Label: ALBUMIN (HUMAN)- albumin human solution
-
Contains inactivated NDC Code(s)
NDC Code(s): 67467-633-01, 67467-633-02 - Packager: Octapharma Pharmazeutika Produktionsgesellschaft m.b.H.
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Drug Label Information
Updated August 1, 2008
If you are a healthcare professional or from the pharmaceutical industry please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20%.
ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20%
For intravenous use only
20% solution
Initial U.S. Approval: 2006INDICATIONS AND USAGE
•ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% is indicated for the restoration and maintenance of circulating blood volume for: (1)
•Hypovolemia. (1.1) (1)
•Hypoalbuminemia. (1.2) (1)
•Prevention of central volume depletion after paracentesis due to cirrhotic ascites. (1.3) (1)
•Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). (1.4) (1)
•Adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). (1.5) (1)
•Acute nephrosis. (1.6) (1)
•Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN). (1.7) (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
•Intravenous use only. (2)
•Daily dose should not exceed 2 g per kg body weight. (2.1) (2)
• (2)
Indication Dose Hypovolemia (2)
Adults: 25 g (2.1) (2)
Children (less than 13 years): 2.5 to 1.25 g (2.1) (2)
Hypoalbuminemia (2)
Adults: 50 to 75 g (2.1) (2)
Prevention of volume depletion after paracentesis (2)
Adults: 8 g for every 1,000 mL of ascitic fluid removed (2.1) (2)
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (2)
Adults: 50 to 100 g over 4 hours and repeated at 4-12 hour intervals as necessary (2.1) (2)
Adult respiratory distress syndrome (2)
Adults: 25 g over 30 minutes and repeated at 8 hours for 3 days, if necessary (2.1) (2)
Acute nephrosis (2)
Adults: 25 g together with diuretic once a day for 7-10 days (2.1) (2)
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn (2)
1 g per kilogram body weight prior or during exchange transfusion (2.1) (2)
•Do not dilute with sterile water for injection as this may cause hemolysis in recipients. (5.6) (2)
•Store protected from light. (16) (2)
•Do not freeze. (16) (2)
•If large volumes (greater than 1500 ml) are administered, warm the product to room temperature before use. (2.2) (2)
•Bottles are for single use only. (2.2) (2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Do not use in individuals who are hypersensitive to albumin preparations, any ingredient in the formulation, or components of the container. (4) (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
•Hypersensitivity or allergic reactions have been observed, and may in some cases progress to severe anaphylaxis. Epinephrine should be available immediately to treat any acute hypersensitivity reaction. (5.1) (5)
•Hypervolemia: Use with caution in patients who are at risk of hypervolemia or hemodilution. Stop infusion if signs of cardiovascular overload occur. (5.2) (5)
•Electrolyte imbalances have been observed. Monitor electrolyte status. (5.3) (5)
•Ensure adequate substitution of other blood constituents. Monitor coagulation status and hematocrit. (5.4) (5)
•Hypotension has been observed. Monitor hemodynamic performance. (5.5) (5)
•Do not dilute solution with sterile water for injection. (5.6) (5)
•This product is made from human plasma and may contain infectious agents, e.g., viruses and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease agent. (5.7) (5)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
•Pregnancy: No human or animal data. Use only if needed. (8.1) (8)
•Pediatric use: The product should only be administered to pediatric patients if needed. (8.4) (8)
• (8)
• (8)
• (8)
•_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ (8)
• (8)
• (8)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 8/2008
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Hypovolemia
1.2 Hypoalbuminemia
1.3 Prevention of Central Volume Depletion after Paracentesis due to Cirrhotic Ascites (Treatment Adjunct)
1.4 Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
1.5 Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) (Treatment Adjunct)
1.6 Acute Nephrosis (Treatment Adjunct)
1.7 Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN)
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.2 Dosage
2.1 Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity
5.2 Hypervolemia/Hemodilution
5.3 Electrolyte Imbalance
5.4 Coagulation Abnormalities
5.5 Laboratory Monitoring
5.6 Application Precautions
5.7 Infection Risk from Human Plasma
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 General
6.2 Clinical Studies Experience
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Labor and Delivery
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
13 NON-CLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Information for Patients
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Hypovolemia
ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% is indicated in the emergency treatment of hypovolemia with or without shock. Its effectiveness in reversing hypovolemia depends largely upon its ability to draw interstitial fluid into the circulation. It is most effective in patients who are well hydrated. When blood volume deficit is the result of hemorrhage, compatible red blood cells or whole blood should be administered as quickly as possible. [1, 2]
When hypovolemia is long standing and hypoalbuminemia exists accompanied by adequate hydration or edema, 20% - 25% albumin solutions should be used. [ 1 ]
1.2 Hypoalbuminemia
For subjects with hypoalbuminemia who are critically ill and/or are bleeding actively, ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% infusions may be indicated. [ 3 ] When albumin deficit is the result of excessive protein loss, the effect of administration of ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% will be temporary unless the underlying disorder is reversed.
1.3 Prevention of Central Volume Depletion after Paracentesis due to Cirrhotic Ascites (Treatment Adjunct)
ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% may be used to maintain cardiovascular function following the removal of large volumes of ascitic fluid after paracentesis due to cirrhotic ascites. [ 2 ]
1.4 Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% may be used as a plasma expander in fluid management relating to severe forms of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). [7, 8]
1.5 Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) (Treatment Adjunct)
ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% infusions may be indicated in conjunction with diuretics to correct the fluid volume overload associated with ARDS. [ 5 ]
1.6 Acute Nephrosis (Treatment Adjunct)
ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% may be used to treat edema in patients with acute nephrosis who are refractory to cyclophosphamide and corticosteroid therapy. [ 1 ]
1.7 Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn (HDN)
ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% is indicated in the treatment of hyperbilirubinemia. It may be used prior to or during an exchange procedure in an attempt to bind free and to enhance its removal. [ 6 ]
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.2 Dosage
General Recommendations
The concentration of the albumin preparation, dosage and the infusion rate should be adjusted to the patient’s individual requirements.
The dose required depends on the body weight of the patient, the severity of trauma or illness and on continuing fluid and protein losses. Measures of adequacy of circulating volume and not plasma albumin levels should be used to determine the dose required.
The daily dose should not exceed 2 g of ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% per kg of body weight.
Hypovolemia
In adults, an intravenous infusion of 25 g should be given. If adequate response (stabilization of circulation) is not achieved within 15 to 30 minutes, an additional dose may be given.
In spite of limited information about the efficacy in pediatric subjects, an intravenous infusion of 2.5 to 12.5 g or 0.5 to 1 g/kg body weight may be given. If adequate response (stabilization of circulation) is not achieved within 15 to 30 minutes, an additional dose may be given.
Hemodilution may follow administration of ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20%. If hemorrhage has occurred, this may result in relative anemia. This condition should be controlled by the supplemental administration of compatible red blood cells or compatible whole blood.
Hypoalbuminemia
In adults, intravenous infusion of 50 to 75 g of ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% may be used. Hypoalbuminemia is usually accompanied by a hidden extravascular albumin deficiency of equal magnitude. This total body albumin deficit must be considered when determining the amount of albumin necessary to reverse the hypoalbuminemia.
In burns, therapy usually starts with the administration of large volumes of crystalloid injection to maintain plasma volume. After 24 hours, ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% may be added at an initial dose of 25 g with the dose adjusted thereafter to maintain a plasma protein concentration of 2.5 g per 100 mL or a serum protein concentration of 5.2 g/100 mL.
Prevention of Central Volume Depletion after Paracentesis due to Cirrhotic Ascites
In adults, intravenous infusion of 8 g of ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% may be given for every 1,000 mL of ascitic fluid removed.
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome
In adults, as a guideline, doses of 50 – 100 g of ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% should be infused over 4 hours and repeated at 4- to 12-hour intervals as necessary, when infusion of normal saline fails to achieve or maintain hemodynamic stability and urine output. [ 7 ]
Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
In adults, a dose of 25 g of ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% can be infused over 30 minutes and repeated at 8 hour intervals for 3 days, if necessary. [ 5 ]
Induction of Diuresis in Patients with Acute Nephrosis
In adults, a dose of 25 g of ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% can be infused, administered with an appropriate diuretic once a day for 7 to 10 days.
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn
In newborns, ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% may be administered prior to or during exchange transfusion at a dose of 1 g per kilogram body weight. [ 6 ]
2.1 Administration
Intravenous use only.
Prior to administration, parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for turbidity and discoloration, whenever solution and container permit.
Do not dilute with sterile water for injection.
Do not use solutions of ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% which are cloudy or have deposits. Once the infusion container has been opened the contents should be used immediately. Discard the unused portion. Filtration of ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% is not required.
The infusion rate should be adjusted according to the individual circumstances and the indication. In plasma exchange during paracentesis, the infusion rate may be higher and should be adjusted to the rate of removal.
If large volumes (greater than 1500 ml) are administered, the product should be warmed to room temperature before use.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity or allergic reactions have been observed, and may in some cases progress to severe anaphylaxis. Epinephrine should be available immediately to treat any acute hypersensitivity reaction.
5.2 Hypervolemia/Hemodilution
Hypervolemia may occur if the dosage and rate of infusion are not adjusted to the patient’s volume status. At the first clinical signs of possible cardiovascular overload, e.g., headache, dyspnea, increased blood pressure, jugular venous distention, elevated central venous pressure, pulmonary edema, the infusion should be stopped immediately and the patient reevaluated. Albumin should be used with caution in conditions where hypervolemia and its consequences or hemodilution could represent a special risk for the patient. Examples of such conditions are:
- Decompensated cardiac insufficiency
- Hypertension
- Esophageal varices
- Pulmonary edema
- Hemorrhagic diathesis
- Severe anemia
- Renal and post-renal anuria.
5.3 Electrolyte Imbalance
20-25% Albumin (Human) is relatively low in electrolytes compared to the 4-5% Albumin (Human) solutions. When albumin is given, monitor the electrolyte status of the patient and take appropriate steps to restore or maintain the electrolyte balance.
5.4 Coagulation Abnormalities
If comparatively large volumes are to be replaced, monitoring of coagulation and hematocrit is necessary. Ensure adequate substitution of other blood constituents (coagulation factors, electrolytes, platelets and erythrocytes).
5.5 Laboratory Monitoring
If ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% is to be administered, monitor hemodynamic performance regularly; this may include:
- Arterial blood pressure and pulse rate
- Central venous pressure
- Pulmonary artery occlusion pressure
- Urine output
- Electrolytes
- Hematocrit/hemoglobin.
5.6 Application Precautions
ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% must not be diluted with sterile water for injection as this may cause hemolysis in recipients.
5.7 Infection Risk from Human Plasma
This product is a derivative of human plasma. Based on effective donor screening and product manufacturing processes it carries an extremely remote risk for transmission of viral diseases. A theoretical risk for transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD) also is considered extremely remote. No cases of transmission of viral diseases or CJD have been identified for ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20%.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 General
The most serious events are anaphylactic shock, circulatory failure, cardiac failure, and pulmonary edema.
The most common adverse events are anaphylactoid type of reactions.
Adverse reactions for ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% normally resolve when the infusion rate is slowed down or the infusion is stopped. In case of severe reactions, the infusion should be stopped and appropriate treatment should be initiated.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of ALBUMIN (HUMAN) (any strength). Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency.
Table 1 Adverse reactions observed for ALBUMIN HUMAN (any strength) during post-marketing phase (in decreasing order of severity)
Observed Adverse Reactions anaphylactic shock
cardiac failure
loss of consciousness
circulatory failure
hypersensitivity
congestive heart failure
pulmonary edema
dyspnea
hypotension
hypertension
tachycardia
bradycardia
vomiting
urticaria
angioneurotic edema
rash erythematous
confusional state
headache
chills
pyrexia
flushing
nausea
pruritus
hyperhidrosis
No drug interaction studies have been conducted.
- 7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C. Animal reproduction studies have not been performed with ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20%. It is also not known whether ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproductive capacity. ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% should be given to a pregnant woman only if necessary.
8.2 Labor and Delivery
It is also not known whether ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% can cause fetal harm when administered to a woman during labor or delivery of if it will affect reproductive capacity. ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% should be given during labor or delivery only if necessary.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% should be given to nursing mothers only if necessary. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% is administered to a lactating woman.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% is a sterile, liquid preparation of albumin derived from large pools of human plasma. All units of human plasma used in the manufacture of ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% are provided by FDA approved blood establishments only.
The product is manufactured by cold ethanol fractionation followed by ultra- and diafiltration. The manufacturing process includes final container pasteurization and additional bulk pasteurization at 60 +/- 0.5°C for 10 – 11 hours. The ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% manufacturing process provides a significant viral reduction in in vitro studies (table 2). These reductions are achieved through a combination of process steps including Cohn fractionation and final container pasteurization.
No procedure, however, has been shown to be completely effective in removing viral infectivity from derivatives of human plasma.[see Warnings and Precautions, Infection Risk from Human Plasma (5.7)]
Table 2 In vitro reduction factor during ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% manufacturing
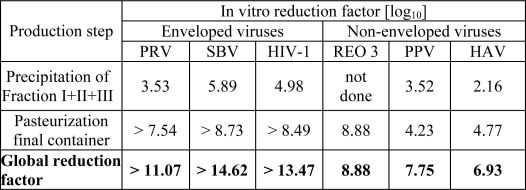
PRV:Pseudorabies Virus
SBV: Sindbis Virus
HIV-1:Human Immunodeficiency Virus - 1
Reo 3:Reovirus Type 3
PPV:Porcine Parvovirus
HAV:Hepatitis A Virus
ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% is a clear, slightly viscous liquid; it is almost colorless or slightly yellow or green.
The composition of ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% is as follows:
Component Quantity/1000 ml Protein, of which greater than or equal to
96% is human albumin
200 g
Sodium
130 – 160 mmol
Potassium
less than or equal to 2 mmol
N-acetyl-DL-tryptophan
0.064 - 0.096 mmol/g protein
Caprylic acid
0.064 - 0.096 mmol/g protein
Water for Injection
ad. 1000 ml
ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% contains no preservatives and components used in its packaging are latex-free.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
No pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic studies with ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% have been conducted.
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Albumin is responsible for 75-80% of the colloid osmotic pressure of normal plasma. Albumin stabilizes circulating blood volume and is a carrier of hormones, enzymes, medicinal products and toxins. [ 3 ]
Albumin is a protein with a total extravascular mass of approximately 160 g and an intravascular mass of about 120 g. [ 3 ]
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The colloid osmotic effect of ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% and 25% is approximately 5 times the volume administered. When injected intravenously, it will increase circulating plasma volume by approximately 3.5 times the volume infused within 15 minutes if the patient is adequately hydrated. This extra fluid reduces hemoconcentration and blood viscosity. The degree and duration of volume expansion depends upon the initial blood volume. When treating patients with diminished blood volume, the effect of infused albumin may persist for many hours. The hemodilution lasts for a shorter time when albumin is administered to individuals with normal blood volume. [ 4 ]
- 13 NON-CLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
-
15 REFERENCES
- Tullis JL: Albumin 2.Guidelines for Clinical Use. JAMA 1977; 237:460-463
- Vermeulen LC et al.: A Paradigm for Consensus. Arch. Intern. Med. 1995; 155:373-379
- Mendez CM, McClain CJ, Marsano LS: Albumin Therapy in Clinical Practice. Nutrition in Clinical Practice 2005; 20: 314-320
- Janeway, C. A. "Human Serum Albumin: Historical Review" in: Proceedings of the Workshop on Albumin. DHEW Publication No. (NIH) 76-925. Sgouris, J. T. and René A. (eds.), Washington, D.C., U.S. Government Printing Office. 1976, pp 3-21.
- Martin GS et al.: A randomized, controlled trail of furosemide with or without albumin in hypoproteinemic patients with acute lung injury. Crit. Care Med. 2005; 33: 1681-1687
- Tsao YC, Yu VY: Albumin in management of neonatal hyperbilirubinaemia. Arch Dis.Child 1972;47:250-256.
- Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. Fertil.Steril. 2006;86:S178-S183.
- Aboulghar M, Evers JH, Al Inany H: Intravenous albumin for preventing severe ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome: a Cochrane review. Hum.Reprod. 2002;17:3027-3032.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% is supplied in 10 g in 50 mL or 20 g in 100 mL single use bottles.
NDC Number NDC Number Size Grams protein Octapharma Pharmazeutika Produktionsges.m.b.H
Octapharma AB
67467-633-01
68209-633-01
50 ml
10
67467-633-02
68209-633-02
100 ml
20
ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% may be stored for 36 months at +2°C to + 25°C (36°F to 77°F) from the date of manufacture.
Store protected from light.
Do not freeze.
Do not use after expiration date.
Do not use if turbid.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Information for Patients
This product is usually given in a hospital setting.
Inform patients being treated with Albumin (Human) 20% about the potential risks and benefits with its use [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Discontinue immediately if allergic symptoms occur (e.g. skin rashes, hives, itching, breathing difficulties, coughing, nausea, vomiting, fall in blood pressure, increased heart rate).
Inform patients that ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% is a derivative of human plasma and may contain infectious agents that cause disease (e.g., viruses, and theoretically, CJD agent). Inform patients that the risk that ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 20% may transmit an infections agent has been reduced by screening plasma donors for prior exposure for certain viruses, by testing the donated plasma for certain virus infections and by inactivating and/or removing certain viruses during manufacturing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Manufactured by:
Octapharma Pharmazeutika Produktionsges.m.b.H.
Oberlaaer Strasse 235
A-1100 Vienna, Austria
Octapharma AB
Elersvägen 40
SE- 112 75, Sweden
U.S. License No. 1646
Distributed by:
Octapharma USA Inc.
121 River Street, 12 th floor
Hoboken, NJ 07030
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ALBUMIN (HUMAN)
albumin human solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:67467-633 Route of Administration Intravenous Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ALBUMIN (HUMAN) (UNII: ZIF514RVZR) (ALBUMIN (HUMAN) - UNII:ZIF514RVZR) ALBUMIN (HUMAN) 200 g in 1000 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:67467-633-01 50 mL in 1 BOTTLE, GLASS 2 NDC:67467-633-02 100 mL in 1 BOTTLE, GLASS Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA125154 10/17/2006 Labeler - Octapharma Pharmazeutika Produktionsgesellschaft m.b.H. (301119178)




