Label: REBLOZYL- luspatercept injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution
- NDC Code(s): 59572-711-01, 59572-775-01
- Packager: Celgene Corporation
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Biologic Licensing Application
Drug Label Information
Updated May 17, 2024
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use REBLOZYL safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for REBLOZYL.
REBLOZYL® (luspatercept-aamt) for injection, for subcutaneous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2019RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
REBLOZYL is an erythroid maturation agent indicated for the treatment of:
- •
- Anemia in adult patients with beta thalassemia who require regular red blood cell (RBC) transfusions (1.1).
- •
- Anemia without previous erythropoiesis stimulating agent use (ESA-naïve) in adult patients with very low- to intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) who may require regular red blood cell (RBC) transfusions (1.2).
- •
- Anemia failing an erythropoiesis stimulating agent and requiring 2 or more RBC units over 8 weeks in adult patients with very low- to intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndromes with ring sideroblasts (MDS-RS) or with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasm with ring sideroblasts and thrombocytosis (MDS/MPN-RS-T) (1.3).
- •
- Limitations of Use: REBLOZYL is not indicated for use as a substitute for RBC transfusions in patients who require immediate correction of anemia (1.4).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None (4).
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- •
- Thrombosis/Thromboembolism: Increased risk in patients with beta thalassemia. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of thromboembolic events and institute treatment promptly (5.1).
- •
- Hypertension: Monitor blood pressure (BP) during treatment. Initiate anti-hypertensive treatment if necessary (5.2).
- •
- Extramedullary Hematopoietic (EMH) Masses: Increased risk in patients with beta thalassemia. Monitor patients for symptoms and signs or complications resulting from the EMH masses. Treat according to clinical guidelines and discontinue treatment in case of serious complications due to EMH masses (5.3).
- •
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: May cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and use of effective contraception (5.4, 8.1, 8.3).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common (>10%) adverse reactions were fatigue, headache, musculoskeletal pain, arthralgia, dizziness/vertigo, nausea, diarrhea, cough, abdominal pain, dyspnea, COVID-19, edema peripheral, hypertension, and hypersensitivity (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Bristol-Myers Squibb at 1-888-423-5436 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 5/2024
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Beta Thalassemia
1.2 Myelodysplastic Syndromes Associated Anemia
1.3 Myelodysplastic Syndromes with Ring Sideroblasts or Myelodysplastic/ Myeloproliferative Neoplasm with Ring Sideroblasts and Thrombocytosis Associated Anemia
1.4 Limitations of Use
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage for Beta Thalassemia
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Myelodysplastic Syndromes Associated Anemia
2.3 Preparation and Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Thrombosis/Thromboembolism
5.2 Hypertension
5.3 Extramedullary Hematopoietic Masses
5.4 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
9.2 Abuse
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.6 Immunogenicity
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Beta Thalassemia
14.2 Treatment of Myelodysplastic Syndromes with Associated Anemia in ESA-naïve Patients
14.3 Myelodysplastic Syndromes with Ring Sideroblasts or Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative Neoplasm with Ring Sideroblasts and Thrombocytosis Associated Anemia in ESA-refractory or -intolerant Patients
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Beta Thalassemia
REBLOZYL is indicated for the treatment of anemia in adult patients with beta thalassemia who require regular red blood cell (RBC) transfusions.
1.2 Myelodysplastic Syndromes Associated Anemia
REBLOZYL is indicated for the treatment of anemia without previous erythropoiesis stimulating agent use (ESA-naïve) in adult patients with very low- to intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) who may require regular red blood cell (RBC) transfusions.
1.3 Myelodysplastic Syndromes with Ring Sideroblasts or Myelodysplastic/ Myeloproliferative Neoplasm with Ring Sideroblasts and Thrombocytosis Associated Anemia
REBLOZYL is indicated for the treatment of anemia failing an erythropoiesis stimulating agent and requiring 2 or more red blood cell units over 8 weeks in adult patients with very low- to intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndromes with ring sideroblasts (MDS-RS) or with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasm with ring sideroblasts and thrombocytosis (MDS/MPN-RS-T).
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage for Beta Thalassemia
The recommended starting dose of REBLOZYL is 1 mg/kg once every 3 weeks by subcutaneous injection for patients with beta thalassemia. Prior to each REBLOZYL dose, review the patient’s hemoglobin and transfusion record. Titrate the dose based on responses according to Table 1. Interrupt treatment for adverse reactions as described in Table 2. Discontinue REBLOZYL if a patient does not experience a decrease in transfusion burden after 9 weeks of treatment (administration of 3 doses) at the maximum dose level or if unacceptable toxicity occurs at any time.
If a planned administration of REBLOZYL is delayed or missed, administer REBLOZYL as soon as possible and continue dosing as prescribed, with at least 3 weeks between doses.
Dose Modifications for Response
Assess and review hemoglobin results prior to each administration of REBLOZYL. If an RBC transfusion occurred prior to dosing, use the pretransfusion hemoglobin for dose evaluation.
If a patient does not achieve a reduction in RBC transfusion burden after at least 2 consecutive doses (6 weeks) at the 1 mg/kg starting dose, increase the REBLOZYL dose to 1.25 mg/kg. Do not increase the dose beyond the maximum dose of 1.25 mg/kg. In the absence of transfusions, if hemoglobin increase is greater than 2 g/dL within 3 weeks or the predose hemoglobin is greater than or equal to 11.5 g/dL, reduce the dose or interrupt treatment with REBLOZYL as described in Table 1.
Dose level modifications for response are provided in Table 1.
Table 1: Beta Thalassemia - REBLOZYL Dose Titration for Response * Do not increase the dose if the patient is experiencing an adverse reaction as described in Table 2. REBLOZYL
Dosing Recommendation*Starting Dose
- •
- 1 mg/kg every 3 weeks
Dose Increases for Insufficient Response at Initiation of Treatment
No reduction in RBC transfusion burden after at least 2 consecutive doses (6 weeks) at the 1 mg/kg starting dose
- •
- Increase the dose to 1.25 mg/kg every 3 weeks
No reduction in RBC transfusion burden after 3 consecutive doses (9 weeks) at 1.25 mg/kg
- •
- Discontinue treatment
Dose Modifications for Predose Hemoglobin Levels or Rapid Hemoglobin Rise
Predose hemoglobin is greater than or equal to 11.5 g/dL in the absence of transfusions
- •
- Interrupt treatment
- •
- Restart when the hemoglobin is no more than 11 g/dL
Increase in hemoglobin greater than 2 g/dL within 3 weeks in the absence of transfusions and
- •
- current dose is 1.25 mg/kg
- •
- current dose is 1 mg/kg
- •
- current dose is 0.8 mg/kg
- •
- current dose is 0.6 mg/kg
- •
- Reduce dose to 1 mg/kg
- •
- Reduce dose to 0.8 mg/kg
- •
- Reduce dose to 0.6 mg/kg
- •
- Discontinue treatment
Dose Modifications for Toxicity
For patients experiencing Grade 3 or higher adverse reactions, modify treatment as described in Table 2.
Table 2: Beta Thalassemia - REBLOZYL Dosing Modifications for Adverse Reactions * Grade 1 is mild, Grade 2 is moderate, Grade 3 is severe, and Grade 4 is life-threatening. REBLOZYL
Dosing Recommendation*Grade 3 or 4 hypersensitivity reactions
- •
- Discontinue treatment
Other Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions
- •
- Interrupt treatment
- •
- Restart when the adverse reaction resolves to no more than Grade 1
Extramedullary hematopoietic (EMH) masses causing serious complications
- •
- Discontinue treatment
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Myelodysplastic Syndromes Associated Anemia
The recommended starting dosage of REBLOZYL is 1 mg/kg once every 3 weeks by subcutaneous injection for the treatment of anemia of MDS. Prior to each REBLOZYL dose, review the patient’s hemoglobin and transfusion record. Titrate the dose based on responses according to Table 3. Interrupt treatment for adverse reactions as described in Table 4. Discontinue REBLOZYL if a patient does not experience a decrease in transfusion burden including no increase from baseline hemoglobin after 9 weeks of treatment (administration of 3 doses) at the maximum dose level (1.75 mg/kg), or if unacceptable toxicity occurs at any time.
If a planned administration of REBLOZYL is delayed or missed, administer REBLOZYL as soon as possible and continue dosing as prescribed, with at least 3 weeks between doses.
Dose Modifications for Response
Assess and review hemoglobin results prior to each administration of REBLOZYL. If an RBC transfusion occurred prior to dosing, use the pretransfusion hemoglobin for dose evaluation.
If a patient is not RBC transfusion-free after at least 2 consecutive doses (6 weeks) at the 1 mg/kg starting dose, increase the REBLOZYL dose to 1.33 mg/kg (Table 3). If a patient is not RBC transfusion-free after at least 2 consecutive doses (6 weeks) at the 1.33 mg /kg dose level, increase the REBLOZYL dose to 1.75 mg/kg. Do not increase the dose more frequently than every 6 weeks (2 doses) or beyond the maximum dose of 1.75 mg/kg.
In the absence of transfusions, if hemoglobin increase is greater than 2 g/dL within 3 weeks or if the predose hemoglobin is greater than or equal to 11.5 g/dL, reduce the dose or interrupt treatment with REBLOZYL as described in Table 3. If, upon dose reduction, the patient loses response (i.e., requires a transfusion) or hemoglobin concentration drops by 1 g/dL or more in 3 weeks in the absence of transfusion, increase the dose by one dose level. Wait a minimum of 6 weeks between dose increases.
Dose modifications for response are provided in Table 3.
Table 3: MDS Associated Anemia - REBLOZYL Dose Titration for Response * Do not increase the dose if the patient is experiencing an adverse reaction as described in Table 4. REBLOZYL
Dosing Recommendation*Starting Dose
- •
- 1 mg/kg every 3 weeks
Dose Increases for Insufficient Response at Initiation of Treatment
Not RBC transfusion-free after at least 2 consecutive doses (6 weeks) at the 1 mg/kg starting dose
- •
- Increase the dose to 1.33 mg/kg every 3 weeks
Not RBC transfusion-free after at least 2 consecutive doses (6 weeks) at 1.33 mg/kg
- •
- Increase the dose to 1.75 mg/kg every 3 weeks
No reduction in RBC transfusion burden including no increase from baseline hemoglobin after at least 3 consecutive doses (9 weeks) at 1.75 mg/kg
- •
- Discontinue treatment
Dose Modifications for Predose Hemoglobin Levels or Rapid Hemoglobin Rise
Predose hemoglobin is greater than or equal to 11.5 g/dL in the absence of transfusions
- •
- Interrupt treatment
- •
- Restart when the hemoglobin is no more than 11 g/dL
Increase in hemoglobin greater than 2 g/dL within 3 weeks in the absence of transfusions and
- •
- current dose is 1.75 mg/kg
- •
- current dose is 1.33 mg/kg
- •
- current dose is 1 mg/kg
- •
- current dose is 0.8 mg/kg
- •
- current dose is 0.6 mg/kg
- •
- Reduce dose to 1.33 mg/kg
- •
- Reduce dose to 1 mg/kg
- •
- Reduce dose to 0.8 mg/kg
- •
- Reduce dose to 0.6 mg/kg
- •
- Discontinue treatment
Dose Modifications for Toxicity
For patients experiencing Grade 3 or higher adverse reactions, modify treatment as described in Table 4.
Table 4: MDS Associated Anemia - REBLOZYL Dosing Modifications for Adverse Reactions * Grade 1 is mild, Grade 2 is moderate, Grade 3 is severe, and Grade 4 is life-threatening.
**Per Table 3 dose reductions above.REBLOZYL
Dosing Recommendation*Grade 3 or 4 hypersensitivity reactions
- •
- Discontinue treatment
Other Grade 3 or 4 adverse reactions
- •
- Interrupt treatment
- •
- When the adverse reaction resolves to no more than Grade 1, restart treatment at the next lower dose level**
- •
- If the dose delay is > 12 consecutive weeks, discontinue treatment
2.3 Preparation and Administration
REBLOZYL should be reconstituted and administered by a healthcare professional.
Reconstitute REBLOZYL with Sterile Water for Injection, USP only.
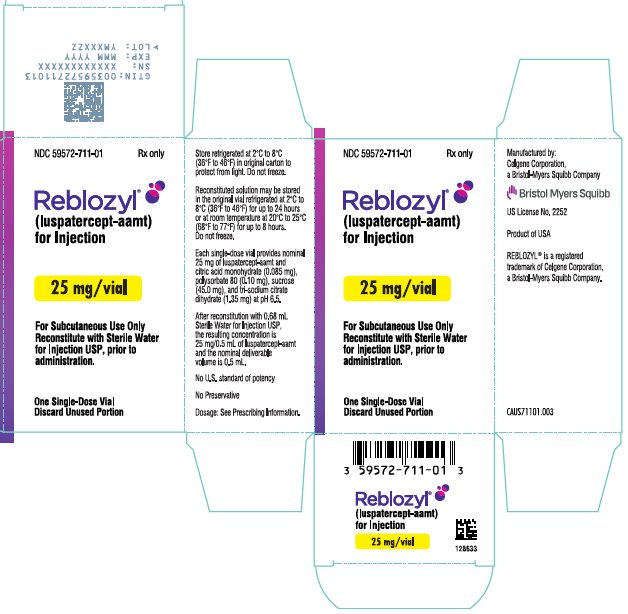
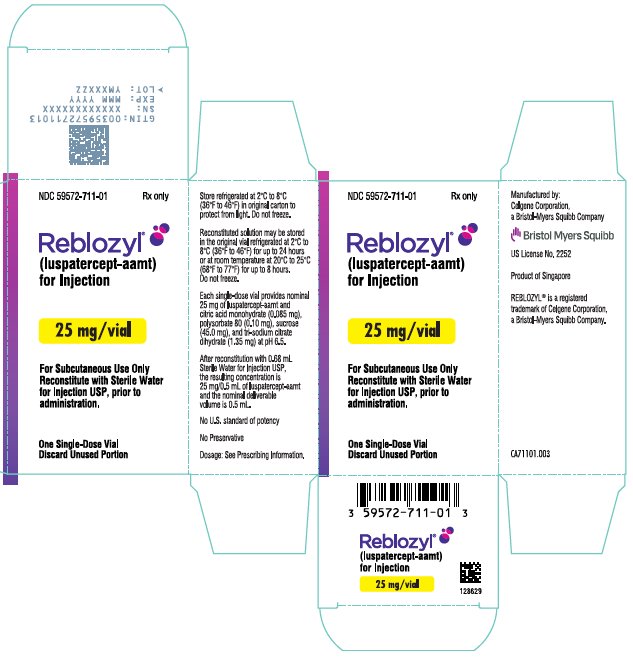
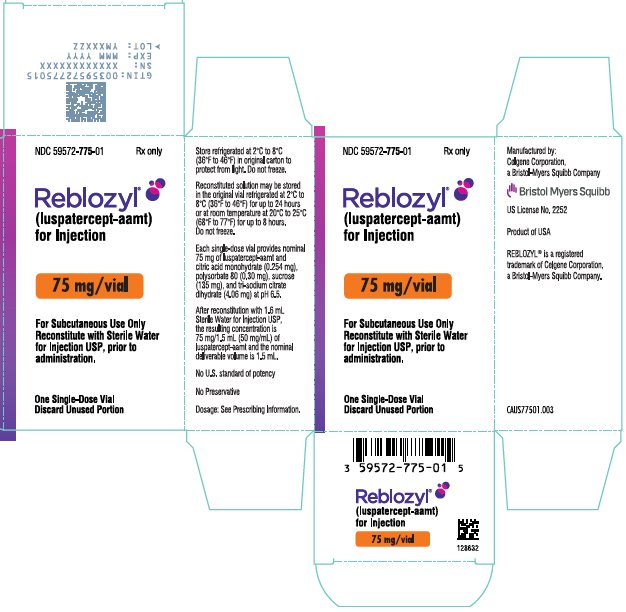
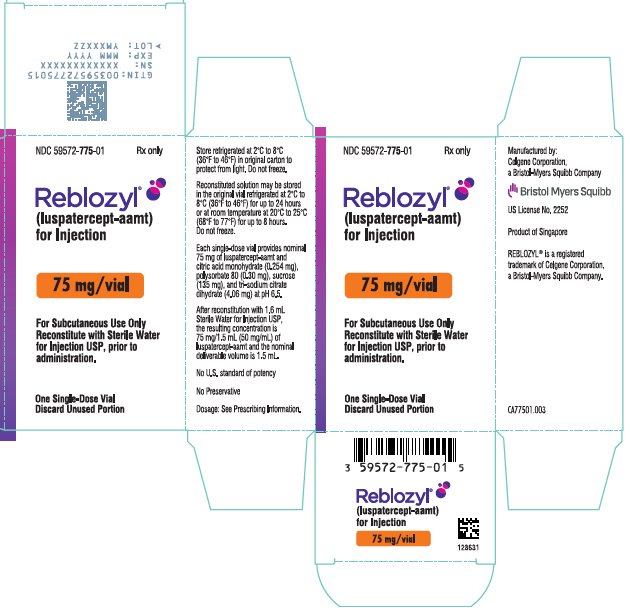
Table 5: Reconstitution Volumes Vial Size Amount of Sterile Water for Injection, USP required for reconstitution Final Concentration Deliverable Volume 25 mg vial
0.68 mL
25 mg/0.5 mL
(50 mg/mL)
0.5 mL
75 mg vial
1.6 mL
75 mg/1.5 mL
1.5 mL
(50 mg/mL)
Reconstitute the number of REBLOZYL vials to achieve the appropriate dose based on the patient’s weight. Use a syringe with suitable graduations for reconstitution to ensure accurate dosage.
Reconstitution Instructions
- 1.
- Reconstitute with Sterile Water for Injection, USP using volumes described in Table 5 (Reconstitution Volumes) with the stream directed onto the lyophilized powder. Allow to stand for one minute.
- 2.
- Discard the needle and syringe used for reconstitution. The needle and syringe used for reconstitution should not be used for subcutaneous injections.
- 3.
- Gently swirl the vial in a circular motion for 30 seconds. Stop swirling and let the vial sit in an upright position for 30 seconds.
- 4.
- Inspect the vial for undissolved particles in the solution. If undissolved powder is observed, repeat step 3 until the powder is completely dissolved.
- 5.
- Invert the vial and gently swirl in an inverted position for 30 seconds. Bring the vial back to the upright position, and let it sit for 30 seconds.
- 6.
- Repeat step 5 seven more times to ensure complete reconstitution of material on the sides of the vial.
- 7.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. REBLOZYL is a colorless to slightly yellow, clear to slightly opalescent solution which is free of foreign particulate matter. Do not use if undissolved product or foreign particulate matter are observed.
- 8.
- If the reconstituted solution is not used immediately:
- •
- Store at room temperature at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) in the original vial for up to 8 hours. Discard if not used within 8 hours of reconstitution.
- •
- Alternatively, store refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for up to 24 hours in the original vial. Remove from refrigerated condition 15-30 minutes prior to injection to allow solution to reach room temperature for a more comfortable injection. Discard if not used within 24 hours of reconstitution.
- •
- Do not freeze the reconstituted solution.
Discard any unused portion. Do not pool unused portions from the vials. Do not administer more than 1 dose from a vial. Do not mix with other medications.
Instructions for Subcutaneous Administration
Calculate the exact total dosing volume of 50 mg/mL solution required for the patient.
Slowly withdraw the dosing volume of the reconstituted REBLOZYL solution from the single-dose vial(s) into a syringe. Divide doses requiring larger reconstituted volumes (i.e., greater than 1.2 mL) into separate similar volume injections and inject into separate sites. If multiple injections are required, use a new syringe and needle for each subcutaneous injection.
Administer the injection subcutaneously into the upper arm, thigh, and/or abdomen.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Thrombosis/Thromboembolism
In adult patients with beta thalassemia, thromboembolic events (TEE) were reported in 8/223 (3.6%) REBLOZYL-treated patients. Reported TEEs included deep vein thromboses, pulmonary embolus, portal vein thrombosis, and ischemic strokes. Patients with known risk factors for thromboembolism, e.g. splenectomy or concomitant use of hormone replacement therapy, may be at further increased risk of thromboembolic conditions. Consider thromboprophylaxis in patients with beta thalassemia at increased risk of TEE.
Monitor patients receiving REBLOZYL for signs and symptoms of thromboembolic events and institute treatment promptly.
5.2 Hypertension
Hypertension was reported in 63/554 (11.4%) of REBLOZYL-treated patients. Across clinical studies, the incidence of Grade 3-4 hypertension ranged from 2% to 9.6%.
In adult patients with beta thalassemia with normal baseline blood pressure, 13 (6.2%) patients developed systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥130 mm Hg and 33 (16.6%) patients developed diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥80 mm Hg.
In ESA-refractory or -intolerant adult patients with MDS with normal baseline blood pressure, 26 (30%) patients developed SBP ≥130 mm Hg and 23 (16%) patients developed DBP ≥80 mm Hg. In ESA-naïve adult patients with MDS with normal baseline blood pressure, 23 (36%) patients developed SBP ≥140 mm Hg and 11 (6%) patients developed DBP ≥80 mm Hg.
Monitor blood pressure prior to each administration. Manage new-onset hypertension or exacerbations of preexisting hypertension using anti-hypertensive agents.
5.3 Extramedullary Hematopoietic Masses
In adult patients with transfusion dependent beta thalassemia, EMH masses were observed in 3.2% of REBLOZYL-treated patients, with spinal cord compression symptoms due to EMH masses occurring in 1.9% of patients (BELIEVE and REBLOZYL long-term follow-up study).
In a study of adult patients with non-transfusion dependent beta thalassemia, a higher incidence of EMH masses was observed in 6.3% of REBLOZYL-treated patients vs. 2% of placebo-treated patients in the double-blind phase of the study, with spinal cord compression due to EMH masses occurring in 1 patient with a prior history of EMH. REBLOZYL is not indicated for use in patients with non-transfusion dependent beta-thalassemia.
Possible risk factors for the development of EMH masses in patients with beta thalassemia include history of EMH masses, splenectomy, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, or low baseline hemoglobin (<8.5 g/dL). Signs and symptoms may vary depending on the anatomical location. Monitor patients with beta thalassemia at initiation and during treatment for symptoms and signs or complications resulting from the EMH masses and treat according to clinical guidelines. Discontinue treatment with REBLOZYL in case of serious complications due to EMH masses. Avoid use of REBLOZYL in patients requiring treatment to control the growth of EMH masses.
5.4 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal reproductive studies, REBLOZYL may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, administration of luspatercept-aamt to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis resulted in adverse developmental outcomes including increased embryo-fetal mortality, alterations to growth, and structural abnormalities at exposures (based on area under the curve [AUC]) above those occurring at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 1.75 mg/kg.
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use an effective method of contraception during treatment with REBLOZYL and for at least 3 months after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- •
- Thrombosis/Thromboembolism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- •
- Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- •
- Extramedullary Hematopoietic Masses [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data in the WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS reflect exposure to REBLOZYL as a single agent administered across a range of doses (0.125 mg/kg to 1.75 mg/kg) in 571 patients in 4 trials.
Beta Thalassemia
The safety of REBLOZYL in patients with beta thalassemia was evaluated in the BELIEVE trial [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].Key eligibility criteria included adult patients with beta thalassemia (with the exception of patients with hemoglobin S or alpha-thalassemia disease) without major organ damage or recent DVT stroke and platelet counts less than or equal to 1000 x 109/L.
Patients received a starting dose of REBLOZYL 1 mg/kg subcutaneous injection every 3 weeks. Overall, 53% of patients had their dose increased to 1.25 mg/kg (46% REBLOZYL, n = 223) or placebo (66%, n = 109). The median duration of treatment was similar between the REBLOZYL and placebo arms (63.3 weeks vs. 62.1 weeks, respectively). Per protocol, patients in the REBLOZYL and placebo arms were to remain on therapy for at least 48 weeks in the double-blind phase of the trial.
Among patients receiving REBLOZYL, 94% were exposed for 6 months or longer and 72% were exposed for greater than one year.
The median age of patients who received REBLOZYL was 30 years (range: 18, 66); 59% female; 54% White and 36% Asian.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 3.6% of patients on REBLOZYL. Serious adverse reactions reported in 1% of patients were cerebrovascular accident and deep vein thrombosis. A fatal adverse reaction occurred in one patient treated with REBLOZYL who died due to an unconfirmed case of AML (M6).
Permanent discontinuation due to an adverse reaction (Grades 1-4) occurred in 5.4% of patients who received REBLOZYL. Most frequent adverse reactions requiring permanent discontinuation in patients who received REBLOZYL included arthralgia (1%), back pain (1%), bone pain (<1%), and headache (<1%).
Dosage reductions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 2.7% of patients who received REBLOZYL. Most frequent adverse reactions requiring dosage reduction in >0.5% of patients who received REBLOZYL included hypertension and headache.
Dosage interruptions due to an adverse reaction occurred in 15.2% of patients who received REBLOZYL. Most frequent adverse reactions requiring dosage interruption in >1% of patients who received REBLOZYL included upper respiratory tract infection, ALT increase, and cough.
The most common adverse reactions (at least 10% for REBLOZYL and 1% more than placebo) were headache (26%), bone pain (20%), arthralgia (19%), fatigue (14%), cough (14%), abdominal pain (14%), diarrhea (12%), and dizziness (11%).
Table 6 summarizes the adverse reactions in BELIEVE.
Table 6: Adverse Drug Reactions (>5%) in Patients with Beta Thalassemia Receiving REBLOZYL with a Difference Between Arms of 1% in BELIEVE Trial Body System REBLOZYL
(N=223)Placebo
(N=109)Adverse Reaction All Grades
n (%)Grades ≥3a
n (%)All Grades
n (%)Grades ≥3
n (%)a Limited to Grade 3 reactions with the exception of 4 events of Grade 4 hyperuricemia.
b Grouped term includes abdominal pain and abdominal pain upper.
c Grouped term includes essential hypertension, hypertension, and hypertensive crisis.Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Bone Pain
44 (20)
3 (1)
9 (8)
0 (0)
Arthralgia
43 (19)
0 (0)
13 (12)
0 (0)
Infections and infestation
Influenza
19 (9)
0 (0)
6 (6)
0 (0)
Viral Upper Respiratory Infection
14 (6)
1 (0.4)
2 (2)
0 (0)
Nervous system disorders
Headache
58 (26)
1 (<1)
26 (24)
1 (1)
Dizziness
25 (11)
0 (0)
5 (5)
0 (0)
General disorders and administration site conditions
Fatigue
30 (14)
0 (0)
14 (13)
0 (0)
Gastrointestinal disorders
Abdominal Pain b
31 (14)
0 (0)
13 (12)
0 (0)
Diarrhea
27 (12)
1 (<1)
11 (10)
0 (0)
Nausea
20 (9)
0 (0)
6 (6)
0 (0)
Vascular disorders
Hypertension c
18 (8)
4 (2)
3 (3)
0 (0)
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
Hyperuricemia
16 (7)
6 (3)
0 (0)
0 (0)
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Cough
32 (14)
0 (0)
12 (11)
0 (0)
Clinically relevant adverse reactions in <5% of patients include vertigo/vertigo positional, syncope/presyncope, injection site reactions, hypersensitivity, extramedullary hematopoietic masses, and spinal cord compression.
Liver function abnormalities in the BELIEVE trial are shown in Table 7.
Table 7: Liver Function Laboratory Abnormalities in Patients with Beta Thalassemia in the BELIEVE Trial REBLOZYL
N = 223
n (%)Placebo
N = 109
n (%)ALP = alkaline phosphatase; ALT = alanine aminotransferase;
AST = aspartate aminotransferase; ULN = upper limit of normal.ALT ≥ 3 × ULN
26 (12)
13 (12)
AST ≥ 3 × ULN
25 (11)
5 (5)
ALP ≥ 2 × ULN
17 (8)
1 (<1)
Total bilirubin ≥ 2 × ULN
143 (64)
51 (47)
Direct bilirubin ≥ 2 × ULN
13 (6)
4 (4)
Treatment of Myelodysplastic Syndromes Associated Anemia in ESA-naïve Patients
The safety of REBLOZYL in patients with very low‑ to intermediate‑risk myelodysplastic syndromes was evaluated in the COMMANDS trial in 356 randomized patients [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. Key eligibility criteria included adult patients who were ESA‑naïve with endogenous sEPO levels of < 500 U/L and who required regular RBC transfusions.
The median time on treatment with REBLOZYL was 41.6 weeks (range, 0 – 165 weeks); 71.3% of patients were exposed for 24 weeks and 45.5% completed 48 weeks of treatment.
Among the 178 patients treated with REBLOZYL, 17 (9.6%) discontinued due to an adverse reaction, 48 (27%) had a dose interruption due to an adverse reaction, and 5 (2.8%) had a dose reduction due to an adverse reaction. The most common (>10%) all‑grade adverse reactions included diarrhea, fatigue, hypertension, edema peripheral, nausea, and dyspnea. The most common (>2%) Grade > 3 adverse reactions included hypertension and dyspnea. Selected laboratory abnormalities that changed from Grade 0‑2 at baseline to Grade > 2 at any time during the studies in at least 10% of patients were glomerular filtration rate and total bilirubin increased.
Table 8 shows the most common adverse reactions for patients treated with REBLOZYL or epoetin alfa in the COMMANDS trial [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Table 8: Adverse Reactions (≥5%) in Patients Receiving REBLOZYL in COMMANDS Trial a Reaction includes similar/grouped terms.
b Includes asthenic conditions.Body System /Adverse Reaction
REBLOZYL
(N=178)
Epoetin Alfa
(N=176)
All Grades
n (%)
Grade ≥3
n (%)
All Grades
n (%)
Grade ≥3
n (%)
General disorders and administration site conditions
Fatigue a,b
38 (22)
0 (0)
12 (7)
0 (0)
Edema peripheral
23 (13)
0 (0)
12 (7)
0 (0)
Non-cardiac chest pain
9 (5)
1 (1)
6 (3)
0 (0)
Pyrexia
9 (5)
1 (1)
12 (7)
1 (1)
Gastrointestinal disorders
Diarrhea
26 (15)
0 (0)
20 (11)
0 (0)
Nausea
21 (12)
0 (0)
13 (7)
0 (0)
Vascular disorders
Hypertension a
25 (14)
17 (10)
13 (7)
9 (5)
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Dyspnea
21 (12)
7 (4)
13 (7)
2 (1)
Dyspnea exertional
9 (5)
0 (0)
1 (1)
0 (0)
Nervous system disorders
Dizziness
16 (9)
1 (1)
15 (9)
0 (0)
Headache
15 (8)
0 (0)
12 (7)
1 (1)
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Back Pain
16 (9)
2 (1)
13 (7)
3 (2)
Arthralgia
10 (6)
0 (0)
14 (8)
0 (0)
Myalgia
9 (5)
0 (0)
5 (3)
0 (0)
Osteoarthritis
9 (5)
1 (1)
4 (2)
0 (0)
Infections and infestations
COVID-19
19 (11)
6 (3)
17 (10)
2 (1)
Urinary tract infection
13 (7)
0 (0)
7 (4)
0 (0)
Pneumonia
8 (5)
7 (4)
15 (9)
11 (6)
Metabolism and nutrition disorders
Hyperuricemia
12 (7)
1 (1)
10 (6)
1 (1)
Decreased appetite
8 (5)
0 (0)
11 (6)
0 (0)
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Thrombocytopenia
11 (6)
7 (4)
3 (2)
1 (1)
Neutropenia
9 (5)
7 (4)
13 (7)
10 (6)
Psychiatric disorders
Insomnia
9 (5)
0 (0)
6 (3)
0 (0)
Other clinically relevant adverse reactions reported in <5% of patients are injection site reactions, including erythema, pruritus, and rash.
Shifts from Grades 0‑2 at baseline to Grades 2‑3 abnormalities for selected laboratory tests in the COMMANDS trial are shown in Table 9.
Table 9: Selected Treatment‑Emergent Laboratory Abnormalities in COMMANDS Trial that Shift to Grades 2‑3 a Number of patients at Grades 0-1 at baseline.
b GFR= glomerular filtration rate (mL/min)Parameter
REBLOZYL
Epoetin Alfa
N a
n (%)
N a
n (%)
Total bilirubin
171
38 (22)
165
19 (12)
GFR b
171
60 (35)
167
36 (22)
Myelodysplastic Syndromes with Ring Sideroblasts or Myelodysplastic / Myeloproliferative Neoplasm with Ring Sideroblasts and Thrombocytosis Associated Anemia in ESA-refractory or -intolerant patients
The safety of REBLOZYL at the recommended dose and schedule was evaluated in 242 patients with MDS with ring sideroblasts (n=192) or other myeloid neoplasms (n=50) in the MEDALIST trial. The safety population included 63% males and 37% females of median age 72 years (range, 30 – 95 years); of these patients, 81% were White, 0.4% Black, 0.4% Other, and race was not reported in 18.2% of patients. The median time on treatment with REBLOZYL was 50.4 weeks (range, 3 – 221 weeks); 67% of patients were exposed for 6 months or longer and 49% were exposed for greater than one year.
Among the 242 patients treated with REBLOZYL, 5 (2.1%) had a fatal adverse reaction, 11 (4.5%) discontinued due to an adverse reaction, and 7 (2.9%) had a dose reduction due to an adverse reaction. The most common (≥10%) all-grade adverse reactions included fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, dizziness, diarrhea, nausea, hypersensitivity reactions, hypertension, headache, upper respiratory tract infection, bronchitis, and urinary tract infection. The most common (≥2%) Grade ≥ 3 adverse reactions included fatigue, hypertension, syncope and musculoskeletal pain. Selected laboratory abnormalities that changed from Grade 0-1 at baseline to Grade ≥ 2 at any time during the studies in at least 10% of patients included creatinine clearance decreased, total bilirubin increased, and alanine aminotransferase increased.
Table 10 shows the most common adverse reactions for patients treated with REBLOZYL or placebo through the first 8 cycles in the MEDALIST trial [see Clinical Studies (14.3)].
Table 10: Adverse Reactions (≥5%) in Patients Receiving REBLOZYL with a Difference Between Arms of >2% in MEDALIST Trial Through Cycle 8 Body System /Adverse Reaction REBLOZYL
(N=153)Placebo
(N=76)All Grades
n (%)Grade 3
n (%)All Grades
n (%)Grade 3
n (%)a Includes asthenic conditions.
b Reaction includes similar/grouped terms.General disorders and administration site conditions
Fatigue a, b
63 (41)
11 (7)
17 (22)
2 (3)
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Musculoskeletal pain b
30 (20)
3 (2)
11 (14)
0 (0)
Nervous system disorders
Dizziness/vertigo
28 (18)
1 (<1)
5 (7)
1 (1)
Headache b
21 (14)
0 (0)
5 (7)
0 (0)
Syncope / presyncope
8 (5)
5 (3)
0 (0)
0 (0)
Gastrointestinal disorders
Nausea b
25 (16)
1 (<1)
8 (11)
0 (0)
Diarrhea b
25 (16)
0 (0)
7 (9)
0 (0)
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorder
Dyspnea b
20 (13)
2 (1)
4 (5)
1 (1)
Immune system disorders
Hypersensitivity reactions b
15 (10)
1 (<1)
5 (7)
0 (0)
Renal and urinary disorders
Renal impairment b
12 (8)
3 (2)
3 (4)
0 (0)
Cardiac disorders
Tachycardia b
12 (8)
0 (0)
1 (1)
0 (0)
Injury poisoning and procedural complications
Injection site reactions
10 (7)
0 (0)
3 (4)
0 (0)
Infections and infestations
Upper respiratory tract infection
10 (7)
1 (<1)
2 (3)
0 (0)
Influenza / influenza like illness
9 (6)
0 (0)
2 (3)
0 (0)
Other clinically relevant adverse reactions reported in <5% of patients include bronchitis, urinary tract infection, and hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Shifts from Grades 0-1 to Grades 2-4 abnormalities for selected laboratory tests during the first 8 cycles in the MEDALIST trial are shown in Table 11.
Table 11: Selected Grades 2-4 Treatment-Emergent Laboratory Abnormalities Through Cycle 8 in the MEDALIST Trial a Number of patients at Grades 0-1 at baseline.
ALT = alanine aminotransferase; AST = aspartate aminotransferase.Parameter
REBLOZYL
Placebo
Na
n (%)
Na
n (%)
ALT elevated
151
13 (9)
74
5 (7)
AST elevated
152
6 (4)
76
0 (0)
Total bilirubin elevated
140
17 (12)
66
3 (5)
Creatinine clearance reduced
113
30 (27)
62
13 (21)
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings in animal reproduction studies, REBLOZYL may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data on REBLOZYL use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In animal reproduction studies, administration of luspatercept-aamt to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in adverse developmental outcomes including embryo-fetal mortality, alterations to growth, and structural abnormalities at exposures (based on area under the curve [AUC]) above those occurring at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In embryo-fetal development studies, luspatercept-aamt was administered subcutaneously at 5, 15, or 30 mg/kg on gestation days 3 and 10 (rats) or 5, 20, or 40 mg/kg on gestation days 4 and 11 (rabbits). Effects in both species included reductions in numbers of live fetuses and fetal body weights, and increases in resorptions, post-implantation losses, and skeletal variations (such as asymmetric sternal centra in rats and angulated hyoid in rabbits). Effects were observed at exposures (based on AUC) approximately 7-times (rats) and 16-times (rabbits) the MRHD of 1.75 mg/kg.
In a pre- and postnatal development study, pregnant rats were administered luspatercept-aamt subcutaneously at 3, 10, or 30 mg/kg once every 2 weeks during organogenesis and through weaning, gestation day 6 through postnatal day 20. At all dose levels lower F1 pup body weights and adverse kidney findings (such as membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, tubular atrophy/hypoplasia, and vessel ectasia occasionally associated with hemorrhage) were observed. These effects were observed at exposures (based on AUC) approximately 1.6-times the MRHD of 1.75 mg/kg.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Luspatercept-aamt was detected in milk of lactating rats. When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that the drug will be present in human milk. There are no data on the presence of REBLOZYL in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in the breastfed child, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with REBLOZYL, and for 3 months after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Pregnancy testing is recommended for females of reproductive potential before starting REBLOZYL treatment.
Contraception
Females
REBLOZYL may cause embryo-fetal harm when administered to pregnant women [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Advise female patients of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with REBLOZYL and for at least 3 months after the last dose.
Infertility
Females
Based on findings in animals, REBLOZYL may impair female fertility [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. Adverse effects on fertility in female rats were reversible after a 14-week recovery period.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established. Based on findings in juvenile animals, REBLOZYL is not recommended for use in pediatric patients [see Non-Clinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of REBLOZYL in beta thalassemia did not include sufficient numbers of patients age 65 years and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients.
Clinical studies of REBLOZYL for treatment of anemia in ESA-naïve and ESA-refractory or -intolerant MDS included 347 (82%) patients ≥ 65 years of age and 167 (39%) patients ≥ 75 years of age. No differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between older (≥ 65 years) and younger patients.
-
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.2 Abuse
Abuse is the intentional, non-therapeutic use of a drug, even once, for its desirable psychological or physiological effects. Abuse of REBLOZYL may be seen in athletes for the effects on erythropoiesis to enhance athletic performance. Abuse of drugs that increase erythropoiesis, such as REBLOZYL, by healthy persons may lead to polycythemia, which may be associated with life-threatening cardiovascular complications (e.g., stroke, myocardial infarction, and thromboembolism).
Luspatercept-aamt and its metabolites neither selectively penetrate the central nervous system, nor produce behavioral effects in animals that are consistent with central nervous system activity.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Luspatercept-aamt is an erythroid maturation agent. Luspatercept-aamt is a receptor fusion protein consisting of a modified extracellular domain of the human activin receptor type IIB linked to a human IgG1 Fc domain with a calculated molecular mass of approximately 76 kD. Luspatercept is produced in Chinese hamster ovary cells by recombinant DNA technology.
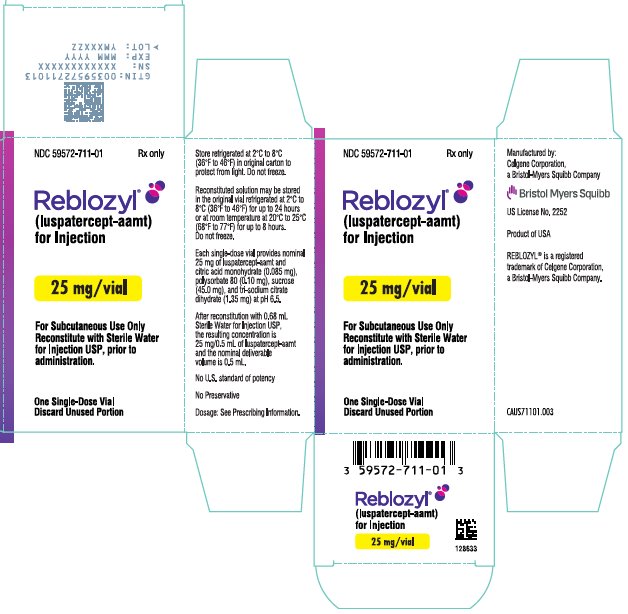
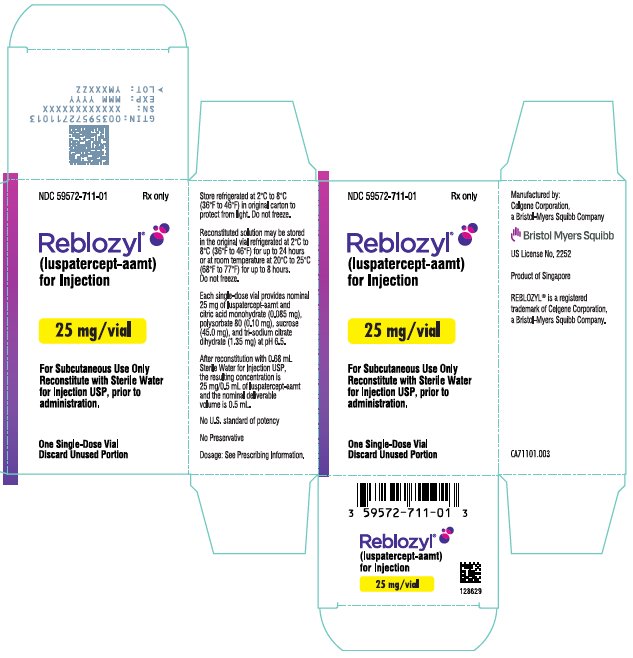
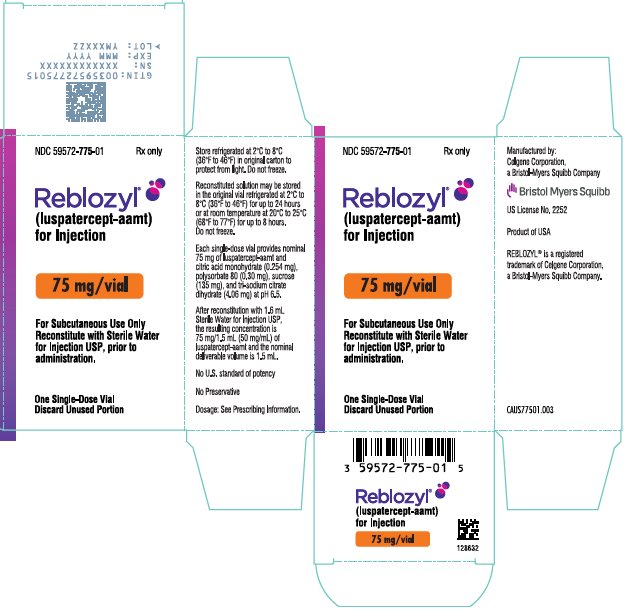
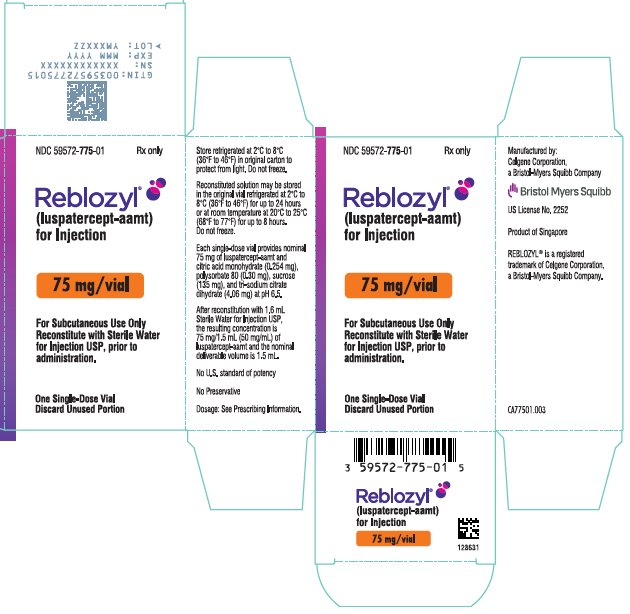
REBLOZYL (luspatercept-aamt) for injection is a sterile, preservative-free, white to off-white, lyophilized powder in single-dose vials for subcutaneous use after reconstitution.
Each 25 mg single-dose vial provides nominal 25 mg of luspatercept-aamt and citric acid monohydrate (0.085 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.10 mg), sucrose (45.0 mg), and tri-sodium citrate dihydrate (1.35 mg) at pH 6.5. After reconstitution with 0.68 mL Sterile Water for Injection USP, the resulting concentration is 25 mg/0.5 mL of luspatercept-aamt and the nominal deliverable volume is 0.5 mL.
Each 75 mg single-dose vial provides nominal 75 mg of luspatercept-aamt and citric acid monohydrate (0.254 mg), polysorbate 80 (0.30 mg), sucrose (135 mg), and tri-sodium citrate dihydrate (4.06 mg) at pH 6.5. After reconstitution with 1.6 mL Sterile Water for Injection USP, the resulting concentration is 75 mg/1.5 mL (50 mg/mL) of luspatercept-aamt and the nominal deliverable volume is 1.5 mL.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Luspatercept-aamt is a recombinant fusion protein that binds several endogenous TGF-β superfamily ligands, thereby diminishing Smad2/3 signaling. In models of β-thalassemia and MDS, luspatercept-aamt decreased abnormally elevated Smad2/3 signaling and improved hematology parameters associated with ineffective erythropoiesis in mice. Luspatercept-aamt promoted erythroid maturation through differentiation and increasing the percentage of late-stage erythroid precursors (normoblasts) in the bone marrow of mice and increased erythroid precursors in humans, thereby increasing erythropoiesis.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Increases in Hemoglobin in Patients with Low RBC Transfusion Burden
In patients having received < 4 units of RBC transfusion within 8 weeks prior to study, hemoglobin increased within 7 days of initiating REBLOZYL and correlated with the time to luspatercept-aamt maximum serum concentration (Cmax). The greatest hemoglobin (Hgb) increase occurred after the first dose; approximately 0.75 g/dL at a dose of 0.6 to 1.25 times the recommended starting dose for beta thalassemia, or approximately 1 g/dL at a dose of 0.75 to 1.75 times the recommended starting dose for MDS. Additional smaller increases were observed after subsequent doses. Hemoglobin levels returned to baseline approximately 6 to 8 weeks from the last dose following administration of luspatercept-aamt (0.6 to 1.75 mg/kg).
Increasing luspatercept-aamt serum exposure (AUC) was associated with greater Hgb increase in patients with beta thalassemia or MDS who had a baseline transfusion burden < 4 units/8 weeks. Increasing luspatercept-aamt serum exposure (time-averaged AUC) was associated with greater probability of achieving transfusion independence for at least 8 consecutive weeks in ESA-refractory or -intolerant patients with MDS requiring transfusions (≥ 2 units of RBC transfusion within 8 weeks).
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Luspatercept-aamt exhibited linear pharmacokinetics (PK) over the dose range of 0.2 to 1.25 mg/kg (0.2 to 1.25 times the recommended starting dosage) in patients with beta thalassemia, and from 0.125 mg/kg to 1.75 mg/kg (0.125 to 1.75 times the recommended starting dosage) in patients with MDS. The geometric mean (% coefficient of variation [%CV]) steady-state AUC at the starting dose of 1 mg/kg was 126 (35.9%) day•µg/mL for patients with beta thalassemia and 154 (37.4%) day•µg/mL for patients with MDS. Luspatercept-aamt serum concentration reached steady state after 3 doses when administered every 3 weeks. The accumulation ratio of luspatercept-aamt was approximately 1.5.
Absorption
The median [range] time to maximum concentration (Tmax) of luspatercept-aamt was observed at approximately 5 [3 to 8] days post-dose in adult patients with beta thalassemia or 6 [3 to 7] days post-dose in adult patients with MDS. The absorption of luspatercept-aamt was not significantly affected by the subcutaneous injection sites (upper arm, thigh, or abdomen).
Distribution
The geometric mean (%CV) apparent volume of distribution (Vd/F) of luspatercept-aamt was 7.1 (26.7%) L for patients with beta thalassemia and 9.6 (26.7%) L for patients with MDS.
Elimination
The geometric mean (%CV) half-lives (t1/2) of luspatercept-aamt were approximately 11 (25.7%) days in patients with beta thalassemia and 14 (31.7%) days in patients with MDS. The geometric mean (%CV) apparent total clearance (CL/F) of luspatercept-aamt was 0.44 (38.5%) L/day in patients with beta thalassemia and 0.47 (42.9%) L/day in patients with MDS.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the luspatercept-aamt PK were observed based on age (18 to 95 years), sex, race/ethnicity (Asian, White), mild to severe hepatic impairment (total bilirubin ≤ upper limit of normal [ULN] and aspartate aminotransaminase [AST] or alanine transaminase [ALT] > ULN, or total bilirubin > ULN and any AST or ALT), mild to moderate renal impairment (estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] 30 to 89 mL/min), baseline albumin (30 to 56 g/L), baseline serum erythropoietin (2.4 to 2920 U/L), red blood cell (RBC) transfusion burden (0 to 43 units/24 weeks), beta thalassemia genotype (β0/β0 vs. non-β0/β0), splenectomy, and ring sideroblasts status in MDS (negative vs. positive). The effect of AST or ALT >3 x ULN and the effect of severe renal impairment (eGFR <30 mL/min) on luspatercept-aamt PK is unknown.
12.6 Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies (ADA) is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies, including those of REBLOZYL or of other luspatercept products.
In the BELIEVE trial, the median duration of exposure was 64 weeks, with a median ADA sampling period of 50 weeks. Of the 220 patients in the BELIEVE trial with beta thalassemia who require regular RBC transfusions treated with REBLOZYL and evaluable for the presence of anti-luspatercept-aamt antibodies, 4 patients (1.81%) tested positive for treatment-emergent anti-luspatercept-aamt antibodies, including 2 patients (0.9%) who had neutralizing antibodies detected. The majority of anti-luspatercept-aamt antibodies were of low titers.
In the COMMANDS trial, the median duration of exposure was 42 weeks, with the median ADA sampling period of 27 weeks. In the MEDALIST trial, the median duration of exposure was 49 weeks, with the median ADA sampling period of 46 weeks. Of the 331 ESA-naïve (COMMANDS trial) and ESA-refractory or -intolerant (MEDALIST trial) patients with MDS who were treated with REBLOZYL, 21 patients (6.3%) tested positive for treatment-emergent anti-luspatercept-aamt antibodies, including 14 patients (4.2%) who had neutralizing antibodies. The majority of anti-luspatercept-aamt antibodies were of low titers.
There were no severe acute systemic hypersensitivity reactions reported for patients with anti-luspatercept-aamt antibodies in REBLOZYL clinical trials, and there was no association between hypersensitivity type reaction or injection site reaction and presence of anti-luspatercept-aamt antibodies. There was no apparent effect of anti-luspatercept-aamt antibodies on clinical response.
Anti-Drug Antibody Effects on Pharmacokinetics
Among patients in the BELIEVE trial with luspatercept-aamt exposure data available, luspatercept‑aamt mean trough concentration (Ctrough) was approximately 35% lower in 4 patients with beta thalassemia who tested positive for treatment‑emergent anti‑luspatercept‑aamt antibodies (2.19 μg/mL) compared to patients with beta thalassemia who did not develop treatment‑emergent anti‑luspatercept‑aamt antibodies (3.38 μg/mL). There is insufficient data to assess whether the observed anti-luspatercept-aamt antibody associated pharmacokinetic changes reduce effectiveness in patients with beta thalassemia.
Among 21 ESA-naïve and ESA-refractory or -intolerant patients with MDS in the COMMANDS and MEDALIST trials who tested positive for treatment-emergent anti‑luspatercept‑aamt antibodies, there were no identified clinically significant effects of anti‑luspatercept‑aamt antibodies on pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, safety, or effectiveness of luspatercept‑aamt over the treatment duration.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No carcinogenicity or mutagenicity studies have been conducted with luspatercept-aamt.
In a repeat-dose toxicity study, juvenile rats were administered luspatercept-aamt subcutaneously at 1, 3, or 10 mg/kg once every 2 weeks from postnatal day 7 to 91. Hematologic malignancies (granulocytic leukemia, lymphocytic leukemia, malignant lymphoma) were observed at 10 mg/kg resulting in exposures (based on area under the curve [AUC]) approximately 4.4 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 1.75 mg/kg.
In a combined male and female fertility and early embryonic development study in rats, luspatercept-aamt was administered subcutaneously to animals at doses of 1 to 15 mg/kg. There were significant reductions in the average numbers of corpora lutea, implantations, and viable embryos in luspatercept-aamt-treated females. Effects on female fertility were observed at the highest dose with exposures (based on AUC) approximately 7-times the MRHD of 1.75 mg/kg. Adverse effects on fertility in female rats were reversible after a 14-week recovery period. No adverse effects were noted in male rats.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Beta Thalassemia
The efficacy of REBLOZYL was evaluated in adult patients with beta thalassemia in the BELIEVE trial (NCT02604433). BELIEVE was a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in which (n=336) patients with beta thalassemia requiring regular red blood cell transfusions (6-20 RBC units per 24 weeks) with no transfusion-free period greater than 35 days during that period were randomized 2:1 to REBLOZYL (n=224) or placebo (n=112). In BELIEVE, REBLOZYL was administered subcutaneously once every 3 weeks as long as a reduction in transfusion requirement was observed or until unacceptable toxicity. All patients were eligible to receive best supportive care, which included RBC transfusions; iron-chelating agents; use of antibiotic, antiviral, and antifungal therapy; and/or nutritional support, as needed.
The BELIEVE trial excluded patients with a diagnosis of Hemoglobin S/β-thalassemia or isolated alpha (α)-thalassemia (e.g., Hemoglobin H) or who had major organ damage (liver disease, heart disease, lung disease, renal insufficiency). Patients with recent deep vein thrombosis or stroke or recent use of ESA, immunosuppressant, or hydroxyurea therapy were also excluded. The median age was 30 years (range: 18-66). The trial was comprised of patients who were 42% male, 54.2% White, 34.8% Asian, and 0.3% Black or African American. The percent of patients reporting their race as “other” was 7.7%, and race was not collected or reported for 3% of patients.
Table 12 summarizes the baseline disease-related characteristics in the BELIEVE study.
Table 12: Baseline Disease Characteristics of Patients with Beta Thalassemia in BELIEVE HbE=hemoglobin E.
a "Missing" category includes patients in the population who had no result for the parameter listed.Disease Characteristic
REBLOZYL
(N=224)Placebo
(N=112)Beta thalassemia diagnosis, n (%)
Beta-thalassemia
174 (77.7)
83 (74.1)
HbE/beta thalassemia
31 (13.8)
21 (18.8)
Beta thalassemia combined with alpha-thalassemia
18 (8)
8 (7.1)
Missing a
1 (0.4)
0
Baseline transfusion burden 12 weeks prior to randomization
Median (min, max) (Units/12 weeks)
6.12 (3, 14)
6.27 (3, 12)
Beta thalassemia gene mutation grouping, n (%)
β0/β0
68 (30.4)
35 (31.3)
Non-β0/β0
155 (69.2)
77 (68.8)
Missing a
1 (0.4)
0
Baseline serum ferritin level (μg/L)
N
220
111
Median (min, max)
1441.25 (88, 6400)
1301.50 (136, 6400)
Splenectomy, n (%)
Yes
129 (57.6)
65 (58)
No
95 (42.4)
47 (42)
Age patient started regular transfusions (years)
N
169
85
Median (min, max)
2 (0, 52)
2 (0, 51)
The efficacy of REBLOZYL in adult patients with beta thalassemia was established based upon the proportion of patients achieving RBC transfusion burden reduction (≥33% reduction from baseline) with a reduction of at least 2 units from Week 13 to Week 24.
Efficacy results are shown in Table 13.
Table 13: Efficacy Results in Beta Thalassemia - BELIEVE Endpoint
REBLOZYL
(N=224)Placebo
(N=112)Risk Difference
(95% CI)p-value
≥33% Reduction from baseline in RBC transfusion burden with a reduction of at least 2 units for 12 consecutive weeks
Primary endpoint – Week 13 to Week 24
47 (21.0)
5 (4.5)
16.5 (9.9, 23.1)
<0.0001
Week 37 to Week 48
44 (19.6)
4 (3.6)
16.1 (9.8, 22.4)
<0.0001
≥50% Reduction from baseline in RBC transfusion burden with a reduction of at least 2 units for 12 consecutive weeks
Week 13 to Week 24
16 (7.1)
2 (1.8)
5.4 (1.2, 9.5)
0.0402
Week 37 to Week 48
23 (10.3)
1 (0.9)
9.4 (5, 13.7)
0.0017
14.2 Treatment of Myelodysplastic Syndromes with Associated Anemia in ESA-naïve Patients
The efficacy of REBLOZYL was evaluated in the COMMANDS trial (NCT03682536), a multi‑center, open‑label, randomized active‑controlled trial comparing REBLOZYL versus epoetin alfa in patients with anemia due to IPSS‑R very low, low, or intermediate‑risk myelodysplastic syndromes or with myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasm with ring sideroblasts and thrombocytosis (MDS/MPN RS‑T) in ESA‑naïve patients (with endogenous sEPO levels of < 500 U/L) who require regular red blood cell transfusions. For eligibility, patients were required to have had 2 to 6 RBC units/8 weeks confirmed for a minimum of 8 weeks immediately preceding randomization.
The COMMANDS trial included 356 patients randomized 1:1 to REBLOZYL (N=178) or epoetin alfa (N=178). Randomization was stratified by RBC transfusion burden, RS status, and endogenous serum erythropoietin (sEPO) level at baseline. Treatment was started at 1 mg/kg subcutaneously every 3 weeks. Two dose level increases were allowed (to 1.33 mg/kg and to 1.75 mg/kg). Doses were held and subsequently reduced for adverse reactions, reduced if the hemoglobin increased by ≥ 2 g/dL from the prior cycle, and held if the predose hemoglobin was ≥ 12 g/dL.
All patients received best supportive care, which included RBC transfusions as needed. Patients were treated for 24 weeks and were assessed for efficacy at that time point. Treatment beyond 24 weeks was optional based upon response to treatment and absence of disease progression.
The median age of the 356 study participants was 74 years (range: 33, 93 years). The trial population was 56% male and 44% female; 79.5% were White, 0.6% Black or African American, 12.1% Asian, and race was not reported in 7.9% of patients. Ethnicities were reported as 85.4% for Not Hispanic or Latino patients, 6.5% for Hispanic or Latino patients, 7.6% for patients with no ethnicity reported, and 0.6% were unknown. IPSS‑R risk classification at baseline was 9.3% very low, 72.2% low, 17.4% intermediate, 0.3% high, and 0.8% missing. Table 14 summarizes the baseline disease‑related characteristics in the COMMANDS study.
Table 14: Baseline Disease Characteristics of Patients in COMMANDS Disease Characteristic
REBLOZYL
(N=178)
Epoetin Alfa
(N=178)
Hemoglobin (g/dL) – n (%)
Median (min, max)
7.80 (4.7, 9.2)
7.80 (4.5, 10.2)
Serum EPO (U/L) – n (%)
Median (min, max)
78.7 (7.8, 495.8)
85.9 (4.6, 462.5)
IPSS-R risk classification at baseline – n (%)
Very low
16 (9.0)
17 (9.6)
Low
126 (70.8)
131 (73.6)
Intermediate
34 (19.1)
28 (15.7)
High
1 (0.6)
0 (0)
Missing
1 (0.6)
2 (1.1)
Ring sideroblast status (per WHO criteria) – n (%)
RS+
130 (73.0)
128 (71.9)
RS-
48 (27.0)
49 (27.5)
Missing
0 (0)
1 (0.6)
SF3B1 mutation status – n (%)
Mutated
111 (62.4)
99 (55.6)
Non-mutated
65 (36.5)
72 (40.4)
Missing
2 (1.1)
7 (3.9)
The efficacy of REBLOZYL in the treatment of anemia in ESA‑naïve adult patients with MDS was established at the time of the interim efficacy analysis based upon the proportion of patients who experienced both red blood cell transfusion independence (RBC‑TI) [defined as the absence of any RBC transfusion during any consecutive 12‑week period] and an associated concurrent mean improvement in hemoglobin by at least 1.5 g/dL for any consecutive 12 week period during Weeks 1-24.
At the time of the interim efficacy analysis, 301 subjects were included in the efficacy analysis, of which 147 were in the luspatercept arm and 154 were in the epoetin alfa arm, which is about 85% of the total information. The key efficacy results are shown in Table 15.
Table 15: Key Efficacy Results in COMMANDS EOT = End of treatment; HI-E = Hematologic Improvement – Erythroid Response; NE = Not Estimable; RBC-TI = red blood cell transfusion independence
a The majority of study participants (>90%) were outside of the United States and a non-U.S.-licensed epoetin alfa product was used in the control arm for such patients. Direct comparisons have not been established between REBLOZYL and U.S. licensed epoetin alfa product for the treatment of patients with anemia due to IPSS-R very low, low, or intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndromes or MDS/MPN RS-T in ESA-naïve patients.
b Common rate difference is based on the Mantel-Haenszel stratum weights.
c Based on CMH test stratified by baseline RBC transfusion burden (< 4, ≥ 4 pRBC units), RS status (RS+, RS-) and sEPO level (≤ 200, > 200 U/L). 2-sided p-value is presented. The statistical significance level at the second interim analysis is two-sided p-value 0.03.Endpoint
REBLOZYL
(N=147)
Epoetin Alfa a
(N=154)
RBC-TI for ≥12 weeks with associated concurrent mean Hgb increase of ≥ 1.5 g/dL (Weeks 1-24)
Response rate, n (%)
(95% CI)
86 (58.5)
(50.1, 66.6)
48 (31.2)
(24.0, 39.1)
Common Rate Difference (95% CI) b
26.6 (15.8, 37.4)
p-value c
<0.0001
Mean Hgb increase ≥ 1.5 g/dL (Weeks 1-24)
Response rate, n (%)
(95% CI)
106 (72.1)
(64.1, 79.2)
75 (48.7)
(40.6, 56.9)
Common Rate Difference (95% CI) b
23.2 (12.2, 34.1)
HI-E per IWG ≥8 weeks (Weeks 1-24)
Response rate, n (%)
(95% CI)
109 (74.1)
(66.3, 81.0)
79 (51.3)
(43.1, 59.4)
Common Rate Difference (95% CI) b
22.3 (11.8, 32.8)
p-value c
<0.0001
RBC-TI for 24 weeks (Weeks 1-24)
Response rate, n (%)
(95% CI)
70 (47.6)
(39.3, 56.0)
45 (29.2)
(22.2, 37.1)
Common Rate Difference (95% CI) b
17.0 (6.7, 27.2)
p-value c
0.0012
RBC-TI for ≥12 weeks (Weeks 1-24)
Response rate, n (%)
(95% CI)
98 (66.7)
(58.4, 74.2)
71 (46.1)
(38.1, 54.3)
Common Rate Difference (95% CI) b
19.1 (8.6, 29.6)
p-value c
0.0003
No major outliers were observed in clinically relevant baseline demographic and disease characteristic subgroups.
14.3 Myelodysplastic Syndromes with Ring Sideroblasts or Myelodysplastic/Myeloproliferative Neoplasm with Ring Sideroblasts and Thrombocytosis Associated Anemia in ESA-refractory or -intolerant Patients
The efficacy of REBLOZYL was evaluated in the MEDALIST trial (NCT02631070), a multi-center, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in patients with IPSS-R very low, low, or intermediate-risk myelodysplastic syndromes who have ring sideroblasts and require red blood cell transfusions (2 or more RBC units over 8 weeks). For eligibility, patients were required to have had an inadequate response to prior treatment with an erythropoiesis-stimulating agent (ESA), be intolerant of ESAs, or have a serum erythropoietin > 200 U/L. The MEDALIST trial excluded patients with deletion 5q (del 5q), white blood cell count > 13 Gi/L, neutrophils < 0.5 Gi/L, platelets < 50 Gi/L, or with prior use of a disease modifying agent for treatment of MDS.
The MEDALIST trial included 229 patients randomized 2:1 to REBLOZYL (n=153) or placebo (n=76). Randomization was stratified by baseline RBC transfusion burden and baseline IPSS-R. Treatment was started at 1 mg/kg subcutaneously every 3 weeks; the dose could be increased after completion of the first 2 cycles if the patient had at least one RBC transfusion in the prior 6 weeks. Two dose level increases were allowed (to 1.33 mg/kg and to 1.75 mg/kg). Doses were held and subsequently reduced for adverse reactions, reduced if the hemoglobin increased by ≥ 2 g/dL from the prior cycle, and held if the predose hemoglobin was ≥ 11.5 g/dL.
All patients received best supportive care, which included RBC transfusions as needed. The primary efficacy assessment was conducted after completion of 24 weeks on study drug. Patients with a decrease in transfusion requirement or increase in hemoglobin could continue on blinded study drug thereafter until unacceptable toxicity, loss of efficacy, or disease progression.
The median age of the 229 study participants was 71 years (range: 26, 95 years). The trial population was 63% male and 69% White. Table 16 summarizes the baseline disease-related characteristics in the MEDALIST study.
Table 16: Baseline Disease Characteristics of Patients in MEDALIST EPO=erythropoietin; IPSS R=International Prognostic Scoring System-Revised; ITT=intent-to-treat; MDS=myelodysplastic syndromes; RARS=refractory anemia with ring sideroblasts; RBC=red blood cell; RCMD=refractory cytopenia with multilineage dysplasia; SD=standard deviation; WHO=World Health Organization.
a Time since original MDS diagnosis was defined as the number of years from the date of original diagnosis to the date of informed consent.
b Baseline EPO was defined as the highest EPO value within 35 days of the first dose of study drug.
c Includes MDS-RS-MLD and MDS-RS-SLD.
d Includes MDS-EB-1, MDS-EB-2, and MDS-U.Disease Characteristic
REBLOZYL
(N=153)Placebo
(N=76)Time Since Original MDS Diagnosis a (months)
Median (range)
44.0 (3, 421)
36.1 (4, 193)
Serum EPO (U/L) Categories b, n (%)
< 200
88 (57.5)
50 (65.8)
200 to 500
43 (28.1)
15 (19.7)
> 500
21 (13.7)
11 (14.5)
Missing
1 (0.7)
0
Diagnosis per WHO Criteria, n (%)
MDS-RS c
135 (88.2)
65 (85.5)
MDS/MPN-RS-T
14 (9.2)
9 (11.8)
Other d
4 (2.6)
2 (2.6)
IPSS-R Classification Risk Category, n (%)
Very low
18 (11.8)
6 (7.9)
Low
109 (71.2)
57 (75)
Intermediate
25 (16.3)
13 (17.1)
High
1 (0.7)
0
RBC Transfusions/8 Weeks Over 16 Weeks Categories, n (%)
< 4 units
46 (30.1)
20 (26.3)
≥ 4 and < 6 units
41 (26.8)
23 (30.3)
≥ 6 units
66 (43.1)
33 (43.4)
The efficacy of REBLOZYL in adult patients with MDS-RS and MDS-RS-T was established based upon the proportion of patients who were red blood cell transfusion independent (RBC-TI), defined as the absence of any RBC transfusion during any consecutive 8-week period occurring entirely within Weeks 1 through 24.
The efficacy results are shown in Tables 17 and 18.
Table 17: Efficacy Results in MEDALIST * The median (range) duration of treatment was 49 weeks (6 to 114 weeks) on the REBLOZYL arm and 24 weeks (7 to 89 weeks) on the placebo arm. Endpoint
REBLOZYL
(N=153)
n, %
(95% CI)Placebo
(N=76)
n, %
(95% CI)Common Risk Difference
(95% CI)p-value
RBC-TI ≥ 8 weeks during Weeks 1-24
58 (37.9)
(30.2, 46.1)10 (13.2)
(6.5, 22.9)24.6
(14.5, 34.6)<0.0001
RBC-TI ≥ 12 weeks during Weeks 1-24
43 (28.1)
(21.1, 35.9)6 (7.9)
(3.0, 16.4)20.0
(10.9, 29.1)0.0002
RBC-TI ≥ 12 weeks during Weeks 1-48*
51 (33.3)
(25.9, 41.4)9 (11.8)
(5.6, 21.3)21.4
(11.2, 31.5)0.0003
Table 18 shows the proportion of patients who achieved RBC-TI ≥ 8 weeks during Weeks 1-24 by diagnosis and baseline transfusion requirement.
Table 18: RBC-TI ≥ 8 Weeks during Weeks 1-24 By Diagnosis and Baseline Transfusion Burden in MEDALIST a Includes MDS-EB-1, MDS-EB-2, and MDS-U.
b Includes patients who received 3.5 units.
c Includes patients who received 5.5 units.Responders / N
% Response (95% CI)
REBLOZYL
Placebo
REBLOZYL
Placebo
WHO 2016 Diagnosis
MDS-RS
46 / 135
8 / 65
34.1 (26.1, 42.7)
12.3 (5.5, 22.8)
MDS/MPN-RS-T
9 / 14
2 / 9
64.3 (35.1, 87.2)
22.2 (2.8, 60.0)
Other a
3 / 4
0 / 2
75.0 (19.4, 99.4)
0.0 (0.0, 84.2)
Baseline RBC Transfusion Burden
2 - 3 units/8 weeks b
37 / 46
8 / 20
80.4 (66.1, 90.6)
40.0 (19.1, 63.9)
4 - 5 units/8 weeks c
15 / 41
1 / 23
36.6 (22.1, 53.1)
4.3 (0.1, 21.9)
≥ 6 units/8 weeks
6 / 66
1 / 33
9.1 (3.4, 18.7)
3.0 (0.1, 15.8)
- 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Discuss the following with patients prior to and during treatment with REBLOZYL.
Thromboembolic Events
Advise beta thalassemia patients of the potential risk of thromboembolic events. Review known risk factors for developing thromboembolic events and advise patients to reduce modifiable risk factors (e.g., smoking, use of oral contraceptives) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Effects on Blood Pressure
Caution patients that REBLOZYL may cause an increase in blood pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Extramedullary Hematopoietic Masses
Advise patients with beta thalassemia of the potential risk of extramedullary hematopoietic masses. Review possible risk factors for developing extramedullary hematopoietic masses. Instruct patients to report possible signs and symptoms of EMH masses [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception while receiving REBLOZYL and for at least 3 months after the final dose. Advise females to contact their healthcare provider if they become pregnant, or if pregnancy is suspected, during treatment with REBLOZYL [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Lactation
Advise females not to breastfeed during treatment with REBLOZYL and for 3 months after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Manufactured by:
Celgene Corporation, a Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
86 Morris Avenue
Summit, NJ 07901
U.S. License No. 2252REBLOZYL® is a registered trademark of Celgene Corporation, a Bristol-Myers Squibb Company.
REBPI.007
-
PATIENT INFORMATION
REBLOZYL® (REB-low-zil)
(luspatercept-aamt)
for injection, for subcutaneous useWhat is REBLOZYL?
REBLOZYL is a prescription medicine used to treat anemia (low red blood cells) in adults with:
- •
- beta thalassemia who need regular red blood cell (RBC) transfusions.
- •
- myelodysplastic syndromes who may need regular RBC transfusions and have never received an erythropoiesis stimulating agent (ESA).
- •
- myelodysplastic syndromes with ring sideroblasts (MDS-RS) or myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms with ring sideroblasts and thrombocytosis (MDS/MPN-RS-T) who need 2 or more RBC units over 8 weeks and have not responded well to an ESA.
REBLOZYL is not for use as a substitute for RBC transfusions in people who need immediate treatment for anemia.
It is not known if REBLOZYL is safe and effective in children.Before receiving REBLOZYL, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- •
- have or have had blood clots
- •
- take hormone replacement therapy or birth control pills (oral contraceptives)
- •
- have had your spleen removed (splenectomy)
- •
- smoke
- •
- have or have had high blood pressure (hypertension)
- •
- have a history of extramedullary hematopoietic (EMH) masses
- •
- have or have had enlarged spleen or liver
- •
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. REBLOZYL may harm your unborn baby. Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think you may be pregnant during treatment with REBLOZYL.
Females who are able to become pregnant:- o
- Your healthcare provider should do a pregnancy test before you start treatment with REBLOZYL.
- o
- You should use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment with REBLOZYL and for at least 3 months after the last dose.
- •
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if REBLOZYL passes into your breast milk.
- o
- Do not breastfeed during treatment with REBLOZYL and for 3 months after the last dose. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby during this time.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
How will I receive REBLOZYL?
- •
- Your healthcare provider will prescribe REBLOZYL in a dose that is right for you. Depending on how you respond to REBLOZYL, your healthcare provider may adjust your dose or stop treatment.
- •
- REBLOZYL is given as an injection under your skin (subcutaneous) in the upper arm, thigh, or stomach (abdomen) by your healthcare provider.
- •
- Your healthcare provider will do regular blood tests to check your hemoglobin to monitor if your anemia is getting better before each injection and during your treatment with REBLOZYL.
If your scheduled REBLOZYL dose is delayed or missed, your healthcare provider will give your dose of REBLOZYL as soon as possible and continue your treatment as prescribed with at least 3 weeks between doses.
What are the possible side effects of REBLOZYL?
REBLOZYL may cause serious side effects, including:- •
-
Blood clots. Blood clots in the arteries, veins, brain, and lungs have happened in people with beta thalassemia during treatment with REBLOZYL. The risk of blood clots may be higher in people who have had their spleen removed or who take hormone replacement therapy or birth control (oral contraceptives). Call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you get any of these symptoms:
- o
- chest pain
- o
- trouble breathing or shortness of breath
- o
- pain in your leg, with or without swelling
- o
- a cold or pale arm or leg
- o
- sudden numbness or weakness that are both short-term or continue to happen over a long period of time, especially on one side of the body
- o
- severe headache or confusion
- o
- sudden problems with vision, speech, or balance (such as trouble speaking, difficulty walking, or dizziness)
- •
- High blood pressure. REBLOZYL may cause an increase in your blood pressure. Your healthcare provider will check your blood pressure before you receive your REBLOZYL dose. Your healthcare provider may prescribe you medicine to treat high blood pressure or increase the dose of medicine you already take to treat high blood pressure if you develop high blood pressure during treatment with REBLOZYL.
- •
-
Extramedullary Hematopoietic (EMH) Masses. EMH masses have happened in people with beta thalassemia during treatment with REBLOZYL. You may have a higher risk for developing EMH masses if you have a history of EMH masses, have had your spleen removed, have or have had an enlarged spleen or liver, or have low hemoglobin levels. Your healthcare provider will monitor you before you start and during treatment with REBLOZYL. Call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away if you get any of these symptoms:
- o
- severe pain in the back
- o
- numbness, weakness, or loss of voluntary movement in feet, legs, hands, or arms
- o
- loss of bowel and bladder control
The most common side effects of REBLOZYL include:
- •
- tiredness
- •
- headache
- •
- back, joint, muscle, or bone pain
- •
- joint pain
- •
- dizziness
- •
- nausea
- •
- diarrhea
- •
- cough
- •
- stomach (abdominal) pain
- •
- trouble breathing
- •
- swelling of your hands, legs, or feet
- •
- high blood pressure
- •
- allergic reactions
REBLOZYL may cause fertility problems in females. This could affect your ability to become pregnant. Talk to your healthcare provider if this is a concern for you.
These are not all of the possible side effects of REBLOZYL.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.General information about the safe and effective use of REBLOZYL.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about REBLOZYL that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in REBLOZYL?
Active ingredient: luspatercept-aamt
Inactive ingredients: citric acid monohydrate, polysorbate 80, sucrose, and tri-sodium citrate dihydrate.For more information, go to www.REBLOZYL.com or call 1-888-423-5436.
Manufactured by: Celgene Corporation, a Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, 86 Morris Avenue, Summit, NJ 07901
REBLOZYL® is a registered trademark of Celgene Corporation, a Bristol-Myers Squibb Company.
REBPPI V5 8/2023
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
Revised: August 2023
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 25 mg Vial Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 25 mg Vial Carton - USA
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 25 mg Vial Carton - Singapore
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 75 mg Vial Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 75 mg Vial Carton - USA
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 75 mg Vial Carton - Singapore
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
REBLOZYL
luspatercept injection, powder, lyophilized, for solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:59572-711 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LUSPATERCEPT (UNII: AQK7UBA1LS) (LUSPATERCEPT - UNII:AQK7UBA1LS) LUSPATERCEPT 25 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) TRISODIUM CITRATE DIHYDRATE (UNII: B22547B95K) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off-white) Score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:59572-711-01 1 in 1 CARTON 11/08/2019 1 1 in 1 VIAL, GLASS; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761136 11/08/2019 REBLOZYL
luspatercept injection, powder, lyophilized, for solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:59572-775 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LUSPATERCEPT (UNII: AQK7UBA1LS) (LUSPATERCEPT - UNII:AQK7UBA1LS) LUSPATERCEPT 75 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) TRISODIUM CITRATE DIHYDRATE (UNII: B22547B95K) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off-white) Score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:59572-775-01 1 in 1 CARTON 11/08/2019 1 1 in 1 VIAL, GLASS; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761136 11/08/2019 Labeler - Celgene Corporation (174201137) Registrant - Celgene Corporation (174201137) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Vetter Pharma Fertigung GmbH & Co. KG (Ravensburg Schuetzenstrasse) 316126754 ANALYSIS(59572-711, 59572-775)