Label: PRADAXA- dabigatran etexilate mesylate capsule
- NDC Code(s): 50090-4480-0
- Packager: A-S Medication Solutions
- This is a repackaged label.
- Source NDC Code(s): 0597-0360
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Drug Label Information
Updated December 15, 2023
If you are a healthcare professional or from the pharmaceutical industry please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Medication Guide: HTML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PRADAXA Capsules safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for PRADAXA Capsules.
PRADAXA® (dabigatran etexilate) capsules, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2010WARNING: (A) PREMATURE DISCONTINUATION OF PRADAXA INCREASES THE RISK OF THROMBOTIC EVENTS, and (B) SPINAL/EPIDURAL HEMATOMA
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning
(A) PREMATURE DISCONTINUATION OF PRADAXA INCREASES THE RISK OF THROMBOTIC EVENTS: Premature discontinuation of any oral anticoagulant, including PRADAXA, increases the risk of thrombotic events. To reduce this risk, consider coverage with another anticoagulant if PRADAXA is discontinued for a reason other than pathological bleeding or completion of a course of therapy (2.6, 2.7, 2.8, 5.1).
(B) SPINAL/EPIDURAL HEMATOMA: Epidural or spinal hematomas may occur in patients treated with PRADAXA who are receiving neuraxial anesthesia or undergoing spinal puncture. These hematomas may result in long-term or permanent paralysis (5.3). Monitor patients frequently for signs and symptoms of neurological impairment and if observed, treat urgently. Consider the benefits and risks before neuraxial intervention in patients who are or who need to be anticoagulated (5.3).
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
PRADAXA Capsules is a direct thrombin inhibitor indicated:
- To reduce the risk of stroke and systemic embolism in adult patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation (1.1)
- For the treatment of deep venous thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE) in adult patients who have been treated with a parenteral anticoagulant for 5-10 days (1.2)
- To reduce the risk of recurrence of DVT and PE in adult patients who have been previously treated (1.3)
- For the prophylaxis of DVT and PE in adult patients who have undergone hip replacement surgery (1.4)
- For the treatment of venous thromboembolic events (VTE) in pediatric patients 8 to less than 18 years of age who have been treated with a parenteral anticoagulant for at least 5 days (1.5)
- To reduce the risk of recurrence of VTE in pediatric patients 8 to less than 18 years of age who have been previously treated (1.6)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Non-valvular Atrial Fibrillation in Adult Patients:
-
Treatment of DVT and PE in Adult Patients:
- For patients with CrCl > 30 mL/min: 150 mg orally, twice daily after 5-10 days of parenteral anticoagulation (2.2)
-
Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of DVT and PE in Adult Patients:
- For patients with CrCl > 30 mL/min: 150 mg orally, twice daily after previous treatment (2.2)
-
Prophylaxis of DVT and PE Following Hip Replacement Surgery in Adult Patients:
- For patients with CrCl > 30 mL/min: 110 mg orally first day, then 220 mg once daily (2.2)
-
Treatment of Pediatric VTE:
- For pediatric patients: weight-based dosage, twice daily after at least 5 days of parenteral anticoagulant (2.3)
-
Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of Pediatric VTE:
- For pediatric patients: weight-based dosage, twice daily after previous treatment (2.3)
- Pradaxa Capsules are NOT substitutable on a milligram-to-milligram basis with other dabigatran etexilate dosage forms
- Review recommendations for converting to or from other oral or parenteral anticoagulants (2.6, 2.7)
- Temporarily discontinue PRADAXA before invasive or surgical procedures when possible, then restart promptly (2.8)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules: 75 mg, 110 mg and 150 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (> 15%) are gastrointestinal adverse reactions and bleeding (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at (800) 542-6257 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 12/2023
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: (A) PREMATURE DISCONTINUATION OF PRADAXA INCREASES THE RISK OF THROMBOTIC EVENTS, and (B) SPINAL/EPIDURAL HEMATOMA
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Reduction of Risk of Stroke and Systemic Embolism in Non-valvular Atrial Fibrillation in Adult Patients
1.2 Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients
1.3 Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients
1.4 Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients Following Hip Replacement Surgery
1.5 Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Events in Pediatric Patients
1.6 Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of Venous Thromboembolic Events in Pediatric Patients
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosage Information
2.2 Recommended PRADAXA Capsules Dosage for Adults
2.3 Recommended PRADAXA Capsules Dosage for Pediatrics
2.4 Dosage Adjustments
2.5 Administration
2.6 Converting from or to Warfarin
2.7 Converting from or to Parenteral Anticoagulants
2.8 Discontinuation for Surgery and Other Interventions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Increased Risk of Thrombotic Events after Premature Discontinuation
5.2 Risk of Bleeding
5.3 Spinal/Epidural Anesthesia or Puncture
5.4 Thromboembolic and Bleeding Events in Patients with Prosthetic Heart Valves
5.5 Effect of P-gp Inducers and Inhibitors on Dabigatran Exposure
5.6 Increased Risk of Thrombosis in Patients with Triple-Positive Antiphospholipid Syndrome
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Reduction of Risk of Stroke and Systemic Embolism in Non-valvular Atrial Fibrillation in Adult Patients
7.2 Treatment and Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients
7.3 Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients Following Hip Replacement Surgery
7.4 Treatment and Reduction in Risk of Recurrence of VTE in Pediatric Patients
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Reduction of Risk of Stroke and Systemic Embolism in Non-valvular Atrial Fibrillation in Adult Patients
14.2 Treatment and Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients
14.3 Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients Following Hip Replacement Surgery
14.4 Treatment of VTE in Pediatric Patients
14.5 Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of VTE in Pediatric Patients
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: (A) PREMATURE DISCONTINUATION OF PRADAXA INCREASES THE RISK OF THROMBOTIC EVENTS, and (B) SPINAL/EPIDURAL HEMATOMA
(A) PREMATURE DISCONTINUATION OF PRADAXA INCREASES THE RISK OF THROMBOTIC EVENTS
Premature discontinuation of any oral anticoagulant, including PRADAXA, increases the risk of thrombotic events. If anticoagulation with PRADAXA is discontinued for a reason other than pathological bleeding or completion of a course of therapy, consider coverage with another anticoagulant [see Dosage and Administration (2.6, 2.7, 2.8) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
(B) SPINAL/EPIDURAL HEMATOMA
Epidural or spinal hematomas may occur in patients treated with PRADAXA who are receiving neuraxial anesthesia or undergoing spinal puncture. These hematomas may result in long-term or permanent paralysis. Consider these risks when scheduling patients for spinal procedures. Factors that can increase the risk of developing epidural or spinal hematomas in these patients include:
- use of indwelling epidural catheters
- concomitant use of other drugs that affect hemostasis, such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), platelet inhibitors, other anticoagulants
- a history of traumatic or repeated epidural or spinal punctures
- a history of spinal deformity or spinal surgery
- optimal timing between the administration of PRADAXA and neuraxial procedures is not known
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Monitor patients frequently for signs and symptoms of neurological impairment. If neurological compromise is noted, urgent treatment is necessary [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Consider the benefits and risks before neuraxial intervention in patients anticoagulated or to be anticoagulated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Reduction of Risk of Stroke and Systemic Embolism in Non-valvular Atrial Fibrillation in Adult Patients
PRADAXA Capsules is indicated to reduce the risk of stroke and systemic embolism in adult patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation.
1.2 Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients
PRADAXA Capsules is indicated for the treatment of deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in adult patients who have been treated with a parenteral anticoagulant for 5-10 days.
1.3 Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients
PRADAXA Capsules is indicated to reduce the risk of recurrence of deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in adult patients who have been previously treated.
1.4 Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients Following Hip Replacement Surgery
PRADAXA Capsules is indicated for the prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in adult patients who have undergone hip replacement surgery.
1.5 Treatment of Venous Thromboembolic Events in Pediatric Patients
PRADAXA Capsules is indicated for the treatment of venous thromboembolic events (VTE) in pediatric patients 8 to less than 18 years of age who have been treated with a parenteral anticoagulant for at least 5 days [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
1.6 Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of Venous Thromboembolic Events in Pediatric Patients
PRADAXA Capsules is indicated to reduce the risk of recurrence of VTE in pediatric patients 8 to less than 18 years of age who have been previously treated [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosage Information
Dabigatran etexilate is available in different dosage forms and not all dosage forms are approved for the same indications and age groups. In addition, there are differences between the dosage forms with respect to dosing due to differences in bioavailability. Do not substitute different dosage forms on a milligram-to-milligram basis and do not combine more than one dosage form to achieve the total dose [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.2 Recommended PRADAXA Capsules Dosage for Adults
Indication Dosage Reduction in Risk of Stroke and Systemic Embolism in Non-valvular AF CrCl > 30 mL/min: 150 mg twice daily CrCl 15 to 30 mL/min: 75 mg twice daily CrCl < 15 mL/min or on dialysis: Dosing recommendations cannot be provided CrCl 30 to 50 mL/min with concomitant use of P-gp inhibitors: Reduce dosage to 75 mg twice daily if given with P-gp inhibitors dronedarone or systemic ketoconazole. CrCl < 30 mL/min with concomitant use of P-gp inhibitors: Avoid coadministration Treatment of DVT and PE CrCl > 30 mL/min: 150 mg twice daily Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of DVT and PE CrCl ≤ 30 mL/min or on dialysis: Dosing recommendations cannot be provided CrCl < 50 mL/min with concomitant use of P-gp inhibitors: Avoid coadministration Prophylaxis of DVT and PE Following Hip Replacement Surgery CrCl > 30 mL/min: 110 mg for first day, then 220 mg once daily CrCl ≤ 30 mL/min or on dialysis: Dosing recommendations cannot be provided CrCl < 50 mL/min with concomitant use of P-gp inhibitors: Avoid coadministration Reduction of Risk of Stroke and Systemic Embolism in Non-valvular Atrial Fibrillation in Adult Patients
For patients with creatinine clearance (CrCl) > 30 mL/min, the recommended dosage of PRADAXA Capsules is 150 mg taken orally, twice daily. For patients with severe renal impairment (CrCl 15-30 mL/min), the recommended dosage of PRADAXA Capsules is 75 mg twice daily [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Dosing recommendations for patients with a CrCl < 15 mL/min or on dialysis cannot be provided.
Treatment of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients
For patients with CrCl > 30 mL/min, the recommended dosage of PRADAXA Capsules is 150 mg taken orally, twice daily, after 5-10 days of parenteral anticoagulation. Dosing recommendations for patients with a CrCl ≤ 30 mL/min or on dialysis cannot be provided [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients
For patients with CrCl > 30 mL/min, the recommended dosage of PRADAXA Capsules is 150 mg taken orally, twice daily after previous treatment. Dosing recommendations for patients with a CrCl ≤ 30 mL/min or on dialysis cannot be provided [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients Following Hip Replacement Surgery
For patients with CrCl > 30 mL/min, the recommended dosage of PRADAXA Capsules is 110 mg taken orally 1-4 hours after surgery and after hemostasis has been achieved, then 220 mg taken once daily for 28-35 days. If PRADAXA is not started on the day of surgery, after hemostasis has been achieved initiate treatment with 220 mg once daily. Dosing recommendations for patients with a CrCl ≤ 30 mL/min or on dialysis cannot be provided [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2, 12.3)].
2.3 Recommended PRADAXA Capsules Dosage for Pediatrics
PRADAXA Capsules can be used in pediatric patients aged 8 to less than 18 years of age who are able to swallow the capsules whole. Other age-appropriate pediatric dosage forms of dabigatran etexilate are available for pediatric patients less than 8 years of age. For the treatment of VTE in pediatric patients, initiate treatment following treatment with a parenteral anticoagulant for at least 5 days. For reduction in risk of recurrence of VTE, initiate treatment following previous treatment.
PRADAXA Capsules is dosed orally twice daily, one dose in the morning and one dose in the evening, at approximately the same time every day. The dosing interval should be as close to 12 hours as possible.
The recommended dosage of PRADAXA Capsules for the treatment of or reducing the risk of VTE in pediatric patients 8 to less than 18 years of age is based on the patient's actual weight as shown in Table 1 below. Administer PRADAXA twice daily. Adjust the dosage according to actual weight as treatment progresses [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)].
Table 1 Weight-Based PRADAXA Capsules Dosage for Pediatric Patients Aged 8 to Less Than 18 Years Actual Weight (kg) Dosage (mg) Number of Capsules Needed 11 kg to less than 16 kg 75 mg twice daily one 75 mg capsule twice daily 16 kg to less than 26 kg 110 mg twice daily one 110 mg capsule twice daily 26 kg to less than 41 kg 150 mg twice daily one 150 mg capsule twice daily
or
two 75 mg capsules twice daily41 kg to less than 61 kg 185 mg twice daily one 110 mg capsule plus one 75 mg capsule twice daily 61 kg to less than 81 kg 220 mg twice daily two 110 mg capsule twice daily 81 kg or greater 260 mg twice daily one 150 mg capsule plus one 110 mg capsule twice daily
or
one 110 mg capsule plus two 75 mg capsules twice daily2.4 Dosage Adjustments
Adult patients with renal impairment
Assess renal function prior to initiation of treatment with PRADAXA Capsules. Periodically assess renal function as clinically indicated (i.e., more frequently in clinical situations that may be associated with a decline in renal function) and adjust therapy accordingly. Discontinue PRADAXA in patients who develop acute renal failure while on PRADAXA and consider alternative anticoagulant therapy.
Generally, in adult patients, the extent of anticoagulation does not need to be assessed. When necessary, use aPTT or ECT, and not INR, to assess for anticoagulant activity in adult patients on PRADAXA Capsules [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Reduction of Risk of Stroke and Systemic Embolism in Non-valvular Atrial Fibrillation
In patients with moderate renal impairment (CrCl 30-50 mL/min), concomitant use of the P-gp inhibitor dronedarone or systemic ketoconazole can be expected to produce dabigatran exposure similar to that observed in severe renal impairment. Reduce the dosage of PRADAXA Capsules to 75 mg twice daily [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Drug Interactions (7.1), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Treatment and Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
Dosing recommendations for patients with CrCl ≤ 30 mL/min cannot be provided. Avoid use of concomitant P-gp inhibitors in patients with CrCl < 50 mL/min [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Drug Interactions (7.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Following Hip Replacement Surgery
Dosing recommendations for patients with CrCl ≤ 30 mL/min or on dialysis cannot be provided. Avoid use of concomitant P-gp inhibitors in patients with CrCl < 50 mL/min [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Drug Interactions (7.3), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2, 12.3)].
Pediatric patients with renal impairment
Treatment and reduction in risk of recurrence of VTE in pediatric patients
Due to lack of data in pediatric patients with eGFR < 50 mL/min/1.73 m2 and the risk of increased exposure, avoid use of PRADAXA Capsules in these patients. Prior to the initiation of treatment with PRADAXA Capsules, estimate the glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) using the Schwartz formula: eGFR (Schwartz) = (0.413 × height in cm) / serum creatinine in mg/dL.
Treat patients with an eGFR > 50 mL/min/1.73 m2 with the dosage according to Table 1 [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
2.5 Administration
PRADAXA Capsules should be swallowed whole. PRADAXA Capsules should be taken with a full glass of water. Breaking, chewing, or emptying the contents of the capsule can result in increased exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
If a dose of PRADAXA Capsules is not taken at the scheduled time, the dose should be taken as soon as possible on the same day; the missed dose should be skipped if it cannot be taken at least 6 hours before the next scheduled dose. The dose of PRADAXA Capsules should not be doubled to make up for a missed dose.
Consider administration with food if gastrointestinal distress occurs with PRADAXA Capsules.
2.6 Converting from or to Warfarin
When converting patients from warfarin therapy to PRADAXA Capsules, discontinue warfarin and start PRADAXA Capsules when the INR is below 2.0.
When converting from PRADAXA Capsules to warfarin, adjust the starting time of warfarin as follows:
Adults
- For CrCl ≥ 50 mL/min, start warfarin 3 days before discontinuing PRADAXA Capsules.
- For CrCl 30-50 mL/min, start warfarin 2 days before discontinuing PRADAXA Capsules.
- For CrCl 15-30 mL/min, start warfarin 1 day before discontinuing PRADAXA Capsules.
- For CrCl < 15 mL/min, no recommendations can be made.
Pediatrics
- For eGFR ≥ 50 mL/min/1.73 m2, start warfarin 3 days before discontinuing PRADAXA Capsules.
- Pediatric patients with an eGFR < 50 mL/min/1.73 m2 have not been studied. Avoid use of PRADAXA Capsules in these patients.
Because PRADAXA Capsules can increase INR, the INR will better reflect warfarin's effect only after PRADAXA Capsules has been stopped for at least 2 days [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
2.7 Converting from or to Parenteral Anticoagulants
For adult and pediatric patients currently receiving a parenteral anticoagulant, start PRADAXA Capsules 0 to 2 hours before the time that the next dose of the parenteral drug was to have been administered or at the time of discontinuation of a continuously administered parenteral drug (e.g., intravenous unfractionated heparin).
For adult patients currently taking PRADAXA Capsules wait 12 hours (CrCl ≥ 30 mL/min) or 24 hours (CrCl < 30 mL/min) after the last dose of PRADAXA Capsules before initiating treatment with a parenteral anticoagulant [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
For pediatric patients currently taking PRADAXA, wait 12 hours after the last dose before switching to a parenteral anticoagulant.
2.8 Discontinuation for Surgery and Other Interventions
If possible, discontinue PRADAXA Capsules in adults 1 to 2 days (CrCl ≥ 50 mL/min) or 3 to 5 days (CrCl < 50 mL/min) before invasive or surgical procedures because of the increased risk of bleeding. Consider longer times for patients undergoing major surgery, spinal puncture, or placement of a spinal or epidural catheter or port, in whom complete hemostasis may be required [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
For pediatric patients, discontinue PRADAXA Capsules 24 hours before an elective surgery (eGFR > 80 mL/min/1.73 m2) or 2 days before an elective surgery (eGFR 50-80 mL/min/1.73 m2). Pediatric patients with an eGFR <50 mL/min/1.73 m2 have not been studied, avoid use of PRADAXA Capsules in these patients.
If surgery cannot be delayed, there is an increased risk of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. This risk of bleeding should be weighed against the urgency of intervention [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3)]. Use a specific reversal agent (idarucizumab) in case of emergency surgery or urgent procedures when reversal of the anticoagulant effect of dabigatran is needed in adults. Efficacy and safety of idarucizumab have not been established in pediatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Refer to the idarucizumab prescribing information for additional information. Restart PRADAXA Capsules as soon as medically appropriate.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
150 mg capsules with a light blue opaque cap imprinted in black with the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol and a white opaque body imprinted in black with "R150".
110 mg capsules with a light blue opaque cap imprinted in black with the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol and a light blue opaque body imprinted in black with "R110".
75 mg capsules with a white opaque cap imprinted in black with the Boehringer Ingelheim company symbol and a white opaque body imprinted in black with "R75".
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
PRADAXA is contraindicated in patients with:
- Active pathological bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)]
- History of a serious hypersensitivity reaction to dabigatran, dabigatran etexilate, or to one of the excipients of the product (e.g., anaphylactic reaction or anaphylactic shock) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]
- Mechanical prosthetic heart valve [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Increased Risk of Thrombotic Events after Premature Discontinuation
Premature discontinuation of any oral anticoagulant, including PRADAXA, in the absence of adequate alternative anticoagulation increases the risk of thrombotic events. If PRADAXA Capsules is discontinued for a reason other than pathological bleeding or completion of a course of therapy, consider coverage with another anticoagulant and restart PRADAXA Capsules as soon as medically appropriate [see Dosage and Administration (2.6, 2.7, 2.8)].
5.2 Risk of Bleeding
PRADAXA increases the risk of bleeding and can cause significant and, sometimes, fatal bleeding. Promptly evaluate any signs or symptoms of blood loss (e.g., a drop in hemoglobin and/or hematocrit or hypotension). Discontinue PRADAXA Capsules in patients with active pathological bleeding [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Risk factors for bleeding include the concomitant use of other drugs that increase the risk of bleeding (e.g., anti-platelet agents, heparin, fibrinolytic therapy, and chronic use of NSAIDs). PRADAXA's anticoagulant activity and half-life are increased in patients with renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Reversal of Anticoagulant Effect
In adults, a specific reversal agent (idarucizumab) for PRADAXA is available when reversal of the anticoagulant effect of dabigatran is needed:
- For emergency surgery/urgent procedures
- In life-threatening or uncontrolled bleeding
In pediatric patients, the efficacy and safety of idarucizumab have not been established.
Hemodialysis can remove dabigatran; however the clinical experience supporting the use of hemodialysis as a treatment for bleeding is limited [see Overdosage (10)]. Prothrombin complex concentrates, or recombinant Factor VIIa may be considered but their use has not been evaluated in clinical trials. Protamine sulfate and vitamin K are not expected to affect the anticoagulant activity of dabigatran. Consider administration of platelet concentrates in cases where thrombocytopenia is present or long-acting antiplatelet drugs have been used.
5.3 Spinal/Epidural Anesthesia or Puncture
When neuraxial anesthesia (spinal/epidural anesthesia) or spinal puncture is employed, patients treated with anticoagulant agents are at risk of developing an epidural or spinal hematoma which can result in long-term or permanent paralysis [see Boxed Warning].
To reduce the potential risk of bleeding associated with the concurrent use of PRADAXA and epidural or spinal anesthesia/analgesia or spinal puncture, consider the pharmacokinetic profile of dabigatran [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Placement or removal of an epidural catheter or lumbar puncture is best performed when the anticoagulant effect of dabigatran is low; however, the exact timing to reach a sufficiently low anticoagulant effect in each patient is not known.
Should the physician decide to administer anticoagulation in the context of epidural or spinal anesthesia/analgesia or lumbar puncture, monitor frequently to detect any signs or symptoms of neurological impairment, such as midline back pain, sensory and motor deficits (numbness, tingling, or weakness in lower limbs), bowel and/or bladder dysfunction. Instruct patients to immediately report if they experience any of the above signs or symptoms. If signs or symptoms of spinal hematoma are suspected, initiate urgent diagnosis and treatment including consideration for spinal cord decompression even though such treatment may not prevent or reverse neurological sequelae.
5.4 Thromboembolic and Bleeding Events in Patients with Prosthetic Heart Valves
The safety and efficacy of PRADAXA Capsules in adult patients with bileaflet mechanical prosthetic heart valves was evaluated in the RE-ALIGN trial, in which patients with bileaflet mechanical prosthetic heart valves (recently implanted or implanted more than three months prior to enrollment) were randomized to dose-adjusted warfarin or 150 mg, 220 mg, or 300 mg of PRADAXA Capsules twice a day. RE-ALIGN was terminated early due to the occurrence of significantly more thromboembolic events (valve thrombosis, stroke, transient ischemic attack, and myocardial infarction) and an excess of major bleeding (predominantly post-operative pericardial effusions requiring intervention for hemodynamic compromise) in the PRADAXA Capsules treatment arm as compared to the warfarin treatment arm. These bleeding and thromboembolic events were seen both in patients who were initiated on PRADAXA Capsules postoperatively within three days of mechanical bileaflet valve implantation, as well as in patients whose valves had been implanted more than three months prior to enrollment. Therefore, the use of PRADAXA is contraindicated in all patients with mechanical prosthetic valves [see Contraindications (4)].
The use of PRADAXA for the prophylaxis of thromboembolic events in patients with atrial fibrillation in the setting of other forms of valvular heart disease, including the presence of a bioprosthetic heart valve, has not been studied and is not recommended.
5.5 Effect of P-gp Inducers and Inhibitors on Dabigatran Exposure
The concomitant use of PRADAXA with P-gp inducers (e.g., rifampin) reduces exposure to dabigatran and should generally be avoided [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
P-gp inhibition and impaired renal function are the major independent factors that result in increased exposure to dabigatran [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Concomitant use of P-gp inhibitors in patients with renal impairment is expected to produce increased exposure of dabigatran compared to that seen with either factor alone.
Reduction of Risk of Stroke and Systemic Embolism in Non-valvular Atrial Fibrillation in Adult Patients
Reduce the dosage of PRADAXA Capsules to 75 mg twice daily when dronedarone or systemic ketoconazole is co-administered with PRADAXA Capsules in patients with moderate renal impairment (CrCl 30-50 mL/min). Avoid use of PRADAXA Capsules and P-gp inhibitors in patients with severe renal impairment (CrCl 15-30 mL/min) [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Treatment and Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients
Avoid use of PRADAXA Capsules and concomitant P-gp inhibitors in patients with CrCl < 50 mL/min [see Drug Interactions (7.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients Following Hip Replacement Surgery
Avoid use of PRADAXA Capsules and concomitant P-gp inhibitors in patients with CrCl < 50 mL/min [see Drug Interactions (7.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
5.6 Increased Risk of Thrombosis in Patients with Triple-Positive Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Direct-acting oral anticoagulants (DOACs), including PRADAXA, are not recommended for use in patients with triple-positive antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). For patients with APS (especially those who are triple-positive [positive for lupus anticoagulant, anticardiolipin, and anti-beta 2-glycoprotein I antibodies]), treatment with DOACs has been associated with increased rates of recurrent thrombotic events compared with vitamin K antagonist therapy.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Increased Risk of Thrombotic Events after Premature Discontinuation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Risk of Bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Spinal/Epidural Anesthesia or Puncture [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Thromboembolic and Bleeding Events in Patients with Prosthetic Heart Valves [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Increased Risk of Thrombosis in Patients with Triple-Positive Antiphospholipid Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
The most serious adverse reactions reported with PRADAXA were related to bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reactions rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adult Trials
Reduction of Risk of Stroke and Systemic Embolism in Non-valvular Atrial Fibrillation
The RE-LY (Randomized Evaluation of Long-term Anticoagulant Therapy) study provided safety information on the use of two doses of PRADAXA Capsules and warfarin [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The numbers of patients and their exposures are described in Table 2. Limited information is presented on the 110 mg dosing arm because this dose is not approved.
Table 2 Summary of Treatment Exposure in RE-LY PRADAXA Capsules 110 mg twice daily PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg twice daily Warfarin Total number treated 5,983 6,059 5,998 Exposure > 12 months 4,936 4,939 5,193 > 24 months 2,387 2,405 2,470 Mean exposure (months) 20.5 20.3 21.3 Total patient-years 10,242 10,261 10,659 Drug Discontinuation in RE-LY
The rates of adverse reactions leading to treatment discontinuation were 21% for PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg and 16% for warfarin. The most frequent adverse reactions leading to discontinuation of PRADAXA Capsules were bleeding and gastrointestinal events (i.e., dyspepsia, nausea, upper abdominal pain, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, and diarrhea).
Bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Table 3 shows the number of adjudicated major bleeding events during the treatment period in the RE-LY study, with the bleeding rate per 100 subject-years (%). Major bleeding is defined as bleeding accompanied by one or more of the following: a decrease in hemoglobin of ≥ 2 g/dL, a transfusion of ≥ 2 units of packed red blood cells, bleeding at a critical site or with a fatal outcome. Intracranial hemorrhage included intracerebral (hemorrhagic stroke), subarachnoid, and subdural bleeds.
Table 3 Adjudicated Major Bleeding Events in Treated Patientsa Event PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg
N = 6,059
n (%/yearb)Warfarin
N = 5,998
n (%/yearb)PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg vs Warfarin
HR (95% CI)aPatients during treatment or within 2 days of stopping study treatment. Major bleeding events within each subcategory were counted once per patient, but patients may have contributed events to multiple subcategories.
bAnnual event rate per 100 pt-years = 100 * number of subjects with event/subject-years. Subject-years is defined as cumulative number of days from first drug intake to event date, date of last drug intake + 2, death date (whatever occurred first) across all treated subjects divided by 365.25. In case of recurrent events of the same category, the first event was considered.
cDefined as bleeding accompanied by one or more of the following: a decrease in hemoglobin of ≥ 2 g/dL, a transfusion of 2 or more units of packed red blood cells, bleeding at a critical site or with fatal outcome.
dIntracranial bleed included intracerebral (hemorrhagic stroke), subarachnoid, and subdural bleeds.
eOn-treatment analysis based on the safety population, compared to ITT analysis presented in Section 14 Clinical Studies.
fFatal bleed: Adjudicated major bleed as defined above with investigator reported fatal outcome and adjudicated death with primary cause from bleeding.
gNon-intracranial fatal bleed: Adjudicated major bleed as defined above and adjudicated death with primary cause from bleeding but without symptomatic intracranial bleed based on investigator's clinical assessment.Major Bleedingc 350 (3.47) 374 (3.58) 0.97 (0.84, 1.12) Intracranial Hemorrhage (ICH)d 23 (0.22) 82 (0.77) 0.29 (0.18, 0.46) Hemorrhagic Strokee 6 (0.06) 40 (0.37) 0.16 (0.07, 0.37) Other ICH 17 (0.17) 46 (0.43) 0.38 (0.22, 0.67) Gastrointestinal 162 (1.59) 111 (1.05) 1.51 (1.19, 1.92) Fatal Bleedingf 7 (0.07) 16 (0.15) 0.45 (0.19, 1.10) ICH 3 (0.03) 9 (0.08) 0.35 (0.09, 1.28) Non-intracranialg 4 (0.04) 7 (0.07) 0.59 (0.17, 2.02) There was a higher rate of any gastrointestinal bleeds in patients receiving PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg than in patients receiving warfarin (6.6% vs 4.2%, respectively).
The risk of major bleeds was similar with PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg and warfarin across major subgroups defined by baseline characteristics (see Figure 1), with the exception of age, where there was a trend toward a higher incidence of major bleeding on PRADAXA Capsules (hazard ratio 1.2, 95% CI: 1.0 to 1.5) for patients ≥ 75 years of age.
Figure 1 Adjudicated Major Bleeding by Baseline Characteristics Including Hemorrhagic Stroke Treated Patients
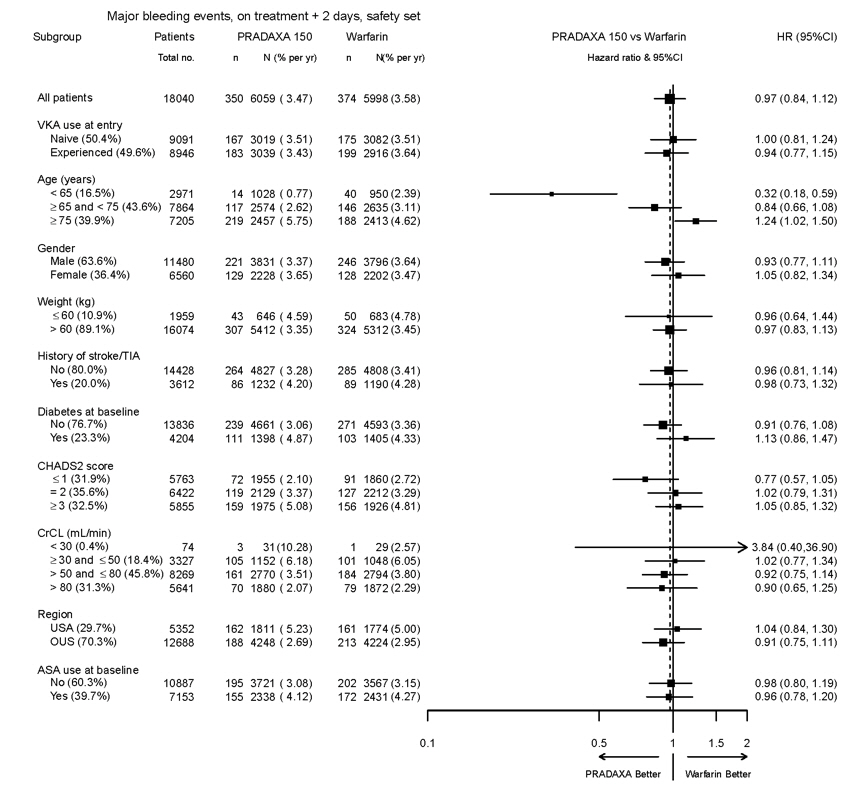
Note: The figure above presents effects in various subgroups all of which are baseline characteristics and all of which were pre-specified. The 95% confidence limits that are shown do not take into account how many comparisons were made, nor do they reflect the effect of a particular factor after adjustment for all other factors. Apparent homogeneity or heterogeneity among groups should not be over-interpreted.
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
Patients on PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg had an increased incidence of gastrointestinal adverse reactions (35% vs 24% on warfarin). These were commonly dyspepsia (including abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain, abdominal discomfort, and epigastric discomfort) and gastritis-like symptoms (including GERD, esophagitis, erosive gastritis, gastric hemorrhage, hemorrhagic gastritis, hemorrhagic erosive gastritis, and gastrointestinal ulcer).
Treatment and Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism
PRADAXA Capsules was studied in 4,387 patients in 4 pivotal, parallel, randomized, double-blind trials. Three of these trials were active-controlled (warfarin) (RE-COVER, RE-COVER II, and RE-MEDY), and one study (RE-SONATE) was placebo-controlled. The demographic characteristics were similar among the 4 pivotal studies and between the treatment groups within these studies. Approximately 60% of the treated patients were male, with a mean age of 55.1 years. The majority of the patients were white (87.7%), 10.3% were Asian, and 1.9% were black with a mean CrCl of 105.6 mL/min.
Bleeding events for the 4 pivotal studies were classified as major bleeding events if at least one of the following criteria applied: fatal bleeding, symptomatic bleeding in a critical area or organ (intraocular, intracranial, intraspinal or intramuscular with compartment syndrome, retroperitoneal bleeding, intra-articular bleeding, or pericardial bleeding), bleeding causing a fall in hemoglobin level of 2.0 g/dL (1.24 mmol/L or more, or leading to transfusion of 2 or more units of whole blood or red cells).
RE-COVER and RE-COVER II studies compared PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg twice daily and warfarin for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Patients received 5-10 days of an approved parenteral anticoagulant therapy followed by 6 months, with mean exposure of 164 days, of oral only treatment; warfarin was overlapped with parenteral therapy. Table 4 shows the number of patients experiencing bleeding events in the pooled analysis of RE-COVER and RE-COVER II studies during the full treatment including parenteral and oral only treatment periods after randomization.
Table 4 Bleeding Events in RE-COVER and RE-COVER II Treated Patients Bleeding Events—Full Treatment Period Including Parenteral Treatment Note: MBE can belong to more than one criterion.
aPatients with at least one MBE.
bBleeding site based on investigator assessment. Patients can have more than one site of bleeding.
cConfidence intervalPRADAXA Capsules
150 mg twice daily
N (%)Warfarin
N (%)Hazard Ratio
(95% CI)cPatients N=2,553 N=2,554 Major bleeding eventa 37 (1.4) 51 (2.0) 0.73 (0.48, 1.11) Fatal bleeding 1 (0.04) 2 (0.1) Bleeding in a critical area or organ 7 (0.3) 15 (0.6) Fall in hemoglobin ≥ 2 g/dL or transfusion ≥ 2 units of whole blood or packed red blood cells 32 (1.3) 38 (1.5) Bleeding sites for MBEb Intracranial 2 (0.1) 5 (0.2) Retroperitoneal 2 (0.1) 1 (0.04) Intraarticular 2 (0.1) 4 (0.2) Intramuscular 2 (0.1) 6 (0.2) Gastrointestinal 15 (0.6) 14 (0.5) Urogenital 7 (0.3) 14 (0.5) Other 8 (0.3) 8 (0.3) Clinically relevant non-major bleeding 101 (4.0) 170 (6.7) 0.58 (0.46, 0.75) Any bleeding 411 (16.1) 567 (22.7) 0.70 (0.61, 0.79) The rate of any gastrointestinal bleeds in patients receiving PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg in the full treatment period was 3.1% (2.4% on warfarin).
The RE-MEDY and RE-SONATE studies provided safety information on the use of PRADAXA Capsules for the reduction in the risk of recurrence of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.
RE-MEDY was an active-controlled study (warfarin) in which 1,430 patients received PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg twice daily following 3 to 12 months of oral anticoagulant regimen. Patients in the treatment studies who rolled over into the RE-MEDY study had a combined treatment duration of up to more than 3 years, with mean exposure of 473 days. Table 5 shows the number of patients experiencing bleeding events in the study.
Table 5 Bleeding Events in RE-MEDY Treated Patients PRADAXA Capsules
150 mg twice daily
N (%)Warfarin
N (%)Hazard Ratio
(95% CI)cNote: MBE can belong to more than one criterion.
aPatients with at least one MBE.
bBleeding site based on investigator assessment. Patients can have more than one site of bleeding.
cConfidence intervalPatients N=1,430 N=1,426 Major bleeding eventa 13 (0.9) 25 (1.8) 0.54 (0.25, 1.16) Fatal bleeding 0 1 (0.1) Bleeding in a critical area or organ 7 (0.5) 11 (0.8) Fall in hemoglobin ≥ 2 g/dL or transfusion ≥ 2 units of whole blood or packed red blood cells 7 (0.5) 16 (1.1) Bleeding sites for MBEb Intracranial 2 (0.1) 4 (0.3) Intraocular 4 (0.3) 2 (0.1) Retroperitoneal 0 1 (0.1) Intraarticular 0 2 (0.1) Intramuscular 0 4 (0.3) Gastrointestinal 4 (0.3) 8 (0.6) Urogenital 1 (0.1) 1 (0.1) Other 2 (0.1) 4 (0.3) Clinically relevant non-major bleeding 71 (5.0) 125 (8.8) 0.56 (0.42, 0.75) Any bleeding 278 (19.4) 373 (26.2) 0.71 (0.61, 0.83) In the RE-MEDY study, the rate of any gastrointestinal bleeds in patients receiving PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg was 3.1% (2.2% on warfarin).
RE-SONATE was a placebo-controlled study in which 684 patients received PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg twice daily following 6 to 18 months of oral anticoagulant regimen. Patients in the treatment studies who rolled over into the RE-SONATE study had combined treatment duration up to 9 months, with mean exposure of 165 days. Table 6 shows the number of patients experiencing bleeding events in the study.
Table 6 Bleeding Events in RE-SONATE Treated Patients PRADAXA Capsules
150 mg twice daily
N (%)Placebo
N (%)Hazard Ratio
(95% CI)cNote: MBE can belong to more than one criterion.
aPatients with at least one MBE.
bBleeding site based on investigator assessment. Patients can have more than one site of bleeding.
cConfidence intervalPatients N=684 N=659 Major bleeding eventa 2 (0.3) 0 Bleeding in a critical area or organ 0 0 Gastrointestinalb 2 (0.3) 0 Clinically relevant non-major bleeding 34 (5.0) 13 (2.0) 2.54 (1.34, 4.82) Any bleeding 72 (10.5) 40 (6.1) 1.77 (1.20, 2.61) In the RE-SONATE study, the rate of any gastrointestinal bleeds in patients receiving PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg was 0.7% (0.3% on placebo).
Clinical Myocardial Infarction Events
In the active-controlled VTE studies, a higher rate of clinical myocardial infarction was reported in patients who received PRADAXA Capsules [20 (0.66 per 100 patient-years)] than in those who received warfarin [5 (0.17 per 100 patient-years)]. In the placebo-controlled study, a similar rate of nonfatal and fatal clinical myocardial infarction was reported in patients who received PRADAXA Capsules [1 (0.32 per 100 patient-years)] and in those who received placebo [1 (0.34 per 100 patient-years)].
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
In the four pivotal studies, patients on PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg had a similar incidence of gastrointestinal adverse reactions (24.7% vs 22.7% on warfarin). Dyspepsia (including abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain, abdominal discomfort, and epigastric discomfort) occurred in patients on PRADAXA Capsules 7.5% vs 5.5% on warfarin, and gastritis-like symptoms (including gastritis, GERD, esophagitis, erosive gastritis and gastric hemorrhage) occurred at 3.0% vs 1.7%, respectively.
Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism Following Hip Replacement Surgery
PRADAXA Capsules was studied in 5,476 patients, randomized and treated in two double-blind, active-controlled non-inferiority trials (RE-NOVATE and RE-NOVATE II). The demographic characteristics were similar across the two studies and between the treatment groups within these studies. Approximately 45.3% of the treated patients were male, with a mean age of 63.2 years. The majority of the patients were white (96.1%), 3.6% were Asian, and 0.3% were black with a mean CrCl of 92 mL/min.
Bleeding events for the RE-NOVATE and RE-NOVATE II studies were classified as major bleeding events if at least one of the following criteria applied: fatal bleeding, symptomatic bleeding in a critical area or organ (intraocular, intracranial, intraspinal or retroperitoneal bleeding), bleeding causing a fall in hemoglobin level of 2.0 g/dL (1.24 mmol/L) or more, or leading to transfusion of 2 or more units of whole blood or red cells, requiring treatment cessation or leading to re-operation.
The RE-NOVATE study compared PRADAXA Capsules 75 mg taken orally 1-4 hours after surgery followed by 150 mg once daily, PRADAXA Capsules 110 mg taken orally 1-4 hours after surgery followed by 220 mg once daily and subcutaneous enoxaparin 40 mg once daily initiated the evening before surgery for the prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in patients who had undergone hip replacement surgery. The RE-NOVATE II study compared PRADAXA Capsules 110 mg taken orally 1-4 hours after surgery followed by 220 mg once daily and subcutaneous enoxaparin 40 mg once daily initiated the evening before surgery for the prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in patients who had undergone hip replacement surgery. In the RE-NOVATE and RE-NOVATE II studies, patients received 28-35 days of PRADAXA Capsules or enoxaparin with median exposure of 33 days. Tables 7 and 8 show the number of patients experiencing bleeding events in the analysis of RE-NOVATE and RE-NOVATE II.
Table 7 Bleeding Events in RE-NOVATE Treated Patients PRADAXA Capsules 220 mg
N (%)Enoxaparin
N (%)Patients N=1,146 N=1,154 Major bleeding event 23 (2.0) 18 (1.6) Clinically relevant non-major bleeding 48 (4.2) 40 (3.5) Any bleeding 141 (12.3) 132 (11.4) Table 8 Bleeding Events in RE-NOVATE II Treated Patients PRADAXA Capsules 220 mg
N (%)Enoxaparin
N (%)Patients N=1,010 N=1,003 Major bleeding event 14 (1.4) 9 (0.9) Clinically relevant non-major bleeding 26 (2.6) 20 (2.0) Any bleeding 98 (9.7) 83 (8.3) In the two studies, the rate of major gastrointestinal bleeds in patients receiving PRADAXA Capsules and enoxaparin was the same (0.1%) and for any gastrointestinal bleeds was 1.4% for PRADAXA Capsules 220 mg and 0.9% for enoxaparin.
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
In the two studies, the incidence of gastrointestinal adverse reactions for patients on PRADAXA Capsules 220 mg and enoxaparin was 39.5% and 39.5%, respectively. Dyspepsia (including abdominal pain upper, abdominal pain, abdominal discomfort, and epigastric discomfort) occurred in patients on PRADAXA Capsules 220 mg in 4.1% vs. 3.8% on enoxaparin, and gastritis-like symptoms (including gastritis, GERD, esophagitis, erosive gastritis and gastric hemorrhage) occurred at 0.6% vs 1.0%, respectively.
Pediatric Trials
Treatment of VTE in Pediatric Patients
The safety of PRADAXA in the treatment of VTE in pediatric patients was studied in one phase III trial (DIVERSITY). The DIVERSITY study was a randomized, open-label, active-controlled, parallel-group trial comparing PRADAXA with standard of care – SOC (vitamin K antagonists, low molecular weight heparin, or fondaparinux). There were 266 pediatric patients who received study treatment, 176 patients treated with PRADAXA and 90 patients treated with SOC. Patients on PRADAXA received age- and weight-adjusted dosages of an age-appropriate formulation of PRADAXA (capsules, pellets, or oral solution) twice daily.
Patients had a median age of 14 years (range: 0-17 years), 92% were white, and half the patients were male (50%). Following at least 5 days of parenteral anticoagulant therapy, the median duration of treatment with PRADAXA was 85 days (range: 1-105). Patients with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) < 50 mL/min/1.73m2 were excluded from the trial.
Bleeding
Data on adjudicated major bleeding, clinically relevant non-major (CRNM) bleeding and minor bleeding events, for the PRADAXA group and the SOC group in the DIVERSITY study, are reported in Table 9. There was no statistically significant difference in the time to first major bleeding event.
Table 9 Summary of All Adjudicated Bleeding Events During On-Treatment Period in DIVERSITY PRADAXA
N (%)Standard of Care (SOC)
N (%)1 Major bleeding event if at least one of the following criteria applied: fatal bleeding, symptomatic bleeding in a critical area or organ (intraocular, intracranial, intraspinal or intramuscular with compartment syndrome, retroperitoneal bleeding, intra-articular bleeding, or pericardial bleeding), bleeding causing a fall in hemoglobin level of 2.0 g/dL (1.24 mmol/L) or more, or leading to transfusion of 2 or more units of whole blood or red cells. Patients N=176 N=90 Major bleeding event1 4 (2.3) 2 (2.2) Fatal bleeding 0 1 (1.1) Clinically relevant non-major bleeding 2 (1.1) 1 (1.1) Minor bleeding 33 (19) 21 (23) Major and clinically relevant non-major bleeding 6 (3.4) 3 (3.3) Any bleeding 38 (22) 22 (24) Site-specific bleeding rates were comparable between the two arms, with the exception of the rate of any gastrointestinal bleeds (5.7% in PRADAXA arm vs 1.8% in SOC arm).
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
The incidence of gastrointestinal adverse reactions for patients on PRADAXA and SOC was 32% and 12%, respectively, with the following occurring in ≥ 5% of patients taking PRADAXA: dyspepsia (including term gastro-esophageal reflux disease, gastric pH decreased and esophagitis) in 9% (vs 2%), upper abdominal pain in 5% (vs 1%), vomiting in 8% (vs 2%), nausea 5% (vs 4%), and diarrhea 5% (vs 1%).
Reduction in Risk of Recurrence of VTE in Pediatric Patients
The safety of PRADAXA in the reduction in the risk of recurrence of VTE in pediatric patients was studied in one open-label single-arm trial (Study 2). Study 2 enrolled patients who required further anticoagulation due to the presence of a clinical risk factor after completing the initial treatment for confirmed VTE (for at least 3 months) or after completing the DIVERSITY study and received PRADAXA until the clinical risk factor resolved, or up to a maximum of 12 months. There were 213 pediatric patients treated with PRADAXA, in a similar fashion as in the DIVERSITY trial.
Patients had a median age of 14 years (range: 0-18 years), 91% were white, and 55% of patients were male. Patients previously enrolled on DIVERSITY accounted for 43% of patients enrolled on Study 2 (29% from PRADAXA arm and 14% from SOC arm). The median duration of treatment with PRADAXA in Study 2 was 42 weeks (range: 0-56 weeks), with 45% of patients completing the 12-month planned duration, 17% stopping due to resolution of VTE risk factors, 12% stopping due to failure to attain target dabigatran concentration and 6% had an adverse event leading to discontinuation.
During the on-treatment period of Study 2, 3 patients (1.4%) had a major bleeding event, 3 patients (1.4%) had a clinically relevant non-major bleeding event, and 44 patients (20%) had a minor bleeding event. The most common drug-related adverse reactions were dyspepsia (5%), epistaxis (3.3%), nausea (3.3%) and menorrhagia (2.8%).
The adverse reaction profile in pediatric patients was generally consistent with that of adult patients.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of PRADAXA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Agranulocytosis, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Esophageal ulcer
Immune System Disorders: Angioedema
Renal and Urinary Disorders: Anticoagulant-related nephropathy
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Alopecia -
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Reduction of Risk of Stroke and Systemic Embolism in Non-valvular Atrial Fibrillation in Adult Patients
The concomitant use of PRADAXA with P-gp inducers (e.g., rifampin) reduces exposure to dabigatran and should generally be avoided [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
P-gp inhibition and impaired renal function are the major independent factors that result in increased exposure to dabigatran [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Concomitant use of P-gp inhibitors in patients with renal impairment is expected to produce increased exposure of dabigatran compared to that seen with either factor alone.
In patients with moderate renal impairment (CrCl 30-50 mL/min), reduce the dosage of PRADAXA to 75 mg twice daily when administered concomitantly with the P-gp inhibitors dronedarone or systemic ketoconazole. The use of the P-gp inhibitors verapamil, amiodarone, quinidine, clarithromycin, and ticagrelor does not require a dosage adjustment of PRADAXA. These results should not be extrapolated to other P-gp inhibitors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
The concomitant use of PRADAXA and P-gp inhibitors in patients with severe renal impairment (CrCl 15-30 mL/min) should be avoided [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 Treatment and Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients
Avoid use of PRADAXA and P-gp inhibitors in patients with CrCl < 50 mL/min [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.3 Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients Following Hip Replacement Surgery
In patients with CrCl ≥ 50 mL/min who have concomitant administration of P-gp inhibitors such as dronedarone or systemic ketoconazole, it may be helpful to separate the timing of administration of PRADAXA and the P-gp inhibitor by several hours. The concomitant use of PRADAXA and P-gp inhibitors in patients with CrCl < 50 mL/min should be avoided [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2, 12.3)].
7.4 Treatment and Reduction in Risk of Recurrence of VTE in Pediatric Patients
The concomitant use of PRADAXA with P-gp inhibitors has not been studied in pediatric patients but may increase exposure to dabigatran [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The limited available data on PRADAXA use in pregnant women are insufficient to determine drug-associated risks for adverse developmental outcomes. There are risks to the mother associated with untreated venous thromboembolism in pregnancy and a risk of hemorrhage in the mother and fetus associated with the use of anticoagulants (see Clinical Considerations). In pregnant rats treated from implantation until weaning, dabigatran increased the number of dead offspring and caused excess vaginal/uterine bleeding close to parturition at an exposure 2.6 times the human exposure. At a similar exposure, dabigatran decreased the number of implantations when rats were treated prior to mating and up to implantation (gestation Day 6). Dabigatran administered to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis up to exposures 8 and 13 times the human exposure, respectively, did not induce major malformations. However, the incidence of delayed or irregular ossification of fetal skull bones and vertebrae was increased in the rat (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2%-4% and 15%-20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
Pregnancy confers an increased risk for thromboembolism that is higher for women with underlying thromboembolic disease and certain high-risk pregnancy conditions. Published data describe that women with a previous history of venous thrombosis are at high risk for recurrence during pregnancy.
Fetal/Neonatal adverse reaction
Use of anticoagulants, including PRADAXA, may increase the risk of bleeding in the fetus and neonate. Monitor neonates for bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Labor or delivery
All patients receiving anticoagulants, including pregnant women, are at risk for bleeding. PRADAXA use during labor or delivery in women who are receiving neuraxial anesthesia may result in epidural or spinal hematomas. Consider discontinuation or use of shorter acting anticoagulant as delivery approaches [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)].
Data
Animal Data
Dabigatran has been shown to decrease the number of implantations when male and female rats were treated at a dosage of 70 mg/kg (about 2.6 to 3.0 times the human exposure at MRHD of 300 mg/day based on area under the curve [AUC] comparisons) prior to mating and up to implantation (gestation Day 6). Treatment of pregnant rats after implantation with dabigatran at the same dose increased the number of dead offspring and caused excess vaginal/uterine bleeding close to parturition. Dabigatran administered to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis up to maternally toxic doses of 200 mg/kg (8 and 13 times the human exposure, respectively, at a MRHD of 300 mg/day based on AUC comparisons) did not induce major malformations, but increased the incidence of delayed or irregular ossification of fetal skull bones and vertebrae in the rat.
Death of offspring and mother rats during labor in association with uterine bleeding occurred during treatment of pregnant rats from implantation (gestation Day 7) to weaning (lactation Day 21) with dabigatran at a dose of 70 mg/kg (about 2.6 times the human exposure at MRHD of 300 mg/day based on AUC comparisons).
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Females of reproductive potential requiring anticoagulation should discuss pregnancy planning with their physician.
The risk of clinically significant uterine bleeding, potentially requiring gynecological surgical interventions, identified with oral anticoagulants including PRADAXA should be assessed in females of reproductive potential and those with abnormal uterine bleeding.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of PRADAXA Capsules for the treatment and the reduction in risk of recurrence of venous thromboembolism have been established in pediatric patients 8 to less than 18 years of age. Use of PRADAXA for this indication is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in pediatric patients. These studies included an open-label, randomized, parallel-group study and an open-label, single-arm safety study [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14.4, 14.5)]. Other age-appropriate pediatric dosage forms of dabigatran etexilate are available for pediatric patients less than 8 years of age for these indications.
Safety and effectiveness of PRADAXA Capsules have not been established in pediatric patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation or those who have undergone hip replacement surgery.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total number of patients in the RE-LY study, 82% were 65 and over, while 40% were 75 and over. The risk of stroke and bleeding increases with age, but the risk-benefit profile is favorable in all age groups [see Warnings and Precautions (5), Adverse Reactions (6.1), and Clinical Studies (14.1)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Reduction of Risk of Stroke and Systemic Embolism in Non-valvular Atrial Fibrillation in Adult Patients
No dose adjustment of PRADAXA is recommended in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Reduce the dose of PRADAXA in patients with severe renal impairment (CrCl 15-30 mL/min) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.4) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Dosing recommendations for patients with CrCl < 15 mL/min or on dialysis cannot be provided.
Adjust dose appropriately in patients with renal impairment receiving concomitant P-gp inhibitors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Drug Interactions (7.1), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Treatment and Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients
Patients with severe renal impairment (CrCl ≤ 30 mL/min) were excluded from RE-COVER.
Dosing recommendations for patients with CrCl ≤ 30 mL/min or on dialysis cannot be provided. Avoid use of PRADAXA with concomitant P-gp inhibitors in patients with CrCl < 50 mL/min [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Drug Interactions (7.2), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients Following Hip Replacement Surgery
Patients with severe renal impairment (CrCl < 30 mL/min) were excluded from RE-NOVATE and RE-NOVATE II.
Dosing recommendations for patients with CrCl < 30 mL/min or on dialysis cannot be provided.
Avoid use of PRADAXA with concomitant P-gp inhibitors in patients with CrCl < 50 mL/min [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Drug Interactions (7.3), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2, 12.3)].
Treatment and Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of VTE in Pediatric Patients
PRADAXA has not been studied in pediatric patients with eGFR < 50 mL/min/1.73 m2. Reduced renal function could increase exposure. Dosing recommendations cannot be provided for treatment of these patients. Avoid use of PRADAXA Capsules in these patients [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Accidental overdose may lead to hemorrhagic complications. In the event of hemorrhagic complications, initiate appropriate clinical support, discontinue treatment with PRADAXA, and investigate the source of bleeding. A specific reversal agent (idarucizumab) is available for adult patients.
Dabigatran is primarily eliminated by the kidneys with a low plasma protein binding of approximately 35%. Hemodialysis can remove dabigatran; however, data supporting this approach are limited. Using a high-flux dialyzer, blood flow rate of 200 mL/min, and dialysate flow rate of 700 mL/min, approximately 49% of total dabigatran can be cleared from plasma over 4 hours. At the same dialysate flow rate, approximately 57% can be cleared using a dialyzer blood flow rate of 300 mL/min, with no appreciable increase in clearance observed at higher blood flow rates. Upon cessation of hemodialysis, a redistribution effect of approximately 7% to 15% is seen. The effect of dialysis on dabigatran's plasma concentration would be expected to vary based on patient specific characteristics. Measurement of aPTT or ECT may help guide therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
-
11 DESCRIPTION
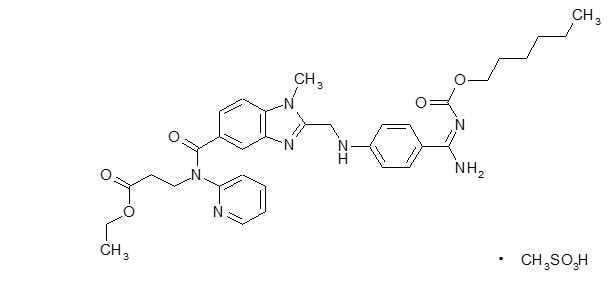
The chemical name for dabigatran etexilate mesylate, a direct thrombin inhibitor, is β-Alanine, N-[[2-[[[4-[[[(hexyloxy)carbonyl]amino]iminomethyl] phenyl]amino]methyl]-1-methyl-1H-benzimidazol-5-yl]carbonyl]-N-2-pyridinyl-,ethyl ester, methanesulfonate. The empirical formula is C34H41N7O5 ∙ CH4O3S and the molecular weight is 723.86 (mesylate salt), 627.75 (free base). The structural formula is:
Dabigatran etexilate mesylate is a yellow-white to yellow powder. A saturated solution in pure water has a solubility of 1.8 mg/mL. It is freely soluble in methanol, slightly soluble in ethanol, and sparingly soluble in isopropanol.
PRADAXA Capsules are supplied in 75 mg, 110 mg, and 150 mg strengths for oral administration. Each capsule contains dabigatran etexilate mesylate as the active ingredient: 150 mg dabigatran etexilate (equivalent to 172.95 mg dabigatran etexilate mesylate), 110 mg dabigatran etexilate (equivalent to 126.83 mg dabigatran etexilate mesylate), or 75 mg dabigatran etexilate (equivalent to 86.48 mg dabigatran etexilate mesylate) along with the following inactive ingredients: acacia, dimethicone, hypromellose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, talc, and tartaric acid. The capsule shell is composed of carrageenan, hypromellose, potassium chloride, titanium dioxide, black edible ink, and FD&C Blue No. 2 (150 mg and 110 mg capsules only).
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Dabigatran and its acyl glucuronides are competitive, direct thrombin inhibitors. Because thrombin (serine protease) enables the conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin during the coagulation cascade, its inhibition prevents the development of a thrombus. Both free and clot-bound thrombin, and thrombin-induced platelet aggregation are inhibited by the active moieties.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
At recommended therapeutic doses, dabigatran etexilate prolongs the coagulation markers such as aPTT, ECT, TT, and dTT. INR is relatively insensitive to the exposure to dabigatran and cannot be interpreted the same way as used for warfarin monitoring.
Adults
The aPTT test provides an approximation of PRADAXA's anticoagulant effect. The average time course for effects on aPTT, following approved dosing regimens in patients with various degrees of renal impairment is shown in Figure 2. The curves represent mean levels without confidence intervals; variations should be expected when measuring aPTT. While advice cannot be provided on the level of recovery of aPTT needed in any particular clinical setting, the curves can be used to estimate the time to get to a particular level of recovery, even when the time since the last dose of PRADAXA is not precisely known. In the RE-LY trial, the median (10th to 90th percentile) trough aPTT in patients receiving the 150 mg dose was 52 (40 to 76) seconds.
Figure 2 Average Time Course for Effects of Dabigatran on aPTT, Following Approved PRADAXA Dosing Regimens in Adult Patients with Various Degrees of Renal Impairment*
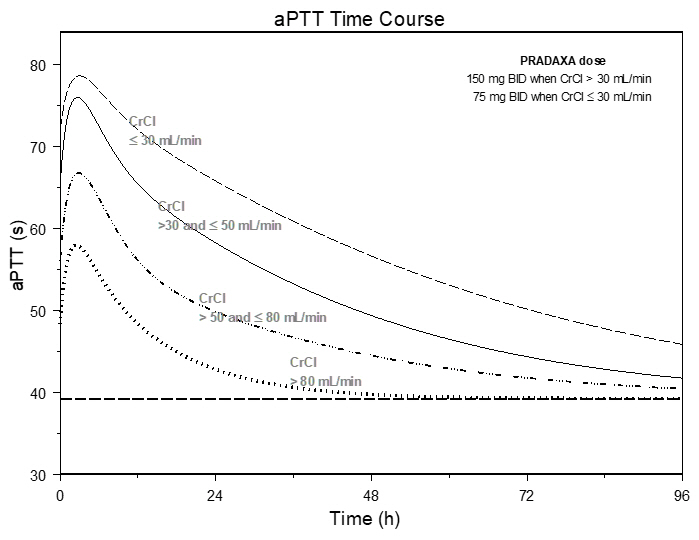
*Simulations based on PK data from a study in subjects with renal impairment and PK/aPTT relationships derived from the RE-LY study; aPTT prolongation in RE-LY was measured centrally in citrate plasma using PTT Reagent Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany. There may be quantitative differences between various established methods for aPTT assessment.
The degree of anticoagulant activity can also be assessed by the ecarin clotting time (ECT). This test is a more specific measure of the effect of dabigatran than activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT). In the RE-LY trial, the median (10th to 90th percentile) trough ECT in patients receiving the 150 mg dose was 63 (44 to 103) seconds.
In orthopedic hip surgery patients, maximum aPTT response (Emax) to dabigatran and baseline aPTT were higher shortly after surgery than at later time points (e.g. ≥ 3 days after surgery).
Pediatrics
As in adults, there is a correlation between plasma dabigatran concentrations and the degree of its anticoagulant effect in pediatric patients with venous thromboembolism. The parameters dTT and ECT increased in direct linear proportion to the plasma concentration of dabigatran, whereas aPTT prolongation increases in a nonlinear fashion with dabigatran plasma concentrations.
Similar PK/PD relationships for aPTT, ECT, and dTT were observed across age groups of pediatric patients (ages 26 days to < 18 years) and between pediatric and adult patients with venous thromboembolism. This similarity in PK/PD relationship suggests that similar exposure-response relationship is expected for dabigatran etexilate treatment across the pediatric age groups and adult patients.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Dabigatran etexilate mesylate is absorbed as the dabigatran etexilate ester. The ester is then hydrolyzed, forming dabigatran, the active moiety. Dabigatran is metabolized to four different acyl glucuronides and both the glucuronides and dabigatran have similar pharmacological activity. Pharmacokinetics described here refer to the sum of dabigatran and its glucuronides. Dabigatran displays dose-proportional pharmacokinetics in healthy adult subjects and adult patients in the range of doses from 10 to 400 mg. Given twice daily, dabigatran's accumulation factor in adults and pediatrics is approximately two.
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of dabigatran following oral administration of dabigatran etexilate is approximately 3% to 7%. Dabigatran etexilate is a substrate of the efflux transporter P-gp. After oral administration of dabigatran etexilate in healthy volunteers, Cmax occurs at 1-hour post-administration in the fasted state. Coadministration of PRADAXA with a high-fat meal delays the time to Cmax by approximately 2 hours but has no effect on the bioavailability of dabigatran; PRADAXA may be administered with or without food.
The oral bioavailability of dabigatran etexilate increases by 75% when the pellets are taken without the capsule shell compared to the intact capsule formulation based on a single-dose relative bioavailability study. PRADAXA Capsules should therefore not be broken, chewed, or opened before administration.
PRADAXA is available in capsules and oral pellets. The approved indications and intended age groups are not the same. Oral absorption of dabigatran etexilate is formulation-dependent. At steady-state, dabigatran etexilate oral pellets show 37% higher relative bioavailability in healthy adults compared to dabigatran etexilate capsules based on a multiple-dose relative bioavailability study. In addition, the relative bioavailability between the two dosage forms is age-dependent. The relative bioavailability observed in adults cannot be translated to pediatrics.
Distribution
Dabigatran is approximately 35% bound to human plasma proteins. The red blood cell to plasma partitioning of dabigatran measured as total radioactivity is less than 0.3. The volume of distribution of dabigatran is 50 to 70 L.
Elimination
Dabigatran is eliminated primarily in the urine. Renal clearance of dabigatran is 80% of total clearance after intravenous administration. After oral administration of radiolabeled dabigatran, 7% of radioactivity is recovered in urine and 86% in feces. The half-life of dabigatran in healthy adult subjects is 12 to 17 hours. Population pharmacokinetic simulation shows that the elimination half-life in pediatric patients is 12 to14 hours.
Metabolism
After oral administration, dabigatran etexilate is converted to dabigatran. The cleavage of the dabigatran etexilate by esterase-catalyzed hydrolysis to the active principal dabigatran is the predominant metabolic reaction. Dabigatran is not a substrate, inhibitor, or inducer of CYP450 enzymes. Dabigatran is subject to conjugation, forming pharmacologically active acyl glucuronides. Four positional isomers, 1-O, 2-O, 3-O, and 4-O-acylglucuronide exist, and each accounts for less than 10% of total dabigatran in plasma.
Specific Populations
Pediatric Patients
The pharmacokinetics of dabigatran was characterized in two clinical studies (DIVERSITY and Study 2) following multiple doses in pediatric patients from birth to less than 18 years old. In pediatric patients taking age- and weight-adjusted dosages of PRADAXA Capsules (aged 8-18 years), the observed geometric mean steady-state trough concentration was 97.9 ng/mL (63.7 to 151 ng/mL, 10th to 90th percentile) compared to the steady-state geometric mean trough concentration of 59.7 ng/mL (26.3 to 146 ng/mL, 10th to 90th percentile) observed in adult patients with DVT/PE.
Renal Impairment
An open, parallel-group, single-center study compared dabigatran pharmacokinetics in healthy adult subjects and adult patients with mild to moderate renal impairment receiving a single dose of PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg. Exposure to dabigatran increases with severity of renal function impairment (Table 10). Similar findings were observed in the RE-LY, RE-COVER and RE-NOVATE II trials.
Table 10 Impact of Renal Impairment on Dabigatran Pharmacokinetics Renal Function CrCl
(mL/min)Increase in AUC Increase in Cmax t1/2
(h)+Patients with severe renal impairment were not studied in RE-LY, RE-COVER and RE-NOVATE II. Dosing recommendations in subjects with severe renal impairment are based on pharmacokinetic modeling [see Dosage and Administration (2.2, 2.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)]. Normal ≥ 80 1× 1× 13 Mild 50-80 1.5× 1.1× 15 Moderate 30-50 3.2× 1.7× 18 Severe+ 15-30 6.3× 2.1× 27 Hepatic Impairment
Administration of PRADAXA Capsules in adult patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B) showed a large inter-subject variability, but no evidence of a consistent change in exposure or pharmacodynamics.
Drug Interactions
A summary of the effect of coadministered drugs on dabigatran exposure in healthy adult subjects is shown in Figures 3.1 and 3.2.
In the orthopedic hip surgery patients, limited clinical data with P-gp inhibitors is available.
Figure 3.1 Effect of P-gp Inhibitor or Inducer (rifampicin) Drugs on Peak and Total Exposure to Dabigatran (Cmax and AUC). Shown are the Geometric Mean Ratios (Ratio) and 90% Confidence Interval (90% CI). The Perpetrator and Dabigatran Etexilate Dosage and Dosage Frequency are given as well as the Time of Perpetrator Dosage in Relation to Dabigatran Etexilate Dosage (Time Difference) 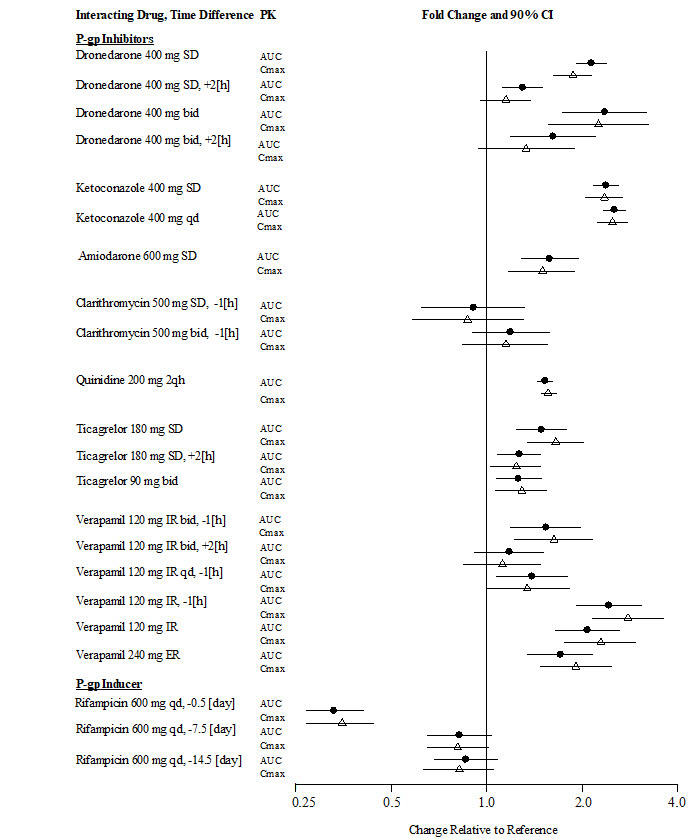
Figure 3.2 Effect of Non-P-gp Inhibitor or Inducer, Other Drugs, on Peak and Total Exposure to Dabigatran (Cmax and AUC). Shown are the Geometric Mean Ratios (Ratio) and 90% Confidence Interval (90% CI). The Perpetrator and Dabigatran Etexilate Dosage and Dosage Frequency are given as well as the Time of Perpetrator Dosage in Relation to Dabigatran Etexilate Dosage (Time Difference) 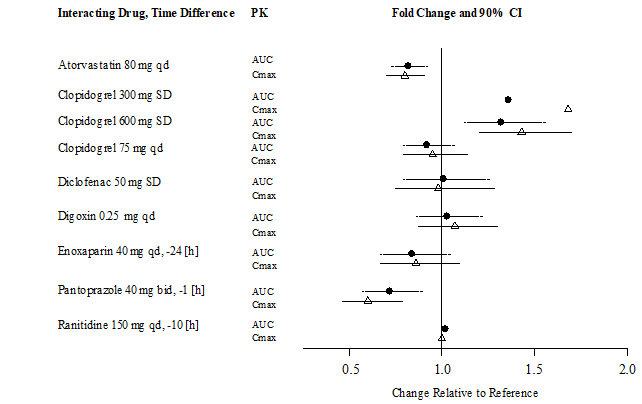
In RE-LY, dabigatran plasma samples were also collected. The concomitant use of proton pump inhibitors, H2 antagonists, and digoxin did not appreciably change the trough concentration of dabigatran.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Dabigatran was not carcinogenic when administered by oral gavage to mice and rats for up to 2 years. The highest doses tested (200 mg/kg/day) in mice and rats were approximately 3.6 and 6 times, respectively, the human exposure at MRHD of 300 mg/day based on AUC comparisons.
Dabigatran was not mutagenic in in vitro tests, including bacterial reversion tests, mouse lymphoma assay and chromosomal aberration assay in human lymphocytes, and the in vivo micronucleus assay in rats.
In the rat fertility study with oral gavage doses of 15, 70, and 200 mg/kg, males were treated for 29 days prior to mating, during mating up to scheduled termination, and females were treated 15 days prior to mating through gestation Day 6. No adverse effects on male or female fertility were observed at 200 mg/kg or 9 to 12 times the human exposure at MRHD of 300 mg/day based on AUC comparisons. However, the number of implantations decreased in females receiving 70 mg/kg, or 3 times the human exposure at MRHD based on AUC comparisons.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Reduction of Risk of Stroke and Systemic Embolism in Non-valvular Atrial Fibrillation in Adult Patients
The clinical evidence for the efficacy of PRADAXA Capsules was derived from RE-LY (Randomized Evaluation of Long-term Anticoagulant Therapy), a multi-center, multi-national, randomized, parallel group trial comparing two blinded dosages of PRADAXA Capsules (110 mg twice daily and 150 mg twice daily) with open-label warfarin (dosed to target INR of 2 to 3) in patients with non-valvular, persistent, paroxysmal, or permanent atrial fibrillation and one or more of the following additional risk factors:
- Previous stroke, transient ischemic attack (TIA), or systemic embolism
- Left ventricular ejection fraction < 40%
- Symptomatic heart failure, ≥ New York Heart Association Class 2
- Age ≥ 75 years
- Age ≥ 65 years and one of the following: diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease (CAD), or hypertension
The primary objective of this study was to determine if PRADAXA Capsules was non-inferior to warfarin in reducing the occurrence of the composite endpoint, stroke (ischemic and hemorrhagic) and systemic embolism. The study was designed to ensure that PRADAXA Capsules preserved more than 50% of warfarin's effect as established by previous randomized, placebo-controlled trials of warfarin in atrial fibrillation. Statistical superiority was also analyzed.
A total of 18,113 patients were randomized and followed for a median of 2 years. The patients' mean age was 71.5 years and the mean CHADS2 score was 2.1. The patient population was 64% male, 70% Caucasian, 16% Asian, and 1% black. Twenty percent of patients had a history of a stroke or TIA and 50% were vitamin K antagonist (VKA) naïve, defined as less than 2 months total lifetime exposure to a VKA. Thirty-two percent of the population had never been exposed to a VKA. Concomitant diseases of patients in this trial included hypertension 79%, diabetes 23%, and CAD 28%. At baseline, 40% of patients were on aspirin and 6% were on clopidogrel. For patients randomized to warfarin, the mean percentage of time in therapeutic range (INR 2 to 3) was 64%.
Relative to warfarin and to PRADAXA Capsules 110 mg twice daily, PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg twice daily significantly reduced the primary composite endpoint of stroke and systemic embolism (see Table 11 and Figure 4).
Table 11 First Occurrence of Stroke or Systemic Embolism in the RE-LY Study* PRADAXA Capsules
150 mg twice dailyPRADAXA Capsules
110 mg twice dailyWarfarin * Randomized ITT Patients randomized 6,076 6,015 6,022 Patients (% per yr) with events 135 (1.12%) 183 (1.54%) 203 (1.72%) Hazard ratio vs warfarin (95% CI) 0.65 (0.52, 0.81) 0.89 (0.73, 1.09) P-value for superiority 0.0001 0.27 Hazard ratio vs PRADAXA 110 mg (95% CI) 0.72 (0.58, 0.91) P-value for superiority 0.005 Figure 4 Kaplan-Meier Curve Estimate of Time to First Stroke or Systemic Embolism
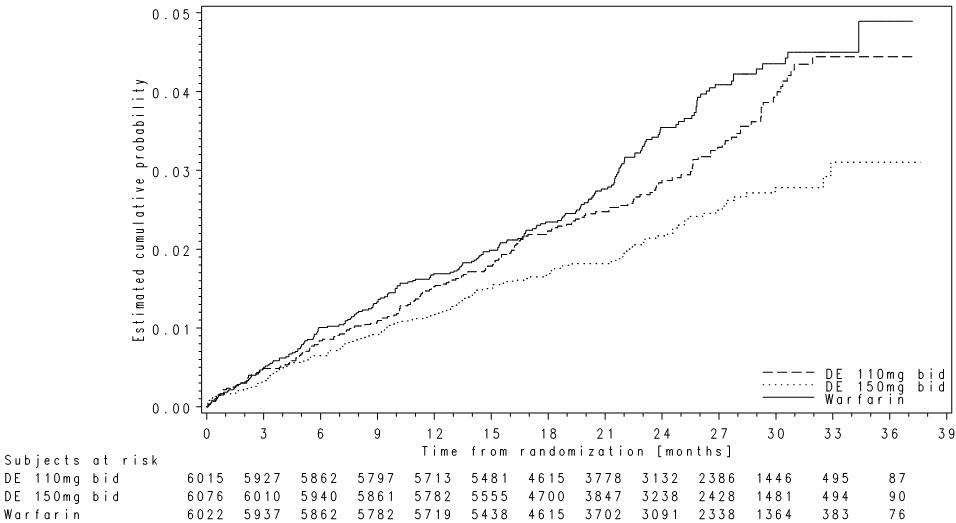
The contributions of the components of the composite endpoint, including stroke by subtype, are shown in Table 12. The treatment effect was primarily a reduction in stroke. PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg twice daily was superior in reducing ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes relative to warfarin.
Table 12 Strokes and Systemic Embolism in the RE-LY Study PRADAXA Capsules
150 mg twice dailyWarfarin Hazard ratio vs warfarin
(95% CI)Patients randomized 6,076 6,022 Stroke 123 187 0.64 (0.51, 0.81) Ischemic stroke 104 134 0.76 (0.59, 0.98) Hemorrhagic stroke 12 45 0.26 (0.14, 0.49) Systemic embolism 13 21 0.61 (0.30, 1.21) In the RE-LY trial, the rate of all-cause mortality was lower on PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg than on warfarin (3.6% per year versus 4.1% per year). The rate of vascular death was lower on PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg compared to warfarin (2.3% per year versus 2.7% per year). Non-vascular death rates were similar in the treatment arms.
The efficacy of PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg twice daily was generally consistent across major subgroups (see Figure 5).
Figure 5 Stroke and Systemic Embolism Hazard Ratios by Baseline Characteristics*
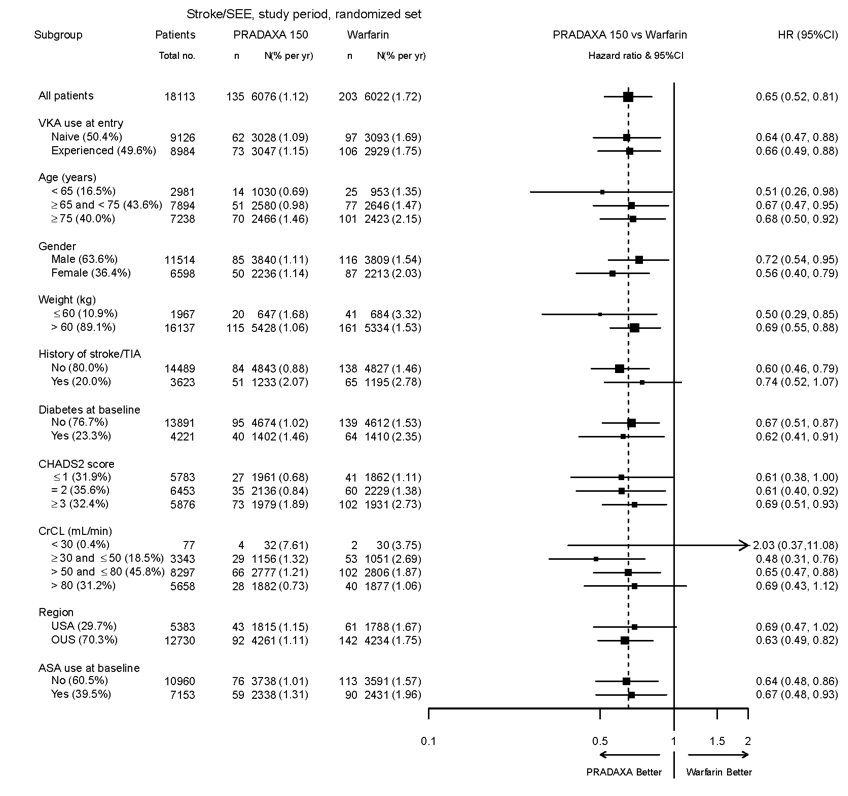
* Randomized ITT
Note: The figure above presents effects in various subgroups all of which are baseline characteristics and all of which were pre-specified. The 95% confidence limits that are shown do not take into account how many comparisons were made, nor do they reflect the effect of a particular factor after adjustment for all other factors. Apparent homogeneity or heterogeneity among groups should not be over-interpreted.In RE-LY, a higher rate of clinical myocardial infarction was reported in patients who received PRADAXA Capsules (0.7 per 100 patient-years for 150 mg dose) than in those who received warfarin (0.6).
14.2 Treatment and Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients
In the randomized, parallel group, double-blind trials, RE-COVER and RE-COVER II, patients with deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism received PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg twice daily or warfarin (dosed to target INR of 2 to 3) following initial treatment with an approved parenteral anticoagulant for 5 to 10 days.
In RE-COVER, the median treatment duration during the oral only treatment period was 174 days. A total of 2,539 patients (30.9% patients with symptomatic PE with or without DVT and 68.9% with symptomatic DVT only) were treated with a mean age of 54.7 years. The patient population was 58.4% male, 94.8% white, 2.6% Asian, and 2.6% black. The concomitant diseases of patients in this trial included hypertension (35.9%), diabetes mellitus (8.3%), coronary artery disease (6.5%), active cancer (4.8%), and gastric or duodenal ulcer (4.4%). Concomitant medications included agents acting on renin-angiotensin system (25.2%), vasodilators (28.4%), serum lipid-reducing agents (18.2%), NSAIDs (21%), beta-blockers (14.8%), calcium channel blockers (8.5%), ASA (8.6%), and platelet inhibitors excluding ASA (0.6%). Patients randomized to warfarin had a mean percentage of time in the INR target range of 2.0 to 3.0 of 60% in RE-COVER study.
In RE-COVER II, the median treatment duration during the oral only treatment period was 174 days. A total of 2,568 patients (31.8% patients with symptomatic PE with or without DVT and 68.1% with symptomatic DVT only) were treated with a mean age of 54.9 years. The patient population was 60.6% male, 77.6% white, 20.9% Asian, and 1.5% black. The concomitant diseases of patients in this trial included hypertension (35.1%), diabetes mellitus (9.8%), coronary artery disease (7.1%), active cancer (3.9%), and gastric or duodenal ulcer (3.8%). Concomitant medications included agents acting on renin-angiotensin system (24.2%), vasodilators (28.6%), serum lipid-reducing agents (20.0%), NSAIDs (22.3%), beta-blockers (14.8%), calcium channel blockers (10.8%), ASA (9.8%), and platelet inhibitors excluding ASA (0.8%). Patients randomized to warfarin had a mean percentage of time in the INR target range of 2.0 to 3.0 of 57% in RE-COVER II study.
In studies RE-COVER and RE-COVER II, the protocol specified non-inferiority margin (2.75) for the hazard ratio was derived based on the upper limit of the 95% confidence interval of the historical warfarin effect. PRADAXA Capsules was demonstrated to be non-inferior to warfarin (dosed to target INR of 2 to 3) (Table 13) based on the primary composite endpoint (fatal PE or symptomatic non-fatal PE and/or DVT) and retains at least 66.9% (RE-COVER) and 63.9% (RE-COVER II) of the historical warfarin effect, respectively.
Table 13 Primary Efficacy Endpoint for RE-COVER and RE-COVER II – Modified ITTa Population PRADAXA Capsules
150 mg twice daily
N (%)Warfarin
N (%)Hazard ratio vs warfarin (95% CI) aModified ITT analyses population consists of all randomized patients who received at least one dose of study medication.
bNumber of patients with one or more event.
cNumber of events. For patients with multiple events each event is counted independently.RE-COVER N=1,274 N=1,265 Primary Composite Endpointb 34 (2.7) 32 (2.5) 1.05 (0.65, 1.70) Fatal PEc 1 (0.1) 3 (0.2) Symptomatic non-fatal PEc 16 (1.3) 8 (0.6) Symptomatic recurrent DVTc 17 (1.3) 23 (1.8) RE-COVER II N=1,279 N=1,289 Primary Composite Endpointb 34 (2.7) 30 (2.3) 1.13 (0.69, 1.85) Fatal PEc 3 (0.2) 0 Symptomatic non-fatal PEc 9 (0.7) 15 (1.2) Symptomatic recurrent DVTc 30 (2.3) 17 (1.3) In the randomized, parallel-group, double-blind, pivotal trial, RE-MEDY, patients received PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg twice daily or warfarin (dosed to target INR of 2 to 3) following 3 to 12 months of treatment with anticoagulation therapy for an acute VTE. The median treatment duration during the treatment period was 534 days. A total of 2,856 patients were treated with a mean age of 54.6 years. The patient population was 61% male, and 90.1% white, 7.9% Asian and 2.0% black. The concomitant diseases of patients in this trial included hypertension (38.6%), diabetes mellitus (9.0%), coronary artery disease (7.2%), active cancer (4.2%), and gastric or duodenal ulcer (3.8%). Concomitant medications included agents acting on renin-angiotensin system (27.9%), vasodilators (26.7%), serum lipid reducing agents (20.6%), NSAIDs (18.3%), beta-blockers (16.3%), calcium channel blockers (11.1%), aspirin (7.7%), and platelet inhibitors excluding ASA (0.9%). Patients randomized to warfarin had a mean percentage of time in the INR target range of 2.0 to 3.0 of 62% in the study.
In study RE-MEDY, the protocol specified non-inferiority margin (2.85) for the hazard ratio was derived based on the point estimate of the historical warfarin effect. PRADAXA Capsules was demonstrated to be non-inferior to warfarin (dosed to target INR of 2 to 3) (Table 14) based on the primary composite endpoint (fatal PE or symptomatic non-fatal PE and/or DVT) and retains at least 63.0% of the historical warfarin effect. If the non-inferiority margin was derived based on the 50% retention of the upper limit of the 95% confidence interval, PRADAXA Capsules was demonstrated to retain at least 33.4% of the historical warfarin effect based on the composite primary endpoint.
Table 14 Primary Efficacy Endpoint for RE-MEDY – Modified ITTa Population PRADAXA Capsules
150 mg twice daily
N=1,430
N (%)Warfarin
N=1,426
N (%)Hazard ratio vs warfarin (95% CI) aModified ITT analyses population consists of all randomized patients who received at least one dose of study medication.
bNumber of patients with one or more event.
cNumber of events. For patients with multiple events each event is counted independently.Primary Composite Endpointb 26 (1.8) 18 (1.3) 1.44 (0.78, 2.64) Fatal PEc 1 (0.07) 1 (0.07) Symptomatic non-fatal PEc 10 (0.7) 5 (0.4) Symptomatic recurrent DVTc 17 (1.2) 13 (0.9) In a randomized, parallel-group, double-blind, pivotal trial, RE-SONATE, patients received PRADAXA Capsules 150 mg twice daily or placebo following 6 to 18 months of treatment with anticoagulation therapy for an acute VTE. The median treatment duration was 182 days. A total of 1,343 patients were treated with a mean age of 55.8 years. The patient population was 55.5% male, 89.0% white, 9.3% Asian, and 1.7% black. The concomitant diseases of patients in this trial included hypertension (38.8%), diabetes mellitus (8.0%), coronary artery disease (6.0%), history of cancer (6.0%), gastric or duodenal ulcer (4.5%), and heart failure (4.6%). Concomitant medications included agents acting on renin-angiotensin system (28.7%), vasodilators (19.4%), beta-blockers (18.5%), serum lipid reducing agents (17.9%), NSAIDs (12.1%), calcium channel blockers (8.9%), aspirin (8.3%), and platelet inhibitors excluding ASA (0.7%). Based on the outcome of the primary composite endpoint (fatal PE, unexplained death, or symptomatic non-fatal PE and/or DVT), PRADAXA was superior to placebo (Table 15).
Table 15 Primary Efficacy Endpoint for RE-SONATE – Modified ITTa Population PRADAXA Capsules
150 mg twice daily
N=681
N (%)Placebo
N=662
N (%)Hazard ratio vs placebo (95% CI) aModified ITT analyses population consists of all randomized patients who received at least one dose of study medication.
bNumber of patients with one or more events.
cNumber of events. For patients with multiple events each event is counted independently.Primary Composite Endpointb 3 (0.4) 37 (5.6) 0.08 (0.02, 0.25)
p-value <0.0001Fatal PE and unexplained deathc 0 2 (0.3) Symptomatic non-fatal PEc 1 (0.1) 14 (2.1) Symptomatic recurrent DVTc 2 (0.3) 23 (3.5) 14.3 Prophylaxis of Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Adult Patients Following Hip Replacement Surgery
In the randomized, parallel-group, double-blind, non-inferiority trials, RE-NOVATE and RE-NOVATE II patients received PRADAXA Capsules 75 mg orally 1-4 hours after surgery followed by 150 mg daily (RE-NOVATE), PRADAXA Capsules 110 mg orally 1-4 hours after surgery followed by 220 mg daily (RE-NOVATE and RE-NOVATE II) or subcutaneous enoxaparin 40 mg once daily initiated the evening before surgery (RE-NOVATE and RE-NOVATE II) for the prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism in patients who have undergone hip replacement surgery.
Overall, in RE-NOVATE and RE-NOVATE II, the median treatment duration was 33 days for PRADAXA Capsules and 33 days for enoxaparin. A total of 5,428 patients were treated with a mean age of 63.2 years. The patient population was 45.3% male, 96.1% white, 3.6% Asian, and 0.4 % black. The concomitant diseases of patients in these trials included hypertension (46.1%), venous insufficiency (15.4%), coronary artery disease (8.2%), diabetes mellitus (7.9%), reduced renal function (5.3%), heart failure (3.4%), gastric or duodenal ulcer (3.0%), VTE (2.7%), and malignancy (0.1%). Concomitant medications included cardiac therapy (69.7%), NSAIDs (68%), vasoprotectives (29.7%), agents acting on renin-angiotensin system (29.1%), beta-blockers (21.5%), diuretics (20.8%), lipid modifying agents (18.2%), any antithrombin/anticoagulant (16.0%), calcium channel blockers (13.6%), low molecular weight heparin (7.8%), aspirin (7.0%), platelet inhibitors excluding ASA (6.9%), other antihypertensives (6.7%), and peripheral vasodilators (2.6%).
For efficacy evaluation all patients were to have bilateral venography of the lower extremities at 3 days after last dose of study drug unless an endpoint event had occurred earlier in the study. In the primary efficacy analysis, PRADAXA Capsules 110 mg orally 1-4 hours after surgery followed by 220 mg daily was non-inferior to enoxaparin 40 mg once daily in a composite endpoint of confirmed VTE (proximal or distal DVT on venogram, confirmed symptomatic DVT, or confirmed PE) and all cause death during the treatment period (Tables 16 and 17). In the studies 2628 (76.5%) patients in RE-NOVATE and 1572 (78.9%) patients in RE-NOVATE II had evaluable venograms at study completion.
Table 16 Primary Efficacy Endpoint for RE-NOVATE PRADAXA Capsules
220 mg
N (%)Enoxaparin
N (%)aFull Analysis Set (FAS): The FAS included all randomized patients who received at least one subcutaneous injection or one oral dose of study medication, underwent surgery and subjects for whom the presence or absence of an efficacy outcome at the end of the study was known, i.e., an evaluable negative venogram for both distal and proximal DVT in both legs or any of the following: positive venography in one or both legs, or confirmed symptomatic DVT, PE, or death during the treatment period.
bVTE is defined as proximal DVT and PENumber of Patientsa N=880 N= 897 Primary Composite Endpoint 53 (6.0) 60 (6.7) Risk difference (%) vs enoxaparin (95% CI) -0.7 (-2.9, 1.6) Number of Patients N=909 N=917 Composite endpoint of major VTEb and VTE related mortality 28 (3.1) 36 (3.9) Number of Patients N=905 N=914 Proximal DVT 23 (2.5) 33 (3.6) Number of Patients N=874 N=894 Total DVT 46 (5.3) 57 (6.4) Number of Patients N=1,137 N=1,142 Symptomatic DVT 6 (0.5) 1 (0.1) PE 5 (0.4) 3 (0.3) Death 3 (0.3) 0 Table 17 Primary Efficacy Endpoint for RE-NOVATE II PRADAXA Capsules
220 mg
N (%)Enoxaparin
N (%)aFull Analysis Set (FAS): The FAS included all randomized patients who received at least one subcutaneous injection or one oral dose of study medication, underwent surgery and subjects for whom the presence or absence of an efficacy outcome at the end of the study was known, i.e., an evaluable negative venogram for both distal and proximal DVT in both legs or any of the following: positive venography in one or both legs, or confirmed symptomatic DVT, PE, or death during the treatment period.
bVTE is defined as proximal DVT and PENumber of Patientsa N=792 N= 786 Primary Composite Endpoint 61 (7.7) 69 (8.8) Risk difference (%) vs enoxaparin (95% CI) -1.1 (-3.8, 1.6) Number of Patients N=805 N=795 Composite endpoint of major VTEb and VTE related mortality 18 (2.2) 33 (4.2) Number of Patients N=804 N=793 Proximal DVT 17 (2.1) 31 (3.9) Number of Patients N=791 N=784 Total DVT 60 (7.6) 67 (8.5) Number of Patients N=1,001 N=992 Symptomatic DVT 0 4 (0.4) PE 1 (0.1) 2 (0.2) Death 0 1 (0.1) 14.4 Treatment of VTE in Pediatric Patients
The DIVERSITY study was conducted to demonstrate the efficacy and safety of PRADAXA compared to standard of care (SOC) for the treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE) in pediatric patients from birth to less than 18 years of age. The study was designed as an open-label, randomized, parallel-group, non-inferiority study. Patients enrolled were randomized according to a 2:1 scheme to either an age-appropriate formulation (capsules, oral pellets, or oral solution) of PRADAXA (doses adjusted for age and weight) after at least 5 days and no longer than 21 days of treatment with a parenteral anticoagulant, or to SOC comprised of low molecular weight heparins (LMWH) or vitamin K antagonists (VKA) or fondaparinux. For patients on PRADAXA, drug concentration was determined prior to the 7th dose and a single titration was permitted to achieve drug target levels of 50-250 ng/mL. Inability to achieve target, after one up-titration, resulted in premature termination of study drug in 12 patients (6.8%).
The median treatment duration during the treatment period was 85 days. In total, 267 patients entered the study (leading index VTE was 64% deep vein thrombosis, 10% cerebral venous thrombosis or sinus thrombosis, and 9.0% pulmonary embolism), with 18% of patients having a central line-associated thrombosis. The patient population was 49.8% male, 91.8% white, 4.9% Asian, and 1.5% black; 168 patients were 12 to < 18 years old, 64 patients 2 to < 12 years, and 35 patients were younger than 2 years. The concomitant VTE-related risk factors of patients in this trial among study arms were as follows: inherited thrombophilia disorder (PRADAXA: 20%, SOC: 22%), congenital heart disease (PRADAXA: 12%, SOC: 30%), heart failure (PRADAXA: 3%, SOC: 18%), history of cancer (PRADAXA: 10%, SOC: 1%), CVL insertion (PRADAXA: 23%, SOC: 27%), immobility (PRADAXA: 13%, SOC: 10%) and significant infection (PRADAXA: 15%, SOC: 13%). The number of patients taking concomitant medications with hemostatic effects were similar in both treatment groups (PRADAXA: 15%, SOC: 16%).
The efficacy of PRADAXA was established based on a composite endpoint of patients with complete thrombus resolution, freedom from recurrent venous thromboembolic event, and freedom from mortality related to venous thromboembolic event (composite primary endpoint). Of the 267 randomized patients, 81 patients (45.8%) in the PRADAXA group and 38 patients (42.2%) in the SOC group met the criteria for the composite primary endpoint. The corresponding rate difference and 95% CI was -0.038 (-0.161, 0.086) and thus demonstrated non-inferiority of PRADAXA to SOC, since the upper bound of the 95% CI was lower than the predefined non-inferiority margin of 20% (see Table 18).
Table 18: Efficacy Results [ITT population] DIVERSITY Study PRADAXA Standard of Care 1 Mantel-Haenszel weighted difference with age group as stratification factor Number of patients randomized (%) 177 (100.0) 90 (100.0) Complete thrombus resolution 81 (45.8) 38 (42.2) Freedom from recurrent VTE 170 (96.0) 83 (92.2) Freedom from mortality related to VTE 177 (100.0) 89 (98.9) Composite endpoint met 81 (45.8) 38 (42.2) Difference in rate (95% CI)1 -0.038 (-0.161, 0.086) p-value for non-inferiority < 0.0001 p-value for superiority 0.2739 Subgroup analyses showed that there were no outliers in the treatment effect for the subgroups by age, sex, region, and presence of certain risk factors (central venous line, congenital heart disease, malignant disease). For the 3 different age strata, the proportions of patients that met the efficacy endpoint in the PRADAXA and SOC groups, respectively, were 13/22 (59.1%) and 7/13 (53.8%) for patients from birth to < 2 years [Rate Difference -0.052; (95%CI: -0.393, 0.288)], 21/43 (48.8%) and 12/21 (57.1%) for patients aged 2 to < 12 years [Rate Difference 0.083; (95%CI: -0.176, 0.342)], and 47/112 (42.0%) and 19/56 (33.9%) for patients aged 12 to < 18 years [Rate Difference -0.080; (95%CI: -0.234, 0.074)].
14.5 Reduction in the Risk of Recurrence of VTE in Pediatric Patients
Study 2 was an open-label, single-arm safety study to assess the safety of PRADAXA for the prevention of recurrent VTE in pediatric patients from birth to < 18 years. Patients who required further anticoagulation due to the presence of a clinical risk factor after completing the initial treatment for confirmed VTE (for at least 3 months) or after completing the DIVERSITY study were included in the study. Eligible patients received age- and weight adjusted dosages of an age-appropriate formulation (capsules or oral pellets) of PRADAXA until the clinical risk factor resolved, or up to a maximum of 12 months. The primary endpoints of the study included the recurrence of VTE, major and minor bleeding events, and mortality (overall and related to thrombotic or thromboembolic events) at 6 and 12 months.
Of the 214 patients in the study, 162 patients were 12 to < 18 years old, 43 patients were 2 to < 12 years old, and 9 patients were aged 6 months to < 2 years old.
The overall probability of being free from recurrence of VTE during the on-treatment period was 0.990 (95% CI: 0.960, 0.997) at 3 months, 0.984 (95% CI: 0.950, 0.995) at 6 months, and 0.984 (95% CI: 0.950, 0.995) at 12 months. The probability of being free from bleeding events during the on-treatment period was 0.849 (95% CI: 0.792, 0.891) at 3 months, 0.785 (95% CI: 0.718, 0.838) at 6 months, and 0.723 (95% CI: 0.645, 0.787) at 12 months. No on-treatment deaths occurred.
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient or caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Instructions for Patients
- Tell patients to take PRADAXA Capsules exactly as prescribed.
- Remind patients not to discontinue PRADAXA Capsules without talking to the healthcare provider who prescribed it.
- Keep PRADAXA Capsules in the original bottle to protect from moisture. Do not put PRADAXA Capsules in pill boxes or pill organizers.
- When more than one bottle is dispensed to the patient, instruct them to open only one bottle at a time.
- Instruct patient to remove only one capsule from the opened bottle at the time of use. The bottle should be immediately and tightly closed.
- Advise patients not to chew or break the capsules before swallowing them and not to open the capsules and take the pellets alone.
- Advise patients that the capsule should be taken with a full glass of water.
Bleeding
Inform patients that they may bleed more easily, may bleed longer, and should call their healthcare provider for any signs or symptoms of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Instruct patients to seek emergency care right away if they have any of the following, which may be a sign or symptom of serious bleeding:
- Unusual bruising (bruises that appear without known cause or that get bigger)
- Pink or brown urine
- Red or black, tarry stools
- Coughing up blood
- Vomiting blood, or vomit that looks like coffee grounds
Instruct patients to call their healthcare provider or to get prompt medical attention if they experience any signs or symptoms of bleeding:
- Pain, swelling or discomfort in a joint
- Headaches, dizziness, or weakness
- Reoccurring nose bleeds
- Unusual bleeding from gums
- Bleeding from a cut that takes a long time to stop
- Menstrual bleeding or vaginal bleeding that is heavier than normal
If patients have had neuraxial anesthesia or spinal puncture, and particularly, if they are taking concomitant NSAIDs or platelet inhibitors, advise patients to watch for signs and symptoms of spinal or epidural hematoma, such as back pain, tingling, numbness (especially in the lower limbs), muscle weakness, and stool or urine incontinence. If any of these symptoms occur, advise the patient to contact his or her physician immediately [see Boxed Warning].
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
Instruct patients to call their healthcare provider if they experience any signs or symptoms of dyspepsia or gastritis:
- Dyspepsia (upset stomach), burning, or nausea
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Epigastric discomfort, GERD (gastric indigestion)
[see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]
Invasive or Surgical Procedures
Instruct patients to inform their healthcare provider that they are taking PRADAXA before any invasive procedure (including dental procedures) is scheduled [see Dosage and Administration (2.8)].
Concomitant Medications
Ask patients to list all prescription medications, over-the-counter medications, or dietary supplements they are taking or plan to take so their healthcare provider knows about other treatments that may affect bleeding risk (e.g., aspirin or NSAIDs) or dabigatran exposure (e.g., dronedarone or systemic ketoconazole) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.5)].
Prosthetic Heart Valves
Instruct patients to inform their healthcare provider if they will have or have had surgery to place a prosthetic heart valve [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Allergic Reactions
Advise adult patients and caregivers that some adults taking PRADAXA have developed symptoms of an allergic reaction. Advise adult patients or caregivers to inform their healthcare provider if they or their child develop symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as hives, rash, or itching. Advise adult patients or caregivers to seek emergency medical attention if they or their child develop chest pain or tightness, swelling of the face or tongue, trouble breathing or wheezing, or feeling dizzy or faint.
Pregnancy
Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider immediately if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during treatment with PRADAXA Capsules [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Lactation
Advise patients not to breastfeed if they are taking PRADAXA Capsules [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Revised: November 2023 MEDICATION GUIDE
PRADAXA (pra dax a)
(dabigatran etexilate)
CapsulesThis Medication Guide is for PRADAXA Capsules. If your healthcare provider prescribes PRADAXA Oral Pellets for you, read the Medication Guide that comes with your medicine.
Read this Medication Guide before you start taking PRADAXA Capsules and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication Guide does not take the place of talking with your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.What is the most important information I should know about PRADAXA? - People with atrial fibrillation (a type of irregular heartbeat) are at an increased risk of forming a blood clot in the heart, which can travel to the brain, causing a stroke, or to other parts of the body. PRADAXA lowers your chance of having a stroke by helping to prevent clots from forming. If you stop taking PRADAXA, you may have increased risk of forming a clot in your blood.
Do not stop taking PRADAXA Capsules without talking to the healthcare provider who prescribes it for you. Stopping PRADAXA increases your risk of having a stroke.
PRADAXA may need to be stopped, if possible, before surgery or a medical or dental procedure. Ask the healthcare provider who prescribed PRADAXA for you when you should stop taking it. Your healthcare provider will tell you when you may start taking PRADAXA again after your surgery or procedure. If you have to stop taking PRADAXA, your healthcare provider may prescribe another medicine to help prevent a blood clot from forming. - PRADAXA can cause bleeding which can be serious, and sometimes lead to death. This is because PRADAXA is a blood thinner medicine that lowers the chance of blood clots forming in your body.
-
You may have a higher risk of bleeding if you take PRADAXA and:
- are over 75 years old
- have kidney problems
- have stomach or intestine bleeding that is recent or keeps coming back, or you have a stomach ulcer
- take other medicines that increase your risk of bleeding, including:
- aspirin or aspirin-containing products
- long-term (chronic) use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- a medicine that contains warfarin sodium
- a medicine that contains heparin
- a medicine that contains clopidogrel bisulfate
- a medicine that contains prasugrel
- have certain kidney problems and also take a medicine that contains dronedarone or ketoconazole tablets.
Tell your healthcare provider if you take any of these medicines. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure if your medicine is one listed above.
- PRADAXA can increase your risk of bleeding because it lessens the ability of your blood to clot. During treatment with PRADAXA:
- you may bruise more easily
- it may take longer for any bleeding to stop
- unexpected bleeding or bleeding that lasts a long time, such as:
- unusual bleeding from the gums
- nose bleeds that happen often
- menstrual bleeding or vaginal bleeding that is heavier than normal
- bleeding that is severe or you cannot control
- pink or brown urine
- red or black stools (looks like tar)
- bruises that happen without a known cause or get larger
- cough up blood or blood clots
- vomit blood or your vomit looks like "coffee grounds"
- unexpected pain, swelling, or joint pain
- headaches, feeling dizzy or weak
-
Spinal or epidural blood clots (hematoma). People who take a blood thinner medicine (anticoagulant) like PRADAXA, and have medicine injected into their spinal and epidural area, or have a spinal puncture have a risk of forming a blood clot that can cause long-term or permanent loss of the ability to move (paralysis). Your risk of developing a spinal or epidural blood clot is higher if:
- a thin tube called an epidural catheter is placed in your back to give you certain medicine
- you take NSAIDs or a medicine to prevent blood from clotting
- you have a history of difficult or repeated epidural or spinal punctures
- you have a history of problems with your spine or have had surgery on your spine
What is PRADAXA?
PRADAXA is a prescription medicine that is used to:-
in adults:
- reduce the risk of stroke and blood clots in adults who have a medical condition called atrial fibrillation that is not caused by a heart valve problem. With atrial fibrillation, part of the heart does not beat the way it should. This can lead to blood clots forming and increase your risk of a stroke.
- treat blood clots in the veins of your legs (deep vein thrombosis) and lungs (pulmonary embolism) after you have been treated with an injectable medicine to treat your blood clots for 5 to 10 days.
- reduce your risk of blood clots from happening again in the veins of your legs (deep vein thrombosis) and lungs (pulmonary embolism) after you have received treatment for blood clots.
- help prevent blood clots in your legs (venous thrombosis) and lungs (pulmonary embolism) after you have just had hip replacement surgery.
-
in children:
- treat blood clots in children 8 years to less than 18 years of age who have received an injectable medicine to treat their blood clots for at least 5 days.
- reduce the risk of blood clots from happening again in children 8 years to less than 18 years of age who have received treatment for blood clots.
Do not take PRADAXA if you: - currently have certain types of abnormal bleeding. Talk to your healthcare provider before taking PRADAXA if you currently have unusual bleeding.
- have had a serious allergic reaction to any of the ingredients in PRADAXA. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in PRADAXA. Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure.
- have ever had or plan to have a valve in your heart replaced with a mechanical (artificial) prosthetic heart valve
Before taking PRADAXA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - have kidney problems
- have ever had bleeding problems
- have ever had stomach ulcers
- have antiphospholipid syndrome (APS)
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if PRADAXA will harm your unborn baby. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant during treatment with PRADAXA.
Females who are able to become pregnant: Talk with your healthcare provider about pregnancy planning during treatment with PRADAXA. Talk with your healthcare provider about your risk for severe uterine bleeding if you are treated with blood thinner medicines, including PRADAXA. - are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if PRADAXA passes into your breast milk. You should not breastfeed during treatment with PRADAXA Capsules. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby during treatment with PRADAXA Capsules.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Some of your other medicines may affect the way PRADAXA works. Certain medicines may increase your risk of bleeding. See "What is the most important information I should know about PRADAXA?"
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take a medicine that contains rifampin.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.How should I take PRADAXA Capsules? - PRADAXA comes as capsules and oral pellets. If you have a child who is older than 8 years of age and who is prescribed PRADAXA, your healthcare provider will prescribe the type of PRADAXA that is right for your child.
- Your healthcare provider will decide how long you should take PRADAXA. Do not stop taking PRADAXA Capsules without first talking with your healthcare provider. Stopping PRADAXA may increase your risk of having a stroke or forming blood clots.
- Take PRADAXA Capsules exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- If PRADAXA is prescribed for your child, your healthcare provider will determine the correct dose of PRADAXA Capsules for your child based on their weight. Your healthcare provider may increase or decrease your child's dose as they grow during treatment and as needed.
- In adults: Take PRADAXA Capsules 2 times a day. If you are taking PRADAXA after hip replacement surgery, take PRADAXA 1 time a day.
- In children: Take PRADAXA Capsules 2 times a day. Take 1 dose in the morning and 1 dose in the evening about every 12 hours, at about the same time each day.
- You can take PRADAXA Capsules with or without food. Taking PRADAXA Capsules with food may help if you have an upset stomach.
- Swallow PRADAXA Capsules whole with a full glass of water. Tell your healthcare provider if you or your child are not able to swallow the capsules whole. Do not break, chew, or empty the pellets from the capsule.
- Do not run out of PRADAXA Capsules. Refill your prescription before you run out. If you plan to have surgery, or a medical or a dental procedure, tell your healthcare provider and dentist that you are taking PRADAXA. You may have to stop taking PRADAXA for a short time. See "What is the most important information I should know about PRADAXA?"
- If you miss a dose of PRADAXA Capsules, take it as soon as you remember. If your next dose is less than 6 hours away, skip the missed dose. Do not take two doses of PRADAXA Capsules at the same time.
- If you take too much PRADAXA Capsules, go to the nearest hospital emergency room or call your healthcare provider.
- Call your healthcare provider right away if you fall or injure yourself, especially if you hit your head. Your healthcare provider may need to check you.
- PRADAXA Capsules come in a bottle or in a blister package.
- Only open 1 bottle of PRADAXA Capsules at a time. Finish your opened bottle of PRADAXA Capsules before opening a new bottle.
- After opening a bottle of PRADAXA Capsules, use within 4 months. See "How should I store PRADAXA Capsules?"
- When it is time for you to take a dose of PRADAXA Capsules, only remove your prescribed dose of PRADAXA Capsules from your open bottle or blister package.
- Tightly close your bottle of PRADAXA Capsules right away after you take your dose.
What are the possible side effects of PRADAXA?
PRADAXA can cause serious side effects. See "What is the most important information I should know about PRADAXA?"-
Allergic Reactions. Some adults taking PRADAXA Capsules have developed symptoms of an allergic reaction.
- Call your healthcare provider if you or your child gets symptoms of an allergic reaction, such as:
- hives
- rash
- itching
- Get medical help right away if you or your child gets any of the following symptoms of a serious allergic reaction with PRADAXA Capsules:
- chest pain or chest tightness
- swelling of your face or tongue
- trouble breathing or wheezing
- feeling dizzy or faint
Common side effects of PRADAXA in adults and children include: - indigestion, upset stomach, or burning
- stomach-area (abdominal) pain or discomfort
In children, common side effects also include:- nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
These are not all of the possible side effects of PRADAXA.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.How should I store PRADAXA Capsules? - Store PRADAXA Capsules at room temperature 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- After opening the bottle, use PRADAXA Capsules within 4 months. Safely throw away any unused PRADAXA Capsules after 4 months.
- Keep PRADAXA Capsules in the original bottle or blister package to keep them dry (protect the capsules from moisture). Do not put PRADAXA Capsules in pill boxes or pill organizers.
- Tightly close your bottle of PRADAXA Capsules right away after you take your dose.
General information about the safe and effective use of PRADAXA
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use PRADAXA Capsules for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give PRADAXA Capsules to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about PRADAXA. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about PRADAXA that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in PRADAXA Capsules?
Active ingredient: dabigatran etexilate mesylate
Inactive ingredients: acacia, dimethicone, hypromellose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, talc, and tartaric acid. The capsule shell is composed of carrageenan, hypromellose, potassium chloride, titanium dioxide, black edible ink, and FD&C Blue No. 2 (150 mg and 110 mg capsules only).
Distributed by: Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Ridgefield, CT 06877 USA
For more information about PRADAXA, including current prescribing information and Medication Guide, go to www.pradaxa.com or call Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-542-6257 or scan the code to go to www.pradaxa.com.
Copyright © 2023 Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
COL8774EK272023 - People with atrial fibrillation (a type of irregular heartbeat) are at an increased risk of forming a blood clot in the heart, which can travel to the brain, causing a stroke, or to other parts of the body. PRADAXA lowers your chance of having a stroke by helping to prevent clots from forming. If you stop taking PRADAXA, you may have increased risk of forming a clot in your blood.
- dabigatran etexilate mesylate
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PRADAXA
dabigatran etexilate mesylate capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:50090-4480(NDC:0597-0360) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DABIGATRAN ETEXILATE MESYLATE (UNII: SC7NUW5IIT) (DABIGATRAN - UNII:I0VM4M70GC) DABIGATRAN ETEXILATE 150 mg Product Characteristics Color BLUE, WHITE Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 22mm Flavor Imprint Code R150 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:50090-4480-0 1 in 1 CARTON 08/28/2019 1 60 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA022512 07/28/2017 Labeler - A-S Medication Solutions (830016429) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations A-S Medication Solutions 830016429 RELABEL(50090-4480)


