Label: ENROQUIN ANTIBACTERIAL- enrofloxacin injection
- NDC Code(s): 17033-324-20
- Packager: Dechra Vet Products, LLC
- Category: PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Abbreviated New Animal Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated March 23, 2022
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
- SAFE HANDLING WARNING
- VETERINARY INDICATIONS
-
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION:
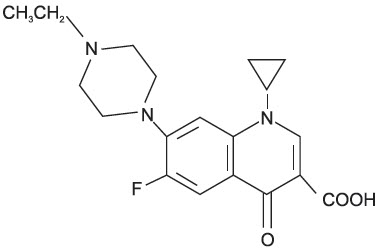
Enrofloxacin is a synthetic chemotherapeutic agent from the class of the quinolone carboxylic acid derivatives. It has antibacterial activity against a broad spectrum of Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria (See Tables I and II). Each mL of injectable solution contains: enrofloxacin 22.7 mg, n-butyl alcohol 30 mg, potassium hydroxide for pH adjustment and water for injection, q.s.
-
MECHANISM OF ACTION
ACTIONS:
Microbiology: Quinolone carboxylic acid derivatives are classified as DNA gyrase inhibitors. The mechanism of action of these compounds is very complex and not yet fully understood. The site of action is bacterial gyrase, a synthesis promoting enzyme. The effect on Escherichia coli is the inhibition of DNA synthesis through prevention of DNA supercoiling. Among other things, such compounds lead to the cessation of cell respiration and division. They may also interrupt bacterial membrane integrity.1
Enrofloxacin is bactericidal, with activity against both Gram negative and Gram positive bacteria. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) were determined for a series of 37 isolates representing 9 genera of bacteria from natural infections in dogs, selected principally because of resistance to one or more of the following antibiotics: ampicillin, cephalothin, colistin, chloramphenicol, erythromycin, gentamicin, kanamycin, penicillin, streptomycin, tetracycline, triple sulfa and sulfa/trimethoprim. The MIC values for enrofloxacin against these isolates are presented in Table I. Most strains of these organisms were found to be susceptible to enrofloxacin in vitro but the clinical significance has not been determined for some of the isolates.
The susceptibility of organisms to enrofloxacin should be determined using enrofloxacin 5 mcg disks. Specimens for susceptibility testing should be collected prior to the initiation of enrofloxacin therapy.
TABLE I-MIC Values for Enrofloxacin Against Canine Pathogens (Diagnostic laboratory isolates, 1984) Organisms Isolates MIC Range
(mcg/mL)Bacteroides spp. 2 2 Bordetella bronchiseptica 3 0.125-0.5 Brucella canis 2 0.125-0.25 Clostridium perfringens 1 0.5 Escherichia coli 4 ≤0.016-0.031 Klebsiella spp. 10 0.031-0.5 Proteus mirabilis 6 0.062-0.125 Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4 0.5-8 Staphylococcus spp. 5 0.125 The inhibitory activity on 120 isolates of seven canine urinary pathogens was also investigated and is listed in Table II.
TABLE II - MIC Values for Enrofloxacin Against Canine Urinary Pathogens (Diagnostic laboratory isolates, 1985) Organisms Isolates MIC Range
(mcg/mL)E. coli 30 0.06-2.0 P. mirabilis 20 0.125-2.0 K. pneumoniae 20 0.06-0.5 P. aeruginosa 10 1.0-8.0 Enterobacter spp. 10 0.06-1.0 Staph. (coag. +) 20 0.125-0.5 Strep. (alpha hemol.) 10 0.5-8.0 Distribution in the Body: Enrofloxacin penetrates into all canine tissues and body fluids. Concentrations of drug equal to or greater than the MIC for many pathogens (See Tables I, II and III) are reached in most tissues by two hours after dosing at 2.5 mg/kg and are maintained for 8-12 hours after dosing. Particularly high levels of enrofloxacin are found in urine. A summary of the body fluid/tissue drug levels at 2 to 12 hours after dosing at 2.5 mg/kg is given in Table III.
TABLE III - Body Fluid/Tissue distribution of Enrofloxacin in Dogs Single Oral Dose = 2.5 mg/kg (1.13 mg/lb) Post-treatment Enrofloxacin Levels
Canine (n=2)Body Fluids (mcg/mL) 2 Hr. 8 Hr. Urine 43.05 55.35 Eye Fluids 0.53 0.66 Whole Blood 1.01 0.36 Plasma 0.67 0.33 Tissues (mcg/g) Hematopoietic System Liver 3.02 1.36 Spleen 1.45 0.85 Bone Marrow 2.10 1.22 Lymph Node 1.32 0.91 Urogenital System Kidney 1.87 0.99 Bladder Wall 1.36 0.98 Testes 1.36 1.10 Prostate 1.36 2.20 Uterine Wall 1.59 0.29 Gastrointestinal and Cardiopulmonary Systems Lung 1.34 0.82 Heart 1.88 0.78 Stomach 3.24 2.16 Small Intestine 2.10 1.11 Other Fat 0.52 0.40 Skin 0.66 0.48 Muscle 1.62 0.77 Brain 0.25 0.24 Mammary Gland 0.45 0.21 Feces 1.65 9.97 Pharmacokinetics: In dogs, the absorption and elimination characteristics of the oral formulation are linear (plasma concentrations increase proportionally with dose) when enrofloxacin is administered at up to 11.5 mg/kg, twice daily2. Approximately 80% of the orally administered dose enters the systemic circulation unchanged. The eliminating organs, based on the drug's body clearance time, can readily remove the drug with no indication that the eliminating mechanisms are saturated. The primary route of excretion is via the urine. The absorption and elimination characteristics beyond this point are unknown. Saturable absorption and/or elimination processes may occur at greater doses. When saturation of the absorption process occurs, the plasma concentration of the active moiety will be less than predicted based on the concept of dose proportionality.
Following an oral dose in dogs of 2.5 mg/kg (1.13 mg/lb), enrofloxacin reached 50% of its maximum serum concentration in 15 minutes and peak serum level was reached in one hour. The elimination half-life in dogs is approximately 2½-3 hours at that dose.
A graph indicating the mean serum levels following a dose of 2.5 mg/kg (1.13 mg/lb) in dogs (oral and intramuscular) is shown in Figure 1.
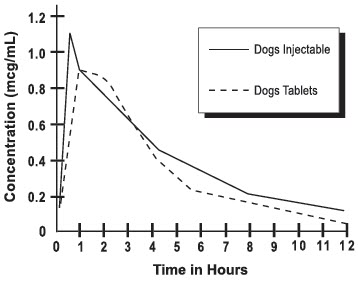
Figure 1-Serum Concentrations of Enrofloxacin Following a Single Oral or Intramuscular Dose at 2.5 mg/kg in Dogs.
Breakpoint: Based on pharmacokinetic studies of enrofloxacin in dogs after a single oral administration of 2.5 mg enrofloxacin/kg BW (i.e. half of the lowest-end single daily dose range) and the data listed in Tables I and II, the following breakpoints are recommended for canine isolates.
Zone Diameter (mm) MIC (μg/mL) Interpretation ≥21 ≤0.5 Susceptible (S) 18 - 20 1 Intermediate (I) ≤17 ≥2 Resistant (R) A report of "Susceptible" indicates that the pathogen is likely to be inhibited by generally achievable plasma levels. A report of "Intermediate" is a technical buffer and isolates falling into this category should be retested. Alternatively the organism may be successfully treated if the infection is in a body site where drug is physiologically concentrated. A report of "resistant" indicates that the achievable drug concentrations are unlikely to be inhibitory and other therapy should be selected.
Standardized procedures require the use of laboratory control organisms for both standardized disk diffusion assays and standardized dilution assays. The 5 µg enrofloxacin disk should give the following zone diameters and enrofloxacin powder should provide the following MIC values for reference strains.
QC strains MIC (μg/mL) Zone Diameter (mm) E. coli ATCC 25922 0.008 - 0.03 32 - 40 P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 1 - 4 15 - 19 S. aureus ATCC 25923 27 - 31 S. aureus ATCC 29213 0.03 - 0.12 - VETERINARY INDICATIONS
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
EFFICACY CONFIRMATION:
Clinical efficacy was established in dermal infections (wounds and abscesses) associated with susceptible strains of Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, and Staphylococcus intermedius; respiratory infections (pneumonia, tonsillitis, rhinitis) associated with susceptible strains of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus; and urinary cystitis associated with susceptible strains of Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, and Staphylococcus aureus.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Enrofloxacin is contraindicated in dogs known to be hypersensitive to quinolones.
Based on the studies discussed under the section on Animal Safety Summary, the use of enrofloxacin is contraindicated in small and medium breeds of dogs during the rapid growth phase (between 2 and 8 months of age). The safe use of enrofloxacin has not been established in large and giant breeds during the rapid growth phase. Large breeds may be in this phase for up to one year of age and the giant breeds for up to 18 months. In clinical field trials utilizing a daily oral dose of 5.0 mg/kg, there were no reports of lameness or joint problems in any breed. However, controlled studies with histological examination of the articular cartilage have not been conducted in the large or giant breeds.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
No drug-related side effects were reported in 122 clinical cases treated with enrofloxacin injectable solution followed by enrofloxacin tablets at 5.0 mg/kg per day.
To report suspected adverse drug events, for technical assistance or to obtain a copy of the Safety Data Sheet, contact Dechra at (866) 933-2472. For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or http://www.fda.gov/reportanimalae.
-
ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY & OR TOXICOLOGY
ANIMAL SAFETY SUMMARY:
Adult dogs receiving enrofloxacin orally at a daily dosage rate 52 mg/kg for 13 weeks had only isolated incidences of vomition and inappetence. Adult dogs receiving the tablet formulation for 30 consecutive days at a daily treatment of 25 mg/kg did not exhibit significant clinical signs nor were there effects upon the clinical chemistry, hematological or histological parameters. Daily doses of 125 mg/kg for up to 11 days induced vomition, inappetence, depression, difficult locomotion and death while adult dogs receiving 50 mg/kg/day for 14 days had clinical signs of vomition and inappetence.
Adult dogs dosed intramuscularly for three treatments at 12.5 mg/kg followed by 57 oral treatments at 12.5 mg/kg, all at 12 hour intervals, did not exhibit either significant clinical signs or effects upon the clinical chemistry, hematological or histological parameters.
Oral treatment of 15 to 28 week old growing puppies with daily dosage rates of 25 mg/kg has induced abnormal carriage of the carpal joint and weakness in the hindquarters. Significant improvement of clinical signs is observed following drug withdrawal. Microscopic studies have identified lesions of the articular cartilage following 30 day treatments at either 5, 15 or 25 mg/kg in this age group. Clinical signs of difficult ambulation or associated cartilage lesions have not been observed in 29 to 34 week old puppies following daily treatments of 25 mg/kg for 30 consecutive days nor in 2 week old puppies with the same treatment schedule.
Tests indicated no effect on circulating microfilariae or adult heartworms (Dirofilaria immitis) when dogs were treated at a daily dosage rate of 15 mg/kg for 30 days. No effect on cholinesterase values was observed.
No adverse effects were observed on reproductive parameters when male dogs received 10 consecutive daily treatments of 15 mg/kg/day at 3 intervals (90, 45 and 14 days) prior to breeding or when female dogs received 10 consecutive daily treatments of 15 mg/kg/day at 4 intervals; between 30 and 0 days prior to breeding, early pregnancy (between 10th & 30th days), late pregnancy (between 40th & 60th days), and during lactation (the first 28 days).
-
DRUG INTERACTIONS
DRUG INTERACTIONS:
Concomitant therapy with other drugs that are metabolized in the liver may reduce the clearance rates of the quinolone and the other drug.
Enrofloxacin has been administered to dogs at a daily dosage rate of 10 mg/kg concurrently with a wide variety of other health products including anthelmintics (praziquantel, febantel), insecticides (pyrethrins), heartworm preventatives (diethylcarbamazine) and other antibiotics (ampicillin, gentamicin sulfate, penicillin). No incompatibilities with other drugs are known at this time.
-
WARNINGS
WARNINGS:
For use in animals only. The use of this product in cats may result in Retinal Toxicity. Keep out of reach of children. Avoid contact with eyes. In case of contact, immediately flush eyes with copious amounts of water for 15 minutes. In case of dermal contact, wash skin with soap and water. Consult a physician if irritation persists following ocular or dermal exposure. Individuals with a history of hypersensitivity to quinolones should avoid this product. In humans, there is a risk of user photosensitization within a few hours after excessive exposure to quinolones. If excessive accidental exposure occurs, avoid direct sunlight.
For customer service or to obtain product information, including Safety Data Sheet, call (866) 933-2472.
-
PRECAUTIONS
PRECAUTION:
Quinolone-class drugs should be used with caution in animals with known or suspected Central Nervous System (CNS) disorders. In such animals, quinolones have, in rare instances, been associated with CNS stimulation which may lead to convulsive seizures.
Quinolone-class drugs have been associated with cartilage erosions in weight-bearing joints and other forms of arthropathy in immature animals of various species.
The use of fluoroquinolones in cats has been reported to adversely affect the retina. Such products should be used with caution in cats.
-
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
Enroquin Injectable Solution may be used as the initial dose at 2.5 mg/kg. It should be administered intramuscularly (IM) as a single dose, followed by initiation of enrofloxacin tablet therapy.
Enroquin Injectable Solution may be administered as follows:
Weight of Animal Enroquin Injectable Solution* 2.5 mg/kg - *
- The initial Enroquin injectable administration should be followed 12 hours later by initiation of enrofloxacin tablet therapy.
9.1 kg
(20 lb)1.00 mL 27.2 kg
(60 lb)3.00 mL The lower limit of the dose range was based on efficacy studies in dogs where enrofloxacin was administered at 2.5 mg/kg twice daily. Target animal safety and toxicology studies were used to establish the upper limit of the dose range and treatment duration.
-
STORAGE AND HANDLING
STORAGE:
Protect from direct sunlight. Do not freeze. Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° and 30°C (59° and 86°F).
Use within 90 days of first puncture and puncture a maximum of 20 times. Any product remaining after 20 punctures or more than 90 days after initial puncture should be discarded.
- HOW SUPPLIED
-
REFERENCES
REFERENCES:
1Dougherty, T.J. and Saukkonen, J.J. Membrane Permeability Changes Associated with DNA Gyrase Inhibitors in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob. Agents and Chemoth., V. 28, Aug. 1985: 200- 206.
2Walker, R.D., et al. Pharmacokinetic Evaluation of Enrofloxacin Administered Orally to Healthy Dogs. Am.J. Res., V. 53, No. 12, Dec. 1992: 2315-2319.
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Approved by FDA under ANADA # 200-708
Distributed by:
Dechra Veterinary Products
7015 College Boulevard, Suite 525
Overland Park, KS 66211 USAMade in India
Neutral Code No. PON/DRUGS/08 22 2288Enroquin® is a registered trademark of Dechra Veterinary Products, LLC.
©2021 Dechra Veterinary Products, LLC.
Rev. December 2021
204000722
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 20 mL Vial Label
PEEL
HERENDC: 17033-324-20
Enroquin®
(enrofloxacin)
Antibacterial Injectable Solution 2.27%
For The Treatment of Susceptible Bacterial Pathogens In Dogs OnlyCAUTION: Federal (U.S.A.) law restricts this drug to
use by or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.Federal law prohibits the extralabel use
of this drug in food-producing animals.Approved by FDA under ANADA # 200-708
Net Contents: 20 mL
Dechra

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ENROQUIN ANTIBACTERIAL
enrofloxacin injectionProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:17033-324 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Enrofloxacin (UNII: 3DX3XEK1BN) (Enrofloxacin - UNII:3DX3XEK1BN) Enrofloxacin 22.7 mg in 1 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:17033-324-20 20 mL in 1 VIAL, GLASS Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANADA ANADA200708 03/17/2022 Labeler - Dechra Vet Products, LLC (362142734)