Label: baclofen- Baclofen tablet
-
Contains inactivated NDC Code(s)
NDC Code(s): 57664-291-13, 57664-291-18, 57664-291-88, 57664-292-13, view more57664-292-18, 57664-292-88 - Packager: CARACO PHARMACEUTICAL LABORATORIES, LTD.
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
Drug Label Information
Updated March 30, 2007
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
- N/A - Section Title Not Found In Database
-
DESCRIPTION
Baclofen is a muscle relaxant and antispastic.
Its chemical name is 4-amino-3-(4-chlorophenyl) butanoic acid. The structural formula is:
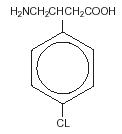
C1OH12CINO2 M.W.213.66
Baclofen USP is a white to off-white, odorless or practically odorless crystalline powder. It is slightly soluble in water, very slightly soluble in methanol and insoluble in chloroform.
Each tablet, for oral administration, contains 10 mg or 20 mg Baclofen. In addition, each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: pregelatinized starch, colloidal silicon dioxide, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and sodium starch glycolate.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
The precise mechanism of action of baclofen is not fully known. Baclofen is capable of inhibiting both monosynaptic and polysynaptic reflexes at the spinal level, possibly by hyperpolarization of afferent terminals, although actions at supraspinal sites may also occur and contribute to its clinical effect. Although baclofen is an analog of the putative inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), there is no conclusive evidence that actions on GABA systems are involved in the production of its clinical effects. In studies with animals baclofen has been shown to have general CNS depressant properties as indicated by the production of sedation with tolerance, somnolence, ataxia, and respiratory and cardiovascular depression. Baclofen is rapidly and extensively absorbed and eliminated. Absorption may be dose-dependent, being reduced with increasing doses. Baclofen is excreted primarily by the kidney in unchanged form and there is relatively large inter-subject variation in absorption and/or elimination.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Baclofen is useful for the alleviation of signs and symptoms of spasticity resulting from multiple sclerosis, particularly for the relief of flexor spasms and concomitant pain, clonus, and muscular rigidity.
Patients should have reversible spasticity so that baclofen treatment will aid in restoring residual function. Baclofen may also be of some value in patients with spinal cord injuries and other spinal cord diseases.
Baclofen is not indicated in the treatment of skeletal muscle spasm resulting from rheumatic disorders. The efficacy of baclofen in stroke, cerebral palsy, and Parkinson's disease has not been established and, therefore, it is not recommended for these conditions.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
a. Abrupt Drug Withdrawal: Hallucinations and seizures have occurred on abrupt withdrawal of baclofen. Therefore, except for serious adverse reactions, the dose should be reduced slowly when the drug is discontinued.
b. Impaired Renal Function: Because baclofen is primarily excreted unchanged through the kidneys, it should be given with caution, and it may be necessary to reduce the dosage.
c. Stroke: Baclofen has not significantly benefited patients with stroke. These patients have also shown poor tolerability to the drug.
d. Pregnancy: Baclofen has been shown to increase the incidence of omphaloceles (ventral hernias) in fetuses of rats given approximately 13 times the maximum dose recommended for human use, at a dose which caused significant reductions in food intake and weight gain in dams. This abnormality was not seen in mice or rabbits.
There was also an increased incidence of incomplete sternebral ossification in fetuses of rats given approximately 13 times the maximum recommended human dose, and an increased incidence of unossified phalangeal nuclei of forelimbs and hindlimbs in fetuses of rabbits given approximately 7 times the maximum recommended human dose. In mice, no teratogenic effects were observed, although reductions in mean fetal weight with consequent delays in skeletal ossification were present when dams were given 17 and 34 times the human daily dose. There are no studies in pregnant women. Baclofen should be used during pregnancy only if the benefit clearly justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
-
PRECAUTIONS
Safe use of baclofen in children under age 12 has not been established, and it is therefore, not recommended for use in children.
Because of the possibility of sedation, patients should be cautioned regarding the operation of automobiles or other dangerous machinery, and activities made hazardous by decreased alertness. Patients should also be cautioned that the central nervous system effects of baclofen may be additive to those of alcohol and other CNS depressants. Baclofen should be used with caution where spasticity is utilized to sustain upright posture and balance in locomotion or whenever spasticity is utilized to obtain increased function. In patients with epilepsy, the clinical state and electroencephalogram should be monitored at regular intervals, since deterioration in seizure control and EEG have been reported occasionally in patients taking baclofen.
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. As a general rule, nursing should not be undertaken while a patient is on a drug since many drugs are excreted in human milk.
A dose-related increase in incidence of ovarian cysts and a less marked increase in enlarged and/or hemorrhagic adrenal glands was observed in female rats treated chronically with baclofen.
Ovarian cysts have been found by palpation in about 4% of the multiple sclerosis patients that were treated with baclofen for up to one year. In most cases these cysts disappeared spontaneously while patients continued to receive the drug. Ovarian cysts are estimated to occur spontaneously in approximately 1% to 5% of the normal female population.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common is transient drowsiness (10-63%). In one controlled study of 175 patients, transient drowsiness was observed in 63% of those receiving baclofen compared to 36% of those in the placebo group. Other common adverse reactions are dizziness (5-15%), weakness (5-15%) and fatigue (2-4%)
Others reported
Neurospsychiatric: Confusion (1-11%), headache (4-8%), insomnia (2-7%); and rarely, euphoria, excitement, depression, hallucinations, paresthesia, muscle pain, tinnitus, slurred speech, coordination disorder, tremor, rigidity, dystonia, ataxia, blurred vision, nystagmus, strabismus, miosis, mydriasis, diplopia, dysarthria, epileptic seizure.
Cardiovascular: Hypotension (0-9%). Rare instances of dyspnea, palpitation, chest pain, syncope.
Gastrointestinal: Nausea (4-12%), constipation (2-6%); and rarely, dry mouth, anorexia, taste disorder, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, and positive test for occult blood in stool.
Genitourinary: Urinary frequency (2-6%); and rarely, enuresis, urinary retention, dysuria, impotence, inability to ejaculate, nocturia, hematuria.
Other: Instances of rash, pruritis, ankle edema, excessive perspiration, weight gain, nasal congestion. Some of the CNS and genitourinary symptoms may be related to the underlying disease rather than to drug therapy. The following laboratory tests have been found to be abnormal in a few patients receiving baclofen; increased SGOT, elevated alkaline phosphatase, and elevation of blood sugar.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Signs and Symptoms: Vomiting, muscular hypotonia, drowsiness, accommodation disorders, coma, respiratory depression and seizures.
Treatment: In the alert patient, empty the stomach promptly by induced emesis followed by lavage. In the obtunded patient, secure the airway with a cuffed endotracheal tube before beginning lavage (do not induce emesis). Maintain adequate respiratory exchange, do not use respiratory stimulants.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The determination of optimal dosage requires individual titration. Start therapy at a low dosage and increase gradually until optimum effect is achieved (usually between 40-80 mg daily).
The following dosage titration schedule is suggested:
5 mg t.i.d. for 3 days
10 mg t.i.d. for 3 days
15 mg t.i.d. for 3 days
20 mg t.i.d. for 3 days
Thereafter additional increases may be necessary but the total dose should not exceed a maximum of 80 mg daily (20 mg q.i.d).
The lowest dose compatible with an optimal response is recommended. If benefits are not evident after a reasonable trial period, patients should be slowly withdrawn from the drug (see WARNINGS Abrupt Drug Withdrawal).
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Baclofen Tablets, USP, 10 mg are white to off white, round, flat face bevel edge, uncoated tablets debossed ‘291’ on one side and scored on other side are available as follows:
Bottles of 100 NDC 57664-291-88
Bottles of 500 NDC 57664-291-13
Bottles of 1000 NDC 57664-291-18Baclofen Tablets, USP, 20 mg are white to off white, round, flat face bevel edge, uncoated tablets debossed ‘292’ on one side and scored on other side are available as follows:
Bottles of 100 NDC 57664-292-88
Bottles of 500 NDC 57664-292-13
Bottles of 1000 NDC 57664-292-18PHARMACIST: Dispense in well closed container with child resistant closure as defined in USP.
Store at 20 - 25° C (68 - 77° F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
C.S. No.: 5532T01
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
BACLOFEN
baclofen tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:57664-291 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Baclofen (UNII: H789N3FKE8) (Baclofen - UNII:H789N3FKE8) 10 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength pregelatinized starch () colloidal silicon dioxide () magnesium stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) microcrystalline cellulose () sodium starch glycolate () Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off white) Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND (ROUND) Size 7mm Flavor Imprint Code 291 Contains Coating false Symbol false Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:57664-291-88 100 in 1 BOTTLE 2 NDC:57664-291-13 500 in 1 BOTTLE 3 NDC:57664-291-18 1000 in 1 BOTTLE BACLOFEN
baclofen tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:57664-292 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Baclofen (UNII: H789N3FKE8) (Baclofen - UNII:H789N3FKE8) 20 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength pregelatinized starch () colloidal silicon dioxide () magnesium stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) microcrystalline cellulose () sodium starch glycolate () Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off white) Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND (ROUND) Size 9mm Flavor Imprint Code 292 Contains Coating false Symbol false Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:57664-292-88 100 in 1 BOTTLE 2 NDC:57664-292-13 500 in 1 BOTTLE 3 NDC:57664-292-18 1000 in 1 BOTTLE Labeler - CARACO PHARMACEUTICAL LABORATORIES, LTD.
