Label: ERYTHROMYCIN solution
- NDC Code(s): 68071-4791-6
- Packager: NuCare Pharmaceuticals,Inc.
- This is a repackaged label.
- Source NDC Code(s): 45802-038
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Abbreviated New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated June 14, 2024
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
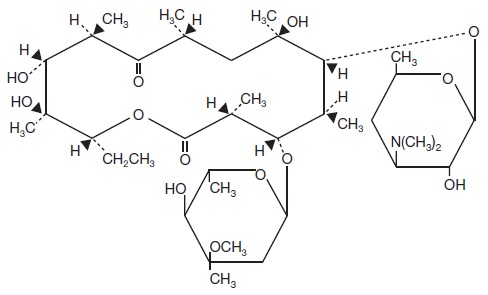
Erythromycin Topical Solution USP, 2% contains erythromycin for topical dermatologic use. Erythromycin is a macrolide antibiotic produced from a strain of Saccaropolyspora erythraea (formerly Streptomyces erythreus). It is a base and readily forms salts with acids. Chemically, erythromycin is: (3 R*,4 S*,5 S*,6 R*,7 R*,9 R*,11 R*,12 R*,13 S*,14 R*)-4-[(2,6-Dideoxy-3- C-methyl-3- 0-methyl-α-L- ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy -3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyl-6-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-ß-D- xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]oxacyclotetradecane-2,10-dione. It has the following structural formula:
Molecular Formula: C 37H 67NO 13
Molecular Weight: 733.94
Erythromycin is a white or slightly yellow crystalline powder that is slightly soluble in water, freely soluble in alcohols, acetone, chloroform, acetonitrile, ethyl acetate, and moderately soluble in ether, ethylene dichloride and amyl acetate.
Each mL of Erythromycin Topical Solution USP, 2% contains 20 mg of erythromycin base in a vehicle consisting of alcohol (66%), citric acid, and propylene glycol.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
The exact mechanism by which erythromycin reduces lesions of acne vulgaris is not fully known; however, the effect appears to be due in part to the antibacterial activity of the drug.
Microbiology –
Erythromycin acts by inhibition of protein synthesis in susceptible organisms by reversibly binding to 50S ribosomal subunits, thereby inhibiting translocation of aminoacyl transfer-RNA and inhibiting polypeptide synthesis. Antagonism has been demonstrated in vitro between erythromycin, lincomycin, chloramphenicol, and clindamycin.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
Pseudomembranous colitis has been reported with nearly all antibacterial agents, including erythromycin, and may range in severity from mild to life-threatening. Therefore, it is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who present with diarrhea subsequent to the administration of antibacterial agents.
Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon and may permit overgrowth of clostridia. Studies indicate that a toxin produced by Clostridium difficile is one primary cause of “antibiotic-associated colitis”.
After the diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis has been established, therapeutic measures should be initiated. Mild cases of pseudomembranous colitis usually respond to drug discontinuation alone. In moderate to severe cases, consideration should be given to management with fluids and electrolytes, protein supplementation and treatment with an antibacterial drug clinically effective against C. difficile colitis.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General -
For topical use only; not for ophthalmic use. Concomitant topical acne therapy should be used with caution because a possible cumulative irritancy effect may occur, especially with the use of peeling, desquamating or abrasive agents.
The use of antibiotic agents may be associated with the overgrowth of antibiotic-resistant organisms. If this occurs, discontinue use and take appropriate measures.
Avoid contact with eyes and all mucous membranes.
Information for Patients -
Patients using Erythromycin Topical Solution USP, 2% should receive the following information and instructions:
- This medication is to be used as directed by the physician. It is for external use only. Avoid contact with the eyes, nose, mouth, and all mucous membranes.
- This medication should not be used for any disorder other than that for which it was prescribed.
- Patients should not use any other topical acne medication unless otherwise directed by their physician.
- Patients should report to their physician any signs of local adverse reactions.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility -
No animal studies have been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic and mutagenic potential or effects on fertility of topical erythromycin. However, long-term (2 years) oral studies in rats with erythromycin ethylsuccinate and erythromycin base did not provide evidence of tumorigenicity. There was no apparent effect on male or female fertility in rats fed erythromycin (base) at levels up to 0.25% of diet.
Pregnancy:
Teratogenic Effects:
Pregnancy Category B -
There was no evidence of teratogenicity or any other adverse effect on reproduction in female rats fed erythromycin base (up to 0.25% of diet) prior to and during mating, during gestation and through weaning of two successive litters.
There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used in pregnancy only if clearly needed. Erythromycin has been reported to cross the placental barrier in humans, but fetal plasma levels are generally low.
Nursing Mothers -
It is not known whether erythromycin is excreted in human milk after topical application. However, erythromycin is excreted in human milk following oral and parenteral erythromycin administration. Therefore, caution should be exercised when erythromycin is administered to a nursing woman.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following local adverse reactions have been reported occasionally: peeling, dryness, itching, erythema, and oiliness. Irritation of the eyes and tenderness of the skin have also been reported with topical use of erythromycin. Generalized urticarial reactions possibly related to the use of erythromycin, which required systemic steroid therapy have been reported.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Erythromycin Topical Solution USP, 2% should be applied over the affected areas twice a day (morning and evening) after the skin is thoroughly washed with warm water and soap and patted dry. Acne lesions on the face, neck, shoulders, chest, and back may be treated in this manner.
This medication should be applied with applicator top. If fingertips are used, wash hands after application. Drying and peeling may be controlled by reducing the frequency of applications.
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- Package/Label Display Panel
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ERYTHROMYCIN
erythromycin solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:68071-4791(NDC:45802-038) Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ERYTHROMYCIN (UNII: 63937KV33D) (ERYTHROMYCIN - UNII:63937KV33D) ERYTHROMYCIN 20 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ALCOHOL (UNII: 3K9958V90M) CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:68071-4791-6 60 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 03/04/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA063038 12/19/2011 Labeler - NuCare Pharmaceuticals,Inc. (010632300) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations NuCare Pharmaceuticals,Inc. 010632300 relabel(68071-4791)