Label: MOXIDECTIN tablet
- NDC Code(s): 71705-050-01
- Packager: Medicines Development for Global Health
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Drug Label Information
Updated May 2, 2024
If you are a healthcare professional or from the pharmaceutical industry please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
MOXIDECTIN tablets, for oral use
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use MOXIDECTIN safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for MOXIDECTIN .
Initial U.S. Approval: 2018INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Moxidectin is an anthelmintic indicated for the treatment of onchocerciasis due to Onchocerca volvulus in patients aged 12 years and older. ( 1)
Limitations of Use:
- Moxidectin Tablets do not kill adult
O. volvulus parasites. Follow-up is advised.
- The safety and efficacy of repeat administration of Moxidectin Tablets in patients with O. volvulus has not been studied.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Patients aged 12 years and older: Take 8 mg (four 2 mg tablets) as a single oral dose, with or without food. ( 2.1)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 2 mg. ( 3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. ( 4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
-
Cutaneous, Ophthalmological and/or Systemic Adverse Reactions of Varying Severity (Mazzotti Reaction): This may occur in patients with onchocerciasis following treatment with Moxidectin Tablets. Monitor patients for symptoms, including symptomatic orthostatic hypotension. (
5.1)
-
Symptomatic Orthostatic Hypotension: Episodes of symptomatic orthostatic hypotension including inability to stand without support may occur in patients following treatment with Moxidectin Tablets. (
5.2)
-
Encephalopathy in Loa loa Co-Infected Patients: Serious or even fatal encephalopathy following treatment with Moxidectin Tablets may occur in patients co-infected with
Loa loa. Assess patients for loiasis in
Loa loa endemic areas prior to treatment. (
5.3)
- Edema and Worsening of Onchodermatitis: Patients with hyper-reactive onchodermatitis (sowda) may be more likely than others to experience severe edema and aggravation of onchodermatitis. ( 5.4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (incidence > 10%) were: eosinophilia, pruritus, musculoskeletal pain, headache, lymphopenia, tachycardia, rash, abdominal pain, hypotension, pyrexia, leukocytosis, influenza-like illness, neutropenia, cough, lymph node pain, dizziness, diarrhea, hyponatremia and peripheral swelling. ( 6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Medicines Development for Global Health at 1 800 MDGH 456 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Lactation: Breastfeeding not recommended during treatment with Moxidectin Tablets and for 7 days after treatment. ( 8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 3/2021
- Moxidectin Tablets do not kill adult
O. volvulus parasites. Follow-up is advised.
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage in Patients Aged 12 Years and Older
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cutaneous, Ophthalmological and/or Systemic Adverse Reactions
5.2 Symptomatic Orthostatic Hypotension
5.3 Encephalopathy in Loa loa Co-infected Patients
5.4 Edema and Worsening of Onchodermatitis
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.4 Microbiology
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Moxidectin Tablets are indicated for the treatment of onchocerciasis due to Onchocerca volvulus in patients aged 12 years and older [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Limitations of Use:
Moxidectin Tablets do not kill adult O. volvulus. Follow-up evaluation is advised.
The safety and efficacy of repeat administration of Moxidectin Tablets in patients with O. volvulus has not been studied.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage in Patients Aged 12 Years and Older
The recommended dosage of Moxidectin Tablet is a single dose of 8 mg (four 2 mg tablets) taken orally with or without food [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cutaneous, Ophthalmological and/or Systemic Adverse Reactions
Treatment with Moxidectin Tablets may cause cutaneous, ophthalmological and/or systemic reactions of varying severity (Mazzotti reaction). These adverse reactions are due to allergic and inflammatory host responses to the death of microfilariae [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. There is a trend toward an increased incidence of these adverse reactions in patients with higher microfilarial burden.
The clinical manifestations of Mazzotti reaction includes pruritus, headache, pyrexia, rash, urticaria, hypotension (including symptomatic orthostatic hypotension and dizziness) [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)], tachycardia, edema, lymphadenopathy, arthralgia, myalgia, chills, paresthesia and asthenia. Ophthalmological manifestations include conjunctivitis, eye pain, eye pruritus, eyelid swelling, blurred vision, photophobia, changes in visual acuity, hyperemia, ocular discomfort and watery eyes. These adverse reactions generally occur and resolve in the first week post-treatment. Laboratory changes include eosinophilia, eosinopenia, lymphocytopenia, neutropenia, and increases in alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). Proteinuria has also been reported.
Treatment of severe Mazzotti reactions has not been evaluated in controlled clinical trials. Symptomatic treatments such as oral hydration, recumbency, intravenous normal saline, and/or parenteral corticosteroids have been used to treat orthostatic hypotension. Antihistamines and/or analgesics have been used for most mild to moderate cases.
5.2 Symptomatic Orthostatic Hypotension
An increased number of patients who received Moxidectin Tablets developed symptomatic orthostatic hypotension with inability to stand without support after lying down for 5 minutes (in an orthostatic hypotension provocation test); 47/978 (5%) compared with 8/494 (2%) who received ivermectin. The decreases in blood pressure were transient, managed by resumption of recumbency and most commonly occurred on Days 1 and 2 post-treatment. Advise patients that if they feel dizzy or light-headed after taking Moxidectin Tablets, they should lie down until the symptoms resolve.
5.3 Encephalopathy in Loa loa Co-infected Patients
Patients with onchocerciasis who are also infected with Loa loa may develop a serious or even fatal encephalopathy following treatment with Moxidectin Tablets.
Moxidectin Tablets have not been studied in patients co-infected with Loa loa. Therefore, it is recommended that individuals who warrant treatment with Moxidectin Tablets and have had exposure to Loa loa-endemic areas undergo diagnostic screening for loiasis prior to treatment.
5.4 Edema and Worsening of Onchodermatitis
Patients with hyper-reactive onchodermatitis (sowda) may be more likely than others to experience severe edema and worsening of onchodermatitis following the use of Moxidectin Tablets. Symptomatic treatment has been used to manage patients who have experienced edema and worsening of onchodermatitis.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described in greater detail in other labeling sections:
- Cutaneous, Ophthalmological and/or Systemic Adverse Reactions
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Symptomatic Orthostatic Hypotension
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Encephalopathy in
Loa loa Co-infection
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Edema and Worsening of Onchodermatitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under varying controlled conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in one clinical trial cannot be directly compared to rates observed in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety of Moxidectin Tablets was evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, active-controlled studies (Trial 1 and Trial 2) [see Clinical Studies (14)]. In Trial 1, 978 patients received Moxidectin Tablets as a single oral dose of 8 mg and 494 patients received ivermectin as a single oral dose of approximately 150 mcg/kg. In Trial 2, 127 patients received Moxidectin Tablets as a single oral dose ranging from 2 mg (this is not an approved dose) to 8 mg (38 received the recommended 8 mg dose) and 45 patients received ivermectin as a single oral dose of approximately 150 mcg/kg.
Most Common Adverse Reactions
No patients withdrew from either trial due to adverse reactions. Adverse Reactions reported in Trial 1 in > 10% of patients are summarized in Table 1. Most were related to physical, vital signs and laboratory changes associated with Mazzotti reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Occurring in > 10% of Moxidectin-treated Patients with Onchocerciasis in Trial 1 Adverse Reaction Moxidectin
N = 978
n (%)Ivermectin
N = 494
n (%)Eosinophilia 721 (74) 390 (79) Pruritus 640 (65) 268 (54) Musculoskeletal pain a 623 (64) 257 (52) Headache 566 (58) 267 (54) Lymphocytopenia* 470 (48) 215 (44) Tachycardia b 382 (39) 148(30) Orthostatic tachycardia c 333 (34) 130 (26) Non-orthostatic tachycardia d 179 (18) 57 (12) Rash e 358 (37) 103 (21) Abdominal pain f 305 (31) 173 (35) Hypotension g 289 (30) 125 (25) Orthostatic hypotension h 212 (22) 81 (16) Pyrexia/Chills 268 (27) 88 (18) Leukocytosis 240 (25) 125 (25) Influenza like illness 226 (23) 102 (21) Neutropenia** 197 (20) 112 (23) Cough 168 (17) 88 (18) Lymph node pain 129 (13) 28 (6) Dizziness 121 (12) 44 (9) Diarrhea/Gastroenteritis/Enteritis 144 (15) 84 (17) Hyponatremia 112 (12) 65 (13) Peripheral swelling 107 (11) 30 (6) a Includes “myalgia”, “arthralgia”, “musculoskeletal pain”, “pain” and “back pain”
b Includes “orthostatic heart rate increased”, “postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome”, “heart rate increased” and “sinus tachycardia”
c Includes “orthostatic heart rate increased” and “postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome”
d Includes “heart rate increased”, “tachycardia”, and “sinus tachycardia”
e Includes “rash,” “papular rash” and “urticaria”
f Includes “abdominal pain”, “abdominal pain upper” and “abdominal pain lower”
g Includes “orthostatic hypotension”, “blood pressure orthostatic decreased”, “blood pressure decreased”, “mean arterial pressure decreased”, “hypotension”
h Includes “orthostatic hypotension”, and “blood pressure orthostatic decreased”
*Lymphocytopenia is defined as absolute lymphocyte count less than 1 x 10 9/L
**Neutropenia is defined as absolute neutrophil count less than 1 x 10 9/L
The most common adverse reactions in patients (n = 38) treated with 8 mg moxidectin in Trial 2 were similar to the adverse reactions noted in Trial 1 described in Table 1 above.
Other Adverse Reactions Reported in Clinical Trials
The following adverse reactions occurred in less than 10% of subjects receiving Moxidectin Tablets in Trial 1:
Ocular Adverse Reactions: In Trial 1, the most common ocular adverse reactions (occurring in ≥ 0.5% of patients) is shown in Table 2.
Table 2: Ocular Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥ 0.5% Moxidectin-treated Patients Adverse Reaction Moxidectin
N = 978
n (%)Ivermectin
N = 494
n (%)Eye pain 78 (8) 28 (6) Eye pruritus 64 (7) 26 (5) Visual impairment* 25 (3) 9 (2) Eyelid edema 21 (2) 5 (1) Conjunctivitis allergic 19 (2) 11 (2) Ocular discomfort** 18 (2) 11 (2) Ocular and conjunctival hyperemia 17 (2) 3 (1) Lacrimation increased 13 (1) 10 (2) *Includes “visual impairment”, “blurred vision” and “low vision acuity”
**Includes “foreign body sensation”, “ocular discomfort” and “abnormal sensation in the eye”
Hepatobiliary Adverse Reactions
More patients in the moxidectin arm experienced elevation in bilirubin above the upper limit of normal and elevation in transaminases > 5x upper limit of normal. Twenty-seven (2.8%) patients in the moxidectin arm and 3 (0.6%) patients in the ivermectin arm had hyperbilirubinemia. Most of the patients had single measurements of hyperbilirubinemia without concurrent elevation in transaminases.
Nine (1%) patients in the moxidectin arm and 2 (0.4%) patients in the ivermectin arm had elevation in ALT of more than 5x upper limit of normal; ten (1%) patients in the moxidectin arm and 3 (0.6%) patients in the ivermectin arm had elevation in AST to more than 5x upper limit of normal.
Laboratory Abnormalities
Laboratory abnormalities occurring in at least 1% of patients in the Trial 1 are described in Table 3.
Table 3: Laboratory Abnormalities in at least 1% of Moxidectin-treated Patients Parameter MOXIDECTIN
(N = 978)
n (%)Ivermectin
(N = 494)
n (%)Hematology Severe eosinophilia (> 5 x10 9/L) 173 (18) 111 (23) Grade 3 lymphocytopenia (< 0.5 x10 9/L) 220 (23) 98 (20) Grade 4 Neutrophils (< 0.5 x10 9/L) 65 (7) 46 (9) Eosinopenia (<0.045 x10 9/L) 51 (5) 21 (4) Hepatobiliary GGT (> 5x upper limit of normal) 26 (3) 16 (3) Bilirubin (> 2x upper limit of normal) 14 (1.4) 2 (0.4) AST (> 5x upper limit of normal) 10 (1) 3 (0.6) ALT (> 5x upper limit of normal) 9 (1) 2 (0.4) - Cutaneous, Ophthalmological and/or Systemic Adverse Reactions
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Midazolam (CYP3A4 substrate)
In healthy subjects, concomitant administration of a single 8 mg oral dose of Moxidectin Tablets did not have an effect on the pharmacokinetics of midazolam [ see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Moxidectin can be co-administered with CYP3A4 substrates.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from clinical trials on the use of Moxidectin Tablets in pregnant women are insufficient to establish whether there is a moxidectin-associated risk for major birth defects and miscarriage . Moxidectin administered orally to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis was not associated with significant embryo-fetal developmental effects at doses of approximately 15 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area (BSA) comparison. When moxidectin was dosed orally to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis, no embryo-fetal developmental effects were observed at oral doses of moxidectin up to 24 times the recommended human dose based on BSA comparison (see Data).
Daily administration of moxidectin by oral gavage to maternal female rats during organogenesis and through lactation was associated with decreased survival, adverse clinical signs, and decreased body weights in first-generation offspring during the lactation period at a moxidectin dose less than 2-times the recommended human dose based on BSA comparison. Additional findings in first-generation offspring at the same dose included delays in pinna unfolding, eye opening, and vaginal opening. Other parameters, including reproduction and neurological development in first-generation offspring were not affected at any moxidectin dose (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In a rat embryo-fetal development study, daily oral administration of moxidectin at 12 mg/kg/day (approximately 15 times the recommended human dose of 8 mg based on BSA comparison) during Gestation Days (GDs) 6 to 15 significantly increased the fetal incidence, but not the litter incidence of cleft palate and the fetal and litter incidence of a skeletal variation, wavy ribs, at a maternally toxic dose. Mean maternal food consumption, body weights, and body weight gain were significantly decreased at moxidectin doses of 10 and 12 mg/kg/day compared to control values. The no observed adverse effect level (NOAEL) value for maternal and fetal toxicity was considered to be 5 and 10 mg/kg/day respectively (approximately 6 and 12 times, respectively, the recommended human dose based on BSA comparison). In the rabbit, daily oral administration of moxidectin at ≥ 5 mg/kg/day from GD 7 to GD 19 was not associated with fetal weight loss or malformations but resulted in significantly decreased maternal food consumption and body weight gains. The NOAEL values for maternal and fetal toxicity in the rabbit was 1 mg/kg/day and 10 mg/kg/day respectively (approximately 2 times and 24 times, respectively, the recommended human dose based on BSA comparison).
In a pre-postnatal study, moxidectin doses of 0.2 and 0.5 mg/kg/day were administered by oral gavage to maternal female rats from GD 6 throughout the lactation period until LD 21. A third dose group that received maternal doses of 1.5 mg/kg/day moxidectin (less than 2-times the recommended human dose based on BSA comparison) was divided into two cohorts with Cohort 1 receiving maternal doses from GD 6 until LD 10 and Cohort 2 receiving maternal doses from GD 6 until each individual animal littered, but not during the lactation period. First-generation offspring in Cohort 1 had adverse clinical signs (small body size, thin, weak, subdued/sluggish, pale, cold to touch, respiratory distress, blue coloration and/or no visible milk in stomach) and decreased survival and body weights during the lactation period. However, first-generation offspring in Cohort 2 did not experience adverse clinical signs, body weight loss, or reduced survival suggesting moxidectin in lactation milk was responsible for the adverse effects in offspring in Cohort 1. Additional findings included delays in pinna unfolding and eye opening in male and female offspring in both cohorts and delay of vaginal opening in female offspring in Cohort 2. No adverse effects were noted in offspring at a maternal dose of 0.5 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.6 times the recommended human dose based on BSA comparison). Reproductive performance based on mating and fertility indices and neurological development were not affected in male and female first-generation offspring at any of the administered moxidectin doses.
In another pre-postnatal study in rats, parental oral administration of dietary moxidectin prior to mating, through mating, gestation, and lactation did not produce adverse effects in first-generation or second-generation offspring at a maternal NOAEL dose of 0.824 mg/kg/day (approximately equivalent to the recommended human dose based on BSA comparison). However, at moxidectin doses ≥ 1.1 mg/kg/day (approximately equivalent to 1.3 times the recommended human dose based on BSA comparison), the survival and body weights of first-generation offspring were significantly decreased during the lactation period, and the number of live fetuses at birth was significantly decreased with a maternal moxidectin dose of 11 mg/kg/day (approximately equivalent to 13 times the recommended human dose based on BSA comparison). In this study, offspring were assessed for survival, body weights, and fertility, and developmental milestones were not assessed.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Moxidectin was detected in the milk of lactating women following a single 8 mg dose of Moxidectin Tablets (see Data). There are no data on the effects of Moxidectin Tablets on the breast-fed infant or milk production. In a pre-postnatal study in rats, oral gavage administration of moxidectin at a dose less than 2-times the recommended human dose based on BSA comparison during the lactation period resulted in adverse clinical signs, weight loss, and increased mortality in rat pups suggesting moxidectin in lactation milk was responsible for the adverse effects [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1), and Data].
Because of serious findings from the rat pre-postnatal study including weight loss and death, advise women that breastfeeding is not recommended at the time of treatment with Moxidectin Tablets and for 7 days after treatment.
Data
A pharmacokinetic study in twelve healthy adult lactating women who were 21 to 100 weeks post partum evaluated the concentrations of moxidectin in plasma and breast milk collected over a period of 28 days following a single 8 mg dose of Moxidectin Tablets. The mean (± SD) exposure ratio of moxidectin present in human breast milk to that of human plasma was approximately 1.77 (± 0.66) over a collection period of 28 days. The estimated mean (± SD) total infant dose, assuming the infants would consume all the breast milk collected during the study, was 0.056 mg (± 0.024 mg), which would be approximately 0.70% (± 0.30%) of the maternal dose. Relative infant dose was estimated to be 8.73% (± 0.024 mg). The effects of moxidectin or its metabolites on the breast-fed child or milk production were not evaluated.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Moxidectin Tablets have been established in pediatric patients 12 years of age and older. In Trial 1, (n = 53 patients aged 12 to 17 years), the safety and effectiveness was similar to that observed in adults [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), and Clinical Studies (14)]. The safety and effectiveness of Moxidectin Tablets in pediatric patients under 12 years of age has not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total number of patients included in Trial 1 that were treated with Moxidectin Tablets, 83 were aged 65 and over. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out [see Clinical Studies (14) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
No dose adjustment of Moxidectin Tablets is necessary for patients with mild (creatinine clearance (CrCL) 60 to 89 mL/min) to moderate (CrCL 30 to 59 mL/min) renal impairment. The safety of Moxidectin Tablets in patients with severe renal impairment (CrCL 15 to 29 mL/min) or end stage renal disease, is unknown [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
No specific antidote is available for overdose with Moxidectin Tablets. If overdose occurs, the patient should be monitored for evidence of toxicity. Treatment of overdose with Moxidectin Tablets consists of general supportive measures including monitoring of vital signs as well as observation of the clinical status of the patient. Supportive therapy, if indicated, should include parenteral fluids and electrolytes, respiratory support (oxygen and mechanical ventilation if necessary) and pressor agents if clinically significant hypotension is present.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Moxidectin Tablets contain moxidectin, an anthelmintic drug and a macrocyclic lactone of the milbemycin class derived from the actinomycete Streptomyces cyanogriseus.
The chemical name of moxidectin is (2aE,4E,5'R,6R,6'S,8E,11R,13S,15S,17aR,20R,20aR,20bS)-6'-[(E)-1,3-dimethyl-1-butenyl]-5',6,6',7,10,11,14,15,17a,20,20a,20b-dodecahydro-20,20b-dihydroxy-5',6,8,19-tetramethylspiro[11,15-methano-2H,13H,17H-furo[4,3,2-pq][2,6]benzodioxacyclooctadecin-13,2'-[2H]pyran]-4',17(3'H)-dione 4'-(E)-(O-methyloxime). The structural formula is:
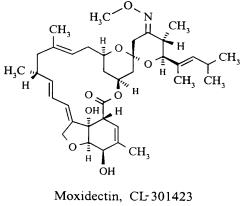
Figure 1: Moxidectin Structure
Moxidectin is a white or pale-yellow, amorphous powder. The empirical formula is C 37H 53NO 8 and the molecular weight is 639.82 Dalton. Moxidectin is readily soluble in organic solvents such as methylene chloride, diethyl ether, ethanol, acetonitrile, and ethyl acetate. It is only slightly soluble in water (0.51 mg/L) and the melting point range for moxidectin powder is 145°C to 154°C.
Moxidectin Tablets are for oral administration. Each tablet contains 2 mg of moxidectin. The tablets are uncoated and include the following inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, lactose anhydrous, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and sodium lauryl sulfate.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Moxidectin, a macrocyclic lactone, is an anthelmintic drug [see Microbiology (12.4)].
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At a dose 4.5 times the approved recommended dose, moxidectin does not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetic parameters of moxidectin following a single 8 mg oral dose of Moxidectin Tablets to healthy subjects and patients with onchocerciasis under fasted conditions are shown in Table 4. Mean moxidectin C max and AUC increased approximately proportionally to dose over a dose range of 2 to 36 mg (0.25 to 4.5 times the approved recommended dose) in healthy subjects under fasted conditions.
Table 4: Mean (± SD) Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Moxidectin Following a Single 8 mg Oral Dose of Moxidectin Tablets to Healthy Subjects and Patients with Onchocerciasis Under Fasted Conditions PK Parameter Healthy Subjects
(N = 27)Patients with Onchocerciasis
(N = 31)Cmax (ng/mL) 58.9 ± 12.5 63.1 ± 20.0 Tmax* (hours) 4 (2, 8) 4 (1, 4) AUCinf (ng•h/mL) 3387 ± 1328 2738 ± 1606 Half-life (hours) 784 ± 347 559 ± 525 C max = maximum plasma concentration; T max = time to reach C max; AUC inf = area under the plasma concentration-time curve from time 0 to infinity; * Median (range)
Absorption
Effect of Food
Moxidectin mean C max and AUC increased on average by 34% and 39%, respectively, when administered with a standard high fat meal (900 calories, with a nutritional distribution of approximately 55% fat, 31% carbohydrates and 14% protein), compared to fasted conditions [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Distribution
The apparent mean ± SD volume of distribution of moxidectin is 2421 ± 1658 L in patients with onchocerciasis. The plasma protein binding in humans is unknown.
Elimination
The mean terminal half-life of moxidectin in patients with onchocerciasis is 23.3 days (559 hours) following a single 8 mg dose of Moxidectin Tablets.
The apparent mean ± SD total clearance of moxidectin is approximately 3.50 ± 1.23 L/hour in patients with onchocerciasis.
Metabolism
The hepatic metabolism of moxidectin is minimal.
Excretion
Following administration of a single 8 mg oral dose of Moxidectin Tablets to healthy subjects, 2% of the dose is eliminated unchanged in the feces within the first 72 hours. Renal elimination of intact drug is negligible.
Specific Populations
In clinical studies, no clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of moxidectin were observed based on age (18 to 60 years), sex, weight (42.7 to 107.2 kg), or renal impairment (creatinine clearance (CrCL) 47 to 89 mL/min, estimated by Cockcroft-Gault). The pharmacokinetics of moxidectin in patients with CrCL less than 47 mL/min is unknown. The pharmacokinetics of moxidectin in patients with hepatic impairment is unknown.
Patients with Renal Impairment
Based on a population pharmacokinetic analysis and the fact that renal elimination of intact drug is negligible, mild (creatinine clearance (CrCL), estimated by Cockcroft-Gault of 60 to 89 mL/min) and moderate (CrCL 30 to 59 mL/min) renal impairment is not likely to have an impact on the exposure of moxidectin. The effect of severe renal impairment (CrCL 15 to 29 mL/min) or of end-stage renal disease on the pharmacokinetics of moxidectin is unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Study with Midazolam (CYP3A4 substrate)
Co-administration of a single 8 mg dose of Moxidectin Tablets with a single oral 7.5 mg dose of midazolam (a sensitive CYP3A substrate) to healthy subjects (n = 37) did not affect the pharmacokinetics of midazolam or its major metabolite, 1-hydroxy midazolam.
In Vitro Studies
CYP Enzymes: Moxidectin is not a substrate or inhibitor of CYP enzymes.
Uridine 5'-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs): Moxidectin is not a UGT substrate.
Transporter Systems: Moxidectin is not a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) nor breast cancer resistance protein 1 (BCRP1).
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism by which moxidectin exhibits its effect against O. volvulus is not known. Studies with other nematodes suggest that moxidectin binds to glutamate-gated chloride channels (GluCl), gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors and/or ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. This leads to increased permeability, influx of chloride ions, hyperpolarization and muscle paralysis. Additionally, there is a reduction in motility of all stages of the parasite, excretion of immunomodulatory proteins, and the fertility of both male and female adult worms.
Antimicrobial activity
Moxidectin is active against the microfilariae of O. volvulus [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Studies suggest that moxidectin is not effective in killing the adult worms, however, it inhibits intra-uterine embryogenesis and release of microfilariae from the adult worms.
Resistance
Studies in vitro and in infected animals suggest a potential for development of resistance to moxidectin and cross-resistance with other macrocyclic lactones, such as ivermectin. However, the clinical relevance of these findings is not known.
The mechanism of resistance may be multifactorial that include alteration in the target GluCl, GABA receptors and/or ABC transporters.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Two-year carcinogenicity studies in mice and rats were conducted with moxidectin. Mice were administered a mean dietary dose of 8.7 mg/kg/day moxidectin which is approximately equivalent to 5 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area comparison. Rats were administered a mean dietary dose of 6.1 mg/kg/day moxidectin which is approximately equivalent to 7 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area comparison. There was no evidence of tumorigenicity in either study.
Mutagenesis
Moxidectin was shown to be negative for genotoxicity in a battery of in vitro assays including a bacterial mutagenicity assay, mouse lymphoma cell mutagenicity assay, unscheduled DNA synthesis assay, and a chromosome aberration assay, as well as in vivo in a micronucleus assay in mice and a chromosome aberration assay in rats.
Impairment of Fertility
In fertility evaluations, male and female mating and fertility indices were not inhibited by oral-dietary moxidectin doses of approximately 0.86 mg/kg/day which is approximately equivalent to the recommended human dose based on body surface area comparison.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Moxidectin was associated with transient CNS-related clinical signs. In rats, a single dose of 20 mg/kg (equivalent to approximately 24 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area comparison) moxidectin was associated with piloerection, reduced arousal and body tone, abnormal gait, slowed breathing, and impaired righting reflex. In dogs, repeated doses of 1.6 mg/kg/day moxidectin (equivalent to approximately 7 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area comparison) was associated with lacrimation, languid appearance, tremors, slight salivation, and slight ataxia.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The assessment of the safety and efficacy of Moxidectin Tablets 8 mg in the treatment of onchocerciasis is based on data from two randomized, double-blind, active-controlled trials in patients with O. volvulus infection, Trial 1 in 1472 patients (NCT 00790998), and Trial 2, a dose-ranging trial (NCT 00300768). Patients in the trials received a single oral dose of moxidectin or ivermectin, the active control medication.
Efficacy was assessed by skin microfilarial density (microfilariae/mg skin) from the mean of 4 skin snips per person per time point up to 18 months post-treatment.
Trial 1 recruited adult and adolescent patients ≥ 12 years with a body weight ≥ 30 kg and ≥ 10 microfilariae/mg skin. Mean (± SD) age was 42.5 (± 16.3) years, height 1.59 (± 0.09) meters, weight 51.6 (± 8.2) kg; 36.1% were female and 100% were black. Mean (± SD) pretreatment skin microfilarial density was 39.5 (± 30.7) microfilariae/mg skin, 69.6% had ≥ 20 microfilariae/mg skin and 39.7% had at least one ocular microfilaria.
Patients who were not previously exposed to ivermectin community directed treatment programs were recruited from the sub-Saharan African region (Democratic Republic of Congo, Liberia, and Ghana). Table 5 reports mean skin microfilarial density and the proportion of patients with undetectable skin microfilariae at Months 1, 6, and 12.
Table 5: Mean Microfilarial Density and Percentage of Undetectable Microfilariae in Skin of O. volvulus Patients (12 Years of Age and Older) at Months 1, 6, and 12 in Trial 1 Endpoint Moxidectin
N = 977Ivermectin
N = 495Difference
(95% Confidence Interval)1 month Mean Microfilarial Density a 0.10 2.30 -2.20 (-2.83, -1.58)
p < 0.0001% Undetectable Microfilariae b 83.4% 42.9% 40.5% (35.7, 45.3)
p < 0.00016 months Mean Microfilarial Density a 0.14 3.71 -3.57(-4.11, -3.03)
p < 0.0001% Undetectable Microfilariae b 91.0% 11.5% 79.6% (76.3, 82.9)
p < 0.000112 months Mean Microfilarial Density a 1.79 9.83 -8.04 (-9.11, -6.98)
p < 0.0001% Undetectable Microfilariae b 45.9% 5.4% 40.4% (36.7, 44.1)
p < 0.0001a Mean microfilarial density in skin is the average microfilarial density (microfilariae count/mg skin) over skin snips from four sites.
b Proportion of subjects undetectable (defined as a mean skin microfilariae density of zero across all 4 skin snips).
Additionally, safety and efficacy was assessed in a smaller single ascending dose trial (Trial 2, NCT 00300768) comparing 2 mg (n = 44), 4 mg (n = 45) (2 mg and 4 mg are not approved doses) and 8 mg (n = 38) single doses of moxidectin to ivermectin. Trial 2 was conducted in Ghana in adults aged ≥ 18 to ≤ 60 years with O. volvulus infection. Analysis of the baseline-to-12-month change in skin microfilarial density for the proposed moxidectin 8 mg dose showed statistically significant superiority to ivermectin, p < 0.001.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Moxidectin Tablets containing 2 mg moxidectin are white to pale yellow uncoated oval-shaped tablets, debossed on one side with “AKKA”. Each high-density polyethylene bottle contains 500 tablets (NDC 71705-050-01), a silica gel desiccant and polyester coil.
Store below 30°C (86°F).
- Protect from light.
- Once open, the full contents of the container should be used within 24 hours with any unused content discarded.
- Protect from light.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Signs and Symptoms Associated with Microfilarial Death
Advise patients that they are likely to have flu like symptoms including malaise, myalgia, headache, tachycardia, hypotension and pruritus, most commonly during the first week after treatment.
Symptomatic Orthostatic Hypotension
Advise patients that if they feel dizzy, faint or light-headed after taking Moxidectin Tablets, they should lie down until the symptoms resolve.
Absence of Macrofilarial Activity
Advise patients that treatment with Moxidectin Tablets does not kill adult O. volvulus and that follow up evaluation is usually required.
Edema and Worsening of Onchodermatitis
Advise patients with hyper-reactive onchodermatitis that they may be more likely to experience severe adverse reactions.
Encephalopathy in Loa loa Co-infected Patients
Advise patients to report any symptoms of encephalopathy to their healthcare provider.
Lactation
Advise women that breastfeeding is not recommended at the time of treatment with Moxidectin Tablets and for 7 days after treatment.
Manufactured for: Medicines Development for Global Health, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia
© 2021 Medicines Development for Global Health. All rights reserved.
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
MOXIDECTIN
moxidectin tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:71705-050 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength MOXIDECTIN (UNII: NGU5H31YO9) (MOXIDECTIN - UNII:NGU5H31YO9) MOXIDECTIN 2 mg Product Characteristics Color white (White to pale yellow) Score no score Shape OVAL Size 8mm Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:71705-050-01 500 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/02/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA210867 12/02/2019 Labeler - Medicines Development for Global Health (754191398)


