Label: PREDNISOLONE syrup
- NDC Code(s): 0527-5406-68, 0527-5406-70
- Packager: Lannett Company, Inc.
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Abbreviated New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated February 14, 2024
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP) contains prednisolone which is a glucocorticoid. Glucocorticoids are adrenocortical steroids, both naturally occurring and synthetic, which are readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Prednisolone is a white to practically white, odorless, crystalline powder. It is very slightly soluble in water; soluble in methanol and in dioxane; sparingly soluble in acetone and in alcohol; slightly soluble in chloroform.
The chemical name for prednisolone is Pregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione,11,17,21-trihydroxy-,(11β).
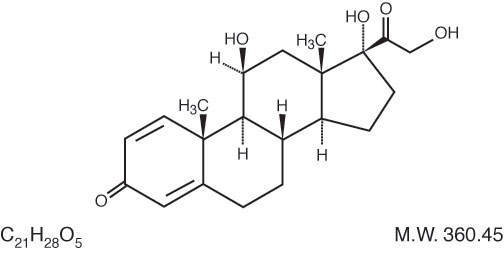
Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP) contains 15 mg of prednisolone in each 5 mL. Benzoic acid, 0.1% is added as a preservative. It also contains alcohol 5% v/v, cherry flavor, citric acid, edetate disodium, FD&C Blue #1, FD&C Red #40, glycerin, propylene glycol, purified water, sodium saccharin, and sucrose. Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP) may contain sodium citrate for pH adjustment.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Naturally occurring glucocorticoids (hydrocortisone and cortisone), which also have salt-retaining properties, are used as replacement therapy in adrenocortical deficiency states. Their synthetic analogs such as prednisolone are primarily used for their potent anti-inflammatory effects in disorders of many organ systems.
Glucocorticoids such as prednisolone cause profound and varied metabolic effects. In addition, they modify the body's immune responses to diverse stimuli.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP) is indicated in the following conditions:
1. Endocrine Disorders
Primary or secondary adrenocortical insufficiency (hydrocortisone or cortisone is the first choice: synthetic analogs may be used in conjunction with mineralocorticoids where applicable; in infancy mineralocorticoid supplementation is of particular importance).
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Nonsuppurative thyroiditis
Hypercalcemia associated with cancer
2. Rheumatic Disorders
As adjunctive therapy for short-term administration (to tide the patient over an acute episode or exacerbation) in:
Psoriatic arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis, including juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (selected cases may require low-dose maintenance therapy)
Ankylosing spondylitis
Acute and subacute bursitis
Acute nonspecific tenosynovitis
Acute gouty arthritis
Post-traumatic osteoarthritis
Synovitis of osteoarthritis
Epicondylitis
3. Collagen Diseases
During an exacerbation or as maintenance therapy in selected cases of:
Systemic lupus erythematosus
Acute rheumatic carditis
4. Dermatologic Diseases
Pemphigus
Bullous dermatitis herpetiformis
Severe erythema multiforme (Stevens-Johnson syndrome)
Exfoliative dermatitis
Mycosis fungoides
Severe psoriasis
Severe seborrheic dermatitis
5. Allergic States
Control of severe or incapacitating allergic conditions intractable to adequate trials of conventional treatment:
Seasonal or perennial allergic rhinitis
Bronchial asthma
Contact dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis
Serum sickness
Drug hypersensitivity reactions
6. Ophthalmic Diseases
Severe acute and chronic allergic and inflammatory processes involving the eye and its adnexa such as:
Allergic corneal marginal ulcers
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
Anterior segment inflammation
Diffuse posterior uveitis and choroiditis
Sympathetic ophthalmia
Allergic conjunctivitis
Keratitis
Chorioretinitis
Optic neuritis
Iritis and iridocyclitis
7. Respiratory Diseases
Symptomatic sarcoidosis Loeffler's syndrome not manageable by other means
Berylliosis
Fulminating or disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis when used concurrently with appropriate chemotherapy
Aspiration pneumonitis
8. Hematologic Disorders
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in adults
Secondary thrombocytopenia in adults
Acquired (autoimmune) hemolytic anemia
Erythroblastopenia (RBC anemia)
Congenital (erythroid) hypoplastic anemia
9. Neoplastic Diseases
For palliative management of:
Leukemias and lymphomas in adults
Acute leukemia of childhood
10. Edematous States
To induce a diuresis or remission of proteinuria in the nephrotic syndrome, without uremia, of the idiopathic type or that due to lupus erythematosus.
11. Gastrointestinal Diseases
To tide the patient over a critical period of the disease in:
Ulcerative colitis
Regional enteritis
12. Miscellaneous
Tuberculous meningitis with subarachnoid block or impending block used concurrently with appropriate antituberculous chemotherapy. Trichinosis with neurologic or myocardial involvement.
In addition to the above indications Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP) is indicated for systemic dermatomyositis (polymyositis).
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
In patients on corticosteroid therapy subjected to unusual stress, increased dosage of rapidly acting corticosteroids before, during, and after the stressful situation is indicated.
Immunosuppression and Increased Risk of Infection
Corticosteroids, including Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP), suppress the immune system and increase the risk of infection with any pathogen, including viral, bacterial, fungal, protozoan, or helminthic pathogens. Corticosteroids can:
- Reduce resistance to new infections
- Exacerbate existing infections
- Increase the risk of disseminated infections
- Increase the risk of reactivation or exacerbation of latent infections
- Mask some signs of infection
Corticosteroid-associated infections can be mild but can be severe and at times fatal. The rate of infectious complications increases with increasing corticosteroid dosages.
Monitor for the development of infection and consider Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP) withdrawal or dosage reduction as needed.
Do not administer Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP) by an intraarticular, intrabursal, intratendinous, or intralesional route in the presence of acute local infection.
Tuberculosis
If Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP) is used to treat a condition in patients with latent tuberculosis or tuberculin reactivity, reactivation of tuberculosis may occur. Closely monitor such patients for reactivation. During prolonged Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP) therapy, patients with latent tuberculosis or tuberculin reactivity should receive chemoprophylaxis.
Varicella Zoster and Measles Viral Infections
Varicella and measles can have a serious or even fatal course in non-immune patients taking corticosteroids, including Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP). In corticosteroid-treated patients who have not had these diseases or are non-immune, particular care should be taken to avoid exposure to varicella and measles:
- If a Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP)-treated patient is exposed to varicella, prophylaxis with varicella zoster immune globulin may be indicated. If varicella develops, treatment with antiviral agents may be considered.
- If a Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP)-treated patient is exposed to measles, prophylaxis with immunoglobulin may be indicated.
Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation
Hepatitis B virus reactivation can occur in patients who are hepatitis B carriers treated with immunosuppressive dosages of corticosteroids, including Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP). Reactivation can also occur infrequently in corticosteroid-treated patients who appear to have resolved hepatitis B infection.
Screen patients for hepatitis B infection before initiating immunosuppressive (e.g., prolonged) treatment with Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP). For patients who show evidence of hepatitis B infection, recommend consultation with physicians with expertise in managing hepatitis B regarding monitoring and consideration for hepatitis B antiviral therapy.
Fungal Infections
Corticosteroids, including Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP), may exacerbate systemic fungal infections; therefore, avoid Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP) use in the presence of such infections unless Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP) is needed to control drug reactions. For patients on chronic Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP) therapy who develop systemic fungal infections, Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP) withdrawal or dosage reduction is recommended.
Amebiasis
Corticosteroids, including Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP), may activate latent amebiasis. Therefore, it is recommended that latent amebiasis or active amebiasis be ruled out before initiating Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP) in patients who have spent time in the tropics or patients with unexplained diarrhea.
Strongyloides Infestation
Corticosteroids, including Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP), should be used with great care in patients with known or suspected Strongyloides (threadworm) infestation. In such patients, corticosteroid-induced immunosuppression may lead to Strongyloides hyperinfection and dissemination with widespread larval migration, often accompanied by severe enterocolitis and potentially fatal gram-negative septicemia.
Cerebral Malaria
Avoid corticosteroids, including Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP), in patients with cerebral malaria.
Kaposi’s Sarcoma
Kaposi’s sarcoma has been reported to occur in patients receiving corticosteroid therapy, most often for chronic conditions. Discontinuation of corticosteroids may result in clinical improvement of Kaposi’s sarcoma.
Prolonged use of corticosteroids may produce posterior subcapsular cataracts, glaucoma with possible damage to the optic nerves, and may enhance the establishment of secondary ocular infections due to fungi or viruses.
Average and large doses of hydrocortisone or cortisone can cause elevation of blood pressure, salt and water retention, and increased excretion of potassium. These effects are less likely to occur with the synthetic derivatives except when used in large doses. Dietary salt restriction and potassium supplementation may be necessary. All corticosteroids increase calcium excretion.
While on corticosteroid therapy, patients should not be vaccinated against smallpox. Other immunization procedures should not be undertaken in patients who are on corticosteroids, especially on high dose, because of possible hazards of neurological complications and a lack of antibody response.
Use in Pregnancy: Since adequate human reproduction studies have not been done with corticosteroids, the use of these drugs in pregnancy, nursing mothers or women of childbearing potential requires that the possible benefits of the drug be weighed against the potential hazards to the mother and embryo or fetus. Infants born of mothers who have received substantial doses of corticosteroids during pregnancy should be carefully observed for signs of hypoadrenalism.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General:
Drug-induced secondary adrenocortical insufficiency may be minimized by gradual reduction of dosage. This type of relative insufficiency may persist for months after discontinuation of therapy; therefore, in any situation of stress occurring during that period, hormone therapy should be reinstituted. Since mineralocorticoid secretion may be impaired, salt and/or a mineralocorticoid should be administered concurrently.
There is an enhanced effect of corticosteroids on patients with hypothyroidism and in those with cirrhosis.
Corticosteroids should be used cautiously in patients with ocular herpes simplex because of possible corneal perforation.
The lowest possible dose of corticosteroid should be used to control the condition under treatment, and when reduction in dosage is possible, the reduction should be gradual.
Psychic derangements may appear when corticosteroids are used, ranging from euphoria, insomnia, mood swings, personality changes, and severe depression, to frank psychotic manifestations. Also, existing emotional instability or psychotic tendencies may be aggravated by corticosteroids.
Aspirin should be used cautiously in conjunction with corticosteroids in hypoprothrombinemia.
Steroids should be used with caution in nonspecific ulcerative colitis, if there is a probability of impending perforation, abscess or other pyogenic infections; diverticulitis; fresh intestinal anastomoses; active or latent peptic ulcer; renal insufficiency; hypertension; osteoporosis; and myasthenia gravis.
Growth and development of infants and children on prolonged corticosteroid therapy should be carefully observed.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Fluid and Electrolyte Disturbances
Sodium retention
Fluid retention
Congestive heart failure in susceptible patients
Potassium loss
Hypokalemic alkalosis
HypertensionMusculoskeletal
Muscle weakness
Steroid myopathy
Loss of muscle mass
Osteoporosis
Vertebral compression fractures
Aseptic necrosis of femoral and humeral heads
Pathologic fracture of long bonesGastrointestinal
Peptic ulcer with possible perforation and hemorrhage
Pancreatitis
Abdominal distention
Ulcerative esophagitisDermatologic
Impaired wound healing
Thin fragile skin
Petechiae and ecchymoses
Facial erythema
Increased sweating
May suppress reactions to skin testsNeurological
Convulsions
Increased intracranial pressure with papilledema (pseudo-tumor cerebri) usually after treatment
Vertigo
HeadacheEndocrine
Menstrual irregularities
Development of Cushingoid state
Suppression of growth in children
Secondary adrenocortical and pituitary unresponsiveness, particularly in times of stress, as in trauma, surgery or illness
Decreased carbohydrate tolerance
Manifestations of latent diabetes mellitus
Increased requirements for insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents in diabeticsOphthalmic
Posterior subcapsular cataracts
Increased intraocular pressure
Glaucoma
ExophthalmosMetabolic
Negative nitrogen balance due to protein catabolismTo report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Lannett Company, Inc. at 1-844-834-0530 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Dosage of Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP) should be individualized according to the severity of the disease and the response of the patient. For infants and children, the recommended dosage should be governed by the same considerations rather than strict adherence to the ratio indicated by age or body weight.
Hormone therapy is an adjunct to and not a replacement for conventional therapy.
Dosage should be decreased or discontinued gradually when the drug has been administered for more than a few days.
The severity, prognosis, expected duration of the disease, and the reaction of the patient to medication are primary factors in determining dosage.
If a period of spontaneous remission occurs in a chronic condition, treatment should be discontinued.
Blood pressure, body weight, routine laboratory studies, including two-hour postprandial blood glucose and serum potassium, and a chest X-ray should be obtained at regular intervals during prolonged therapy. Upper GI X-rays are desirable in patients with known or suspected peptic ulcer disease.
The initial dosage of Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP) may vary from 5 mg to 60 mg per day depending on the specific disease entity being treated. In situations of less severity lower doses will generally suffice while in selected patients higher initial doses may be required. The initial dosage should be maintained or adjusted until a satisfactory response is noted. If after a reasonable period of time there is a lack of satisfactory clinical response, Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP) should be discontinued and the patient transferred to other appropriate therapy. IT SHOULD BE EMPHASIZED THAT DOSAGE REQUIREMENTS ARE VARIABLE AND MUST BE INDIVIDUALIZED ON THE BASIS OF THE DISEASE UNDER TREATMENT AND THE RESPONSE OF THE PATIENT.
After a favorable response is noted, the proper maintenance dosage should be determined by decreasing the initial drug dosage in small decrements at appropriate time intervals until the lowest dosage which will maintain an adequate clinical response is reached. It should be kept in mind that constant monitoring is needed in regard to drug dosage. Included in the situations which may make dosage adjustments necessary are changes in clinical status secondary to remissions or exacerbations in the disease process, the patient's individual drug responsiveness, and the effect of patient exposure to stressful situations not directly related to the disease entity under treatment. In this latter situation it may be necessary to increase the dosage of Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP) for a period of time consistent with the patient's condition. If after long-term therapy the drug is to be stopped, it is recommended that it be withdrawn gradually rather than abruptly.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Prednisolone Syrup (Prednisolone Oral Solution, USP) is a cherry flavored red liquid containing 15 mg of prednisolone in each 5 mL (teaspoonful) and is supplied as follows:
NDC 0527-5406-68 240 mL
NDC 0527-5406-70 480 mL
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PREDNISOLONE
prednisolone syrupProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:0527-5406 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PREDNISOLONE (UNII: 9PHQ9Y1OLM) (PREDNISOLONE - UNII:9PHQ9Y1OLM) PREDNISOLONE 15 mg in 5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength BENZOIC ACID (UNII: 8SKN0B0MIM) ALCOHOL (UNII: 3K9958V90M) CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) EDETATE DISODIUM (UNII: 7FLD91C86K) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) SACCHARIN SODIUM (UNII: SB8ZUX40TY) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) SODIUM CITRATE (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) Product Characteristics Color Score Shape Size Flavor CHERRY Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:0527-5406-68 240 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 09/21/2007 2 NDC:0527-5406-70 480 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 09/21/2007 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA040775 09/21/2007 Labeler - Lannett Company, Inc. (002277481)


