Label: DAISY- leucanthemum vulgare solution
DANDELION- taraxacum officinale solution
SUNFLOWER- helianthus annuus solution
-
NDC Code(s):
22840-1500-2,
22840-1500-4,
22840-1501-1,
22840-1502-1, view more22840-1503-2, 22840-1503-4, 22840-1504-2, 22840-1505-1, 22840-1506-1, 22840-1569-2, 22840-1570-2, 22840-1570-4, 22840-1571-2, 22840-1571-4, 22840-1572-2, 22840-1573-2, 22840-1573-4, 22840-5500-2, 22840-5500-5, 22840-5501-2, 22840-5501-4, 22840-5501-5, 22840-5502-2, 22840-5502-4, 22840-5502-5
- Packager: Greer Laboratories, Inc.
- Category: NON-STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Biologic Licensing Application
Drug Label Information
Updated November 20, 2023
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts (Pollens, Molds, Epidermals, Insects, Foods and Miscellaneous Inhalants) safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts.
Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts (Pollens, Molds, Epidermals, Insects, Foods, and Miscellaneous Inhalants)
Solutions for percutaneous, intradermal or subcutaneous administration.
Initial U.S. Approval: 1968
WARNING: SEVERE ALLERGIC REACTIONS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts can cause severe life-threatening systemic reactions, including anaphylaxis. (5.1)
- Do not administer these products to patients with severe, unstable or uncontrolled asthma. (4)
- Observe patients in the office for at least 30 minutes following treatment.Emergency measures and personnel trained in their use must be available immediately in the event of a life-threatening reaction. (5.1)
- Patients with extreme sensitivity to these products, on an accelerated immunotherapy build-up, switching to another lot, receiving high doses of these products, and patients exposed to similar allergens may be at increased risk of a severe allergic reaction. (5.1)
- These products may not be suitable for patients with certain underlying medical conditions that may reduce their ability to survive a systemic allergic reaction, and for patients receiving medications such as beta-blockers that may make them unresponsive to epinephrine or inhaled bronchodilators. (5.1, 5.2)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Warning and Precautions, Anaphylaxis Following False Negative Food Allergen Skin Test Results (5.3) 01/2023INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts are indicated for:
- Skin test diagnosis of patients with a clinical history of allergies to one or more of the specific allergens. (1)
- Immunotherapy for reduction of allergen-induced allergic symptoms confirmed by appropriate positive skin tests or in vitro testing for allergen-specific IgE antibodies. (1)
Food extracts have not been proven safe or effective in allergen immunotherapy.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For percutaneous, intradermal or subcutaneous use only.
The extracts are diluted with sterile diluents when used for intradermal testing or subcutaneous immunotherapy. For percutaneous testing, the extracts are diluted with sterile diluents in patients expected to be at greater risk for systemic allergic reaction. Dosages vary by mode of administration and by individual response. See full prescribing information for instructions on preparation, administration, and adjustments of dose. (2.1)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts are labeled in weight/volume and/or protein nitrogen units (PNU)/milliliter (a measure of total protein), and are supplied as sterile aqueous stock concentrates at up to 1:10 weight/volume or 40,000 PNU/milliliter, or 50% glycerin stock concentrates at up to 1:20 weight/volume. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Severe, unstable or uncontrolled asthma. (4)
- History of any severe systemic or local allergic reaction to an allergen extract. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Severe allergic reactions have occurred following the administration of other allergenic extracts and may occur in individuals following the administration of Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts in the following situations:
- Extreme sensitivity to Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts, receipt of high doses of Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts, or concomitant exposure to similar environmental allergens. (5.1)
- Receiving an accelerated immunotherapy build-up schedule (e.g., “rush” immunotherapy), or changing from one allergenic lot to another. (5.1)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions, occurring in 26 to 82% of all patients who receive subcutaneous immunotherapy, are local adverse reactions at the injection site (e.g., erythema, itching, swelling, tenderness, pain). (6)
Systemic adverse reactions, occurring in ≤ 7% of patients who receive subcutaneous immunotherapy, include generalized skin erythema, urticaria, pruritus, angioedema, rhinitis, wheezing, laryngeal edema, and hypotension. These can be fatal. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact GREER Laboratories, Inc. at 1-855-274-1322 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Antihistamines and other medications that suppress histamine, including topical corticosteroids, topical anesthetics and tricyclic antidepressants can interfere with skin test results. (7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
-
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: SEVERE ALLERGIC REACTIONS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Preparation for Administration
2.2 Diagnostic Testing
2.3 Immunotherapy
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Systemic Adverse Reactions
5.2 Epinephrine
5.3 Anaphylaxis Following False Negative Food Allergen Skin Test Results
5.4 Cross-Reactions and Dose Sensitivity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Antihistamines
7.2 Topical Corticosteroids and Topical Anesthetics
7.3 Tricyclic Antidepressants
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
*Sections or subsections omitted from the Full Prescribing Information are not listed. -
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: SEVERE ALLERGIC REACTIONS
- Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts can cause severe life-threatening systemic reactions, including anaphylaxis. (5.1)
- Do not administer these products to patients with severe, unstable, or uncontrolled asthma. (4)
- Observe patients in the office for at least 30 minutes following treatment. Emergency measures and personnel trained in their use must be available immediately in the event of a life-threatening reaction. (5.1)
- Patients with extreme sensitivity to these products, those on an accelerated immunotherapy build-up schedule, those switching to another allergenic lot, those receiving high doses of Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts, or those also exposed to similar allergens may be at increased risk of a severe allergic reaction. (5.1)
- These products may not be suitable for patients with certain underlying medical conditions that may reduce their ability to survive a serious allergic reaction. (5.1)
- These products may not be suitable for patients who may be unresponsive to epinephrine or inhaled bronchodilators, such as those taking beta-blockers. (5.2)
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts are indicated for:
- Skin test diagnosis of patients with a clinical history of allergies to one or more of the specific non-standardized allergens.
- Immunotherapy for the reduction of allergen-induced allergic symptoms confirmed by appropriate positive skin tests or by in vitro testing for allergen-specific IgE antibodies.
Food extracts have not been proven safe or effective in allergen immunotherapy.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For percutaneous, intradermal or subcutaneous use only.
The extracts are diluted with sterile diluents when used for intradermal testing or subcutaneous immunotherapy. For percutaneous testing, the extracts are diluted with sterile diluents in patients expected to be at greater risk for systemic allergic reaction. Dosages vary by mode of administration and by individual response.
2.1 Preparation for Administration
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Discard solution if either of these conditions exist.
The extracts are diluted with sterile diluents when used for percutaneous and intradermal testing, or for subcutaneous immunotherapy.
Extracts labeled “For Diagnostic Use Only” are intended for percutaneous and intradermal testing only. These extracts have not been shown by adequate data to be safe and effective for therapeutic use. The extracts labeled For Diagnostic Use Only are the foods Barley, Coffee, Oat, Pineapple, Rye, Spinach, Wheat, the insects Flea, House Fly, Mosquito, and the plant and plant parts Cottonseed and Flax.
Undiluted 50% glycerin stock concentrate is used for percutaneous testing. To prepare 10-fold dilutions for percutaneous testing in patients suspected to be at greater risk for systemic allergic reaction, start with the stock concentrate. Proceed as shown in Table 1. The 10-fold dilution series uses 0.5 milliliters of concentrate added to 4.5 milliliters of sterile 50% glycerin diluent. Subsequent dilutions are made in a similar manner.
To prepare 10-fold dilutions for intradermal testing and immunotherapy, start with a 1:10 weight/volume, 1:20 weight/volume, or up to a 40,000 PNU/milliliter stock concentrate. Proceed as shown in Table 1. The 10-fold dilution series uses 0.5 milliliter of concentrate added to 4.5 milliliters of sterile diluent (glycerin-free diluents for intradermal testing, glycerin-free or 10% glycerin-saline diluents for immunotherapy). Subsequent dilutions are made in a similar manner.
Table 1: 10-fold Dilution Series* Dilution Extract Milliliters of Diluent Dilution Strength (w/v) Dilution Strength (w/v) Dilution Strength (PNU/milliliter) 0 Concentrate 1:10 1:20 20,000 1 0.5 mL Concentrate 4.5 1:100 1:200 2,000 2 0.5 mL Dilution 1 4.5 1:1,000 1:2,000 200 3 0.5 mL Dilution 2 4.5 1:10,000 1:20,000 20 4 0.5 mL Dilution 3 4.5 1:100,000 1:200,000 2 5 0.5 mL Dilution 4 4.5 1:1,000,000 1:2,000,000 0.2 6 0.5 mL Dilution 5 4.5 1:10,000,000 1:20,000,000 0.02 *There is no direct potency correlation across the table between PNU/milliliter and w/v.
Undiluted 50% glycerin stock concentrate is used for percutaneous testing. To prepare 5-fold dilutions for percutaneous testing in patients suspected to be at greater risk for systemic allergic reaction, start with the stock concentrate. Proceed as shown in Table 2. The 5-fold dilution series uses 1 milliliter of concentrate added to 4 milliliters of sterile 50% glycerin diluent. Subsequent dilutions are made in a similar manner.
To prepare 5-fold dilutions for intradermal testing or immunotherapy, start with a 1:10 weight/volume, 1:20 weight/volume, or up to a 40,000 PNU/milliliter stock concentrate. Proceed as shown in Table 2. The 5-fold dilution series uses 1 milliliter of concentrate added to 4 milliliters of sterile diluent (glycerin-free diluents for intradermal testing, glycerin-free or 10% glycerin-saline diluents for immunotherapy). Subsequent dilutions are made in a similar manner.
Table 2: 5-fold Dilution Series* Dilution Extract Milliliters of Diluent Dilution Strength (w/v) Dilution Strength (w/v) Dilution Strength (PNU/milliliter) 0 Concentrate 1:10 1:20 20,000 1 1 mL Concentrate 4 1:50 1:100 4,000 2 1 mL Dilution 1 4 1:250 1:500 800 3 1 mL Dilution 2 4 1:1,250 1:2,500 160 4 1 mL Dilution 3 4 1:6,250 1:12,500 32 5 1 mL Dilution 4 4 1:31,250 1:62,500 6.4 6 1 mL Dilution 5 4 1:156,250 1:312,500 1.28 *There is no direct potency correlation across the table between PNU/milliliter and w/v.
2.2 Diagnostic Testing
Diagnostic testing can be performed via percutaneous or intradermal administration of the Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts. A positive skin test reaction should be interpreted in relation to the patient’s history and known exposure to the specific allergen(s).
Percutaneous Skin Testing
Preparation and Dose
For percutaneous testing (prick or puncture), use glycerinated extract; use the extracts at the highest available stock concentration. In patients suspected to be at greater risk for systemic allergic reaction, use 10-fold or 5-fold dilutions of the concentrate.
Prick test: Place one drop of extract with appropriate controls on the skin and with a skin test device, pierce through the drop into the skin with a slight lifting motion. Alternatively, use skin test devices loaded with the extract from the storage trays in a similar manner or in accordance with the device manufacturer’s recommendations.
Puncture test: Place one drop of extract or control on the skin and pierce the skin through the drop with a skin test device perpendicular to the skin. Alternatively, use skin test devices loaded with the extract from the storage trays in a similar manner or in accordance with the device manufacturer’s recommendations.
Interpreting Results
When using percutaneous skin test devices, follow the directions provided with the test devices. A glycerinated histamine control solution (6 milligrams/milliliter or 1 milligram/milliliter histamine base) may be used as the positive control. A 50% glycerin-saline solution may be used as the negative control.
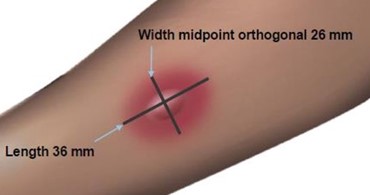
Read and record skin test responses 15 to 20 minutes after exposure. Individual patient reactivity can vary with time, allergen potency, and/or immunotherapy, as well as testing technique. The most reliable method of recording a skin test reaction is to measure the largest diameter of both wheal and erythema. While some correlation exists between the size of the skin test reaction and the degree of sensitivity, other factors should be considered in the diagnosis of allergy to specific allergens (see Figure 1 below).
Figure 1: Measurement of Wheal and Flare
Use a paper or plastic millimeter skin reaction guide as shown below.

Fifteen minutes after application of the skin test, measure the length and midpoint orthogonal width of each flare and wheal from the inner edge of the reaction.

The length of the skin test is defined as the largest diameter and the width of the skin test is defined as the diameter perpendicular to the length at its midpoint. Consider the wheal and flare as separate entities. First, measure the flare and then independently measure the wheal.
Measuring the Flare
Measuring the Wheal
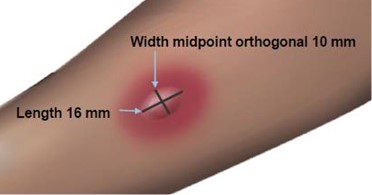
The average diameter measurement in the example above of the flare is (26 mm + 36 mm)/ 2 = 31 mm and the average diameter of the wheal is (10 mm + 16 mm)/2 = 13 mm.
Responses to positive controls should be at least 3 millimeters larger than responses to the negative controls.
Negative controls should elicit no reaction or only reactions of small diameter (less than 2 millimeters wheal, less than 5 millimeters erythema).
If either the positive or negative control response does not meet the above criteria, results for the allergenic extracts tested at the same time should be considered invalid and be repeated.
Intradermal Skin Testing
Preparation and Dose
For intradermal testing, dilute stock concentrate to 1:100 to 1:1000 volume to volume of Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts stock concentrate solution. Dilute the stock concentrate solution with sterile diluent [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. Use normal or buffered saline or normal saline with human serum albumin (HSA) diluent. If the result from the initial test dose is negative, subsequent intradermal tests using increasingly stronger doses may be performed up to the maximum recommended strength of 1:25 volume to volume dilution of the extract concentrate solution.
Inject 0.02 milliliters of the extract solution intradermally according to the algorithms shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Algorithm for Dilution of Stock Concentrate Solution of Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts for Intradermal Skin Testing
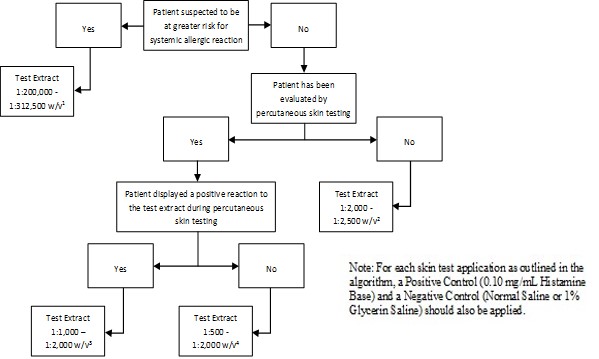
1 Corresponds to 1:10,000 - 1:15,625 volume to volume dilution of 1:20 weight/volume glycerinated extract concentrates
2 Corresponds to 1:100 - 1:125 volume to volume dilution of 1:20 weight/volume glycerinated extract concentrates
3 Corresponds to 1:50 - 1:100 volume to volume dilution of 1:20 weight/volume glycerinated extract concentrates
4 Corresponds to 1:25 - 1:100 volume to volume dilution of 1:20 weight/volume glycerinated extract concentrates
2.3 Immunotherapy
For subcutaneous administration only.
Preparation and Dose
Stock concentrates of Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts are available in aqueous (up to 1:10 weight/volume or 40,000 PNU/milliliter) and 50% glycerin (up to 1:20 weight/volume) strengths for immunotherapy. Stock concentrates are diluted in normal saline, buffered saline, HSA-saline, or 10% glycerin-saline, depending on the patient’s reactivity to the diluent. See Table 1 and Table 2 for dilution preparation.
Administration of Immunotherapy
Administer immunotherapy by subcutaneous injection in the lateral aspect of the upper arm or thigh. Avoid injection directly into any blood vessel.
The optimal interval between doses of allergenic extract varies among individuals. Injections are usually given 1 to 2 times per week until the maintenance dose is reached, at which time the injection interval is increased to 2, then 3, and finally 4 weeks. Dosages vary by mode of administration, and by clinical response and tolerance. The minimum course of treatment may be three to five years, depending on the clinical response.
Guidelines for Immunotherapy
The initial dose of the extract should be based on the skin test reactivity. In patients suspected to be at greater risk for systemic allergic reaction by history and skin test, the initial dose of the extract should be 0.05 milliliter of a 1:20,000,000 to 1:2,000,000 weight/volume extract dilution. Patients not suspected to be at greater risk for systemic allergic reaction may be started at 0.1 milliliter of a 1:200,000 to 1:20,000 weight/volume extract dilution.
The dose of allergenic extract is increased at each injection by no more than 50% of the previous dose, and the next increment is governed by the response to the last injection.
Select the maximum tolerated maintenance dose based on the patient’s clinical response and tolerance. Doses larger than 0.2 milliliter of the stock concentrate are rarely administered because an extract in 50% glycerin diluent can cause discomfort upon injection.
Dosage Modification Guidelines for Immunotherapy
The following conditions may indicate a need to withhold or reduce the dosage of immunotherapy.
- Symptoms of rhinitis and/or asthma
- Infection accompanied by fever
- Exposure to excessive amounts of clinically relevant environmental allergen prior to a scheduled injection
- Large local reactions that persist for longer than 24 hours can be an indication for repeating the previous dose or reducing the dose at the next administration
Any evidence of a systemic reaction is an indication for a significant reduction (at least 75%) in the subsequent dose. Repeated systemic adverse reactions are sufficient reason for the cessation of further attempts to increase the dose.
Local adverse reactions require a decrease in the next dose by at least 50%. Proceed cautiously in subsequent dosing. In situations prompting dose reduction, once the reduced dose is tolerated, a cautious increase in dosage can be attempted.
Changing extract to a different lot or from a different manufacturer: When switching to a different lot of extract, or from another manufacturer’s extract, decrease the starting dose. Because manufacturing processes and sources of raw materials differ among manufacturers, the interchangeability of extracts from different manufacturers cannot be assured. In general, a dose reduction of 50 to 75% of the previous dose should be adequate, but each situation must be evaluated separately, considering the patient’s history of sensitivity, tolerance of previous injections, and other factors. Dose intervals should not exceed one week when rebuilding the dose.
Unscheduled gaps between treatments: Patients can lose tolerance to allergen injections during prolonged periods between doses, which increases their risk for an adverse reaction. The duration of tolerance between injections varies from patient to patient.
During the build-up phase, when patients receive injections 1 to 2 times per week, repeat or reduce the extract dosage if there has been a substantial time interval between injections. This depends on: 1) the concentration of allergen immunotherapy extract that is to be administered; 2) a previous history of systemic reactions; and 3) the degree of variation from the prescribed interval of time, with longer intervals since the last injection leading to greater reductions in the dose to be administered.
This suggested approach to dose modification, due to unscheduled gaps between treatments during the build-up phase, is not based on published evidence. The individual physician should use this or a similar protocol for the specific clinical setting.
Similarly, if unscheduled gaps occur during maintenance therapy, it may be necessary to reduce the dosage and bring the patient up to maintenance dosing using an established build-up protocol.
Changing from non-stabilized to human serum albumin (HSA) stabilized diluents: Allergenic extracts prepared with diluents containing HSA and 0.4% phenol are more stable than those prepared with diluents that do not contain stabilizers. When switching from a non-stabilized to an HSA-stabilized diluent, consider lowering the dose for immunotherapy.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts are labeled in weight/volume and/or protein nitrogen units (PNU)/milliliter (a measure of total protein), and are supplied as sterile aqueous stock concentrates at up to 1:10 weight/volume or 40,000 PNU/milliliter, or 50% glycerin stock concentrates at up to 1:20 weight/volume.
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Systemic Adverse Reactions
Serious systemic adverse reactions have occurred following the administration of other allergenic extracts and may occur in individuals following the administration of Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts in the following situations:
- Extreme sensitivity to the specific allergen(s)
- Receipt of an accelerated immunotherapy build-up schedule (e.g., “rush” immunotherapy)
- Receipt of high doses of allergenic extracts or concomitant exposure to similar environmental allergens
- Change from one allergenic extract lot to another allergenic extract lot
High-risk patients have had fatal reactions. Consider using more dilute preparations in patients suspected to be at greater risk of systemic allergic reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Administer Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts in a healthcare setting under the supervision of a physician prepared to manage a severe systemic or a severe local allergic reaction.Observe patients in the office for at least 30 minutes following administration. 1
5.2 Epinephrine
Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts may not be suitable for patients with certain medical conditions that may reduce the ability to survive a serious allergic reaction or increase the risk of adverse reactions after epinephrine administration. Examples of these medical conditions include but are not limited to: markedly compromised lung function (either chronic or acute), unstable angina, recent myocardial infarction, significant arrhythmia, and uncontrolled hypertension.
These products may not be suitable for patients who are taking medications that can potentiate or inhibit the effect of epinephrine. These medications include:
Βeta-adrenergic blockers: Patients taking beta-adrenergic blockers may be unresponsive to the usual doses of epinephrine used to treat serious systemic reactions, including anaphylaxis. Specifically, beta-adrenergic blockers antagonize the cardiostimulating and bronchodilating effects of epinephrine.
Alpha-adrenergic blockers, ergot alkaloids: Patients taking alpha-adrenergic blockers may be unresponsive to the usual doses of epinephrine used to treat serious systemic reactions, including anaphylaxis. Specifically, alpha-adrenergic blockers antagonize the vasoconstricting and hypertensive effects of epinephrine. Similarly, ergot alkaloids may reverse the pressor effects of epinephrine.
Tricyclic antidepressants, levothyroxine sodium, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and certain antihistamines: The adverse effects of epinephrine may be potentiated in patients taking tricyclic antidepressants, levothyroxine sodium, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, and the antihistamines chlorpheniramine, and diphenhydramine.
Cardiac glycosides, diuretics: Patients who receive epinephrine while taking cardiac glycosides or diuretics should be observed carefully for the development of cardiac arrhythmias.
5.3 Anaphylaxis Following False Negative Food Allergen Skin Test Results
False negative skin test results associated with anaphylaxis from subsequent exposure to the allergen have been reported during postmarketing diagnostic use of some food allergenic extracts. Based on the patient’s clinical history and index of suspicion, healthcare providers should consider confirming negative skin testing with serologic testing by measuring specific serum IgE or with a medically-supervised oral food challenge.5.4 Cross-Reactions and Dose Sensitivity
When determining the final dose of an allergen mixture for immunotherapy, consider cross-reactivity among component extracts.
Determine the initial dilution of allergenic extract, starting dose, and progression of dosage based on the patient’s history and results of skin tests 2 [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. Strongly positive skin tests can be indicators for potential adverse reactions.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions, occurring in 26 to 82% of all patients who receive subcutaneous immunotherapy are local adverse reactions at the injection site (e.g., erythema, itching, swelling, tenderness, pain). 1 Systemic adverse reactions, occurring in < 7% of patients who receive subcutaneous immunotherapy, 3 include generalized skin erythema, urticaria, pruritus, angioedema, rhinitis, wheezing, laryngeal edema, and hypotension. These adverse reactions can be fatal. 1
The allergenic extracts labeled “For Diagnostic Use Only” that contain sodium formaldehyde sulfoxylate (SFS) can cause slight discoloration of the skin at the site of administration. This discoloration can remain for extended amounts of time.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Antihistamines
Do not perform skin testing with allergenic extracts within 3 to 10 days of use of first-generation H 1-histamine receptor blockers (e.g., clemastine, diphenhydramine) and second-generation antihistamines (e.g., loratadine, cetirizine). These products suppress histamine skin test reactions and could mask a positive response. 2
7.2 Topical Corticosteroids and Topical Anesthetics
Topical corticosteroids can suppress skin reactivity; therefore, discontinue use at the skin test site for 2 to 3 weeks before skin testing. Avoid use of topical local anesthetics at skin test sites as they can suppress flare responses. 2
7.3 Tricyclic Antidepressants
Tricyclic antidepressants can have potent antihistamine effects that can affect skin testing. If tricyclic medication has been recently discontinued, allow 7 to 14 days before initiating skin testing. 2
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
All pregnancies have a risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively. There are no human or animal data to establish the presence or absence of Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts-associated risks during pregnancy.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts are present in human milk. Data are not available to assess the effects of these extracts on the breastfed child or on milk production/excretion. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from the extracts or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
For use of these products in children younger than 5 years of age, consideration should be given to the patient’s ability to comply and cooperate with allergen immunotherapy and the potential for difficulty in communicating with the child regarding systemic reactions. 1
8.5 Geriatric Use
Data are not available to determine if subjects 65 years of age and older respond differently to allergen immunotherapy than younger subjects.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts are sterile solutions used for percutaneous testing, intradermal testing, or subcutaneous immunotherapy. Aqueous extracts contain the soluble extractants of the source material in water for injection, 0.5% sodium chloride, 0.54% sodium bicarbonate, and 0.4% phenol. Glycerinated extracts contain the soluable extractants of the source material in water for injection and 50% glycerin, 0.25% sodium chloride, 0.27% sodium bicarbonate, and 0.2% phenol. The pH of the extracts range from 6 to 9.
Certain food extracts (Barley, Oat, Pineapple, Rye, Spinach, and Wheat), labeled “For Diagnostic Use Only”, contain 0.1% sodium formaldehyde sulfoxylate as an antioxidant.
Source materials used in the manufacture of allergenic extracts are collected from natural sources or from laboratory cultures.
Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts appear as clear and colorless to dark brown solutions that should be free of particulate matter.
Extracts are labeled either as weight-to-volume based on the weight of the source material to the volume of the extracting fluid, or as PNU/milliliter with one PNU representing 0.00001 mg of protein nitrogen per milliliter.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The skin test reaction results from interaction of the introduced allergen and allergen-specific IgE antibodies bound to mast cells, leading to mast cell degranulation and release of histamine, tryptase and other mediators, which results in the formation of the wheal and flare.
The precise mechanisms of action of allergen immunotherapy are not known. Immunologic responses to immunotherapy include changes in allergen-specific IgE levels, allergen-specific IgG levels, and regulatory T cell responses. 1
- 14 CLINICAL STUDIES
-
15 REFERENCES
- Cox LJ, Nelson H, Lockey R.Allergen immunotherapy: A practice parameter third update. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127:(1)S1-55.
- Bernstein IL, Li JT, Bernstein DI, et al.Allergy diagnostic testing: an updated practice parameter. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2008;100:S1-148.
- Greenberg MA, Kaufman CR, Gonzalez GE, et al. Late and immediate systemic-allergic reactions to inhalant allergen immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1986;77:865-870.
- Federal Register Proposed Rule: Biological Products: Implementation of Efficacy Review, Allergenic Extracts, Federal Register 1985;50: 3082-3288.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts and mixes may be supplied as aqueous stock concentrates of up to 1:10 weight/volume or 40,000 PNU/milliliter for intradermal and subcutaneous testing. The extracts may also be supplied as 50% glycerin stock concentrates of up to 1:20 weight/volume for use in percutaneous skin testing and subcutaneous immunotherapy. Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts are labeled in weight/volume and/or PNU/milliliter and may be provided in 5, 10, and 50 milliliter vials. Glycerinated extracts are also supplied in 5 milliliter dropper vials for prick or puncture testing.
Non-Standardized Allergenic Extracts available are as follows:
Pollens ‑ Grasses Bahia Grass, Paspalum notatum Brome, Smooth, Bromus inermis Canarygrass, Reed, Phalaris arundinacea Johnson Grass, Sorghum halepense Quack (Couch) Grass, Elymus repens Ryegrass, Giant Wild, Leymus condensatus Ryegrass, Italian, Lolium multiflorum Velvetgrass, Holcus lanatus Wheatgrass, Western, Pascopyrum smithii Pollens - Trees Acacia, Acacia dealbata Alder, Hazel, Alnus serrulata Alder, Red, Alnus rubra Alder, White, Alnus rhombifolia Ash, Arizona (Velvet), Fraxinus velutina Ash, Green, Fraxinus pennsylvanica Ash Mix (Equal parts Fraxinus pennsylvanica, Fraxinus americana) Ash, Oregon, Fraxinus latifolia Ash, White, Fraxinus americana Aspen, Populus tremuloides Beech, American, Fagus grandifolia Birch, Black-Sweet, Betula lenta Birch, Mix (Equal parts Betula lenta, Betula nigra, Betula populifolia) Birch, River, Betula nigra Birch, Spring, Betula occidentalis Birch, White, Betula populifolia Box Elder, Acer negundo Cedar, Mountain, Juniperus ashei Cedar, Red, Juniperus virginiana Cedar, Salt (Tamarisk), Tamarix gallica Central/Eastern 4 Tree Mix (Equal parts Ulmus americana, Acer negundo, Carya illinoinensis, Quercus virginiana) Cottonwood, Arizona (Fremont), Populus fremontii Cottonwood, Black, Populus trichocarpa Cottonwood, Eastern, Populus deltoides Cottonwood, Western, Populus deltoides ssp. monilifera Cypress, Arizona, Callitropsis arizonica Cypress, Bald, Taxodium distichum Eastern Oak Mix (Equal parts Quercus velutina, Quercus rubra, Quercus alba) Eastern 6 Tree Mix (Equal parts Fagus grandifolia, Populus deltoides, Quercus rubra, Betula nigra, Carya ovata, Fraxinus americana) Eastern 7 Tree Mix (Equal parts Ulmus americana, Fagus grandifolia, Populus deltoides, Quercus rubra, Betula nigra, Carya ovata, Fraxinus americana) Eastern 8 Tree Mix (Equal parts Ulmus americana, Fagus grandifolia, Populus deltoides, Quercus rubra, Betula nigra, Carya ovata, Fraxinus americana, Acer saccharum) Eastern 10 Tree Mix (Equal parts Platanus occidentalis, Ulmus americana, Fagus grandifolia, Populus deltoides, Quercus rubra, Betula nigra, Carya ovata, Fraxinus americana, Acer saccharum, Liquidambar styraciflua) Elm, American, Ulmus americana Elm, Cedar, Ulmus crassifolia Elm Mix (Equal parts Ulmus americana, Ulmus pumila) Elm, Siberian, Ulmus pumila Eucalyptus, Bluegum, Eucalyptus globulus Hackberry, Celtis occidentalis Hazelnut, American, Corylus americana Hickory Mix (Equal parts Carya glabra, Carya ovata, Carya laciniosa, Carya tomentosa) Hickory-Pecan Mix (Equal parts Carya illinoinensis, Carya ovata) Hickory, Shagbark, Carya ovata Hickory, Shellbark, Carya laciniosa Hickory, White, Carya tomentosa Juniper Mix (Equal parts Juniperus monosperma, Juniperus scopulorum) Juniper, Oneseed, Juniperus monosperma Juniper, Pinchot, Juniperus pinchotii Juniper, Rocky Mountain, Juniperus scopulorum Juniper, Utah, Juniperus osteosperma Juniper, Western, Juniperus occidentalis Locust Blossom, Black, Robinia pseudoacacia Mango Blossom, Mangifera indica Maple-Box Elder Mix (Equal parts Acer saccharum, Acer negundo) 2 Maple Mix (Equal parts Acer rubrum, Acer saccharum) 3 Maple Mix (Equal parts Acer rubrum, Acer saccharinum, Acer saccharum) Maple, Red, Acer rubrum Maple, Silver/Soft, Acer saccharinum Maple, Sugar/Hard, Acer saccharum Melaleuca, Melaleuca quinquenervia Mesquite, Velvet, Prosopis velutina Mulberry, Paper, Broussonetia papyrifera Mulberry, Red, Morus rubra Mulberry, White, Morus alba Oak, Arizona (Gambel), Quercus gambelii Oak, Black, Quercus velutina Oak, Bur, Quercus macrocarpa Oak, California Black, Quercus kelloggii Oak, California Live, Quercus agrifolia Oak, California White, Quercus lobata Oak, Post, Quercus stellata Oak, Red, Quercus rubra Oak, Virginia Live, Quercus virginiana Oak, Water, Quercus nigra Oak, Western White, Quercus garryana Oak, White, Quercus alba Olive, Olea europaea Olive, Russian, Elaeagnus angustifolia Orange Pollen, Citrus X sinensis Palm, Queen, Syagrus romanzoffiana Pecan, Carya illinoinensis Peppertree Mix (Equal parts Schinus molle, Schinus terebinthifolius) Pine, Australian (Beefwood), Casuarina equisetifolia Pine, Loblolly, Pinus taeda Pine, Longleaf, Pinus palustris Pine Mix (Equal parts Pinus taeda, Pinus strobus, Pinus echinata) Pine, Ponderosa, Pinus ponderosa Pine, Virginia Scrub, Pinus virginiana Pine, White (Eastern), Pinus strobus Pine, White (Western), Pinus monticola Pine, Yellow, Pinus echinata Poplar, Lombardy’s, Populus nigra Poplar, White, Populus alba Privet, Ligustrum vulgare Sweetgum, Liquidambar styraciflua Sycamore, American, Platanus occidentalis Sycamore, California (Western), Platanus racemosa 11 Tree Mix (Equal parts Fagus grandifolia, Platanus occidentalis, Ulmus americana, Juglans nigra, Salix nigra, Populus deltoides, Quercus rubra, Betula nigra, Carya ovata, Acer saccharum, Fraxinus americana) Walnut, Black, Juglans nigra Walnut, California Black, Juglans californica Walnut, English, Juglans regia Wax Myrtle, Morella cerifera Western Oak Mix (Equal parts Quercus kelloggii, Quercus agrifolia, Quercus garryana) Western 3 Tree Mix (Equal parts Olea europaea, Ulmus pumila, Platanus racemosa) Western 10 Tree Mix (Equal parts Acacia dealbata, Acer negundo, Populus fremontii, Olea europaea, Ulmus pumila, Betula occidentalis, Juniperus occidentalis, Platanus racemosa, Quercus garryana, Morus alba) Western Walnut Mix (Equal parts Juglans californica, Juglans regia) Willow, Arroyo, Salix lasiolepis Willow, Black, Salix nigra Pollens - Weeds and Garden Plants Allscale, Atriplex polycarpa Amaranth, Green, Amaranthus hybridus Baccharis Mix (Equal parts Baccharis sarothroides, Baccharis halimifolia) Burningbush (Kochia), Kochia scoparia spp. scoparia Burrobrush, Ambrosia salsola Central/Western Weed Mix (Equal parts Kochia scoparia ssp. scoparia, Chenopodium album, Salsola kali) Cocklebur, Xanthium strumarium Common Weed Mix (Equal parts Xanthium strumarium, Plantago lanceolata, Chenopodium album, Amaranthus retroflexus, Salsola kali) Dock-Sorrel Mix (Equal parts Rumex acetosella, Rumex crispus) Dock, Yellow (Curly), Rumex crispus Dogfennel, Eupatorium capillifolium Goldenrod, Solidago canadensis Iodinebush, Allenrolfea occidentalis Lamb's Quarters, Chenopodium album Lenscale (Quailbrush), Atriplex lentiformis Marsh Elder, True (Rough), Iva annua Marshelder, Burweed (Giant Poverty), Cyclachaena xanthiifolia Mixed Amaranths (Equal parts Amaranthus hybridus, Amaranthus palmeri, Amaranthus retroflexus) Mugwort, Common, Artemisia vulgaris National Weed Mix (Equal parts Xanthium strumarium, Ambrosia trifida, Chenopodium album, Amaranthus retroflexus, Ambrosia artemisiifolia) Nettle, Urtica dioica Palmer's Amaranth, Amaranthus palmeri Pigweed, Rough Redroot, Amaranthus retroflexus Pigweed, Spiny, Amaranthus spinosus Plantain, English, Plantago lanceolata Plantain-Sorrel Mix (Equal parts Plantago lanceolata, Rumex acetosella) Rabbit Bush, Ambrosia deltoidea Ragweed, Desert, Ambrosia dumosa Ragweed, False, Ambrosia acanthicarpa Ragweed, Giant (Tall), Ambrosia trifida Ragweed, Lanceleaf, Ambrosia bidentata Ragweed, Slender, Ambrosia confertiflora Ragweed, Western, Ambrosia psilostachya Russian Thistle, Salsola kali Sagebrush, Common, Artemisia tridentata Sage Mix (Equal parts Artemisia tridentata, Artemisia ludoviciana) Sage, Prairie, Artemisia ludoviciana Saltbush, Annual, Atriplex wrightii Scale/Atriplex Mix (Equal parts Atriplex polycarpa, Atriplex lentiformis, Atriplex canescens) Sorrel, Sheep (Red), Rumex acetosella Waterhemp, Tall, Amaranthus tuberculatus 3 Weed Mix (Equal parts Xanthium strumarium, Chenopodium album, Amaranthus retroflexus) Western Ragweed Mix (Equal parts Ambrosia acanthicarpa, Ambrosia psilostachya) Wingscale, Atriplex canescens Plants and Plant Parts Cotton Linters, Gossypium hirsutum Cottonseed, Gossypium hirsutum (For Diagnostic Use Only) Flax, Linum usitatissimum (For Diagnostic Use Only) Gum, Arabic, Acacia senegal Gum, Karaya, Sterculia urens Gum, Tragacanth, Astragalus gummifer Kapok, Ceiba pentandra Orris Root, Iris germanica Pyrethrum, Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium Tobacco, Cultivated, Leaf, Nicotiana tabacum Pollens - Cultivated Farm Plants Alfalfa, Medicago sativa Beet, Sugar, Beta vulgaris Corn, Cultivated, Zea mays Oat, Cultivated, Avena sativa Rape (Mustard), Brassica napus Red Clover, Trifolium pratense Rye, Cultivated, Secale cereale Wheat, Cultivated, Triticum aestivum Pollens - Flowers Daisy, Leucanthemum vulgare Dandelion, Taraxacum officinale Sunflower, Helianthus annuus Molds, Rusts and Smuts AHH Mold Mix (Equal parts Alternaria alternata, Bipolaris sorokiniana, Cladosporium sphaerospermum) Alternaria alternata Alternaria/Hormodendrum Mix (Equal parts Alternaria alternata, Cladosporium sphaerospermum) Aspergillus amstelodami Aspergillus flavus Aspergillus fumigatus Aspergillus Mix (Equal parts Aspergillus amstelodami, Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus nidulans, Aspergillus niger) Aspergillus nidulans Aspergillus niger Aureobasidium pullulans Bermuda Grass Smut, Ustilago cynodontis Bipolaris sorokiniana Botrytis cinerea Candida albicans Chaetomium globosum Cladosporium herbarum Cladosporium sphaerospermum Corn Smut, Ustilago maydis Curvularia spicifera Dematiaceae Mix (Equal parts Alternaria alternata, Aureobasidium pullulans, Bipolaris sorokiniana, Cladosporium herbarum, Curvularia spicifera, Helminthosporium solani) Epicoccum nigrum Epidermophyton floccosum Fusarium Mix (Equal parts Gibberella fujikuroi, Fusarium solani) Fusarium solani Geotrichum candidum Gibberella fujikuroi Gliocladium viride Grain Smut Mix (Equal parts Ustilago maydis, Ustilago tritici, Ustilago nuda, Ustilago avenae) Grass Smut Mix (Equal parts Ustilago cynodontis, Sporisorium cruentum) Helminthosporium solani Hypomyces perniciousus Loose Kernel Smut, Sporisorium cruentum Loose Smut, Wheat, Ustilago tritici Microsporum canis Mold Mix #1 (Equal parts Alternaria alternata, Aspergillus niger, Bipolaris sorokiniana, Cladosporium sphaerospermum, Penicillium chrysogenum var. chrysogenum) Mold Mix #2 (Equal parts Aureobasidium pullulans, Curvularia spicifera, Gibberella fujikuroi, Mucor plumbeus, Rhizopus stolonifer) Mold Mix #3 (Equal parts Alternaria alternata, Aspergillus niger, Cladosporium sphaerospermum, Penicillium chrysogenum var. chrysogenum) Monilia Mix (Equal parts Candida albicans, Neurospora intermedia) Mucor circinelloides f. circinelloides Mucor circinelloides f. lusitanicus Mucor Mix (Equal parts Mucor circinelloides f. lusitanicus, Mucor plumbeus) Mucor plumbeus Neurospora intermedia New Stock Fungi Mix (Equal parts Sarocladium strictum, Alternaria alternata, Aspergillus niger, Aureobasidium pullulans, Bipolaris sorokiniana, Botrytis cinerea, Candida albicans, Chaetomium globosum, Cladosporium sphaerospermum, Epicoccum nigrum, Gibberella fujikuroi, Mucor plumbeus, Penicillium chrysogenum var. chrysogenum, Phoma betae, Rhizopus stolonifer, Trichophyton mentagrophytes) Oat Smut, Ustilago avenae Paecilomyces variotii Penicillium chrysogenum var. chrysogenum Penicillium digitatum Penicillium Mix (Equal parts Penicillium camemberti, Penicillium chrysogenum, Penicillium digitatum, Penicillium chrysogenum var. chrysogenum, Penicillium roqueforti) Phoma betae Phycomycetes Mix (Equal parts Mucor circinelloides f. lusitanicus, Rhizopus stolonifer) Rhizopus arrhizus Rhizopus Mix (Equal parts Rhizopus stolonifer, Rhizopus arrhizus) Rhizopus stolonifer Rhodotorula mucilaginosa Saccharomyces cerevisiae Sarocladium strictum Stemphylium solani Trichoderma harzianum Trichophyton mentagrophytes Trichophyton rubrum Trichothecium roseum Animal Allergens Canary Feathers, Serinus canaria Cattle Epithelia, Bos taurus Chicken Feathers, Gallus gallus Dog Epithelia, Canis lupus familiaris Duck Feathers, Anas platyrhynchos Gerbil Epithelia, Meriones unguiculatus Goat Epithelia, Capra hircus Goose Feathers, Anser anser Guinea Pig Epithelia, Cavia porcellus Hamster Epithelia, Mesocricetus auratus Hog Epithelia, Sus scrofa Horse Epithelia, Equus caballus Mixed Feathers (Equal parts Gallus gallus, Anas platyrhynchos, Anser anser) Mouse Epithelia, Mus musculus Parakeet Feathers, Melopsittacus undulatus Rabbit Epithelia, Oryctolagus cuniculus Rat Epithelia, Rattus norvegicus Silk Worm Cocoon, Bombyx mori Insects (Whole Body) Ant, Black Carpenter, Camponotus pennsylvanicus Ant, Fire, Solenopsis invicta Ant, Fire, Solenopsis richteri Cockroach, American, Periplaneta americana Cockroach, German, Blattella germanica 2 Cockroach Mix (Equal parts Periplaneta americana, Blattella germanica) Deer Fly, Chrysops vittatus Flea, Ctenocephalis felis (For Dagnostic Use Only) House Fly, Musca domestica (For Dagnostic Use Only) Mosquito, Aedes taeniorhynchus (For Diagnostic Use Only) Food - Animal Products and Poultry Products Beef, Bos taurus Chicken Meat, Gallus gallus Egg, White, Chicken, Gallus gallus Egg, Whole, Chicken, Gallus gallus Egg, Yolk, Chicken, Gallus gallus Lamb, Ovis aries Pork, Sus scrofa Turkey Meat, Meleagris gallopavo Food - Dairy Products Milk, Cow, Bos taurus Food - Fish and Shellfish Bass, Black, Centropristis striata Catfish, Channel, Ictalurus punctatus Clam, Northern Quahog, Mercenaria mercenaria Cod, Atlantic, Gadus morhua Crab, Blue, Callinectes sapidus Fish Mix (Equal parts Gadus morhua, Paralichthys lethostigma, Hippoglossus hippoglossus, Scomber scombrus, Thunnus albacares) Flounder, Southern, Paralichthys lethostigma Lobster, American, Homarus americanus Mackerel, King/Atlantic, Scomber scombrus Oyster, Atlantic/Eastern, Crassostrea virginica Perch, Ocean, Sebastes alutus Salmon, Atlantic, Salmo salar Scallops, Sea, Placopecten magellanicus Shellfish Mix (Equal parts Mercenaria mercenaria, Callinectes sapidus, Crassostrea virginica, Placopecten magellanicus, Farfantepenaeus aztecus) Shrimp, Brown, Farfantepenaeus aztecus Trout, Rainbow, Oncorhynchus mykiss Tuna, Yellowfin, Thunnus albacares Food - Plant Source Almond, Prunus dulcis Apple, Malus pumila Apricot, Prunus armeniaca Banana, Musa acuminata Barley, Whole Grain, Hordeum vulgare (For Diagnostic Use Only, Contains SFS*) Bean, Lima, Phaseolus lunatus Bean, Navy, Phaseolus vulgaris Bean, String Green, Phaseolus vulgaris Blueberry, Velvetleaf, Vaccinium myrtilloides Brazil Nut, Bertholletia excelsa Broccoli, Brassica oleracea var. botrytis Buckwheat, Fagopyrum esculentum Cabbage, Brassica oleracea var. capitata Cacao Bean, Theobroma cacao Cantaloupe, Cucumis melo Carrot, Daucus carota Cashew Nut, Anacardium occidentale Cauliflower, Brassica oleracea var. botrytis Celery, Apium graveolens var. dulce Cherry, Sweet, Prunus avium Cinnamon, Cinnamomum verum Coconut, Cocos nucifera Coffee, Coffea arabica (For Diagnostic Use Only) Corn, Zea mays Cranberry, Vaccinium macrocarpon Cucumber, Cucumis sativus Garlic, Allium sativum Ginger, Zingiber officinale Grape, White Seedless, Vitis vinifera Grapefruit, Citrus X paradisi Hazelnut (Filbert), Corylus americana Hops, Humulus lupulus Lemon, Citrus X limon Lettuce, Lactuca sativa Malt (Barley), Hordeum vulgare Mushroom, Agaricus campestris Mustard Seed, Sinapis alba Nutmeg, Myristica fragrans Oat, Avena sativa (For Diagnostic Use Only, Contains SFS*) Olive, Green, Olea europaea Onion, Allium cepa Orange, Citrus X sinensis Pea, Green or English, Pisum sativum Peach, Prunus persica Peanut, Arachis hypogaea Pear, Pyrus communis Pecan, Carya illinoinensis Pepper, Black, Piper nigrum Pepper, Green, Capsicum annuum Pineapple, Ananas comosus (For Diagnostic Use Only, Contains SFS*) Potato, Sweet, Ipomoea batatas Potato, White, Solanum tuberosum Raspberry, Red, Rubus idaeus Rice, Oryza sativa Rye, Secale cereale (For Diagnostic Use Only, Contains SFS*) Sesame Seed, Sesamum indicum Soybean, Glycine max Spinach, Spinacia oleracea (For Diagnostic Use Only, Contains SFS*) Squash, Yellow Summer, Cucurbita pepo var. ovifera Strawberry, Fragaria X ananassa Tomato, Solanum lycopersicum Vanilla, Vanilla planifolia Walnut, Black, Juglans nigra Walnut, English, Juglans regia Watermelon, Citrullus lanatus Wheat, Whole, Triticum aestivum (For Diagnostic Use Only, Contains SFS*) *SFS – Sodium Formadehyde Sulfoxylate
16.2 Storage and Handling
Maintain at 2 to 8°C (36 to 46°F) during storage and use.
Dilutions of concentrated extracts that result in a glycerin content of less than 50% can reduce extract stability. Extract dilutions at 1:100 volume to volume should be kept no longer than a month, and more dilute solutions no more than a week. The potency of a dilution can be checked by skin test comparison to a fresh dilution of the extract on a known allergic patient.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Instruct patient to remain under observation in the office for 30 minutes or longer after an injection.
Caution patient that reactions can occur more than 30 minutes after skin testing or an injection.
Instruct patient to recognize the following symptoms as adverse reactions and to immediately return to the office or immediately seek other medical attention if any of these symptoms occur following skin testing or an injection:
- Unusual swelling and/or tenderness at the injection site
- Hives or itching of the skin
- Swelling of the face and/or mouth
- Sneezing, coughing or wheezing
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea
- Dizziness or faintness
Manufacturer:
U.S. License No. 308
Greer Laboratories, Inc.
Lenoir, NC 28645 U.S.A
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
DAISY
leucanthemum vulgare solutionProduct Information Product Type NON-STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC:22840-1570 Route of Administration INTRADERMAL, PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LEUCANTHEMUM VULGARE POLLEN (UNII: H9E0IX4MOX) (LEUCANTHEMUM VULGARE POLLEN - UNII:H9E0IX4MOX) LEUCANTHEMUM VULGARE POLLEN 0.1 g in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:22840-1570-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC:22840-1570-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101833 09/15/1981 DANDELION
taraxacum officinale solutionProduct Information Product Type NON-STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC:22840-1502 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN (UNII: WQ3S5294XY) (TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN - UNII:WQ3S5294XY) TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN 0.001 g in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:22840-1502-1 5 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101833 09/15/1981 DANDELION
taraxacum officinale solutionProduct Information Product Type NON-STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC:22840-1501 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN (UNII: WQ3S5294XY) (TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN - UNII:WQ3S5294XY) TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN 1000 [PNU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:22840-1501-1 5 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101833 09/15/1981 DANDELION
taraxacum officinale solutionProduct Information Product Type NON-STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC:22840-1572 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN (UNII: WQ3S5294XY) (TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN - UNII:WQ3S5294XY) TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN 20000 [PNU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:22840-1572-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101833 09/15/1981 DAISY
leucanthemum vulgare solutionProduct Information Product Type NON-STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC:22840-1569 Route of Administration INTRADERMAL, PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LEUCANTHEMUM VULGARE POLLEN (UNII: H9E0IX4MOX) (LEUCANTHEMUM VULGARE POLLEN - UNII:H9E0IX4MOX) LEUCANTHEMUM VULGARE POLLEN 40000 [PNU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:22840-1569-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101833 09/15/1981 SUNFLOWER
helianthus annuus solutionProduct Information Product Type NON-STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC:22840-1503 Route of Administration INTRADERMAL, PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength HELIANTHUS ANNUUS POLLEN (UNII: 28D6K7E9IP) (HELIANTHUS ANNUUS POLLEN - UNII:28D6K7E9IP) HELIANTHUS ANNUUS POLLEN 0.1 g in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:22840-1503-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC:22840-1503-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101833 09/15/1981 DANDELION
taraxacum officinale solutionProduct Information Product Type NON-STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC:22840-5501 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN (UNII: WQ3S5294XY) (TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN - UNII:WQ3S5294XY) TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN 0.05 g in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:22840-5501-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC:22840-5501-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC:22840-5501-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101833 09/15/1981 DANDELION
taraxacum officinale solutionProduct Information Product Type NON-STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC:22840-1571 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN (UNII: WQ3S5294XY) (TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN - UNII:WQ3S5294XY) TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN 0.05 g in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:22840-1571-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC:22840-1571-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101833 09/15/1981 SUNFLOWER
helianthus annuus solutionProduct Information Product Type NON-STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC:22840-1506 Route of Administration INTRADERMAL, PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength HELIANTHUS ANNUUS POLLEN (UNII: 28D6K7E9IP) (HELIANTHUS ANNUUS POLLEN - UNII:28D6K7E9IP) HELIANTHUS ANNUUS POLLEN 0.001 g in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:22840-1506-1 5 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101833 09/15/1981 DANDELION
taraxacum officinale solutionProduct Information Product Type NON-STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC:22840-1573 Route of Administration PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN (UNII: WQ3S5294XY) (TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN - UNII:WQ3S5294XY) TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN 40000 [PNU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:22840-1573-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC:22840-1573-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101833 09/15/1981 SUNFLOWER
helianthus annuus solutionProduct Information Product Type NON-STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC:22840-1504 Route of Administration INTRADERMAL, PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength HELIANTHUS ANNUUS POLLEN (UNII: 28D6K7E9IP) (HELIANTHUS ANNUUS POLLEN - UNII:28D6K7E9IP) HELIANTHUS ANNUUS POLLEN 40000 [PNU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:22840-1504-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101833 09/15/1981 SUNFLOWER
helianthus annuus solutionProduct Information Product Type NON-STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC:22840-5502 Route of Administration INTRADERMAL, PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength HELIANTHUS ANNUUS POLLEN (UNII: 28D6K7E9IP) (HELIANTHUS ANNUUS POLLEN - UNII:28D6K7E9IP) HELIANTHUS ANNUUS POLLEN 0.05 g in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:22840-5502-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC:22840-5502-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC:22840-5502-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101833 09/15/1981 DAISY
leucanthemum vulgare solutionProduct Information Product Type NON-STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC:22840-5500 Route of Administration INTRADERMAL, PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LEUCANTHEMUM VULGARE POLLEN (UNII: H9E0IX4MOX) (LEUCANTHEMUM VULGARE POLLEN - UNII:H9E0IX4MOX) LEUCANTHEMUM VULGARE POLLEN 0.05 g in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:22840-5500-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC:22840-5500-5 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, DROPPER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101833 09/15/1981 DANDELION
taraxacum officinale solutionProduct Information Product Type NON-STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC:22840-1500 Route of Administration SUBCUTANEOUS, PERCUTANEOUS, INTRADERMAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN (UNII: WQ3S5294XY) (TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN - UNII:WQ3S5294XY) TARAXACUM OFFICINALE POLLEN 0.1 g in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:22840-1500-2 10 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC:22840-1500-4 50 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101833 09/15/1981 SUNFLOWER
helianthus annuus solutionProduct Information Product Type NON-STANDARDIZED ALLERGENIC Item Code (Source) NDC:22840-1505 Route of Administration INTRADERMAL, PERCUTANEOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength HELIANTHUS ANNUUS POLLEN (UNII: 28D6K7E9IP) (HELIANTHUS ANNUUS POLLEN - UNII:28D6K7E9IP) HELIANTHUS ANNUUS POLLEN 1000 [PNU] in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SODIUM BICARBONATE (UNII: 8MDF5V39QO) PHENOL (UNII: 339NCG44TV) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:22840-1505-1 5 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA101833 09/15/1981 Labeler - Greer Laboratories, Inc. (024671414) Registrant - Greer Laboratories, Inc. (024671414) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Greer Laboratories, Inc. 024671414 manufacture(22840-1569, 22840-1570, 22840-5500, 22840-1500, 22840-1502, 22840-1571, 22840-1572, 22840-1573, 22840-5501, 22840-1503, 22840-1504, 22840-1506, 22840-5502, 22840-1501, 22840-1505)








