Label: BEXACAT- bexagliflozin tablets tablet
- NDC Code(s): 58198-5315-1, 58198-5315-2
- Packager: Elanco US Inc.
- Category: PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG LABEL
Drug Label Information
Updated January 25, 2023
If you are a healthcare professional or from the pharmaceutical industry please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
CAUTION
Federal law restricts this drug to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.
WARNING: DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS/EUGLYCEMIC DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS
- -
- Cats treated with Bexacat may be at an increased risk of diabetic ketoacidosis or euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis (see Adverse Reactions). As diabetic ketoacidosis and euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis in cats treated with Bexacat may result in death, development of these conditions should be treated promptly, including insulin administration and discontinuation of Bexacat (see Monitoring).
- -
- Due to the risk of developing diabetic ketoacidosis or euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis, do not use Bexacat in cats with diabetes mellitus who have previously been treated with insulin, who are receiving insulin, or in cats with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (see Contraindications).
- -
- Bexacat should not be initiated in cats with anorexia, dehydration or lethargy at the time of diagnosis of diabetes mellitus or without appropriate screening tests (see Animal Safety Warnings).
-
DESCRIPTION
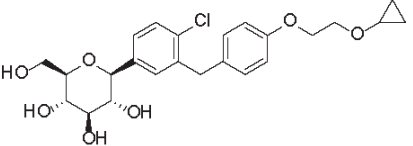
Bexacat (bexagliflozin tablets) are flavored pentagonal, 10 mm, speckled white, brown, or tan biconvex with a characteristic odor. The empirical formula is C24H29ClO7 and the molecular weight is 464.94 g/mol. The chemical name is (2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-2-(4-chloro-3-(4-(2-cyclopropoxyethoxy)benzyl)phenyl)-6-(hydroxymethyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-3,4,5-triol. The chemical structure of bexagliflozin is:
- INDICATION
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Always provide the Client Information Sheet with the prescription.
Dosing Instructions
Administer one tablet by mouth to cats weighing 6.6 lbs (3.0 kg) or greater once daily, at approximately the same time each day, with or without food, and regardless of blood glucose level.
- •
- Sudden onset of hyporexia/anorexia, lethargy, dehydration, or weight loss in cats receiving Bexacat should prompt immediate discontinuation of Bexacat and assessment for diabetic ketoacidosis, regardless of blood glucose level.
- •
- During treatment with Bexacat, blood glucose, fructosamine, serum β-hydroxybutyrate (BHBA), serum feline pancreas-specific lipase (fPL), liver parameters, serum cholesterol and triglycerides; and body weight and clinical signs should be routinely monitored.
- o
- Increasing or persistently elevated feline pancreas-specific lipase or liver parameters should prompt further evaluation for pancreatitis and/or hepatic disease and consideration for discontinuing Bexacat.
- o
- BHBA is the predominate ketoacid in diabetic ketoacidosis. Bexacat should be discontinued if a notable reduction in BHBA is not observed after initiation of Bexacat, or if BHBA persistently rises after an initial reduction.
- o
- Cats with increasing or persistently elevated cholesterol and triglyceride levels may be at an increased risk for developing diabetic ketoacidosis or euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis.
- o
- Bexacat should be discontinued if poor glycemic control, as described below, develops.
- •
- During the first 8 weeks after initiation of Bexacat, assessment of glycemic control and clinical improvement should be evaluated.
- o
- A physical examination, an 8-hour blood glucose curve, serum fructosamine and body weight should be assessed at 2, 4 and 8 weeks.
- o
- Cats demonstrating poor glycemic control, including weight loss, an average blood glucose concentration from an 8-hour blood glucose curve ≥ 250 mg/dL, and/or a fructosamine indicating poor glycemic control should be closely monitored.
- o
- Bexacat should be discontinued, and initiation of insulin considered in cats demonstrating poor glycemic control, as described above, at 8 weeks.
- •
- Cats may present with diabetic ketoacidosis and a normal blood glucose concentration (euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis). Delay in recognition and treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis and euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis may result in increased morbidity and mortality.
- •
- Development of diabetic ketoacidosis and euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis requires the following actions:
- o
- Discontinuation of Bexacat
- o
- Prompt initiation of insulin therapy
- o
- Administration of dextrose or other carbohydrate source, regardless of blood glucose concentration
- o
- Appropriate nutritional support should be promptly initiated to prevent or treat hepatic lipidosis.
For more information refer to CONTRAINDICATIONS and WARNINGS.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- •
- Do not use Bexacat in cats with diabetes mellitus who have previously been treated with insulin, who are receiving insulin, or in cats with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. The use of Bexacat in cats with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, or the withdrawal of insulin and initiation of Bexacat, is associated with an increased risk of diabetic ketoacidosis or euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis and death.
- •
- Due to risk of severe adverse reactions, do not use Bexacat in cats with evidence of hepatic disease or reduced renal function.
-
WARNINGS
User Safety Warnings
Not for use in humans. Keep out of reach of children. Consult a physician in case of accidental ingestion by humans.
- •
- Bexacat should not be initiated in cats with:
- o
- Anorexia, dehydration, or lethargy at the time of diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, as it may indicate the presence of other concurrent disease and increase the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis.
- o
- An fPL level > 5.3 mcg/L, diagnostic imaging consistent with pancreatitis, a history of pancreatitis, or current clinical signs suggestive of pancreatitis.
- o
- Laboratory values consistent with diabetic ketoacidosis, including elevated urine or serum ketones, and metabolic acidosis (high anion gap, or decreased bicarbonate, pH, or partial pressure carbon dioxide [PaCO2] levels).
- o
- A BHBA > 37 mg/dL, or if BHBA is > 25 mg/dL and the cat has a history of renal disease or metabolic acidosis.
- •
- Persistent plasma bexagliflozin concentrations and reduced clearance of Bexacat, represented as the presence of plasma half-lives in excess of 24 hours, may result in prolonged clinical effects such as glucosuria and/or euglycemia despite discontinuation of Bexacat in some cats with hepatic disease and/or reduced renal function, including cats with clinically undetectable disease at the time of Bexacat initiation. Reduced clearance of Bexacat may contribute to persistent glucosuria, resulting in an osmotic diuresis and dehydration that requires appropriate hydration support. These cats may require hospitalization, which may be protracted, for sequalae such as diabetic ketoacidosis, euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis, or hepatic lipidosis.
- •
- Cats should be screened for urinary tract infections and treated, if indicated, when initiating Bexacat. Treatment with Bexacat may increase the risk for urinary tract infections (see Adverse Reactions). Cats treated with Bexacat should be monitored for urinary tract infections and treated promptly. Consider discontinuation of Bexacat in cats with recurrent urinary tract infections.
- •
- Bexacat may cause increased serum calcium concentrations. Bexacat should be discontinued in cats with persistent increases in serum total calcium or ionized calcium because of increased risk of forming calcium containing uroliths (see Adverse Reactions).
- •
- Long term use of Bexacat may increase the risk of urothelial carcinoma (see Adverse Reactions).
- •
- Keep Bexacat in a secure location out of reach of dogs, cats, and other animals to prevent accidental ingestion or overdose.
-
PRECAUTIONS
- •
- Bexacat should be discontinued in cats who develop diarrhea unresponsive to conventional therapy.
- •
- Consider temporary discontinuation of Bexacat in cats during times of decreased caloric intake, such as surgery or decreased appetite, as administration of Bexacat in these cats may increase the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis or hepatic lipidosis.
- •
- The osmotic diuretic effects of Bexacat may contribute to inappropriate urination in some cats (see Adverse Reactions).
- •
- Polyphagia as a compensatory response to caloric wasting from glucosuria may persist in up to 80% of cats, despite evidence of adequate glycemic control, and may lead to progressive weight gain.
- •
- Approximately 20-30% of cats may have persistent polyuria and/or polydipsia secondary to Bexacat-induced osmotic diuresis and may be a risk factor for dehydration-associated diabetic ketoacidosis.
- •
- The concurrent use of volume depleting drugs in cats treated with Bexacat has not been evaluated.
- •
- The safety of Bexacat in breeding, pregnant, and lactating cats has not been evaluated.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Field Study
Eighty-four cats with newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus were enrolled in a 180-day multicenter field effectiveness and safety study. Safety data were evaluated in 84 cats treated with at least one dose of Bexacat. All cats received one tablet, once daily, regardless of body weight or blood glucose level. Seventy-two of the 84 enrolled cats completed the study. The most common adverse reactions included elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN), vomiting, elevated urine specific gravity (USG), elevated serum fPL, diarrhea, anorexia, lethargy, and dehydration. The adverse reactions seen during the field study are summarized in Table 1 below.
Table 1. Adverse Reactions (n=84) * Most cats had elevations < 1.5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN).
† Elevations were predominantly attributable to dehydration and/or glucosuria.
‡ Most cats had one or more isolated elevations, followed by a return to previous values.
§ Of nine cats with elevations ≥ 1.5X ULN, 2 cats developed diabetic ketoacidosis and were transitioned to insulin. One cat developed diabetic ketoacidosis and hepatic lipidosis resulting in death (euthanasia). One cat developed anemia, progressive weight loss and fPL elevations resulting in death.
** Observations included hiding, agitation, aggression, vocalization, and anxious behavior.Adverse Reaction
Number (%)
Elevated BUN*
46 (54.8)
Vomiting
42 (50.0)
Elevated USG†
33 (39.3)
Elevated fPL‡
33 (39.3)
Diarrhea
32 (38.1)
Anorexia
31 (37.0)
Lethargy
17 (20.2)
Dehydration
16 (19.0)
Elevated symmetrical dimethylarginine (SDMA)
13 (15.5)
Weight loss
13 (15.5)
Urinary tract infection
12 (14.3)
Elevated ALT and/or AST§
11 (13.1)
Hypercalcemia
8 (9.5)
Behavioral changes**
6 (7.1)
Proteinuria
5 (6.0)
Elevated creatinine
4 (4.8)
Elevated creatine kinase
4 (4.8)
Inappropriate urination
4 (4.8)
Death
3 (3.6)
Diabetic ketoacidosis
3 (3.6)
Pancreatitis
3 (3.6)
Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis
2 (2.4)
Hepatic lipidosis
2 (2.4)
Elevated alkaline phosphatase
2 (2.4)
Elevated total bilirubin
2 (2.4)
Constipation
2 (2.4)
Nine serious adverse reactions associated with Bexacat administration occurred during the study, including three cats who died or were euthanized. Of the three cats who died or were euthanized, two cats became clinically ill within 5 doses of Bexacat administration (range 3 to 5 doses). One cat with euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis and hepatic lipidosis was euthanized due to further deterioration of its clinical condition, despite supportive treatment. One cat demonstrating anorexia, lethargy, dehydration, azotemia, and hypokalemia was euthanized without supportive treatment. One cat, who demonstrated a lack of effectiveness, anemia and hepatic lipidosis died on Day 77 despite supportive treatment and additional diagnostics. Six of the nine cats had serious adverse reactions that did not result in death or euthanasia. Five cats were treated for their clinical conditions and transitioned to insulin. Serious adverse reactions in these cats were associated with the following conditions (number of cats): euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis (1); lack of effectiveness, diabetic ketoacidosis, elevated liver parameters (1); diabetic ketoacidosis (1); diabetic ketoacidosis and pyelonephritis (1); and lack of effectiveness, weight loss, dehydration (1). One cat with constipation and pancreatitis received supportive treatment and remained on Bexacat (bexagliflozin tablets).
Pilot Field Study
Eighty-nine cats with newly diagnosed diabetes mellitus were enrolled in a 56-day multicenter pilot field effectiveness and safety study, with continued use for up to 180 days. All cats received one tablet, once daily, regardless of body weight or blood glucose level. Safety data were evaluated for all 89 cats treated with at least one dose of bexagliflozin. The most common adverse reactions included elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN), elevated urine specific gravity (USG), elevated serum feline pancreas-specific lipase, vomiting, diarrhea/loose stool, hyporexia/anorexia, lethargy, elevated serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and/or aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and urinary tract infections. The adverse reactions seen in the pilot study are summarized in Table 2 below.
Table 2. Adverse Reactions (n=89) * Most cats had elevations ≤ 1.5X upper limit of normal (ULN).
† Elevations were predominantly attributable to dehydration and/or glucosuria.
‡ Most cats had one or more isolated elevations, followed by a return to previous values.
§ Most elevations were ≤ 2X ULN. One cat had marked ALT and AST (9X and 6X upper limit of normal, respectively) elevations on Day 28. Following discontinuation of bexagliflozin, the liver enzymes decreased within 24 hours and returned to within reference range in 10 days.
** Observations included hiding, hyperactivity, vocalization, and abnormal behavior.Adverse Reaction
Number (%)
Elevated BUN*
51 (57.3)
Elevated USG†
43 (48.3)
Elevated fPL‡
39 (43.8)
Vomiting
39 (43.8)
Diarrhea/Loose Stool
29 (32.6)
Hyporexia/Anorexia
28 (31.4)
Lethargy
16 (18.0)
Elevated ALT and/or AST§
13 (14.6)
Urinary tract infection
13 (14.6)
Dehydration
10 (11.2)
Elevated symmetrical dimethylarginine (SDMA)
10 (11.2)
Behavioral changes**
9 (10.1)
Ketosis/Ketonuria
8 (9.0)
Weight loss
8 (9.0)
Proteinuria
8 (9.0)
Pancreatitis
7 (7.9)
Death
6 (6.7)
Anemia
6 (6.7)
Hepatopathy
6 (6.7)
Hypercalcemia
4 (4.5)
Elevated creatine kinase
4 (4.5)
Inappropriate urination
4 (4.5)
Peritonitis
3 (3.4)
Constipation
3 (3.4)
Elevated creatinine
2 (2.2)
Euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis
2 (2.2)
Diabetic ketoacidosis
2 (2.2)
Hemolytic anemia
2 (2.2)
Elevated total bilirubin
2 (2.2)
Twenty cats (22%) had at least one blood glucose value < 65 mg/dL recorded during 8-hour blood glucose curves. No clinical signs of hypoglycemia were observed and bexagliflozin dosing was not adjusted in any cat due to documented hypoglycemia. Nine serious adverse reactions associated with bexagliflozin administration occurred during the study, including six cats who died or were euthanized. Of the six cats who died or were euthanized, five became clinically ill within receiving 5 doses of bexagliflozin (range 1 to 5 doses). Four of the cats were euthanized due to further deterioration of their clinical condition despite supportive treatment. One cat died despite supportive treatment. Deaths were associated with the following conditions (number of cats): necrotizing pancreatitis and pancreatic abscess (1), pancreatitis and hepatic lipidosis (1), euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis and severe hepatic lipidosis (1), pancreatitis and hepatic abscesses (1), diabetic ketoacidosis (1), and persistent polyuria and polydipsia and quality of life concerns (1).
Three of nine serious adverse reactions that did not result in death or euthanasia included the following (number of cats): acute hepatocellular injury (1), immune-mediated hemolytic anemia (1), and euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis with concurrent pancreatitis and hepatopathy (1). Two cats with serious adverse reactions demonstrated persistent bexagliflozin blood plasma levels and elimination half-lives after discontinuation of bexagliflozin. One cat with renal and liver values within the reference range at screening was euthanized due to a continued decline in clinical condition despite treatment for euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis and severe hepatic lipidosis. The second cat, noted to have IRIS (International Renal Interest Society) stage II renal disease and liver values within the reference range at screening, recovered following treatment for marked liver enzyme elevations above the reference range on Day 28.
Extended Use Field Study
One hundred twenty-five cats with diabetes mellitus that had previously completed a bexagliflozin field study were enrolled in a multicenter extended use field study. Cats were enrolled in the study for a range of 7 to 1064 days, with a mean of 329 days. Safety data were evaluated for all 125 cats treated with at least one dose of Bexacat (bexagliflozin tablets). All cats received one tablet, once daily, regardless of body weight or blood glucose level. Forty-nine of the 125 enrolled cats were withdrawn from the study due to adverse reactions, serious adverse reactions, death/euthanasia, lack of effectiveness, suspected diabetic remission, withdrawal of owner consent, or lost to follow up. The most common adverse reactions were similar to those noted in the previous field studies and included elevated USG (35.2%), vomiting (27.2%), elevated fPL (26.4%), anorexia (24.0%), diarrhea (22.4%), urinary tract infections (17.6%), lethargy (16.8%), and death (16.0%).
Twenty serious adverse reactions associated with Bexacat administration occurred during the study, all resulting in death or euthanasia. Clinical signs of hypoglycemia were observed in two of these cats. Deaths were associated with the following conditions (number of cats), with some cats experiencing multiple comorbidities (necropsy was not granted in all cases): euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis (8); diabetic ketoacidosis (4); hepatic lipidosis (5); pancreatic necrosis/peripancreatic fat saponification (3); urothelial carcinoma (2); hypercalcemia, recurrent calcium containing cystic calculi (1); lack of effectiveness, weight loss, anorexia (1); lethargy, weight loss, pallor (1); chronic renal disease, glomerulonephritis (1); chronic enteropathy (1); hypoglycemia, possible pancreatitis (1).
-
CONTACT INFORMATION
To report suspected adverse events, for technical assistance, or to obtain a copy of the Safety Data Sheet (SDS), contact Elanco US Inc at 1-888-545-5973.
For additional information about reporting adverse drug experiences for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or http://www.fda.gov/reportanimalae
- INFORMATION FOR CAT OWNERS
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action
Bexagliflozin is an inhibitor of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2), the renal transporter responsible for reabsorption of glucose from the glomerular filtrate back into the circulation. By inhibiting SGLT2, bexagliflozin reduces renal reabsorption of filtered glucose and lowers the renal threshold for glucose, thereby increasing urinary glucose excretion.
Pharmacokinetics
In a laboratory pilot study conducted to determine the prandial state of maximum exposure, systemic exposure for bexagliflozin was greater in the fasted state than in the fed state by 82% for the mean maximum observed plasma concentration (Cmax), and by 54% for the mean area under the plasma concentration versus time curve (AUC) from dosing (time 0) to the last quantifiable concentration (AUC0-last), respectively.
In a well-controlled margin of safety study (see Target Animal Safety), mean Cmax was approximately dose-proportional over a dosage range of 5 mg/kg (1X) to 25 mg/kg (5X). Mean AUC from time 0 to 24 hours exposure was approximately dose-proportional over a dosage range of 5 to 15 mg/kg, but more than dose-proportional at 15 to 25 mg/kg. An increase in exposure (AUC0-24 and Cmax), was observed in female cats compared to male cats on all evaluation days. Median time to reach peak plasma concentration (Tmax) was approximately 0.5 hours (range 0.5 to 2 hours) and mean half-life (T1/2) was approximately 5 hours across all dose groups. There was no accumulation of bexagliflozin following daily dosing of 5, 15, and 25 mg/kg in healthy non-diabetic cats. However, field studies showed that some diabetic cats had persistent bexagliflozin blood levels after discontinuation of the drug, which may be related to a decrease in liver function in some cats (see Animal Safety Warnings)
-
EFFECTIVENESS
Field Study
Eighty-four cats diagnosed with diabetes mellitus were enrolled in a 180-day multicenter field effectiveness and safety study. Enrolled cats included purebreds and mixed breeds, ranging in age from 3 to 19 years, and weighing between 7.3 to 24.3 lbs (3.3 to 11.3 kg). Cats received one tablet, once daily, regardless of body weight or blood glucose level. Treatment success was defined as improvement in at least one blood glucose variable (blood glucose curve mean or fructosamine) and improvement in at least one clinical sign of diabetes mellitus (polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia, or body weight [weight gain or no weight loss]).
Of 77 cats included in the effectiveness-evaluable population:
- •
- 64 cats (83.1%) were considered a treatment success on Day 56.
- •
- The lower bound two-sided 90% confidence interval was 74.5%. Effectiveness was demonstrated if the lower bound of the confidence interval was > 66%.
- •
- Mean blood glucose curve mean decreased from 284 mg/dL on Day 0 to 143 mg/dL on Day 56.
- •
- Mean fructosamine levels decreased from 544 µmol/L prior to Day 0 to 295 µmol/L on Day 56.
- •
- Improvements in the clinical signs of polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia, and body weight on Day 56 were observed in 53 (68.8%), 57 (74.0%), 44 (57.1%), and 42 (54.6%) cats, respectively.
- •
- 66 cats (85.7%) completed the 180-day study.
Pilot Field Study
Eighty-nine cats diagnosed with diabetes mellitus were enrolled in a 56-day, multicenter pilot field effectiveness and safety study with continued use for up to 180 days. Enrolled cats included purebreds and mixed breeds, ranging in age from 3 to 17 years and weighing 6.4 to 22.9 lbs (2.9 to 10.4 kg). Cats received one tablet, once daily, regardless of weight. Treatment success was defined as improvement in at least one blood glucose variable (blood glucose curve mean or fructosamine) and improvement in at least one clinical sign of diabetes mellitus (polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia, or body weight [weight gain or no weight loss]). Of the 72 cats included in the effectiveness-evaluable population, 58 (80.6%) were considered treatment successes on Day 56
-
TARGET ANIMAL SAFETY
In a well-controlled laboratory margin of safety study, Bexacat was administered orally to 28 fasted, healthy, lean, intact adult cats at doses of at least 1X (8 cats), 3X (8 cats), and 5X (12 cats) the maximum exposure dose (5 mg/kg) once daily for 26 weeks. The control group (8 cats) was sham dosed. The maximum exposure dose (5 mg/kg) was based on the assessment that the minimum weight of an eligible cat with diabetes mellitus is approximately 3 kg. Polyuria, glucosuria (with a corresponding increase in food consumption), loose stools and diarrhea, and ketonuria were reported more frequently in cats that received Bexacat than in control cats. There were drug-related clinically insignificant increases in calcium, magnesium, and cholesterol levels, and decreases in creatinine and amylase levels, and blood pressure and heart rate values. Gross necropsy demonstrated treatment-related observations of mild, diffuse zonal patterns in the liver. One cat with the observed zonal pattern had mild elevations of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and a histopathological observation of minimal, multifocal necrosis in the liver. The histopathological finding did not correspond to the zonal patterns observed grossly. There were no clinically relevant, drug-related effects on hematology and coagulation parameters and organ weight values
- STORAGE CONDITIONS
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Flavored tablet each containing 15 mg bexagliflozin; 30 or 90 tablets per bottle.
Approved by FDA under NADA # 141-566
Manufactured for: Elanco US Inc, Greenfield, IN 46140
Bexacat, Elanco and the diagonal bar logo are trademarks of Elanco or its affiliates.
© 2022 Elanco or its affiliatesSeptember 2022
PA103742 -
Client Information
ElancoTM
BexacatTM
(bexagliflozin tablets)
15 mg flavored tabletsClient Information Sheet
The Client Information Sheet contains important information about Bexacat. You should read this information before you start giving Bexacat to your cat and review it each time the prescription is refilled as there may be new information. This sheet is provided only as a summary and does not take the place of instructions from your veterinarian. Talk with your veterinarian if you do not understand any of this information or if you want to know more about Bexacat.
What is Bexacat?
Bexacat is a drug used to lower the amount of glucose (sugar) in the blood of otherwise healthy cats with diabetes mellitus not previously treated with insulin. Bexacat causes sugar to be passed out in the urine by preventing the kidneys from pulling sugar back into the blood.
What is diabetes mellitus (commonly called diabetes)?
Diabetes is a disease that affects how your cat’s body uses the sugar in its blood. Sugar is an important source of energy for the cells in your cat’s body. Cats with diabetes have high blood sugar because the sugar cannot get into the cells to be used for energy. Insulin helps sugar get into your cat’s cells for energy. Cats with diabetes may show an increase in thirst, hunger, and urination; weight loss; and/or weakness in the back legs.
Cats may have diabetes because, although they make enough insulin, their cells do not react to the insulin like they should (insulin resistant) or they do not make enough insulin and need to be given insulin for the cells to work the right way (insulin dependent). Some cats may begin as insulin resistant but may slowly become insulin dependent over time. Cats who are insulin dependent should not be treated with Bexacat because it may cause serious, sometimes fatal, side effects.
How does my veterinarian know if my cat is making enough insulin?
There is no test available for your veterinarian to know if your cat makes enough insulin or not. Based on your cat’s history and overall health, your veterinarian has decided Bexacat should be used to treat your cat’s diabetes.
What are some of the possible side effects of Bexacat?
Serious side effects have occurred, with or without warning, and have sometimes led to death in cats treated with Bexacat. Serious side effects may require your cat to be hospitalized and to be given specific treatments, including insulin. The most common side effects include vomiting, diarrhea or runny stools, less interest in food or not eating, lack of energy, and dehydration. Regular check-ups by your veterinarian are needed to monitor for side effects and to tell if your cat’s blood sugar is responding to Bexacat as expected.
STOP BEXACAT IMMEDIATELY AND CONTACT YOUR VETERINARIAN IF YOU NOTICE ANY OF THE FOLLOWING CHANGES OR SIDE EFFECTS IN YOUR CAT:
- •
- Less interest in food or not eating
- •
- Lack of energy or change in normal activity (for example, hiding or decreased grooming)
- •
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- •
- Weakness, difficulty walking or standing
What should I tell my veterinarian about my cat before starting Bexacat?
- •
- Tell your veterinarian if your cat has ever been treated with insulin, and about any medications your cat is taking, including prescription drugs and over-the-counter medications.
- •
- Tell your veterinarian about your cat’s past and present medical conditions, including a previous diagnosis of diabetes, diabetic ketoacidosis (a buildup of acids in the blood), hepatic lipidosis (fatty liver), pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas), or urinary tract infections.
- •
- Tell your veterinarian if your cat has any planned procedures that involve anesthesia, such as surgery or dentistry.
How will Bexacat affect my cat?
You may see a decrease in the amount of thirst, urine, and hunger in your cat, and your cat may gain weight.
How do I give Bexacat to my cat?
Give one tablet of Bexacat to your cat by mouth once daily. If you miss giving a tablet of Bexacat, give it as soon as you remember on the same day. Then continue giving Bexacat on your regular schedule. If you accidentally give your cat more than one tablet of Bexacat on the same day, contact your veterinarian if you see any side effects. If no side effects are seen, keep giving Bexacat on your regular schedule. Do not skip a dose.
To report side effects in your cat, call Elanco US Inc at 1-888-545-5973. For additional information about reporting side effects, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or http://www.fda.gov/reportanimalae.
Approved by FDA under NADA # 141-566
September 2022
Bexacat, Elanco and the diagonal bar logo are trademarks of Elanco or its affiliates.
© 2022 Elanco or its affiliates
PA103742B
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
30 tablets
ElancoTM
BexacatTM
(bexagliflozin tablets)15 mg flavored tablets
For oral use in cats only
Sodium-glucose
cotransporter 2
(SGLT2) inhibitorCAUTION: Federal law restricts this drug
to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.WARNING: Due to serious animal
safety concerns, read the entire
package insert before using this drug,
including the complete boxed warning.Bexacat is indicated to improve glycemic control
in otherwise healthy cats with diabetes mellitus
not previously treated with insulin.30 tablets
BexacatTM
(bexagliflozin tablets)15 mg flavored tablets
For oral use in cats only
WARNING: Due to serious animal
safety concerns, read the entire
package insert before using this drug,
including the complete boxed warning.CAUTION: Federal law restricts
this drug to use by or on the
order of a licensed veterinarian.Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2
(SGLT2) inhibitorProvide the Client Information Sheet to
owners before administering Bexacat.Approved by FDA under
NADA # 141-56690 tablets
ElancoTM
BexacatTM
(bexagliflozin tablets)15 mg flavored tablets
For oral use in cats only
Sodium-glucose
cotransporter 2
(SGLT2) inhibitorCAUTION: Federal law restricts this drug
to use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.WARNING: Due to serious animal
safety concerns, read the entire
package insert before using this drug,
including the complete boxed warning.Bexacat is indicated to improve glycemic
control in otherwise healthy cats with diabetes
mellitus not previously treated with insulin.90 tablets
Elanco
BexacatTM
(bexagliflozin tablets)15 mg flavored tablets
For oral use in cats only
WARNING: Due to serious
animal safety concerns, read
the entire package insert before
using this drug, including the
complete boxed warning.Bexacat is indicated to improve glycemic
control in otherwise healthy cats with diabetes
mellitus not previously treated with insulin.CAUTION: Federal law
restricts this drug to use
by or on the order of a
licensed veterinarian.Sodium-glucose
cotransporter 2
(SGLT2) inhibitorProvide the Client Information
Sheet to owners before
administering Bexacat.Approved by FDA under
NADA # 141-566 -
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
BEXACAT
bexagliflozin tablets tabletProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:58198-5315 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength BEXAGLIFLOZIN (UNII: EY00JF42FV) (BEXAGLIFLOZIN - UNII:EY00JF42FV) BEXAGLIFLOZIN 15 mg Product Characteristics Color BROWN (Light brown with white, brown, or tan speckles) Score no score Shape PENTAGON (5 sided) (Pentagonal, biconvex tablets) Size 10mm Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:58198-5315-1 1 in 1 CARTON 1 30 in 1 BOTTLE 2 NDC:58198-5315-2 1 in 1 CARTON 2 90 in 1 BOTTLE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NADA NADA141566 12/08/2022 Labeler - Elanco US Inc. (966985624)