Label: IMKELDI- imatinib oral solution
- NDC Code(s): 81927-201-01
- Packager: Shorla Oncology Inc.,
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated December 5, 2024
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use IMKELDI safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for IMKELDI.
IMKELDI (imatinib) oral solution
Initial U.S. Approval: 2001INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Imkeldi is a kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of:
- Newly diagnosed adult and pediatric patients with Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia (Ph+ CML) in chronic phase. (1.1)
- Patients with Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia (Ph+ CML) in blast crisis (BC), accelerated phase (AP), or in chronic phase (CP) after failure of interferon-alpha therapy. (1.2)
- Adult patients with relapsed or refractory Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL). (1.3)
- Pediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL) in combination with chemotherapy. (1.4)
- Adult patients with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases (MDS/MPD) associated with platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) gene re-arrangements. (1.5)
- Adult patients with aggressive systemic mastocytosis (ASM) without the D816V c-Kit mutation or with c-Kit mutational status unknown. (1.6)
- Adult patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES) and/or chronic eosinophilic leukemia (CEL) who have the FIP1L1-PDGFRα fusion kinase (mutational analysis or fluorescence in situ hybridization [FISH] demonstration of CHIC2 allele deletion) and for patients with HES and/or CEL who are FIP1L1-PDGFRα fusion kinase negative or unknown. (1.7)
- Adult patients with unresectable, recurrent and/or metastatic dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP). (1.8)
- Patients with Kit (CD117) positive unresectable and/or metastatic malignant gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST). (1.9)
- Adjuvant treatment of adult patients following resection of Kit (CD117) positive GIST. (1.10)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Adults with Ph+ CML CP (2.2): 400 mg/day
- Adults with Ph+ CML AP or BC (2.2): 600 mg/day
- Pediatrics with Ph+ CML CP (2.3): 340 mg/m2/day
- Adults with Ph+ ALL (2.4): 600 mg/day
- Pediatrics with Ph+ ALL (2.5): 340 mg/m2/day
- Adults with MDS/MPD (2.6): 400 mg/day
- Adults with ASM (2.7): 100 mg/day or 400 mg/day
- Adults with HES/CEL (2.8): 100 mg/day or 400 mg/day
- Adults with DFSP (2.9): 800 mg/day
- Adults with metastatic and/or unresectable GIST (2.10): 400 mg/day
- Adjuvant treatment of adults with GIST (2.11): 400 mg/day
- Patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment (2.12): 400 mg/day
- Patients with severe hepatic impairment (2.12): 300 mg/day
All doses of Imkeldi should be taken with a meal and a large glass of water. Doses of 400 mg or 600 mg should be administered once daily, whereas a dose of 800 mg should be administered as 400 mg twice a day. Imkeldi is intended for oral use only. It is important that Imkeldi be measured with an accurate measuring device. A household teaspoon is not an accurate measuring device. A pharmacist can provide an appropriate press-in bottle adapter and oral dispensing syringe and can provide instructions for measuring the correct dose. (2.1, 5.15)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Oral solution: 80 mg/mL of imatinib (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Fluid Retention and Edema: Edema and severe fluid retention have occurred. Weigh patients regularly and manage unexpected rapid weight gain by drug interruption and diuretics. (5.1, 6.1)
- Hematologic Toxicity: Cytopenias, particularly anemia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia, have occurred. Manage with dose reduction, dose interruption, or discontinuation of treatment. Perform complete blood counts weekly for the first month, biweekly for the second month, and periodically thereafter. (5.2)
- Congestive Heart Failure and Left Ventricular Dysfunction: Severe congestive heart failure and left ventricular dysfunction have been reported, particularly in patients with comorbidities and risk factors. Monitor and treat patients with cardiac disease or risk factors for cardiac failure. (5.3)
- Hepatotoxicity: Severe hepatotoxicity, including fatalities may occur. Assess liver function before initiation of treatment and monthly thereafter or as clinically indicated. Monitor liver function when combined with chemotherapy known to be associated with liver dysfunction. (5.4)
- Hemorrhage: Grade 3/4 hemorrhage has been reported in clinical studies in patients with newly diagnosed CML and with GIST. GI tumor sites may be the source of GI bleeds in GIST. (5.5)
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Gastrointestinal (GI) perforations, some fatal, have been reported. (5.6)
- Hypereosinophilic Cardiac Toxicity: Cardiogenic shock/left ventricular dysfunction has been associated with the initiation of Imkeldi in patients with conditions associated with high eosinophil levels (e.g., HES, MDS/MPD, and ASM). (5.7)
- Dermatologic Toxicities: Bullous dermatologic reactions (e.g., erythema multiforme and Stevens-Johnson syndrome) have been reported with the use of Imkeldi. (5.8)
- Hypothyroidism: Hypothyroidism has been reported in thyroidectomy patients undergoing levothyroxine replacement. Closely monitor TSH levels in such patients. (5.9)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to the fetus, and to use effective contraception. (5.10, 8.1)
- Growth Retardation in Children and Adolescents: Growth retardation occurring in children and pre-adolescents receiving Imkeldi has been reported. Close monitoring of growth in children under Imkeldi treatment is recommended. (5.11, 6.2)
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome: Close monitoring is recommended. (5.12)
- Impairments Related to Driving and Using Machinery: Motor vehicle accidents have been reported in patients receiving imatinib. Caution patients about driving a car or operating machinery. (5.13)
- Renal Toxicity: A decline in renal function may occur in patients receiving Imkeldi. Evaluate renal function at baseline and during therapy, with attention to risk factors for renal dysfunction. (5.14)
- Measuring Device: Advise patients to measure IMKELDI with an accurate milliliter measuring device. Inform patients that a household teaspoon is not an accurate measuring device and could lead to overdosage, which can result in serious adverse reactions. Advise patients to ask their pharmacist to recommend an appropriate press-in bottle adapter and oral dispensing syringe and for instructions for measuring the correct dose. (5.15)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequently reported adverse reactions (≥30%) are edema, nausea, vomiting, muscle cramps, musculoskeletal pain, diarrhea, rash, fatigue, and abdominal pain. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Shorla Oncology at 844-9-SHORLA or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
• CYP3A4 inducers: Avoid or increase imatinib dosage if unavoidable. (7.1)
• CYP3A4 inhibitors: Use caution. Avoid grapefruit juice. (7.2)
• CYP3A4 substrates: Use caution. Patients who require anticoagulation should receive other anticoagulants instead of warfarin. (7.3)
• CYP2D6 substrates: Use caution. (7.4)USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Lactation: Advise not to breastfeed.(8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 11/2024
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Newly Diagnosed Philadelphia Positive Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (Ph+ CML)
1.2 Ph+ CML in Blast Crisis (BC), Accelerated Phase (AP) or Chronic Phase (CP) After Interferon-alpha (IFN) Therapy
1.3 Adult Patients With Ph+ Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
1.4 Pediatric Patients With Ph+ Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
1.5 Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative Diseases (MDS/MPD)
1.6 Aggressive Systemic Mastocytosis (ASM)
1.7 Hypereosinophilic Syndrome (HES) and/or Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia (CEL)
1.8 Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans (DFSP)
1.9 Kit+ Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST)
1.10 Adjuvant Treatment of GIST
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
2.2 Adult Patients With Ph+ CML CP, AP, or BC
2.3 Pediatric Patients With Ph+ CML CP
2.4 Adult Patients With Ph+ ALL
2.5 Pediatric Patients With Ph+ ALL
2.6 Adult Patients With MDS/MPD
2.7 Adult Patients With ASM
2.8 Adult Patients With HES/CEL
2.9 Adult Patients With DFSP
2.10 Adult Patients With Metastatic and/or Unresectable GIST
2.11 Adult Patients With Adjuvant GIST
2.12 Dosage Modifications for Drug Interactions, Hepatic Impairment, and Renal Impairment
2.13 Dosage Modifications for Hepatotoxicity and Non-Hematologic Adverse Reactions
2.14 Dosage Modifications for Hematologic Adverse Reactions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Fluid Retention and Edema
5.2 Hematologic Toxicity
5.3 Congestive Heart Failure and Left Ventricular Dysfunction
5.4 Hepatotoxicity
5.5 Hemorrhage
5.6 Gastrointestinal Disorders
5.7 Hypereosinophilic Cardiac Toxicity
5.8 Dermatologic Toxicities
5.9 Hypothyroidism
5.10 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
5.11 Growth Retardation in Children and Adolescents
5.12 Tumor Lysis Syndrome
5.13 Impairments Related to Driving and Using Machinery
5.14 Renal Toxicity
5.15 Measuring Device
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Agents Inducing CYP3A Metabolism
7.2 Agents Inhibiting CYP3A Metabolism
7.3 Interactions With Drugs Metabolized by CYP3A4
7.4 Interactions With Drugs Metabolized by CYP2D6
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
8.7 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
14.2 Pediatric CML
14.3 Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
14.4 Pediatric ALL
14.5 Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative Diseases
14.6 Aggressive Systemic Mastocytosis
14.7 Hypereosinophilic Syndrome/Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia
14.8 Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans
14.9 Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Newly Diagnosed Philadelphia Positive Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (Ph+ CML)
Newly diagnosed adult and pediatric patients with Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia (Ph+ CML) in chronic phase.
1.2 Ph+ CML in Blast Crisis (BC), Accelerated Phase (AP) or Chronic Phase (CP) After Interferon-alpha (IFN) Therapy
Patients with Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia in blast crisis, accelerated phase, or in chronic phase after failure of interferon-alpha therapy.
1.3 Adult Patients With Ph+ Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
Adult patients with relapsed or refractory Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL).
1.4 Pediatric Patients With Ph+ Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
Pediatric patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL) in combination with chemotherapy.
1.5 Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative Diseases (MDS/MPD)
Adult patients with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases associated with platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) gene re-arrangements.
1.6 Aggressive Systemic Mastocytosis (ASM)
Adult patients with aggressive systemic mastocytosis without the D816V c-Kit mutation or with c-Kit mutational status unknown.
1.7 Hypereosinophilic Syndrome (HES) and/or Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia (CEL)
Adult patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome and/or chronic eosinophilic leukemia who have the FIP1L1-PDGFRα fusion kinase (mutational analysis or fluorescence in situ hybridization [FISH] demonstration of CHIC2 allele deletion) and for patients with HES and/or CEL who are FIP1L1-PDGFRα fusion kinase negative or unknown.
1.8 Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans (DFSP)
Adult patients with unresectable, recurrent and/or metastatic dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
All doses of Imkeldi should be taken with a meal and a large glass of water. Doses of 400 mg or 600 mg should be administered once daily, and a dose of 800 mg should be administered as 400 mg twice a day. If a dose is missed, the patient should wait until the next scheduled dose and not take two doses at the same time.
Imkeldi is intended for oral use only. It is important that Imkeldi be measured with an accurate measuring device [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15), Instructions for Use]. A household teaspoon is not an accurate measuring device. A pharmacist can provide a press-in bottle adapter and oral dispensing syringe and can provide instructions for measuring the correct dose.
Recommendations for Dose Rounding
Round each dose to the nearest measurable graduation mark on the oral syringe, if necessary [see Instructions for Use].
Continue treatment until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Imkeldi is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures1.
2.2 Adult Patients With Ph+ CML CP, AP, or BC
The recommended dosage of Imkeldi is 400 mg/day for adult patients in chronic phase CML and 600 mg/day for adult patients in accelerated phase or blast crisis.
In CML, a dose increase from 400 mg to 600 mg in adult patients with chronic phase disease, or from 600 mg to 800 mg (given as 400 mg twice daily) in adult patients in accelerated phase or blast crisis may be considered in the absence of severe adverse drug reaction and severe non-leukemia related neutropenia or thrombocytopenia in the following circumstances: disease progression (at any time), failure to achieve a satisfactory hematologic response after at least 3 months of treatment, failure to achieve a cytogenetic response after 6 to 12 months of treatment, or loss of a previously achieved hematologic or cytogenetic response.
2.3 Pediatric Patients With Ph+ CML CP
The recommended dosage of Imkeldi for pediatric patients with newly diagnosed Ph+ CML is 340 mg/m2/day (not to exceed 600 mg). Imkeldi treatment can be given as a once daily dose or the daily dose may be split into two–one portion doses in the morning and one portion in the evening. There is no experience with Imkeldi treatment in children under 1 year of age.
Follow recommendations for dose rounding [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
2.4 Adult Patients With Ph+ ALL
The recommended dosage of Imkeldi is 600 mg/day for adult patients with relapsed/refractory Ph+ ALL.
2.5 Pediatric Patients With Ph+ ALL
The recommended dosage of Imkeldi to be given in combination with chemotherapy to pediatric patients with newly diagnosed Ph+ ALL is 340 mg/m2/day (not to exceed 600 mg). Imkeldi treatment can be given as a once daily dose.
Follow recommendations for dose rounding [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
2.6 Adult Patients With MDS/MPD
Determine PDGFRb gene rearrangements status prior to initiating treatment.
The recommended dosage of Imkeldi is 400 mg/day for adult patients with MDS/MPD.
2.7 Adult Patients With ASM
Determine D816V c-Kit mutation status prior to initiating treatment.
The recommended dosage of Imkeldi is 400 mg/day for adult patients with ASM without the D816V c-Kit mutation. If c- Kit mutational status is not known or unavailable, treatment with Imkeldi 400 mg/day may be considered for patients with ASM not responding satisfactorily to other therapies. For patients with ASM associated with eosinophilia, a clonal hematological disease related to the fusion kinase FIP1L1-PDGFRα, a starting dose of 100 mg/day is recommended. Dose increase from 100 mg to 400 mg for these patients may be considered in the absence of adverse drug reactions if assessments demonstrate an insufficient response to therapy.
2.8 Adult Patients With HES/CEL
The recommended dosage of Imkeldi is 400 mg/day for adult patients with HES/CEL. For HES/CEL patients with demonstrated FIP1L1-PDGFRα fusion kinase, a starting dose of 100 mg/day is recommended. Dose increase from 100 mg to 400 mg for these patients may be considered in the absence of adverse drug reactions if assessments demonstrate an insufficient response to therapy.
2.9 Adult Patients With DFSP
The recommended dosage of Imkeldi is 800 mg/day for adult patients with DFSP.
2.10 Adult Patients With Metastatic and/or Unresectable GIST
The recommended dosage of Imkeldi is 400 mg/day for adult patients with unresectable and/or metastatic, malignant GIST. A dose increase up to 800 mg daily (given as 400 mg twice daily) may be considered, as clinically indicated, in patients showing clear signs or symptoms of disease progression at a lower dose and in the absence of severe adverse drug reactions.
2.11 Adult Patients With Adjuvant GIST
The recommended dosage of Imkeldi is 400 mg/day for the adjuvant treatment of adult patients following complete gross resection of GIST. In clinical trials, one year of imatinib and three years of imatinib were studied. In the patient population defined in Study 2, three years of Imkeldi is recommended [see Clinical Studies (14.8)]. The optimal treatment duration with Imkeldi is not known.
2.12 Dosage Modifications for Drug Interactions, Hepatic Impairment, and Renal Impairment
Drug Interactions
Concomitant Strong CYP3A4 inducers
Avoid concomitant use of strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., dexamethasone, phenytoin, carbamazepine, rifampin, rifabutin, rifampacin, phenobarbital) with Imkeldi. If concomitant use with a strong CYP3A4 inducer cannot be avoided the Imkeldi dosage should be increased by at least 50%, and clinical response should be carefully monitored [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Hepatic Impairment
A 25% decrease in the approved recommended Imkeldi dosage should be used for patients with severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin ˃3 to 10 times upper limit of normal [ULN] and any value for AST) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Patients with mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin ≤ ULN and aspartate aminotransferase [AST] > ULN, or total bilirubin ˃1 to 1.5 times ULN and any value for AST) and moderate hepatic impairment (total bilirubin ˃ 1.5 to 3 times ULN and any value for AST) do not require a dose adjustment and should be treated per the approved recommended dosage.
Renal Impairment
Imkeldi should be used with caution in patients with severe renal impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Patients with moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance [CLcr] = 20-39 mL/min) should receive a 50% decrease in the recommended starting dose and future doses can be increased as tolerated. Doses greater than 600 mg are not recommended in patients with mild renal impairment (CLcr = 40-59 mL/min). Doses greater than 400 mg are not recommended for patients with moderate renal impairment.
2.13 Dosage Modifications for Hepatotoxicity and Non-Hematologic Adverse Reactions
If elevations in bilirubin greater than 3 times the institutional upper limit of normal (IULN) or in liver transaminases greater than 5 times the IULN occur, Imkeldi should be withheld until bilirubin levels have returned to a less than 1.5 times the IULN and transaminase levels to less than 2.5 times the IULN. In adults, treatment with Imkeldi may then be continued at a reduced daily dose (i.e., 400 mg to 300 mg, 600 mg to 400 mg, or 800 mg to 600 mg). In children, daily doses can be reduced under the same circumstances from 340 mg/m2/day to 260 mg/m2/day.
If a severe non-hematologic adverse reaction develops (such as severe hepatotoxicity or severe fluid retention), Imkeldi should be withheld until the event has resolved. Thereafter, treatment can be resumed as appropriate depending on the initial severity of the reaction.
2.14 Dosage Modifications for Hematologic Adverse Reactions
Dose reduction or treatment interruptions for severe neutropenia and thrombocytopenia are recommended as indicated in Table 1.
Table 1: Dose Adjustments for Neutropenia and Thrombocytopenia ASM associated with eosinophilia (starting dose 100 mg)
ANC less than 1 x 109/L and/or
platelets less than 50 x 109/L
- Stop Imkeldi until ANC greater than or equal to 1.5 x 109/L and platelets greater than or equal to 75 x 109/L
- Resume treatment with Imkeldi at previous dose (i.e., dose before severe adverse reaction)
HES/CEL with FIP1L1-PDGFRα
fusion kinase (starting dose 100 mg)
ANC less than 1 x 109/L and/or
platelets less than 50 x 109/L
- Stop Imkeldi until ANC greater than or equal to 1.5 x 109/L and platelets greater than or equal to 75 x 109/L
- Resume treatment with Imkeldi at previous dose (i.e., dose before severe adverse reaction)
Chronic Phase CML (starting dose 400 mg)
MDS/MPD, ASM and HES/CEL
(starting dose 400 mg)
GIST (starting dose 400 mg)
ANC less than 1 x 109/L and/or
platelets less than 50 x 109/L- Stop Imkeldi until ANC greater than or equal to 1.5 x 109/L and platelets greater than or equal to 75 x 109/L
- Resume treatment with Imkeldi at the original starting dose of 400 mg
- If recurrence of ANC less than 1 x 109/L and/or platelets less than 50 x 109/L, repeat step 1 and resume Imkeldi at a reduced dose of 300 mg
Ph+ CML: Accelerated Phase and Blast Crisis (starting dose 600 mg)
Ph+ ALL
(starting dose 600 mg)
ANC less than 0.5 x 109/L and/or
platelets less than 10 x 109/L
- Check if cytopenia is related to leukemia (marrow aspirate or biopsy)
- If cytopenia is unrelated to leukemia, reduce dose of Imkeldi to 400 mg
- If cytopenia persists 2 weeks, reduce further to 300 mg
- If cytopenia persists 4 weeks and is still unrelated to leukemia, stop Imkeldi until ANC greater than or equal to 1 x 109/L and platelets greater than or equal to 20 x 109/L and then resume treatment at 300 mg
DFSP
(starting dose 800 mg)
ANC less than 1 x 109/L and/or
platelets less than 50 x 109/L
- Stop Imkeldi until ANC greater than or equal to 1.5 x 109/L and platelets greater than or equal to 75 x 109/L
- Resume treatment with Imkeldi at 600 mg
- In the event of recurrence of ANC less than 1 x 109/L and/or platelets less than 50 x 109/L, repeat step 1 and resume Imkeldi at reduced dose of 400 mg
Pediatric newly diagnosed chronic phase CML
(starting dose 340 mg/m2)
ANC less than 1 x 109/L and/or
platelets less than 50 x 109/L
- Stop Imkeldi until ANC greater than or equal to 1.5 x 109/L and platelets greater than or equal to 75 x 109/L
- Resume treatment with Imkeldi at previous dose (i.e., dose before severe adverse reaction)
- In the event of recurrence of ANC less than 1 x 109/L and/or platelets less than 50 x 109/L, repeat step 1 and resume Imkeldi at reduced dose of 260 mg/m2
Abbreviations: ANC, absolute neutrophil count; ASM, aggressive systemic mastocytosis; CEL, chronic eosinophilic leukemia; CML, chronic myeloid leukemia; DFSP, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans; HES, hypereosinophilic syndrome; MDS/MPD, myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative diseases; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor; Ph+ CML, Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia; Ph+ ALL, Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Fluid Retention and Edema
Imatinib can cause edema and occasionally serious fluid retention [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Weigh and monitor patients regularly for signs and symptoms of fluid retention. Investigate unexpected rapid weight gain carefully and provide appropriate treatment. The probability of edema was increased with higher imatinib dose and age greater than 65 years in the CML studies. Severe superficial edema was reported in 1.5% of newly diagnosed CML patients taking imatinib, and in 2% to 6% of other adult CML patients taking imatinib. In addition, other severe fluid retention (e.g., pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, pulmonary edema, and ascites) reactions were reported in 1.3% of newly diagnosed CML patients taking imatinib, and in 2% to 6% of other adult CML patients taking imatinib. Severe fluid retention was reported in 9% to 13.1% of patients taking imatinib for GIST [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. In a randomized trial in patients with newly diagnosed Ph+ CML in chronic phase comparing imatinib and nilotinib, severe (Grade 3 or 4) fluid retention occurred in 2.5% of patients receiving imatinib and in 3.9% of patients receiving nilotinib 300 mg twice daily.
Effusions (including pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, ascites) or pulmonary edema were observed in 2.1% (none were Grade 3 or 4) of patients in the imatinib arm and 2.2% (0.7% Grade 3 or 4) of patients in the nilotinib 300 mg twice daily arm.
5.2 Hematologic Toxicity
Treatment with imatinib can cause anemia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia. Perform complete blood counts weekly for the first month, biweekly for the second month, and periodically thereafter as clinically indicated (for example, every 2 to 3 months). In CML, the occurrence of these cytopenias is dependent on the stage of disease and is more frequent in patients with accelerated phase CML or blast crisis than in patients with chronic phase CML. In pediatric CML patients the most frequent toxicities observed were Grade 3 or 4 cytopenias, including neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and anemia. These generally occur within the first several months of therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.14)].
5.3 Congestive Heart Failure and Left Ventricular Dysfunction
Congestive heart failure and left ventricular dysfunction have been reported in patients taking imatinib. Cardiac adverse reactions were more frequent in patients with advanced age or co-morbidities, including previous medical history of cardiac disease. In an international randomized Phase 3 study in 1106 patients with newly diagnosed Ph+ CML in chronic phase, severe cardiac failure and left ventricular dysfunction were observed in 0.7% of patients taking imatinib compared to 0.9% of patients taking IFN + Ara-C. In another randomized trial with newly diagnosed Ph+ CML patients in chronic phase that compared imatinib and nilotinib, cardiac failure was observed in 1.1% of patients in the imatinib arm and 2.2% of patients in the nilotinib 300 mg twice daily arm and severe (Grade 3 or 4) cardiac failure occurred in 0.7% of patients in each group. Carefully monitor patients with cardiac disease or risk factors for cardiac or history of renal failure.
Evaluate and treat any patient with signs or symptoms consistent with cardiac or renal failure.
5.4 Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity, occasionally severe, may occur with Imkeldi [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Cases of fatal liver failure and severe liver injury requiring liver transplants have been reported with both short-term and long-term use of imatinib. Monitor liver function (transaminases, bilirubin, and alkaline phosphatase) before initiation of treatment and monthly, or as clinically indicated. Manage laboratory abnormalities with Imkeldi interruption and/or dose reduction [see Dosage and Administration (2.13)]. When imatinib is combined with chemotherapy, liver toxicity in the form of transaminase elevation and hyperbilirubinemia has been observed. Additionally, there have been reports of acute liver failure.
Monitoring of hepatic function is recommended.
5.5 Hemorrhage
In a trial of imatinib versus IFN+Ara-C in patients with the newly diagnosed CML, 1.8% of patients had Grade 3/4 hemorrhage. In the Phase 3 unresectable or metastatic GIST studies, 211 patients (12.9%) reported Grade 3/4 hemorrhage at any site. In the Phase 2 unresectable or metastatic GIST study, 7 patients (5%) had a total of 8 CTC Grade 3/4 hemorrhages; gastrointestinal (GI) (3 patients), intra-tumoral (3 patients) or both (1 patient). Gastrointestinal tumor sites may have been the source of GI hemorrhages. In a randomized trial in patients with newly diagnosed Ph+ CML in chronic phase comparing imatinib and nilotinib, GI hemorrhage occurred in 1.4% of patients in the imatinib arm, and in 2.9% of patients in the nilotinib 300 mg twice daily arm. None of these events were Grade 3 or 4 in the imatinib arm; 0.7% were Grade 3 or 4 in the nilotinib 300 mg twice daily arm. In addition, gastric antral vascular ectasia has been reported in postmarketing experience.
5.6 Gastrointestinal Disorders
Imatinib can cause GI irritation. Imkeldi should be taken with food and a large glass of water to minimize this problem. There have been rare reports, including fatalities, of GI perforation.
5.7 Hypereosinophilic Cardiac Toxicity
In patients with hypereosinophilic syndrome with occult infiltration of HES cells within the myocardium, cases of cardiogenic shock/left ventricular dysfunction have been associated with HES cell degranulation upon the initiation of Imkeldi therapy. The condition was reported to be reversible with the administration of systemic steroids, circulatory support measures and temporarily withholding Imkeldi.
Myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative disease and systemic mastocytosis may be associated with high eosinophil levels. Consider performing an echocardiogram and determining serum troponin in patients with HES/CEL, and in patients with MDS/MPD or ASM associated with high eosinophil levels. If either is abnormal, consider prophylactic use of systemic steroids (1-2 mg/kg) for one to two weeks concomitantly with Imkeldi at the initiation of therapy.
5.8 Dermatologic Toxicities
Bullous dermatologic reactions, including erythema multiforme and Stevens-Johnson syndrome, have been reported with use of imatinib. In some cases of bullous dermatologic reactions, including erythema multiforme and Stevens-Johnson syndrome reported during postmarketing surveillance, a recurrent dermatologic reaction was observed upon rechallenge. Several foreign postmarketing reports have described cases in which patients tolerated the reintroduction of imatinib therapy after resolution or improvement of the bullous reaction. In these instances, imatinib was resumed at a dose lower than that at which the reaction occurred and some patients also received concomitant treatment with corticosteroids or antihistamines.
5.9 Hypothyroidism
Clinical cases of hypothyroidism have been reported in thyroidectomy patients undergoing levothyroxine replacement during treatment with imatinib. Monitor TSH levels in such patients.
5.10 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Imkeldi can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Imatinib mesylate was teratogenic in rats when administered during organogenesis at doses approximately equal to the maximum human dose of 800 mg/day based on body surface area (BSA). Significant post-implantation loss was seen in female rats administered imatinib mesylate at doses approximately one-half the maximum human dose of 800 mg/day based on BSA. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception (methods that result in less than 1% pregnancy rates) when using Imkeldi and for 14 days after stopping Imkeldi. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
5.11 Growth Retardation in Children and Adolescents
Growth retardation has been reported in children and pre-adolescents receiving imatinib. The long-term effects of prolonged treatment with Imkeldi on growth in children are unknown. Therefore, monitor growth in children under Imkeldi treatment [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.12 Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Cases of Tumor Lysis Syndrome (TLS), including fatal cases, have been reported in patients with CML, GIST, ALL, and eosinophilic leukemia receiving imatinib. The patients at risk of TLS are those with tumors having a high proliferative rate or high tumor burden prior to treatment. Monitor these patients closely and take appropriate precautions. Due to possible occurrence of TLS, correct clinically significant dehydration and treat high uric acid levels prior to initiation of Imkeldi.
5.13 Impairments Related to Driving and Using Machinery
Motor vehicle accidents have been reported in patients receiving imatinib. Advise patients that they may experience side effects, such as dizziness, blurred vision, or somnolence during treatment with Imkeldi. Recommend caution when driving a car or operating machinery.
5.14 Renal Toxicity
A decline in renal function may occur in patients receiving Imkeldi. Median estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) values in patients on imatinib 400 mg daily for newly-diagnosed CML (four randomized trials) and malignant GIST (one single-arm trial) declined from a baseline value of 85 mL/min/1.73 m2 (N = 1190) to 75 mL/min/1.73 m2 at 12 months (N = 1082) and 69 mL/min/1.73 m2 at 60 months (N = 549). Evaluate renal function prior to initiating Imkeldi and monitor during therapy, with attention to risk factors for renal dysfunction, such as preexisting renal impairment, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and congestive heart failure.
5.15 Measuring Device
Advise patients to measure Imkeldi with an accurate milliliter measuring device. Inform patients that a household teaspoon is not an accurate measuring device and could lead to overdosage, which can result in serious adverse reactions. Advise patients to ask their pharmacist to recommend an appropriate press-in bottle adapter and oral dispensing syringe and for instructions for measuring the correct dose [see Instructions for Use].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Fluid Retention and Edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hematologic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Congestive Heart Failure and Left Ventricular Dysfunction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hemorrhage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Gastrointestinal Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Hypereosinophilic Cardiac Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Dermatologic Toxicities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Hypothyroidism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Growth Retardation in Children and Adolescents [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Impairments Related to Driving and Using Machinery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Renal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
The majority of imatinib-treated patients experienced adverse reactions at some time. Imatinib was discontinued due to drug-related adverse reactions in 2.4% of patients receiving imatinib in the randomized trial of newly diagnosed patients with Ph+ CML in chronic phase comparing imatinib versus IFN+Ara-C, and in 12.5% of patients receiving imatinib in the randomized trial of newly diagnosed patients with Ph+ CML in chronic phase comparing imatinib and nilotinib. Imatinib was discontinued due to drug-related adverse reactions in 4% of patients in chronic phase after failure of interferon-alpha therapy, in 4% of patients in accelerated phase and in 5% of patients in blast crisis.
The most frequently reported drug-related adverse reactions were edema, nausea and vomiting, muscle cramps, musculoskeletal pain, diarrhea and rash (Table 2 and Table 3 for newly diagnosed CML, Table 4 for other CML patients). Edema was most frequently periorbital or in lower limbs and was managed with diuretics, other supportive measures, or by reducing the dose of imatinib [see Dosage and Administration (2.13)]. The frequency of severe superficial edema was 1.5%-6%.
A variety of adverse reactions represent local or general fluid retention, including pleural effusion, ascites, pulmonary edema, and rapid weight gain with or without superficial edema. These reactions appear to be dose related, were more common in the blast crisis and accelerated phase studies (where the dose was 600 mg/day), and are more common in the elderly. These reactions were usually managed by interrupting imatinib treatment and using diuretics or other appropriate supportive care measures. These reactions may be serious or life threatening.
Adverse reactions, regardless of relationship to study drug, that were reported in at least 10% of the imatinib-treated patients are shown in Tables 2, 3, and 4.
Table 2: Adverse Reactions Regardless of Relationship to Study Drug Reported in Newly Diagnosed CML Clinical Trial in the Imatinib Versus IFN+Ara-C Study (Greater Than or Equal to 10% of Imatinib-Treated Patients)* - *
- All adverse reactions occurring in greater than or equal to 10% of imatinib-treated patients are listed regardless of suspected relationship to treatment.
- †
- NCI Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 3.0.
- ‡
- Other fluid retention reactions include pleural effusion, ascites, pulmonary edema, pericardial effusion, anasarca, edema aggravated, and fluid retention not otherwise specified.
All Grades CTC Grades† 3/4 Preferred term Imatinib
N = 551 (%)IFN+Ara-C
N = 533 (%)Imatinib
N = 551 (%)IFN+Ara-C
N = 533 (%)Fluid retention 61.7 11.1 2.5 0.9 - Superficial edema 59.9 9.6 1.5 0.4 - Other fluid retention reactions‡ 6.9 1.9 1.3 0.6 Nausea 49.5 61.5 1.3 5.1 Muscle cramps 49.2 11.8 2.2 0.2 Musculoskeletal pain 47.0 44.8 5.4 8.6 Diarrhea 45.4 43.3 3.3 3.2 Rash and related terms 40.1 26.1 2.9 2.4 Fatigue 38.8 67.0 1.8 25.1 Headache 37.0 43.3 0.5 3.8 Joint pain 31.4 38.1 2.5 7.7 Abdominal pain 36.5 25.9 4.2 3.9 Nasopharyngitis 30.5 8.8 0 0.4 Hemorrhage 28.9 21.2 1.8 1.7 - GI hemorrhage 1.6 1.1 0.5 0.2 - CNS hemorrhage 0.2 0.4 0 0.4 Myalgia 24.1 38.8 1.5 8.3 Vomiting 22.5 27.8 2.0 3.4 Dyspepsia 18.9 8.3 0 0.8 Cough 20.0 23.1 0.2 0.6 Pharyngolaryngeal pain 18.1 11.4 0.2 0 Upper respiratory tract infection 21.2 8.4 0.2 0.4 Dizziness 19.4 24.4 0.9 3.8 Pyrexia 17.8 42.6 0.9 3.0 Weight increased 15.6 2.6 2.0 0.4 Insomnia 14.7 18.6 0 2.3 Depression 14.9 35.8 0.5 13.1 Influenza 13.8 6.2 0.2 0.2 Bone pain 11.3 15.6 1.6 3.4 Constipation 11.4 14.4 0.7 0.2 Sinusitis 11.4 6.0 0.2 0.2 Abbreviations: CML, chronic myeloid leukemia; CNS, central nervous system; CTC, common terminology criteria; GI, gastrointestinal; IFN, Interferon-alpha. Table 3: Most Frequently Reported Non-Hematologic Adverse Reactions (regardless of relationship to study drug) in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Ph+ CML-CP in the Imatinib Versus Nilotinib Study (Greater Than or Equal to 10% in Imatinib 400 mg Once Daily or Nilotinib 300 mg Twice Daily Groups) 60-Month Analysis* Patients with newly diagnosed Ph+ CML-CP Imatinib
400 mg
once daily
N = 280
Nilotinib
300 mg
twice daily
N = 279
Imatinib
400 mg
once daily
N = 280
Nilotinib
300 mg
twice daily
N = 279
Body system and preferred term All Grades (%) CTC Grades† 3/4 (%) Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders Rash > 19 38 2 < 1 Pruritus 7 21 0 < 1 Alopecia 7 13 0 0 Dry skin 6 12 0 0 Gastrointestinal disorders Nausea 41 22 2 2 Constipation 8 20 0 < 1 Diarrhea 46 19 4 1 Vomiting 27 15 < 1 < 1 Abdominal pain upper 14 18 < 1 1 Abdominal pain 12 15 0 2 Dyspepsia 12 10 0 0 Nervous system disorders Headache 23 32 < 1 3 Dizziness 11 12 < 1 < 1 General disorders and administration-site conditions Fatigue 20 23 1 1 Pyrexia 13 14 0 < 1 Asthenia 12 14 0 < 1 Peripheral edema 20 9 0 < 1 Face edema 14 < 1 < 1 0 Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders Myalgia 19 19 < 1 < 1 Arthralgia 17 22 < 1 < 1 Muscle spasms 34 12 1 0 Pain in extremity 16 15 < 1 < 1 Back pain 17 19 1 1 Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders Cough 13 17 0 0 Oropharyngeal pain 6 12 0 0 Dyspnea 6 11 < 1 2 Infections and infestations Nasopharyngitis 21 27 0 0 Upper respiratory tract infection 14 17 0 < 1 Influenza 9 13 0 0 Gastroenteritis 10 7 < 1 0 Eye disorders Eyelid edema 19 1 < 1 0 Periorbital edema 15 < 1 0 0 Psychiatric disorders Insomnia 9 11 0 0 Vascular disorder Hypertension 4 10 < 1 1 Abbreviation: Ph+ CML-CP, Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia-chronic phase. Table 4: Adverse Reactions Regardless of Relationship to Study Drug Reported in Other CML Clinical Trials (Greater Than or Equal to 10% of All Patients in Any Trial)* - *
- All adverse reactions occurring in greater than or equal to 10% of patients are listed regardless of suspected relationship to treatment.
- †
- Other fluid retention reactions include pleural effusion, ascites, pulmonary edema, pericardial effusion, anasarca, edema aggravated, and fluid retention not otherwise specified.
Myeloid blast Crisis
(n = 260)Accelerated phase
(n = 235)
Chronic phase, IFN failure
(n = 532)
% % % Preferred term All Grades Grade 3/4 All Grades Grade 3/4 All Grades Grade 3/4 Fluid retention 72 11 76 6 69 4 -Superficial edema 66 6 74 3 67 2 -Other fluid retention reactions † 22 6 15 4 7 2 Nausea 71 5 73 5 63 3 Muscle cramps 28 1 47 0.4 62 2 Vomiting 54 4 58 3 36 2 Diarrhea 43 4 57 5 48 3 Hemorrhage 53 19 49 11 30 2 - CNS hemorrhage 9 7 3 3 2 1 - GI hemorrhage 8 4 6 5 2 0.4 Musculoskeletal pain 42 9 49 9 38 2 Fatigue 30 4 46 4 48 1 Skin rash 36 5 47 5 47 3 Pyrexia 41 7 41 8 21 2 Arthralgia 25 5 34 6 40 1 Headache 27 5 32 2 36 0.6 Abdominal pain 30 6 33 4 32 1 Weight increased 5 1 17 5 32 7 Cough 14 0.8 27 0.9 20 0 Dyspepsia 12 0 22 0 27 0 Myalgia 9 0 24 2 27 0.2 Nasopharyngitis 10 0 17 0 22 0.2 Asthenia 18 5 21 5 15 0.2 Dyspnea 15 4 21 7 12 0.9 Upper respiratory tract infection 3 0 12 0.4 19 0 Anorexia 14 2 17 2 7 0 Night sweats 13 0.8 17 1 14 0.2 Constipation 16 2 16 0.9 9 0.4 Dizziness 12 0.4 13 0 16 0.2 Pharyngitis 10 0 12 0 15 0 Insomnia 10 0 14 0 14 0.2 Pruritus 8 1 14 0.9 14 0.8 Hypokalemia 13 4 9 2 6 0.8 Pneumonia 13 7 10 7 4 1 Anxiety 8 0.8 12 0 8 0.4 Liver toxicity 10 5 12 6 6 3 Rigors 10 0 12 0.4 10 0 Chest pain 7 2 10 0.4 11 0.8 Influenza 0.8 0.4 6 0 11 0.2 Sinusitis 4 0.4 11 0.4 9 0.4 Abbreviations: CML, chronic myeloid leukemia; IFN, Interferon-alpha. Hematologic and Biochemistry Laboratory Abnormalities
Cytopenias, and particularly neutropenia and thrombocytopenia, were a consistent finding in all studies, with a higher frequency at doses greater than or equal to 750 mg (Phase 1 study). The occurrence of cytopenias in CML patients was also dependent on the stage of the disease.
In patients with newly diagnosed CML, cytopenias were less frequent than in the other CML patients (see Tables 5, 6, and 7). The frequency of Grade 3 or 4 neutropenia and thrombocytopenia was between 2- and 3-fold higher in blast crisis and accelerated phase compared to chronic phase (see Tables 4 and 5). The median duration of the neutropenic and thrombocytopenic episodes varied from 2 to 3 weeks, and from 2 to 4 weeks, respectively.
These reactions can usually be managed with either a reduction of the dose or an interruption of treatment with imatinib, but may require permanent discontinuation of treatment.
Table 5: Laboratory Abnormalities in Newly Diagnosed CML Clinical Trial (Imatinib Versus IFN+Ara-C) - *
- p less than 0.001 (difference in Grade 3 plus 4 abnormalities between the two treatment groups).
Imatinib
N = 551
IFN+Ara-C
N = 533
% % CTC Grades Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 3 Grade 4 Hematology parameters* - Neutropenia* 13.1 3.6 20.8 4.5 - Thrombocytopenia* 8.5 0.4 15.9 0.6 - Anemia 3.3 1.1 4.1 0.2 Biochemistry parameters - Elevated creatinine 0 0 0.4 0 - Elevated bilirubin 0.9 0.2 0.2 0 - Elevated alkaline phosphatase 0.2 0 0.8 0 - Elevated SGOT (AST)/SGPT (ALT) 4.7 0.5 7.1 0.4 Abbreviations: CML, chronic myeloid leukemia; IFN, Interferon-alpha; SGOT, serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase is now referred to as aspartate aminotransferase (AST); SGPT, serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase is now referred to as alanine aminotransferase (ALT). Table 6: Percent Incidence of Clinically Relevant Grade 3/4* Laboratory Abnormalities in the Newly Diagnosed CML Clinical Trial (Imatinib Versus Nilotinib) - *
- NCI Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 3.0.
Imatinib 400 mg
once dailyNilotinib 300 mg
twice dailyN = 280 N = 279 (%) (%) Hematologic parameters Thrombocytopenia 9 10 Neutropenia 22 12 Anemia 6 4 Biochemistry parameters Elevated lipase 4 9 Hyperglycemia < 1 7 Hypophosphatemia 10 8 Elevated bilirubin (total) < 1 4 Elevated SGPT (ALT) 3 4 Hyperkalemia 1 2 Hyponatremia < 1 1 Hypokalemia 2 < 1 Elevated SGOT (AST) 1 1 Decreased albumin < 1 0 Hypocalcemia < 1 < 1 Elevated alkaline phosphatase < 1 0 Elevated creatinine < 1 0 Abbreviations: CML, chronic myeloid leukemia; SGOT, serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase is now referred to as aspartate aminotransferase (AST); SGPT, serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase is now referred to as alanine aminotransferase (ALT). Table 7: Laboratory Abnormalities in Other CML Clinical Trials - *
- CTC Grades: neutropenia (Grade 3 greater than or equal to 0.5-1.0 x 109/L, Grade 4 less than 0.5 x 109/L), thrombocytopenia (Grade 3 greater than or equal to 10-50 x 109/L, Grade 4 less than 10 x 109/L), anemia (hemoglobin greater than or equal to 65-80 g/L, Grade 4 less than 65 g/L), elevated creatinine (Grade 3 greater than 3-6 x upper limit normal range [ULN], Grade 4 greater than 6 x ULN), elevated bilirubin (Grade 3 greater than 3-10 x ULN, Grade 4 greater than 10 x ULN), elevated alkaline phosphatase (Grade 3 greater than 5-20 x ULN, Grade 4 greater than 20 x ULN), elevated SGOT or SGPT (Grade 3 greater than 5-20 x ULN, Grade 4 greater than 20 x ULN).
Myeloid blast crisis Accelerated phase Chronic phase, IFN failure (n = 260) (n = 235) (n = 532) 600 mg n = 223 600 mg n = 158 400 mg n = 37 400 mg n = 77 400 mg % % % CTC Grades * Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 3 Grade 4 Hematology parameters - Neutropenia 16 48 23 36 27 9 - Thrombocytopenia 30 33 31 13 21 < 1 - Anemia 42 11 34 7 6 1 Biochemistry parameters - Elevated creatinine 1.5 0 1.3 0 0.2 0 - Elevated bilirubin 3.8 0 2.1 0 0.6 0 - Elevated alkaline phosphatase 4.6 0 5.5 0.4 0.2 0 - Elevated SGOT (AST) 1.9 0 3.0 0 2.3 0 - Elevated SGPT (ALT) 2.3 0.4 4.3 0 2.1 0 Abbreviations: CML, chronic myeloid leukemia; CTC, common terminology criteria; IFN, Interferon-alpha; SGOT, serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase is now referred to as aspartate aminotransferase (AST); SGPT, serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase is now referred to as alanine aminotransferase (ALT). Hepatotoxicity
Severe elevation of transaminases or bilirubin occurred in approximately 5% of CML patients (see Tables 6 and 7) and were usually managed with dose reduction or interruption (the median duration of these episodes was approximately 1 week). Treatment was discontinued permanently because of liver laboratory abnormalities in less than 1.0% of CML patients. One patient, who was taking acetaminophen regularly for fever, died of acute liver failure. In the Phase 2 GIST trial, Grade 3 or 4 SGPT (ALT) elevations were observed in 6.8% of patients and Grade 3 or 4 SGOT (AST) elevations were observed in 4.8% of patients. Bilirubin elevation was observed in 2.7% of patients.
Adverse Reactions in Pediatric Population
Single-Agent Therapy
The overall safety profile of pediatric patients treated with imatinib in 93 children studied was similar to that found in studies with adult patients, except that musculoskeletal pain was less frequent (20.5%) and peripheral edema was not reported. Nausea and vomiting were the most commonly reported individual adverse reactions with an incidence similar to that seen in adult patients. Most patients experienced adverse reactions at some time during the study. The incidence of Grade 3/4 events across all types of adverse reactions was 75%; the events with the highest Grade 3/4 incidence in CML pediatric patients were mainly related to myelosuppression.
In Combination with Multi-Agent Chemotherapy
Pediatric and young adult patients with very high risk ALL, defined as those with an expected 5 year event-free survival (EFS) less than 45%, were enrolled after induction therapy on a multicenter, non-randomized cooperative group pilot protocol. The study population included patients with a median age of 10 years (1 to 21 years), 61% of whom were male, 75% were White, 7% were Black, and 6% were Asian/Pacific Islander. Patients with Ph+ ALL (n = 92) were assigned to receive imatinib and treated in 5 successive cohorts. Imatinib exposure was systematically increased in successive cohorts by earlier introduction and more prolonged duration.
The safety of imatinib given in combination with intensive chemotherapy was evaluated by comparing the incidence of Grade 3 and 4 adverse events, neutropenia (less than 750/mcL) and thrombocytopenia (less than 75,000/mcL) in the 92 patients with Ph+ ALL compared to 65 patients with Ph- ALL enrolled on the trial who did not receive imatinib. The safety was also evaluated comparing the incidence of adverse events in cycles of therapy administered with or without imatinib. The protocol included up to 18 cycles of therapy. Patients were exposed to a cumulative total of 1425 cycles of therapy, 778 with imatinib, and 647 without imatinib. The adverse events that were reported with a 5% or greater incidence in patients with Ph+ ALL compared to Ph- ALL or with a 1% or greater incidence in cycles of therapy that included imatinib are presented in Table 8.
Table 8: Adverse Reactions Reported More Frequently in Patients Treated With Study Drug (Greater Than 5%) or in Cycles With Study Drug (Greater Than 1%) - *
- Defined as the frequency of adverse events (AEs) per patient per treatment cycles that included imatinib (includes patients with Ph+ ALL that received cycles with imatinib).
- †
- Defined as the frequency of AEs per patient per treatment cycles that did not include imatinib (includes patients with Ph+ ALL that received cycles without imatinib as well as all patients with Ph- ALL who did not receive imatinib in any treatment cycle).
Adverse event Per patient incidence Ph+ ALL
with Imatinib N = 92
n (%)Per patient incidence Ph- ALL
no Imatinib N = 65 n (%)Per patient per cycle incidence
with Imatinib* N = 778
n (%)Per patient per cycle incidence
no Imatinib† N = 647
n (%)Grade 3 and 4 adverse events Nausea and/or vomiting 15 (16) 6 (9) 28 (4) 8 (1) Hypokalemia 31 (34) 16 (25) 72 (9) 32 (5) Pneumonitis 7 (8) 1 (1) 7 (1) 1 (< 1) Pleural effusion 6 (7) 0 6 (1) 0 Abdominal pain 8 (9) 2 (3) 9 (1) 3 (< 1) Anorexia 10 (11) 3 (5) 19 (2) 4 (1) Hemorrhage 11 (12) 4 (6) 17 (2) 8 (1) Hypoxia 8 (9) 2 (3) 12 (2) 2 (< 1) Myalgia 5 (5) 0 4 (1) 1 (< 1) Stomatitis 15 (16) 8 (12) 22 (3) 14 (2) Diarrhea 8 (9) 3 (5) 12 (2) 3 (< 1) Rash/Skin disorder 4 (4) 0 5 (1) 0 Infection 49 (53) 32 (49) 131 (17) 92 (14) Hepatic (transaminase and/or bilirubin) 52 (57) 38 (58) 172 (22) 113 (17) Hypotension 10 (11) 5 (8) 16 (2) 6 (1) Myelosuppression Neutropenia (< 750/mcL) 92 (100) 63 (97) 556 (71) 218 (34) Thrombocytopenia (< 75,000/mcL) 90 (92) 63 (97) 431 (55) 329 (51) Abbreviations: Ph+ ALL, Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia; Ph- ALL, Philadelphia chromosome negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Adverse Reactions in Other Subpopulations
In older patients (greater than or equal to 65 years old), with the exception of edema, where it was more frequent, there was no evidence of an increase in the incidence or severity of adverse reactions. In women there was an increase in the frequency of neutropenia, as well as Grade 1/2 superficial edema, headache, nausea, rigors, vomiting, rash, and fatigue. No differences were seen that were related to race but the subsets were too small for proper evaluation.
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
The adverse reactions were similar for Ph+ ALL as for Ph+ CML. The most frequently reported drug-related adverse reactions reported in the Ph+ ALL studies were mild nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, myalgia, muscle cramps, and rash. Superficial edema was a common finding in all studies and were described primarily as periorbital or lower limb edemas. These edemas were reported as Grade 3/4 events in 6.3% of the patients and may be managed with diuretics, other supportive measures, or in some patients by reducing the dose of imatinib.
Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative Diseases
Adverse reactions, regardless of relationship to study drug, that were reported in at least 10% of the patients treated with imatinib for MDS/MPD in the Phase 2 study, are shown in Table 9.
Table 9: Adverse Reactions Regardless of Relationship to Study Drug Reported (More Than One Patient) in MPD Patients in the Phase 2 Study (Greater Than or Equal to 10% All Patients) All Grades N = 7 Preferred term n (%) Nausea 4 (57.1) Diarrhea 3 (42.9) Anemia 2 (28.6) Fatigue 2 (28.6) Muscle cramp 3 (42.9) Arthralgia 2 (28.6) Periorbital edema 2 (28.6) Abbreviation: MPD, myeloproliferative disease. Aggressive Systemic Mastocytosis
All aggressive systemic mastocytosis (ASM) patients experienced at least one adverse reaction at some time. The most frequently reported adverse reactions were diarrhea, nausea, ascites, muscle cramps, dyspnea, fatigue, peripheral edema, anemia, pruritus, rash, and lower respiratory tract infection. None of the 5 patients in the Phase 2 study with ASM discontinued imatinib due to drug-related adverse reactions or abnormal laboratory values.
Hypereosinophilic Syndrome and Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia
The safety profile in the HES/CEL patient population does not appear to be different from the safety profile of imatinib observed in other hematologic malignancy populations, such as Ph+ CML. All patients experienced at least one adverse reaction, the most common being GI, cutaneous and musculoskeletal disorders. Hematological abnormalities were also frequent, with instances of CTC Grade 3 leukopenia, neutropenia, lymphopenia, and anemia.
Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans
Adverse reactions, regardless of relationship to study drug, that were reported in at least 10% of the 12 patients treated with imatinib for DFSP in the Phase 2 study are shown in Table 10.
Table 10: Adverse Reactions Regardless of Relationship to Study Drug Reported in DFSP Patients in the Phase 2 Study (Greater Than or Equal to 10% All Patients) All Grades N = 12 Preferred term n (%) Nausea 5 (41.7) Diarrhea 3 (25.0) Vomiting 3 (25.0) Periorbital edema 4 (33.3) Face edema 2 (16.7) Rash 3 (25.0) Fatigue 5 (41.7) Peripheral edema 4 (33.3) Pyrexia 2 (16.7) Eye edema 4 (33.3) Lacrimation increased 3 (25.0) Dyspnea exertional 2 (16.7) Anemia 3 (25.0) Rhinitis 2 (16.7) Anorexia 2 (16.7) Abbreviation: DFSP, dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. Clinically relevant or severe laboratory abnormalities in the 12 patients treated with imatinib for DFSP in the Phase 2 study are presented in Table 11.
Table 11: Laboratory Abnormalities Reported in DFSP Patients in the Phase 2 Study - *
- CTC Grades: neutropenia (Grade 3 greater than or equal to 0.5-1.0 x 109/L, Grade 4 less than 0.5 x 109/L), thrombocytopenia (Grade 3 greater than or equal to 10-50 x 109/L, Grade 4 less than 10 x 109/L), anemia (Grade 3 greater than or equal to 65-80 g/L, Grade 4 less than 65 g/L), elevated creatinine (Grade 3 greater than 3-6 x upper limit normal range [ULN], Grade 4 greater than 6 x ULN).
N = 12 CTC Grades * Grade 3
%Grade 4
%Hematology parameters - Anemia 17 0 - Thrombocytopenia 17 0 - Neutropenia 0 8 Biochemistry parameters - Elevated creatinine 0 8 Abbreviation: CTC, common terminology criteria. Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
Unresectable and/or Malignant Metastatic GIST
In the Phase 3 trials, the majority of imatinib-treated patients experienced adverse reactions at some time. The most frequently reported adverse reactions were edema, fatigue, nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, rash, vomiting, myalgia, anemia, and anorexia. Drug was discontinued for adverse reactions in a total of 89 patients (5.4%). Superficial edema, most frequently periorbital or lower extremity edema was managed with diuretics, other supportive measures, or by reducing the dose of imatinib [see Dosage and Administration (2.13)]. Severe (CTC Grade 3/4) edema was observed in 182 patients (11.1%).
Adverse reactions, regardless of relationship to study drug, that were reported in at least 10% of the patients treated with imatinib are shown in Table 12.
Overall the incidence of all grades of adverse reactions and the incidence of severe adverse reactions (CTC Grade 3 and above) were similar between the two treatment arms except for edema, which was reported more frequently in the 800 mg group.
Table 12: Number (%) of Patients With Adverse Reactions Regardless of Relationship to Study Drug Where Frequency is Greater Than or Equal to 10% in any One Group (Full Analysis Set) in the Phase 3 Unresectable and/or Malignant Metastatic GIST Clinical Trials Imatinib 400 mg
N = 818Imatinib 800 mg
N = 822All Grades Grades 3/4/5 All Grades Grades 3/4/5
Reported or specified term% % % % Edema 76.7 9.0 86.1 13.1 Fatigue/lethargy, malaise, asthenia 69.3 11.7 74.9 12.2 Nausea 58.1 9.0 64.5 7.8 Abdominal pain/cramping 57.2 13.8 55.2 11.8 Diarrhea 56.2 8.1 58.2 8.6 Rash/desquamation 38.1 7.6 49.8 8.9 Vomiting 37.4 9.2 40.6 7.5 Myalgia 32.2 5.6 30.2 3.8 Anemia 32.0 4.9 34.8 6.4 Anorexia 31.1 6.6 35.8 4.7 Other GI toxicity 25.2 8.1 28.1 6.6 Headache 22.0 5.7 19.7 3.6 Other pain (excluding tumor related pain) 20.4 5.9 20.8 5.0 Other dermatology/skin toxicity 17.6 5.9 20.1 5.7 Leukopenia 17.0 0.7 19.6 1.6 Other constitutional symptoms 16.7 6.4 15.2 4.4 Cough 16.1 4.5 14.5 3.2 Infection (without neutropenia) 15.5 6.6 16.5 5.6 Pruritus 15.4 5.4 18.9 4.3 Other neurological toxicity 15.0 6.4 15.2 4.9 Constipation 14.8 5.1 14.4 4.1 Other renal/genitourinary toxicity 14.2 6.5 13.6 5.2 Arthralgia (joint pain) 13.6 4.8 12.3 3.0 Dyspnea (shortness of breath) 13.6 6.8 14.2 5.6 Fever in absence of neutropenia (ANC < 1.0 x 109/L) 13.2 4.9 12.9 3.4 Sweating 12.7 4.6 8.5 2.8 Other hemorrhage 12.3 6.7 13.3 6.1 Weight gain 12.0 1.0 10.6 0.6 Alopecia 11.9 4.3 14.8 3.2 Dyspepsia/heartburn 11.5 0.6 10.9 0.5 Neutropenia/granulocytopenia 11.5 3.1 16.1 4.1 Rigors/chills 11.0 4.6 10.2 3.0 Dizziness/lightheadedness 11.0 4.8 10.0 2.8 Creatinine increase 10.8 0.4 10.1 0.6 Flatulence 10.0 0.2 10.1 0.1 Stomatitis/pharyngitis (oral/pharyngeal mucositis) 9.2 5.4 10.0 4.3 Lymphopenia 6.0 0.7 10.1 1.9 Abbreviations: ANC, absolute neutrophil count; GI, gastrointestinal; GIST, gastrointestinal stromal tumors.
Clinically relevant or severe abnormalities of routine hematologic or biochemistry laboratory values were not reported or evaluated in the Phase 3 GIST trials. Severe abnormal laboratory values reported in the Phase 2 GIST trial are presented in Table 13.
Table 13: Laboratory Abnormalities in the Phase 2 Unresectable and/or Malignant Metastatic GIST Trial - *
- CTC Grades: neutropenia (Grade 3 greater than or equal to 0.5-1.0 x 109/L, Grade 4 less than 0.5 x 109/L), thrombocytopenia (Grade 3 greater than or equal to 10-50 x 109/L, Grade 4 less than 10 x 109/L), anemia (Grade 3 greater than or equal to 65-80 g/L, Grade 4 less than 65 g/L), elevated creatinine (Grade 3 greater than 3-6 x upper limit normal range [ULN], Grade 4 greater than 6 x ULN), elevated bilirubin (Grade 3 greater than 3-10 x ULN, Grade 4 greater than 10 x ULN), elevated alkaline phosphatase, SGOT or SGPT (Grade 3 greater than 5-20 x ULN, Grade 4 greater than 20 x ULN), albumin (Grade 3 less than 20 g/L).
400 mg
(n = 73)
%600 mg
(n = 74)
%CTC Grades* Grade 3 Grade 4 Grade 3 Grade 4 Hematology parameters - Anemia 3 0 8 1 - Thrombocytopenia 0 0 1 0 - Neutropenia 7 3 8 3 Biochemistry parameters - Elevated creatinine 0 0 3 0 - Reduced albumin 3 0 4 0 - Elevated bilirubin 1 0 1 3 - Elevated alkaline phosphatase 0 0 3 0 - Elevated SGOT (AST) 4 0 3 3 - Elevated SGPT (ALT) 6 0 7 1 Abbreviations: CTC, common terminology criteria; GIST, gastrointestinal stromal tumors; SGOT, serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase is now referred to as aspartate aminotransferase (AST); SGPT, serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase is now referred to as alanine aminotransferase (ALT). Adjuvant Treatment of GIST
In Study 1, the majority of both imatinib and placebo-treated patients experienced at least one adverse reaction at some time. The most frequently reported adverse reactions were similar to those reported in other clinical studies in other patient populations and include diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, edema, decreased hemoglobin, rash, vomiting, and abdominal pain. No new adverse reactions were reported in the adjuvant GIST-treatment setting that had not been previously reported in other patient populations, including patients with unresectable and/or malignant metastatic GIST. Drug was discontinued for adverse reactions in 57 patients (17%) and 11 patients (3%) of the imatinib and placebo-treated patients, respectively. Edema, GI disturbances (nausea, vomiting, abdominal distention, and diarrhea), fatigue, low hemoglobin, and rash were the most frequently reported adverse reactions at the time of discontinuation.
In Study 2, discontinuation of therapy due to adverse reactions occurred in 15 patients (8%) and 27 patients (14%) of the imatinib 12-month, and 36-month treatment arms, respectively. As in previous trials the most common adverse reactions were diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, edema, decreased hemoglobin, rash, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
Adverse reactions, regardless of relationship to study drug, that were reported in at least 5% of the patients treated with imatinib are shown in Table 14 (Study 1) and Table 15 (Study 2). There were no deaths attributable to imatinib treatment in either trial.
Table 14: Adverse Reactions Regardless of Relationship to Study Drug Reported in Study 1 (Greater Than or Equal to 5% of Imatinib-Treated Patients)* - *
- All adverse reactions occurring in greater than or equal to 5% of patients are listed regardless of suspected relationship to treatment. A patient with multiple occurrences of an adverse reaction is counted only once in the adverse reaction category.
- †
- NCI Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 3.0.
All CTC Grades CTC Grade 3† and Above Imatinib Placebo Imatinib Placebo (n = 337) (n = 345) (n = 337) (n = 345) Preferred term % % % % Diarrhea 59.3 29.3 3.0 1.4 Fatigue 57.0 40.9 2.1 1.2 Nausea 53.1 27.8 2.4 1.2 Periorbital edema 47.2 14.5 1.2 0 Hemoglobin decreased 46.9 27.0 0.6 0 Peripheral edema 26.7 14.8 0.3 0 Rash (Exfoliative) 26.1 12.8 2.7 0 Vomiting 25.5 13.9 2.4 0.6 Abdominal pain 21.1 22.3 3.0 1.4 Headache 19.3 20.3 0.6 0 Dyspepsia 17.2 13.0 0.9 0 Anorexia 16.9 8.7 0.3 0 Weight increased 16.9 11.6 0.3 0 Liver enzymes (ALT) increased 16.6 13.0 2.7 0 Muscle spasms 16.3 3.3 0 0 Neutrophil count decreased 16.0 6.1 3.3 0.9 Arthralgia 15.1 14.5 0 0.3 White blood cell count decreased 14.5 4.3 0.6 0.3 Constipation 12.8 17.7 0 0.3 Dizziness 12.5 10.7 0 0.3 Liver enzymes (AST) increased 12.2 7.5 2.1 0 Myalgia 12.2 11.6 0 0.3 Blood creatinine increased 11.6 5.8 0 0.3 Cough 11.0 11.3 0 0 Pruritus 11.0 7.8 0.9 0 Weight decreased 10.1 5.2 0 0 Hyperglycemia 9.8 11.3 0.6 1.7 Insomnia 9.8 7.2 0.9 0 Lacrimation increased 9.8 3.8 0 0 Alopecia 9.5 6.7 0 0 Flatulence 8.9 9.6 0 0 Rash 8.9 5.2 0.9 0 Abdominal distension 7.4 6.4 0.3 0.3 Back pain 7.4 8.1 0.6 0 Pain in extremity 7.4 7.2 0.3 0 Hypokalemia 7.1 2.0 0.9 0.6 Depression 6.8 6.4 0.9 0.6 Facial edema 6.8 1.2 0.3 0 Blood alkaline phosphatase increased 6.5 7.5 0 0 Dry skin 6.5 5.2 0 0 Dysgeusia 6.5 2.9 0 0 Abdominal pain upper 6.2 6.4 0.3 0 Neuropathy peripheral 5.9 6.4 0 0 Hypocalcemia 5.6 1.7 0.3 0 Leukopenia 5.0 2.6 0.3 0 Platelet count decreased 5.0 3.5 0 0 Stomatitis 5.0 1.7 0.6 0 Upper respiratory tract infection 5.0 3.5 0 0 Vision blurred 5.0 2.3 0 0 Abbreviations: CTC, common terminology criteria; GIST, gastrointestinal stromal tumors; SGOT, serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase is now referred to as aspartate aminotransferase (AST); SGPT, serum glutamic-pyruvic transaminase is now referred to as alanine aminotransferase (ALT). Table 15: Adverse Reactions Regardless of Relationship to Study Drug by Preferred Term All Grades and 3/4 Grades (Greater Than or Equal to 5% of Imatinib-Treated Patients) Study 2* - *
- All adverse reactions occurring in greater than or equal to 5% of patients are listed regardless of suspected relationship to treatment. A patient with multiple occurrences of an adverse reaction is counted only once in the adverse reaction category.
Preferred term All CTC Grades CTC Grades 3 and above Imatinib
12 MonthsImatinib
36 MonthsImatinib
12 MonthsImatinib
36 Months(N = 194) (N = 198) (N = 194) (N = 198) % % % % Patients with at least one AE 99.0 100.0 20.1 32.8 Hemoglobin decreased 72.2 80.3 0.5 0.5 Periorbital edema 59.3 74.2 0.5 1.0 Blood lactate dehydrogenase increased 43.3 60.1 0 0 Diarrhea 43.8 54.0 0.5 2.0 Nausea 44.8 51.0 1.5 0.5 Muscle spasms 30.9 49.0 0.5 1.0 Fatigue 48.5 48.5 1.0 0.5 White blood cell count decreased 34.5 47.0 2.1 3.0 Pain 25.8 45.5 1.0 3.0 Blood creatinine increased 30.4 44.4 0 0 Peripheral edema 33.0 40.9 0.5 1.0 Dermatitis 29.4 38.9 2.1 1.5 Aspartate aminotransferase increased 30.9 37.9 1.5 3.0 Alanine aminotransferase increased 28.9 34.3 2.1 3.0 Neutrophil count decreased 24.2 33.3 4.6 5.1 Hypoproteinemia 23.7 31.8 0 0 Infection 13.9 27.8 1.5 2.5 Weight increased 13.4 26.8 0 0.5 Pruritus 12.9 25.8 0 0 Flatulence 19.1 24.7 1.0 0.5 Vomiting 10.8 22.2 0.5 1.0 Dyspepsia 17.5 21.7 0.5 1.0 Hypoalbuminemia 11.9 21.2 0 0 Edema 10.8 19.7 0 0.5 Abdominal distension 11.9 19.2 0.5 0 Headache 8.2 18.2 0 0 Lacrimation increased 18.0 17.7 0 0 Arthralgia 8.8 17.2 0 1.0 Blood alkaline phosphatase increased 10.8 16.7 0 0.5 Dyspnea 6.2 16.2 0.5 1.5 Myalgia 9.3 15.2 0 1.0 Platelet count decreased 11.3 14.1 0 0 Blood bilirubin increased 11.3 13.1 0 0 Dysgeusia 9.3 12.6 0 0 Paresthesia 5.2 12.1 0 0.5 Vision blurred 10.8 11.1 1.0 0.5 Alopecia 11.3 10.6 0 0 Decreased appetite 9.8 10.1 0 0 Constipation 8.8 9.6 0 0 Pyrexia 6.2 9.6 0 0 Depression 3.1 8.1 0 0 Abdominal pain 2.6 7.6 0 0 Conjunctivitis 5.2 7.6 0 0 Photosensitivity reaction 3.6 7.1 0 0 Dizziness 4.6 6.6 0.5 0 Hemorrhage 3.1 6.6 0 Dry skin 6.7 6.1 0.5 Nasopharyngitis 1.0 6.1 0 0.5 Palpitations 5.2 5.1 0 0 Abbreviations: AE, adverse event; CTC, common terminology criteria. Adverse Reactions from Multiple Clinical Trials
Cardiac Disorders:
Estimated 1%-10%: palpitations, pericardial effusion
Estimated 0.1%-1%: congestive cardiac failure, tachycardia, pulmonary edema
Estimated 0.01%-0.1%: arrhythmia, atrial fibrillation, cardiac arrest, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris
Vascular Disorders:
Estimated 1%-10%: flushing, hemorrhage
Estimated 0.1%-1%: hypertension, hypotension, peripheral coldness, Raynaud’s phenomenon, hematoma, subdural hematoma
Investigations:
Estimated 1%-10%: blood creatine phosphokinase (CPK) increased, blood amylase increased Estimated 0.1%-1%: blood lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) increased
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders:
Estimated 1%-10%: dry skin, alopecia, face edema, erythema, photosensitivity reaction, nail disorder, purpura
Estimated 0.1%-1%: exfoliative dermatitis, bullous eruption, psoriasis, rash pustular, contusion, sweating increased, urticaria, ecchymosis, increased tendency to bruise, hypotrichosis, skin hypopigmentation, skin hyperpigmentation, onychoclasis, folliculitis, petechiae, erythema multiforme, panniculitis (including erythema nodosum)
Estimated 0.01%-0.1%: vesicular rash, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis (Sweet’s syndrome), nail discoloration, angioneurotic edema, leucocytoclastic vasculitis
Gastrointestinal Disorders:
Estimated 1%-10%: abdominal distention, gastroesophageal reflux, dry mouth, gastritis
Estimated 0.1%-1%: gastric ulcer, stomatitis, mouth ulceration, eructation, melena, esophagitis, ascites, hematemesis, chelitis, dysphagia, pancreatitis
Estimated 0.01%-0.1%: colitis, ileus, inflammatory bowel disease
General Disorders and Administration-Site Conditions:
Estimated 1%-10%: weakness, anasarca, chills Estimated 0.1%-1%: malaise
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders:
Estimated 1%-10%: pancytopenia, febrile neutropenia, lymphopenia, eosinophilia Estimated 0.1%-1%: thrombocythemia, bone marrow depression, lymphadenopathy Estimated 0.01%-0.1%: hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia
Hepatobiliary Disorders:
Estimated 0.1%-1%: hepatitis, jaundice
Estimated 0.01%-0.1%: hepatic failure and hepatic necrosis1
Immune System Disorders:
Estimated 0.01%-0.1%: angioedema
Infections and Infestations:
Estimated 0.1%-1%: sepsis, herpes simplex, herpes zoster, cellulitis, urinary tract infection, gastroenteritis Estimated 0.01%-0.1%: fungal infection
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders:
Estimated 1%-10%: weight decreased, decreased appetite
Estimated 0.1%-1%: dehydration, gout, increased appetite, hyperuricemia, hypercalcemia, hyperglycemia, hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, hypomagnesemia
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders:
Estimated 1%-10%: joint swelling
Estimated 0.1%-1%: joint and muscle stiffness, muscular weakness, arthritis
Nervous System/Psychiatric Disorders:
Estimated 1%-10%: paresthesia, hypesthesia
Estimated 0.1%-1%: syncope, peripheral neuropathy, somnolence, migraine, memory impairment, libido decreased, sciatica, restless leg syndrome, tremor
Estimated 0.01%-0.1%: increased intracranial pressure1, confusional state, convulsions, optic neuritis
Renal and Urinary Disorders:
Estimated 0.1%-1%: renal failure acute, urinary frequency increased, hematuria, renal pain
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders:
Estimated 0.1%-1%: breast enlargement, menorrhagia, sexual dysfunction, gynecomastia, erectile dysfunction, menstruation irregular, nipple pain, scrotal edema
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders:
Estimated 1%-10%: epistaxis Estimated 0.1%-1%: pleural effusion
Estimated 0.01%-0.1%: interstitial pneumonitis, pulmonary fibrosis, pleuritic pain, pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary hemorrhage
Endocrine Disorders:
Estimated 0.1%-1%: hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism
Eye, Ear, and Labyrinth Disorders:
Estimated 1%-10%: conjunctivitis, vision blurred, orbital edema, conjunctival hemorrhage, dry eye
Estimated 0.1%-1%: vertigo, tinnitus, eye irritation, eye pain, scleral hemorrhage, retinal hemorrhage, blepharitis, macular edema, hearing loss, cataract
Estimated 0.01%-0.1%: papilledema1, glaucoma
1Including some fatalities.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of imatinib. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: thrombotic microangiopathy
Cardiac Disorders: pericarditis, cardiac tamponade1
Eye Disorders: vitreous hemorrhage
Gastrointestinal Disorders: ileus/intestinal obstruction, tumor hemorrhage/tumor necrosis, GI perforation1[see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)], diverticulitis, gastric antral vascular ectasia
Infections: hepatitis B virus reactivation1
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: osteonecrosis, rhabdomyolysis/myopathy, growth retardation in children, musculoskeletal pain upon treatment discontinuation (including myalgia, pain in extremity, arthralgia, bone pain)
Nervous System Disorders: cerebral edema1
Reproduction Disorders: hemorrhagic corpus luteum/hemorrhagic ovarian cyst
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders: acute respiratory failure1, interstitial lung disease
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: lichenoid keratosis, lichen planus, toxic epidermal necrolysis, palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia syndrome, drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), pseudoporphyria, pemphigus
Vascular Disorders: thrombosis/embolism, anaphylactic shock
1Including some fatalities.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Agents Inducing CYP3A Metabolism
Consider alternative therapeutic agents with less enzyme induction potential in patients when rifampin or other strong CYP3A4 inducers are indicated for concomitant use with Imkeldi. The dosage of Imkeldi should be increased if concomitant use with a strong CYP3A4 inducer is required [see Dosage and Administration (2.12)].
Imatinib is a CYP3A substrate. Concomitant use with a strong CYP3A inducer decreases imatinib exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may reduce imatinib efficacy.
7.2 Agents Inhibiting CYP3A Metabolism
Caution is recommended when administering Imkeldi with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. Grapefruit juice should be avoided.
Imatinib is a CYP3A substrate. Concomitant use with a strong CYP3A inhibitor increases imatinib exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of Imkeldi adverse reactions.
7.3 Interactions With Drugs Metabolized by CYP3A4
Use caution when administering Imkeldi with CYP3A4 substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions. Because warfarin is metabolized by both CYP2C9 and CYP3A4, use other anti-coagulants instead of warfarin in patients receiving Imkeldi who require anticoagulation.
Imatinib is a CYP3A inhibitor. Imatinib increases exposure of CYP3A substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates.
7.4 Interactions With Drugs Metabolized by CYP2D6
Use caution when administering Imkeldi with CYP2D6 substrates where minimal concentration changes may lead to serious adverse reactions.
Imatinib is a CYP2D6 inhibitor. Imatinib increases exposure of CYP2D6 substrates [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of adverse reactions related to these substrates.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Imkeldi can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman based on human and animal data. There are no clinical studies regarding use of Imkeldi in pregnant women. There have been postmarket reports of spontaneous abortions and congenital anomalies from women who have been exposed to imatinib during pregnancy. Reproductive studies in rats have demonstrated that imatinib mesylate induced teratogenicity and increased incidence of congenital abnormalities following prenatal exposure to imatinib mesylate at doses equal to the highest recommended human dose of 800 mg/day based on BSA. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is not known; however, in the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects of clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and of miscarriage is 15% to 20%.
Data
Animal Data
In embryo-fetal development studies in rats and rabbits, pregnant animals received oral doses of imatinib mesylate up to 100 mg/kg/day and 60 mg/kg/day, respectively, during the period of organogenesis.
In rats, imatinib mesylate was teratogenic at 100 mg/kg/day (approximately equal to the maximum human dose of 800 mg/day based on BSA), the number of fetuses with encephalocele and exencephaly was higher than historical control values and these findings were associated with missing or underdeveloped cranial bones. Lower mean fetal body weights were associated with retarded skeletal ossifications.
In rabbits, at doses 1.5 times higher than the maximum human dose of 800 mg/day based on BSA, no effects on the reproductive parameters with respect to implantation sites, number of live fetuses, sex ratio or fetal weight were observed. The examinations of the fetuses did not reveal any drug related morphological changes.
In a pre- and postnatal development study in rats, pregnant rats received oral doses of imatinib mesylate during gestation (organogenesis) and lactation up to 45 mg/kg/day. Five animals developed a red vaginal discharge in the 45 mg/kg/day group on Days 14 or 15 of gestation, the significance of which is unknown since all females produced viable litters and none had increased post-implantation loss. Other maternal effects noted only at the dose of 45 mg/kg/day (approximately one-half the maximum human dose of 800 mg/day based on BSA) included an increased number of stillborn pups and pups dying between postpartum Days 0 and 4. In the F1 offspring at this same dose level, mean body weights were reduced from birth until terminal sacrifice and the number of litters achieving criterion for preputial separation was slightly decreased. There were no other significant effects in developmental parameters or behavioral testing. F1 fertility was not affected but reproductive effects were noted at 45 mg/kg/day, including an increased number of resorptions and a decreased number of viable fetuses. The no-observed-effect level (NOEL) for both maternal animals and the F1 generation was 15 mg/kg/day.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Imatinib and its active metabolite are excreted into human milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed children from Imkeldi, advise a lactating woman not to breastfeed during treatment and for 1 month after the last dose.
Human Data
Based on data from 3 breastfeeding women taking imatinib, the milk:plasma ratio is about 0.5 for imatinib and about 0.9 for the active metabolite. Considering the combined concentration of imatinib and active metabolite, a breastfed child could receive up to 10% of the maternal therapeutic dose based on body weight.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Based on human postmarketing reports and animal studies, Imkeldi can cause fetal harm [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify pregnancy status in females with reproductive potential prior to the initiation of treatment with Imkeldi.
Contraception
Females
Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use effective contraception (methods that result in less than 1% pregnancy rates) when using Imkeldi during treatment and for fourteen days after stopping treatment with Imkeldi [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Infertility
The risk of infertility in females or males of reproductive potential has not been studied in humans. In a rat study, the fertility in males and females was not affected [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Imkeldi have been established in pediatric patients with newly diagnosed Ph+ chronic phase CML and Ph+ ALL [see Clinical Studies (14.2, 14.4)]. There are no data in pediatric patients under 1 year of age.
The safety and efficacy of Imkeldi have not been established in pediatric patients for all other indications [see Indications and Usage (1)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
In the CML clinical studies, approximately 20% of patients were older than 65 years. In the study of patients with newly diagnosed CML, 6% of patients were older than 65 years. The frequency of edema was higher in patients older than 65 years as compared to younger patients; no other difference in the safety profile was observed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. The efficacy of imatinib was similar in older and younger patients.
In the unresectable or metastatic GIST study, 16% of patients were older than 65 years. No obvious differences in the safety or efficacy profile were noted in patients older than 65 years as compared to younger patients, but the small number of patients does not allow a formal analysis.
In the adjuvant GIST study, 221 patients (31%) were older than 65 years. No difference was observed in the safety profile in patients older than 65 years as compared to younger patients, with the exception of a higher frequency of edema. The efficacy of imatinib was similar in patients older than 65 years and younger patients.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Reduce the dose by 25% for patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.12)]. Patients with mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin ≤ upper limit of normal [ULN] and aspartate aminotransferase [AST] >ULN, or total bilirubin ˃1 to 1.5 times ULN and any value for AST) and moderate hepatic impairment (total bilirubin ˃ 1.5 to 3 times ULN and any value for AST) do not require a dose adjustment.
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of both imatinib and its major metabolite, CGP74588, was assessed in 84 patients with cancer with varying degrees of hepatic impairment at imatinib doses ranging from 100 mg to 800 mg. Mild hepatic impairment (total bilirubin ≤ ULN and aspartate aminotransferase [AST] > ULN, or total bilirubin ˃1 to 1.5 times ULN and any value for AST) and moderate hepatic impairment (total bilirubin ˃1.5 to 3 times ULN and any value for AST) do not influence exposure to imatinib and CGP74588. In patients with severe hepatic impairment, (total bilirubin ˃ 3 to 10 times ULN and any value for AST), the imatinib Cmax and area under curve (AUC) increased by 63% and 45% and the CGP74588 Cmax and AUC increased by 56% and 55%, relative to patients with normal hepatic function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
Dose reductions are necessary for patients with moderate and severe renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.12)].
The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of imatinib was assessed in 59 patients with cancer and varying degrees of renal impairment at single and steady state imatinib doses ranging from 100 to 800 mg/day. The mean exposure to imatinib (dose normalized AUC) in patients with mild (CLcr = 40-59 mL/min) and moderate renal impairment (CLcr = 20-39 mL/min) increased 1.5- to 2-fold compared to patients with normal renal function. There are not sufficient data in patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr = less than 20 mL/min) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Experience with doses greater than 800 mg is limited. Isolated cases of imatinib overdose have been reported. In the event of overdosage, observe the patient and give appropriate supportive treatment.
Adult Overdose
1,200 to 1,600 mg (duration varying between 1 to 10 days): Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, rash erythema, edema, swelling, fatigue, muscle spasms, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, abdominal pain, headache, decreased appetite.
1,800 to 3,200 mg (as high as 3,200 mg daily for 6 days): Weakness, myalgia, increased CPK, increased bilirubin, GI pain.
6,400 mg (single dose): One case in the literature reported one patient who experienced nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, pyrexia, facial swelling, neutrophil count decreased, increase transaminases.
8 to 10 g (single dose): Vomiting and GI pain have been reported.
A patient with myeloid blast crisis experienced Grade 1 elevations of serum creatinine, Grade 2 ascites and elevated liver transaminase levels, and Grade 3 elevations of bilirubin after inadvertently taking 1,200 mg of imatinib daily for 6 days. Therapy was temporarily interrupted and complete reversal of all abnormalities occurred within 1 week. Treatment was resumed at a dose of 400 mg daily without recurrence of adverse reactions. Another patient developed severe muscle cramps after taking 1,600 mg of imatinib daily for 6 days. Complete resolution of muscle cramps occurred following interruption of therapy and treatment was subsequently resumed. Another patient that was prescribed 400 mg daily, took 800 mg of imatinib on Day 1 and 1,200 mg on Day 2. Therapy was interrupted, no adverse reactions occurred and the patient resumed therapy.
Pediatric Overdose
One 3 year old male exposed to a single dose of 400 mg experienced vomiting, diarrhea, and anorexia; and another 3 year old male exposed to a single dose of 980 mg experienced decreased white blood cell (WBC) count and diarrhea.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Imkeldi oral solution contains imatinib mesylate, a kinase inhibitor. Imatinib mesylate is designated chemically as 4-[(4-Methyl-1-piperazinyl)methyl]-N-[4-methyl-3-[[4-(3-pyridinyl)-2- pyrimidinyl]amino]-phenyl]benzamide methanesulfonate and its structural formula is:
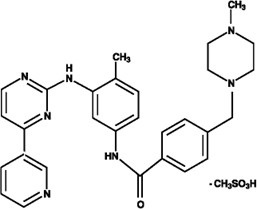
The molecular formula is C29H31N7O · CH4SO3 and its molecular weight is 589.7 g/mol. Imatinib mesylate is soluble in aqueous buffers less than or equal to pH 5.5 but is very slightly soluble to insoluble in neutral/alkaline aqueous buffers. In non-aqueous solvents, the drug substance is freely soluble to very slightly soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide, methanol, and ethanol, but is insoluble in n-octanol, acetone, and acetonitrile.
Imatinib oral solution is a clear, yellow to brownish yellow colored solution. Each mL of Imkeldi contains the equivalent of 80 mg imatinib present as 95.57 mg imatinib mesylate. Inactive Ingredients: acesulfame potassium, citric acid monohydrate, glycerine, liquid maltitol, purified water, sodium benzoate, strawberry flavor (artificial flavors, lactic acid, triacetin).
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Imatinib mesylate is a protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitor that inhibits the BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase, the constitutive abnormal tyrosine kinase created by the Philadelphia chromosome abnormality in CML. Imatinib inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in BCR-ABL positive cell lines as well as fresh leukemic cells from Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia. Imatinib inhibits colony formation in assays using ex vivo peripheral blood and bone marrow samples from CML patients.
In vivo, imatinib inhibits tumor growth of BCR-ABL transfected murine myeloid cells as well as BCR-ABL positive leukemia lines derived from CML patients in blast crisis.
Imatinib is also an inhibitor of the receptor tyrosine kinases for platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and stem cell factor (SCF), c-Kit, and inhibits PDGF- and SCF-mediated cellular events. In vitro, imatinib inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in GIST cells, which express an activating c-Kit mutation.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Imatinib exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamic response are unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of imatinib have been evaluated in studies in healthy subjects and in population pharmacokinetic studies in over 900 patients. No clinically significant difference in imatinib pharmacokinetics were observed between CML and GIST patients. Imatinib AUC increases proportionally with increasing doses ranging from 25 mg to 1000 mg (0.06 to 1.25 times the approved recommended dosage of 400 mg). Imatinib accumulation is 1.5- to 2.5- fold at steady state when imatinib is dosed once daily.
Absorption
Imatinib mean absolute bioavailability is 98%. Imatinib is well absorbed after oral administration with maximum concentration (Cmax ) achieved within 2-4 hours post-dose.
Distribution
Imatinib and the N-demethylated metabolite (CGP74588) plasma protein binding is approximately 95% in vitro, mostly to albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein.
Elimination
The elimination half-life is approximately 18 hours for imatinib and 40 hours for the N-demethyl derivative metabolite (CGP74588), following oral administration in healthy volunteers.
Typical imatinib clearance in a 50-year-old patient weighing 50 kg is expected to be 8 L/h, while for a 50-year-old patient weighing 100 kg the clearance will increase to 14 L/h. The inter-patient variability of 40% in clearance does not warrant initial dose adjustment based on body weight and/or age but indicates the need for close monitoring for treatment-related toxicity.
Metabolism
CYP3A4 is the major enzyme responsible for metabolism of imatinib. Other cytochrome P450 enzymes, such as CYP1A2, CYP2D6, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19, play a minor role in its metabolism. The main circulating active metabolite in humans is the N-demethylated piperazine derivative (CGP74588), formed predominantly by CYP3A4. It shows in vitro potency similar to the parent imatinib. The plasma AUC for this metabolite is about 15% of the AUC for imatinib.
Excretion
Imatinib elimination is predominately in the feces, mostly as metabolites. Following an oral radio-labeled dose of imatinib, approximately 81% of the dose was eliminated within 7 days, in feces (68% of dose) and urine (13% of dose). Unchanged imatinib accounted for 25% of the dose (5% urine, 20% feces), the remainder being metabolites.
Specific Populations
Hepatic Impairment
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of both imatinib and its major metabolite, CGP74588, was assessed in 84 patients with cancer and varying degrees of hepatic impairment at imatinib doses ranging from 100 mg to 800 mg.
Exposure to both imatinib and CGP74588 was comparable between each of the mildly (total bilirubin ≤ upper limit of normal [ULN] and aspartate aminotransferase [AST] > ULN, or total bilirubin ˃1 to 1.5 times ULN) and moderately (total bilirubin ˃ 1.5 to 3 times ULN and any value for AST) hepatically-impaired groups and the normal group.
Patients with severe hepatic impairment (Total bilirubin ˃ 3 to 10 times ULN and any value for AST) tend to have higher exposure to both imatinib and CGP74588 than patients with normal hepatic function. At steady state, the mean Cmax/dose and AUC/dose for imatinib increased by about 63% and 45%, respectively, in patients with severe hepatic impairment compared to patients with normal hepatic function. The mean Cmax/dose and AUC/dose for CGP74588 increased by about 56% and 55%, respectively, in patients with severe hepatic impairment compared to patients with normal hepatic function.
Renal Impairment
The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of imatinib was assessed in 59 cancer patients with varying degrees of renal impairment at single and steady state imatinib doses ranging from 100 to 800 mg/day.
The mean exposure to imatinib (AUC/dose) in patients with mild (CLcr = 40-59 mL/min) and moderate (CLcr = 20-39 mL/min) renal impairment increased 1.5- to 2-fold compared to patients with normal renal function. The AUCs did not increase for doses greater than 600 mg in patients with mild renal impairment.
The AUCs did not increase for doses greater than 400 mg in patients with moderate renal impairment. Two patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr = less than 20 mL/min) were dosed with 100 mg/day and their exposures were similar to those seen in patients with normal renal function receiving 400 mg/day.
Pediatric Use
Dosing in a limited number of children at both 260 mg/m2 and 340 mg/m2 (0.76 and 1 times the approved recommended dosage) achieved an AUC similar to the 400 mg dose in adults. The comparison of AUC on Day 8 vs Day 1 at 260 mg/m2 and 340 mg/m2 dose levels revealed a 1.5- and 2.2-fold drug accumulation, respectively, after repeated once-daily dosing. Mean imatinib AUC did not increase proportionally with increasing dose. Another analysis suggested that exposure of imatinib in pediatric patients receiving 260 mg/m2 once daily (not exceeding 400 mg once daily) or 340 mg/m2 once daily (not exceeding 600 mg once daily) were similar to those in adult patients who received imatinib 400 mg or 600 mg once daily.
Imatinib time to Cmax is 2-4 hours in pediatric patients which is similar to adult patients. Apparent oral clearance was also similar to adult values (11.0 L/hr/m2 in children vs 10.0 L/hr/m2 in adults), as was the half-life (14.8 hours in children vs 17.1 hours in adults).
Imatinib clearance increases with increasing BSA in pediatric patients with hematological disorders (CML, Ph+ ALL, or other hematological disorders treated with imatinib). After correcting for this BSA effect, other demographics, such as age, body weight, and body mass index did not have clinically significant effects on the exposure of imatinib.
Drug Interactions
Clinical Studies
Agents Inducing CYP3A Metabolism
Imatinib oral-dose clearance increased by 3.8-fold, which significantly (p less than 0.05) decreased mean Cmax and AUC, following pretreatment of healthy volunteers with multiple doses of rifampin followed by a single dose of imatinib.
Similar findings were observed in patients receiving 400 to 1200 mg/day imatinib concomitantly with enzyme-inducing anti-epileptic drugs (EIAED) (e.g., carbamazepine, oxcarbamazepine, phenytoin, fosphenytoin, phenobarbital, and primidone). The mean dose normalized AUC for imatinib in the patients receiving EIAED’s decreased by 73% compared to patients not receiving EIAED.
Concomitant administration of imatinib and St. John’s Wort led to a 30% reduction in the AUC of imatinib.
Agents Inhibiting CYP3A Metabolism
There was a significant increase in imatinib exposure (mean Cmax increased by 26% and mean AUC increased by 40%) in healthy subjects following concomitant use of imatinib with a single dose of ketoconazole (CYP3A4 inhibitor).
Interactions with Drugs Metabolized by CYP3A4
Simvastatin (CYP3A4 substrate) mean Cmax increased 2-fold and AUC 3.5-fold, following concomitant use with imatinib.
Interactions with Drugs Metabolized by CYP2D6
Metoprolol (CYP2D6 substrate) mean Cmax and AUC increased by approximately 23% following concomitant use with imatinib.
Interactions with Acetaminophen
Imatinib inhibits the acetaminophen O-glucuronidate pathway in vitro. No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of acetaminophen or imatinib were observed when acetaminophen (1,000 mg single dose on Day 8) was used concomitantly with imatinib (400 mg/day for 8 days) in patients with CML. There is no pharmacokinetic or safety data on the concomitant use of imatinib at doses greater than 400 mg/day or the chronic use of concomitant acetaminophen and imatinib.
In vitro Studies
CYP450 Metabolism: Imatinib is a substrate of CYP3A4, CYP1A2, CYP2D6, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19. Imatinib is a competitive inhibitor of CYP2C9, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4/5.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In the 2-year rat carcinogenicity study administration of imatinib at 15, 30, and 60 mg/kg/day resulted in a statistically significant reduction in the longevity of males at 60 mg/kg/day and females at greater than or equal to 30 mg/kg/day. Target organs for neoplastic changes were the kidneys (renal tubule and renal pelvis), urinary bladder, urethra, preputial and clitoral gland, small intestine, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands and non-glandular stomach. Neoplastic lesions were not seen at: 30 mg/kg/day for the kidneys, urinary bladder, urethra, small intestine, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands and non-glandular stomach, and 15 mg/kg/day for the preputial and clitoral gland. The papilloma/carcinoma of the preputial/clitoral gland were noted at 30 and 60 mg/kg/day, representing approximately 0.5 to 4 or 0.3 to 2.4 times the human daily exposure (based on AUC) at 400 mg/day or 800 mg/day, respectively, and 0.4 to 3.0 times the daily exposure in children (based on AUC) at 340 mg/m2. The renal tubule adenoma/carcinoma, renal pelvis transitional cell neoplasms, the urinary bladder and urethra transitional cell papillomas, the small intestine adenocarcinomas, the parathyroid glands adenomas, the benign and malignant medullary tumors of the adrenal glands and the non-glandular stomach papillomas/carcinomas were noted at 60 mg/kg/day. The relevance of these findings in the rat carcinogenicity study for humans is not known.
Positive genotoxic effects were obtained for imatinib in an in vitro mammalian cell assay (Chinese hamster ovary) for clastogenicity (chromosome aberrations) in the presence of metabolic activation. Two intermediates of the manufacturing process, which are also present in the final product, are positive for mutagenesis in the Ames assay. One of these intermediates was also positive in the mouse lymphoma assay. Imatinib was not genotoxic when tested in an in vitro bacterial cell assay (Ames test), an in vitro mammalian cell assay (mouse lymphoma) and an in vivo rat micronucleus assay.
In a study of fertility, male rats were dosed for 70 days prior to mating and female rats were dosed 14 days prior to mating and through to gestational Day 6. Testicular and epididymal weights and percent motile sperm were decreased at 60 mg/kg, approximately three-fourths the maximum clinical dose of 800 mg/day based on BSA. This was not seen at doses less than or equal to 20 mg/kg (one-fourth the maximum human dose of 800 mg). The fertility of male and female rats was not affected.
Fertility was not affected in the preclinical fertility and early embryonic development study although lower testes and epididymal weights as well as a reduced number of motile sperm were observed in the high dose males rats. In the preclinical pre- and postnatal study in rats, fertility in the first generation offspring was also not affected by imatinib mesylate.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Toxicities from Long-Term Use
It is important to consider potential toxicities suggested by animal studies, specifically, liver, kidney, and cardiac toxicity and immunosuppression. Severe liver toxicity was observed in dogs treated for 2 weeks, with elevated liver enzymes, hepatocellular necrosis, bile duct necrosis, and bile duct hyperplasia. Renal toxicity was observed in monkeys treated for 2 weeks, with focal mineralization and dilation of the renal tubules and tubular nephrosis. Increased blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine were observed in several of these animals. An increased rate of opportunistic infections was observed with chronic imatinib treatment in laboratory animal studies. In a 39 week monkey study, treatment with imatinib resulted in worsening of normally suppressed malarial infections in these animals. Lymphopenia was observed in animals (as in humans). Additional long-term toxicities were identified in a 2-year rat study. Histopathological examination of the treated rats that died on study revealed cardiomyopathy (both sexes), chronic progressive nephropathy (females) and preputial gland papilloma as principal causes of death or reasons for sacrifice. Non-neoplastic lesions seen in this 2-year study which were not identified in earlier preclinical studies were the cardiovascular system, pancreas, endocrine organs, and teeth. The most important changes included cardiac hypertrophy and dilatation, leading to signs of cardiac insufficiency in some animals.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Chronic Phase, Newly Diagnosed:
An open-label, multicenter, international randomized Phase 3 study (imatinib versus IFN+Ara-C) has been conducted in patients with newly diagnosed Philadelphia chromosome positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) in chronic phase. This study compared treatment with either single-agent imatinib or a combination of interferon-alpha (IFN) plus cytarabine (Ara-C). Patients were allowed to cross over to the alternative treatment arm if they failed to show a complete hematologic response (CHR) at 6 months, a major cytogenetic response (MCyR) at 12 months, or if they lost a CHR or MCyR. Patients with increasing WBC or severe intolerance to treatment were also allowed to cross over to the alternative treatment arm with the permission of the study monitoring committee (SMC). In the imatinib arm, patients were treated initially with 400 mg daily. Dose escalations were allowed from 400 mg daily to 600 mg daily, then from 600 mg daily to 800 mg daily. In the IFN arm, patients were treated with a target dose of IFN of 5 MIU/m2/day subcutaneously in combination with subcutaneous Ara-C 20 mg/m2/day for 10 days/month.
A total of 1106 patients were randomized from 177 centers in 16 countries, 553 to each arm. Baseline characteristics were well balanced between the two arms. Median age was 51 years (range, 18 to 70 years), with 21.9% of patients greater than or equal to 60 years of age. There were 59% males and 41% females; 89.9% White and 4.7% Black patients. At the cut-off for this analysis (7 years after last patient had been recruited), the median duration of first-line treatment was 82 and 8 months in the imatinib and IFN arm, respectively. The median duration of second-line treatment with imatinib was 64 months. Sixty percent of patients randomized to imatinib are still receiving first-line treatment. In these patients, the average dose of imatinib was 403 mg ± 57 mg. Overall, in patients receiving first line imatinib, the average daily dose delivered was 406 mg ± 76 mg. Due to discontinuations and cross-overs, only 2% of patients randomized to IFN were still on first-line treatment. In the IFN arm, withdrawal of consent (14%) was the most frequent reason for discontinuation of first-line therapy, and the most frequent reason for cross over to the imatinib arm was severe intolerance to treatment (26%) and progression (14%).
The primary efficacy endpoint of the study was progression-free survival (PFS). Progression was defined as any of the following events: progression to accelerated phase or blast crisis (AP/BC), death, loss of CHR or MCyR, or in patients not achieving a CHR an increasing WBC despite appropriate therapeutic management. The protocol specified that the progression analysis would compare the intent to treat (ITT) population: patients randomized to receive imatinib were compared with patients randomized to receive IFN. Patients that crossed over prior to progression were not censored at the time of cross-over, and events that occurred in these patients following cross-over were attributed to the original randomized treatment. The estimated rate of progression-free survival at 84 months in the ITT population was 81.2% [95% CI: 78, 85] in the imatinib arm and 60.6% [56, 65] in the IFN arm (p less than 0.0001, log-rank test), (Figure 1).
With 7 years follow up there were 93 (16.8%) progression events in the imatinib arm: 37 (6.7%) progression to AP/BC, 31 (5.6%) loss of MCyR, 15 (2.7%) loss of CHR or increase in WBC and 10 (1.8%) CML unrelated deaths. In contrast, there were 165 (29.8%) events in the IFN+Ara-C arm of which 130 occurred during first-line treatment with IFN-Ara-C. The estimated rate of patients free of progression to accelerated phase (AP) or blast crisis (BC) at 84 months was 92.5% [90, 95] in the imatinib arm compared to the 85.1%, [82, 89] (p less than or equal to 0.001) in the IFN arm, (Figure 2). The annual rates of any progression events have decreased with time on therapy. The probability of remaining progression free at 60 months was 95% for patients who were in complete cytogenetic response (CCyR) with molecular response (greater than or equal to 3 log reduction in BCR-ABL transcripts as measured by quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction) at 12 months, compared to 89% for patients in CCyR but without a major molecular response and 70% in patients who were not in CCyR at this time point (p less than 0.001).
Figure 1: Progression Free Survival (ITT Principle)
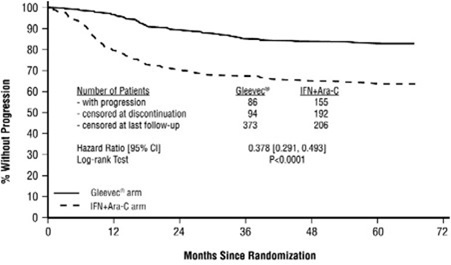
Figure 2: Time to Progression to AP or BC (ITT Principle)
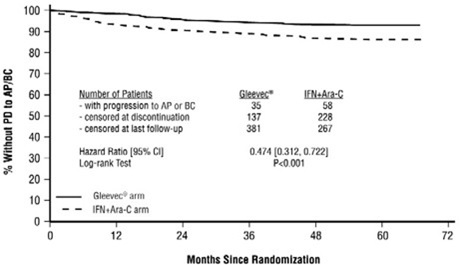
A total of 71 (12.8%) and 85 (15.4%) patients died in the imatinib and IFN+Ara-C group, respectively. At 84 months the estimated overall survival is 86.4% (83, 90) vs 83.3% (80, 87) in the randomized imatinib and the IFN+Ara-C group, respectively (p = 0.073 log-rank test). The hazard ratio is 0.750 with 95% CI 0.547-1.028. This time-to-event endpoint may be affected by the high crossover rate from IFN+Ara-C to imatinib. Major cytogenetic response, hematologic response, evaluation of minimal residual disease (molecular response), time to accelerated phase or blast crisis and survival were main secondary endpoints. Response data are shown in Table 18. Complete hematologic response, major cytogenetic response and CCyR were also statistically significantly higher in the imatinib arm compared to the IFN + Ara- C arm (no cross-over data considered for evaluation of responses). Median time to CCyR in the 454 responders was 6 months (range, 2 to 64 months, 25th to 75th percentiles = 3 to 11 months) with 10% of responses seen only after 22 months of therapy.
Table 18: Response in Newly Diagnosed CML Study (84-Month Data) - *
- Hematologic response criteria (all responses to be confirmed after greater than or equal to 4 weeks): WBC less than 10 x 109/L, platelet less than 450 x 109/L, myelocyte + metamyelocyte less than 5% in blood, no blasts and promyelocytes in blood, no extramedullary involvement.
- †
- p less than 0.001, Fischer's exact test.
- ‡
- Cytogenetic response criteria (confirmed after greater than or equal to 4 weeks): complete (0% Ph+ metaphases) or partial (1%- 35%). A major response (0%-35%) combines both complete and partial responses.
- §
- Unconfirmed cytogenetic response is based on a single bone marrow cytogenetic evaluation, therefore unconfirmed complete or partial cytogenetic responses might have had a lesser cytogenetic response on a subsequent bone marrow evaluation.
Imatinib IFN+Ara-C Best response rate n = 553 n = 553 Hematologic response* CHR rate n (%) 534 (96.6%)† 313 (56.6%)† [95% CI] [94.7%, 97.9%] [52.4%, 60.8%] Cytogenetic response‡ Major cytogenetic response n (%) 472 (85.4%)† 93 (16.8%)† [95% CI] [82.1%, 88.2%] [13.8%, 20.2%] Unconfirmed§ 88.6%† 23.3%† Complete cytogenetic response n (%) 413 (74.7%)† 36 (6.5%)† [95% CI] [70.8, 78.3] [4.6, 8.9] Unconfirmed§ 82.5%† 11.6%† Molecular response was defined as follows: in the peripheral blood, after 12 months of therapy, reduction of greater than or equal to 3 logarithms in the amount of BCR-ABL transcripts (measured by real-time quantitative reverse transcriptase PCR assay) over a standardized baseline. Molecular response was only evaluated in a subset of patients who had a CCyR by 12 months or later (N = 333). The molecular response rate in patients who had a CCyR in the imatinib arm was 59% at 12 months and 72% at 24 months.
Physical, functional, and treatment-specific biologic response modifier scales from the FACT-BRM (Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy - Biologic Response Modifier) instrument were used to assess patient-reported general effects of interferon toxicity in 1,067 patients with CML in chronic phase. After one month of therapy to 6 months of therapy, there was a 13% to 21% decrease in median index from baseline in patients treated with IFN, consistent with increased symptoms of IFN toxicity. There was no apparent change from baseline in median index for patients treated with imatinib.
An open-label, multicenter, randomized trial (imatinib versus nilotinib) was conducted to determine the efficacy of imatinib versus nilotinib in adult patients with cytogenetically confirmed, newly diagnosed Ph+ CML-CP. Patients were within 6 months of diagnosis and were previously untreated for CML-CP, except for hydroxyurea and/or anagrelide.
Efficacy was based on a total of 846 patients: 283 patients in the imatinib 400 mg once daily group, 282 patients in the nilotinib 300 mg twice daily group, 281 patients in the nilotinib 400 mg twice daily group.
Median age was 46 years in the imatinib group and 47 years in both nilotinib groups, with 12%, 13%, and 10% of patients greater than or equal to 65 years of age in imatinib 400 mg once daily, nilotinib 300 mg twice daily and nilotinib 400 mg twice daily treatment groups, respectively. There were slightly more male than female patients in all groups (56%, 56%, and 62% in imatinib 400 mg once daily, nilotinib 300 mg twice daily and nilotinib 400 mg twice-daily treatment groups, respectively). More than 60% of all patients were White, and 25% were Asian.
The primary data analysis was performed when all 846 patients completed 12 months of treatment or discontinued earlier. Subsequent analyses were done when patients completed 24, 36, 48, and 60 months of treatment or discontinued earlier. The median time on treatment was approximately 61 months in all three treatment groups.
The primary efficacy endpoint was major molecular response (MMR) at 12 months after the start of study medication. MMR was defined as less than or equal to 0.1% BCR-ABL/ABL % by international scale measured by RQ-PCR, which corresponds to a greater than or equal to 3 log reduction of BCR-ABL transcript from standardized baseline. Efficacy endpoints are summarized in Table 19.
Twelve patients in the imatinib arm progressed to either accelerated phase or blast crises (7 patients within first 6 months, 2 patients within 6 to 12 months, 2 patients within 12 to 18 months and 1 patient within 18 to 24 months) while two patients on the nilotinib arm progressed to either accelerated phase or blast crisis (both within the first 6 months of treatment).
Table 19: Efficacy (MMR and CCyR) of Imatinib Compared to Nilotinib in Newly Diagnosed Ph+ CML-CP Imatinib
400 mg
once daily
Nilotinib
300 mg
twice daily
N = 283 N = 282 MMR at 12 months (95% CI) 22% (17.6, 27.6) 44% (38.4, 50.3) P-Value* < 0.0001 CCyR† by 12 months (95% CI) 65% (59.2, 70.6) 80% (75.0, 84.6) MMR at 24 months (95% CI) 38% (31.8, 43.4) 62% (55.8, 67.4) CCyR† y 24 months (95% CI) 77% (71.7, 81.8) 87% (82.4, 90.6) Abbreviations: CCyR, complete cytogenetic response; MMR, major molecular response; Ph+ CML-CP, Philadelphia chromosome positive chronic myeloid leukemia-chronic phase. By 60 months, MMR was achieved by 60% of patients on imatinib and 77% of patients on nilotinib.
Median overall survival was not reached in either arm. At the time of the 60-month final analysis, the estimated survival rate was 91.7% for patients on imatinib and 93.7% for patients on nilotinib.
Late Chronic Phase CML and Advanced Stage CML: Three international, open-label, single-arm Phase 2 studies were conducted to determine the safety and efficacy of imatinib in patients with Ph+ CML: 1) in the chronic phase after failure of IFN therapy, 2) in accelerated phase disease, or 3) in myeloid blast crisis. About 45% of patients were women and 6% were Black. In clinical studies, 38% to 40% of patients were greater than or equal to 60 years of age and 10% to 12% of patients were greater than or equal to 70 years of age.
Chronic Phase, Prior Interferon-Alpha Treatment: 532 patients were treated at a starting dose of 400 mg; dose escalation to 600 mg was allowed. The patients were distributed in three main categories according to their response to prior interferon: failure to achieve (within 6 months), or loss of a complete hematologic response (29%), failure to achieve (within 1 year) or loss of a major cytogenetic response (35%), or intolerance to interferon (36%). Patients had received a median of 14 months of prior IFN therapy at doses greater than or equal to 25 x 106 units/week and were all in late chronic phase, with a median time from diagnosis of 32 months. Effectiveness was evaluated on the basis of the rate of hematologic response and by bone marrow exams to assess the rate of major cytogenetic response (up to 35% Ph+ metaphases) or CCyR (0% Ph+ metaphases). Median duration of treatment was 29 months with 81% of patients treated for greater than or equal to 24 months (maximum = 31.5 months). Efficacy results are reported in Table 20. Confirmed major cytogenetic response rates were higher in patients with IFN intolerance (66%) and cytogenetic failure (64%), than in patients with hematologic failure (47%). Hematologic response was achieved in 98% of patients with cytogenetic failure, 94% of patients with hematologic failure, and 92% of IFN-intolerant patients.
Accelerated Phase: 235 patients with accelerated phase disease were enrolled. These patients met one or more of the following criteria: greater than or equal to 15% - less than 30% blasts in PB or BM; greater than or equal to 30% blasts + promyelocytes in PB or BM; greater than or equal to 20% basophils in PB; and less than 100 x 109/L platelets. The first 77 patients were started at 400 mg, with the remaining 158 patients starting at 600 mg.
Effectiveness was evaluated primarily on the basis of the rate of hematologic response, reported as either complete hematologic response, no evidence of leukemia (i.e., clearance of blasts from the marrow and the blood, but without a full peripheral blood recovery as for complete responses), or return to chronic phase CML. Cytogenetic responses were also evaluated. Median duration of treatment was 18 months with 45% of patients treated for greater than or equal to 24 months (maximum = 35 months). Efficacy results are reported in Table 20. Response rates in accelerated phase CML were higher for the 600 mg dose group than for the 400 mg group: hematologic response (75% vs 64%), confirmed and unconfirmed major cytogenetic response (31% vs 19%).
Myeloid Blast Crisis: 260 patients with myeloid blast crisis were enrolled. These patients had greater than or equal to 30% blasts in PB or BM and/or extramedullary involvement other than spleen or liver; 95 (37%) had received prior chemotherapy for treatment of either accelerated phase or blast crisis (“pretreated patients”) whereas 165 (63%) had not (“untreated patients”). The first 37 patients were started at 400 mg; the remaining 223 patients were started at 600 mg.
Effectiveness was evaluated primarily on the basis of rate of hematologic response, reported as either complete hematologic response, no evidence of leukemia, or return to chronic phase CML using the same criteria as for the study in accelerated phase. Cytogenetic responses were also assessed. Median duration of treatment was 4 months with 21% of patients treated for greater than or equal to 12 months and 10% for greater than or equal to 24 months (maximum = 35 months). Efficacy results are reported in Table 20. The hematologic response rate was higher in untreated patients than in treated patients (36% vs 22%, respectively) and in the group receiving an initial dose of 600 mg rather than 400 mg (33% vs 16%). The confirmed and unconfirmed major cytogenetic response rate was also higher for the 600-mg dose group than for the 400-mg dose group (17% vs 8%).
Table 20: Response in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Studies - *
- Hematologic response criteria (all responses to be confirmed after greater than or equal to 4 weeks): CHR: Chronic phase study [WBC less than 10 x 109/L, platelet less than 450 x 109/L, myelocytes + metamyelocytes less than 5% in blood, no blasts and promyelocytes in blood, basophils less than 20%, no extramedullary involvement] and in the accelerated and blast crisis studies [absolute neutrophil count (ANC) greater than or equal to 1.5 x 109/L, platelets greater than or equal to 100 x 109/L, no blood blasts, BM blasts less than 5% and no extramedullary disease]. NEL: Same criteria as for CHR but ANC greater than or equal to 1 x 109/L and platelets greater than or equal to 20 x 109/L (accelerated and blast crisis studies). RTC: less than 15% blasts BM and PB, less than 30% blasts + promyelocytes in BM and PB, less than 20% basophils in PB, no extramedullary disease other than spleen and liver (accelerated and blast crisis studies).
- †
- Cytogenetic response criteria (confirmed after greater than or equal to 4 weeks): complete (0% Ph+ metaphases) or partial (1%- 35%). A major response (0%-35%) combines both complete and partial responses.
- ‡
- Unconfirmed cytogenetic response is based on a single bone marrow cytogenetic evaluation, therefore unconfirmed complete or partial cytogenetic responses might have had a lesser cytogenetic response on a subsequent bone marrow evaluation.
- §
- Complete cytogenetic response confirmed by a second bone marrow cytogenetic evaluation performed at least 1 month after the initial bone marrow study.
Chronic phase IFN failure
(n = 532)
Accelerated phase
(n = 235)
Myeloid blast crisis
(n = 260)
600 mg n = 158 600 mg n = 223 400 mg 400 mg n = 77 400 mg n = 37 % of patients [CI 95%] Hematologic response* 95% [92.3-96.3] 71% [64.8-76.8] 31% [25.2-36.8] Complete hematologic response (CHR) 95% 38% 7% No evidence of leukemia (NEL) Not applicable 13% 5% Return to chronic phase (RTC) Not applicable 20% 18% Major cytogenetic response† 60% [55.3-63.8] 21% [16.2-27.1] 7% [4.5-11.2] (Unconfirmed‡) (65%) (27%) (15%) Complete§ (Unconfirmed‡) 39% (47%) 16% (20%) 2% (7%) Abbreviations: BM, bone marrow; PB, peripheral blood. The median time to hematologic response was 1 month. In late chronic phase CML, with a median time from diagnosis of 32 months, an estimated 87.8% of patients who achieved MCyR maintained their response 2 years after achieving their initial response. After 2 years of treatment, an estimated 85.4% of patients were free of progression to AP or BC, and estimated overall survival was 90.8% [88.3, 93.2]. In accelerated phase, median duration of hematologic response was 28.8 months for patients with an initial dose of 600 mg (16.5 months for 400 mg). An estimated 63.8% of patients who achieved MCyR were still in response 2 years after achieving initial response. The median survival was 20.9 [13.1, 34.4] months for the 400 mg group and was not yet reached for the 600 mg group (p = 0.0097). An estimated 46.2% [34.7, 57.7] vs 65.8% [58.4, 73.3] of patients were still alive after 2 years of treatment in the 400 mg vs 600 mg dose groups, respectively. In blast crisis, the estimated median duration of hematologic response is 10 months. An estimated 27.2% [16.8, 37.7] of hematologic responders maintained their response 2 years after achieving their initial response. Median survival was 6.9 [5.8, 8.6] months, and an estimated 18.3% [13.4, 23.3] of all patients with blast crisis were alive 2 years after start of study.
Efficacy results were similar in men and women and in patients younger and older than age 65. Responses were seen in Black patients, but there were too few Black patients to allow a quantitative comparison.
14.2 Pediatric CML
A total of 51 pediatric patients with newly diagnosed and untreated CML in chronic phase were enrolled in an open-label, multicenter, single-arm Phase 2 trial. Patients were treated with imatinib 340 mg/m2/day, with no interruptions in the absence of dose limiting toxicity. Complete hematologic response (CHR) was observed in 78% of patients after 8 weeks of therapy. The complete cytogenetic response rate (CCyR) was 65%, comparable to the results observed in adults.
Additionally, partial cytogenetic response (PCyR) was observed in 16%. The majority of patients who achieved a CCyR developed the CCyR between Months 3 and 10 with a median time to response based on the Kaplan-Meier estimate of 6.74 months. Patients were allowed to be removed from protocol therapy to undergo alternative therapy, including hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Thirty-one children received stem cell transplantation. Of the 31 children, 5 were transplanted after disease progression on study and 1 withdrew from study during first week treatment and received transplant approximately 4 months after withdrawal. Twenty-five children withdrew from protocol therapy to undergo stem cell transplant after receiving a median of 9 twenty-eight day courses (range, 4 to 24). Of the 25 patients 13 (52%) had CCyR and 5 (20%) had PCyR at the end of protocol therapy.
One open-label, single-arm study enrolled 14 pediatric patients with Ph+ chronic phase CML recurrent after stem cell transplant or resistant to interferon-alpha therapy. These patients had not previously received imatinib and ranged in age from 3 to 20 years old; 3 were 3 to 11 years old, 9 were 12 to 18 years old, and 2 were greater than 18 years old. Patients were treated at doses of 260 mg/m2/day (n = 3) (approximately 0.8 times the recommended pediatric dosage of Imkeldi), 340 mg/m2/day (n = 4), 440 mg/m2/day (n = 5) (approximately 1.3 times the recommended pediatric dosage of Imkeldi) and 570 mg/m2/day (n = 2) (approximately 1.7 times the recommended pediatric dosage of Imkeldi). In the 13 patients for whom cytogenetic data are available, 4 achieved a major cytogenetic response, 7 achieved a CCyR, and 2 had a minimal cytogenetic response.
In a second study, 2 of 3 patients with Ph+ chronic phase CML resistant to interferon-alpha therapy achieved a CCyR at doses of 242 mg/m2/day and 257 mg/m2/day (0.7 and 0.8 times the recommended pediatric dosage of Imkeldi, respectively).
14.3 Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
A total of 48 Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph+ ALL) patients with relapsed/refractory disease were studied, 43 of whom received the recommended imatinib dose of 600 mg/day. In addition 2 patients with relapsed/refractory Ph+ ALL received imatinib 600 mg/day in a Phase 1 study.
Confirmed and unconfirmed hematologic and cytogenetic response rates for the 43 relapsed/refractory Ph+ ALL Phase 2 study patients and for the 2 Phase 1 patients are shown in Table 21. The median duration of hematologic response was 3.4 months and the median duration of MCyR was 2.3 months.
Table 21: Effect of Imatinib on Relapsed/Refractory Ph+ ALL Phase 2 study
(N = 43)
n (%)Phase 1 study
(N = 2)
n (%)CHR 8 (19) 2 (100) NEL 5 (12) RTC/PHR 11 (26) MCyR 15 (35) CCyR 9 (21) PCyR 6 (14) Abbreviations: CCyR, complete cytogenetic response; CHR, complete hematologic response; MCyR, major cytogenetic response; NEL, no evidence of leukemia; PCyR, partial cytogenic response; Ph+ ALL, Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia; PHR, partial hematologic response; RTC, return to chronic phase.
14.4 Pediatric ALL
Pediatric and young adult patients with very high risk ALL, defined as those with an expected 5-year event-free survival (EFS) less than 45%, were enrolled after induction therapy on a multicenter, non-randomized cooperative group pilot protocol.
The safety and effectiveness of imatinib (340 mg/m2/day) in combination with intensive chemotherapy was evaluated in a subgroup of patients with Ph+ ALL. The protocol included intensive chemotherapy and hematopoietic stem cell transplant after 2 courses of chemotherapy for patients with an appropriate HLA-matched family donor. There were 92 eligible patients with Ph+ ALL enrolled. The median age was 9.5 years (1 to 21 years: 2.2% between 1 and less than 2 years, 56.5% between 2 and less than 12 years, 34.8% between 12 and less than 18 years, and 6.5% between 18 and 21 years). Sixty-four percent were male, 75% were White, 9% were Asian/Pacific Islander, and 5% were Black. In 5 successive cohorts of patients, imatinib exposure was systematically increased by earlier introduction and prolonged duration. Cohort 1 received the lowest intensity and cohort 5 received the highest intensity of imatinib exposure.
There were 50 patients with Ph+ ALL assigned to cohort 5 all of whom received imatinib plus chemotherapy; 30 were treated exclusively with chemotherapy and imatinib and 20 received chemotherapy plus imatinib and then underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplant, followed by further imatinib treatment. Patients in cohort 5 treated with chemotherapy received continuous daily exposure to imatinib beginning in the first course of post induction chemotherapy continuing through maintenance cycles 1 through 4 chemotherapy. During maintenance cycles 5 through 12, imatinib was administered 28 days out of the 56 day cycle. Patients who underwent hematopoietic stem cell transplant received 42 days of imatinib prior to HSCT, and 28 weeks (196 days) of imatinib after the immediate post transplant period. The estimated 4-year EFS of patients in cohort 5 was 70% (95% CI: 54, 81). The median follow-up time for EFS at data cutoff in cohort 5 was 40.5 months.
14.5 Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative Diseases
An open-label, multicenter, Phase 2 clinical trial was conducted testing imatinib in diverse populations of patients suffering from life-threatening diseases associated with Abl, Kit or PDGFR protein tyrosine kinases. This study included 7 patients with MDS/MPD. These patients were treated with imatinib 400 mg daily. The ages of the enrolled patients ranged from 20 to 86 years. A further 24 patients with MDS/MPD aged 2 to 79 years were reported in 12 published case reports and a clinical study. These patients also received imatinib at a dose of 400 mg daily with the exception of three patients who received lower doses. Of the total population of 31 patients treated for MDS/MPD, 14 (45%) achieved a complete hematological response and 12 (39%) a major cytogenetic response (including 10 with a CCyR). Sixteen patients had a translocation, involving chromosome 5q33 or 4q12, resulting in a PDGFR gene re-arrangement. All of these patients responded hematologically (13 completely). Cytogenetic response was evaluated in 12 out of 14 patients, all of whom responded (10 patients completely). Only 1 (7%) out of the 14 patients without a translocation associated with PDGFR gene re-arrangement achieved a complete hematological response and none achieved a major cytogenetic response. A further patient with a PDGFR gene re-arrangement in molecular relapse after bone marrow transplant responded molecularly. Median duration of therapy was 12.9 months (0.8 to 26.7) in the 7 patients treated within the Phase 2 study and ranged between 1 week and more than 18 months in responding patients in the published literature.
Results are provided in Table 22. Response durations of Phase 2 study patients ranged from 141+ days to 457+ days.
Table 22: Response in MDS/MPD Number of
patientsComplete hematologic response Major cytogenetic response N N (%) N (%) Overall population 31 14 (45) 12 (39) Chromosome 5 translocation 14 11 (79) 11 (79) Chromosome 4 translocation 2 2 (100) 1 (50) Others/no translocation 14 1 (7) 0 Molecular relapse 1 NE NE Abbreviations: NE, not evaluable; MDS/MPD, myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative disease.
14.6 Aggressive Systemic Mastocytosis
One open-label, multicenter, Phase 2 study was conducted testing imatinib in diverse populations of patients with life- threatening diseases associated with Abl, Kit or PDGFR protein tyrosine kinases. This study included 5 patients with ASM treated with 100 mg to 400 mg of imatinib daily. These 5 patients ranged from 49 to 74 years of age. In addition to these 5 patients, 10 published case reports and case series describe the use of imatinib in 23 additional patients with ASM aged 26 to 85 years who also received 100 mg to 400 mg of imatinib daily.
Cytogenetic abnormalities were evaluated in 20 of the 28 ASM patients treated with imatinib from the published reports and in the Phase 2 study. Seven of these 20 patients had the FIP1L1-PDGFRα fusion kinase (or CHIC2 deletion). Patients with this cytogenetic abnormality were predominantly males and had eosinophilia associated with their systemic mast cell disease. Two patients had a Kit mutation in the juxtamembrane region (one Phe522Cys and one K509I) and four patients had a D816V c-Kit mutation (not considered sensitive to imatinib), one with concomitant CML.
Of the 28 patients treated for ASM, 8 (29%) achieved a complete hematologic response and 9 (32%) a partial hematologic response (PHR) (61% overall response rate). Median duration of imatinib therapy for the 5 ASM patients in the Phase 2 study was 13 months (range, 1.4 to 22.3 months) and between 1 month and more than 30 months in the responding patients described in the published medical literature. A summary of the response rates to imatinib in ASM is provided in Table 23. Response durations of literature patients ranged from 1+ to 30+ months.
Table 23: Response in ASM - *
- Patient had concomitant chronic myeloid leukemia CML and ASM.
Cytogenetic abnormality Number of
patientsComplete hematologic
responsePartial hematologic
responseN N (%) N (%) FIP1L1-PDGFRα fusion kinase (or CHIC2 deletion) 7 7 (100) 0 Juxtamembrane mutation 2 0 2 (100) Unknown or no cytogenetic abnormality detected 15 0 7 (44) D816V mutation 4 1* (25) 0 Total 28 8 (29) 9 (32) Abbreviations: ASM, aggressive systemic mastocytosis; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Imatinib has not been shown to be effective in patients with less aggressive forms of systemic mastocytosis (SM). Imkeldi is therefore not recommended for use in patients with cutaneous mastocytosis, indolent systemic mastocytosis (smoldering SM or isolated bone marrow mastocytosis), SM with an associated clonal hematological non-mast cell lineage disease, mast cell leukemia, mast cell sarcoma or extracutaneous mastocytoma. Patients that harbor the D816V mutation of c-Kit are not sensitive to imatinib and should not receive imatinib.
14.7 Hypereosinophilic Syndrome/Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia
One open-label, multicenter, Phase 2 study was conducted testing imatinib in diverse populations of patients with life- threatening diseases associated with Abl, Kit or PDGFR protein tyrosine kinases. This study included 14 patients with Hypereosinophilic Syndrome/Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia (HES/CEL). HES patients were treated with 100 mg to 1,000 mg (2.5 times the recommended dosage of Imkeldi) of imatinib daily. The ages of these patients ranged from 16 to 64 years. A further 162 patients with HES/CEL aged 11 to 78 years were reported in 35 published case reports and case series. These patients received imatinib at doses of 75 mg to 800 mg daily. Hematologic response rates are summarized in Table 24. Response durations for literature patients ranged from 6+ weeks to 44 months.
Table 24: Response in HES/CEL Cytogenetic abnormality Number of
patientsComplete hematological
responsePartial hematological
responseN (%) N (%) Positive FIP1L1-PDGFRα fusion kinase 61 61 (100) 0 Negative FIP1L1-PDGFRα fusion kinase 56 12 (21) 9 (16) Unknown cytogenetic abnormality 59 34 (58) 7 (12) Total 176 107 (61) 23 (13) Abbreviations: CEL, chronic eosinophilic leukemia; HES, hypereosinophilic syndrome; PDGFR, platelet-derived growth factor receptor.
14.8 Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans
Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans (DFSP) is a cutaneous soft tissue sarcoma. It is characterized by a translocation of chromosomes 17 and 22 that results in the fusion of the collagen type 1 alpha 1 gene and the PDGF B gene.
An open-label, multicenter, Phase 2 study was conducted testing imatinib in a diverse population of patients with life- threatening diseases associated with Abl, Kit or PDGFR protein tyrosine kinases. This study included 12 patients with DFSP who were treated with imatinib 800 mg daily (age range, 23 to 75 years). DFSP was metastatic, locally recurrent following initial surgical resection and not considered amenable to further surgery at the time of study entry. A further 6 DFSP patients treated with imatinib are reported in 5 published case reports, their ages ranging from 18 months to 49 years. The total population treated for DFSP therefore comprises 18 patients, 8 of them with metastatic disease. The adult patients reported in the published literature were treated with either 400 mg (4 cases) or 800 mg (1 case) imatinib daily. A single pediatric patient received 400 mg/m2/daily, subsequently increased to 520 mg/m2/daily. Ten patients had the PDGF B gene rearrangement, 5 had no available cytogenetics and 3 had complex cytogenetic abnormalities. Responses to treatment are described in Table 25.
Table 25: Response in DFSP - *
- 5 patients made disease free by surgery.
Number of patients (n = 18) % Complete response 7 39 Partial response* 8 44 Total responders 15 83 Twelve of these 18 patients either achieved a complete response (7 patients) or were made disease free by surgery after a partial response (5 patients, including one child) for a total complete response rate of 67%. A further 3 patients achieved a partial response, for an overall response rate of 83%. Of the 8 patients with metastatic disease, five responded (62%), three of them completely (37%). For the 10 study patients with the PDGF B gene rearrangement, there were 4 complete and 6 partial responses. The median duration of response in the Phase 2 study was 6.2 months, with a maximum duration of 24.3 months, while in the published literature it ranged between 4 weeks and more than 20 months.
14.9 Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors
Unresectable and/or Malignant Metastatic GIST
Two open-label, randomized, multinational Phase 3 studies were conducted in patients with unresectable or metastatic malignant GIST. The two study designs were similar allowing a predefined combined analysis of safety and efficacy. A total of 1640 patients were enrolled into the two studies and randomized 1:1 to receive either 400 mg or 800 mg orally daily continuously until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Patients in the 400 mg daily treatment group who experienced disease progression were permitted to crossover to receive treatment with 800 mg daily. The studies were designed to compare response rates, progression-free survival and overall survival between the dose groups. Median age at patient entry was 60 years. Males comprised 58% of the patients enrolled. All patients had a pathologic diagnosis of CD117 positive unresectable and/or metastatic malignant GIST.
The primary objective of the two studies was to evaluate either progression-free survival (PFS) with a secondary objective of overall survival (OS) in one study or overall survival with a secondary objective of PFS in the other study. A planned analysis of both OS and PFS from the combined datasets from these two studies was conducted. Results from this combined analysis are shown in Table 26.
Table 26: Overall Survival, Progression-Free Survival and Tumor Response Rates in the Phase 3 GIST Trials Imatinib 400 mg Imatinib 800 mg N = 818 N = 822 Progression-free survival (months) Median 18.9 23.2 95% CI 17.4–21.2 20.8–24.9 Overall survival (months) 49.0 48.7 95% CI 45.3–60.0 45.3–51.6 Best overall tumor response Complete response 43 (5.3%) 41 (5.0%) Partial response 377 (46.1%) 402 (48.9%) Abbreviation: GIST, gastrointestinal stromal tumors.
Median follow up for the combined studies was 37.5 months. There were no observed differences in overall survival between the treatment groups (p = 0.98). Patients who crossed over following disease progression from the 400 mg/day treatment group to the 800 mg/day treatment group (n = 347) had a 3.4 month median and a 7.7 month mean exposure to imatinib following crossover.
One open-label, multinational Phase 2 study was conducted in patients with Kit (CD117) positive unresectable or metastatic malignant GIST. In this study, 147 patients were enrolled and randomized to receive either 400 mg or 600 mg orally every day for up to 36 months. The primary outcome of the study was objective response rate. Tumors were required to be measurable at entry in at least one site of disease, and response characterization was based on Southwestern Oncology Group (SWOG) criteria. There were no differences in response rates between the 2 dose groups. The response rate was 68.5% for the 400 mg group and 67.6% for the 600 mg group. The median time to response was 12 weeks (range was 3 to 98 weeks) and the estimated median duration of response is 118 weeks (95% CI: 86, not reached).
Adjuvant Treatment of GIST
In the adjuvant setting, imatinib was investigated in a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial involving 713 patients (Study 1). Patients were randomized one to one to imatinib at 400 mg/day or matching placebo for 12 months. The ages of these patients ranged from 18 to 91 years. Patients were included who had a histologic diagnosis of primary GIST, expressing KIT protein by immunochemistry and a tumor size greater than or equal to 3 cm in maximum dimension with complete gross resection of primary GIST within 14 to 70 days prior to registration.
Recurrence-free survival (RFS) was defined as the time from date of randomization to the date of recurrence or death from any cause. In a planned interim analysis, the median follow up was 15 months in patients without a RFS event; there were 30 RFS events in the 12-month imatinib arm compared to 70 RFS events in the placebo arm with a hazard ratio of 0.398 (95% CI: 0.259, 0.610), p less than 0.0001. After the interim analysis of RFS, 79 of the 354 patients initially randomized to the placebo arm were eligible to cross over to the 12-month imatinib arm. Seventy-two of these 79 patients subsequently crossed over to imatinib therapy. In an updated analysis, the median follow-up for patients without a RFS event was 50 months. There were 74 (21%) RFS events in the 12-month imatinib arm compared to 98 (28%) events in the placebo arm with a hazard ratio of 0.718 (95% CI: 0.531-0.971) (Figure 3). The median follow-up for OS in patients still living was 61 months. There were 26 (7%) and 33 (9%) deaths in the 12-month imatinib and placebo arms, respectively with a hazard ratio of 0.816 (95% CI: 0.488-1.365).
Figure 3: Study 1 Recurrence-Free Survival (ITT Population)
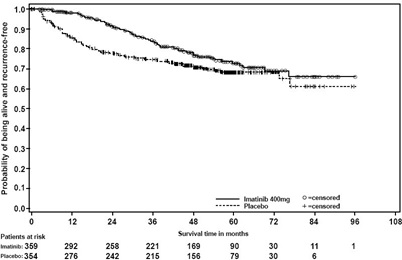
A second randomized, multicenter, open-label, Phase 3 trial in the adjuvant setting (Study 2) compared 12 months of imatinib treatment to 36 months of imatinib treatment at 400 mg/day in adult patients with KIT (CD117) positive GIST after surgical resection with one of the following: tumor diameter greater than 5 cm and mitotic count greater than 5/50 high power fields (HPF), or tumor diameter greater than 10 cm and any mitotic count, or tumor of any size with mitotic count greater than 10/50 HPF, or tumors ruptured into the peritoneal cavity. There were a total of 397 patients randomized in the trial with 199 patients on the 12-month treatment arm and 198 patients on the 36-month treatment arm. The median age was 61 years (range, 22 to 84 years).
RFS was defined as the time from date of randomization to the date of recurrence or death from any cause. The median follow-up for patients without a RFS event was 42 months. There were 84 (42%) RFS events in the 12-month treatment arm and 50 (25%) RFS events in the 36-month treatment arm. Thirty-six months of imatinib treatment significantly prolonged RFS compared to 12 months of imatinib treatment with a hazard ratio of 0.46 (95% CI: 0.32, 0.65), p less than 0.0001 (Figure 4).
The median follow-up for overall survival (OS) in patients still living was 48 months. There were 25 (13%) deaths in the 12-month treatment arm and 12 (6%) deaths in the 36-month treatment arm. Thirty-six months of imatinib treatment significantly prolonged OS compared to 12 months of imatinib treatment with a hazard ratio of 0.45 (95% CI: 0.22, 0.89), p = 0.0187 (Figure 5).
Figure 4: Study 2 Recurrence-Free Survival (ITT Population)
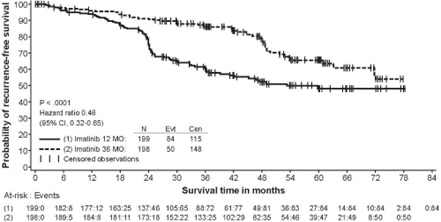
Figure 5: Study 2 Overall Survival (ITT Population)
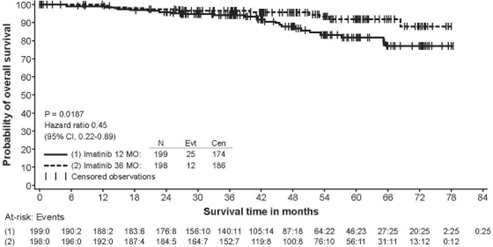
- 15 REFERENCES
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
Imkeldi oral solution 80 mg/mL is supplied as 140 mL of clear yellow to brownish yellow colored solution with a strawberry flavor in an amber PET bottle with a child resistant tamper-evident closure.
NDC 81927-201-01
Storage and Handling
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C (59°F and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Store and dispense in original container only. Any open bottle should be discarded after 30 days.
Imkeldi is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures1.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Instructions for Use).
Fluid Retention and Edema
Inform patients of the possibility of developing edema and fluid retention. Advise patients to contact their health care provider if unexpected rapid weight gain occurs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Hepatotoxicity
Inform patients of the possibility of developing liver function abnormalities and serious hepatic toxicity. Advise patients to immediately contact their health care provider if signs of liver failure occur, including jaundice, anorexia, bleeding, or bruising [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise pregnant women and females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to inform their healthcare provider if they are pregnant or become pregnant [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with Imkeldi and for 14 days after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with Imkeldi and for 1 month after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Drug Interactions
Imkeldi and certain other medicines, such as warfarin, erythromycin, and phenytoin, including over-the-counter medications, such as herbal products, can interact with each other. Advise patients to tell their doctor if they are taking or plan to take iron supplements. Avoid grapefruit juice and other foods known to inhibit CYP3A4 while taking Imkeldi [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Pediatric
Advise patients that growth retardation has been reported in children and pre-adolescents receiving imatinib. The long term effects of prolonged treatment with Imkeldi on growth in children are unknown. Therefore, closely monitor growth in children under Imkeldi treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
Driving and Using Machines
Advise patients that they may experience side effects, such as dizziness, blurred vision, or somnolence during treatment with Imkeldi. Therefore, caution patients about driving a car or operating machinery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
Accurate Measuring Device and Dosing and Administration
Advise patients and caregivers to measure Imkeldi with an accurate milliliter measuring device. A household teaspoon is not an accurate measuring device. Advise patients and caregivers to ask their pharmacist to recommend an appropriate press-in bottle adapter and oral dispensing syringe and for instructions for measuring the correct dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)].
Advise patients to take Imkeldi with a meal and a large glass of water. Advise patients that, if a dose is missed, they should wait until the next scheduled dose and not take two doses at the same time. Advise patients to take Imkeldi exactly as prescribed, not to change their dose or to stop taking Imkeldi unless they are told to do so by their doctor [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Manufactured for:
Shorla Oncology Inc.
Cambridge, MA 02142, USA
Patent Information: U.S. Patent: 11,957,681
Version: IMAPI007
-
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
IMKELDI (IM-KELL-DEE)
(imatinib) oral solution
80 mg/mL
This Instructions for Use contains information on how to take (or give) IMKELDI.
Read this Instructions for Use before you (or your child) start using IMKELDI oral solution and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This important information does not take the place of talking to your (or your child’s) healthcare provider about your (or your child’s) medical condition or treatment.
Supplies needed (Figure A)
IMKELDI bottle with child resistant cap
Oral dispensing syringe (not included with IMKELDI)
Bottle adapter (not included with IMKELDI)
Disposable gloves (not included with IMKELDI)
Figure A
Important Information You Need to Know Before Taking IMKELDI
For oral use only (taken by mouth).
Always use the oral dispensing syringe and bottle adapter provided by your pharmacist. If you did not receive the oral dispensing syringe and bottle adapter, contact your pharmacist.
Ask your pharmacist to show you how to measure your prescribed doses.
Take IMKELDI exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not stop taking IMKELDI without first speaking with your healthcare provider.
All doses of IMKELDI should be taken with a meal and a large glass of water. Taking IMKELDI with certain medicines and grapefruit juice may affect each other. Talk to your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take.
If you miss a dose of IMKELDI, do not take the missed dose. Take your next dose at your regular time.
IMKELDI is a hazardous drug. Do not prepare, withdraw, take, or give IMKELDI without wearing disposable gloves.
IMKELDI may cause dizziness, blurred vision, or sleepiness during treatment.
Preparing a new bottle of IMKELDI before first time use
1. Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water (Figure B).
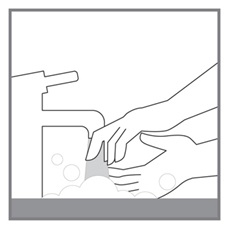
Figure B
2. Wear disposable gloves while preparing, withdrawing, taking, or giving IMKELDI to avoid direct contact with the medicine.
3. Check the expiration date on the bottle. Do not use IMKELDI if the expiration date on the bottle has passed. Contact your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
4. Remove the child-resistant bottle cap by pushing it down firmly and twisting it counter-clockwise (to the left) (Figure C). Do not throw away the child-resistant bottle cap.
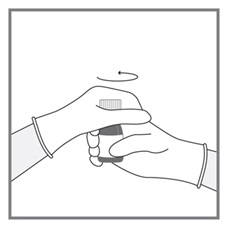
Figure C
5. Place the open bottle upright on a clean flat surface. Hold the bottle firmly and push the ribbed end of the bottle adapter firmly into the neck of the bottle as far as it will go (Figure D). Do not remove the bottle adapter from the bottle after it is inserted.
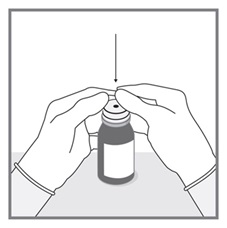
Figure D
6. Put the child-resistant cap back on the bottle by turning it clockwise (to the right) (Figure E). Make sure that the child-resistant cap is tightly closed.
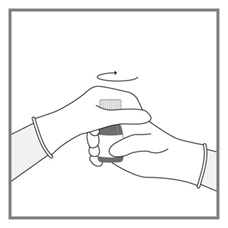
Figure E
7. Write the date of first opening on the bottle label.
Preparing and withdrawing a dose of IMKELDI
8. Repeat Step 1 to Step 4 above.
9. Place the IMKELDI bottle on a clean flat surface.
10. Check your prescription to find out the number of mL you are supposed to take. Find the number line on the oral dispensing syringe barrel that matches your dose.
11. Push the plunger of the oral dispensing syringe all the way up towards the tip of the oral dispensing syringe to remove air (Figure F).
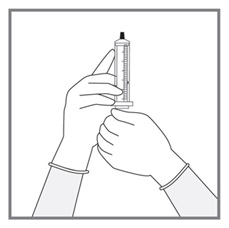
Figure F
12. While keeping the bottle in an upright position, insert the tip of the oral dispensing syringe into the opening of the bottle adapter and push down gently (Figure G).
Do not force the oral dispensing syringe tip into the bottler adapter opening.
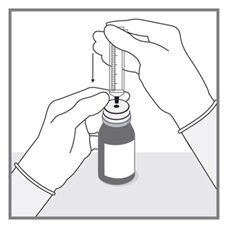
Figure G
13. Hold the oral dispensing syringe tip firmly in the bottle and carefully turn the bottle upside down (Figure H). Slowly pull down the plunger of the oral dispensing syringe until the widest part of the oral dispensing syringe plunger lines up with the prescribed number of mL dose (Figure I).
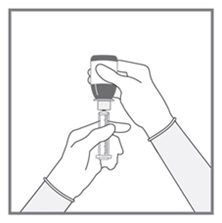
Figure H
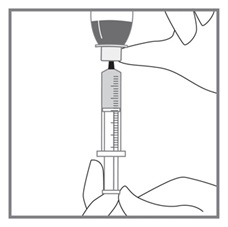
Figure I
14. Leave the oral dispensing syringe tip in the bottle adapter. Check the oral dispensing syringe for air (Figure J). If you see air bubbles, push the plunger all the way back up to push the air into the bottle (Figure K). Then pull the plunger down again to withdraw the prescribed dose.
Repeat this Step until all the air is gone from the oral dispensing syringe.
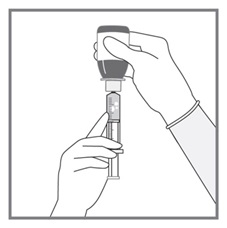
Figure J
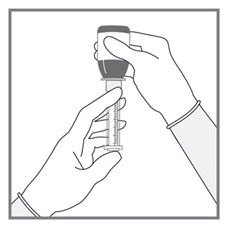
Figure K
15. Leave the oral dispensing syringe tip in the bottle adapter. Turn the bottle back to an upright position and place the bottle on a clean flat surface (Figure L). Without touching the plunger, hold the oral dispensing syringe by the barrel and gently twist and pull the oral dispensing syringe out of the bottle adapter (Figure M).
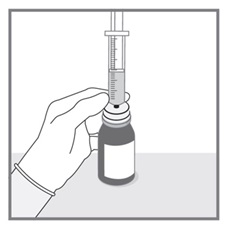
Figure L
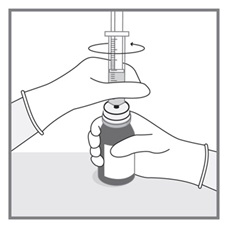
Figure M
16. Inspect the oral dispensing syringe to make sure that it contains the correct dose as described in Step 13 (Figure N).
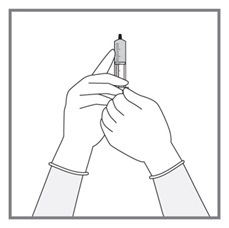
Figure N
Taking (or giving) IMKELDI
17. The child or adult should sit up straight or stand before taking IMKELDI.
18. Gently place the oral dispensing syringe tip in the mouth towards the inside of the cheek (Figure O).
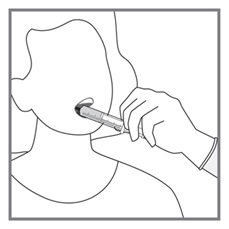
Figure O
19. Slowly and gently push the plunger down to gently squirt the medicine into the inside of the cheek until the plunger no longer moves and all the medicine is out of the oral dispensing syringe (Figure P).
Do not push down too hard on the plunger or squirt the medicine to the back of the mouth or throat as this may cause choking. Remove the oral dispensing syringe from the mouth.
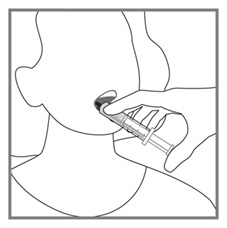
Figure P
20. Swallow the medicine completely. Make sure that no medicine is left in the mouth.
21. After swallowing IMKELDI, eat a meal and drink a large glass of water (Figure Q).
Note: If you do not eat a meal and drink a large glass of water right after swallowing IMKELDI, you may get stomach or intestine problems.

Figure Q
22. Close the bottle by screwing the child-resistant cap back on the bottle in a clockwise direction (to the right) with the adapter left in place. Make sure that the cap is tightly closed (Figure R).
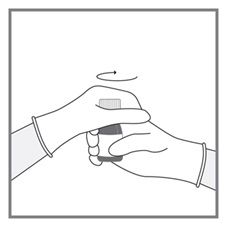
Figure R
Cleaning the oral dispensing syringe after use
23. Right after use, wash the oral dispensing syringe thoroughly with water.
Hold the syringe under water and push the plunger in and out of the oral dispensing syringe several times to remove any medicine from the oral dispensing syringe including the tip (Figure S). Remove the plunger from the oral dispensing syringe barrel and wash both the plunger and oral dispensing syringe barrel thoroughly with cold water.
Repeat this Step until the oral dispensing syringe is clean.
Figure S
24. Shake off excess water from the plunger and the oral dispensing syringe barrel. Dry both the oral dispensing syringe and the oral dispensing syringe plunger with a clean paper towel.
25. Make sure that all oral dispensing syringe parts are fully dry before putting the plunger back in the oral dispensing syringe barrel and using it for the next dose.
26. Throw away (dispose of) the gloves after administration of IMKELDI and cleaning the oral dispensing syringe.
27. Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water.
Storing IMKELDI
Store at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
IMKELDI comes in a child resistant tamper-evident bottle.
Store and give in original bottle only.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Throwing away (disposing of) IMKELDI
Any opened bottle should be thrown away (discarded) 30 days after first opening.
Talk to your healthcare provider or pharmacist about the best way to throw away any unused IMKELDI.
Follow all special handling and throw away (disposal) procedures provided by your healthcare provider and pharmacist.
Additional Information
Call your healthcare provider about side effects. You can report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. You may also report side effects to Shorla Oncology at 844-9-SHORLA
Manufactured for:
Shorla Oncology Inc.
Cambridge, MA 02142, USA
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Approved 11/2024
Version: IMAIFU002
- Principal Display Panel
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
IMKELDI
imatinib oral solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:81927-201 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength IMATINIB MESYLATE (UNII: 8A1O1M485B) (IMATINIB - UNII:BKJ8M8G5HI) IMATINIB 80 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MALTITOL (UNII: D65DG142WK) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) SODIUM BENZOATE (UNII: OJ245FE5EU) ACESULFAME POTASSIUM (UNII: 23OV73Q5G9) CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) LACTIC ACID (UNII: 33X04XA5AT) TRIACETIN (UNII: XHX3C3X673) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Product Characteristics Color yellow (clear yellow to brownish yellow) Score Shape Size Flavor STRAWBERRY Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:81927-201-01 140 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/19/2024 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA219097 12/19/2024 Labeler - Shorla Oncology Inc., (118055608) Registrant - Shorla Pharma Ltd. (985706879) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations L M Manufacturing Limited 220231510 manufacture(81927-201)