS/PEDIATRIC USE and ANIMAL TOXICOLOGY AND/OR PHARMACOLOGY).
Labor and Delivery
In humans, measurable levels of midazolam were found in maternal venous serum, umbilical venous and arterial serum and amniotic fluid, indicating placental transfer of the drug. Following intramuscular administration of 0.05 mg/kg of midazolam, both the venous and the umbilical arterial serum concentrations were lower than maternal concentrations.
The use of injectable midazolam in obstetrics has not been evaluated in clinical studies. Because midazolam is transferred transplacentally and because other benzodiazepines given in the last weeks of pregnancy have resulted in neonatal CNS depression, midazolam is not recommended for obstetrical use.
Nursing Mothers
Midazolam is excreted in human milk. Caution should be exercised when midazolam is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
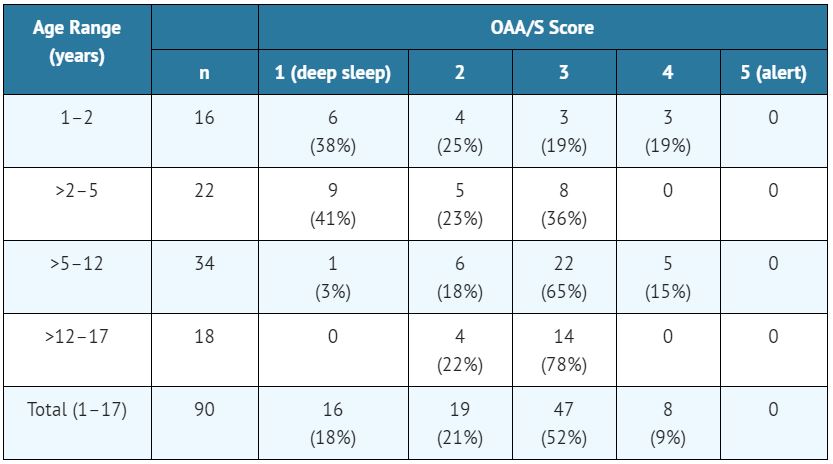
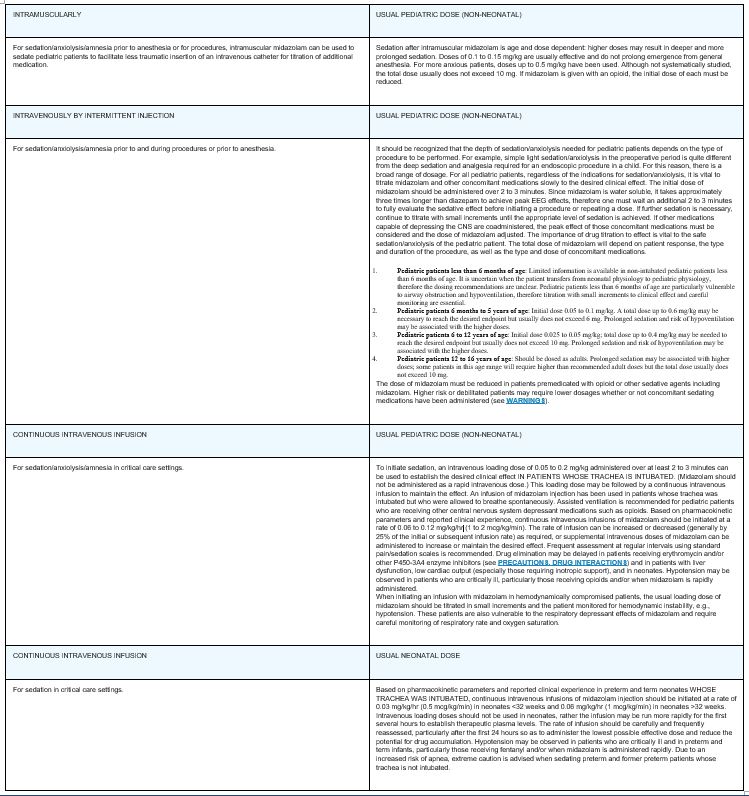
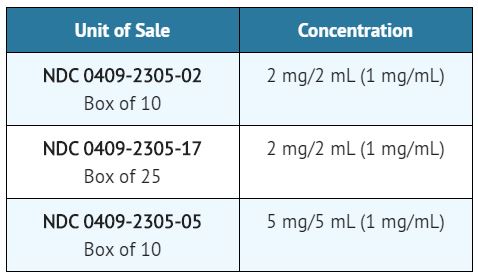
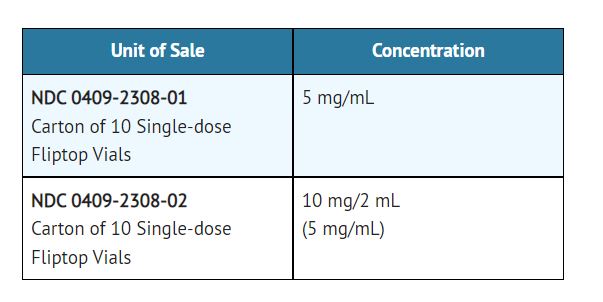
The safety and efficacy of midazolam for sedation/anxiolysis/amnesia following single dose intramuscular administration, intravenously by intermittent injections and continuous infusion have been established in pediatric and neonatal patients. For specific safety monitoring and dosage guidelines see BOXED WARNING, CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, INDICATIONS, WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS, ADVERSE REACTIONS, OVERDOSAGE and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION. UNLIKE ADULT PATIENTS, PEDIATRIC PATIENTS GENERALLY RECEIVE INCREMENTS OF MIDAZOLAM ON A MG/KG BASIS. As a group, pediatric patients generally require higher dosages of midazolam (mg/kg) than do adults. Younger (less than six years) pediatric patients may require higher dosages (mg/kg) than older pediatric patients, and may require closer monitoring. In obese PEDIATRIC PATIENTS, the dose should be calculated based on ideal body weight. When midazolam is given in conjunction with opioids or other sedatives, the potential for respiratory depression, airway obstruction, or hypoventilation is increased. The health care practitioner who uses this medication in pediatric patients should be aware of and follow accepted professional guidelines for pediatric sedation appropriate to their situation.
Midazolam should not be administered by rapid injection in the neonatal population. Severe hypotension and seizures have been reported following rapid intravenous administration, particularly, with concomitant use of fentanyl.
Animal Data
Published juvenile animal studies demonstrate that the administration of anesthetic and sedation drugs, such as Midazolam Injection USP, that either block NMDA receptors or potentiate the activity of GABA during the period of rapid brain growth or synaptogenesis, results in widespread neuronal and oligodendrocyte cell loss in the developing brain and alterations in synaptic morphology and neurogenesis. Based on comparisons across species, the window of vulnerability to these changes is believed to correlate with exposures in the third trimester of gestation through the first several months of life, but may extend out to approximately 3 years of age in humans.
In primates, exposure to 3 hours of ketamine that produced a light surgical plane of anesthesia did not increase neuronal cell loss, however, treatment regimens of 5 hours or longer of isoflurane increased neuronal cell loss. Data from isoflurane-treated rodents and ketamine-treated primates suggest that the neuronal and oligodendrocyte cell losses are associated with prolonged cognitive deficits in learning and memory. The clinical significance of these nonclinical findings is not known, and healthcare providers should balance the benefits of appropriate anesthesia in pregnant women, neonates, and young children who require procedures with the potential risks suggested by the nonclinical data (see WARNINGS/PEDIATRIC NEUROTOXICITY, PRECAUTIONS/PREGNANCY and ANIMAL TOXICOLOGY AND/ORPHARMACOLOGY).
Geriatric Use
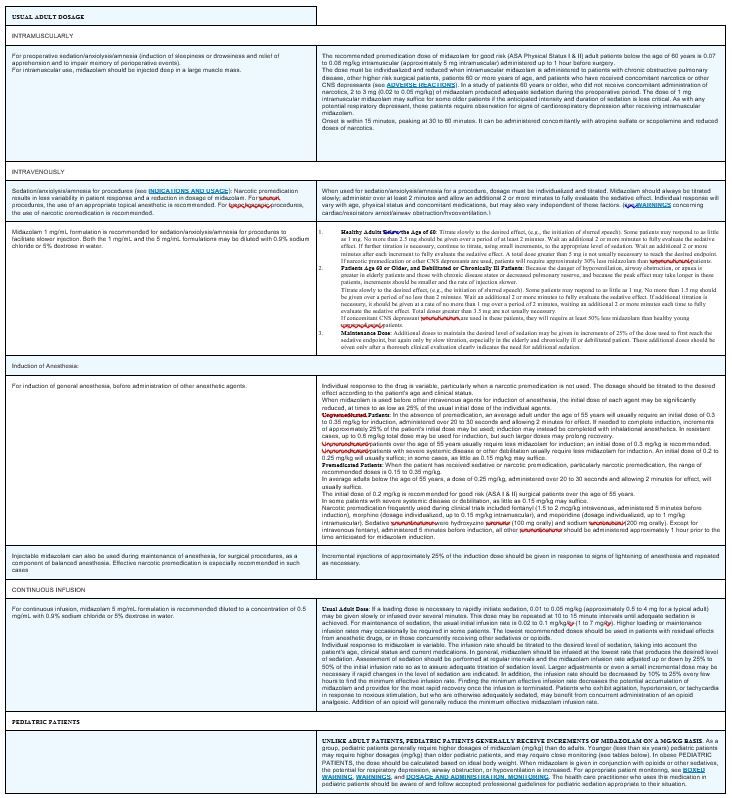
Because geriatric patients may have altered drug distribution and diminished hepatic and/or renal function, reduced doses of midazolam are recommended. Intravenous and intramuscular doses of midazolam should be decreased for elderly and for debilitated patients (see WARNINGS and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION) and subjects over 70 years of age may be particularly sensitive. These patients will also probably take longer to recover completely after midazolam administration for the induction of anesthesia. Administration of intramuscular and intravenous midazolam to elderly and/or high risk surgical patients has been associated with rare reports of death under circumstances compatible with cardiorespiratory depression. In most of these cases, the patients also received other central nervous system depressants capable of depressing respiration, especially narcotics (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Specific dosing and monitoring guidelines for geriatric patients are provided in the DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section for premedicated patients for sedation/anxiolysis/amnesia following intravenous and intramuscular administration, for induction of anesthesia following intravenous administration and for continuous infusion.
Close
 ...
...