Label: VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE injection, solution
-
NDC Code(s):
0338-0122-04,
0338-0124-04,
0338-3551-48,
0338-3552-48, view more0338-3580-48, 0338-3581-01, 0338-3582-01, 0338-3583-01
- Packager: Baxter Healthcare Corporation
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated June 7, 2024
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use VANCOMYCIN INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for VANCOMYCIN INJECTION.
VANCOMYCIN injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1958INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Vancomycin Injection is a glycopeptide antibacterial indicated for the treatment of the following infections in adult and pediatric patients for whom appropriate dosing with this formulation can be achieved:
- •
- Septicemia (1.1)
- •
- Infective Endocarditis (1.2)
- •
- Skin and Skin Structure Infections (1.3)
- •
- Bone Infections (1.4)
- •
- Lower Respiratory Tract Infections (1.5)
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Vancomycin Injection and other antibacterial drugs, Vancomycin Injection should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. (1.6)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- •
- If a dose of Vancomycin Injection is required that does not equal 500 mg, 750 mg, 1 g, 1.25 g or 1.5 g, this product is not recommended for use and an alternative formulation of vancomycin should be considered. (2.1)
- •
- For Intravenous use only. Do not administer orally. (2.1).
- •
- Administer Vancomycin Injection by intravenous infusion over 60 minutes or greater to reduce the risk of infusion reactions. (2.1).
- •
- Recommended Dosage in Adult Patients with Normal Renal Function: 2 g divided either as 0.5 grams (g) every 6 hours or 1 g every 12 hours. (2.2)
- •
- Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients with Normal Renal Function: 10 mg/kg per dose given every 6 hours. (2.3)
- •
- Recommended Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment: See full prescribing information for recommended doses in patients with renal impairment. (2.4)
- •
- See full prescribing information for further important preparation and administration instructions. (2.1, 2.5)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- •
- Injection: Vancomycin Injection (in 5% Dextrose) 500 mg/100 mL; 750 mg/150 mL; 1 g/200 mL; 1.25 g/250 mL; 1.5 g/300 mL (5 mg/mL) in single-dose GALAXY container. (3)
- •
- Injection: Vancomycin Injection (in 0.9% Sodium Chloride) 500 mg/100 mL; 750 mg/150 mL; 1 g/200 mL (5 mg/mL) in single dose GALAXY container. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity to vancomycin (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- •
- Infusion Reactions: Hypotension, including shock and cardiac arrest, wheezing, dyspnea, urticaria, muscular and chest pain, and “vancomycin infusion reaction” which manifests as pruritus and erythema that involves the face, neck and upper body may occur with rapid intravenous administration. To reduce the risk of infusion reactions, administer Vancomycin Injection over a period of 60 minutes or greater and also prior to intravenous anesthetic agents. (2.1, 5.1)
- •
- Nephrotoxicity: Monitor renal function in all patients receiving Vancomycin Injection. (5.2)
- •
- Ototoxicity: Serial tests of auditory function may be helpful. (5.3)
- •
- Severe Dermatologic Reactions: Discontinue Vancomycin Injection at the first appearance of signs and symptoms of TEN, SJS, DRESS, AGEP, or LABD. (5.4)
- •
- Clostridioides Difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD): Evaluate patients if diarrhea occurs. (5.5)
- •
- Neutropenia: Periodically monitor leukocyte count. (5.7)
- •
- Phlebitis and Other Administration Site Reactions: Vancomycin is irritating to tissue and must be given by a secure intravenous route of administration. (5.8)
- •
- Risk of High Sodium Load: Avoid use of Vancomycin Injection in patients with congestive heart failure, elderly patients and patients requiring restricted sodium intake. (5.10)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions are anaphylaxis, “vancomycin infusion reaction”, acute kidney injury, hearing loss, neutropenia. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Baxter Healthcare at 1-866-888-2472 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- •
- Anesthetic Agents: Concomitant administration of vancomycin and anesthetic agents has been associated with erythema and histamine-like flushing. (2.1, 7.1)
- •
- Piperacillin/Tazobactam: Increased incidence of acute kidney injury in patients receiving concomitant piperacillin/tazobactam and vancomycin as compared to vancomycin alone. Monitor kidney function in patients. (7.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 6/2024
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Septicemia
1.2 Infective Endocarditis
1.3 Skin and Skin Structure Infections
1.4 Bone Infection
1.5 Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
1.6 Usage
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
2.2 Recommended Dosage in Adult Patients with Normal Renal Function
2.3 Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients with Normal Renal Function
2.4 Recommended Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment
2.5 Administration and Preparation Instructions for Vancomycin Injection
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Infusion Reactions
5.2 Nephrotoxicity
5.3 Ototoxicity
5.4 Severe Dermatologic Reactions
5.5 Clostridioides Difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD)
5.6 Hemorrhagic Occlusive Retinal Vasculitis (HORV)
5.7 Neutropenia
5.8 Phlebitis and Other Administration Site Reactions
5.9 Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria
5.10 Risk of High Sodium Load
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Anesthetic Agents
7.2 Piperacillin-Tazobactam
7.3 Ototoxic and/or Nephrotoxic Drugs
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.4 Microbiology
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Septicemia
Vancomycin Injection is indicated in adults and pediatric patients for whom appropriate dosing with this formulation can be achieved [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)] for the treatment of septicemia due to:
- •
- Susceptible isolates of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and coagulase negative staphylococci.
- •
- Methicillin-susceptible staphylococci in penicillin-allergic patients, or those patients who cannot receive or who have failed to respond to other drugs, including penicillins or cephalosporins.
1.2 Infective Endocarditis
Vancomycin Injection is indicated in adults and pediatric patients for whom appropriate dosing with this formulation can be achieved [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)] for the treatment of infective endocarditis due to:
- •
- Susceptible isolates of MRSA.
- •
- Viridans group streptococci or Streptococcus gallolyticus (previously known as Streptococcus bovis) and Enterococcus species and Corynebacterium species. For enterococcal endocarditis (e.g., E. faecalis), use Vancomycin Injection in combination with an aminoglycoside.
- •
- Methicillin-susceptible staphylococci in penicillin-allergic patients, or those patients who cannot receive or who have failed to respond to other drugs, including penicillins or cephalosporins.
Vancomycin Injection is indicated in adults and pediatric patients for the treatment of early-onset prosthetic valve endocarditis caused by Staphylococcus epidermidis in combination with rifampin and an aminoglycoside.
1.3 Skin and Skin Structure Infections
Vancomycin Injection is indicated in adults and pediatric patients for whom appropriate dosing with this formulation can be achieved [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)] for the treatment of skin and skin structure infections due to:
- •
- Susceptible isolates of MRSA and coagulase negative staphylococci.
- •
- Methicillin-susceptible staphylococci in penicillin-allergic patients, or those patients who cannot receive or who have failed to respond to other drugs, including penicillins or cephalosporins.
1.4 Bone Infection
Vancomycin Injection is indicated in adults and pediatric patients (and older) for whom appropriate dosing with this formulation can be achieved [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)] for the treatment of bone infections due to:
- •
- Susceptible isolates of MRSA and coagulase negative staphylococci.
- •
- Methicillin-susceptible staphylococci in penicillin-allergic patients, or those patients who cannot receive or who have failed to respond to other drugs, including penicillins or cephalosporins.
1.5 Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
Vancomycin Injection is indicated in adults and pediatric patients for whom appropriate dosing with this formulation can be achieved [see Dosage and Administration (2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)] for the treatment of lower respiratory tract infections due to:
- •
- Susceptible isolates of MSRA.
- •
- Methicillin-susceptible staphylococci in penicillin-allergic patients, or those patients who cannot receive or who have failed to respond to other drugs, including penicillins or cephalosporins.
1.6 Usage
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Vancomycin Injection and other antibacterial drugs, Vancomycin Injection should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
- •
- If a dose of Vancomycin Injection is required that does not equal 500 mg, 750 mg, 1 g, 1.25 g or 1.5 g, this product is not recommended for use and an alternative formulation of vancomycin should be considered.
- •
- Vancomycin Injection is intended for intravenous use only.
- •
- Vancomycin Injection is not to be administered orally.
- •
- To reduce the risk of infusion related adverse reactions, administer Vancomycin Injection by intravenous infusion over 60 minutes or greater [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. An infusion rate of 10 mg/min or less is associated with fewer infusion-related adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Infusion related adverse reactions may occur, however, at any rate or concentration.
- •
- Drug additives should not be made to this solution.
- •
- Vancomycin Injection concentrations of no more than 5 mg/mL are recommended in adults [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. See also age-specific recommendations [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- •
- Administer Vancomycin by a secure intravenous route of administration to reduce the risk of local irritation and phlebitis reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
- •
- Administer Vancomycin Injection prior to intravenous anesthetic agents to reduce the risk of infusion related adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage in Adult Patients with Normal Renal Function
The usual daily intravenous dosage of Vancomycin Injection is 2 grams (g) divided either as 500 mg every 6 hours or 1 g every 12 hours. Administer each dose by intravenous infusion over a period of 60 minutes or greater. Other patient factors, such as age or obesity, may call for modification of the usual intravenous daily dose. The initial daily dose should be no less than 15 mg/kg.
2.3 Recommended Dosage in Pediatric Patients with Normal Renal Function
If a dose of Vancomycin Injection is required that does not equal 500 mg, 750 mg, 1 g, 1.25 g or 1.5 g, this product is not recommended for use and an alternative formulation of vancomycin should be considered [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Pediatric Patients (Aged 1 Month and Older)
The usual intravenous dosage of vancomycin is 10 mg/kg per dose given every 6 hours. Each dose should be administered over a period of at least 60 minutes. Close monitoring of serum concentrations of vancomycin may be warranted in these patients.
Pediatric Patients (Younger than 1 Month Old)
In pediatric patients up to the age of 1 month, the total daily intravenous dosage may be lower. In neonates, an initial dose of 15 mg/kg is suggested, followed by 10 mg/kg every 12 hours for neonates in the 1st week of life and every 8 hours thereafter up to the age of 1 month. Each dose should be administered over 60 minutes. In premature infants, vancomycin clearance decreases as postconceptional age decreases. Therefore, longer dosing intervals may be necessary in premature infants. Close monitoring of serum concentrations of vancomycin is recommended in these patients.
2.4 Recommended Dosage in Patients with Renal Impairment
Dosage adjustment must be made in patients with renal impairment. The initial dose should be no less than 15 mg/kg in patients with any degree of renal impairment. Measure trough vancomycin serum concentrations to guide therapy, especially in seriously ill patients with changing renal function.
For functionally anephric patients, an initial dose of 15 mg/kg of body weight should be given to achieve prompt therapeutic serum concentrations. Measure vancomycin serum concentrations at 24 hours following the first dose to guide further intravenous therapy.
2.5 Administration and Preparation Instructions for Vancomycin Injection
Administration Instructions
Vancomycin Injection, in GALAXY plastic container is for intravenous administration only. Intermittent infusion is the recommended method of administration.
Store the frozen Vancomycin Injection container in a freezer capable of maintaining a temperature at or below -20°C (-4°F) [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)].
Preparation for Intravenous Administration:
Thawing of Plastic Containers
- 1.
- Thaw frozen containers at room temperature (25°C/77°F) or under refrigeration (5°C/41°F). Product should not be thawed by immersion in waters baths or by microwave irradiation. Do not force thaw.
- 2.
- Check for minute leaks by squeezing the bag firmly. If leaks are detected, discard solution because sterility may be impaired.
- 3.
- Do not add supplemental medication.
- 4.
- Visually inspect the container. If the outlet port protector is damaged, detached, or not present, discard container as solution path sterility may be impaired.
- 5.
- Components of the solution may precipitate in the frozen state and will dissolve upon reaching room temperature with little or no agitation. Potency is not affected. Agitate after solution has reached room temperature.
- 6.
- If after visual inspection the solution remains cloudy or if an insoluble precipitate is noted or if any seals are not intact, discard the container.
- 7.
- The thawed solution in GALAXY plastic container remains chemically stable for 72 hours at room temperature (25°C/77°F) or for 30 days when stored under refrigeration (5°C/41°F).
- 8.
- Handle frozen product containers with care. Product containers may be fragile in the frozen state.
- 9.
- Do not refreeze thawed Vancomycin Injection.
- Directions for Administration
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration.
- 1.
- Suspend container from eyelet support.
- 2.
- Remove protector from outlet port at bottom of container.
- 3.
- Attach administration set. Refer to complete directions accompanying set.
- 4.
- Use sterile equipment.
Do not use plastic containers in series connections. Such use could result in an embolism due to residual air being drawn from the primary container before administration of the fluid from the secondary container is complete.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: Vancomycin Injection USP, is a frozen, iso-osmotic, sterile, nonpyrogenic premixed solution available in the following strengths:
- •
- 500 mg/100 mL (5 mg/mL); Each 100 mL single-dose GALAXY container contains 500 mg Vancomycin (as Vancomycin hydrochloride) in 5% Dextrose or 0.9% Sodium Chloride.
- •
- 750 mg/150 mL (5 mg/mL); Each 150 mL single-dose GALAXY container contains 750 mg Vancomycin (as Vancomycin hydrochloride) in 5% Dextrose or 0.9% Sodium Chloride.
- •
- 1 g/200 mL (5 mg/mL); Each 200 mL single-dose GALAXY container contains 1 g Vancomycin (as Vancomycin hydrochloride) in 5% Dextrose or 0.9% Sodium Chloride.
- •
- 1.25 g/250 mL (5 mg/mL): Each 250 mL single-dose GALAXY container contains 1.25 g of Vancomycin (as Vancomycin hydrochloride) in 5 % Dextrose.
- •
- 1.5 g/300 mL (5 mg/mL): Each 250 mL single-dose GALAXY container contains 1.5 g of Vancomycin (as Vancomycin hydrochloride) in 5 % Dextrose.
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Infusion Reactions
Hypotension including shock and cardiac arrest, wheezing, dyspnea, urticaria or pruritus, muscular and chest pain may occur with rapid Vancomycin Injection administration. (e.g., over several minutes). The reactions may be more severe in pediatric patients [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Rapid intravenous administration of Vancomycin Injection may also be associated with “vancomycin infusion reaction”, which manifests as pruritus and erythema that involves the face, neck and upper body or pain and muscle spasm of the chest and back. There have been reports that the frequency of infusion-related reactions (including hypotension, flushing, erythema, urticaria, and pruritus) increases with the concomitant administration of anesthetic agents.
Infusion-related adverse reactions are related to both the concentration and the rate of administration of Vancomycin for Injection. Infusion-related adverse reactions may occur, however, at any rate or concentration.
Administer Vancomycin Injection over a period of 60 minutes or greater to reduce the risk of rapid-infusion-related adverse reactions. In selected patients in need of fluid restriction, a concentration up to 10 mg/mL may be used; use of such higher concentrations may increase the risk of infusion-related adverse reactions.
Administer Vancomycin Injection as a 60-minute infusion prior to administration of anesthetic agents when feasible to minimize infusion-related adverse reactions. Stop the infusion if a reaction occurs because this usually results in prompt cessation of these reactions.
5.2 Nephrotoxicity
Vancomycin Injection can result in acute kidney injury (AKI), including acute renal failure, mainly due to interstitial nephritis or less commonly acute tubular necrosis. AKI is manifested by increasing blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine (Cr). The risk of AKI increases with higher vancomycin serum levels, prolonged exposure, concomitant administration of other nephrotoxic drugs, concomitant administration of piperacillin-tazobactam [see Drug Interactions (7.2)], volume depletion, pre-existing renal impairment and in critically ill patients and patients with co-morbid conditions that predispose to renal impairment.
Monitor serum vancomycin concentrations and renal function in all patients receiving Vancomycin Injection. More frequent monitoring is recommended in patients with comorbidities that predispose to impairment in renal function or are concomitantly receiving other nephrotoxic drugs, in critically ill patients, in patients with changing renal function, and in patients requiring higher therapeutic vancomycin levels. If acute kidney injury occurs, discontinue Vancomycin Injection, or reduce the dose [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.3 Ototoxicity
Ototoxicity has occurred in patients receiving Vancomycin Injection. It may be reversible or permanent. Ototoxicity manifests as tinnitus, hearing loss, dizziness or vertigo. The risk is higher in older patients, patients who are receiving higher doses, who have an underlying hearing loss, who are receiving concomitant therapy with another ototoxic agent, such as an aminoglycoside or who have underlying renal impairment. Monitor for signs and symptoms of ototoxicity during therapy. Monitor serum vancomycin concentrations and renal function in all patients receiving parenteral vancomycin. Discontinue Vancomycin Injection if ototoxicity occurs. Dosage of Vancomycin Injection must be adjusted for patients with renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Serial tests of auditory function may be helpful in order to minimize the risk of ototoxicity.
5.4 Severe Dermatologic Reactions
Severe dermatologic reactions such as toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), and linear IgA bullous dermatosis (LABD) have been reported in association with the use of vancomycin. Cutaneous signs or symptoms reported include skin rashes (including exfoliative dermatitis), mucosal lesions, and blisters.
Discontinue Vancomycin Injection at the first appearance of signs and symptoms of TEN, SJS, DRESS, AGEP, or LABD.
5.5 Clostridioides Difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD)
Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including Vancomycin Injection, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibacterial use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibacterial use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibacterial treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
Prolonged use of vancomycin may result in the overgrowth of nonsusceptible microorganisms. Careful observation of the patient is essential. If superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken. In rare instances, there have been reports of pseudomembranous colitis due to C. difficile developing in patients who received intravenous vancomycin.
5.6 Hemorrhagic Occlusive Retinal Vasculitis (HORV)
Hemorrhagic occlusive retinal vasculitis, including permanent loss of vision, occurred in patients receiving intracameral or intravitreal administration of vancomycin during or after cataract surgery. The safety and efficacy of vancomycin administered by the intracameral or the intravitreal route have not been established by adequate and well-controlled trials. Vancomycin is not indicated for prophylaxis of endophthalmitis.
5.7 Neutropenia
Reversible neutropenia has been reported in patients receiving vancomycin [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Patients who will undergo prolonged therapy with vancomycin or those who are receiving concomitant drugs that may cause neutropenia should have periodic monitoring of the leukocyte count.
Reversible neutropenia, usually starting 1 week or more after onset of therapy with vancomycin or after a total dosage of more than 25 g, has been reported for several dozen patients. Neutropenia appears to be promptly reversible when vancomycin is discontinued. Thrombocytopenia has been reported. Although a causal relationship has not been established, reversible agranulocytosis (granulocytes <500/mm3) has been reported.
5.8 Phlebitis and Other Administration Site Reactions
Inflammation at the injection site has been reported. Vancomycin is irritating to tissue and must be given by a secure intravenous route of administration. Thrombophlebitis may occur, the frequency and severity of which can be minimized by slow infusion of the drug and by rotation of venous access sites.
Administration of Vancomycin Injection by intramuscular (IM), intraperitoneal, intrathecal intraventricular, or intravitreal routes has not been approved and is not recommended. The safety and efficacy of vancomycin administered by these routes of administration have not been established by adequate and well controlled trials. Pain, tenderness, and necrosis occur with intramuscular (IM) injection of vancomycin or with inadvertent extravasation. There have been reports that the frequency of infusion-related events (including hypotension, flushing, erythema, urticaria, and pruritus) increases with the concomitant administration of anesthetic agents. Infusion-related events may be minimized by the administration of vancomycin as a 60-minute infusion prior to anesthetic induction.
Administration of sterile vancomycin by the intraperitoneal route during continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) has been reported to result in a syndrome of chemical peritonitis. Manifestations of this syndrome range from a cloudy dialysate alone to a cloudy dialysate accompanied by variable degrees of abdominal pain and fever. This syndrome appears to be resolved after discontinuation of intraperitoneal vancomycin.
About 60% of an intraperitoneal dose of vancomycin administered during peritoneal dialysis is absorbed systemically in 6 hours. Serum concentrations of about 10 mcg/mL are achieved by intraperitoneal injection of 30 mg/kg of vancomycin. However, the safety and efficacy of the intraperitoneal use of vancomycin has not been established in adequate and well-controlled trials.
5.9 Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria
Prescribing Vancomycin Injection in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
5.10 Risk of High Sodium Load
Each 100 mL solution of Vancomycin Injection contains 354 mg of sodium, each 150 mL solution of Vancomycin Injection contains 531 mg of sodium, and each 200 mL solution of Vancomycin Injection contains 708 mg of sodium. Avoid use of Vancomycin Injection, in patients with congestive heart failure, elderly patients and patients requiring restricted sodium intake.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- •
- Infusion Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- •
- Nephrotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- •
- Ototoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- •
- Severe Dermatologic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- •
- Clostridioides Difficile-Associated Diarrhea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- •
- Hemorrhagic Occlusive Retinal Vasculitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- •
- Neutropenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- •
- Phlebitis and Other Administration Site Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice. The following adverse reactions associated with the use of vancomycin were identified in clinical trials:
Immune System Disorders: Anaphylaxis and “vancomycin infusion reaction”
Renal and urinary Disorders: Acute kidney injury and interstitial nephritis
Ear and Labyrinth Disorders: Hearing loss, vertigo, and tinnitus
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Rashes including exfoliative dermatitis, and Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS)
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Clostridioides difficile colitis, nausea
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Agranulocytosis, neutropenia, pancytopenia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia
Cardiac Disorders: Cardiac arrest, chest pain
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions: General discomfort, drug fever, chills, phlebitis, injection site irritation, injection site pain and necrosis following intramuscular injection, chemical peritonitis following intraperitoneal administration (Vancomycin Injection is not approved for intramuscular and intraperitoneal administration)
Laboratory Abnormalities: Elevated blood urea nitrogen, elevated serum creatinine
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: Muscle pain
Nervous system disorders: Dizziness
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: Wheezing, dyspnea
Vascular disorders: Hypotension, shock, vasculitis
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postmarketing use of vancomycin. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Severe dermatologic reactions such as toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), Drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), and linear IgA bullous dermatosis (LABD).
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Anesthetic Agents
Concomitant administration of vancomycin and anesthetic agents has been associated with erythema and histamine-like flushing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
7.2 Piperacillin-Tazobactam
Studies have detected an increased incidence of acute kidney injury in patients administered concomitant piperacillin/tazobactam and vancomycin as compared to vancomycin alone. Monitor kidney function in patients receiving concomitant piperacillin/tazobactam and Vancomycin Injection. No pharmacokinetic interactions have been noted between piperacillin/tazobactam and vancomycin.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data over several decades of vancomycin use in pregnant women have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes (see Data). Vancomycin did not show adverse developmental effects when administered intravenously to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis at doses less than or equal to the recommended maximum human dose (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
A published study evaluated hearing loss and nephrotoxicity in infants of 10 pregnant intravenous drug users treated with intravenously administered vancomycin for suspected or documented methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus-aureus (MRSA) in the second or third trimester. The comparison groups were 10 non-intravenous drug-dependent patients who received no treatment, and 10 untreated intravenous drug-dependent patients who served as substance abuse controls. No infant in the vancomycin exposed group had abnormal sensorineural hearing at 3 months of age or nephrotoxicity.
A published prospective study assessed outcomes in 55 pregnant women with a positive Group B streptococcus (GBS) culture and a high-risk penicillin allergy with resistance to clindamycin or unknown sensitivity who were administered vancomycin at the time of delivery. Vancomycin dosing ranged from the standard 1 g intravenously every 12 hours to 20 mg/kg intravenous every 8 hours (maximum individual dose 2 g). No major adverse reactions were recorded either in the mothers or their newborns.
None of the newborns had sensorineural hearing loss. Neonatal renal function was not examined, but all of the newborns were discharged in good condition.
Animal Data
Vancomycin did not cause fetal malformations when administered during organogenesis to pregnant rats (gestation days 6 to 15) and rabbits (gestation days 6 to 18) at the equivalent recommended maximum human dose (based on body surface area comparisons) of 200 mg/kg/day IV to rats or 120 mg/kg/day IV to rabbits. No effects on fetal weight or development were seen in rats at the highest dose tested or in rabbits given 80 mg/kg/day (approximately 1 and 0.8 times the recommended maximum human dose based on body surface area, respectively). Maternal toxicity was observed in rats (at doses 120 mg/kg and above) and rabbits (at 80 mg/kg and above).1
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Vancomycin is present in human milk following intravenous administration, however, there are insufficient data to inform the levels. There are no data on the effects of vancomycin on the breastfed infant or milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for vancomycin and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from vancomycin or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Vancomycin Injection is indicated in pediatric patients for the treatment of septicemia, infective endocarditis, skin and skin structure infections, bone infections and lower respiratory tract infections for whom appropriate dosing with this formulation can be achieved [see Indications and Usage (1.1 to 1.5) and Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.3)].
Because of the limitations of the available strengths and administration requirements (i.e., administration of fractional doses is not recommended) of Vancomycin Injection, and to avoid unintentional overdose, this product is not recommended for use if a dose of Vancomycin Injection that does not equal 500 mg, 750 mg, 1 g, 1.25 g or 1.5 g is required, and an alternative formulation of vancomycin should be considered [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.3)].
More severe infusion related reactions related to vancomycin administration may occur in pediatric patients. In pediatric patients, monitor vancomycin serum concentration and renal function when administering Vancomycin injection [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Concomitant administration of vancomycin and intravenous anesthetic agents has been associated with erythema and histamine-like flushing in all patients including pediatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Vancomycin injection is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)], and it may be useful to monitor renal function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Dosage adjustment of Vancomycin Injection must be made in patients with impaired renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. Measure trough vancomycin serum concentrations to guide intravenous therapy, especially in patients with impaired renal function or fluctuating renal function.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Supportive care is advised, with maintenance of glomerular filtration. Vancomycin is poorly removed by dialysis.
Hemofiltration and hemoperfusion with polysulfone resin have been reported to result in increased vancomycin clearance.
For current information on the management of overdosage, contact the National Poison Control Center at 1-800-222-1222 or www.poison.org.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
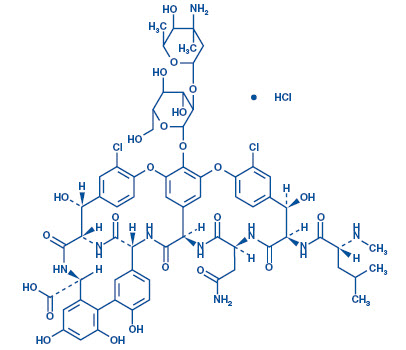
Vancomycin Injection USP, in the GALAXY plastic container contains vancomycin, added as Vancomycin Hydrochloride USP. It is a tricyclic glycopeptide antibacterial derived from Amycolatopsis orientalis (formerly Nocardia orientalis). The chemical name of vancomycin hydrochloride is (Sa)-(3S, 6R, 7R, 22R, 23S, 26S, 36R, 38aR)-44-[[2-O-(3-Amino-2, 3, 6-trideoxy-3-Cmethyl-α-L-lyxo-hexopyranosyl)-β-D-glucopyranosyl]oxy]-3-(carbamoylmethyl)- 10,19dichloro 2,3,4,5,6,7,23,24,25,26,36,37,38,38a-tetradecahydro-7,22,28,30,32-pentahydroxy-6[(2R)-4-methyl-2-(methylamino) valeramido]-2,5,24,38,39-pentaoxo-22H-8,11:18,21-dietheno23, 36-(iminomethano)-13, 16:31, 35-dimetheno-1H, 16H-[l, 6, 9] oxadiazacyclohexadecino [4, 5-m] [10, 2, 16]-benzoxadiazacyclotetracosine-26-carboxylic acid, monohydrochloride. The molecular formula is C66H75Cl2N9O24·HCl and the molecular weight is 1,485.71. Vancomycin hydrochloride has the following structural formula:
Vancomycin Injection, USP in the GALAXY container is a frozen, iso-osmotic, sterile, nonpyrogenic, premixed single-dose formulation. The composition of Vancomycin Injection, USP, available in the following strengths are:
- •
- 500 mg/100 mL (5 mg/mL): containing 500 mg of vancomycin (equivalent to 513 mg of vancomycin hydrochloride); approximately 5 g of dextrose hydrous or 0.9 g of sodium chloride (equivalent to 354 mg total sodium content)
- •
- 750 mg/150 mL (5 mg/mL): containing 750 mg of vancomycin (equivalent to 769 mg of vancomycin hydrochloride); approximately 7.5 g of dextrose hydrous or 1.35 g of sodium chloride (equivalent to 531 mg total sodium content)
- •
- 1 g/200 mL (5 mg/mL): containing 1 g of vancomycin (equivalent to 1.025 g of vancomycin hydrochloride); approximately 10 g of dextrose hydrous or 1.8 g of sodium chloride (equivalent to 708 mg total sodium content)
- •
- 1.25 g/250 mL (5 mg/mL): containing 1.25 g of vancomycin (equivalent to 1.281 g of vancomycin hydrochloride); approximately 12.5 g of dextrose hydrous.
- •
- 1.5 g/300 mL (5 mg/mL): containing 1.5 g of vancomycin (equivalent to 1.538 g of vancomycin hydrochloride); approximately 15 g of dextrose hydrous.
The pH of the solution may have been adjusted with hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide. Thawed solutions have a pH in the range of 3.0 to 5.0. After thawing to room temperature, this solution is intended for intravenous use only.
This GALAXY container is fabricated from a specially designed multilayer plastic. Solutions are in contact with the polyethylene layer of this container and can leach out certain chemical components of the plastic in very small amounts within the expiration period. The suitability of the plastic has been confirmed in tests in animals according to USP biological tests for plastic containers as well as by tissue culture toxicity studies.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Based on animal models of infection, the antimicrobial activity of vancomycin appears to correlate with the AUC/MIC (area under the concentration-time curve/minimum inhibitory concentration) ratio for certain pathogens, including methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. The principal pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic parameter best associated with clinical and microbiological cure has not been elucidated in clinical trials2,3.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
General Pharmacokinetics
In subjects with normal kidney function, multiple intravenous dosing of 1 g of vancomycin (15 mg/kg) infused over 60 minutes produces mean plasma concentrations of approximately 63 mcg/mL immediately after the completion of infusion, mean plasma concentrations of approximately 23 mcg/mL 2 hours after infusion, and mean plasma concentrations of approximately 8 mcg/mL 11 hours after the end of the infusion. Multiple dosing of 500 mg infused over 30 minutes produces mean plasma concentrations of about 49 mcg/mL at the completion of infusion, mean plasma concentrations of about 19 mcg/mL 2 hours after infusion, and mean plasma concentrations of about 10 mcg/mL 6 hours after infusion. The plasma concentrations during multiple dosing are similar to those after a single dose.
Distribution
The distribution coefficient is from 0.3 to 0.43 L/kg. Vancomycin is approximately 55% serum protein bound as measured by ultrafiltration at vancomycin serum concentrations of 10 to 100 mcg/mL. After IV administration of vancomycin, inhibitory concentrations are present in pleural, pericardial, ascitic, and synovial fluids; in urine; in peritoneal dialysis fluid; and in atrial appendage tissue. Vancomycin does not readily diffuse across normal meninges into the spinal fluid; but, when the meninges are inflamed, penetration into the spinal fluid occurs.
Elimination
Mean plasma clearance is about 0.058 L/kg/h, and mean renal clearance is about 0.048 L/kg/h. The mean elimination half-life of vancomycin from plasma is 4 to 6 hours in subjects with normal renal function. In anephric patients, the average half-life of elimination is 7.5 days. Total systemic and renal clearance of vancomycin may be reduced in the elderly.
Metabolism
There is no apparent metabolism of vancomycin.
Excretion
In the first 24 hours, about 75% of an administered dose of vancomycin is excreted in urine by glomerular filtration. Renal dysfunction slows excretion of vancomycin.
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
The bactericidal action of vancomycin results primarily from inhibition of cell-wall biosynthesis. In addition, vancomycin alters bacterial-cell-membrane permeability and RNA synthesis.
Resistance
There is no cross-resistance between vancomycin and other antibacterial(s). Vancomycin is not active in vitro against gram-negative bacilli, mycobacteria, or fungi.
Interaction With Other Antimicrobials
The combination of vancomycin and an aminoglycoside acts synergistically in vitro against many isolates of Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus gallolyticus (previously known as Streptococcus bovis), Enterococcus spp, and the viridans group streptococci.
Antimicrobial Activity
Vancomycin has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following bacteria, both in vitro and in clinical infections [see Indications and Usage section (1)].
Aerobic bacteria
Gram-positive bacteria
-
Corynebacterium spp.
Enterococcus spp. (including Enterococcus faecalis)
Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible isolates) - Coagulase negative staphylococci (including S. epidermidis and methicillin-resistant isolates)
- Streptococcus gallolyticus (previously known as Streptococcus bovis)
- Viridans group streptococci
The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown. At least 90 percent of the following bacteria exhibit an in vitro minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) less than or equal to the susceptible breakpoint for vancomycin against isolates of similar genus or organism group. However, the efficacy of vancomycin in treating clinical infections caused by these bacteria has not been established in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials.
Aerobic bacteria
Gram-positive bacteria
-
Listeria monocytogenes
Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus agalactiae
Anaerobic bacteria
Gram-positive bacteria
-
Actinomyces spp
Lactobacillus spp
Susceptibility Testing
For specific information regarding susceptibility test interpretive criteria and associated test methods and quality control standards recognized by FDA for this drug, please see: https://www.fda.gov/STIC.
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
-
15 REFERENCES
- 1.
- Byrd RA., Gries CL, Buening M.: Developmental Toxicology Studies of Vancomycin Hydrochloride Administered Intravenously to Rats and Rabbits. Fundam Appl Toxicol 1994; 23: 590-597.
- 2.
- Rybak MJ. The pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties of vancomycin. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2006;42(Supplement_1): S35-S39.
- 3.
- Rybak MJ, Le J, Lodise TP, et al. Therapeutic monitoring of vancomycin for serious methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: a revised consensus guideline and review by the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2020;71(6):1361-1364.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
Vancomycin Injection, USP is supplied as a frozen, iso-osmotic, premixed solution packaged in a single-dose GALAXY plastic container and is available as follows:
Supply Information for Vancomycin Injection, in 5% Dextrose
Strength
Number of Containers/ Carton
NDC
500 mg of vancomycin / 100 mL (5 mg/mL)
12 count
0338-3551-48
750 mg of vancomycin / 150 mL (5 mg/mL)
6 count
0338-3580-48
1 g of vancomycin / 200 mL (5mg/mL)
6 count
0338-3552-48
1.25 g of vancomycin / 250 mL (5 mg/mL)
4 count
0338-0122-04
1.5 g of vancomycin / 300 mL (5 mg/mL)
4 count
0338-0124-04
Supply Information for Vancomycin Injection, in 0.9% Sodium Chloride
Strength
Number of Containers/ Carton
NDC
500 mg of vancomycin / 100 mL (5 mg/mL)
12 count
0338-3581-01
750 mg vancomycin / 150 mL (5 mg/mL)
6 count
0338-3582-01
1 g of vancomycin / 200 mL (5mg/mL)
6 count
0338-3583-01
Storage
Store Vancomycin Injection at or below -20°C (-4°F) or Store in a freezer capable of maintaining a temperature at or below -20°C (-4°F). Storage of the thawed solution is described elsewhere in the labeling [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]
Handling
Handle frozen product containers with care. Product containers may be fragile in the frozen state.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Infusion Reactions During or After Intravenous Use
Advise patients that generalized skin redness, skin rash, itching, flushing, muscle pain, chest pain, shortness of breath, wheezing, or dizziness may occur during intravenous infusion of Vancomycin Injection. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Acute Kidney Injury
Advise patients that Vancomycin Injection can result in kidney damage and that blood tests are required to monitor vancomycin blood levels and kidney function during therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Hearing Loss or Balance Problems
Advise patients that Vancomycin injection may result in decreased hearing and to report hearing loss or balance problems to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Severe Dermatologic Reactions
Advise patients about the signs and symptoms of serious skin manifestations. Instruct patients to stop Vancomycin Injection immediately and promptly seek medical attention at the first signs or symptoms of skin rash, mucosal lesions and blisters [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Diarrhea
Diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibacterial drugs, including Vancomycin Injection, which usually ends when the antibacterial drug is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibacterial drugs, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibacterial drug. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Antibacterial Resistance
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including Vancomycin Injection, should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When Vancomycin Injection is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by Vancomycin Injection or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Manufactured by, Packed by, Distributed by:
Baxter Healthcare Corporation
Deerfield, IL 60015 USA
Made in the USA07-19-03-984
Baxter and Galaxy are trademarks of Baxter International Inc. or its subsidiaries.
-
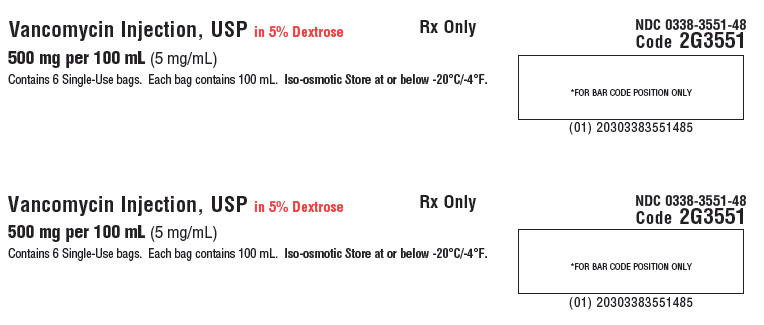
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Container Label
NDC 0338-3551-48
Vancomycin Injection, USP
in 5% Dextrose500 mg per 100 mL
(5 mg/mL)GALAXY
Single-Dose Container
Discard unused portionCode 2G3551
Sterile Nonpyrogenic
Iso-osmoticEach 100 mL contains: Vancomycin Hydrochloride, USP equivalent to
500 mg vancomycin with approx. 5 g Dextrose Hydrous, USP in Water for
Injection, USP. pH may have been adjusted with hydrochloric acid and/or
sodium hydroxide.Dosage: For intravenous use only. See prescribing information.
Cautions: Do not add supplementary medication or additives.
Rx Only
Store at or below -20°C (-4°F). Thaw at room temperature
(25°C/77°F) or under refrigeration (5°C/41°F). Product should not
be thawed by immersion in water baths or by microwave irradiation.
Do not force thaw. Thawed solution is stable for 30 days under
refrigeration or 72 hours at room temperature. Do not refreeze.PL 2040 Plastic
Baxter Logo
Baxter and Galaxy are trademarks of
Baxter International Inc.
Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Deerfield, IL 60015 USA07-34-74-761
Carton Label
Thaw at room temperature (25°C/77°F) or under refrigeration (5°C/41°F). Product should not be thawed by immersion in water baths or by microware irradiation. Do not force thaw. The thawed solution in GALAXY plastic container (PL 2040) remains chemically stable for 72 hours at room temperature or for 30 days when stored under refrigeration. Do not refreeze.
Handle frozen product containers with care. Product containers may be fragile in the frozen state.
PL 2040 Plastic 07-04-74-764
Vancomycin Injection, USP in 5% Dextrose
500 mg per 100 mL (5 mg/ mL)
Contains 6 Single-Use bags. Each bag contains 100 mL. Iso-osmotic. Store at or below -20°C/-4°F.Rx Only
NDC 0338-3551-48
Code 2G3551*FOR BAR CODE POSITION ONLY
(01) 20303383551485GALAXY Container
Sterile Nonpyrogenic
Each 100 mL contains: Vancomycin Hydrochloride, USP equivalent to 500 mg vancomycin with approx. 5 g Dextrose Hydrous, USP in Water for Injection, USP. pH may have been adjusted with hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide.
Dosage: For intravenous use only. See prescribing information.
Cautions: Do not add supplementary medication or additives.Baxter Logo
Baxter and Galaxy are registered trademarks of Baxter International Inc.
Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Deerfield, IL 60015 USANDC 0338-3552-48
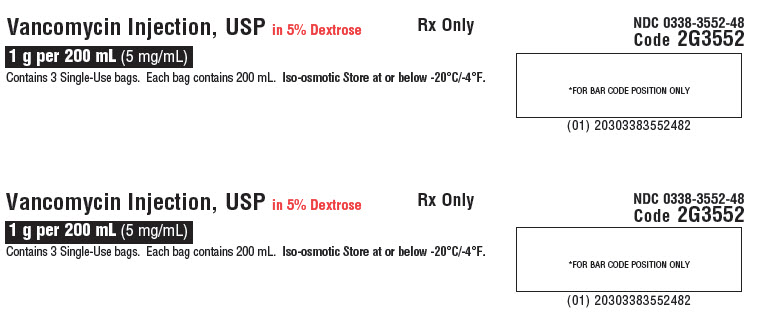
Vancomycin Injection, USP
in 5% Dextrose1 g per 200 mL
(5 mg/mL)GALAXY
Single-Dose Container
Discard unused portionCode 2G3552
Sterile Nonpyrogenic
Iso-osmoticEach 100 mL contains: Vancomycin Hydrochloride, USP
equivalent to 500 mg vancomycin with approx. 5 g Dextrose
Hydrous, USP in Water for Injection, USP. pH may have been
adjusted with hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide.Dosage: For intravenous use only. See prescribing information.
Cautions: Do not add supplementary medication or additives.
Rx Only
Store at or below -20°C (-4°F). Thaw at room temperature
(25°C/77°F) or under refrigeration (5°C/41°F). Product should
not be thawed by immersion in water baths or by microwave
irradiation. Do not force thaw. Thawed solution is stable for 30
days under refrigeration or 72 hours at room temperature.
Do not refreeze.PL 2040 Plastic
Baxter Logo
Baxter and Galaxy are trademarks of
Baxter International Inc.
Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Deerfield, IL 60015 USA07-34-74-763
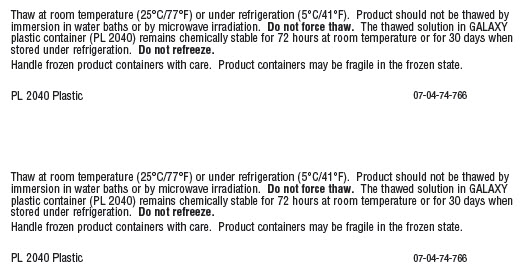
Thaw at room temperature (25°C/77°F) or under refrigeration (5°C/41°F). Product should not be thawed by immersion in water baths or by microware irradiation. Do not force thaw. The thawed solution in GALAXY plastic container (PL 2040) remains chemically stable for 72 hours at room temperature or for 30 days when stored under refrigeration. Do not refreeze.
Handle frozen product containers with care. Product containers may be fragile in the frozen state.
PL 2040 Plastic 07-04-74-766
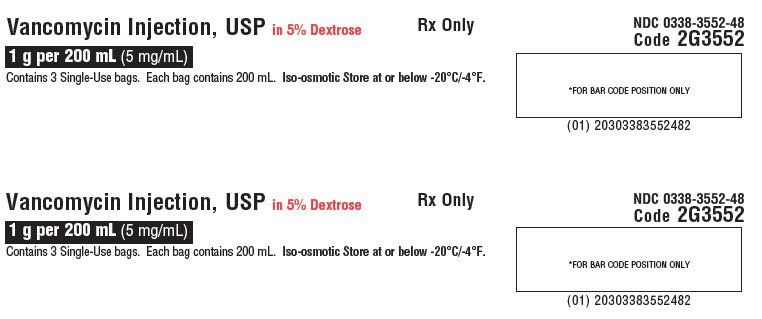
Vancomycin Injection, USP in 5% Dextrose
1 g per 200 mL (5 mg/ mL)
Contains 3 Single-Use bags. Each bag contains 200 mL. Iso-osmotic. Store at or below -20°C/-4°F.Rx Only
NDC 0338-3552-48
Code 2G3552*FOR BAR CODE POSITION ONLY
(01) 20303383552482GALAXY Container
Sterile Nonpyrogenic
Each 100 mL contains: Vancomycin Hydrochloride, USP equivalent to 500 mg vancomycin with approx. 5 g Dextrose Hydrous, USP in Water for Injection, USP. pH may have been adjusted with hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide.
Dosage: For intravenous use only. See prescribing information.
Cautions: Do not add supplementary medication or additives.Baxter Logo
Baxter and Galaxy are registered trademarks of Baxter International Inc.
Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Deerfield, IL 60015 USAContainer Label
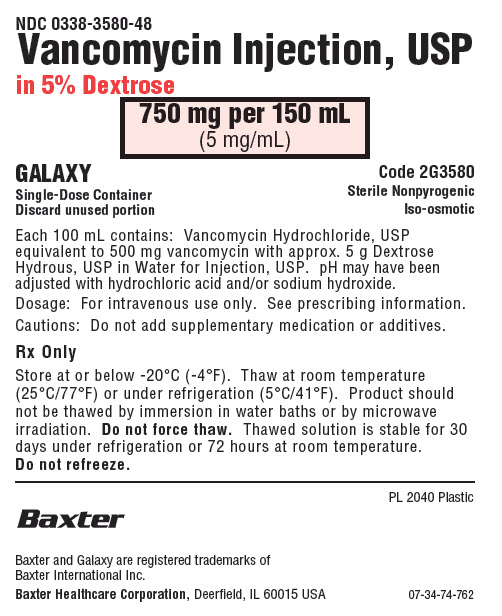
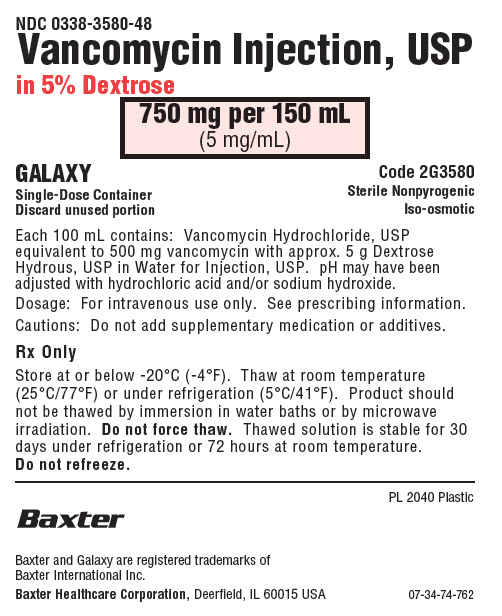
NDC 0338-3580-48
Vancomycin Injection, USP
in 5% Dextrose750 mg per 150 mL
(5 mg/mL)GALAXY
Single-Dose Container
Discard unused portionCode 2G3580
Sterile Nonpyrogenic
Iso-osmoticEach 100 mL contains: Vancomycin Hydrochloride, USP
equivalent to 500 mg vancomycin with approx. 5 g Dextrose
Hydrous, USP in Water for Injection, USP. pH may have been
adjusted with hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide.Dosage: For intravenous use only. See prescribing information.
Cautions: Do not add supplementary medication or additives.
Rx Only
Store at or below -20°C (-4°F). Thaw at room temperature
(25°C/77°F) or under refrigeration (5°C/41°F). Product should
not be thawed by immersion in water baths or by microwave
irradiation. Do not force thaw. Thawed solution is stable for 30
days under refrigeration or 72 hours at room temperature.
Do not refreeze.PL 2040 Plastic
Baxter Logo
Baxter and Galaxy are trademarks of
Baxter International Inc.
Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Deerfield, IL 60015 USA07-34-74-762
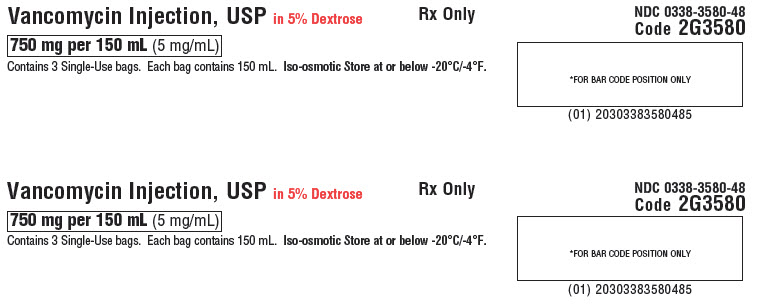
Carton Labels
Thaw at room temperature (25°C/77°F) or under refrigeration (5°C/41°F). Product should not be thawed by immersion in water baths or by microware irradiation. Do not force thaw. The thawed solution in GALAXY plastic container (PL 2040) remains chemically stable for 72 hours at room temperature or for 30 days when stored under refrigeration. Do not refreeze.
Handle frozen product containers with care. Product containers may be fragile in the frozen state.
PL 2040 Plastic 07-04-74-765
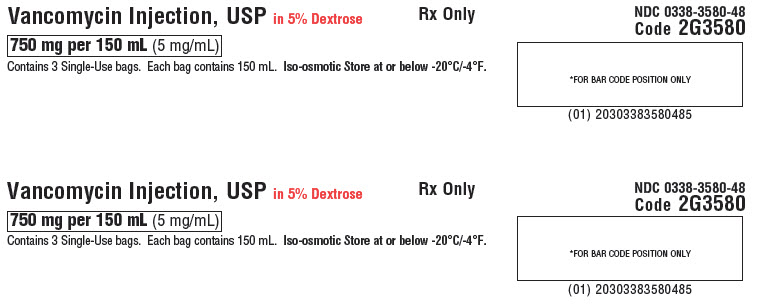
Vancomycin Injection, USP in 5% Dextrose
750 mg per 150 mL (5 mg/ mL)
Contains 3 Single-Use bags. Each bag contains 150 mL. Iso-osmotic. Store at or below -20°C/-4°F.Rx Only
NDC 0338-3580-48
Code 2G3580*FOR BAR CODE POSITION ONLY
(01) 20303383580485GALAXY Container
Sterile Nonpyrogenic
Each 100 mL contains: Vancomycin Hydrochloride, USP equivalent to 500 mg vancomycin with approx. 5 g Dextrose Hydrous, USP in Water for Injection, USP. pH may have been adjusted with hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide.
Dosage: For intravenous use only. See prescribing information.
Cautions: Do not add supplementary medication or additives.Baxter Logo
Baxter and Galaxy are registered trademarks of Baxter International Inc.
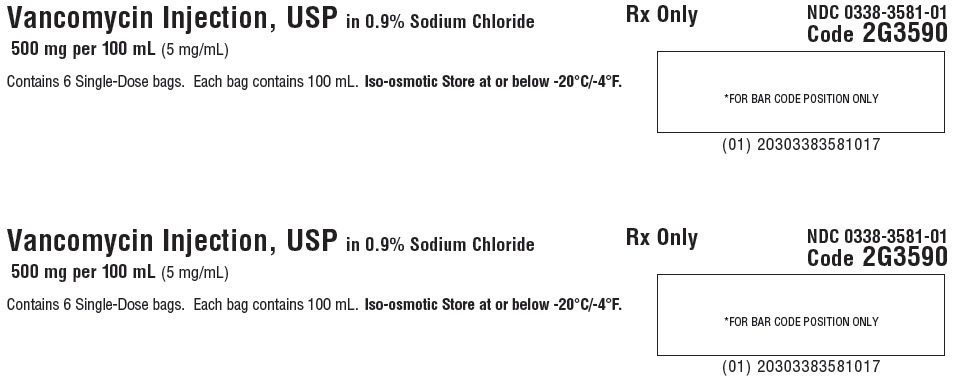
Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Deerfield, IL 60015 USANDC 0338-3581-01
Vancomycin Injection, USP
in 0.9% Sodium Chloride500 mg per 100 mL
(5 mg/mL)GALAXY
Single-Dose Container
Discard unused portionCode 2G3590
Sterile Nonpyrogenic
Iso-osmoticEach 100 mL contains: Vancomycin Hydrochloride, USP equivalent to
500 mg vancomycin with approx. 0.9 g Sodium Chloride, USP in Water for
Injection, USP. pH may have been adjusted with hydrochloric acid and/or
sodium hydroxide.Dosage: For intravenous use only. See prescribing information.
Cautions: Do not add supplementary medication or additives.
Rx Only
Store at or below -20°C (-4°F). Thaw at room temperature
(25°C/77°F) or under refrigeration (5°C/41°F). Product should not
be thawed by immersion in water baths or by microwave irradiation.
Do not force thaw. Thawed solution is stable for 30 days under
refrigeration or 72 hours at room temperature. Do not refreeze.PL 2040 Plastic
Baxter Logo
Baxter and Galaxy are trademarks of
Baxter International Inc.
Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Deerfield, IL 60015 USA07-34-74-548
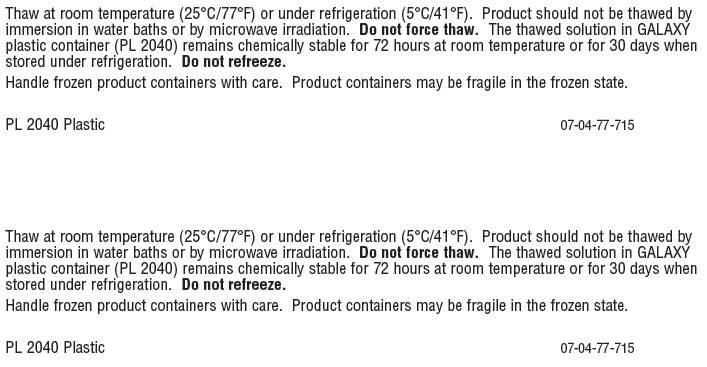
Thaw at room temperature (25°C/77°F) or under refrigeration (5°C/41°F). Product should not be thawed by immersion in water baths or by microware irradiation. Do not force thaw. The thawed solution in GALAXY plastic container (PL 2040) remains chemically stable for 72 hours at room temperature or for 30 days when stored under refrigeration. Do not refreeze.
Handle frozen product containers with care. Product containers may be fragile in the frozen state.
PL 2040 Plastic 07-04-77-715
Vancomycin Injection, USP in 0.9% Sodium Chloride
500 mg per 100 mL (5 mg/ mL)
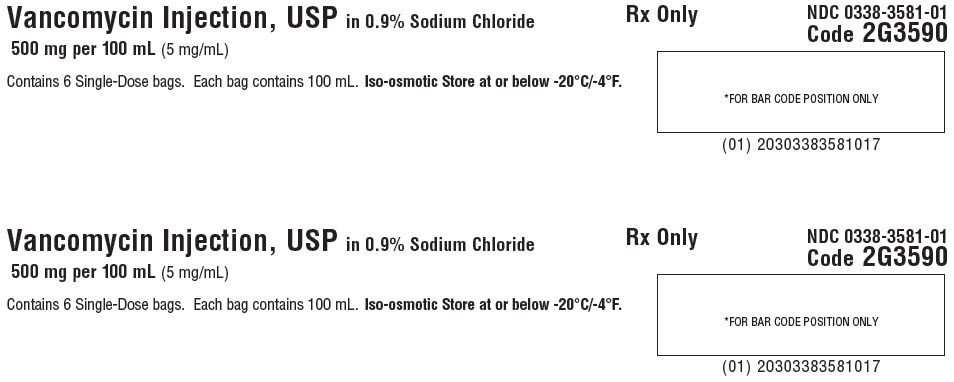
Contains 6 Single-Dose bags. Each bag contains 100 mL. Iso-osmotic. Store at or below -20°C/-4°F.Rx Only
NDC 0338-3581-01
Code 2G3590*FOR BAR CODE POSITION ONLY
(01) 20303383581017GALAXY Container
Sterile Nonpyrogenic
Each 100 mL contains: Vancomycin Hydrochloride, USP equivalent to 500 mg vancomycin with approx. 0.9 Sodium Chloride, USP in Water for Injection, USP. pH may have been adjusted with hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide.
Dosage: For intravenous use only. See prescribing information.
Cautions: Do not add supplementary medication or additives.Baxter Logo
Baxter and Galaxy are registered trademarks of Baxter International Inc.
Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Deerfield, IL 60015 USAContainer Label
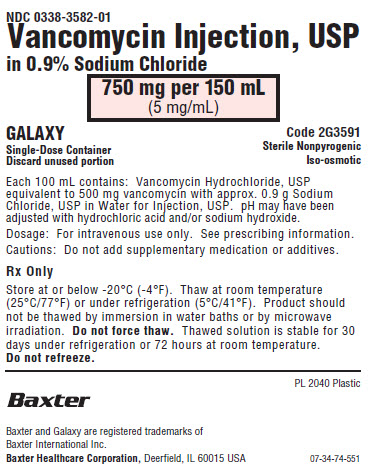
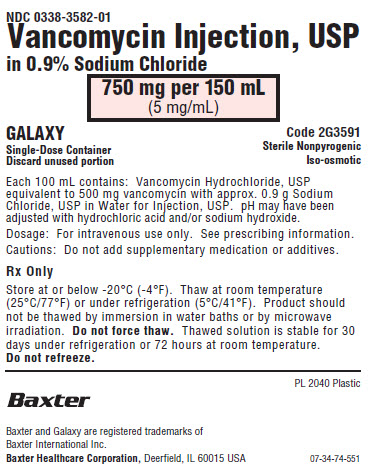
NDC 0338-3582-01
Vancomycin Injection, USP
in 0.9% Sodium Chloride750 mg per 150 mL
(5 mg/mL)GALAXY
Single-Dose Container
Discard unused portionCode 2G3591
Sterile Nonpyrogenic
Iso-osmoticEach 100 mL contains: Vancomycin Hydrochloride, USP
equivalent to 500 mg vancomycin with approx. 0.9 g Sodium
Chloride, USP in Water for Injection, USP. pH may have been
adjusted with hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide.Dosage: For intravenous use only. See prescribing information.
Cautions: Do not add supplementary medication or additives.
Rx Only
Store at or below -20°C (-4°F). Thaw at room temperature
(25°C/77°F) or under refrigeration (5°C/41°F). Product should
not be thawed by immersion in water baths or by microwave
irradiation. Do not force thaw. Thawed solution is stable for 30
days under refrigeration or 72 hours at room temperature.
Do not refreeze.PL 2040 Plastic
Baxter Logo
Baxter and Galaxy are trademarks of
Baxter International Inc.
Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Deerfield, IL 60015 USA07-34-74-551
Thaw at room temperature (25°C/77°F) or under refrigeration (5°C/41°F). Product should not be thawed by immersion in water baths or by microware irradiation. Do not force thaw. The thawed solution in GALAXY plastic container (PL 2040) remains chemically stable for 72 hours at room temperature or for 30 days when stored under refrigeration. Do not refreeze.
Handle frozen product containers with care. Product containers may be fragile in the frozen state.
PL 2040 Plastic 07-04-77-715
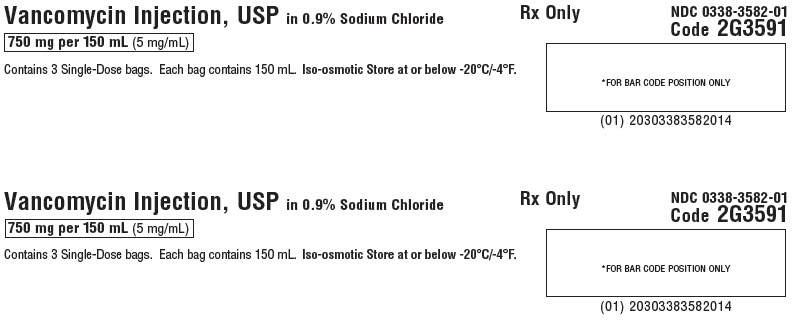
Vancomycin Injection, USP in 0.9 Sodium Chloride
750 mg per 150 mL (5 mg/ mL)
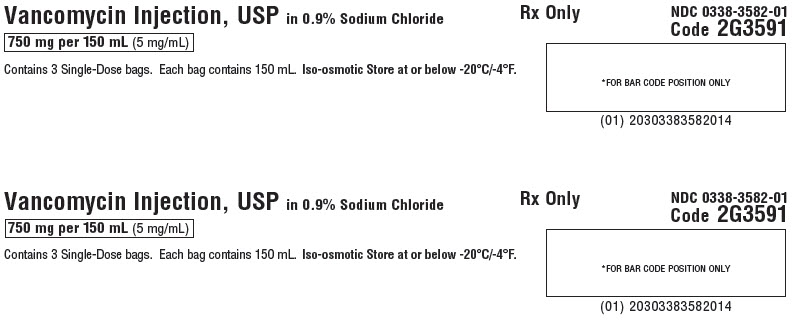
Contains 3 Single-Dose bags. Each bag contains 150 mL. Iso-osmotic. Store at or below -20°C/-4°F.Rx Only
NDC 0338-3582-01
Code 2G3591*FOR BAR CODE POSITION ONLY
(01) 20303383582014GALAXY Container
Sterile Nonpyrogenic
Each 100 mL contains: Vancomycin Hydrochloride, USP equivalent to 500 mg vancomycin with approx. 0.9 Sodium Chloride, USP in Water for Injection, USP. pH may have been adjusted with hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide.
Dosage: For intravenous use only. See prescribing information.
Cautions: Do not add supplementary medication or additives.Baxter Logo
Baxter and Galaxy are registered trademarks of Baxter International Inc.
Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Deerfield, IL 60015 USAContainer Label
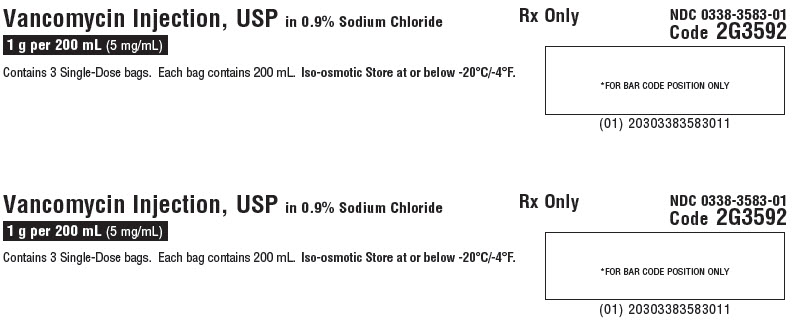
NDC 0338-3583-01
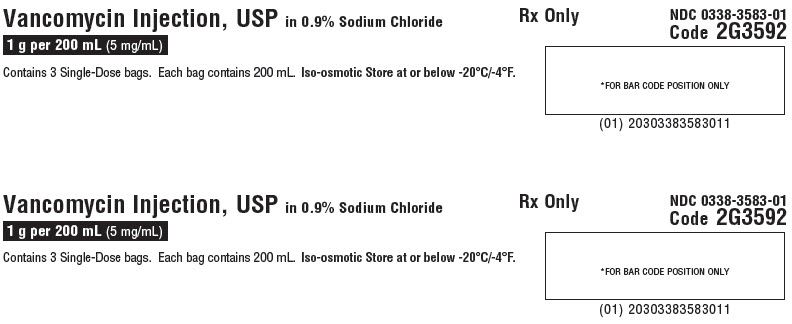
Vancomycin Injection, USP
in 0.9% Sodium Chloride1 g per 200 mL
(5 mg/mL)GALAXY
Single-Dose Container
Discard unused portionCode 2G3592
Sterile Nonpyrogenic
Iso-osmoticEach 100 mL contains: Vancomycin Hydrochloride, USP
equivalent to 500 mg vancomycin with approx. 0.9 g Sodium
Chloride, USP in Water for Injection, USP. pH may have been
adjusted with hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide.Dosage: For intravenous use only. See prescribing information.
Cautions: Do not add supplementary medication or additives.
Rx Only
Store at or below -20°C (-4°F). Thaw at room temperature
(25°C/77°F) or under refrigeration (5°C/41°F). Product should
not be thawed by immersion in water baths or by microwave
irradiation. Do not force thaw. Thawed solution is stable for 30
days under refrigeration or 72 hours at room temperature.
Do not refreeze.PL 2040 Plastic
Baxter Logo
Baxter and Galaxy are trademarks of
Baxter International Inc.
Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Deerfield, IL 60015 USA07-34-74-553
Thaw at room temperature (25°C/77°F) or under refrigeration (5°C/41°F). Product should not be thawed by immersion in water baths or by microware irradiation. Do not force thaw. The thawed solution in GALAXY plastic container (PL 2040) remains chemically stable for 72 hours at room temperature or for 30 days when stored under refrigeration. Do not refreeze.
Handle frozen product containers with care. Product containers may be fragile in the frozen state.
PL 2040 Plastic 07-04-77-717
Vancomycin Injection, USP in 0.9 Sodium Chloride
1 g per 200 mL (5 mg/ mL)
Contains 3 Single-Dose bags. Each bag contains 200 mL. Iso-osmotic. Store at or below -20°C/-4°F.Rx Only
NDC 0338-3583-01
Code 2G3592*FOR BAR CODE POSITION ONLY
(01) 20303383583011GALAXY Container
Sterile Nonpyrogenic
Each 100 mL contains: Vancomycin Hydrochloride, USP equivalent to 500 mg vancomycin with approx. 0.9 Sodium Chloride, USP in Water for Injection, USP. pH may have been adjusted with hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide.
Dosage: For intravenous use only. See prescribing information.
Cautions: Do not add supplementary medication or additives.Baxter Logo
Baxter and Galaxy are registered trademarks of Baxter International Inc.
Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Deerfield, IL 60015 USANDC 0338-0122-04
1.25 g
Vancomycin Injection, USP
in 5% Dextrose1.25 g per 250 mL (5 mg/mL)
For Intravenous Infusion Only
Single-Dose GALAXY Container
Discard Unused PortionRx Only
SterileEach 100 mL contains: Vancomycin Hydrochloride, USP equivalent to 500 mg
vancomycin with approx. 5 g Dextrose Hydrous, USP in Water for Injection, USP.
Dosage: See prescribing information.Store frozen at or below -20°C /-4°F.
Thaw at room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) or under refrigeration 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F)
and store thawed solution as follows:
– Refrigerated Storage: Use within 30 days
– Room Temperature Storage: Use within 72 hours
Do not force thaw. Do not refreeze the thawed solution.
Do not add supplemental medication or additives.Code 2G3557
Baxter Logo
Baxter and Galaxy are trademarks of Baxter International Inc. or its subsidiaries.
Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Deerfield, IL 60015 USA07-34-00-1841
*UPC-A BAR CODE
POSITION ONLY309440495057
Store frozen at or below -20°C /-4°F. Thaw at room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) or under refrigeration
2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) and store thawed solution as follows:
– Refrigerated Storage: Use within 30 days
– Room Temperature Storage: Use within 72 hours
Do not force thaw. Do not refreeze the thawed solution
Handle frozen product containers with care. Product containers may be fragile in the frozen state.07-04-00-0961
1.25 g
Vancomycin Injection, USP
in 5% Dextrose1.25 g per 250 mL (5 mg/mL)
For Intravenous Infusion Only.
Contains 2 units of Single-Dose bags.
Each bag contains 250 mL.
Store at or below -20°C/-4°F.Rx Only
NDC 0338-0122-04
Code 2G3557*FOR BAR CODE POSITION ONLY
(01)00000000000000GALAXY Container
SterileEach 100 mL contains: Vancomycin Hydrochloride, USP equivalent to 500 mg vancomycin with approx.
5 g Dextrose Hydrous, USP in Water for Injection, USP.Dosage: See prescribing information.
Do not add supplementary medication or additives.Baxter Logo
Baxter and Galaxy are trademarks of Baxter International Inc. or its subsidiaries.
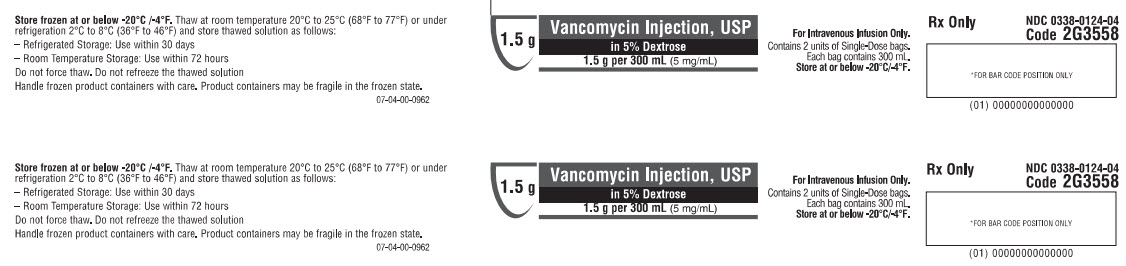
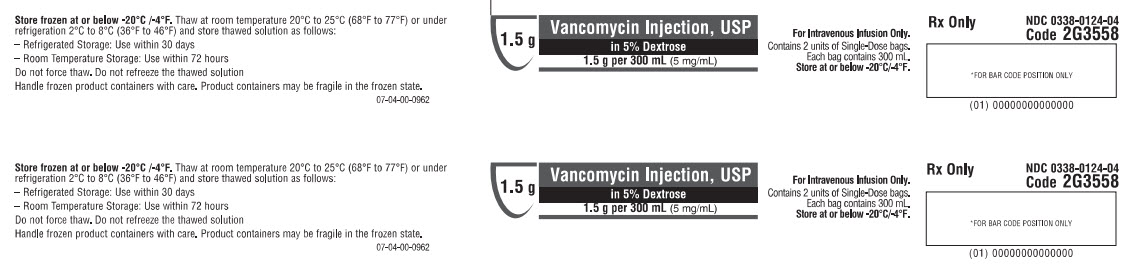
Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Deerfield, IL 60015 USANDC 0338-0124-04
1.5 g
Vancomycin Injection, USP
in 5% Dextrose1.5 g per 300 mL (5 mg/mL)
For Intravenous Infusion Only
Single-Dose GALAXY Container
Discard Unused PortionRx Only
SterileEach 100 mL contains: Vancomycin Hydrochloride, USP equivalent to 500 mg
vancomycin with approx. 5 g Dextrose Hydrous, USP in Water for Injection, USP.
Dosage: See prescribing information.Store frozen at or below -20°C /-4°F.
Thaw at room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) or under refrigeration 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F)
and store thawed solution as follows:
– Refrigerated Storage: Use within 30 days
– Room Temperature Storage: Use within 72 hours
Do not force thaw. Do not refreeze the thawed solution.
Do not add supplemental medication or additives.Code 2G3558
Baxter Logo
Baxter and Galaxy are trademarks of Baxter International Inc. or its subsidiaries.
Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Deerfield, IL 60015 USA07-34-00-1842
*UPC-A BAR CODE
POSITION ONLY309440495057
Store frozen at or below -20°C /-4°F. Thaw at room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) or under refrigeration
2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) and store thawed solution as follows:
– Refrigerated Storage: Use within 30 days
– Room Temperature Storage: Use within 72 hours
Do not force thaw. Do not refreeze the thawed solution
Handle frozen product containers with care. Product containers may be fragile in the frozen state.07-04-00-0962
1.5 g
Vancomycin Injection, USP
in 5% Dextrose1.5 g per 300 mL (5 mg/mL)
For Intravenous Infusion Only.
Contains 2 units of Single-Dose bags.
Each bag contains 300 mL.
Store at or below -20°C/-4°F.Rx Only
NDC 0338-0124-04
Code 2G3558*FOR BAR CODE POSITION ONLY
(01)00000000000000GALAXY Container
SterileEach 100 mL contains: Vancomycin Hydrochloride, USP equivalent to 500 mg vancomycin with approx.
5 g Dextrose Hydrous, USP in Water for Injection, USP.
Dosage: See prescribing information.
Do not add supplementary medication or additives.Baxter Logo
Baxter and Galaxy are trademarks of Baxter International Inc. or its subsidiaries.
Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Deerfield, IL 60015 USA -
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE
vancomycin hydrochloride injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:0338-3552 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 71WO621TJD) (VANCOMYCIN - UNII:6Q205EH1VU) VANCOMYCIN 1 g in 200 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength DEXTROSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: LX22YL083G) 10 g in 200 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:0338-3552-48 200 mL in 1 BAG; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/14/1958 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA050671 11/14/1958 VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE
vancomycin hydrochloride injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:0338-3551 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 71WO621TJD) (VANCOMYCIN - UNII:6Q205EH1VU) VANCOMYCIN 500 mg in 100 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength DEXTROSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: LX22YL083G) 5 g in 100 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:0338-3551-48 100 mL in 1 BAG; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/14/1958 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA050671 11/14/1958 VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE
vancomycin hydrochloride injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:0338-3580 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 71WO621TJD) (VANCOMYCIN - UNII:6Q205EH1VU) VANCOMYCIN 750 mg in 150 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength DEXTROSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: LX22YL083G) 7.5 g in 150 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:0338-3580-48 200 mL in 1 BAG; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 11/14/1958 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA050671 11/14/1958 VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE
vancomycin hydrochloride injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:0338-3581 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 71WO621TJD) (VANCOMYCIN - UNII:6Q205EH1VU) VANCOMYCIN 500 mg in 100 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) 0.9 g in 100 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:0338-3581-01 100 mL in 1 BAG; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/18/2015 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA050671 11/14/1958 VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE
vancomycin hydrochloride injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:0338-3582 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 71WO621TJD) (VANCOMYCIN - UNII:6Q205EH1VU) VANCOMYCIN 750 mg in 150 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) 1.35 g in 150 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:0338-3582-01 150 mL in 1 BAG; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/18/2015 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA050671 11/14/1958 VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE
vancomycin hydrochloride injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:0338-3583 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 71WO621TJD) (VANCOMYCIN - UNII:6Q205EH1VU) VANCOMYCIN 1 g in 200 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) 1.8 g in 200 mL WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:0338-3583-01 200 mL in 1 BAG; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/18/2015 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA050671 11/14/1958 VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE
vancomycin hydrochloride injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:0338-0122 Route of Administration INTRAVITREAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 71WO621TJD) (VANCOMYCIN - UNII:6Q205EH1VU) VANCOMYCIN 1.25 g in 250 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength DEXTROSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: LX22YL083G) 12.50 g in 250 mL HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:0338-0122-04 250 mL in 1 BAG; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/25/2024 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA050671 11/14/1958 VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE
vancomycin hydrochloride injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:0338-0124 Route of Administration INTRAVITREAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength VANCOMYCIN HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 71WO621TJD) (VANCOMYCIN - UNII:6Q205EH1VU) VANCOMYCIN 1.50 g in 300 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength DEXTROSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: LX22YL083G) 15 g in 300 mL HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:0338-0124-04 300 mL in 1 BAG; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/25/2024 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA050671 11/14/1958 Labeler - Baxter Healthcare Corporation (005083209) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Baxter Healthcare Corporation 194684502 ANALYSIS(0338-3552, 0338-3551, 0338-3580, 0338-3581, 0338-3582, 0338-3583, 0338-0122, 0338-0124) , MANUFACTURE(0338-3552, 0338-3551, 0338-3580, 0338-3581, 0338-3582, 0338-3583, 0338-0122, 0338-0124) , LABEL(0338-3552, 0338-3551, 0338-3580, 0338-3581, 0338-3582, 0338-3583, 0338-0122, 0338-0124) , PACK(0338-3552, 0338-3551, 0338-3580, 0338-3581, 0338-3582, 0338-3583, 0338-0122, 0338-0124) , STERILIZE(0338-3552, 0338-3551, 0338-3580, 0338-3581, 0338-3582, 0338-3583, 0338-0122, 0338-0124)