Label: KYLEENA- levonorgestrel intrauterine device
- NDC Code(s): 50419-424-01, 50419-424-08, 50419-424-71
- Packager: Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Drug Label Information
Updated March 13, 2023
If you are a healthcare professional or from the pharmaceutical industry please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use KYLEENA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for KYLEENA.
KYLEENA (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system)
Initial U.S. Approval: 2000RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
- Dosage and Administration (2.4) 3/2023
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Kyleena is a progestin-containing intrauterine system (IUS) indicated for prevention of pregnancy for up to 5 years. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- •
- Release rate of levonorgestrel (LNG) is 17.5 mcg/day after 24 days and declines to 7.4 mcg/day after 5 years; Kyleena must be removed or replaced after 5 years. (2.1)
- •
- To be inserted by a trained healthcare provider using strict aseptic technique. Follow insertion instructions exactly as described. (2.2)
- •
- Patient should be re-examined and evaluated 4 to 6 weeks after insertion; then yearly or more often if clinically indicated. (2.3)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- •
- One sterile intrauterine system consisting of a T-shaped polyethylene frame with a steroid reservoir containing 19.5 mg levonorgestrel, packaged within a sterile inserter (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- •
- Pregnancy or suspicion of pregnancy. Cannot be used for post-coital contraception (emergency contraception) (4)
- •
- Congenital or acquired uterine anomaly if it distorts the uterine cavity (4)
- •
- Acute pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or a history of PID unless there has been a subsequent intrauterine pregnancy (4)
- •
- Postpartum endometritis or infected abortion in the past 3 months (4)
- •
- Known or suspected uterine or cervical malignancy (4)
- •
- Known or suspected breast cancer or other progestin-sensitive cancer (4)
- •
- Uterine bleeding of unknown etiology (4)
- •
- Untreated acute cervicitis or vaginitis or other lower genital tract infections (4)
- •
- Acute liver disease or liver tumor (benign or malignant) (4)
- •
- Increased susceptibility to pelvic infection (4)
- •
- A previous intrauterine device (IUD) that has not been removed (4)
- •
- Hypersensitivity to any component of Kyleena (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- •
- Remove Kyleena if pregnancy occurs with Kyleena in place. If pregnancy occurs, there is increased risk of ectopic pregnancy including loss of fertility, pregnancy loss, septic abortion (including septicemia, shock and death), and premature labor and delivery. (5.1, 5.2)
- •
- Group A streptococcal infection has been reported following insertion of LNG IUS; strict aseptic technique is essential during insertion. (5.3)
- •
- Before using Kyleena, consider the risks of PID. (5.4)
- •
- Uterine perforation may occur and may reduce contraceptive effectiveness or require surgery. Risk is increased if inserted in lactating women and may be increased if inserted in women with fixed retroverted uteri and postpartum. (5.5)
- •
- Partial or complete expulsion may occur, which can be unnoticed, leading to loss of contraceptive efficacy. (5.6)
- •
- Evaluate persistent enlarged ovarian follicles or ovarian cysts. (5.7)
- •
- Bleeding patterns become altered, may remain irregular and amenorrhea may ensue. (5.8)
- •
- Kyleena can be safely scanned with MRI only under certain conditions. (5.11)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions reported (≥ 5% users) were vulvovaginitis, ovarian cysts, abdominal pain/pelvic pain, headache/migraine, acne/seborrhea, dysmenorrhea/uterine spasm, breast pain/breast discomfort, and increased bleeding. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc. at 1-888-842-2937 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 3/2023
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing Over Time
2.2. Insertion Instructions
2.3 Patient Follow-up
2.4 Removal of Kyleena
2.5 Continuation of Contraception after Removal
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Ectopic Pregnancy
5.2 Risks with Intrauterine Pregnancy
5.3 Sepsis
5.4 Pelvic Infection
5.5 Perforation
5.6 Expulsion
5.7 Ovarian Cysts
5.8 Bleeding Pattern Alterations
5.9 Breast Cancer
5.10 Clinical Considerations for Use and Removal
5.11 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Information
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
11.1 Kyleena
11.2 Inserter
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing Over Time
Kyleena contains 19.5 mg of levonorgestrel (LNG) released in vivo at a rate of approximately 17.5 mcg/day after 24 days. This rate decreases progressively to 9.8 mcg/day after 1 year and to 7.4 mcg/day after 5 years. The average in vivo release rate of LNG is approximately 12.6 mcg/day over the first year and 9.0 mcg/day over a period of 5 years. [See Clinical Pharmacology (12.3).]
Kyleena must be removed by the end of the fifth year and can be replaced at the time of removal with a new Kyleena if continued contraceptive protection is desired.
Kyleena can be physically distinguished from other intrauterine systems (IUSs) by the combination of the visibility of the silver ring on ultrasound and the blue color of the removal threads.
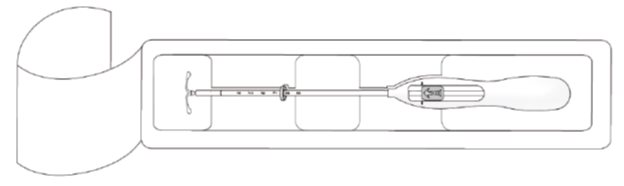
Kyleena is supplied in a sterile package within an inserter that enables single-handed loading (see Figure 1). Do not open the package until required for insertion [see Description (11.2)]. Do not use if the seal of the sterile package is broken or appears compromised. Use strict aseptic techniques throughout the insertion procedure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
2.2. Insertion Instructions
- •
- Obtain a complete medical and social history to determine conditions that might influence the selection of a levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system (LNG IUS) for contraception. If indicated, perform a physical examination and appropriate tests for any forms of genital or other sexually transmitted infections. [See Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.10).] Because irregular bleeding/spotting is common during the first months of Kyleena use, exclude endometrial pathology (polyps or cancer) prior to the insertion of Kyleena in women with persistent or uncharacteristic bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
- •
- Follow the insertion instructions exactly as described to ensure proper placement and avoid premature release of Kyleena from the inserter. Once released, Kyleena cannot be re-loaded.
- •
- Check expiration date of Kyleena prior to initiating insertion.
- •
- Kyleena should be inserted by a trained healthcare provider. Healthcare providers should become thoroughly familiar with the insertion instructions before attempting insertion of Kyleena.
- •
- Insertion may be associated with some pain and/or bleeding or vasovagal reactions (for example, syncope, bradycardia), or with seizure, especially in patients with a predisposition to these conditions. Consider administering analgesics prior to insertion.
Timing of Insertion
Table 1: When to Insert Kyleena Starting Kyleena in women not currently using hormonal or intrauterine contraception
- •
- Insert Kyleena any time there is reasonable certainty that the woman is not pregnant. Consider the possibility of ovulation and conception prior to initiation of this product [see Contraindications (4)].
- •
- If Kyleena is inserted during the first seven days of the menstrual cycle or immediately after a first trimester abortion, back-up contraception is not needed.
- •
- If Kyleena is not inserted during the first seven days of the menstrual cycle, a barrier method of contraception should be used, or the patient should abstain from vaginal intercourse for seven days to prevent pregnancy.
Switching to Kyleena from an oral, transdermal or vaginal hormonal contraceptive
- •
- Insert Kyleena at any time, including during the hormone-free interval of the previous method.
- •
- If inserted during active use of the previous method, continue that method for 7 days after Kyleena insertion or until the end of the current treatment cycle.
- •
- If the woman was using continuous hormonal contraception, discontinue that method seven days after Kyleena insertion.
Switching to Kyleena from an injectable progestin contraceptive
- •
- Insert Kyleena at any time; a non-hormonal back-up birth control (such as condoms or spermicide) should also be used for 7 days if Kyleena is inserted more than 3 months (13 weeks) after the last injection.
Switching to Kyleena from a contraceptive implant or another IUS
- •
- Insert Kyleena on the same day the implant or IUS is removed.
- •
- Insert Kyleena at any time during the menstrual cycle.
Inserting Kyleena after first trimester abortion or miscarriage
- •
- Insert Kyleena immediately after a first-trimester abortion or miscarriage, unless it is a septic abortion [see Contraindications (4)].
Inserting Kyleena after childbirth or second-trimester abortion or miscarriage
- •
- Immediate insertion after childbirth or second-trimester abortion or miscarriage
Interval insertion following complete involution of the uterus
- •
- Wait a minimum of 6 weeks or until the uterus is fully involuted before inserting Kyleena (5.5, 5.6), Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
- •
- Insert Kyleena any time there is reasonable certainty the woman is not pregnant.
- •
- If Kyleena is not inserted during the first 7 days of the menstrual cycle, a back-up method of contraception should be used, or the woman should abstain from vaginal intercourse for 7 days to prevent pregnancy [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Tools for Insertion
Note: The inserter provided with Kyleena (see Figure 1) and the Insertion Procedure described in this section are not applicable for immediate insertion after childbirth or second-trimester abortion or miscarriage. For immediate insertion, remove Kyleena from the inserter by first loading (see Figure 2) and then releasing (see Figure 7) Kyleena from the inserter, and insert according to accepted practice.
Preparation for insertion
- •
- Exclude pregnancy and confirm that there are no other contraindications to the use of Kyleena.
- •
- With the patient comfortably in lithotomy position, do a bimanual exam to establish the size, shape and position of the uterus.
- •
- Gently insert a speculum to visualize the cervix.
- •
- Thoroughly cleanse the cervix and vagina with a suitable antiseptic solution.
- •
- Prepare to sound the uterine cavity. Grasp the upper lip of the cervix with a tenaculum forceps and gently apply traction to stabilize and align the cervical canal with the uterine cavity. Perform a paracervical block if needed. If the uterus is retroverted, it may be more appropriate to grasp the lower lip of the cervix. The tenaculum should remain in position and gentle traction on the cervix should be maintained throughout the insertion procedure.
- •
- Gently insert a uterine sound to check the patency of the cervix, measure the depth of the uterine cavity in centimeters, confirm cavity direction, and detect the presence of any uterine anomaly. If you encounter difficulty or cervical stenosis, use dilatation, and not force, to overcome resistance. If cervical dilatation is required, consider using a paracervical block.
Insertion Procedure
Proceed with insertion only after completing the above steps and ascertaining that the patient is appropriate for Kyleena. Ensure use of aseptic technique throughout the entire procedure.
Step 1–Opening of the package
- •
- Open the package (Figure 1). The contents of the package are sterile.
Figure 1. Opening the Kyleena Package
- •
- Using sterile gloves, lift the handle of the sterile inserter and remove from the sterile package.
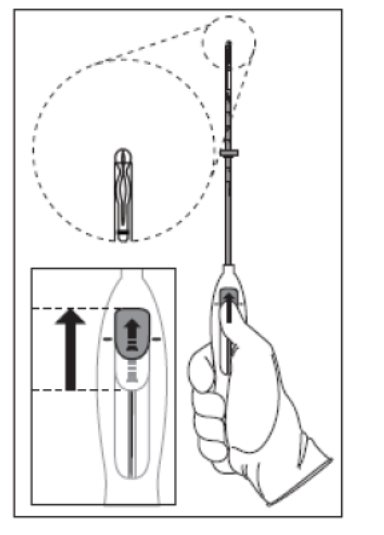
Step 2–Load Kyleena into the insertion tube
- •
- Push the slider forward as far as possible in the direction of the arrow, thereby moving the insertion tube over the Kyleena T-body to load Kyleena into the insertion tube (Figure 2). The tips of the arms will meet to form a rounded end that extends slightly beyond the insertion tube.
Figure 2. Move slider all the way to the forward position to load Kyleena
- •
- Maintain forward pressure with your thumb or forefinger on the slider. DO NOT move the slider downward at this time as this may prematurely release the threads of Kyleena. Once the slider is moved below the mark, Kyleena cannot be re-loaded.
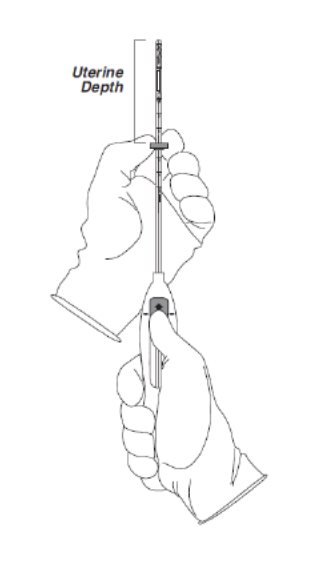
Step 3–Setting the Flange
- •
- Holding the slider in this forward position, set the upper edge of the flange to correspond to the uterine depth (in centimeters) measured during sounding (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Setting the flange
Step 4–Kyleena is now ready to be inserted
- •
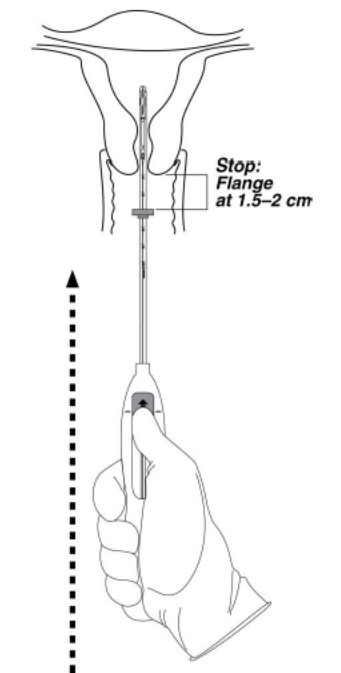
- Continue holding the slider in this forward position. Advance the inserter through the cervix until the flange is approximately 1.5–2 cm from the cervix and then pause (Figure 4).
Figure 4. Advancing insertion tube until flange is 1.5 to 2 cm from the cervix
Do not force the inserter. If necessary, dilate the cervical canal.
Step 5–Open the arms
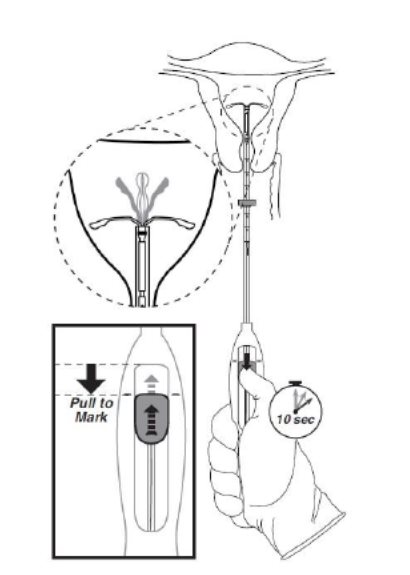
- •
- While holding the inserter steady, move the slider down to the mark to release the arms of Kyleena (Figure 5). Wait 10 seconds for the horizontal arms to open completely.
Figure 5. Move the slider back to the mark to release and open the arms
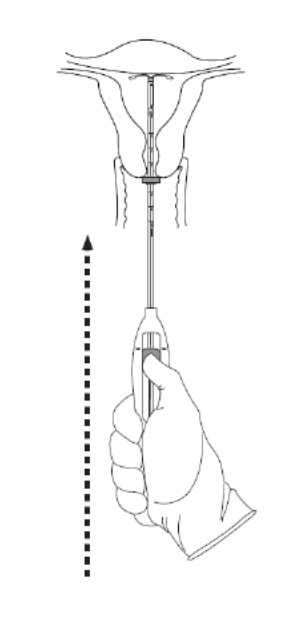
Step 6–Advance to fundal position
Advance the inserter gently towards the fundus of the uterus until the flange touches the cervix. If you encounter fundal resistance do not continue to advance. Kyleena is now in the fundal position (Figure 6). Fundal positioning of Kyleena is important to prevent expulsion.
Figure 6. Move Kyleena into the fundal position
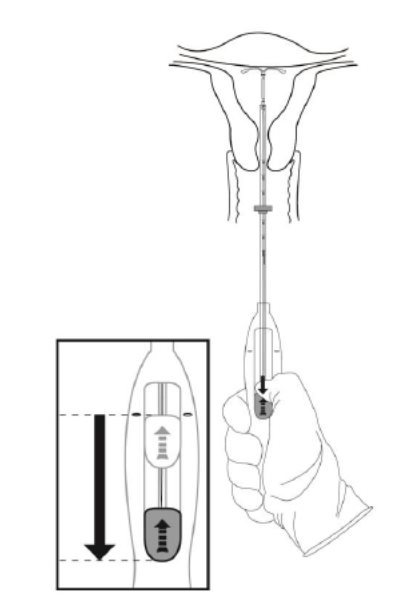
Step 7–Release Kyleena and withdraw the inserter
- •
- Holding the entire inserter firmly in place, release Kyleena by moving the slider all the way down (Figure 7).
Figure 7. Move the slider all the way down to release Kyleena from the insertion tube
- •
- Continue to hold the slider all the way down while you slowly and gently withdraw the inserter from the uterus.
- •
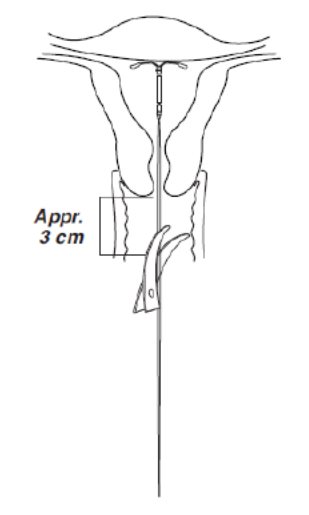
- Using a sharp, curved scissor, cut the threads perpendicular, leaving about 3 cm visible outside of the cervix [cutting threads at an angle may leave sharp ends (Figure 8)]. Do not apply tension or pull on the threads when cutting to prevent displacing Kyleena.
Figure 8. Cutting the threads
Kyleena insertion is now complete. Prescribe analgesics, if indicated. Record the Kyleena lot number in the patient records.
Important information to consider during or after insertion
- •
- If you suspect that Kyleena is not in the correct position, check placement (for example, using transvaginal ultrasound). Remove Kyleena if it is not positioned completely within the uterus. Do not reinsert a removed Kyleena.
- •
- If there is clinical concern, exceptional pain or bleeding during or after insertion, take appropriate steps (such as physical examination and ultrasound) immediately to exclude perforation.
2.3 Patient Follow-up
- •
- Reexamine and evaluate patients 4 to 6 weeks after insertion and once a year thereafter, or more frequently if clinically indicated.
2.4 Removal of Kyleena
Timing of Removal
- •
- Kyleena should not remain in the uterus after 5 years.
- •
- If pregnancy is not desired, remove Kyleena during the first 7 days of the menstrual cycle, provided the woman is still experiencing regular menses. If removal will occur at other times during the cycle or the woman does not experience regular menses, she is at risk of pregnancy; start a new contraceptive method a week prior to removal for these women. [See Dosage and Administration (2.5).]
Removal Procedure
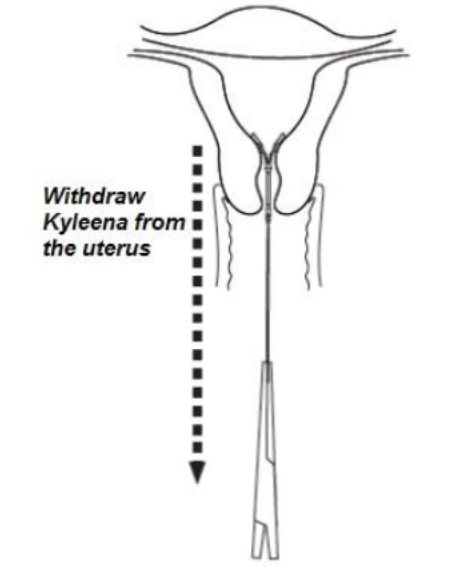
- •
- Remove Kyleena by applying gentle traction on the threads with forceps (Figure 9).
Figure 9. Removal of Kyleena
- •
- If the threads are not visible, determine location of Kyleena by ultrasound [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
- •
- If Kyleena is found to be in the uterine cavity on ultrasound exam, it may be removed using a narrow forceps, such as an alligator forceps. This may require dilation of the cervical canal. After removal of Kyleena, examine the system to ensure that it is intact. If unable to remove with gentle traction, determine Kyleena location and exclude perforation by ultrasound or other imaging [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
- •
- Removal may be associated with some:
- o
- pain and/or bleeding or vasovagal reactions (for example, syncope, bradycardia) or seizure, especially in patients with a predisposition to these conditions.
- o
- breakage or embedment of Kyleena in the myometrium that can make removal difficult [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. Analgesia, paracervical anesthesia, cervical dilation, alligator forceps or other grasping instrument, or hysteroscopy may be used to assist in removal.
2.5 Continuation of Contraception after Removal
- •
- If pregnancy is not desired and if a woman wishes to continue using Kyleena, a new system can be inserted immediately after removal any time during the cycle.
- •
- If a patient with regular cycles wants to start a different contraceptive method, time removal and initiation of the new method to ensure continuous contraception. Either remove Kyleena during the first 7 days of the menstrual cycle and start the new method immediately thereafter or start the new method at least 7 days prior to removing Kyleena if removal is to occur at other times during the cycle.
- •
- If a patient with irregular cycles or amenorrhea wants to start a different contraceptive method, start the new method at least 7 days before removal.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
The use of Kyleena is contraindicated when one or more of the following conditions exist:
- •
- Pregnancy or suspicion of pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]
- •
- For use as post-coital contraception (emergency contraception)
- •
- Congenital or acquired uterine anomaly, including fibroids, that distorts the uterine cavity
- •
- Acute pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) or a history of PID unless there has been a subsequent intrauterine pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- •
- Postpartum endometritis or infected abortion in the past 3 months
- •
- Known or suspected uterine or cervical malignancy
- •
- Known or suspected breast cancer or other progestin-sensitive cancer, now or in the past
- •
- Uterine bleeding of unknown etiology
- •
- Untreated acute cervicitis or vaginitis, including bacterial vaginosis or other lower genital tract infections until infection is controlled
- •
- Acute liver disease or liver tumor (benign or malignant)
- •
- Conditions associated with increased susceptibility to pelvic infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- •
- A previously inserted intrauterine device (IUD) that has not been removed
- •
- Hypersensitivity to any component of this product [see Adverse Reactions (6.2) and Description (11.1)]
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk of Ectopic Pregnancy
Evaluate women for ectopic pregnancy if they become pregnant with Kyleena in place because the likelihood of a pregnancy being ectopic is increased with Kyleena. Approximately one-half of pregnancies that occur with Kyleena in place are likely to be ectopic. Also consider the possibility of ectopic pregnancy in the case of lower abdominal pain, especially in association with missed menses or if an amenorrheic woman starts bleeding.
The incidence of ectopic pregnancy in clinical trials with Kyleena, which excluded women with a history of ectopic pregnancy, was approximately 0.2% per year. The risk of ectopic pregnancy in women who have a history of ectopic pregnancy and use Kyleena is unknown. Women with a previous history of ectopic pregnancy, tubal surgery or pelvic infection carry a higher risk of ectopic pregnancy. Ectopic pregnancy may result in loss of fertility.
5.2 Risks with Intrauterine Pregnancy
If pregnancy occurs while using Kyleena, remove Kyleena because leaving it in place may increase the risk of spontaneous abortion and preterm labor. Removal of Kyleena or probing of the uterus may also result in spontaneous abortion. In the event of an intrauterine pregnancy with Kyleena, consider the following:
Septic abortion
In patients becoming pregnant with an IUS in place, septic abortion—with septicemia, septic shock, and death—may occur.
Continuation of pregnancy
If a woman becomes pregnant with Kyleena in place and if Kyleena cannot be removed or the woman chooses not to have it removed, warn her that failure to remove Kyleena increases the risk of miscarriage, sepsis, premature labor and premature delivery. Advise her of isolated reports of virilization of the female fetus following local exposure to LNG during pregnancy with an LNG IUS in place [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Follow her pregnancy closely and advise her to report immediately any symptom that suggests complications of the pregnancy.
5.3 Sepsis
Severe infection or sepsis, including Group A streptococcal sepsis (GAS), have been reported following insertion of a LNG-releasing IUS. In some cases, severe pain occurred within hours of insertion followed by sepsis within days. Because death from GAS is more likely if treatment is delayed, it is important to be aware of these rare but serious infections. Aseptic technique during insertion of Kyleena is essential in order to minimize serious infections such as GAS.
5.4 Pelvic Infection
Promptly examine users with complaints of lower abdominal or pelvic pain, odorous discharge, unexplained bleeding, fever, genital lesions or sores. Remove Kyleena in cases of recurrent endometritis or pelvic inflammatory disease, or if an acute pelvic infection is severe or does not respond to treatment.
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Kyleena is contraindicated in the presence of known or suspected PID or in women with a history of PID unless there has been a subsequent intrauterine pregnancy [see Contraindications (4)]. IUDs have been associated with an increased risk of PID, most likely due to organisms being introduced into the uterus during insertion. In clinical trials, PID was observed in 0.5% of women overall and occurred more frequently within the first year and most often within the first month after insertion of Kyleena.
Women at increased risk for PID
PID is often associated with a sexually transmitted infection (STI), and Kyleena does not protect against STI. The risk of PID is greater for women who have multiple sexual partners, and also for women whose sexual partner(s) have multiple sexual partners. Women who have had PID are at increased risk for a recurrence or re-infection. In particular, ascertain whether the woman is at increased risk of infection (for example, leukemia, acquired immune deficiency syndrome [AIDS], intravenous drug abuse).
Actinomycosis
Actinomycosis has been associated with IUDs. Remove Kyleena from symptomatic women and treat with antibiotics. The significance of actinomyces-like organisms on Pap smear in an asymptomatic IUD user is unknown, and so this finding alone does not always require Kyleena removal and treatment. When possible, confirm a Pap smear diagnosis with cultures.
5.5 Perforation
Perforation (total or partial, including penetration/embedment of Kyleena in the uterine wall or cervix) may occur most often during insertion, although the perforation may not be detected until sometime later. The incidence of perforation during clinical trials was < 0.1%.
The risk of uterine perforation is increased in women who have recently given birth, and in women who are breastfeeding at the time of insertion. In a large postmarketing safety study conducted in the US, the risk of uterine perforation was highest when insertion occurred within ≤ 6 weeks postpartum, and also higher with breastfeeding at the time of insertion [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
The risk of perforation may be increased if Kyleena is inserted when the uterus is fixed, retroverted or not completely involuted.
If perforation occurs, locate and remove Kyleena. Surgery may be required. Delayed detection or removal of Kyleena in case of perforation may result in migration outside the uterine cavity, adhesions, peritonitis, intestinal perforations, intestinal obstruction, abscesses and erosion of adjacent viscera. In addition, perforation may reduce contraceptive efficacy and result in pregnancy.
5.6 Expulsion
Partial or complete expulsion of Kyleena may occur resulting in the loss of efficacy. Expulsion may be associated with symptoms of bleeding or pain, or it may be asymptomatic and go unnoticed. Kyleena typically decreases menstrual bleeding over time; therefore, an increase of menstrual bleeding may be indicative of an expulsion. Consider further diagnostic imaging, such as x-ray, if expulsion is suspected based on ultrasound [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]. In clinical trials, a 5-year expulsion rate of 3.5% (59 out of 1,690 subjects) was reported.
The risk of expulsion is increased with insertions immediately after delivery and appears to be increased with insertion after second-trimester abortion based on limited data. In a large postmarketing safety study conducted in the US, the risk of expulsion was lower with breastfeeding status [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Remove a partially expelled Kyleena. If expulsion has occurred, a new Kyleena can be inserted any time the provider can be reasonably certain the woman is not pregnant.
5.7 Ovarian Cysts
Because the contraceptive effect of Kyleena is mainly due to its local effects within the uterus, ovulatory cycles with follicular rupture usually occur in women of fertile age using Kyleena. Ovarian cysts (reported as adverse reactions if they were abnormal, non-functional cysts and/or had a diameter >3 cm on ultrasound examination) were reported at least once over the course of clinical trials in 22% of women using Kyleena, and 0.6% of subjects discontinued because of an ovarian cyst. Most ovarian cysts are asymptomatic, although some may be accompanied by pelvic pain or dyspareunia. In most cases the ovarian cysts disappear spontaneously during two to three months observation. Evaluate persistent ovarian cysts. Surgical intervention is not usually required.
5.8 Bleeding Pattern Alterations
Kyleena can alter the bleeding pattern and result in spotting, irregular bleeding, heavy bleeding, oligomenorrhea and amenorrhea. During the first 3–6 months of Kyleena use, the number of bleeding and spotting days may be higher and bleeding patterns may be irregular. Thereafter, the number of bleeding and spotting days usually decreases but bleeding may remain irregular.
In Kyleena clinical trials, amenorrhea developed by the end of the first year of use in approximately 12% of Kyleena users. A total of 81 subjects out of 1,697 (4.8%) discontinued due to uterine bleeding complaints. Table 2 shows the bleeding patterns as documented in the Kyleena clinical trials based on 90-day reference periods. Table 3 shows the number of bleeding and spotting days based on 28-day cycle equivalents.
Table 2: Bleeding Patterns Reported with Kyleena in Contraception Studies (by 90-day reference periods) Kyleena
First 90 days
N=1,566Second 90 days
N=1,511End of year 1
N=1,371End of year 3
N=975End of year 5
N=530
Amenorrhea1
<1%
5%
12%
20%
23%
Infrequent bleeding2
10%
20%
26%
26%
26%
Frequent bleeding3
25%
10%
4%
2%
2%
Prolonged bleeding4
57%
14%
6%
2%
1%
Irregular bleeding5
43%
25%
17%
10%
9%
1Defined as subjects with no bleeding/spotting throughout the 90-day reference period
2Defined as subjects with 1 or 2 bleeding/spotting episodes in the 90-day reference period
3Defined as subjects with more than 5 bleeding/spotting episodes in the 90-day reference period
4Defined as subjects with bleeding/spotting episodes lasting more than 14 days in the 90-day reference period. Subjects with prolonged bleeding may also be included in one of the other categories (excluding amenorrhea)
5Defined as subjects with 3 to 5 bleeding/spotting episodes and less than 3 bleeding/spotting-free intervals of 14 or more days
Table 3: Mean number of Bleeding and Spotting Days per 28-day Cycle Equivalent 28-day Cycle Equivalent
Cycle 1
N=1,619
Cycle 4
N=1,575
Cycle 7
N=1,518
Cycle 13
N=1,394
Cycle 39
N=913
Cycle 65
N=322
Days on treatment
1–28
85–112
169–196
337–364
1065–1092
1793-1820
Mean
(SD)Mean
(SD)Mean
(SD)Mean
(SD)Mean
(SD)Mean
(SD)Number of bleeding days
7.2
(5.9)3.2
(3.6)2.2
(3.0)1.5
(2.4)1.0
(2.0)0.9
(1.8)Number of spotting days
8.6
(6.0)4.6
(4.4)3.5
(3.4)2.9
(3.0)2.2
(2.6)2.1
(2.4)If a significant change in bleeding develops during prolonged use, take appropriate diagnostic measures to rule out endometrial pathology. Consider the possibility of pregnancy if menstruation does not occur within six weeks of the onset of a previous menstruation. Once pregnancy has been excluded, repeated pregnancy tests are generally not necessary in amenorrheic women unless indicated, for example, by other signs of pregnancy or by pelvic pain.
5.9 Breast Cancer
Women who currently have or have had breast cancer, or have a suspicion of breast cancer, should not use hormonal contraception, including Kyleena, because some breast cancers are hormone-sensitive [see Contraindications (4)].
Spontaneous reports of breast cancer have been received during postmarketing experience with a LNG-releasing IUS. Observational studies of the risk of breast cancer with use of a LNG-releasing IUS do not provide conclusive evidence of increased risk.
5.10 Clinical Considerations for Use and Removal
Use Kyleena with caution after careful assessment if any of the following conditions exist, and consider removal of the system if any of them arise during use:
- •
- Coagulopathy or use of anticoagulants
- •
- Migraine, focal migraine with asymmetrical visual loss or other symptoms indicating transient cerebral ischemia
- •
- Exceptionally severe headache
- •
- Marked increase of blood pressure
- •
- Severe arterial disease such as stroke or myocardial infarction
In addition, consider removing Kyleena if any of the following conditions arise during use:
- •
- Uterine or cervical malignancy
- •
- Jaundice
If the threads are not visible or are significantly shortened, they may have broken or retracted into the cervical canal or uterus. Consider the possibility that the system may have been displaced (for example, expelled or perforated the uterus) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.6)]. Exclude pregnancy and verify the location of Kyleena, for example, by sonography, X-ray, or by gentle exploration of the cervical canal with a suitable instrument. If Kyleena is displaced, remove it. A new Kyleena may be inserted at that time or during the next menses if it is certain that conception has not occurred. If Kyleena is in place with no evidence of perforation, no intervention is indicated.
5.11 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Information
Non-clinical testing has demonstrated that Kyleena is MR Conditional. A patient with Kyleena can be safely scanned in an MR system meeting the following conditions:
- •
- Static magnetic field of 3.0 T or less
- •
- Maximum spatial field gradient of 36,000 gauss/cm (360 T/m)
- •
- Maximum MR system reported, whole body averaged specific absorption rate (SAR) of 4W/kg (First Level Controlled Operating Mode)
Under the scan conditions defined above, the Kyleena IUS is expected to produce a maximum temperature rise of less than 2°C after 15 minutes of continuous scanning.
In non-clinical testing, the image artifact caused by the IUS extended up to 5 mm from the IUS when imaged with a gradient echo pulse sequence and a 3.0 T MRI system.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious or otherwise important adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- •
- Ectopic Pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- •
- Intrauterine Pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- •
- Group A Streptococcal Sepsis (GAS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- •
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- •
- Perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- •
- Expulsion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6]
- •
- Ovarian Cysts [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- •
- Bleeding Pattern Alterations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The data described below reflect exposure of 1,697 healthy 18 to 41-year-old women (mean age 27.8 ± 5.2 years) to Kyleena. These data come from two multi-center contraceptive trials: A phase 2 study with a 3-year duration was conducted in Europe enrolling generally healthy, 21 to 41-year old women; 217 subjects were exposed to Kyleena for one year and 174 completed three years. The data in this trial cover approximately 8,000 cycles of exposure. A phase 3 study with a 3-year duration and an optional extension of Kyleena use up to 5 years was conducted in the United States (US), Canada, Europe, and Latin America. The population was generally healthy, 18 to 35-year old women. A total of 1,208 subjects were exposed to Kyleena for at least one year; 707 women entered the optional extension phase after 3 years and 550 completed five years. The data in this trial cover approximately 60,000 cycles.
In total for both studies, 1,425 subjects were exposed for at least 1 year, and 550 subjects completed 5 years of use. Of the total of 1,697 subjects exposed to Kyleena, 563 were from the US and 1,134 were from Europe, Canada and Latin America; 623 (37%) were nulliparous (mean age 24.6 ± 4.5 years) and 1,074 (63%) were parous (mean age 29.7 ± 4.7 years). Most women who received Kyleena were Caucasian (83%) or Black/African American (4.4%); 9.4% of women were of Hispanic ethnicity. The clinical trials had no upper or lower weight or body mass index (BMI) limit. Mean BMI of Kyleena subjects was 25.2 kg/m2 (range 15.2 – 57.6 kg/m2); 16% had a BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2, and 2.0% had a BMI ≥ 40 kg/m2. The frequencies of reported adverse drug reactions represent crude incidences.
The most common adverse reactions (occurring in ≥ 5% users) were vulvovaginitis (24%), ovarian cyst (22%), abdominal pain/pelvic pain (21%), headache/migraine (15%), acne/seborrhea (15%), dysmenorrhea/uterine spasm (10%), breast pain/breast discomfort (10%), and increased bleeding (8%).
In the combined studies, 22% discontinued prematurely due to an adverse reaction. The most common adverse reactions (>1%) leading to discontinuation were increased bleeding (4.5%), abdominal pain/pelvic pain (4.2%), device expulsion (3.1%), acne/seborrhea (2.3%), and dysmenorrhea/uterine spasm (1.3%).
Common adverse reactions (occurring in ≥1% users) are summarized in Table 4 (presented as crude incidences).
Table 4: Adverse reactions that occurred in at least 1% of Kyleena users in clinical trials by System Organ Class (SOC) System Organ Class Adverse Reaction Incidence (%)
(N=1,697)Reproductive System and Breast Disorders
Vulvovaginitis
24.3
Ovarian cysta
22.2
Dysmenorrhea/uterine spasm
8.0/2.4
Increased bleedingb
7.9
Breast pain/discomfort
7.1/3.5
Genital discharge
4.5
Device expulsion (complete and partial)
3.5
Upper genital tract infection
1.5
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Abdominal pain/pelvic pain
13.3/8.2
Nausea
4.7
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders
Acne/Seborrhea
14.1/1.8
Alopecia
1.0
Nervous System Disorders
Headache/Migraine
12.9/3.3
Psychiatric Disorders
Depression/ Depressed mood
4.4/0.2
a Ovarian cysts were reported as adverse events if they were abnormal, non-functional cysts and/or had a diameter >3 cm on ultrasound examination
b Not all bleeding alterations were captured as adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
In the clinical trials, serious adverse reactions occurring in more than a single subject included: ectopic pregnancy/ruptured ectopic pregnancy (10 subjects); pelvic inflammatory disease (6 subjects); missed abortion/incomplete spontaneous abortion/spontaneous abortion (4 subjects); ovarian cyst (3 subjects); abdominal pain (4 subjects); depression/affective disorder (4 subjects); and uterine perforation/embedded device (myometrial perforation) (3 subjects).
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Adverse Reactions from Postmarketing Spontaneous Reports
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of LNG-releasing IUSs. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- •
- Arterial thrombotic and venous thromboembolic events, including cases of pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis and stroke
- •
- Device breakage
- •
- Hypersensitivity (including rash, urticaria, and angioedema)
- •
- Increased blood pressure
Reported Adverse Reactions from Postmarketing Studies
Assessment of Perforation and Expulsion of Intrauterine Devices (APEX IUD) Study
APEX IUD was a large US retrospective cohort study to assess the impact of breastfeeding and timing of postpartum IUD insertion on uterine perforation and IUD expulsion. The analyses included a total of 326,658 insertions, 30% (97,824 insertions) of which were performed in women with a delivery in the previous 12 months. For insertions performed in women who had delivered ≤ 52 weeks before IUD insertion, the majority of postpartum insertions, 57.3% (56,047 insertions) occurred between 6 and 14 weeks postpartum. Breastfeeding data were available in 94,817 insertions performed in women 52 weeks or less after delivery.
The study results indicated that the risk of uterine perforation was highest in women with IUD insertion ≤ 6 weeks postpartum. Immediate postpartum insertion (0–3 days) findings are limited due to the relatively small number of insertions occurring within this time interval. Women who were breastfeeding at the time of insertion were at 33% higher risk of perforation (adjusted hazard ratio [HR]=1.33, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.07–1.64) compared to women who were not breastfeeding at the time of insertion. Progressively lower risk of uterine perforation was observed in postpartum time windows beyond 6 weeks, in both breastfeeding and not breastfeeding women. Table 5 presents the uterine perforation rates for LNG IUS stratified by breastfeeding status and postpartum interval.
Table 5: Uterine Perforation1 rates for LNG IUS, by Breastfeeding Status and Postpartum Interval Breastfeeding at time of insertion
Not breastfeeding at time of insertion
Postpartum interval at time of insertion
Number of events/ insertions
Uterine perforation rate per 1,000 insertions
Number of events/ insertions
Uterine perforation rate
per 1,000 insertions0 to 3 days
8/1,896
4.22
0/277
0.00
4 days to ≤ 6 weeks
120/10,735
11.18
28/2,377
11.78
> 6 to ≤ 14 weeks
268/29,677
9.03
80/12,011
6.66
> 14 to ≤ 52 weeks
43/6,139
7.00
22/9,089
2.42
> 52 weeks or no delivery
no data available
243/184,733
1.32
1Uterine perforation includes both complete and partial perforation
Risk of expulsion was variable over the postpartum intervals through 52 weeks. Women who were breastfeeding were at 28% lower risk of IUD expulsion (adjusted HR=0.72, 95% CI: 0.64-0.80) compared to women who were not breastfeeding at time of insertion. Table 6 presents the IUD expulsion rates for LNG IUS stratified by breastfeeding status and postpartum interval.
Table 6: Expulsion1 Rates for LNG IUS, by Breastfeeding Status and Postpartum Interval Breastfeeding at time of insertion
Not breastfeeding at time of insertion
Postpartum interval at time of insertion
Number of events/ insertions
Expulsion rate
per 1,000 insertionsNumber of events/ insertions
Expulsion rate
per 1,000 insertions0 to 3 days
187/1,896
98.63
12/277
43.32
4 days to ≤ 6 weeks
185/10,735
17.23
52/2,377
21.88
> 6 to ≤ 14 weeks
421/29,677
14.19
306/12,011
25.48
> 14 to ≤ 52 weeks
120/6,139
19.55
273/9,089
30.04
> 52 weeks or no delivery
no data available
5,481/184,733
29.67
1Expulsion includes both complete and partial expulsion
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
No drug-drug interaction studies have been conducted with Kyleena.
Drugs or herbal products that induce or inhibit LNG metabolizing enzymes, including CYP3A4, may decrease or increase, respectively, the serum concentrations of LNG during the use of Kyleena. However, the contraceptive effect of Kyleena is mediated via the direct release of LNG into the uterine cavity and is unlikely to be affected by drug interactions via enzyme induction or inhibition.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The use of Kyleena is contraindicated in pregnancy or with a suspected and Kyleena may cause adverse pregnancy outcomes [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)]. If a woman becomes pregnant with Kyleena in place, the likelihood of ectopic pregnancy is increased and there is an increased risk of miscarriage, sepsis, premature labor, and premature delivery. Remove Kyleena, if possible, if pregnancy occurs in a woman using Kyleena. If Kyleena cannot be removed, follow the pregnancy closely [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
There have been isolated cases of virilization of the external genitalia of the female fetus following local exposure to LNG during pregnancy with an LNG IUS in place. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Kyleena.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Published studies report the presence of LNG in human milk. Small amounts of progestins (approximately 0.1% of the total maternal doses) were detected in the breast milk of nursing mothers who used other LNG-releasing IUSs, resulting in exposure of LNG to the breastfed infants. There are no reports of adverse effects in breastfed infants with maternal use of progestin-only contraceptives. Isolated cases of decreased milk production have been reported with a LNG-releasing IUS. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Kyleena and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from Kyleena or from the underlying maternal condition.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Kyleena (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system) contains 19.5 mg of LNG, a progestin, and is intended to provide an initial release rate of approximately17.5 mcg/day of LNG after 24 days.
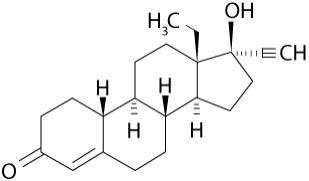
Levonorgestrel USP, (-)-13-Ethyl-17-hydroxy-18,19-dinor-17α-pregn-4-en-20-yn-3-one, the active ingredient in Kyleena, has a molecular weight of 312.4, a molecular formula of C21H28O2, and the following structural formula:
11.1 Kyleena
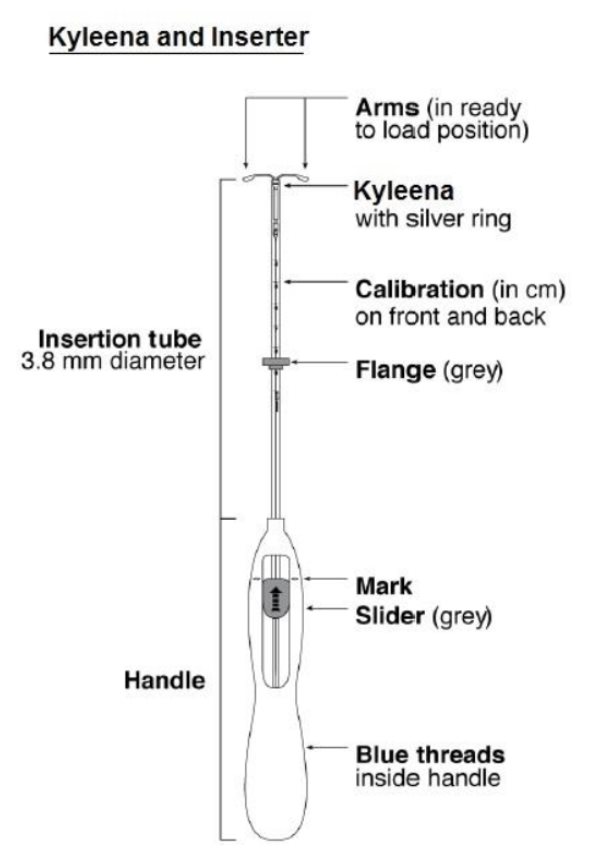
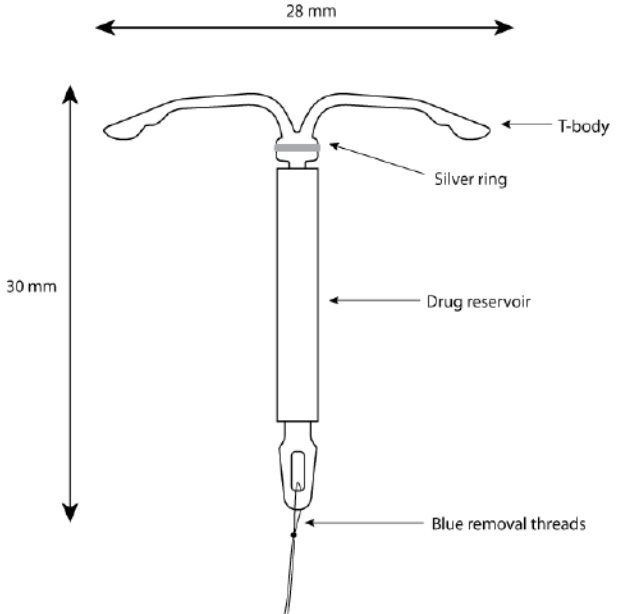
Kyleena consists of a T-shaped polyethylene frame (T-body) with a steroid reservoir (hormone elastomer core) around the vertical stem. The white T-body has a loop at one end of the vertical stem and two horizontal arms at the other end. The reservoir consists of a whitish or pale yellow cylinder, made of a mixture of LNG and silicone (polydimethylsiloxane), containing a total of 19.5 mg LNG. The reservoir is covered by a semi-opaque silicone membrane, composed of polydimethylsiloxane and colloidal silica. A ring composed of 99.95% pure silver is located at the top of the vertical stem close to the horizontal arms and is visible by ultrasound. The polyethylene of the T-body is compounded with barium sulfate, which makes it radiopaque. A monofilament blue polypropylene removal thread is attached to a loop at the end of the vertical stem of the T-body. The polypropylene of the removal thread contains <0.5% phthalocyaninato(2-) copper as a colorant (see Figure 10).
The components of Kyleena, including its packaging, are not manufactured using natural rubber latex.
Figure 10. Kyleena
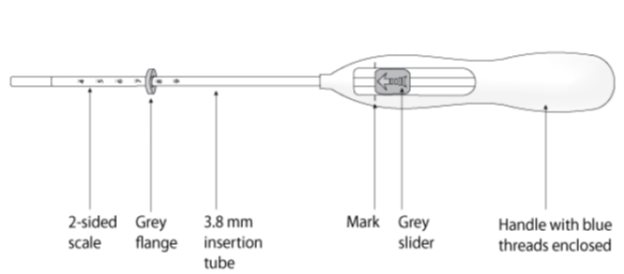
11.2 Inserter
Kyleena is packaged sterile within an inserter. The inserter (Figure 11), which is used for insertion of Kyleena into the uterine cavity, consists of a symmetric two-sided body and slider that are integrated with flange, lock, pre-bent insertion tube and plunger. The outer diameter of the insertion tube is 3.8 mm. The vertical stem of Kyleena is loaded in the insertion tube at the tip of the inserter. The arms are pre-aligned in the horizontal position. The removal threads are contained within the insertion tube and handle. Once Kyleena has been placed, the inserter is discarded.
Figure 11. Diagram of Inserter
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
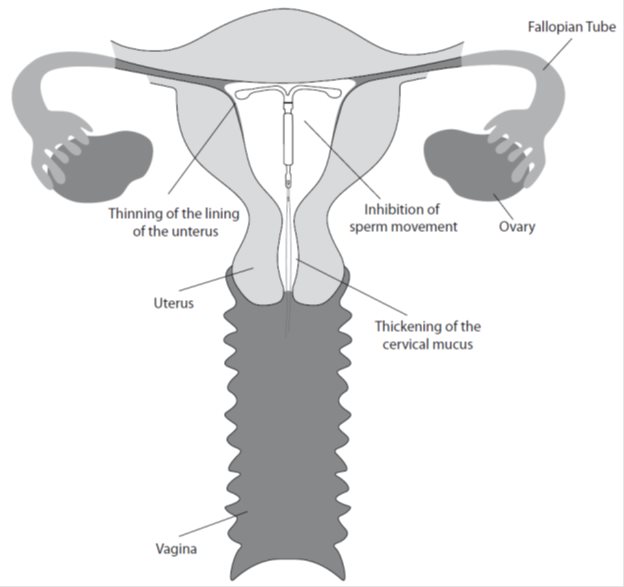
The local mechanism by which continuously released LNG contributes to the contraceptive effectiveness of Kyleena has not been conclusively demonstrated. Studies of Kyleena and similar LNG IUS prototypes have suggested several mechanisms that prevent pregnancy: thickening of cervical mucus preventing passage of sperm into the uterus, inhibition of sperm capacitation or survival, and alteration of the endometrium.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Kyleena has mainly local progestogenic effects in the uterine cavity. The local concentrations of LNG lead to morphological changes including stromal pseudodecidualization, glandular atrophy, a leukocytic infiltration and a decrease in glandular and stromal mitoses.
In clinical trials with Kyleena, ovulation was assessed based on serum progesterone values >2.5 ng/mL in one study and serum progesterone values >2.5 ng/mL together with serum estradiol levels <27.24 pg/mL in another study. Evidence of ovulation by these criteria was seen in 23 out of 26 women in the first year, in 19 out of 20 women in the second year, and in all 16 women in the third year. In the fourth year, evidence of ovulation was observed in the one woman remaining in the subset and in the fifth year, no women remained in this subset.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Low doses of LNG are administered into the uterine cavity with the Kyleena intrauterine delivery system. The in vivo release rate is approximately 17.5 mcg/day after 24 days and is reduced to approximately 15.3 mcg/day after 60 days and to 9.8 mcg/day after 1 year. It then declines progressively to approximately 7.9 mcg/day after 3 years and 7.4 mcg/day after 5 years. The average LNG in vivo release rate is approximately 12.6 mcg/day over the first year and 9.0 mcg/day over the period of 5 years.
In a subset of 6 subjects, the maximum observed serum LNG concentration (mean ±SD) was 302 ± 170 pg/mL, reached after 7.5 days (median) of Kyleena insertion. Thereafter, the LNG serum concentrations (mean ±SD) at Year 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 were 199 ± 171 pg/mL (N=6), 120 ± 57 pg/mL (N=6), 122 ± 65 pg/mL (N=6), 79 ± 12 pg/mL (N=3) and 65 ± 15 pg/mL (N=3), respectively. A population pharmacokinetic evaluation based on a broader database (>1000 patients) showed a similar declining concentration profile, with 175 ± 74 pg/mL at 7 days after placement, 125 ± 50 pg/mL at 1 year, 99 ± 41 pg/mL after 3 years, and 90 ± 35 pg/mL after 5 years.
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution of LNG is reported to be approximately 1.8 L/kg. LNG is bound non-specifically to serum albumin and specifically to sex hormone binding globulin (SHBG). Accordingly, changes in the concentration of SHBG in serum result in an increase (at higher SHBG concentration) or a decrease (at lower SHBG concentration) of the total LNG concentration in serum. In a subset of 6 subjects, the concentration of SHBG declined on average by about 30% during the first 3 months after insertion of Kyleena and remained relatively stable over the 5 year period of use. Less than 2% of the circulating LNG is present as free steroid.
Elimination
Following intravenous administration of 0.09 mg LNG to healthy volunteers, the total clearance of LNG is approximately 1 mL/min/kg and the elimination half-life is approximately 20 hours. Metabolic clearance rates may differ among individuals by several-fold, and this may account in part for wide individual variations in LNG concentrations seen in individuals using LNG–containing contraceptive products.
Metabolism
- Following absorption, LNG is extensively metabolized. The most important metabolic pathways are the reduction of the Δ4-3-oxo group and hydroxylations at positions 2α, 1β and 16β, followed by conjugation. Significant amounts of conjugated and unconjugated 3α, 5β- are also present in serum, along with much smaller amounts of 3α, 5α-tetrahydrolevonorgestrel and 16β-hydroxylevonorgestrel. CYP3A4 is the main enzyme involved in the oxidative metabolism of LNG.
Specific Populations
Pediatric: Safety and efficacy of Kyleena have been established in women of reproductive age. Use of this product before menarche is not indicated.
Geriatric: Kyleena has not been studied in women over age 65 and is not approved for use in this population.
Race: No studies have evaluated the effect of race on the pharmacokinetics of Kyleena.
Hepatic Impairment: No studies were conducted to evaluate the effect of hepatic disease on the disposition of Kyleena.
Renal Impairment: No formal studies were conducted to evaluate the effect of renal disease on the disposition of Kyleena.
Drug-Drug Interactions
No drug-drug interaction studies were conducted with Kyleena [see Drug Interactions (7)].
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The contraceptive efficacy of Kyleena was evaluated in a clinical trial that enrolled generally healthy women aged 18–35, of whom 1,452 received Kyleena. Of these, 40% (574) were nulliparous women, 870 (60%) women completed 3 years of the study, 707 (49%) elected to enroll in an extension phase up to a total of 5 years, and 550 (38%) completed 5 years of use. The trial was a multicenter, multi-national, randomized, open-label study conducted in 11 countries in Europe, Latin America, the US and Canada. Women less than six weeks postpartum, with a history of ectopic pregnancy, with clinically significant ovarian cysts or with HIV or otherwise at high risk for sexually transmitted infections were excluded. A total of 563 (39%) were treated at US sites and 889 (61%) were at non-US sites. The racial demographics of enrolled women who received Kyleena was: Caucasian (80%), Black/African American (5.1%), Other (2.6%) and Asian (1.2%); 11% indicated Hispanic ethnicity. The clinical trial had no upper or lower weight or BMI limit. The weight range was 38 to 173 kg (mean weight: 68.7 kg) and mean BMI was 25.3 kg/m2 (range 15.2–57.6 kg/m2). Of Kyleena-treated women, 22% discontinued the study treatment due to an adverse reaction, 5.0% were lost to follow-up, 2.3% withdrew for unspecified reasons, 1.2% discontinued due to a protocol deviation, 0.9% discontinued due to pregnancy, and 20% discontinued due to other reasons.
The pregnancy rate calculated as the Pearl Index (PI) in women aged 18–35 years was the primary efficacy endpoint used to assess contraceptive reliability. The PI was calculated based on 28-day equivalent exposure cycles; evaluable cycles excluded those in which back-up contraception was used unless a pregnancy occurred in that cycle. The Year 1 PI was based on 2 pregnancies and the cumulative 5-year pregnancy rate was based on 13 pregnancies that occurred after the onset of treatment and within 7 days after Kyleena removal or expulsion. Table 5 shows the calculated annual and cumulative pregnancy rates.
Table 7: Pearl Indices by Year and 5-Year Cumulative Pregnancy Rate Kyleena Clinical Trial
Pearl Index
Cumulative 5-Year Kaplan Meier Rate
Year 1
Year 2
Year 3
Year 4
Year 5
Number of Evaluable 28-day Cycles of Exposure
16,207
13,853
11,610
8,556
7,087
57,313
Pregnancy Rate (95% Confidence Interval)
0.16
(0.02, 0.58)
0.38
(0.10, 0.96)
0.45
(0.12, 1.15)
0.15
(0.00, 0.85)
0.37
(0.04, 1.33)
1.45
(0.82, 2.53)
- 15 REFERENCES
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- Kyleena (levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system), containing a total of 19.5 mg LNG, is available in a carton of one sterile unit. NDC# 50419-424-01
Kyleena is supplied sterile. Kyleena is sterilized with ethylene oxide. Do not resterilize. For single use only. Do not use if the inner package is damaged or open. Insert before the end of the month shown on the label.
Store at 25°C (77°F); with excursions permitted between 15–30°C (59–86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
- •
- Sexually Transmitted Infections: Advise the patient that this product does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- •
- Risk of Ectopic Pregnancy: Advise the patient about the risks of ectopic pregnancy, including the loss of fertility. Teach her to recognize and report to her healthcare provider promptly any symptoms of ectopic pregnancy. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.1).]
- •
- Risks of Intrauterine Pregnancy: Advise the patient to contact her healthcare provider if she thinks she might be pregnant. Inform the patient about the risks of intrauterine pregnancy while using Kyleena, including the risks of leaving Kyleena in place and the risks of removing Kyleena or probing of the uterus. If Kyleena cannot be removed in a pregnant patient, advise her to report immediately any symptom that suggests complications of the pregnancy. Advise her of isolated reports of virilization of the female fetus following local exposure to LNG during pregnancy with an LNG IUS in place. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Use in Special Populations (8.1).]
- •
- Sepsis: Advise the patient that severe infection or sepsis, including Group A streptococcal sepsis (GAS), can occur within the first few days after Kyleena is inserted. Instruct her to contact a healthcare provider immediately if she develops severe pain or fever shortly after Kyleena is inserted. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.3).]
- •
- Pelvic Infection: Advise the patient about the possibility of pelvic infections, including PID, and that these infections can cause tubal damage leading to ectopic pregnancy or infertility, or infrequently can necessitate hysterectomy, or cause death. Teach patients to recognize and report to their healthcare provider promptly any symptoms of pelvic infection. These symptoms include development of menstrual disorders (prolonged or heavy bleeding), unusual vaginal discharge, abdominal or pelvic pain or tenderness, dyspareunia, chills, and fever. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.4).]
- •
- Perforation and Expulsion: Advise the patient that the IUS may be expelled from or perforate the uterus and instruct her on how she can check that the threads still protrude from the cervix. Inform her that excessive pain or vaginal bleeding during Kyleena placement, worsening pain or bleeding after placement, or the inability to feel Kyleena strings may occur with Kyleena perforation and expulsion. Caution her not to pull on the threads and displace Kyleena. Inform her that there is no contraceptive protection if Kyleena is displaced or expelled. Instruct the patient to contact her healthcare provider if she cannot feel the threads and to avoid intercourse or use a non-hormonal back-up birth control (such as condoms or spermicide) until the location of Kyleena has been confirmed. Advise her that if perforation occurs, Kyleena will have to be located and removed; surgery may be required. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.6, 5.10).]
- •
- Ovarian Cysts: Advise the patient regarding the risk of ovarian cysts and that cysts can cause clinical symptoms including pelvic pain, abdominal pain or dyspareunia. Advise the patient to contact her healthcare provider if she experiences these symptoms. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.7).]
- •
- Bleeding Pattern Alterations: Advise the patient that irregular or prolonged bleeding and spotting, and/or cramps may occur during the first few weeks after insertion. Inform the patient that, during the first 6 months of Kyleena use, the number of bleeding and spotting days may be higher and bleeding patterns may be irregular. If her symptoms continue or are severe she should report them to her healthcare provider. [See Warnings and Precautions (5.8).]
- •
- Clinical Considerations for Use and Removal: Advise the patient to contact her healthcare provider if she experiences any of the following:
- •
- A stroke or heart attack
- •
- Very severe or migraine headaches
- •
- Unexplained fever
- •
- Yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes, as these may be signs of serious liver problems
- •
- Pregnancy or suspected pregnancy
- •
- Pelvic pain, abdominal pain, or pain during sex
- •
- HIV positive seroconversion in herself or her partner
- •
- Possible exposure to STIs
- •
- Unusual vaginal discharge or genital sores
- •
- Severe vaginal bleeding or bleeding that lasts a long time, or if she misses a menstrual period
- •
- Inability to feel Kyleena's threads
- •
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Safety Information: Inform the patient that Kyleena can be safely scanned with MRI only under specific conditions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]. Instruct patients who will have an MRI to tell their doctor that they have Kyleena.
- Manufactured for:
- Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Whippany, NJ 07981 - © 2016, Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc.
All rights reserved.
-
Patient Package Insert
- This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.7/2021
-
PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 50419-424-011
Sterile Unit
Rx onlyIMPORTANT: To be inserted in the uterus by or under the supervision of a licensed clinician. See physician insert for detailed instructions for use.
Kyleena
(levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system)
— 19.5 mg levonorgestrel
— 1 sterile unit
— intrauterine use
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
KYLEENA
levonorgestrel intrauterine deviceProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:50419-424 Route of Administration INTRAUTERINE Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LEVONORGESTREL (UNII: 5W7SIA7YZW) (LEVONORGESTREL - UNII:5W7SIA7YZW) LEVONORGESTREL 19.5 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength DIMETHICONE (UNII: 92RU3N3Y1O) BARIUM SULFATE (UNII: 25BB7EKE2E) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:50419-424-01 1 in 1 CARTON; Type 4: Device Coated/Impregnated/Otherwise Combined with Drug 09/19/2016 2 NDC:50419-424-71 1 in 1 CARTON; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 09/19/2016 3 NDC:50419-424-08 1 in 1 CARTON; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 09/19/2016 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA208224 09/19/2016 Labeler - Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals Inc. (005436809) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Bayer Schering Pharma Oy 369758383 MANUFACTURE(50419-424) , ANALYSIS(50419-424) , LABEL(50419-424) , PACK(50419-424) , STERILIZE(50419-424) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Sharp Corporation 143696495 PACK(50419-424) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Bayer AG 314398484 ANALYSIS(50419-424) , API MANUFACTURE(50419-424) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Bayer AG 342872971 PARTICLE SIZE REDUCTION(50419-424) , ANALYSIS(50419-424) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Sterigenics Belgium Petit-Rechain S.A. 370026481 STERILIZE(50419-424)