Label: CEFADROXIL capsule
-
Contains inactivated NDC Code(s)
NDC Code(s): 50090-1915-0, 50090-1915-2 - Packager: A-S Medication Solutions
- This is a repackaged label.
- Source NDC Code(s): 65862-085
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Abbreviated New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated February 25, 2021
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Cefadroxil, USP is a semisynthetic cephalosporin antibiotic intended for oral administration. It is a white to yellowish-white crystalline powder. It is soluble in water and it is acid-stable. It is chemically designated as 5-Thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid, 7-[[amino(4-hydroxyphenyl)acetyl]amino]-3-methyl-8-oxo-, monohydrate, [6R-[6α,7β(R*)]]-. It has the formula C16H17N3O5S · H2O and the molecular weight of 381.40. It has the following structural formula:
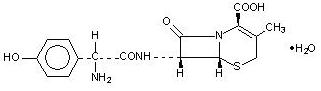
Cefadroxil capsules contain the following inactive ingredients: Lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, FD&C Blue No.1, D&C Red No.28, FD&C Red No. 40, titanium dioxide, gelatin, sodium lauryl sulphate, and edible black ink (black iron oxide).
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Cefadroxil is rapidly absorbed after oral administration. Following single doses of 500 mg and 1000 mg, average peak serum concentrations were approximately 16 and 28 mcg/mL, respectively. Measurable levels were present 12 hours after administration. Over 90% of the drug is excreted unchanged in the urine within 24 hours. Peak urine concentrations are approximately 1800 mcg/mL during the period following a single 500 mg oral dose. Increases in dosage generally produce a proportionate increase in cefadroxil urinary concentration. The urine antibiotic concentration, following a 1 g dose, was maintained well above the MIC of susceptible urinary pathogens for 20 to 22 hours.
Microbiology
In vitro tests demonstrate that the cephalosporins are bactericidal because of their inhibition of cell-wall synthesis. Cefadroxil has been shown to be active against the following organisms both in vitro and in clinical infections (see INDICATIONS AND USAGE):
Beta-hemolytic streptococci
Staphylococci, including penicillinase-producing strains
Streptococcus (Diplococcus) pneumoniae
Escherichia coli
Proteus mirabilis
Klebsiella species
Moraxella (Branhamella) catarrhalis
Note: Most strains of Enterococcus faecalis (formerly Streptococcus faecalis) and Enterococcus faecium (formerly Streptococcus faecium) are resistant to cefadroxil. It is not active against most strains of Enterobacter species, Morganella morganii (formerly Proteus morganii), and P. vulgaris. It has no activity against Pseudomonas species and Acinetobacter calcoaceticus (formerly Mima and Herellea species).
Susceptibility Testing
For specific information regarding susceptibility test interpretive criteria and associated test methods and quality control standards recognized by FDA for this drug, please see: https://www.fda.gov/STIC. -
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Cefadroxil is indicated for the treatment of patients with infection caused by susceptible strains of the designated organisms in the following diseases:
Urinary tract infections caused by E. coli, P. mirabilis, and Klebsiella species.
Skin and skin structure infections caused by staphylococci and/or streptococci.
Pharyngitis and/or tonsillitis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A beta-hemolytic streptococci).
Note: Only penicillin by the intramuscular route of administration has been shown to be effective in the prophylaxis of rheumatic fever. Cefadroxil is generally effective in the eradication of streptococci from the oropharynx. However, data establishing the efficacy of cefadroxil for the prophylaxis of subsequent rheumatic fever are not available.
Note: Culture and susceptibility tests should be initiated prior to and during therapy. Renal function studies should be performed when indicated.
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cefadroxil and other antibacterial drugs, cefadroxil should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy. - CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
BEFORE THERAPY WITH CEFADROXIL IS INSTITUTED, CAREFUL INQUIRY SHOULD BE MADE TO DETERMINE WHETHER THE PATIENT HAS HAD PREVIOUS HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS TO CEFADROXIL, CEPHALOSPORINS, PENICILLINS, OR OTHER DRUGS. IF THIS PRODUCT IS TO BE GIVEN TO PENICILLIN-SENSITIVE PATIENTS, CAUTION SHOULD BE EXERCISED BECAUSE CROSS-SENSITIVITY AMONG BETA-LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS HAS BEEN CLEARLY DOCUMENTED AND MAY OCCUR IN UP TO 10% OF PATIENTS WITH A HISTORY OF PENICILLIN ALLERGY.
IF AN ALLERGIC REACTION TO CEFADROXIL OCCURS, DISCONTINUE THE DRUG. SERIOUS ACUTE HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS MAY REQUIRE TREATMENT WITH EPINEPHRINE AND OTHER EMERGENCY MEASURES, INCLUDING OXYGEN, INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS, INTRAVENOUS ANTIHISTAMINES, CORTICOSTEROIDS, PRESSOR AMINES, AND AIRWAY MANAGEMENT, AS CLINICALLY INDICATED.
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including cefadroxil, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated. -
PRECAUTIONS
General
Cefadroxil should be used with caution in the presence of markedly impaired renal function (creatinine clearance rate of less than 50 mL/min/1.73 m2). (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.) In patients with known or suspected renal impairment, careful clinical observation and appropriate laboratory studies should be made prior to and during therapy.
Prescribing cefadroxil in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
Prolonged use of cefadroxil may result in the overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms. Careful observation of the patient is essential. If superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken.
Cefadroxil should be prescribed with caution in individuals with history of gastrointestinal disease particularly colitis.Information for Patients
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including cefadroxil should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When cefadroxil is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by cefadroxil or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibiotics which usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibiotics, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibiotic. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Positive direct Coombs’ tests have been reported during treatment with the cephalosporin antibiotics. In hematologic studies or in transfusion cross-matching procedures when antiglobulin tests are performed on the minor side or in Coombs’ testing of newborns whose mothers have received cephalosporin antibiotics before parturition, it should be recognized that a positive Coombs’ test may be due to the drug.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No long-term studies have been performed to determine carcinogenic potential. No genetic toxicity tests have been performed.
Pregnancy:
Pregnancy Category B
Reproduction studies have been performed in mice and rats at doses up to 11 times the human dose and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to cefadroxil monohydrate. There are, however, no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.Labor and Delivery
Cefadroxil has not been studied for use during labor and delivery. Treatment should only be given if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
Caution should be exercised when cefadroxil monohydrate is administered to a nursing mother.
Geriatric Use
Of approximately 650 patients who received cefadroxil for the treatment of urinary tract infections in three clinical trials, 28% were 60 years and older, while 16% were 70 years and older. Of approximately 1000 patients who received cefadroxil for the treatment of skin and skin structure infection in 14 clinical trials, 12% were 60 years and older while 4% were 70 years and over. No overall differences in safety were observed between the elderly patients in these studies and younger patients. Clinical studies of cefadroxil for the treatment of pharyngitis or tonsillitis did not include sufficient numbers of patients 65 years and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Other reported clinical experience with cefadroxil has not identified differences in responses between elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
Cefadroxil is substantially excreted by the kidney, and dosage adjustment is indicated for patients with renal impairment (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Renal Impairment). Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function. -
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Gastrointestinal
Onset of pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may occur during or after antibiotic treatment (see WARNINGS). Dyspepsia, nausea and vomiting have been reported rarely. Diarrhea has also occurred.
Hypersensitivity
Allergies (in the form of rash, urticaria, angioedema, and pruritus) have been observed. These reactions usually subsided upon discontinuation of the drug. Anaphylaxis has also been reported.
Other
Other reactions have included hepatic dysfunction including cholestasis and elevations in serum transaminase, genital pruritus, genital moniliasis, vaginitis, moderate transient neutropenia, fever. Agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, idiosyncratic hepatic failure, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, serum sickness, and arthralgia have been rarely reported.
In addition to the adverse reactions listed above which have been observed in patients treated with cefadroxil, the following adverse reactions and altered laboratory tests have been reported for cephalosporin-class antibiotics:
Toxic epidermal necrolysis, abdominal pain, superinfection, renal dysfunction, toxic nephropathy, aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia, hemorrhage, prolonged prothrombin time, positive Coombs’ test, increased BUN, increased creatinine, elevated alkaline phosphatase, elevated aspartate aminotransferase (AST), elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT), elevated bilirubin, elevated LDH, eosinophilia, pancytopenia, neutropenia.
Several cephalosporins have been implicated in triggering seizures, particularly in patients with renal impairment, when the dosage was not reduced (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION and OVERDOSAGE). If seizures associated with drug therapy occur, the drug should be discontinued. Anticonvulsant therapy can be given if clinically indicated. -
OVERDOSAGE
A study of children under six years of age suggested that ingestion of less than 250 mg/kg of cephalosporins is not associated with significant outcomes. No action is required other than general support and observation. For amounts greater than 250 mg/kg, induce gastric emptying.
In five anuric patients, it was demonstrated that an average of 63% of a 1 g oral dose is extracted from the body during a 6 to 8 hour hemodialysis session. -
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Cefadroxil is acid-stable and may be administered orally without regard to meals. Administration with food may be helpful in diminishing potential gastrointestinal complaints occasionally associated with oral cephalosporin therapy.
Adults
Urinary Tract Infections: For uncomplicated lower urinary tract infections (i.e., cystitis) the usual dosage is 1 or 2 g per day in a single (q.d.) or divided doses (b.i.d.).
For all other urinary tract infections the usual dosage is 2 g per day in divided doses (b.i.d.).
Skin and Skin Structure Infections: For skin and skin structure infections the usual dosage is 1 g per day in single (q.d.) or divided doses (b.i.d.).
Pharyngitis and Tonsillitis: Treatment of group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal pharyngitis and tonsillitis—1 g per day in single (q.d.) or divided doses (b.i.d.) for 10 days.Children
For urinary tract infections, the recommended daily dosage for children is 30 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours. For pharyngitis, tonsillitis, and impetigo, the recommended daily dosage for children is 30 mg/kg/day in a single dose or in equally divided doses every 12 hours. For other skin and skin structure infections, the recommended daily dosage is 30 mg/kg/day in equally divided doses every 12 hours. In the treatment of beta-hemolytic streptococcal infections, a therapeutic dosage of cefadroxil should be administered for at least 10 days.
Renal Impairment
In patients with renal impairment, the dosage of cefadroxil should be adjusted according to creatinine clearance rates to prevent drug accumulation. The following schedule is suggested. In adults, the initial dose is 1000 mg of cefadroxil and the maintenance dose (based on the creatinine clearance rate [mL/min/1.73 m2]) is 500 mg at the time intervals listed below.
Creatinine Clearances Dosage Interval 0 to 10 mL/min
36 hours
10 to 25 mL/min
24 hours
25 to 50 mL/min
12 hours
Patients with creatinine clearance rates over 50 mL/min may be treated as if they were patients having normal renal function.
- HOW SUPPLIED
- Cefadroxil
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CEFADROXIL
cefadroxil capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:50090-1915(NDC:65862-085) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CEFADROXIL (UNII: 280111G160) (CEFADROXIL ANHYDROUS - UNII:Q525PA8JJB) CEFADROXIL ANHYDROUS 500 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) D&C RED NO. 28 (UNII: 767IP0Y5NH) FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) GELATIN, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 2G86QN327L) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) Product Characteristics Color RED (Maroon Opaque) , WHITE (White Opaque) Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 21mm Flavor Imprint Code C;97 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:50090-1915-0 10 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/06/2015 2 NDC:50090-1915-2 20 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/06/2015 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA065352 01/25/2007 Labeler - A-S Medication Solutions (830016429) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations A-S Medication Solutions 830016429 RELABEL(50090-1915) , REPACK(50090-1915)


