Label: SUMATRIPTAN AND NAPROXEN SODIUM tablet, film coated
-
Contains inactivated NDC Code(s)
NDC Code(s): 71800-901-01 - Packager: Innovida Phamaceutique Corporation
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Abbreviated New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated December 10, 2020
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Medication Guide: HTML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use SUMATRIPTAN AND NAPROXEN SODIUM TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for SUMATRIPTAN AND NAPROXEN SODIUM TABLETS.
SUMATRIPTAN and NAPROXEN SODIUM tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2008WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use. (5.1)
- Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (4, 5.1)
- NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients and patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding are at greater risk for serious GI events. (5.2)
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are a combination of sumatriptan, a serotonin (5-HT) 1b/1d receptor agonist (triptan), and naproxen sodium, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, indicated for the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older. (1) (1)
Limitations of Use: (1)
- Use only if a clear diagnosis of migraine headache has been established. (1)
- Not indicated for the prophylactic therapy of migraine attacks. (1)
- Not indicated for the treatment of cluster headache. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 85 mg sumatriptan / 500 mg naproxen sodium (3) (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- History of coronary artery disease or coronary vasospasm. (4)
- In the setting of CABG surgery. (4)
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome or other cardiac accessory conduction pathway disorders. (4)
- History of stroke, transient ischemic attack, or hemiplegic or basilar migraine. (4)
- Peripheral vascular disease. (4)
- Ischemic bowel disease. (4)
- Uncontrolled hypertension. (4)
- Recent (within 24 hours) use of another 5-HT1 agonist (e.g., another triptan) or of ergotamine-containing medication. (4)
- Concurrent or recent (past 2 weeks) use of monoamine oxidase-A inhibitor. (4)
- History of asthma, urticaria, other allergic type reactions, rhinitis, or nasal polyps syndrome after taking aspirin or other NSAID/analgesic drugs. (4)
- Known hypersensitivity to sumatriptan, naproxen, or any components of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets (angioedema and anaphylaxis seen). (4)
- Third trimester of pregnancy. (4)
- Severe hepatic impairment. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events: Perform cardiac evaluation in patients with cardiovascular risk factors. (5.1)
- Arrhythmias: Discontinue sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets if occurs. (5.3)
- Chest, Throat, Neck, and/or Jaw Pain/Tightness/Pressure: Generally not associated with myocardial ischemia; evaluate for coronary artery disease in patients at high risk. (5.4)
- Cerebrovascular Events: Discontinue sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets if occurs. (5.5)
- Other Vasospasm Reactions: Discontinue sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets if non-coronary vasospastic reaction occurs. (5.6)
- Hepatotoxicity: Inform patients of warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity. Discontinue if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen or if clinical signs and symptoms of liver disease develop. (5.7)
- Hypertension: Patients taking some antihypertensive medications may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. Monitor blood pressure. (5.8)
- Heart Failure and Edema: Avoid use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets in patients with severe heart failure unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening heart failure. (5.9)
- Medication Overuse Headache: Detoxification may be necessary. (5.10)
- Serotonin Syndrome: Discontinue sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets if occurs. (5.11)
- Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia: Monitor renal function in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, heart failure, dehydration, or hypovolemia. Avoid use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets in patients with advanced renal disease. (5.12)
- Anaphylactic Reactions: Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets should not be given to patients with the aspirin triad. Seep emergency help if an anaphylactic reaction occurs.(5.13)
- Serious Skin Reactions: Discontinue sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets at first sign of rash or other signs of hypersensitivity. (5.14)
- Hematologic Toxicity: Monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit in patients with any signs or symptoms of anemia. (5.16)
- Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity: Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are contraindicated in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma. Monitor patients with preexisting asthma (without aspirin sensitivity). (5.17)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥2%) were: (6)
- Adults: Dizziness, somnolence, nausea, chest discomfort/chest pain, neck/throat/jaw pain/tightness/pressure, paresthesia, dyspepsia, dry mouth. (6.1)
- Pediatrics: Hot flush (i.e., hot flash[es]) and muscle tightness. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc. at 1-800-818-4555 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. (6)
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Drugs that Interfere with Hemostasis (e.g. warfarin, aspirin, SSRIs/SNRIs): Monitor patients for bleeding who are concomitantly taking sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets with drugs that interfere with hemostasis. Concomitant use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets and analgesic doses of aspirin is not generally recommended. (7.1)
- ACE Inhibitors and ARBs: Concomitant use with sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets in elderly, volume depleted, or those with renal impairment may result in deterioration of renal function. In such high risk patients, monitor for signs of worsening renal function. (7.1)
- Diuretics: NSAIDs can reduce natriuretic effect of loop and thiazide diuretics. Monitor patients to assure diuretic efficacy including antihypertensive effects. (7.1)
- Digoxin: Concomitant use with sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets can increase serum concentration and prolong half-life of digoxin. Monitor serum digoxin levels. (7.1)
- Lithium: Increases lithium plasma levels. (7.1)
- Methotrexate: Increases methotrexate plasma levels. (7.1)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm. (8.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 12/2020
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosage in Adults
2.2 Dosage in Pediatric Patients 12 to 17 Years of Age
2.3 Dosage in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
2.4 Administration Information
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
5.2 Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
5.3 Arrhythmias
5.4 Chest, Throat, Neck, and/or Jaw Pain/Tightness/Pressure
5.5 Cerebrovascular Events
5.6 Other Vasospasm Reactions
5.7 Hepatotoxicity
5.8 Hypertension
5.9 Heart Failure and Edema
5.10 Medication Overuse Headache
5.11 Serotonin Syndrome
5.12 Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia
5.13 Anaphylactic Reactions
5.14 Serious Skin Reactions
5.15 Premature Closure of the Ductus Arteriosus
5.16 Hematologic Toxicity
5.17 Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity
5.18 Seizures
5.19 Masking of Inflammation and Fever
5.20 Laboratory Monitoring
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Clinically Significant Drug Interactions with Sumatriptan and Naproxen Sodium Tablets
7.2 Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Labor and Delivery
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Adults
14.2 Pediatric Patients 12 to 17 Years of Age
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery [see Contraindications (4) Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
- NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients and patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding are at greater risk for serious GI events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are indicated for the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older.
Limitations of Use:
- Use only if a clear diagnosis of migraine headache has been established. If a patient has no response to the first migraine attack treated with sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets, reconsider the diagnosis of migraine before sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are administered to treat any subsequent attacks.
- Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are not indicated for the prevention of migraine attacks.
- Safety and effectiveness of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets have not been established for cluster headache.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosage in Adults
The recommended dosage for adults is 1 tablet of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 85 mg/500 mg. sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 85 mg/500 mg contains a dose of sumatriptan higher than the lowest effective dose. The choice of the dose of sumatriptan, and of the use of a fixed combination such as in sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 85 mg/500 mg should be made on an individual basis, weighing the possible benefit of a higher dose of sumatriptan with the potential for a greater risk of adverse reactions.
The maximum recommended dosage in a 24-hour period is 2 tablets, taken at least 2 hours apart.The safety of treating an average of more than 5 migraine headaches in adults in a 30-day period has not been established.
Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
2.2 Dosage in Pediatric Patients 12 to 17 Years of Age
The maximum recommended dosage in a 24-hour period is 1 tablet of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 85/500 mg.
The safety of treating an average of more than 2 migraine headaches in pediatric patients in a 30-day period has not been established.
Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
2.3 Dosage in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Contraindications (4), Use in Specific Populations (8.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals [see Warnings and Precautions (5)]. - 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are contraindicated in the following patients:
- Ischemic coronary artery disease (CAD) (angina pectoris, history of myocardial infarction, or documented silent ischemia) or coronary artery vasospasm, including Prinzmetal’s angina [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- In the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome or arrhythmias associated with other cardiac accessory conduction pathway disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- History of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) or history of hemiplegic or basilar migraine because these patients are at a higher risk of stroke [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- Peripheral vascular disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
- Ischemic bowel disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
- Uncontrolled hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
- Recent use (i.e., within 24 hours) of ergotamine-containing medication, ergot-type medication (such as dihydroergotamine or methysergide), or another 5-hydroxytryptamine1 (5-HT1) agonist [see Drug Interactions (7)].
- Concurrent administration of a monoamine oxidase (MAO)-A inhibitor or recent (within 2 weeks) use of an MAO-A inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- History of asthma, urticaria, or allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, sometimes fatal, anaphylactic reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13, 5.14, 5.17)].
- Known hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylactic reactions, angioedema, and serious skin reactions) to sumatriptan, naproxen, or any components of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)].
- Third trimester of pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
- Severe hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7), Use in Specific Populations (8.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
The use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets is contraindicated in patients with ischemic or vasospastic coronary artery disease (CAD) and in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery due to increased risk of serious cardiovascular events with sumatriptan and NSAIDS [see Contraindications (4)].
Cardiovascular Events with Sumatriptan
There have been rare reports of serious cardiac adverse reactions, including acute myocardial infarction, occurring within a few hours following administration of sumatriptan. Some of these reactions occurred in patients without known CAD. Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets may cause coronary artery vasospasm (Prinzmetal’s angina), even in patients without a history of CAD.
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events with Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs
Clinical trials of several COX-2 selective and nonselective NSAIDs of up to three years duration have shown an increased risk of serious cardiovascular (CV) thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction (MI) and stroke, which can be fatal. Based on available data, it is unclear that the risk for CV thrombotic events is similar for all NSAIDs. The relative increase in serious CV thrombotic events over baseline conferred by NSAID use appears to be similar in those with and without known CV disease or risk factors for CV disease. However, patients with known CV disease or risk factors had a higher absolute incidence of excess serious CV thrombotic events, due to their increased baseline rate. Some observational studies found that this increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events began as early as the first weeks of treatment. The increase in CV thrombotic risk has been observed most consistently at higher doses.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse CV event in NSAID-treated patients, use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible. Physicians and patients should remain alert for the development of such events, throughout the entire treatment course, even in the absence of previous CV symptoms. Patients should be informed about the symptoms of serious CV events and the steps to take if they occur.
There is no consistent evidence that concurrent use of aspirin mitigates the increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events associated with NSAID use. The concurrent use of aspirin and an NSAID, such as naproxen, increases the risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Status Post Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Surgery
Two large, controlled clinical trials of a COX-2 selective NSAID for the treatment of pain in the first 10 to 14 days following CABG surgery found an increased incidence of myocardial infarction and stroke. NSAIDs are contraindicated in the setting of CABG [see Contraindications (4)].
Post-MI Patients
Observational studies conducted in the Danish National Registry have demonstrated that patients treated with NSAIDs in the post-MI period were at increased risk of reinfarction, CV-related death, and all-cause mortality beginning in the first week of treatment. In this same cohort, the incidence of death in the first year post-MI was 20 per 100 person years in NSAID-treated patients compared to 12 per 100 person years in non-NSAID exposed patients. Although the absolute rate of death declined somewhat after the first year post-MI, the increased relative risk of death in NSAID users persisted over at least the next four years of follow-up.
Perform a cardiovascular evaluation in patients who have multiple cardiovascular risk factors (e.g., increased age, diabetes, hypertension, smoking, obesity, strong family history of CAD) prior to receiving sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets. If there is evidence of CAD or coronary artery vasospasm, sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are contraindicated. For patients with multiple cardiovascular risk factors who have a negative cardiovascular evaluation, consider administering the first dose of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets in a medically supervised setting and performing an electrocardiogram (ECG) immediately following administration of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets. For such patients, consider periodic cardiovascular evaluation in intermittent long-term users of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets.
Physicians and patients should remain alert for the development of cardiovascular events, even in the absence of previous cardiovascular symptoms. Patients should be informed about the signs and/or symptoms of serious cardiovascular events and the steps to take if they occur.
5.2 Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
NSAIDs, including naproxen, a component of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets, cause serious gastrointestinal adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can be fatal. These serious adverse events can occur at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated with NSAIDs. Only 1 in 5 patients who develop a serious upper gastrointestinal adverse event on NSAID therapy is symptomatic. Upper gastrointestinal ulcers, gross bleeding, or perforation caused by NSAIDs appear to occur in approximately 1% of patients treated daily for 3 to 6 months and in about 2% to 4% of patients treated for 1 year. However, even short-term therapy is not without risk.
Among 3,302 adult patients with migraine who received sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets in controlled and uncontrolled clinical trials, 1 patient experienced a recurrence of gastric ulcer after taking 8 doses over 3 weeks, and 1 patient developed a gastric ulcer after treating an average of 8 attacks per month over 7 months.
Risk Factors for GI Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
Patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or gastrointestinal bleeding who use NSAIDs have a greater than 10-fold increased risk for developing gastrointestinal bleeding compared with patients with neither of these risk factors. Other factors that increase the risk for gastrointestinal bleeding in patients treated with NSAIDs include longer duration of NSAID therapy; concomitant use of oral corticosteroids, aspirin, anticoagulants, or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs); smoking; use of alcohol; older age; and poor general health status. Most postmarketing reports of fatal gastrointestinal events occurred in elderly or debilitated patients, and therefore special care should be taken in treating this population. Additionally, patients with advanced liver disease and/or coagulopathy are at increased risk for GI bleeding.
Strategies to Minimize the GI Risks in NSAID-treated patients:
- Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest possible duration.
- Avoid administration of more than one NSAID at a time.
- Avoid use in patients at higher risk unless benefits are expected to outweigh the increased risk of bleeding. For high risk patients, as well as those with active GI bleeding, consider alternate therapies other than NSAIDs.
- Remain alert for signs and symptoms of GI ulceration and bleeding during NSAID therapy.
- If a serious GI adverse event is suspected, promptly initiate evaluation and treatment, and discontinue sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets until a serious GI adverse event is ruled out.
- In the setting of concomitant use of low-dose aspirin for cardiac prophylaxis, monitor patients more closely for evidence of GI bleeding [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.3 Arrhythmias
Life-threatening disturbances of cardiac rhythm, including ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation leading to death, have been reported within a few hours following the administration of 5-HT1 agonists. Discontinue sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets if these disturbances occur. Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are contraindicated in patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome or arrhythmias associated with other cardiac accessory conduction pathway disorders.
5.4 Chest, Throat, Neck, and/or Jaw Pain/Tightness/Pressure
Sensations of tightness, pain, pressure, and heaviness in the precordium, throat, neck, and jaw commonly occur after treatment with sumatriptan and are usually non-cardiac in origin. However, perform a cardiac evaluation if these patients are at high cardiac risk. The use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets is contraindicated in patients with CAD and those with Prinzmetal’s variant angina.
5.5 Cerebrovascular Events
Cerebral hemorrhage, subarachnoid hemorrhage, and stroke have occurred in patients treated with 5-HT1 agonists, and some have resulted in fatalities. In a number of cases, it appears possible that the cerebrovascular events were primary, the 5-HT1 agonist having been administered in the incorrect belief that the symptoms experienced were a consequence of migraine when they were not. Also, patients with migraine may be at increased risk of certain cerebrovascular events (e.g., stroke, hemorrhage, TIA). Discontinue sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets if a cerebrovascular event occurs.
Before treating headaches in patients not previously diagnosed as migraineurs, and in migraineurs who present with atypical symptoms, exclude other potentially serious neurological conditions. Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are contraindicated in patients with a history of stroke or TIA [see Contraindications (4)].
5.6 Other Vasospasm Reactions
Sumatriptan may cause non-coronary vasospastic reactions, such as peripheral vascular ischemia, gastrointestinal vascular ischemia and infarction (presenting with abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea), splenic infarction, and Raynaud′s syndrome. In patients who experience symptoms or signs suggestive of non-coronary vasospasm reaction following the use of any 5-HT1 agonist, rule out a vasospastic reaction before receiving additional sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets.
Reports of transient and permanent blindness and significant partial vision loss have been reported with the use of 5-HT1 agonists. Since visual disorders may be part of a migraine attack, a causal relationship between these events and the use of 5-HT1 agonists have not been clearly established.
5.7 Hepatotoxicity
Borderline elevations of 1 or more liver tests may occur in up to 15% of patients who take NSAIDs including naproxen, a component of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets. Hepatic abnormalities may be the result of hypersensitivity rather than direct toxicity. These abnormalities may progress, may remain essentially unchanged, or may be transient with continued therapy. Notable (3 times the upper limit of normal) elevations of SGPT (ALT) or SGOT (AST) have been reported in approximately 1% of patients in clinical trials with NSAIDs. In addition, rare, sometimes fatal cases of severe hepatic injury, including jaundice and fatal fulminant hepatitis, liver necrosis, and hepatic failure have been reported with NSAIDs.
Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. A patient with symptoms and/or signs suggesting liver dysfunction, or in whom an abnormal liver test has occurred, should be evaluated for evidence of the development of a more severe hepatic reaction while on therapy with sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets. Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets should be discontinued if clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash), or if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen.
Inform patients of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, diarrhea, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and "flulike" symptoms). If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.), discontinue sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets immediately, and perform a clinical evaluation of the patient.
5.8 Hypertension
Significant elevation in blood pressure, including hypertensive crisis with acute impairment of organ systems, has been reported on rare occasions in patients treated with 5-HT1 agonists, including sumatriptan, a component of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets. This occurrence has included patients without a history of hypertension.
NSAIDs, including naproxen, a component of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets, can also lead to onset of new hypertension or worsening of preexisting hypertension, either of which may contribute to the increased incidence of cardiovascular events. Patients taking angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), beta-blockers, thiazide diuretics, or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Monitor blood pressure in patients treated with sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets. Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are contraindicated in patients with uncontrolled hypertension [see Contraindications (4)].
5.9 Heart Failure and Edema
The Coxib and traditional NSAID Trialists’ Collaboration meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials demonstrated an approximately two-fold increase in hospitalizations for heart failure in COX-2 selective-treated patients and nonselective NSAID-treated patients compared to placebo-treated patients. In a Danish National Registry study of patients with heart failure, NSAID use increased the risk of MI, hospitalization for heart failure, and death.
Additionally, fluid retention and edema have been observed in some patients treated with NSAIDs. Use of naproxen may blunt the CV effects of several therapeutic agents used to treat these medical conditions (e.g., diuretics, ACE inhibitors, or angiotensin receptor blockers [ARBs]) [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Avoid the use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets in patients with severe heart failure unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of worsening heart failure. If sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are used in patients with severe heart failure, monitor patients for signs of worsening heart failure.
Since each sumatriptan and naproxen sodium 85 mg/500 mg tablet contains approximately 90 mg of sodium, this should be considered in patients whose overall intake of sodium must be severely restricted.
5.10 Medication Overuse Headache
Overuse of acute migraine drugs (e.g., ergotamine, triptans, opioids, or a combination of these drugs for 10 or more days per month) may lead to exacerbation of headache (medication overuse headache). Medication overuse headache may present as migraine-like daily headaches, or as a marked increase in frequency of migraine attacks. Detoxification of patients, including withdrawal of the overused drugs, and treatment of withdrawal symptoms (which often includes a transient worsening of headache) may be necessary.
5.11 Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonin syndrome may occur with sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets, particularly during coadministration with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), and MAO inhibitors [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]]. Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, hyperthermia), neuromuscular aberrations (e.g., hyperreflexia, incoordination), and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). The onset of symptoms usually occurs within minutes to hours of receiving a new or a greater dose of a serotonergic medication. Discontinue sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets if serotonin syndrome is suspected.
5.12 Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia
Renal Toxicity
Long-term administration of NSAIDs has resulted in renal papillary necrosis and other renal injury. Renal toxicity has also been seen in patients in whom renal prostaglandins have a compensatory role in the maintenance of renal perfusion. In these patients administration of an NSAID may cause a dose-dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and, secondarily, in renal blood flow, which may precipitate overt renal decompensation. Patients at greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function, dehydration, hypovolemia, heart failure, liver dysfunction, salt depletion, those taking diuretics and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or ARBs, and the elderly. Discontinuation of NSAID therapy is usually followed by recovery to the pretreatment state.
Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets should be discontinued if clinical signs and symptoms consistent with renal disease develop or if systemic manifestations occur.
Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are not recommended for use in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance [CrCl] <30 mL/min) unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of worsening renal function [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. If sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are used in patients with advanced renal disease, monitor patients for signs of worsening renal function. Monitor renal function in patients with mild (CrCl = 60 to 89 mL/min) or moderate (CrCl = 30 to 59 mL/min) renal impairment, preexisting kidney disease, or dehydration.
The renal effects of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets may hasten the progression of renal dysfunction in patients with preexisting renal disease.
Correct volume status in dehydrated or hypovolemic patients prior to initiating sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets. Monitor renal function in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, heart failure, dehydration, or hypovolemia during use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets [see Drug Interactions (7)]. Avoid the use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets in patients with advanced renal disease unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of worsening renal function. If sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are used in patients with advanced renal disease, monitor patients for signs of worsening renal function.
Hyperkalemia
Increases in serum potassium concentration, including hyperkalemia, have been reported with the use of NSAIDs, even in some patients without renal impairment. In patients with normal renal function, these effects have been attributed to a hyporeninemic-hypoaldosteronism state.
5.13 Anaphylactic Reactions
Anaphylactic reactions may occur in patients without known prior exposure to either component of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets. Such reactions can be life-threatening or fatal. In general, anaphylactic reactions to drugs are more likely to occur in individuals with a history of sensitivity to multiple allergens although anaphylactic reactions with naproxen have occurred in patient without known hypersensitivity to naproxen or to patients with aspirin sensitive asthma [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.17)]. Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets should not be given to patients with the aspirin triad. This symptom complex typically occurs in patients with asthma who experience rhinitis with or without nasal polyps, or who exhibit severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs [see Contraindications (4)].
Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity reaction to sumatriptan, naproxen, or any other component of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets. Naproxen has been associated with anaphylactic reactions in patients without known hypersensitivity to naproxen and in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.17)]. Seek emergency help if an anaphylactic reaction occurs.
5.14 Serious Skin Reactions
NSAID-containing products can cause serious skin adverse reactions such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which can be fatal. These serious events may occur without warning. Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of serious skin reactions and to discontinue the use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity. Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are contraindicated in patients with previous serious skin reactions to NSAIDs [see Contraindications (4)].
5.15 Premature Closure of the Ductus Arteriosus
Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus. Avoid use of NSAIDs, including sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets, in pregnant women starting at 30 weeks of gestation (third trimester) [see Contraindications (4), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
5.16 Hematologic Toxicity
Anemia has occurred in patients receiving NSAIDs. This may be due to fluid retention, occult or gross gastrointestinal blood loss, or an incompletely described effect upon erythropoiesis. If a patient treated with sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets have signs or symptoms of anemia, monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit.
NSAIDs, including sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets, may increase the risk of bleeding events. Co-morbid conditions such as coagulation disorders or concomitant use of warfarin, other anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents (e.g., aspirin), serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) may increase this risk. Monitor these patients for signs of bleeding [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.17 Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity
A subpopulation of patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma which may include chronic rhinosinusitis complicated by nasal polyps; severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm; and/or intolerance to aspirin and other NSAIDs. Because cross-reactivity between aspirin and other NSAIDs has been reported in such aspirin-sensitive patients, sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are contraindicated in patients with this form of aspirin sensitivity and should be used with caution in patients with preexisting asthma [see Contraindications (4)].
When sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are used in patients with preexisting asthma (without known aspirin sensitivity), monitor patients for changes in the signs and symptoms of asthma.
5.18 Seizures
Seizures have been reported following administration of sumatriptan. Some have occurred in patients with either a history of seizures or concurrent conditions predisposing to seizures. There are also reports in patients where no such predisposing factors are apparent. Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets should be used with caution in patients with a history of epilepsy or conditions associated with a lowered seizure threshold.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in labeling:
- Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- GI Bleeding, Ulceration and Perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Arrhythmias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Chest, Throat, Neck, and/or Jaw Pain/Tightness/Pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Cerebrovascular Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Other Vasospasm Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Heart Failure and Edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Medication Overuse Headache [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Serotonin Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Anaphylactic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Serious Skin Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
- Hematological Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16)]
- Exacerbation Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.17)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.18)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adults
The adverse reactions reported below are specific to the clinical trials with sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 85 mg/500 mg. See also the full prescribing information for naproxen and sumatriptan products.
Table 1 lists adverse reactions that occurred in 2 placebo-controlled clinical trials (Study 1 and 2) in adult patients who received 1 dose of study drug. Only adverse reactions that occurred at a frequency of 2% or more in any group treated with sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 85 mg/500 mg and that occurred at a frequency greater than the placebo group are included in Table 1.
Table 1. Adverse Reactions in Pooled Placebo-Controlled Trials in Adult Patients with Migraine
Adverse Reactions
Sumatriptan and Naproxen Sodium Tablets
85mg/500 mg
%
(n = 737)
Placebo
%
(n = 752)
Sumatriptan
85 mg
%
(n = 735)
Naproxen Sodium
500 mg
%
(n = 732)
Nervous system disorders
Dizziness
4
2
2
2
Somnolence
3
2
2
2
Paresthesia
2
<1
2
<1
Gastrointestinal disorders
Nausea
3
1
3
<1
Dyspepsia
2
1
2
1
Dry mouth
2
1
2
<1
Pain and other pressure sensations
Chest discomfort/chest pain
3
<1
2
1
Neck/throat/jaw pain/tightness /pressure
3
1
3
1
The incidence of adverse reactions in controlled clinical trials was not affected by gender or age of the patients. There were insufficient data to assess the impact of race on the incidence of adverse reactions.
Pediatric Patients 12 to 17 Years of Age
In a placebo-controlled clinical trial that evaluated pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age who received 1 dose of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 10/60 mg, 30/180 mg, or 85/500 mg, adverse reactions occurred in 13% of patients who received 10/60 mg, 9% of patients who received 30/180 mg, 13% who received 85/500 mg, and 8% who received placebo. No patients who received sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets experienced adverse reactions leading to withdrawal from the trial. The incidence of adverse reactions in pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age was comparable across all 3 doses compared with placebo. Table 2 lists adverse reactions that occurred in a placebo-controlled trial in pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age at a frequency of 2% or more with sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets and were more frequent than the placebo group.
Table 2. Adverse Reactions in a Placebo-Controlled Trial in Pediatric Patients 12 to 17 Years of Age with Migraine
Adverse Reactions
Sumatriptan and Naproxen Sodium Tablets
10/60 mg
%
(n = 96)
Sumatriptan and Naproxen Sodium Tablets
30/180 mg
%
(n = 97)
Sumatriptan and Naproxen Sodium Tablets
85/500 mg
%
(n = 152)
Placebo
%
(n = 145)
Vascular
Hot flush (i.e., hot flash[es])
0
2
<1
0
Musculoskeletal
Muscle tightness
0
0
2
0
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Clinically Significant Drug Interactions with Sumatriptan and Naproxen Sodium Tablets
See Table 3 for clinically significant drug interactions with NSAIDs or Sumatriptan
Table 3. Clinically Significant Drug Interactions with naproxen or sumatriptan Ergot-Containing Drugs
Clinical Impact:
Ergot-containing drugs have been reported to cause prolonged vasospastic reactions.
Intervention:
Because these effects may be additive, coadministration of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets and ergotamine-containing or ergot-type medications (like dihydroergotamine or methysergide) within 24 hours of each other is contraindicated.
Monoamine Oxidase-A Inhibitors
Clinical Impact:
MAO-A inhibitors increase systemic exposure of orally administered sumatriptan by 7-fold.
Intervention:
The use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets in patients receiving MAO-A inhibitors is contraindicated.
Other 5-HT1 Agonists
Clinical Impact:
5-HT1 agonist drugs can cause vasospastic effects.
Intervention:
Because these effects may be additive, coadministration of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets and other 5 HT1 agonists (e.g., triptans) within 24 hours of each other is contraindicated.
Drugs That Interfere with Hemostasis
Clinical Impact:
- Naproxen and anticoagulants such as warfarin have a synergistic effect on bleeding. The concomitant use of naproxen and anticoagulants have an increased risk of serious bleeding compared to the use of either drug alone.
- Serotonin release by platelets plays an important role in hemostasis. Case-control and cohort epidemiological studies showed that concomitant use of drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and an NSAID may potentiate the risk of bleeding more than an NSAID alone.
Intervention:
Monitor patients with concomitant use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets with anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin), antiplatelet agents (e.g., aspirin), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) for signs of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16)].
Aspirin
Clinical Impact:
A pharmacodynamic (PD) study has demonstrated an interaction in which lower dose naproxen (220mg/day or 220mg twice daily) interfered with the antiplatelet effect of low-dose immediate-release aspirin, with the interaction most marked during the washout period of naproxen [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. There is reason to expect that the interaction would be present with prescription doses of naproxen or with enteric-coated low-dose aspirin; however, the peak interference with aspirin function may be later than observed in the PD study due to the longer washout period.
Controlled clinical studies showed that the concomitant use of NSAIDs and analgesic doses of aspirin does not produce any greater therapeutic effect than the use of NSAIDs alone. In a clinical study, the concomitant use of an NSAID and aspirin was associated with a significantly increased incidence of GI adverse reactions as compared to use of the NSAID alone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Intervention:
Because there may be an increased risk of cardiovascular events following discontinuation of naproxen due to the interference with the antiplatelet effect of aspirin during the washout period, for patients taking low-dose aspirin for cardioprotection who require intermittent analgesics, consider use of an NSAID that does not interfere with the antiplatelet effect of aspirin, or non- NSAID analgesics where appropriate.
Concomitant use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets and analgesic doses of aspirin is not generally recommended because of the increased risk of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16)].
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors/Serotonin Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors and Serotonin Syndrome
Clinical Impact:
Cases of serotonin syndrome have been reported during coadministration of triptans and SSRIs, SNRIs, TCAs, and MAO inhibitors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
Intervention:
Discontinue sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets if serotonin syndrome is suspected.
ACE Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers, and Beta-blockers
Clinical Impact:
- NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), or beta-blockers (including propranolol).
- In patients who are elderly, volume-depleted (including those on diuretic therapy), or have renal impairment, coadministration of an NSAID with ACE inhibitors or ARBs may result in deterioration of renal function, including possible acute renal failure. These effects are usually reversible.
Intervention:
- During concomitant use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets and ACE-inhibitors, ARBs, or beta-blockers, monitor blood pressure to ensure that the desired blood pressure is obtained [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
- During concomitant use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets and ACE-inhibitors or ARBs in patients who are elderly, volume-depleted, or have impaired renal function, monitor for signs of worsening renal function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Diuretics
Clinical Impact:
Clinical studies, as well as postmarketing observations, showed that NSAIDs reduced the natriuretic effect of loop diuretics (e.g., furosemide) and thiazide diuretics in some patients. This effect has been attributed to the NSAID inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis.
Intervention:
During concomitant use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets with diuretics, observe patients for signs of worsening renal function, in addition to assuring diuretic efficacy including antihypertensive effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8, 5.12)].
Digoxin
Clinical Impact:
The concomitant use of naproxen with digoxin has been reported to increase the serum concentration and prolong the half-life of digoxin.
Intervention:
During concomitant use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets and digoxin, monitor serum digoxin levels.
Lithium
Clinical Impact:
NSAIDs have produced elevations in plasma lithium levels and reductions in renal lithium clearance. The mean minimum lithium concentration increased 15%, and the renal clearance decreased by approximately 20%. This effect has been attributed to NSAID inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis.
Intervention:
During concomitant use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets and lithium, monitor patients for signs of lithium toxicity.
Methotrexate
Clinical Impact:
Concomitant administration of some NSAIDs with high-dose methotrexate therapy has been reported to elevate and prolong serum methotrexate levels, resulting in deaths from severe hematologic and gastrointestinal toxicity. Concomitant use of NSAIDs and methotrexate may increase the risk for methotrexate toxicity (e.g., neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, renal dysfunction).
Intervention:
During concomitant use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets and methotrexate, monitor patients for methotrexate toxicity.
Cyclosporine
Clinical Impact:
Concomitant use of NSAIDs and cyclosporine may increase cyclosporine’s nephrotoxicity.
Intervention:
During concomitant use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets and cyclosporine, monitor patients for signs of worsening renal function.
NSAIDs and Salicylates
Clinical Impact:
Concomitant use of naproxen with other NSAIDs or salicylates (e.g., diflunisal, salsalate) increases the risk of GI toxicity, with little or no increase in efficacy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Intervention:
The concomitant use of naproxen with other NSAIDs or salicylates is not recommended.
Pemetrexed
Clinical Impact:
Concomitant use of NSAIDs and pemetrexed may increase the risk of pemetrexed-associated myelosuppression, renal, and GI toxicity (see the pemetrexed prescribing information).
Intervention:
During concomitant use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets and pemetrexed, in patients with renal impairment whose creatinine clearance ranges from 45 to 79 mL/min, monitor for myelosuppression, renal and GI toxicity. NSAIDs with short elimination half-lives (e.g., diclofenac, indomethacin) should be avoided for a period of two days before, the day of, and two days following administration of pemetrexed.
In the absence of data regarding potential interaction between pemetrexed and NSAIDs with longer half-lives (e.g., meloxicam, nabumetone), patients taking these NSAIDs should interrupt dosing for at least five days before, the day of, and two days following pemetrexed administration.
Probenecid
Clinical Impact:
Probenecid given concurrently increases naproxen anion plasma levels and extends its plasma half-life significantly. The clinical significance of this is unknown.
Intervention:
Reduce the frequency of administration of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets when given concurrently with probenecid.
7.2 Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Blood Tests
Naproxen may decrease platelet aggregation and prolong bleeding time. This effect should be kept in mind when bleeding times are determined.
Urine Tests
The administration of naproxen sodium may result in increased urinary values for 17-ketogenic steroids because of an interaction between the drug and/or its metabolites with m-di-nitrobenzene used in this assay. Although 17-hydroxy-corticosteroid measurements (Porter-Silber test) do not appear to be artificially altered, it is suggested that therapy with naproxen be temporarily discontinued 72 hours before adrenal function tests are performed if the Porter-Silber test is to be used.
Naproxen may interfere with some urinary assays of 5-hydroxy indoleacetic acid (5HIAA).
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C during the first two trimesters of pregnancy; Category X during the third trimester of pregnancy. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Sumatriptan and naproxen should be used during the first and second trimester of pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets should not be used during the third trimester of pregnancy because inhibitors of prostaglandin synthesis (including naproxen) are known to cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus in humans. In animal studies, administration of sumatriptan and naproxen, alone or in combination, during pregnancy resulted in developmental toxicity (increased incidences of fetal malformations, embryofetal and pup mortality, decreased embryofetal growth) at clinically relevant doses.
Oral administration of sumatriptan combined with naproxen sodium (5/9, 25/45, or 50/90 mg/kg/day sumatriptan/naproxen sodium) or each drug alone (50/0 or 0/90 mg/kg/day sumatriptan/naproxen sodium) to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in increased total incidences of fetal abnormalities at all doses and increased incidences of specific malformations (cardiac interventricular septal defect in the 50/90 mg/kg/day group, fused caudal vertebrae in the 50/0 and 0/90 mg/kg/day groups) and variations (absent intermediate lobe of the lung, irregular ossification of the skull, incompletely ossified sternal centra) at the highest dose of sumatriptan and naproxen alone and in combination. A no-effect dose for developmental toxicity in rabbits was not established. The lowest effect dose was 5/9 mg/kg/day sumatriptan/naproxen sodium, which was associated with plasma exposures (AUC) to sumatriptan and naproxen that were less than those attained at the maximum human daily dose (MHDD) of 170 mg sumatriptan and 1,000 mg naproxen sodium (two tablets of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium 85 mg/500 mg in a 24-hour period).
In previous developmental toxicity studies of sumatriptan, oral administration to pregnant rats during the period of organogenesis resulted in an increased incidence of fetal blood vessel abnormalities and decreased pup survival at doses of 250 mg/kg/day or higher.
The highest no-effect dose was 60 mg/kg/day, which is approximately 3 times the MHDD of 170 mg sumatriptan on a mg/m2 basis. Oral administration of sumatriptan to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis resulted in increased incidences of vascular and skeletal abnormalities at a dose of 50 mg/kg/day and embryolethality at 100 mg/kg/day. The highest no-effect dose of sumatriptan for developmental toxicity in rabbits was 15 mg/kg/day, or approximately 2 times the MHDD of 170 mg sumatriptan on a mg/m2 basis.
8.2 Labor and Delivery
Naproxen-containing products are not recommended in labor and delivery because, through its prostaglandin synthesis inhibitory effect, naproxen may adversely affect fetal circulation and inhibit uterine contractions, thus increasing the risk of uterine hemorrhage. In rat studies with NSAIDs, as with other drugs known to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, an increased incidence of dystocia, delayed parturition, and decreased pup survival occurred.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Both active components of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets, sumatriptan and naproxen, have been reported to be secreted in human milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets in pediatric patients under 12 years of age have not been established.
The safety and efficacy of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets for the acute treatment of migraine in pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age was established in a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Clinical Studies (14.2)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Elderly patients, compared to younger patients, are at greater risk for NSAID-associated serious cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and/or renal adverse reactions. Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are not recommended for use in elderly patients who have decreased renal function, higher risk for unrecognized CAD, and increases in blood pressure that may be more pronounced in the elderly [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.8,5.12) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
A cardiovascular evaluation is recommended for geriatric patients who have other cardiovascular risk factors (e.g., diabetes, hypertension, smoking, obesity, strong family history of CAD) prior to receiving sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets are not recommended for use in patients with creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min. Monitor the serum creatinine or creatinine clearance in patients with mild (CrCl = 60 to 89 mL/min) or moderate (CrCL = 30 to 59 mL/min) renal impairment, preexisting kidney disease, or dehydration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Patients (N = 670) have received single oral doses of 140 to 300 mg of sumatriptan without significant adverse effects. Volunteers (N = 174) have received single oral doses of 140 to 400 mg without serious adverse events.
Overdose of sumatriptan in animals has been fatal and has been heralded by convulsions, tremor, paralysis, inactivity, ptosis, erythema of the extremities, abnormal respiration, cyanosis, ataxia, mydriasis, salivation, and lacrimation.
Symptoms following acute NSAID overdosages have been typically limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting and epigastric pain. Gastrointestinal bleeding has occurred. Hypertension, acute renal failure, respiratory depression, and coma have occurred, but were rare [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
Manage patients with symptomatic and supportive care following an NSAID overdosage. There are no specific antidotes. Consider emesis and/or activated charcoal (60 to 100 grams in adults, 1 to 2 grams per kg of body weight in pediatric patients) and/or osmotic cathartic in symptomatic patients seen within four hours of ingestion or in patients with a large overdosage (5 to 10 times the recommended dosage). Hemodialysis does not decrease the plasma concentration of naproxen because of the high degree of its protein binding. It is unknown what effect hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis has on the serum concentrations of sumatriptan. Forced diuresis, alkalinization of urine, hemodialysis, or hemoperfusion may not be useful due to high protein binding.
For additional information about overdosage treatment contact a poison control center (1-800-222-1222).
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets contain sumatriptan (as the succinate), a selective 5-hydroxytryptamine1 (5-HT1) receptor subtype agonist, and naproxen sodium, a member of the arylacetic acid group of NSAIDs.
Sumatriptan succinate is chemically designated as 3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-N-methyl-indole-5-methanesulfonamide succinate (1:1), and it has the following structure:
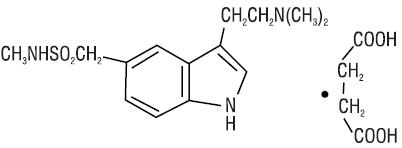
The molecular formula is C14H21N3O2S●C4H6O4, representing a molecular weight of 413.5. Sumatriptan succinate is a white to off- white powder that is soluble in water and in saline.
Naproxen sodium is chemically designated as (S)-6-methoxy-α-methyl-2-naphthaleneacetic acid, sodium salt, and it has the following structure:
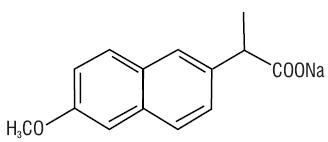
The molecular formula is C14H13NaO3, representing a molecular weight of 252.23. Naproxen sodium is a white-to-creamy white crystalline solid, soluble in water at neutral pH.
Each sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablet 85 mg/500 mg for oral administration contains 119 mg of sumatriptan succinate, USP equivalent to 85 mg of sumatriptan and 500 mg of naproxen sodium, USP. Each tablet also contains the inactive ingredients microcrystalline cellulose, dibasic calcium phosphate anhydrous, hypromellose, povidone, croscarmellose sodium, colloidal silicon dioxide, sodium chloride, sodium citrate, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol, FD&C Blue No. 2, FD&C Yellow No. 6, and iron oxide yellow.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets contain sumatriptan and naproxen.
Sumatriptan binds with high affinity to cloned 5-HT1B/1D receptors. Sumatriptan presumably exerts its therapeutic effects in the treatment of migraine headache through agonist effects at the 5-HT1B/1D receptors on intracranial blood vessels and sensory nerves of the trigeminal system, which result in cranial vessel constriction and inhibition of neuropeptide release.
Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets have analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties. The mechanism of action of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets, like that of other NSAIDs, is not completely understood but involves inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2).
Naproxen is a potent inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis in vitro. Naproxen concentrations reached during therapy have produced in vivo effects. Prostaglandins sensitize afferent nerves and potentiate the action of bradykinin in inducing pain in animal models. Prostaglandins are mediators of inflammation. Because naproxen is an inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis, its mode of action may be due to a decrease of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
In a healthy volunteer study, 10 days of concomitant administration of naproxen 220 mg once-daily with low-dose immediate-release aspirin (81 mg) showed an interaction with the antiplatelet activity of aspirin as measured by % serum thromboxane B2 inhibition at 24 hours following the day 10 dose [98.7% (aspirin alone) vs 93.1% (naproxen and aspirin)]. The interaction was observed even following discontinuation of naproxen on day 11 (while aspirin dose was continued) but normalized by day 13. In the same study, the interaction was greater when naproxen was administered 30 minutes prior to aspirin [98.7% vs 87.7%] and minimal when aspirin was administered 30 minutes prior to naproxen [98.7% vs 95.4%].
Following administration of naproxen 220 mg twice-daily with low-dose immediate–release aspirin (first naproxen dose given 30 minutes prior to aspirin), the interaction was minimal at 24 h following day 10 dose [98.7% vs 95.7%]. However, the interaction was more prominent after discontinuation of naproxen (washout) on day 11 [98.7% vs 84.3%] and did not normalize completely by day 13 [98.5% vs 90.7%] [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Blood Pressure
In a randomized, double-blind, parallel group, active control trial, sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 85 mg/500 mg administered intermittently over 6 months did not increase blood pressure in a normotensive adult population (n = 122). However, significant elevation in blood pressure has been reported with 5-HT1 agonists and NSAIDs in patients with and without a history of hypertension.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and Bioavailability
Sumatriptan, when given as sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 85 mg/500 mg, has a mean Cmax similar to that of sumatriptan succinate 100 mg tablets alone. The median Tmax of sumatriptan, when given as sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 85 mg/500 mg, was 1 hour (range: 0.3 to 4.0 hours), which is slightly different compared with sumatriptan succinate 100 mg tablets (median Tmax of 1.5 hours). Naproxen, when given as sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 85 mg/500 mg, has a Cmax which is approximately 36% lower than naproxen sodium 550 mg tablets and a median Tmax of 5 hours (range: 0.3 to 12 hours), which is approximately 4 hours later than from naproxen sodium tablets 550 mg. AUC values for sumatriptan and for naproxen are similar for sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 85 mg/500 mg compared with sumatriptan succinate 100 mg tablets or naproxen sodium 550 mg tablets, respectively. In a crossover trial in 16 subjects, the pharmacokinetics of both components administered as sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 85 mg/500 mg were similar during a migraine attack and during a migraine-free period.
Bioavailability of sumatriptan is approximately 15%, primarily due to presystemic (first-pass) metabolism and partly due to incomplete absorption.
Naproxen is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract with an in vivo bioavailability of 95%.
Food had no significant effect on the bioavailability of sumatriptan or naproxen administered as sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets, but slightly delayed the Tmax of sumatriptan by about 0.6 hour [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Distribution
Plasma protein binding is 14% to 21%. The effect of sumatriptan on the protein binding of other drugs has not been evaluated. The volume of distribution of sumatriptan is 2.7 L/kg.
The volume of distribution of naproxen is 0.16 L/kg. At therapeutic levels naproxen is greater than 99% albumin bound. At doses of naproxen greater than 500 mg/day, there is a less-than-proportional increase in plasma levels due to an increase in clearance caused by saturation of plasma protein binding at higher doses (average trough Css = 36.5, 49.2, and 56.4 mg/L with 500; 1,000; and 1,500 mg daily doses of naproxen, respectively). However, the concentration of unbound naproxen continues to increase proportionally to dose.
Metabolism
In vitro studies with human microsomes suggest that sumatriptan is metabolized by monoamine oxidase (MAO), predominantly the A isoenzyme. No significant effect was seen with an MAO-B inhibitor.
Naproxen is extensively metabolized to 6-0-desmethyl naproxen, and both parent and metabolites do not induce metabolizing enzymes.
Elimination
The elimination half-life of sumatriptan is approximately 2 hours. Radiolabeled 14C-sumatriptan administered orally is largely renally excreted (about 60%), with about 40% found in the feces. Most of a radiolabeled dose of sumatriptan excreted in the urine is the major metabolite indole acetic acid (IAA) or the IAA glucuronide, both of which are inactive. Three percent of the dose can be recovered as unchanged sumatriptan.
The clearance of naproxen is 0.13 mL/min/kg. Approximately 95% of the naproxen from any dose is excreted in the urine, primarily as naproxen (less than 1%), 6-0-desmethyl naproxen (less than 1%), or their conjugates (66% to 92%). The plasma half-life of the naproxen anion in humans is approximately 19 hours. The corresponding half-lives of both metabolites and conjugates of naproxen are shorter than 12 hours, and their rates of excretion have been found to coincide closely with the rate of naproxen disappearance from the plasma. In patients with renal failure, metabolites may accumulate.
Specific Populations
Geriatrics
The pharmacokinetics of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets in geriatric patients have not been studied. Elderly patients are more likely to have decreased hepatic function and decreased renal function [see Specific Populations (8.5)].
The pharmacokinetics of oral sumatriptan in the elderly (mean age: 72 years, 2 males and 4 females) and in patients with migraine (mean age: 38 years, 25 males and 155 females) were similar to that in healthy male subjects (mean age: 30 years).
Studies indicate that although total plasma concentration of naproxen is unchanged, the unbound plasma fraction, which represents <1% of the total concentration, increased in the elderly (range of unbound trough naproxen from 0.12% to 0.19% in elderly subjects versus 0.05% to 0.075% in younger subjects).
Pediatrics
A pharmacokinetic study compared 3 doses of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets in pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age (n=24) with adults (n=26). The AUC and Cmax of sumatriptan were 50 to 60% higher following a single dose of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 10/60 mg in pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age (n=7) compared with adult subjects (n=8), and were 6 to 26% higher following a single dose of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 30/180 mg or 85/500 mg in pediatrics than adults. Naproxen pharmacokinetic parameters were similar between pediatrics and adults.
Renal Impairment
The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets has not been studied. Since naproxen and its metabolites and conjugates are primarily excreted by the kidney, the potential exists for naproxen metabolites to accumulate in the presence of renal insufficiency. Elimination of naproxen is decreased in patients with severe renal impairment. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Hepatic Impairment
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets has not been studied. In a study in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (n = 8) matched for sex, age, and weight with healthy subjects (n = 8), patients with hepatic impairment had an approximately 70% increase in AUC and Cmax of sumatriptan and a Tmax 40 minutes earlier compared to healthy subjects. The pharmacokinetics of sumatriptan in patients with severe hepatic impairment has not been studied.
Gender
In a pooled analysis of 5 pharmacokinetic trials, there was no effect of gender on the systemic exposure of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets.
Race
The effect of race on the pharmacokinetics of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets has not been studied. The systemic clearance and Cmax of sumatriptan were similar in black (n = 34) and white (n = 38) healthy male subjects.
Drug Interaction Studies
Aspirin
When naproxen was administered with aspirin (>1 gram/day), the protein binding of naproxen was reduced, although the clearance of free naproxen was not altered. See Table 3 for clinically significant drug interactions of naproxen, an NSAID, with aspirin [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Propranolol
Propranolol 80 mg given twice daily had no significant effect on sumatriptan pharmacokinetics. See Table 3 for clinically significant drug interactions of propranolol, a beta-blocker, with sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets [see Drug Interactions (7)].
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
The carcinogenic potential of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets has not been studied.
In carcinogenicity studies in mouse and rat, sumatriptan was administered orally for 78 and 104 weeks, respectively, at doses up to 160 mg/kg/day. The highest doses tested are approximately 5 (mouse) and 9 (rat) times the maximum human daily dose (MHDD) of 170 mg sumatriptan on a mg/m2 basis (two tablets of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium 85 mg/500 mg in a 24-hour period).
The carcinogenic potential of naproxen was evaluated in a 2-year oral carcinogenicity study in rats at doses of 8, 16, and 24 mg/kg/day and in another 2-year oral carcinogenicity study in rats at a dose of 8 mg/kg/day. No evidence of tumorigenicity was found in either study. The highest dose tested is less than the MHDD (1,000 mg) of naproxen, on a mg/m2 basis.
Mutagenesis
Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tested alone and in combination were negative in an in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay, and in an in vivo micronucleus assay in mice.
The combination of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium was negative in an in vitro mouse lymphoma tk assay in the presence and absence of metabolic activation. However, in separate in vitro mouse lymphoma tk assays, naproxen sodium alone was reproducibly positive in the presence of metabolic activation.
Naproxen sodium alone and in combination with sumatriptan was positive in an in vitro clastogenicity assay in mammalian cells in the presence and absence of metabolic activation. The clastogenic effect for the combination was reproducible within this assay and was greater than observed with naproxen sodium alone. Sumatriptan alone was negative in these assays.
Chromosomal aberrations were not induced in peripheral blood lymphocytes following 7 days of twice-daily dosing with sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets in human volunteers.
In previous studies, sumatriptan alone was negative in in vitro (bacterial reverse mutation [Ames], gene cell mutation in Chinese hamster V79/HGPRT, chromosomal aberration in human lymphocytes) and in vivo (rat micronucleus) assays.
Impairment of Fertility
The effect of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets on fertility in animals has not been studied.
When sumatriptan (5, 50, 500 mg/kg/day) was administered orally to male and female rats prior to and throughout the mating period, there was a drug-related decrease in fertility secondary to a decrease in mating in animals treated with doses greater than 5 mg/kg/day (less than the MHDD of 170 mg on a mg/m2 basis). It is not clear whether this finding was due to an effect on males or females or both.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Corneal Opacities
Dogs receiving oral sumatriptan developed corneal opacities and defects in the corneal epithelium. Corneal opacities were seen at the lowest dosage tested, 2 mg/kg/day, and were present after 1 month of treatment. Defects in the corneal epithelium were noted in a 60-week study. Earlier examinations for these toxicities were not conducted and no-effect doses were not established. The lowest dose tested is less than the MHDD (170 mg) of sumatriptan on a mg/m2 basis.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Adults
The efficacy of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets in the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in adults was demonstrated in 2 randomized, double-blind, multicenter, parallel-group trials utilizing placebo and each individual active component of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 85 mg/500 mg (sumatriptan and naproxen sodium) as comparison treatments (Study 1 and Study 2). Patients enrolled in these 2 trials were predominately female (87%) and white (88%), with a mean age of 40 years (range: 18 to 65 years). Patients were instructed to treat a migraine of moderate to severe pain with 1 tablet. No rescue medication was allowed within 2 hours postdose. Patients evaluated their headache pain 2 hours after taking 1 dose of study medication; headache relief was defined as a reduction in headache severity from moderate or severe pain to mild or no pain. Associated symptoms of nausea, photophobia, and phonophobia were also evaluated. Sustained pain free was defined as a reduction in headache severity from moderate or severe pain to no pain at 2 hours postdose without a return of mild, moderate, or severe pain and no use of rescue medication for 24 hours postdose. The results from Study 1 and 2 are summarized in Table 4. In both trials, the percentage of patients achieving headache pain relief 2 hours after treatment was significantly greater among patients receiving sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 85 mg/500 mg (65% and 57%) compared with those who received placebo (28% and 29%).
Further, the percentage of patients who remained pain free without use of other medications through 24 hours postdose was significantly greater among patients receiving a single dose of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 85 mg/500 mg (25% and 23%) compared with those who received placebo (8% and 7%) or either sumatriptan (16% and 14%) or naproxen sodium (10%) alone.
Table 4. Percentage of Adult Patients with 2-Hour Pain Relief and Sustained Pain Free Following Treatment*
Sumatriptan and Naproxen Sodium Tablets85 mg/500 mg
Sumatriptan 85 mg
Naproxen Sodium 500 mg
Placebo
2-Hour Pain Relief
Study 1
65%†
n = 364
55%
n = 361
44%
n = 356
28%
n = 360
Study 2
57%†
n = 362
50%
n = 362
43%
n = 364
29%
n = 382
Sustained Pain Free (2 to 24 Hours)
Study 1
25%‡
n = 364
16%
n = 361
10%
n = 356
8%
n = 360
Study 2
23%‡
n = 362
14%
n = 362
10%
n = 364
7%
n = 382
The percentage of patients achieving initial headache pain relief within 2 hours following treatment with sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 85 mg/500 mg is shown in Figure 1.
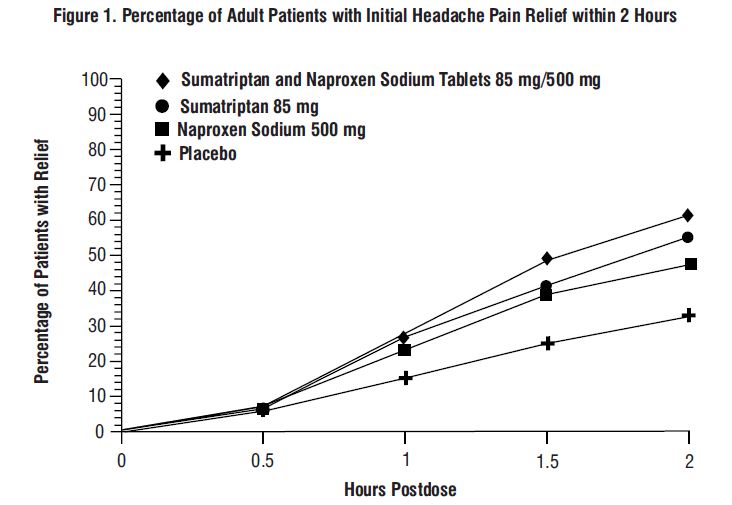
Compared with placebo, there was a decreased incidence of photophobia, phonophobia, and nausea 2 hours after the administration of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 85 mg/500 mg. The estimated probability of taking a rescue medication over the first 24 hours is shown in Figure 2.
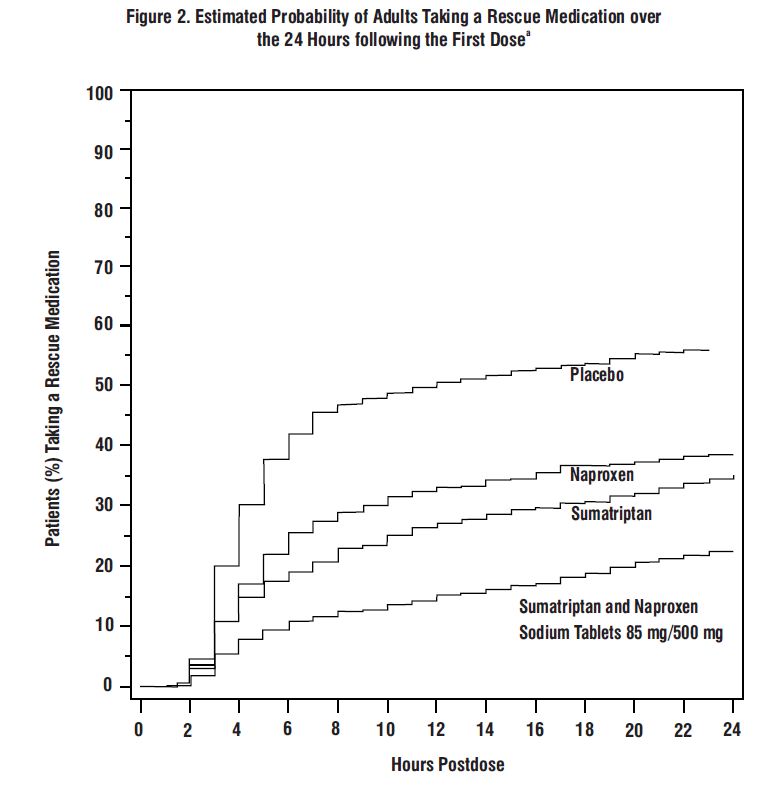
a Kaplan-Meier plot based on data obtained in the 2 clinical controlled trials providing evidence of efficacy with patients not using additional treatments censored to 24 hours. Plot also includes patients who had no response to the initial dose. No rescue medication was allowed within 2 hours postdose.
Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 85 mg/500 mg were more effective than placebo regardless of the presence of aura; duration of headache prior to treatment; gender, age, or weight of the subject; or concomitant use of oral contraceptives or common migraine prophylactic drugs (e.g., beta-blockers, anti-epileptic drugs, tricyclic antidepressants).
14.2 Pediatric Patients 12 to 17 Years of Age
The efficacy of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets in the acute treatment of migraine with or without aura in pediatric patients 12 to 17 years of age was demonstrated in a randomized, double-blind, multicenter, parallel-group, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial comparing 3 doses of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets and placebo (Study 3). Patients enrolled in this trial were mostly female (59%) and white (81%), with a mean age of 15 years.
Patients were required to have at least a 6-month history of migraine attacks with or without aura usually lasting 3 hours or more when untreated. Following a single-blind, placebo run-in phase, placebo nonresponders were randomized to receive a single dose of either sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 10/60 mg, 30/180 mg, 85/500 mg, or placebo. Patients were instructed to treat a single migraine attack with headache pain of moderate to severe intensity. No rescue medication was allowed within 2 hours postdose. Patients evaluated their headache pain 2 hours after taking 1 dose of study medication. Two-hour pain free was defined as a reduction in headache severity from moderate or severe pain to no pain at 2 hours postdose.
Results are summarized in Table 5. The percentage of patients who were pain free at 2 hours postdose was significantly greater among patients who received any of the 3 doses of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets compared with placebo.
Table 5. Percentage of Pediatric Patients 12 to 17 Years of Age with 2-Hour Pain-Free Response Following Treatment in Study 3a
Endpoint
Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets
10/60 mg
(n = 96)
Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets
30/180 mg
(n = 97)
Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets
85/500 mg
(n = 152)
Placebo
(n = 145)
2-Hour Pain Free
29%b
27% b
24% b
10%
aP values provided only for prespecified comparisons.
bP<0.01 versus placebo.
The percentage of pediatric patients who remained pain free without use of other medications 2 through 24 hours postdose was significantly greater after administration of a single dose of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets 85/500 mg compared with placebo. A greater percentage of pediatric patients who received a single dose of 10/60 mg or 30/180 mg remained pain free 2 through 24 hours postdose compared with placebo.
Compared with placebo, the incidence of photophobia and phonophobia was significantly decreased 2 hours after the administration of a single dose of 85/500 mg, whereas, the incidence of nausea was comparable. There was a decreased incidence of photophobia, phonophobia, and nausea 2 hours after single-dose administration of 10/60 mg or 30/180 mg compared with placebo.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets contain 119 mg of sumatriptan succinate, USP equivalent to 85 mg of sumatriptan and 500 mg of naproxen sodium, USP and are supplied as blue, oval, biconvex, film-coated tablets debossed with “410” on one side and plain on other side.
They are supplied as follows:
Bottles of 9’s with Child Resistant Cap.......................................... NDC 71800-901-01
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° and 30°C (59° and 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container with a child-resistant closure.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide) that accompanies each prescription dispensed. Inform patients, families, or their caregivers of the following information before initiating therapy with sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets and periodically during the course of ongoing therapy.
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events, Prinzmetal's Angina, Other Vasospasm-Related Events, Arrhythmias and Cerebrovascular EventsAdvise patients to be alert for the symptoms of cardiovascular thrombotic effects such as myocardial infarction or stroke, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious cardiovascular events can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for signs and symptoms of chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, irregular heartbeat, significant rise in blood pressure, weakness and slurring of speech, and should be advised to report any of these symptoms to their health care provider immediately. Apprise patients of the importance of this follow-up [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3, 5.5, 5.6, 5.8)].
Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and PerforationAdvise patients to report symptoms of ulcerations and bleeding, including epigastric pain, dyspepsia, melena, and hematemesis to their health care provider. In the setting of concomitant use of low-dose aspirin for cardiac prophylaxis, inform patients of the increased risk for and the signs and symptoms of GI bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
HepatotoxicityInform patients of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, diarrhea, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and “flu-like” symptoms). If these occur, instruct patients to stop sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets and seek immediate medical therapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Anaphylactic ReactionsInform patients that anaphylactic reactions have occurred in patients receiving the components of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets. Such reactions can be life-threatening or fatal. In general, anaphylactic reactions to drugs are more likely to occur in individuals with a history of sensitivity to multiple allergens. Inform patients of the signs of an anaphylactic reaction (e.g., difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat). If these occur, patients should be instructed to seek immediate emergency help [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
Serious Skin ReactionsInform patients that sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets, like other NSAID-containing products, may increase the risk of serious skin side effects such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis, which may result in hospitalizations and even death. Although serious skin reactions may occur without warning, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of skin rash and blisters, fever, or other signs of hypersensitivity such as itching and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative signs or symptoms. Advise patients to stop the drug immediately if they develop any type of rash and contact their healthcare providers as soon as possible [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)].
Fetal ToxicityInform patients that sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets should not be used during the third trimester of pregnancy because NSAID-containing products have been shown to cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus. Inform patients that sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets should be used during the first and second trimester of pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.15), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Nursing MothersAdvise patients to notify their healthcare provider if they are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Heart Failure and EdemaAdvise patients to be alert for the symptoms of congestive heart failure including shortness of breath, unexplained weight gain, or edema and to contact their healthcare provider if such symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Concomitant Use with Other Triptans or Ergot MedicationsInform patients that use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets within 24 hours of another triptan or an ergot-type medication (including dihydroergotamine or methysergide) is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4), Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Serotonin SyndromeCaution patients about the risk of serotonin syndrome with the use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets or other triptans, particularly during concomitant use with SSRIs, SNRIs, TCAs, and MAO inhibitors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11), Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Medication Overuse HeadacheInform patients that use of acute migraine drugs for 10 or more days per month may lead to an exacerbation of headache and encourage patients to record headache frequency and drug use (e.g., by keeping a headache diary) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
Ability to Perform Complex TasksTreatment with sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets may cause somnolence and dizziness; instruct patients to evaluate their ability to perform complex tasks after administration of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
AsthmaAdvise patients with preexisting asthma to seek immediate medical attention if their asthma worsens after taking sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets. Patients with a history of aspirin-sensitive asthma should not take sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.17)].
Avoid Concomitant Use of NSAIDsInform patients that the concomitant use of sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets with other NSAIDs or salicylates (e.g., diflunisal, salsalate) is not recommended due to the increased risk of gastrointestinal toxicity, and little or no increase in efficacy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7)]. Alert patients that NSAIDs may be present in “over the counter” medications for treatment of colds, fever, or insomnia.
Use of NSAIDS and Low-Dose AspirinInform patients not to use low-dose aspirin concomitantly with sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablets until they talk to their healthcare provider [see Drug Interactions (7)].
- MEDICATION GUIDE
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANELNDC 71800-901-01
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
SUMATRIPTAN AND NAPROXEN SODIUM
sumatriptan and naproxen sodium tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:71800-901 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SUMATRIPTAN SUCCINATE (UNII: J8BDZ68989) (SUMATRIPTAN - UNII:8R78F6L9VO) SUMATRIPTAN 85 mg NAPROXEN SODIUM (UNII: 9TN87S3A3C) (NAPROXEN - UNII:57Y76R9ATQ) NAPROXEN SODIUM 500 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) ANHYDROUS DIBASIC CALCIUM PHOSPHATE (UNII: L11K75P92J) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) POVIDONE K30 (UNII: U725QWY32X) CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM CITRATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) CROSPOVIDONE (120 .MU.M) (UNII: 68401960MK) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) FD&C BLUE NO. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) FD&C YELLOW NO. 6 (UNII: H77VEI93A8) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) Product Characteristics Color BLUE Score no score Shape OVAL Size 21mm Flavor Imprint Code 410 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:71800-901-01 9 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/09/2020 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA202803 12/09/2020 Labeler - Innovida Phamaceutique Corporation (080892908)