Label: BRINEURA- cerliponase alfa kit
- NDC Code(s): 68135-495-04, 68135-500-00, 68135-811-02
- Packager: BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc.
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Biologic Licensing Application
Drug Label Information
Updated August 5, 2024
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use BRINEURA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for BRINEURA.
BRINEURA (cerliponase alfa) injection, for intraventricular use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2017WARNING: HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS INCLUDING ANAPHYLAXIS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning
- Anaphylaxis has occurred during the early course of enzyme replacement therapy and after extended duration of therapy. (5.1)
- Initiate BRINEURA in a healthcare setting with appropriate medical monitoring and support measures, including access to cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment. (5.1)
- If a severe hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) occurs, discontinue BRINEURA and immediately initiate appropriate medical treatment, including use of epinephrine. (5.1)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
BRINEURA is a hydrolytic lysosomal N-terminal tripeptidyl peptidase indicated to slow the loss of ambulation in pediatric patients with neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis type 2 (CLN2 disease), also known as tripeptidyl peptidase 1 (TPP1) deficiency. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Administration of BRINEURA should be supervised by a healthcare provider knowledgeable in the management of hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis. (2.1)
- BRINEURA should be administered by or under the supervision of a physician experienced in intraventricular administration. (2.1)
- Premedication of patients with antihistamines with or without antipyretics or corticosteroids is recommended. (2.1)
- Prior to each infusion, inspect the scalp for signs of intraventricular access device reservoir leakage, failure, or potential infection. (2.1)
- Recommended BRINEURA dosage is 300 mg administered once every other week as an intraventricular infusion. In patients less than 2 years of age, lower doses are recommended. (2.2)
- Dosing is not recommended in patients less than 37 weeks post-menstrual age or those weighing less than 2.5 kg. (2.2)
- See the full prescribing information for dosage modifications due to hypersensitivity reactions. (2.3)
- See the full prescribing information for preparation and administration instructions. (2.4, 2.6)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: BRINEURA 150 mg/5 mL (30 mg/mL) solution, two single-dose vials per carton co-packaged with Intraventricular Electrolytes Injection 5 mL in a single-dose vial. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Any sign or symptom of acute or unresolved localized infection on or around the device insertion site (e.g. cellulitis or abscess); or suspected or confirmed CNS infection (e.g., cloudy CSF or positive CSF gram stain, or meningitis). (4)
- Any acute intraventricular access device-related complication (e.g., leakage, extravasation of fluid, or device failure). (4)
- Patients with ventriculoperitoneal shunts. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Meningitis and Other Intraventricular Access Device-Related Infections: Monitor the device insertion site for signs of infection. (4, 5.2)
- Intraventricular Access Device-Related Complications: Consult a neurosurgeon for any complications with the implanted device. In case of device-related complication, discontinue the infusion and refer to the device labeling for further instructions. (4, 5.3)
- Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions: Monitor vital signs before, during, and post-infusion. Monitor Electrocardiogram (ECG) in patients with a history of bradycardia, conduction disorder, or with structural heart disease, during the infusion. In patients without cardiac abnormalities, perform regular 12-lead ECG evaluations every 6 months. (2.5, 5.4)
- Infusion-Associated Reactions (IARs): If an IAR occurs, decreasing the infusion rate, temporarily stopping the infusion, and/or administering antihistamines and/or antipyretics may ameliorate the symptoms. (5.5)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (≥8%) are: pyrexia, ECG abnormalities, decreased CSF protein, vomiting, seizures, device-related complications, hypersensitivity, increased CSF protein, hematoma, headache, irritability, pleocytosis, device-related infections, bradycardia, feeling jittery, and hypotension. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact BioMarin at 1-866-906-6100 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 7/2024
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS INCLUDING ANAPHYLAXIS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommendations Prior to BRINEURA Treatment
2.2 Recommended Dosage and Administration
2.3 Administration Modifications due to Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis
2.4 Preparation Instructions for Intraventricular Administration of the Product
2.5 Storage Instructions for the Thawed Product and Product in Syringe
2.6 Administration Instructions for Intraventricular Infusion
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis
5.2 Meningitis and Other Intraventricular Access Device-Related Infections
5.3 Intraventricular Access Device-Related Complications
5.4 Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions
5.5 Infusion-Associated Reactions
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.6 Immunogenicity
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS INCLUDING ANAPHYLAXIS
Patients treated with enzyme replacement therapies have experienced life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis has occurred during the early course of enzyme replacement therapy and after extended duration of therapy.
Initiate BRINEURA in a healthcare setting with appropriate medical monitoring and support measures, including access to cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) occurs, discontinue BRINEURA and immediately initiate appropriate medical treatment, including use of epinephrine. Inform patients of the symptoms of life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and to seek immediate medical care should symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommendations Prior to BRINEURA Treatment
- Administration of BRINEURA should be supervised by a healthcare provider knowledgeable in the management of hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis.
- Initiate BRINEURA in a healthcare setting with appropriate medical monitoring and support measures, including access to cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- BRINEURA should be administered by or under the supervision of a physician experienced in intraventricular administration via a surgically implanted intraventricular access device system which consists of the reservoir and catheter components [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
- Premedication of patients with antihistamines with or without antipyretics or corticosteroids is recommended 30 to 60 minutes prior to the start of infusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.5)].
- Aseptic technique must be strictly observed during preparation and administration [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
- Prior to each infusion of BRINEURA, inspect the scalp for signs of intraventricular access device reservoir leakage, failure or potential infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)].
- Prior to each infusion of BRINEURA and when clinically indicated, obtain a sample of CSF for cell count and culture [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Replace the intraventricular access device reservoir prior to 4 years of single-puncture administrations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage and Administration
The recommended dosage of BRINEURA in pediatric patients is provided in Table 1. The dose is administered once every other week by intraventricular infusion.
BRINEURA is not recommended in patients less than 37 weeks post-menstrual age (gestational age at birth plus post-natal age) or those weighing less than 2.5 kg [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Administer BRINEURA first followed by infusion of the Intraventricular Electrolytes. The complete BRINEURA infusion, including the required infusion of Intraventricular Electrolytes, is approximately 2 to 4.5 hours, depending on the dose and volume administered. See Table 1 for the appropriate volume and infusion rate. For volumes that are not whole numbers, see Dosage and Administration (2.6).
Table 1: BRINEURA Dose, Volume, and Infusion Rate by Age Age groups BRINEURA dose administered every other week Volume of BRINEURA solution Infusion rate Birth to < 6 months 100 mg 3.3 mL 1.25 mL/hr 6 months to < 1 year 150 mg 5 mL 2.5 mL/hr 1 year to < 2 years 200 mg (first 4 doses) 6.7 mL (first 4 doses) 2.5 mL/hr 300 mg (subsequent doses) 10 mL (subsequent doses) 2 years and older 300 mg 10 mL 2.5 mL/hr 2.3 Administration Modifications due to Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis
In the event of a severe hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis), immediately discontinue BRINEURA administration and initiate appropriate medical treatment. If the decision is made to readminister BRINEURA after the occurrence of anaphylaxis, initiate the subsequent infusion at approximately one-half the infusion rate at which the anaphylactic reaction occurred with appropriate premedication. For additional recommendations in the event of a hypersensitivity reaction, see Warnings and Precautions (5.1).
2.4 Preparation Instructions for Intraventricular Administration of the Product
BRINEURA and the Intraventricular Electrolytes must only be administered by the intraventricular route, using the provided Administration Kit for use with BRINEURA. Each vial of BRINEURA and Intraventricular Electrolytes is intended for a single dose only.
BRINEURA is administered into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) by infusion via a surgically implanted reservoir and catheter (the "intraventricular access device system"). BRINEURA is intended to be administered via the Codman® HOLTER RICKHAM Reservoirs (Part Numbers: 82-1625, 82-1621, 82-1616) with the Codman® Ventricular Catheter (Part Number: 82-1650). The intraventricular access device reservoir and catheter must be implanted prior to the first infusion. It is recommended that the first dose be administered at least 5 to 7 days after device implantation.
BRINEURA is intended to be administered with the B Braun Perfusor® Space Infusion Pump System (Product Code: 8713030U). If an alternative pump must be used, the essential performance requirements for this syringe pump used to deliver BRINEURA are as follows:
- Delivery rate of 1.25 or 2.5 mL per hr with delivery accuracy of +/- 1 mL per hr
- Compatible with 20 mL syringes provided in the Administration Kit for use with BRINEURA
- Occlusion alarm setting to ≤ 281 mm Hg
- Cleared for intraventricular route of administration
Administer BRINEURA and the Intraventricular Electrolytes using the provided Administration Kit for use with BRINEURA components [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)].
Each infusion consists of 3.3 to 10 mL of BRINEURA followed by 2 mL of Intraventricular Electrolytes. The complete infusion must be administered using an infusion set with a 0.2 micron inline filter. The Intraventricular Electrolytes are used to flush the infusion line, port needle, and intraventricular access device in order to fully administer BRINEURA and to maintain patency of the intraventricular access device.
Supplies for Infusion Preparation
- BRINEURA and Intraventricular Electrolytes Injection vials (package 1 of 2) [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)]
- Administration Kit for use with BRINEURA (package 2 of 2) [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)]
- Syringe pump (not supplied)
- Empty sterile single-use luer lock syringe, no larger than 3 mL (not supplied)
Inspect the Administration Kit infusion components to ensure the components are in the individual packages and have not been compromised.
Thaw BRINEURA and Intraventricular Electrolytes Injection vials at room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) for approximately 60 minutes. Do not thaw or warm vials any other way. Do not shake vials. Condensation will occur during thawing period. Do not re-freeze vials or freeze syringes containing BRINEURA or Intraventricular Electrolytes.
Inspect fully thawed BRINEURA and Intraventricular Electrolytes Injection vials. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. BRINEURA is a clear to slightly opalescent and colorless to pale yellow solution. Intraventricular Electrolytes is a clear to colorless solution. Do not use if the solutions are discolored or if there is other foreign particulate matter in the solutions. BRINEURA vials may occasionally contain thin translucent fibers or opaque particles. These naturally occurring particles are cerliponase alfa. These particles are removed via the 0.2 micron inline filter without having a detectable effect on the purity or strength of BRINEURA. Intraventricular Electrolytes may contain particles, which appear during the thaw period; however, these dissolve when the solution reaches room temperature.
2.5 Storage Instructions for the Thawed Product and Product in Syringe
Storage of Thawed Product
Use thawed BRINEURA and Intraventricular Electrolytes immediately. If thawed BRINEURA and Intraventricular Electrolytes is not used immediately, store in the refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for no more than 24 hours. Discard the thawed product after 24 hours if refrigerated.
Storage of Product in Syringe
Use product held in labeled syringes immediately. If product held in labeled syringe is not used immediately, store in the refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) for no more than 4 hours prior to infusion. Discard the product held in labeled syringe after 4 hours if refrigerated.
2.6 Administration Instructions for Intraventricular Infusion
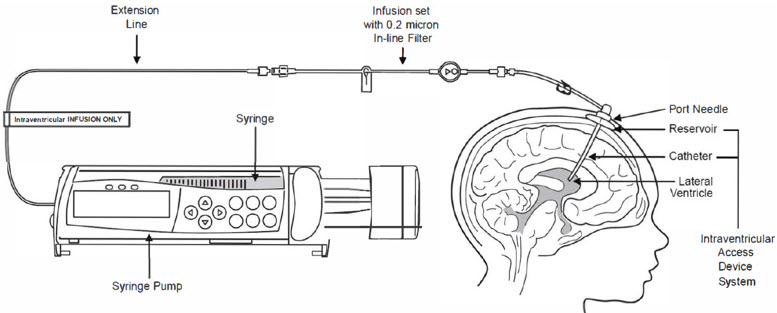
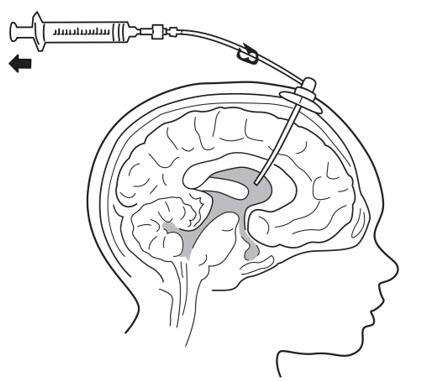
Intraventricular Infusion of BRINEURA
Figure 1 represents the intraventricular infusion system set up. Use aseptic technique during the infusion.
Follow the steps below to proceed with the intraventricular infusion.- 1.
- Use aseptic technique when preparing the BRINEURA syringe for infusion. Label one sterile syringe "BRINEURA" and attach the syringe needle.
- 2.
-
Confirm required dose and volume based on patient age per Table 1. Remove the green flip-off caps from one or both BRINEURA vials. Each BRINEURA vial contains 150 mg or 5 mL. Use the "BRINEURA" labeled syringe to withdraw the volume of BRINEURA solution from the vial per the required dose (see Table 1). Intermediate volumes that fall between 1 mL increments should be drawn up in the syringe to the nearest whole number, specifically 3.3 mL to 4 mL and 6.7 mL to 7 mL. Do not dilute BRINEURA. Do not mix BRINEURA with any other drug.
Discard any unused portion left in the vial. - 3.
- Label the infusion line "intraventricular infusion only" (see Figure 1).
- 4.
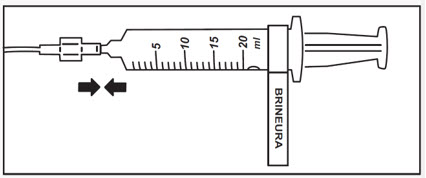
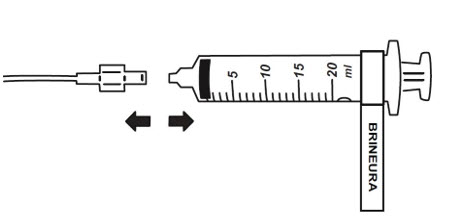
- Attach the syringe containing BRINEURA to the extension line (see Figure 2). Then connect the extension line to the infusion set with a 0.2 micron inline filter (see Figure 1).
- 5.
- Prime the infusion components with BRINEURA.
- 6.
- Inspect scalp for signs of intraventricular access device reservoir leakage or failure and for potential infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)].
- 7.
- Prepare the scalp for intraventricular infusion per institution standard of care.
- 8.
- Insert port needle into intraventricular access device reservoir (see Figure 3).
- 9.
- Connect a separate empty sterile single-use luer lock syringe, no larger than 3 mL (not provided) to the port needle. Withdraw 0.5 mL to 1 mL of CSF to check patency of intraventricular access device (see Figure 4) and send specimen for culture.
- Do not return CSF to intraventricular access device.
- Routinely send CSF samples for infection monitoring [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- 10.
- Attach the infusion set with 0.2 micron inline filter to the port needle (see Figure 1).
- Secure the components per institution standard of care.
- 11.
- Place the syringe containing BRINEURA into the syringe pump and program the pump to deliver at an infusion rate of 1.25 or 2.5 mL per hour (Table 1). Set the pump volume limit to deliver the exact volume that corresponds to the dose of BRINEURA solution appropriate for the patient's age (Table 1). Set the occlusion alarm setting to alert at pressure ≤ 281 mm Hg. See syringe pump operating manual for details. Do not deliver as a bolus or manually.
- 12.
- Administer pre-medication 30 to 60 minutes prior to the start of infusion.
- 13.
- Monitor vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate) prior to the start of infusion, periodically during infusion, and post-infusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- 14.
- Initiate infusion of BRINEURA at a rate of 1.25 or 2.5 mL per hour (Table 1).
- 15.
- Periodically inspect the infusion system during the infusion for signs of leakage or delivery failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- 16.
- When the BRINEURA infusion is complete, detach and remove the syringe from the pump and disconnect from the tubing (see Figure 5). Discard the syringe containing any residual drug. Proceed to Step 16 for Intraventricular Electrolytes infusion.
Intraventricular Infusion of Intraventricular Electrolytes
Administer the Intraventricular Electrolytes provided after BRINEURA infusion is complete.
- 17.
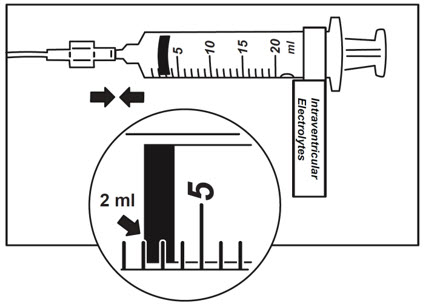
- Use aseptic technique when preparing the Intraventricular Electrolytes syringe for infusion. Label one sterile syringe "Intraventricular Electrolytes" and attach the syringe needle. Remove the yellow flip-off cap from the Intraventricular Electrolytes Injection vial. Withdraw 2 mL of Intraventricular Electrolytes. Discard the remaining unused portion.
- 18.
- Attach the syringe to the extension line (see Figure 6).
- 19.
- Place the syringe containing Intraventricular Electrolytes into the syringe pump and program pump to deliver at an infusion rate of 1.25 or 2.5 mL per hour (Table 1). Set the pump volume limit to deliver 2 mL. Set the occlusion alarm setting to alert at pressure ≤ 281 mm Hg. See syringe pump operating manual for details. Do not deliver as a bolus or manually.
- 20.
- Initiate infusion of Intraventricular Electrolytes at a rate of 2.5 mL per hour.
- 21.
- Periodically inspect the infusion system during the infusion for signs of leakage or delivery failure.
- 22.
- When the Intraventricular Electrolytes infusion is complete, detach and remove the empty syringe from the pump and disconnect from the infusion line.
- 23.
- Remove the port needle. Apply gentle pressure and bandage the infusion site per institution standard of care.
Dispose of the infusion components, needles, unused solutions and other waste materials in accordance with local requirements.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: BRINEURA 150 mg/5 mL (30 mg/mL) solution, two single-dose vials per carton co-packaged with Intraventricular Electrolytes Injection 5 mL in a single-dose vial. BRINEURA is a clear to slightly opalescent and colorless to pale yellow solution. Intraventricular Electrolytes is a clear to colorless solution [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)].
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
BRINEURA is contraindicated in patients with:
- any sign or symptom of acute, unresolved localized infection on or around the device insertion site (e.g., cellulitis or abscess); or suspected or confirmed CNS infection (e.g., cloudy CSF or positive CSF gram stain, or meningitis) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- any acute intraventricular access device-related complication (e.g., leakage, extravasation of fluid, or device failure) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- ventriculoperitoneal shunts.
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis
Life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis have been reported in patients treated with enzyme replacement therapies, including BRINEURA. BRINEURA-treated patients have had these reactions occur in clinical studies and postmarketing use [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. In clinical Trial 1 and Trial 2 to 96 weeks, a total of 11 of 24 (46%) patients experienced hypersensitivity reactions during the infusion or within 24 hours of completion of the infusion. Patients in clinical trials were routinely pre-medicated with antihistamines with or without antipyretics or corticosteroids, prior to infusion of BRINEURA. During postmarketing use, anaphylactic reactions occurred during or within several hours of BRINEURA infusion. Epinephrine was administered in these patients, and they received subsequent BRINEURA infusions without recurrence of anaphylaxis.
In Trial 3, hypersensitivity reactions were reported in 5 of 8 (63 %) patients less than 3 years of age at baseline as compared to 0 of 6 patients ≥ 3 years of age at baseline [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Of the reported hypersensitivity reactions, a single anaphylactic reaction occurred in a subject < 3 years of age.
Anaphylaxis has occurred during the early course of enzyme replacement therapy and after extended duration of therapy. Administration of BRINEURA should be supervised by a healthcare provider knowledgeable in the management of hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis. Initiate BRINERUA in a healthcare setting with appropriate medical monitoring and support measures, including access to cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment. Premedication of patients with antihistamines with or without antipyretics or corticosteroids is recommended 30 to 60 minutes prior to the start of infusion. Observe patients closely during and after the infusion. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) occurs, discontinue BRINEURA and immediately initiate appropriate medical treatment including use of epinephrine. Inform patients and caregivers of the symptoms of life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and to seek immediate medical care should symptoms occur.
The management of hypersensitivity reactions should be based on the severity of the reaction and may include temporarily interrupting the infusion, and/or treatment with antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids. Consider the risks and benefits of readministration of BRINEURA following an anaphylactic reaction. If the decision is made to readminister BRINEURA after the occurrence of anaphylaxis, ensure appropriately trained personnel and equipment for emergency resuscitation (including epinephrine and other emergency medicines) are readily available during infusion. Initiate subsequent infusion at approximately one-half the initial infusion rate at which the anaphylactic reaction occurred.
5.2 Meningitis and Other Intraventricular Access Device-Related Infections
Bacterial meningitis requiring antibiotic treatment and removal of the device was reported during postmarketing use of BRINEURA. Additionally, in clinical trials and during postmarketing use there were reports of other device-related clinical infections which were confirmed by positive CSF cultures, treated with antibiotics and removal of the entire intraventricular access device, and in which patients resumed treatment with BRINEURA after the device was replaced [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. In all cases, antibiotics were administered, the intraventricular access devices were removed and replaced, and patients resumed treatment with BRINEURA.
The signs and symptoms of infections may not be readily apparent in patients with CLN2 disease. To reduce the risk of infectious complications, BRINEURA should be administered by, or under the supervision of, a physician experienced in intraventricular administration. Prior to each infusion of BRINEURA and when clinically indicated, obtain a sample of CSF for cell count and culture. Do not administer BRINEURA if there are localized signs of infection on or around the device insertion site, such as erythema, tenderness, or discharge or suspected or confirmed CNS infection (e.g., cloudy CSF or positive CSF gram stain, or meningitis) [see Contraindications (4)].
Healthcare providers should be vigilant for the development of signs and symptoms of infection, including meningitis, during treatment with BRINEURA and monitor the device insertion site for signs of infection.
5.3 Intraventricular Access Device-Related Complications
During the clinical trials and in postmarketing reports, intraventricular access device-related complications were reported (e.g., device leakage, device failure extravasation of CSF fluid, or bulging of the scalp around or above the intraventricular access device) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. For any complications with the implanted intraventricular access device, consult with a neurosurgeon to confirm the integrity or performance of the device. In case of intraventricular access device-related complications, discontinue the BRINEURA infusion and refer to the device manufacturer's labeling for further instructions [see Contraindications (4)].
Material degradation of the intraventricular access device reservoir was reported after approximately 4 years of administration, which may impact the effective and safe use of the device. During benchtop testing such material degradation was recognized after approximately 105 perforations of the intraventricular access device. The intraventricular access device should be replaced prior to 4 years of single-puncture administrations, which equates to approximately 105 administrations of BRINEURA.
5.4 Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions
Monitor vital signs (blood pressure, heart rate) before infusion starts, periodically during infusion, and post-infusion in a healthcare setting [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)]. Upon completion of the infusion, clinically assess the patient status. Continued observation may be necessary if clinically indicated.
Perform electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring during infusion in patients with a history of bradycardia, conduction disorder, or with structural heart disease, as some patients with CLN2 disease may develop conduction disorders or heart disease. In patients without cardiac abnormalities, regular 12-lead ECG evaluations should be performed every 6 months.
In clinical Trial 1 and Trial 2 to 96 weeks, hypotension was reported in 2 of 24 (8%) patients, which occurred during or up to eight hours after BRINEURA infusion. Patients did not require alteration in treatment, and reactions resolved spontaneously or after intravenous fluid administration [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.5 Infusion-Associated Reactions
Infusion-associated reactions (IARs) such as vomiting, seizure, rash, pyrexia, hypersensitivity, and anaphylactic reaction have been observed in patients treated with BRINEURA [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Premedication of patients with antihistamines with or without antipyretics or corticosteroids is recommended 30 to 60 minutes prior to the start of infusion. If an IAR occurs, decreasing the infusion rate, temporarily stopping the infusion, and/or administering antihistamines and/or antipyretics may ameliorate the symptoms. Closely monitor patients who have experienced IARs when re-administering BRINEURA.
In Trial 3, infusion-associated reactions were reported in 8 of 8 patients less than 3 years of age at baseline as compared to 4 of 6 patients ≥ 3 years of age at baseline.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Meningitis and Other Intraventricular Access Device-Related Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Intraventricular Access Device-Related Complications [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Infusion-Associated Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Trial 1 and Trial 2
The safety of BRINEURA was evaluated in 24 patients with CLN2 disease who received at least one 300 mg dose of BRINEURA given by intraventricular infusion in a clinical trial with extension (Trials 1 and 2) of up to 161 weeks [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Table 2 summarizes the most common adverse reactions that occurred in BRINEURA-treated patients through 96 weeks.
Table 2: Adverse Reactions Reported in ≥ 8% of Symptomatic Pediatric Patients with CLN2 Disease in BRINEURA Trial 1 and Trial 2 at Week 96 Adverse Reaction Patients Treated with BRINEURA
n=24 (%)- *
- Increased body temperature includes: increased body temperature and pyrexia
- †
- ECG abnormalities include: non-specific repolarization abnormality, notched QRS, ST segment elevation, biphasic T wave abnormality, supraventricular extrasystoles, bradycardia, sinus tachycardia, and intraventricular conduction delay
- ‡
- Seizures include: atonic, generalized tonic-clonic, focal, and absence
- §
- Device-related complications include device-related infection, delivery system-related complications (needle issues, device leakage, device malfunction, device difficult to use, medical device site irritation, device breakage, etc.) and pleocytosis.
- ¶
- Hypersensitivity includes only hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- #
- Device-related infections include: Propionibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus epidermidis
Increased body temperature* 17 (71) ECG abnormalities† 17 (71) Decreased CSF protein 17 (71) Vomiting 15 (63) Seizures‡ 12 (50) Device-related complications§ 12 (50) Hypersensitivity¶ 9 (38) Increased CSF protein 5 (21) Hematoma 5 (21) Headache 4 (17) Irritability 4 (17) Pleocytosis 4 (17) Device-related infections# 2 (8) Bradycardia 2 (8) Feeling jittery 2 (8) Hypotension 2 (8) Description of Selected Adverse Reactions from Trial 1 and Trial 2 at 96 weeks
Seizures
Seizures were reported in 12 of 24 (50%) patients. The seizure types reported include atonic, generalized tonic-clonic, focal, and absence. Seizures were managed with standard anti-convulsive therapies and did not result in discontinuation of BRINEURA treatment.
Device-Related Complications
Adverse reactions related to the device were observed in 12 of 24 (50%) of patients. Device-related adverse reactions include infection, delivery system-related complications, and pleocytosis. Nine out of 24 patients (38%) experienced adverse reactions, which involved complications of the non-implanted delivery system components. Four out of 24 patients (16%) had device-related adverse reactions, which required medical intervention, including two patients (8%) with intraventricular access device-related CNS infections, and one patient (4%) each with leakage of the intraventricular access device and pleocytosis. Device-related infections were diagnosed by increased CSF pleocytosis and microbiology culture and organism identification, without accompanying signs and symptoms of meningitis. Intraventricular access devices were replaced and infections were treated with antibiotics. Device-related complications did not result in discontinuation of BRINEURA treatment.
Hematoma
Hematoma adverse reactions were reported in 5 of 24 (21%) patients treated with BRINEURA and presented as hematoma, post procedural hematoma, traumatic hematoma and subdural hematoma. Hematomas did not require treatment and did not interfere with BRINEURA infusion.
Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity reactions were reported in 11 out of 24 patients (46%) treated with BRINEURA during or within 24 hours after completion of the BRINEURA infusion, despite pre-medication with antihistamines with or without antipyretics or corticosteroids. The most common manifestations observed concomitantly with hypersensitivity included pyrexia with vomiting, pleocytosis, or irritability, which are not consistent with classic immune mediated hypersensitivity. Symptoms resolved over time or with administration of antipyretics, antihistamines and/or corticosteroids and no patient discontinued treatment with BRINEURA.
One patient experienced hypoxia (decreased oxygen saturation less than 88% by pulse oximeter), 8 hours after BRINEURA infusion, followed by a low mean arterial pressure at 15 hours post infusion. Symptoms resolved after oxygen administration, airway repositioning and normal saline infusion. One patient reported decreased oxygen saturation (90% by pulse oximeter), 45 minutes after starting BRINEURA with associated low diastolic blood pressures. Hypoxia resolved after oxygen administration. No treatment was administered for the low diastolic blood pressure, which returned to normal while the patient continued to receive BRINEURA infusion without change to the infusion rate or dose.
Trial 3
Trial 3 enrolled 14 patients aged 1 to 6 years at baseline who received BRINEURA at the recommended dose based on the age of the patient, every other week for a median of 142 weeks. Adverse reactions that occurred in at least 5% of patients are described in Table 3.
The most frequent adverse reactions reported in patients < 3 years treated with BRINEURA were similar to those observed in patients ≥ 3 years of age except for hypersensitivity reactions, which were reported in 5 of 8 (63%) in patients < 3 years at baseline compared with 0 of 6 in patients ≥ 3 years of age at baseline. The most common manifestations of hypersensitivity were pyrexia and vomiting and the timing and resolution were similar to Trials 1 and 2. Symptoms of severe hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., anaphylaxis) included tachycardia, bronchospasm, rash, diarrhea, hypotension, increased body temperature and vomiting.
Drug-related IARs
In Trial 3, 12 patients (86%) who received BRINEURA had 83 IARs. Of those, 8 patients were < 3 years of age and 4 were ≥ 3 years of age. The symptoms occurring in more than one patient consisted of vomiting, seizure, rash, pyrexia, hypersensitivity, and abnormal electrocardiogram. Eight (57%) patients had serious IARs: pyrexia, hypersensitivity, anaphylactic reaction, seizure, and pleocytosis.
Device-related IARs
In Trial 3, 3 patients (21%) who received BRINEURA had 3 IARs related to the intraventricular device. Of those, 2 were < 3 years of age and 1 was ≥ 3 years of age. The events were: device leakage, device breakage, and CSF red blood cell count positive. One (7%) patient had a serious IAR of device leakage.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions Reported in ≥ 5% of Pediatric Patients (1 to 6 years of age) with CLN2 Disease treated with BRINEURA in Trial 3 Adverse Reaction Age 1 to 3 years
n=8 (%)Age 3 to 6 years
n=6 (%)Total
n=14 (%)Note: Incidence numbers are based on baseline age group - *
- ECG abnormalities include: non-specific repolarization abnormality, supraventricular extrasystoles, possible left ventricular hypertrophy, intermittent 2nd degree AV Block (type 2 Mobitz), incomplete right bundle branch block, and prominent Q wave.
- †
- Increased body temperature includes: increased body temperature and pyrexia.
- ‡
- Seizures include: atonic, febrile convulsion, generalized tonic-clonic, partial, partial with secondary generalization, petit mal epilepsy, myoclonic and status epilepticus.
- §
- Device-related complications include device-related infection, delivery system-related complications (needle issues, device leakage, device malfunction, device difficult to use, medical device site irritation, device breakage, etc.)
- ¶
- Hypersensitivity includes only the term of hypersensitivity
ECG abnormalities* 8 (100) 6 (100) 14 (100) Decreased CSF protein 8 (100) 4 (67) 12 (86) Increased body temperature† 6 (75) 6 (100) 12 (86) Seizures‡ 4 (50) 4 (67) 8 (57) Device-related complications§ 3 (36) 2 (33) 5 (36) Vomiting 2 (25) 3 (50) 5 (36) Hypersensitivity¶ 4 (50) 0 4 (29) Hematoma 2 (25) 0 2 (14) Increased CSF protein 1 (13) 0 1 (7) Pleocytosis 1 (13) 0 1 (7) Irritability 0 1 (17) 1 (7) Headache 1 (13) 0 1 (7) 6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of BRINEURA. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Immune system disorders: Anaphylactic reaction characterized by acute pyrexia, respiratory distress (bronchospasm, hypoxemia, perioral cyanosis), tachycardia, hypotension, diarrhea, and rash [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Infections and infestations: Bacterial meningitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on BRINEURA use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk of pregnancy-related outcomes. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted using cerliponase alfa.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of cerliponase alfa in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. The lack of clinical data during lactation precludes a clear determination of the risk of BRINEURA to an infant during lactation; therefore, the development and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for BRINEURA and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from BRINEURA or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of BRINEURA have been established to slow the loss of ambulation in pediatric patients with CLN2 disease and the information on this use is discussed throughout the labeling.
BRINEURA is not recommended for use in patients less than 37 weeks post-menstrual age (gestational age at birth plus post-natal age) or those weighing less than 2.5 kg due to physiologic immaturity which may increase risk of serious and clinically significant adverse reactions observed with BRINEURA [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
Patients less than 3 years of age may be at increased risk for developing hypersensitivity reactions with BRINEURA use compared to patients 3 years of age and older [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Cerliponase alfa is a purified human enzyme produced by recombinant DNA technology in a Chinese hamster ovary cell line. The active substance is a recombinant human tripeptidyl peptidase-1 (rhTPP1), a lysosomal exopeptidase. The primary activity of the mature enzyme is the cleavage of N-terminal tripeptides from a broad range of protein substrates.
Cerliponase alfa contains 544 amino acids with an average molecular mass of 59 kDa. The mature enzyme is 368 amino acids in length. There are 5 consensus N-glycosylation sites on rhTPP1 that contain high mannose, phosphorylated high mannose and complex glycosylation structures.
BRINEURA (cerliponase alfa) Injection and Intraventricular Electrolytes Injection are administered by intraventricular infusion. The solutions are sterile, nonpyrogenic, and free of foreign particulates. BRINEURA is a clear to slightly opalescent and colorless to pale yellow solution. Intraventricular Electrolytes is a clear to colorless solution.
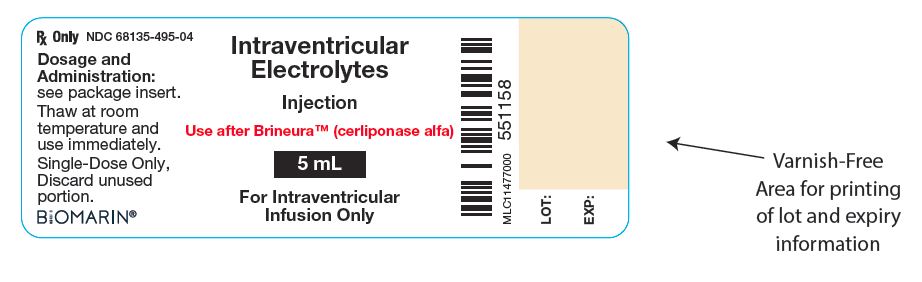
BRINEURA and Intraventricular Electrolytes Injection are packaged in 10 mL clear Type 1 single-dose glass vials [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16)]. Each vial of BRINEURA provides 5 mL of solution containing 150 mg cerliponase alfa. Each vial of Intraventricular Electrolytes Injection provides 5 mL of solution. Both BRINEURA and Intraventricular Electrolytes Injection are formulated with the following excipients: calcium chloride dihydrate (1.05 mg); magnesium chloride hexahydrate (0.8 mg); potassium chloride (1.1 mg); sodium chloride (43.85 mg); sodium phosphate, dibasic, heptahydrate (0.55 mg); sodium phosphate, monobasic, monohydrate (0.4 mg); and Water for Injection, USP. The pH of the solution is between 6.2 to 6.8 for BRINEURA, and between 6.0 to 7.0 for Intraventricular Electrolytes Injection.
Each vial contains: sodium: 0.76 mEq, and potassium: 0.015 mEq.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
CLN2 disease is a neurodegenerative disease caused by deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme tripeptidyl peptidase-1 (TPP1), which catabolizes polypeptides in the CNS. TPP1 has no known substrate specificity. Deficiency in TPP1 activity results in the accumulation of lysosomal storage materials normally metabolized by this enzyme in the central nervous system (CNS), leading to progressive decline in motor function.
Cerliponase alfa (rhTTP1), a proenzyme, is taken up by target cells in the CNS and is translocated to the lysosomes through the Cation Independent Mannose-6-Phosphate Receptor (CI-MPR, also known as M6P/IGF2 receptor). Cerliponase alfa is activated in the lysosome and the activated proteolytic form of rhTPP1 cleaves tripeptides from the N-terminus of proteins.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Patients 3 years of age and older
The pharmacokinetics of cerliponase alfa were evaluated in patients with CLN2 disease who received intraventricular infusions of 30 mg (0.1 times the maximum approved recommended dosage), 100 mg (approximately 0.3 times the maximum approved recommended dosage), and 300 mg over approximately 4.5 hours once every other week.
Cerliponase alfa CSF exposure following the initial single dose administration of BRINEURA increased less than proportionally across doses of 30 mg, 100 mg, and 300 mg. There was no apparent accumulation of cerliponase alfa in CSF or plasma when BRINEURA was administered at a dose of 300 mg once every other week.
Cerliponase alfa pharmacokinetics have high inter-subject and intra-subject variability. Following intraventricular infusions of 300 mg of BRINEURA at Day 1, Week 5, and Week 13, the pharmacokinetic parameters in CSF and plasma were assessed in 14 patients and are summarized in Table 4.
Table 4: Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Cerliponase Alfa Following Intraventricular Infusion (approximately 4.5 hours in duration) of BRINEURA 300 mg Every Two Weeks in Patients ≥ 3 years Parameter Median [Min, Max] Day 1 Week 5 Week 13 N 13 14 13 Tmax*, hr 4.5 [4.3, 5.8] 4.3 [3.8, 4.5] 4.3 [4.0, 4.5] Cmax, mcg/mL 1260 [359, 4380] 1630 [376, 4670] 1390 [1110, 2340] CSF AUC0-t, mcg-hr/mL 9290 [3660, 19000] 12400 [4620, 26200] 10500 [7000, 18200] Vss, mL 245 [78.4, 909] 196 [85.4, 665] 186 [131, 257] CL, mL/hr 32.3 [15.8, 81.9] 24.2 [11.4, 64.9] 28.7 [16.5, 42.9] t1/2, hr 6.2 [5.5, 16.3] 7.4 [3.3, 9.5] 7.7 [5.1, 9.4] N 12 12 9 Plasma† Tmax*, hr 12.0 [4.3, 24.5] 12.0 [7.5, 24.2] 12.3 [4.3, 75.9] Cmax, mcg/mL 1.3 [0.2, 3.9] 1.9 [0.2, 4.3] 1.0 [0.03, 2.6] AUC0-t, mcg-hr/mL 16.2 [1.1, 69.9] 40.1 [11.1, 78.9] 9.5 [0.2, 51.6] N 11 12 9 CSF/Plasma Ratio Cmax 1200 [305, 4530] 809 [202, 9370] 1320 [541, 51200] AUC0-t 393 [115, 1910] 340 [126, 1780] 1330 [167, 38900] The estimated CSF volume of distribution of cerliponase alfa following intraventricular infusion of 300 mg of BRINEURA (median Vss = 245 mL) exceeds the typical CSF volume (100 mL).
Pediatric patients less than 3 years
Pediatric CLN2 patients ages 1 to < 2 years (n=2) and 2 to < 3 years (n=6) were administered cerliponase alfa according to the recommended dosing regimen based on age for up to 144 weeks. CSF exposure with 300 mg cerliponase alfa was within the range characterized to be safe and effective in pivotal Trial 1.
Plasma exposure in younger patients trended higher than the range characterized in the pivotal study. The pharmacokinetic parameters summarized by age at time of visit and dose are shown in Table 5.
Table 5: Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Cerliponase Alfa by Age at Visit and Dose Following Intraventricular Infusion of BRINEURA Every Two Weeks in Pediatric Patients < 3 years Age at Visit Dose
(mg)Parameter Median [Min, Max] 1 to < 2 years 200 CSF N 3 Cmax, mcg/mL 511 [163, 987] AUC0-t, mcg-hr/mL 2720 [1100, 5050] Plasma N 2 Cmax, mcg/mL 10.4 [9.46, 11.3] AUC0-t, mcg-hr/mL 91.8 [72.7, 111] 300 CSF N 2 Cmax, mcg/mL 566 [496, 636] AUC0-t, mcg-hr/mL 8030 [8030, 8030]* Plasma N 2 Cmax, mcg/mL 14.1 [11.2, 17.0] AUC0-t, mcg-hr/mL 145 [82.7, 206] 2 to < 3 years 300 CSF N 6 Cmax, mcg/mL 896 [508, 1790] AUC0-t, mcg-hr/mL 4100 [2380, 6720]† Plasma N 6 Cmax, mcg/mL 14.9 [9.08, 35.3] AUC0-t, mcg-hr/mL 163 [91.5, 320] Cerliponase alfa is a protein and is expected to be degraded through peptide hydrolysis.
12.6 Immunogenicity
The observed incidence of anti-drug antibodies is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Differences in assay methods preclude meaningful comparisons of the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in the studies described below with the incidence of anti-drug antibodies in other studies including cerliponase alfa.
In Trials 1 and 2 [see Clinical Studies (14)], 19 of 24 (79%) and 10 of 24 (42%) patients treated with BRINEURA developed anti-drug antibodies (ADAs) in serum and CSF, respectively. Drug-specific neutralizing antibodies (NAb) capable of inhibiting receptor-mediated cellular uptake of cerliponase alfa were detected in the CSF of 3 of 24 (13%) patients at a single visit and were undetectable in all other CSF samples tested in ADA positive patients. In Trial 3 [see Clinical Studies (14)], 14 of 14 (100%) and 3 of 14 (21%, all of the 3 patients were < 3 years of age) patients treated with BRINEURA developed ADAs in serum and CSF, respectively. NAb responses were not detected in the CSF of any ADA positive patients. Overall, patients younger than 3 years of age had higher ADA titers compared to patients 3 years of age and older.
In Trials 1 and 2, patients who experienced moderate to severe hypersensitivity adverse reactions were tested for drug-specific IgE and found to be negative. No association was found between serum ADA titers and incidence or severity of hypersensitivity. In Trial 3, hypersensitivity occurred in higher percentage in BRINEURA-treated patients < 3 years of age at baseline (amongst these patients, one patient experienced anaphylaxis), and higher ADA titers were also observed in this age group compared to patients ≥ 3 years of age at baseline. There was no identified clinically significant effect of ADA on pharmacokinetics or efficacy of BRINEURA. There is insufficient information to characterize the effects of ADA on safety.
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of BRINEURA was assessed over 96 weeks in a non-randomized single-arm dose escalation clinical study with extension in symptomatic pediatric patients with late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis type 2 (CLN2) disease, confirmed by TPP1 deficiency. BRINEURA-treated patients were compared to untreated patients from a natural history cohort. The Motor domain of a CLN2 Clinical Rating Scale was used to assess disease progression. Scores ranged from 3 (grossly normal) to 0 (profoundly impaired) with unit decrements representing milestone events in the loss of motor function (ability to walk or crawl). Due to the inability to establish comparability for the CLN2 Language domain ratings between the clinical study with extension and the natural history cohort, efficacy of BRINEURA for the Language domain cannot be established.
Twenty-four patients, aged 3 to 8 years were enrolled in the BRINEURA single-arm clinical study (Trial 1, NCT01907087). Sixty-three percent of patients were female and 37% were male. Ninety-six percent of patients were White and 4% were Asian; for ethnicity, 4% identified as Hispanic/Latino, 96% as non-Hispanic/Latino. One patient withdrew after week 1 due to inability to continue with study procedures; 23 patients were treated with BRINEURA 300 mg every other week by intraventricular infusion for 48 weeks, and continued treatment during the 240-week extension period, Trial 2 (NCT02485899), for a total duration of 288 weeks, plus a 24-week safety follow-up.
In the clinical study with extension, patients were assessed for decline in the Motor domain of the CLN2 Clinical Rating Scale at 48, 72 and 96 weeks. Decline was defined as having an unreversed (sustained) 2-category decline or an unreversed score of 0 in the Motor domain of the CLN2 Clinical Rating Scale. Patients' responses to BRINEURA treatment were evaluated if at screening a combined Motor plus Language CLN2 score of less than 6 was recorded. Two patients with a combined Motor plus Language CLN2 score of 6 were excluded from the analyses; they maintained that score throughout the study period. The patient who terminated early was analyzed as having a decline at the time of termination. Data used in the analyses from the natural history cohort began at 36 months of age or greater and at the first time a Motor plus Language CLN2 score less than 6 was recorded.
Motor scores of the 22 BRINEURA-treated patients in the clinical study with extension were compared to scores of the independent natural history cohort that included 42 untreated patients who satisfied inclusion criteria for the clinical study. The results of logistic modeling with covariates (screening age, screening motor score, genotype: 0 key mutations (yes/no)), demonstrated the odds of BRINEURA-treated patients not having a decline by 96 weeks were 13 times the odds of natural history cohort patients not having a decline (Odds Ratio (95% CI): 13.1 (1.2, 146.9)).
Descriptive non-randomized comparison
In an unadjusted non-randomized comparison, of the 22 patients treated with BRINEURA and evaluated for efficacy at week 96, 21 (95%) did not decline, and only the patient who terminated early was deemed to have a decline in the Motor domain of the CLN2 Clinical Rating Scale. Results from the natural history cohort demonstrated progressive decline in motor function; of the 42 patients in the natural history cohort, 21 (50%) experienced an unreversed (sustained) 2-category decline or unreversed score of 0 in the Motor domain of the CLN2 Clinical Rating Scale over 96 weeks.
Given the non-randomized study design, a Cox Proportional Hazards Model adjusted for age, initial motor score, and genotype was used to evaluate time to unreversed 2-category decline or unreversed score of 0 in the Motor domain. This model showed a lesser decrease in motor function in the BRINEURA-treated patients when compared to the natural history cohort (see Figure 7).
Figure 7. Estimated Time to Unreversed (Sustained) 2-Category Decline or Unreversed Score of Zero in Motor Domain for Symptomatic Pediatric Patients in the BRINEURA Trials 1 and 2 at 96 Weeks and for Patients in a Natural History Cohort (Based on the Cox Proportional Hazards Model Adjusting for Covariates) Shading represents 95% confidence intervals.
Follow-up for the natural history cohort begins at 36 months of age or greater and at the first time a Motor plus Language CLN2 score less than 6 was recorded.
The BRINEURA-treated population is the full population (N=24) minus two patients with baseline Motor plus Language CLN2 score = 6.
Covariates: screening age, screening Motor score, genotype: 0 key mutations (yes/no). "Screening age" was defined in the natural history cohort as the age at the first time a Motor plus Language CLN2 score less than 6 was recorded, and no earlier than 36 months of age. The "screening Motor score" of the natural history cohort was defined as the Motor score at the screening age.
Decline is defined as an unreversed (sustained) 2-category decline or unreversed score of 0 in the Motor domain of the CLN2 Clinical Rating Scale.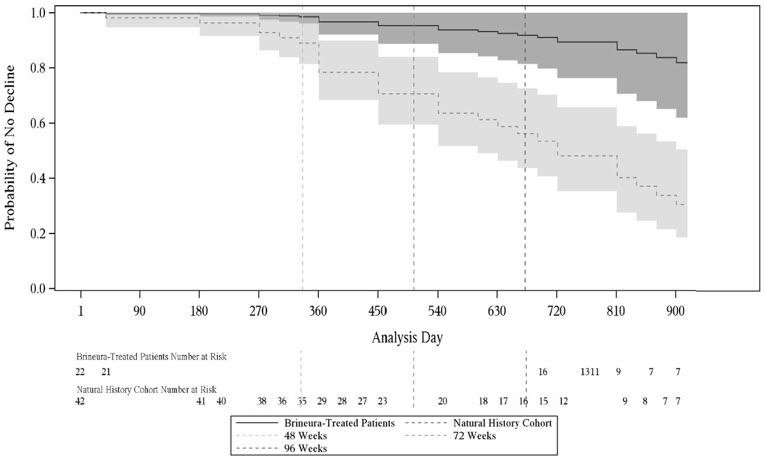
Motor Domain Scores: Matched Patients Only
To further assess efficacy, the 22 patients from the BRINEURA clinical study with a baseline combined Motor plus Language CLN2 score less than 6 were matched to 42 patients in the natural history cohort. Patients were matched based on the following covariates: baseline age at time of screening within 3 months, genotype (0, 1, or 2 key mutations), and baseline Motor domain CLN2 score at time of screening.
Using the Motor domain of the CLN2 Clinical Rating Scale, decline was defined as having an unreversed 2-category decline or an unreversed score of 0. At 96 weeks, the matched analysis based on 17 pairs demonstrated fewer declines in the Motor domain for BRINEURA-treated patients compared to untreated patients in the natural history cohort (see Table 6).
Table 6: Proportion of Matched Symptomatic Pediatric Patients with CLN2 Disease without Decline* in the BRINEURA Trials 1 and 2 and in the Natural History Cohort assessed at Weeks 48, 72, and 96 Time Point/Period Natural History Cohort
(N=17)BRINEURA-Treated (N=17) Difference Odds Ratio† n (%) n (%) % (95% CI‡) OR (95% CI) Matched on baseline age at time of screening within 3 months, genotype (0, 1, or 2 key mutations), and baseline Motor domain CLN2 score at time of screening.
The BRINEURA-treated population is based on the full population minus two patients with baseline Motor plus Language CLN2 score = 6.Follow-up through Week 48 13 (76) 16 (94) 18% (-19, 51) 4 (0.4, 200) Follow-up through Week 72 11 (65) 16 (94) 29% (-7, 61) 5.9 (0.7, 250) Follow-up through Week 96 6 (35) 16 (94) 59% (24, 83) 11 (1.6, 500) Trial 3 (NCT02678689) was a Phase 2, open label clinical study designed to enroll symptomatic and presymptomatic CLN2 patients less than 18 years of age. The trial enrolled 14 patients ranging in age from 1 to 6 years at baseline, including 8 patients less than 3 years of age, the median age was 2.7 years. Patients received BRINEURA at the recommended dose every 2 weeks by intraventricular infusion for 144 weeks (1 patient withdrew to receive treatment commercially). Fifty-seven percent of patients were female and 43% were male. All patients were White; for ethnicity, 14% identified as Hispanic/Latino, 86% as non-Hispanic/Latino. The mean baseline CLN2 Motor score was 2.3 (standard deviation (SD) 0.83) with a range from 1 to 3.
Thirteen of the 14 BRINEURA treated patients were matched with up to 3 natural history comparators on the basis of age within 3 months, equal CLN2 Motor score, and genotype (0, 1, or 2 key mutations). None of the BRINEURA treated patients (N=14) had a 2-point decline or score of zero in the Motor scale by Week 169. Among the matched natural history comparators (N=31), 20 subjects (65%) had an unreversed 2-point decline or score of zero by last assessment.
The median time to an unreversed 2-point decline in Motor score or score of 0 was 133 weeks among the natural history comparators and was not reached by last assessment (Week 169) in patients treated with BRINEURA.
In patients below 3 years of age, none (0%) of the BRINEURA treated patients (N=8) had a 2-point decline or score of zero in the Motor score by Week 169. Among the 8 treated patients, 7 were matched to 18 untreated patients from the natural history cohort. Among the matched natural history comparators (N=18), 11 subjects (61%) had an unreversed 2-point decline or score of zero in the Motor score by last assessment. All seven of the treated patients below 3 years of age with a motor score of 3 at baseline remained at a motor score of 3 at the last measured timepoint, which represents grossly normal gait. In this population BRINEURA treated patients showed a delay in disease onset.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
BRINEURA is supplied as a sterile, clear to slightly opalescent and colorless to pale yellow solution for intraventricular infusion and Intraventricular Electrolytes Injection is supplied as a clear to colorless solution for intraventricular infusion; both are included in package 1 of 2. The Administration Kit for use with BRINEURA is supplied separately as package 2 of 2 [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Package 1 of 2
Each BRINEURA (cerliponase alfa) Injection vial has a green flip-off cap (plastic) and contains 150 mg cerliponase alfa per 5 mL (30 mg/mL).
Each Intraventricular Electrolytes Injection vial has a yellow flip-off cap (plastic) and contains 5 mL of solution.
Contents of Package 1 NDC Number BRINEURA (cerliponase alfa) Injection (2 vials of 150 mg/5 mL)
Intraventricular Electrolytes Injection (1 vial, 5 mL)68135-811-02 Package 2 of 2
The Administration Kit for use with BRINEURA is supplied separately and contains the following single-use, sterile infusion components:
- Two 20-mL syringes
- Two syringe needles (21 G, 25.4 mm)
- One extension line
- One infusion set with 0.2 micron inline filter
- One port needle (22 G, 16 mm)
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis and Infusion-Associated Reactions (IARs)
- Advise patients and caregivers that life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, and IARs may occur with BRINEURA treatment.
- Advise patients and caregivers that anaphylaxis has occurred during the early course of enzyme replacement therapy and after extended duration of therapy.
- Inform patients and caregivers of the symptoms of life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, and IARs and to seek immediate medical care should symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.5)].
- Intraventricular Access Device-Related Infections
Advise patients and caregivers of the risk of device-related infections, including meningitis. Familiarize them with the signs and symptoms of these infections and instruct them to immediately contact their healthcare provider if an infection is suspected [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. - Cardiovascular Adverse Reactions
Advise patients and caregivers that hypotension and/or bradycardia may occur during and following the infusion of BRINEURA. Instruct patients immediately to contact their healthcare provider if these reactions occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis and Infusion-Associated Reactions (IARs)
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Kit Carton - Package 1
NDC 68135-811-02
Brineura®
(cerliponase alfa)
Injection150 mg/5 mL (30 mg/mL)
For Intraventricular Infusion Only
Each vial of Brineura® contains 150 mg cerliponase alfa
in 5 mL of solution (30 mg/mL)No preservatives
Single-Dose Vial. Discard unused portion.Brineura® and Intraventricular Electrolytes must be
administered with the Administration Kit provided.Each carton contains:
2 vials, each containing Brineura®
(cerliponase alfa) Injection, 150 mg/5 mL
1 vial of Intraventricular Electrolytes
Injection, 5 mLPackage 1 of 2
Administration Kit is supplied
and stored separately as
package 2 of 2.Rx Only
BIOMARIN®
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 150 mg/5 mL Vial Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 5 mL Vial Label
-
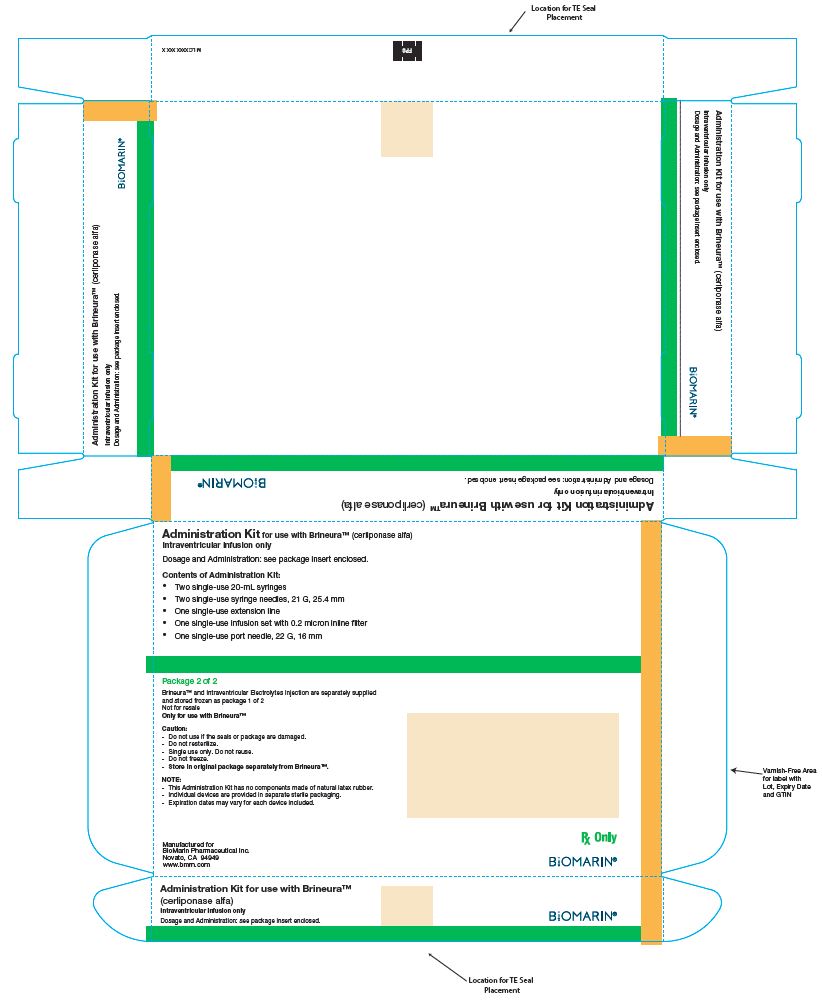
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Kit Carton - Package 2
Administration Kit for use with Brineura® (cerliponase alfa)
Intraventricular infusion onlyRecommended Dosage: See Prescribing Information
Contents of Administration Kit:
- Two single-use 20-mL syringes
- Two single-use syringe needles, 21 G, 25.4 mm
- One single-use extension line
- One single-use infusion set with 0.2 micron inline filter
- One single-use port needle, 22 G, 16 mm
Package 2 of 2
Brineura® and Intraventricular Electrolytes Injection are separately supplied and
stored frozen as package 1 of 2
Not for resale
Only for use with Brineura®Caution:
- -
- Do not use if the seals or package are damaged.
- -
- Do not resterilize.
- -
- Single use only. Do not reuse.
- -
- Do not freeze.
- -
- Store in original package separately from Brineura®.
NOTE:
- -
- This Administration Kit has no components made of natural latex rubber.
- -
- Individual devices are provided in separate sterile packaging.
- -
- Expiration dates may vary for each device included.
Manufactured for
BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc.
Novato, CA 94949
www.bmrn.comRx Only
BIOMARIN®
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
BRINEURA
cerliponase alfa kitProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:68135-811 Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:68135-811-02 1 in 1 CARTON 04/27/2017 Quantity of Parts Part # Package Quantity Total Product Quantity Part 1 2 VIAL, GLASS 10 mL Part 2 1 VIAL, GLASS 5 mL Part 1 of 2 BRINEURA
cerliponase alfa injection, solutionProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC:68135-500 Route of Administration INTRAVENTRICULAR Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CERLIPONASE ALFA (UNII: X8R2D92QP1) (CERLIPONASE ALFA - UNII:X8R2D92QP1) CERLIPONASE ALFA 150 mg in 5 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:68135-500-00 5 mL in 1 VIAL, GLASS; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761052 04/27/2017 Part 2 of 2 INTRAVENTRICULAR ELECTROLYTES
intraventricular electrolytes injection, solutionProduct Information Item Code (Source) NDC:68135-495 Route of Administration INTRAVENTRICULAR Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:68135-495-04 5 mL in 1 VIAL, GLASS; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761052 04/27/2017 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA761052 04/27/2017 Labeler - BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc. (079722386) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Almac Pharma Services (Ireland) Limited 985674500 PACK(68135-811) , LABEL(68135-811)