Label: DORZOLAMIDE HCL solution/ drops
- NDC Code(s): 50090-2406-0
- Packager: A-S Medication Solutions
- This is a repackaged label.
- Source NDC Code(s): 24208-485
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Abbreviated New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated November 11, 2024
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DORZOLAMIDE HYDROCHLORIDE OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DORZOLAMIDE HYDROCHLORIDE OPHTHALMIC SOLUTION.
DORZOLAMIDE HYDROCHLORIDE Ophthalmic Solution 2%, for topical ophthalmic use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1994INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with ocular hypertension or open-angle glaucoma. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The dose is one drop of dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution in the affected eye(s) three times daily. Dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution may be used concomitantly with other topical ophthalmic drug products to lower intraocular pressure. (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Ophthalmic solution containing dorzolamide 2% (20 mg/mL). (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequently reported adverse reactions associated with dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution were ocular burning, stinging, or discomfort immediately following ocular administration (approximately one-third of patients). Approximately one-quarter of patients noted a bitter taste following administration. Superficial punctate keratitis occurred in 10 to 15% of patients and signs and symptoms of ocular allergic reaction in approximately 10%. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Bausch & Lomb Incorporated at 1-800-553-5340 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 11/2024
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Sulfonamide Hypersensitivity
5.2 Bacterial Keratitis
5.3 Corneal Endothelium
5.4 Allergic Reactions
5.5 Acute Angle-Closure Glaucoma
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Oral Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
7.2 High-Dose Salicylate Therapy
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal and Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The dose is one drop of dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution in the affected eye(s) three times daily.
Dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution may be used concomitantly with other topical ophthalmic drug products to lower intraocular pressure. If more than one topical ophthalmic drug is being used, the drugs should be administered at least five minutes apart.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution is contraindicated in patients who are hypersensitive to any component of this product [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Sulfonamide Hypersensitivity
Dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution contains dorzolamide, a sulfonamide; and although administered topically, it is absorbed systemically. Therefore, the same types of adverse reactions that are attributable to sulfonamides may occur with topical administration of dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution. Fatalities have occurred, although rarely, due to severe reactions to sulfonamides including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, fulminant hepatic necrosis, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, and other blood dyscrasias. Sensitization may recur when a sulfonamide is readministered irrespective of the route of administration. If signs of serious reactions or hypersensitivity occur, discontinue the use of this preparation [see Contraindications (4)].
5.2 Bacterial Keratitis
There have been reports of bacterial keratitis associated with the use of multiple-dose containers of topical ophthalmic products. These containers had been inadvertently contaminated by patients who, in most cases, had a concurrent corneal disease or a disruption of the ocular epithelial surface.
5.3 Corneal Endothelium
Carbonic anhydrase activity has been observed in both the cytoplasm and around the plasma membranes of the corneal endothelium. There is an increased potential for developing corneal edema in patients with low endothelial cell counts. Caution should be used when prescribing dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution to this group of patients.
5.4 Allergic Reactions
In clinical studies, local ocular adverse effects, primarily conjunctivitis and lid reactions, were reported with chronic administration of dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution. Many of these reactions had the clinical appearance and course of an allergic-type reaction that resolved upon discontinuation of drug therapy. If such reactions are observed, dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution should be discontinued and the patient evaluated before considering restarting the drug [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Controlled Clinical Trials: The most frequent adverse reactions associated with dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution were ocular burning, stinging, or discomfort immediately following ocular administration (approximately one-third of patients). Approximately one-quarter of patients noted a bitter taste following administration. Superficial punctate keratitis occurred in 10 to 15% of patients and signs and symptoms of ocular allergic reaction in approximately 10%. Reactions occurring in approximately 1 to 5% of patients were conjunctivitis and lid reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)], blurred vision, eye redness, tearing, dryness, and photophobia. Other ocular reactions and systemic reactions were reported infrequently, including headache, nausea, asthenia/fatigue; and, rarely, skin rashes, urolithiasis, and iridocyclitis.
In a 3-month, double-masked, active-treatment-controlled, multicenter study in pediatric patients, the adverse reactions profile of dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution was comparable to that seen in adult patients.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure: signs and symptoms of systemic allergic reactions including angioedema, bronchospasm, pruritus, and urticaria; Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis; dizziness, paresthesia; ocular pain, transient myopia, choroidal detachment following filtration surgery, eyelid crusting; dyspnea; contact dermatitis, epistaxis, dry mouth and throat irritation.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Oral Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
There is a potential for an additive effect on the known systemic effects of carbonic anhydrase inhibition in patients receiving an oral carbonic anhydrase inhibitor and dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution. The concomitant administration of dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution and oral carbonic anhydrase inhibitors is not recommended.
7.2 High-Dose Salicylate Therapy
Although acid-base and electrolyte disturbances were not reported in the clinical trials with dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution, these disturbances have been reported with oral carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and have, in some instances, resulted in drug interactions (e.g., toxicity associated with high-dose salicylate therapy). Therefore, the potential for such drug interactions should be considered in patients receiving dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women with dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution. Dorzolamide caused fetal vertebral malformations when administered orally to rabbits at 2.5 mg/kg/day
(37 times the clinical exposure). Dorzolamide administered during the period of organogenesis was not teratogenic in rabbits dosed up to 1 mg/kg/day (15 times the clinical exposure). Dorzolamide hydrochloride administered
orally to rats during late gestation and lactation caused growth delays in offspring at 7.5 mg/kg/day (52 times the clinical exposure). Growth was not delayed at 1 mg/kg/day (8.0 times the clinical exposure).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Developmental toxicity studies were conducted in pregnant rabbits administered dorzolamide hydrochloride orally during the period of organogenesis from gestation days 6 through 18 at doses of 0.2, 1, 2.5, 5, and 10 mg/kg/day. The developmental lowest observed adverse effect level (LOAEL) was 2.5 mg/kg/day, based on vertebral malformations and
decreased fetal body weight. The maternal LOAEL was 2.5 mg/kg/day, based on metabolic acidosis and reduced weight gain. The maternal and developmental no adverse effect levels (NOAELs) were 1 mg/kg/day. The rabbit doses of 1 and 2.5 mg/kg/day represent estimated plasma Cmax levels in rabbits 15 and 37 times higher than the lower limit of detection in human plasma following ocular administration, respectively.
Dorzolamide hydrochloride was administered orally to rats during late gestation and lactation (gestation day 17 through postpartum day 20) at doses of 0.1, 1, or 7.5 mg/kg/day. The developmental LOAEL was 7.5 mg/kg/day, based on reduced birth weight, reduced weight gain, and a slight delay in postnatal development (incisor eruption, vaginal
canalization and eye openings) secondary to lower offspring body weight. This 7.5 mg/kg/day dose represents an estimated plasma Cmax level in rats 52 times higher than the lower limit of detection in human plasma following ocular administration. The developmental NOAEL was 1 mg/kg/day. The maternal LOAEL was 1 mg/kg/day, based on reduced
body weight gain. The maternal NOAEL was 0.1 mg/kg/day. The rat doses of 1 and 0.1 mg/kg/day represent estimated plasma Cmax levels in rats approximately 8.0 times and approximately equal (1x), respectively to the lower limit of detection in human plasma following ocular administration.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution in human milk, the effects on the breast-fed infant, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding
should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution and any potential adverse effects on the breast-fed child from dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution. Dorzolamide is present in the milk of lactating rats (see Data).
Data
Animal Data
Lactating rats were dosed orally with 7.5 mg/kg/day of dorzolamide hydrochloride; dorzolamide and the N-desethyl metabolite were detected in the milk.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution have been demonstrated in pediatric patients in a 3-month, multicenter, double-masked, active-treatment-controlled trial.
8.5 Geriatric Use
No overall differences in safety or effectiveness have been observed between elderly and younger patients.
8.6 Renal and Hepatic Impairment
Dorzolamide has not been studied in patients with severe renal impairment (CrCl < 30 mL/min). Because dorzolamide and its metabolite are excreted predominantly by the kidney, dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution is not recommended in such patients.
Dorzolamide has not been studied in patients with hepatic impairment and should therefore be used with caution in such patients.
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution, USP is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor formulated for topical ophthalmic use.
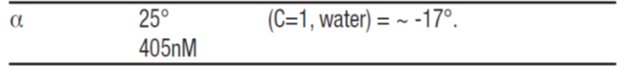
Dorzolamide hydrochloride USP is described chemically as: (4S-trans)-4-(ethylamino)-5,6-dihydro-6-methyl-4H-thieno[2,3-b]thiopyran-2-sulfonamide 7,7-dioxide monohydrochloride. Dorzolamide hydrochloride is optically active. The specific rotation is:
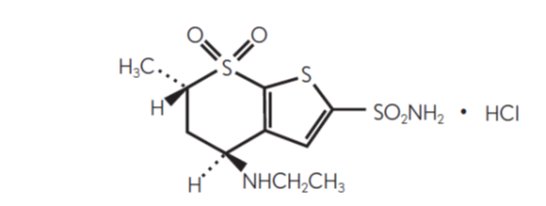
Its empirical formula is C10H16N2O4S3∙HCl and its structural formula is:
Dorzolamide hydrochloride USP has a molecular weight of 360.9 and a melting point of about 264°C. It is a white to off-white, crystalline powder, which is soluble in water and slightly soluble in methanol and ethanol.
Dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution, USP is supplied as a sterile, isotonic, buffered, slightly viscous, aqueous solution of dorzolamide hydrochloride USP. The pH of the solution is approximately 5.6, and the osmolarity is 260-330 mOsM. Each mL of dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution USP, 2% contains 20 mg dorzolamide (equivalent to 22.3 mg of dorzolamide hydrochloride USP). Inactive ingredients are hydroxyethyl cellulose, mannitol, sodium citrate dihydrate, sodium hydroxide (to adjust pH) and water for injection. Benzalkonium chloride 0.0075% is added as a preservative.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Carbonic anhydrase (CA) is an enzyme found in many tissues of the body including the eye. It catalyzes the reversible reaction involving the hydration of carbon dioxide and the dehydration of carbonic acid. In humans, carbonic anhydrase exists as a number of isoenzymes, the most active being carbonic anhydrase II (CA-II), found primarily in red blood cells (RBCs), but also in other tissues. Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase in the ciliary processes of the eye decreases aqueous humor secretion, presumably by slowing the formation of bicarbonate ions with subsequent reduction in sodium and fluid transport. The result is a reduction in intraocular pressure (IOP).
Dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution contains dorzolamide hydrochloride, an inhibitor of human carbonic anhydrase II. Following topical ocular administration, dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution reduces elevated intraocular pressure. Elevated intraocular pressure is a major risk factor in the pathogenesis of optic nerve damage and glaucomatous visual field loss.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
When topically applied, dorzolamide reaches the systemic circulation. To assess the potential for systemic carbonic anhydrase inhibition following topical administration, drug and metabolite concentrations in RBCs and plasma and carbonic anhydrase inhibition in RBCs were measured.
Dorzolamide accumulates in RBCs during chronic dosing as a result of binding to CA-II. The parent drug forms a single N-desethyl metabolite, which inhibits CA-II less potently than the parent drug but also inhibits CA-I. The metabolite also accumulates in RBCs where it binds primarily to CA-I. Plasma concentrations of dorzolamide and metabolite are generally below the assay limit of quantitation (15 nM). Dorzolamide binds moderately to plasma proteins (approximately 33%).
Dorzolamide is primarily excreted unchanged in the urine; the metabolite also is excreted in urine. After dosing is stopped, dorzolamide washes out of RBCs nonlinearly, resulting in a rapid decline of drug concentration initially, followed by a slower elimination phase with a half-life of about four months.
To simulate the systemic exposure after long-term topical ocular administration, dorzolamide was given orally to eight healthy subjects for up to 20 weeks. The oral dose of 2 mg twice daily closely approximates the amount of drug delivered by topical ocular administration of dorzolamide 2% three times daily. Steady state was reached within 8 weeks. The inhibition of CA-II and total carbonic anhydrase activities was below the degree of inhibition anticipated to be necessary for a pharmacological effect on renal function and respiration in healthy individuals.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a two-year study of dorzolamide hydrochloride administered orally to male and female Sprague-Dawley rats, urinary bladder papillomas were seen in male rats in the highest dosage group of 20 mg/kg/day. Papillomas were not seen in rats given oral doses of 1 mg/kg/day. These doses represent estimated plasma Cmax levels in rats, 138 and 7 times higher than the lower limit of detection in human plasma following ocular administration, respectively.
No treatment-related tumors were seen in a 21-month study in female and male mice given oral doses up to 75 mg/kg/day. This dose represents an estimated plasma Cmax level in mice, 582 times higher than the lower limit of detection in human plasma following ocular administration.
The increased incidence of urinary bladder papillomas seen in the high-dose male rats is a class-effect of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors in rats. Rats are particularly prone to developing papillomas in response to foreign bodies, compounds causing crystalluria, and diverse sodium salts.
No changes in bladder urothelium were seen in dogs given oral dorzolamide hydrochloride for one year at 2 mg/kg/day or monkeys dosed topically to the eye for one year. An oral dose of 2 mg/kg/day in dogs represents an estimated plasma Cmax level, 137 times higher than the lower limit of detection in human plasma following ocular administration. The topical ophthalmic dose in monkeys was approximately equivalent to the human topical ophthalmic dose.
The following tests for mutagenic potential were negative: (1) in vivo (mouse) cytogenetic assay; (2) in vitro chromosomal aberration assay; (3) alkaline elution assay; (4) V-79 assay; and (5) Ames test.
In fertility studies of dorzolamide hydrochloride in rats, there were no adverse effects on the reproductive capacity of males or females at doses of 15 and 7.5 mg/kg/day, respectively. These doses represent estimated plasma Cmax levels in rats, 103 and 52 times higher than the lower limit of detection in human plasma following ocular administration, respectively.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution was demonstrated in clinical studies in the treatment of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with glaucoma or ocular hypertension (baseline IOP ≥ 23 mmHg). The IOP-lowering effect of dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution was approximately 3 to 5 mmHg throughout the day and this was consistent in clinical studies of up to one year duration.
The efficacy of dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution when dosed less frequently than three times a day (alone or in combination with other products) has not been established.
In a one year clinical study, the effect of dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution 2% three times daily on the corneal endothelium was compared to that of betaxolol ophthalmic solution twice daily and timolol maleate ophthalmic solution 0.5% twice daily. There were no statistically significant differences between groups in corneal endothelial cell counts or in corneal thickness measurements. There was a mean loss of approximately 4% in the endothelial cell counts for each group over the one year period.
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Instructions for Use).
Sulfonamide Reactions
Dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution is a sulfonamide and although administered topically is absorbed systemically. Therefore the same types of adverse reactions that are attributable to sulfonamides may occur with topical administration. Advise patients that if serious or unusual reactions including severe skin reactions or signs of hypersensitivity occur, they should discontinue the use of the product [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Intercurrent Ocular Conditions
Advise patients that if they have ocular surgery or develop an intercurrent ocular condition (e.g., trauma or infection), they should immediately seek their physician’s advice concerning the continued use of the present multidose container.
Handling Ophthalmic Solutions
Instruct patients to avoid allowing the tip of the dispensing container to contact the eye or surrounding structures.
Instruct patients that ocular solutions, if handled improperly or if the tip of the dispensing container contacts the eye or surrounding structures, can become contaminated by common bacteria known to cause ocular infections. Serious damage to the eye and subsequent loss of vision may result from using contaminated solutions.
Concomitant Topical Ocular Therapy
If more than one topical ophthalmic drug is being used, the drugs should be administered at least five minutes apart.
Contact Lens Use
Advise patients that dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution contains benzalkonium chloride which may be absorbed by soft contact lenses. Contact lenses should be removed prior to administration of the solution. Lenses may be reinserted 15 minutes following dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution administration.
When to Seek Physician Advice
Advise patients that if they develop any ocular reactions, particularly conjunctivitis and lid reactions, they should discontinue use and seek their physician’s advice.
Distributed by:
Bausch & Lomb Americas Inc.
Bridgewater, NJ 08807 USA
Manufactured by:
Bausch & Lomb Incorporated
Tampa, FL 33637 USA
© 2022 Bausch & Lomb Incorporated or its affiliates
9633502 (Folded)
9633402 (Flat) -
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Dorzolamide Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution USP, 2%
(dor-Zoe-la-mide HYE-dro-KLOR-ide)
Before using your dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution
Before using your dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution for the first time, make sure the safety seal strip on the bottle is unbroken. (See Figure A.)
- Step 1. Wash your hands.
- Step 2. Tear off the safety seal strip. See Figure B.
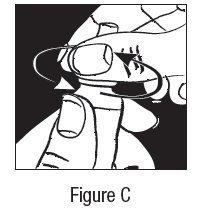
- Step 3. Unscrew the cap by turning counterclockwise. See Figure C.
Giving your dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution drops
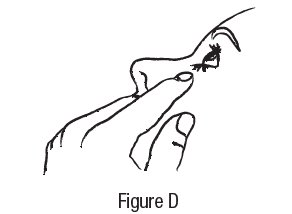
Step 4. Tilt your head back and pull your lower eyelid down slightly to form a pocket between your eyelid and your eye. See Figure D.
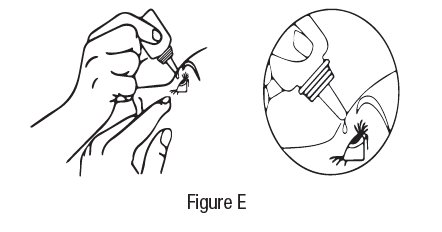
- Step 5. Turn your dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution dispenser upside down until a single drop is placed in your eye. Do not touch your eye or eyelid with the dropper tip. See Figure E.
Step 6. Do not try to make the hole of the dispenser tip larger. The dispenser tip is made to provide a single drop. Repeat Steps 4 and 5 to give your dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution drop.
Step 7. If your doctor has told you to use dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution drops in both eyes, repeat Steps 4 and 5.
After using your dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution
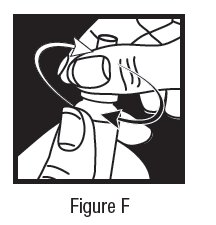
Step 8. Replace the cap by turning it clockwise until it is firmly touching your dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution dispenser. Do not over tighten or you may damage the dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution dispenser and cap. See Figure F.
How should I store dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution?
- •
- Store dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution at 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C)
- •
- Protect from light
- •
- After opening, dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution can be used until the expiration date on the bottle
- •
- Safely throw away medicine that is out of date or no longer needed.
Keep dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution and all medicines out of the reach of children.
Important information about using dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution
- •
- If you have any eye or skin reactions, especially conjunctivitis or eyelid reactions to dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution, stop using it and call your doctor right away.
- •
- If you have eye surgery or have a problem such as trauma or infection of your eye while using dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution, call your doctor right away.
- •
- If you do not handle eye medicines the right way the medicine can become contaminated. If the tip of the dispenser touches your eye or areas around your eye, the tip can become contaminated with bacteria which can cause an eye infection and other serious problems including loss of eyesight.
- •
- If you use other eye medicines dropped onto the eye like dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution, use the medicines at least 5 minutes before or after you use dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution.
Dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution contains benzalkonium chloride which may be absorbed by soft contact lenses. If you wear contact lenses, remove them before you use your dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution. You can place your contact lenses back into your eyes 15 minutes after using your dorzolamide hydrochloride ophthalmic solution.
Distributed by:
Bausch & Lomb Americas Inc.
Bridgewater, NJ 08807 USA
Manufactured by:
Bausch & Lomb Incorporated
Tampa, FL 33637 USA
© 2022 Bausch & Lomb Incorporated or its affiliates
Revised: 12/2022
9633502 (Folded)
9633402 (Flat) - Dorzolamide HCl
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
DORZOLAMIDE HCL
dorzolamide hcl solution/ dropsProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:50090-2406(NDC:24208-485) Route of Administration OPHTHALMIC Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DORZOLAMIDE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: QZO5366EW7) (DORZOLAMIDE - UNII:9JDX055TW1) DORZOLAMIDE 20 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength HYDROXYETHYL CELLULOSE (2000 CPS AT 1%) (UNII: S38J6RZN16) MANNITOL (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) TRISODIUM CITRATE DIHYDRATE (UNII: B22547B95K) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) AQUA (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: F5UM2KM3W7) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:50090-2406-0 1 in 1 CARTON 05/18/2016 1 10 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA090143 06/25/2009 Labeler - A-S Medication Solutions (830016429) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations A-S Medication Solutions 830016429 RELABEL(50090-2406)