Label: DACTINOMYCIN injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution
- NDC Code(s): 71288-129-02
- Packager: Meitheal Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Drug Label Information
Updated November 13, 2020
If you are a healthcare professional or from the pharmaceutical industry please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DACTINOMYCIN FOR INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DACTINOMYCIN FOR INJECTION.
DACTINOMYCIN for injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1964INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Dactinomycin for Injection is an actinomycin indicated for the treatment of:
- adult and pediatric patients with Wilms tumor, as part of a multi-phase, combination chemotherapy regimen. (1.1)
- adult and pediatric patients with rhabdomyosarcoma, as part of a multi-phase, combination chemotherapy regimen. (1.2)
- adult and pediatric patients with Ewing sarcoma, as part of a multi-phase, combination chemotherapy regimen. (1.3)
- adult and pediatric patients with metastatic, nonseminomatous testicular cancer, as part of a multi-phase, combination chemotherapy regimen. (1.4)
- post-menarchal patients with gestational trophoblastic neoplasia, as a single agent or as part of a combination chemotherapy regimen. (1.5)
- adult patients with locally recurrent or locoregional solid malignancies, as a component of palliative or adjunctive regional perfusion. (1.6)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Wilms Tumor: The recommended dose is 45 mcg/kg intravenously once every 3 to 6 weeks for up to 26 weeks, as part of a multi-agent combination chemotherapy regimen. (2.1)
- Rhabdomyosarcoma: The recommended dose is 15 mcg/kg intravenously once daily for 5 days every 3 to 9 weeks for up to 112 weeks, as part of a multi-agent combination chemotherapy regimen. (2.2)
- Ewing Sarcoma: The recommended dose is 1,250 mcg/m2 intravenously once every 3 weeks for 51 weeks, as part of a multi-agent combination chemotherapy regimen. (2.3)
- Metastatic Nonseminomatous Testicular Cancer: The recommended dose is 1,000 mcg/m2 intravenously every 3 weeks, as part of cisplatin-based, multi-drug chemotherapy regimen. (2.4)
- Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia:
- Non-metastatic and Low-risk Metastatic Disease: The recommended dose is 12 mcg/kg intravenously daily for 5 days, as a single agent. (2.5)
- High-risk Metastatic Disease: The recommended dose is 500 mcg intravenously on Days 1 and 2 every 2 weeks for up to 8 weeks, as part of a multi-agent combination chemotherapy regimen. (2.5)
- Regional Perfusion in Locally Recurrent and Locoregional Solid Malignancies:
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
For injection: 500 mcg as a lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Secondary Malignancy or Leukemia: Increased risk of secondary malignancies following treatment. (5.1)
- Veno-occlusive Disease: Can cause severe or fatal VOD. Monitor for elevations in AST, ALT, total bilirubin, hepatomegaly, weight gain, or ascites. Consider delaying next dose. (5.2)
- Extravasation: Immediately interrupt the injection or infusion and apply ice. (2.7, 5.3)
- Myelosuppression: Monitor blood cell counts before each cycle. Delay next dose if severe myelosuppression has not improved. (5.4)
- Immunizations: Vaccination with live viral vaccines is not recommended before or during treatment. (5.5)
- Severe Mucocutaneous Reactions: Discontinue treatment (5.6)
- Renal Toxicity: Monitor creatinine and electrolytes frequently. (5.7)
- Hepatotoxicity: Monitor transaminases, alkaline phosphatase and bilirubin prior to and during treatment. (5.8)
- Potentiation of Radiation Toxicity and Radiation Recall: Reduce dose by 50% during concomitant radiation. Use caution when administering within two months of radiation. (5.9)
- Embryo-fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise patients of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception. (5.10, 8.1, 8.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Common adverse reactions are: infection, alopecia, rash, dysphagia, fatigue, fever, nausea, vomiting, anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, mucositis, and hepatotoxicity (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Meitheal Pharmaceuticals Inc. at 1-844-824-8426 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 8/2020
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Wilms Tumor
1.2 Rhabdomyosarcoma
1.3 Ewing Sarcoma
1.4 Metastatic Nonseminomatous Testicular Cancer
1.5 Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia
1.6 Regional Perfusion in Locally Recurrent and Locoregional Solid Malignancies
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage for Wilms Tumor
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Rhabdomyosarcoma
2.3 Recommended Dosage for Ewing Sarcoma
2.4 Recommended Dosage for Metastatic Nonseminomatous Testicular Cancer
2.5 Recommended Dosage for Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia
2.6 Recommended Dosage for Regional Perfusion in Locally Recurrent and Locoregional Solid Malignancies
2.7 Preparation and Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Secondary Malignancy or Leukemia
5.2 Veno-occlusive Disease
5.3 Extravasation
5.4 Myelosuppression
5.5 Immunizations
5.6 Severe Mucocutaneous Reactions
5.7 Renal Toxicity
5.8 Hepatotoxicity
5.9 Potentiation of Radiation Toxicity and Radiation Recall
5.10 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Wilms Tumor
Dactinomycin for Injection is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with Wilms tumor, as part of a multi-phase, combination chemotherapy regimen.
1.2 Rhabdomyosarcoma
Dactinomycin for Injection is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with rhabdomyosarcoma, as part of a multi-phase, combination chemotherapy regimen.
1.3 Ewing Sarcoma
Dactinomycin for Injection is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with Ewing sarcoma, as part of a multi-phase, combination chemotherapy regimen.
1.4 Metastatic Nonseminomatous Testicular Cancer
Dactinomycin for Injection is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients with metastatic, nonseminomatous testicular cancer, as part of a multi-phase, combination chemotherapy regimen.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage for Wilms Tumor
The recommended dose of dactinomycin for injection, as part of a multi-agent combination chemotherapy regimen, is 45 mcg/kg intravenously once every 3 to 6 weeks for up to 26 weeks.
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Rhabdomyosarcoma
The recommended dose of dactinomycin for injection, as part of a multi-agent combination chemotherapy regimen, is 15 mcg/kg intravenously once daily for 5 days every 3 to 9 weeks for up to 112 weeks.
2.3 Recommended Dosage for Ewing Sarcoma
The recommended dose of dactinomycin for injection, as part of a multi-agent combination chemotherapy regimen, is 1,250 mcg/m2 intravenously once every 3 weeks for 51 weeks.
2.4 Recommended Dosage for Metastatic Nonseminomatous Testicular Cancer
The recommended dose of dactinomycin for injection, as part of a cisplatin-based, multi-agent combination chemotherapy regimen, is 1,000 mcg/m2 intravenously once every 3 weeks for 12 weeks.
2.5 Recommended Dosage for Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia
The recommended dose of dactinomycin for injection for nonmetastatic and low-risk metastatic disease is 12 mcg/kg intravenously daily for five days as a single agent.
The recommended dose of dactinomycin for injection, as part of a multi-agent combination chemotherapy regimen, for high-risk metastatic disease is 500 mcg intravenously on Days 1 and 2 every 2 weeks for up to 8 weeks.
2.6 Recommended Dosage for Regional Perfusion in Locally Recurrent and Locoregional Solid Malignancies
The recommended dose of dactinomycin for injection, in combination with melphalan, is 50 mcg/kg once for lower extremity or pelvis.
The recommended dose of dactinomycin for injection, in combination with melphalan, is 35 mcg/kg once for upper extremity.
Calculate the dose for obese or edematous patients based on ideal body weight.
2.7 Preparation and Administration
- Dactinomycin for injection is a cytotoxic drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures.1
- Visually inspect the vials for particulate matter and discoloration, whenever solution and container permit.
Preparation
- Reconstitute each vial by adding 1.1 mL of Sterile Water for Injection without preservative using aseptic techniques.
- The reconstituted product should be a clear, gold-colored solution at a concentration of 500 mcg per mL.
- Further dilute the reconstituted product with 5% Dextrose Injection or 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection to yield concentrations greater than 10 mcg/mL.
- Store at room temperature for no more than 4 hours from reconstitution to completion of injection or infusion. Discard after 4 hours.
- Dactinomycin for injection does not contain a preservative. Discard any unused portions.
Administration
- Administer the diluted reconstituted product intravenously over 10 to 15 minutes.
- Do not use in-line filters with a cellulose ester membrane.
Management of Extravasation
- Discontinue dactinomycin for injection for burning or stinging sensation or other evidence indicating perivenous infiltration or extravasation.
- Manage confirmed or suspected extravasation as follows:
- Terminate the injection or infusion immediately and restart in another vein.
- Intermittent application of ice to the site for 15 minutes 4 times daily for 3 days [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Secondary Malignancy or Leukemia
The risk of developing secondary malignancies, including leukemia, is increased following treatment with dactinomycin.
5.2 Veno-occlusive Disease
Severe and fatal hepatic veno-occlusive disease (VOD) can occur with dactinomycin. Risk factors for the development of VOD include age younger than 4 years or concomitant radiotherapy. After treatment with dactinomycin, monitor frequently for signs and symptoms of VOD; these include elevations in AST, ALT, total bilirubin, hepatomegaly, weight gain, or ascites. If patients develop VOD, considering delaying next dose of dactinomycin. Resume, reduce dose or permanently discontinue based on severity of reaction and disease being treated.
5.3 Extravasation
Extravasation of dactinomycin can result in severe local tissue injury manifesting as blistering, ulcerations and persistent pain requiring wide excision surgery followed by split-thickness skin grafting. If any signs or symptoms of extravasation occur, immediately interrupt the injection or infusion. Apply ice to the site intermittently for 15 minutes, 4 times a day for 3 days [see Dosage and Administration (2.7)]. Observe closely and consult plastic surgery if necessary based on severity of reaction.
5.4 Myelosuppression
Severe and fatal myelosuppression, which may include neutropenia, thrombocytopenia and anemia, can occur with dactinomycin. The nadir in neutrophil counts generally occurs 14 to 21 days after administration. Obtain complete blood counts prior to each treatment cycle. Delay next dose of dactinomycin if severe myelosuppression has not improved. Consider dose reduction for patients with prolonged myelosuppression based on severity of reaction and disease being treated.
5.5 Immunizations
The safety with live viral vaccines following dactinomycin has not been studied and vaccination with live virus vaccines is not recommended before or during treatment.
5.6 Severe Mucocutaneous Reactions
Severe mucocutaneous reactions, such as Steven-Johnson syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN), can occur with dactinomycin. Permanently discontinue dactinomycin in patients who experience a severe mucocutaneous reaction.
5.7 Renal Toxicity
Abnormalities of renal function can occur with dactinomycin. Monitor creatinine and electrolytes frequently during dactinomycin therapy.
5.8 Hepatotoxicity
Hepatotoxicity can occur with dactinomycin. Monitor AST, ALT, alkaline phosphatase, and bilirubin prior to and during dactinomycin therapy.
5.9 Potentiation of Radiation Toxicity and Radiation Recall
Dactinomycin can increase radiation-induced gastrointestinal toxicity, myelosuppression, or erythema and vesiculation of the skin or buccal and pharyngeal mucosa. Reduce the dose of dactinomycin by 50% during concomitant radiation.
Radiation recall, affecting previously treated radiation fields, can occur in patients who receive dactinomycin after prior radiation therapy. Although the risk can occur with distant radiation exposure, the risk appears highest when dactinomycin is administered within two months of prior radiation.
5.10 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, dactinomycin can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. In animal reproduction studies, administration of dactinomycin to pregnant animals during the period of organogenesis was teratogenic, resulting in malformations at doses lower than the recommended human dose.
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to the fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with dactinomycin and for at least 6 months after the final dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with dactinomycin and for 3 months after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Secondary Malignancy and Leukemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Veno-occlusive Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Extravasation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Immunizations [see Warning and Precautions (5.5)]
- Severe Mucocutaneous Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Renal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Potentiation of Radiation Toxicity and Radiation Recall [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
Common adverse reactions are: infection, alopecia, rash, dysphagia, fatigue, fever, nausea, vomiting, anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, mucositis, and hepatotoxicity.
The following adverse reactions have been identified in clinical studies or postmarketing reports. Because some of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Infections: infections including sepsis with fatal outcome
Hematologic: anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, reticulocytopenia, neutropenia, febrile neutropenia, disseminated intravascular coagulation
Immune system: hypersensitivity
Metabolism and nutrition: anorexia, hypocalcemia, tumor lysis syndrome
Nervous system: peripheral neuropathy
Ocular: optic neuropathy
Vascular: thrombophlebitis, hemorrhage
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal: pneumonitis, pneumothorax
Gastrointestinal: nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, gastrointestinal ulceration, cheilitis, dysphagia, esophagitis, ulcerative stomatitis, ascites, proctitis, mucositis
Hepatobiliary: liver function test abnormalities, hepatomegaly, hepatitis, hepatic failure with reports of death, hepatic veno-occlusive disease
Dermatologic: alopecia, rash, dermatitis, acne, erythema multiforme, Stevens Johnson Syndrome, radiation recall, toxic epidermal necrolysis
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue: myalgia, growth retardation
Renal and urinary: renal impairment, renal failure
General: fatigue, fever, malaise
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings from animal studies and its mechanism of action, dactinomycin can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. In animal reproduction studies, administration of dactinomycin to pregnant animals during the period of organogenesis was teratogenic, resulting in malformations at doses lower than the recommended human dose (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus [see Use in Special Populations (8.3)].
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Dactinomycin was teratogenic in animals. Administration of dactinomycin to pregnant rats, rabbits, and hamsters during the period of organogenesis, increased the incidence of fetal malformations and caused embryotoxicity at doses (based on body surface area) as low as 0.2 times the clinical dose of 1,250 mcg/m2.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of dactinomycin or its metabolites in human milk or their effects on the breastfed infant or on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in breastfed infants from dactinomycin, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with dactinomycin and, based on limited published data regarding the dactinomycin half-life, for 14 days after the final dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating dactinomycin [see Use in Specific Population (8.1)].
Contraception
Dactinomycin can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Females
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with dactinomycin and for at least 6 months after the final dose.
Males
Because of the potential for genotoxicity, advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with dactinomycin and for 3 months after the final dose [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of dactinomycin have been established in pediatric patients with Wilms tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma, Ewing sarcoma, and metastatic nonseminomatous testicular cancer.
The safety and effectiveness of dactinomycin have been established in post-menarchal pediatric patients with gestational trophoblastic neoplasia.
The safety and effectiveness of dactinomycin have not been established in pediatric patients undergoing regional perfusion for locally recurrent or locoregional solid malignancies.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
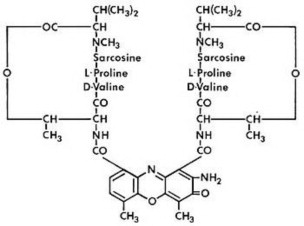
Dactinomycin is an actinomycin. Dactinomycin is produced by Streptomyces parvullus. The chemical name is 8-amino-N-(2-amino-4,6-dimethyl-3-oxo-phenoxazin-1-yl)carbonyl-N'-[8-amino-4,6-dimethyl-7-oxo-9-[[3,6,10-trimethyl-7,14-bis(1-methylethyl)-2,5,8,12,15-pentaoxo-9-oxa-3,6,13,16-tetrazabicyclo[14.3.0]nonadec-11-yl]carbamoyl]phenoxazin-1-yl]carbonyl-4,6-dimethyl-7-oxo-N,N'-bis[3,6,10-trimethyl-7,14-bis(1-methylethyl)-2,5,8,12,15-pentaoxo-9-oxa-3,6,13,16 tetrazabicyclo[14.3.0]nonadec-11-yl]-1,9-bis[[3,6,10-trimethyl-7,14-bis(1-methylethyl)-2,5,8,12,15-pentaoxo-9-oxa-3,6,13,16-tetrazabicyclo[14.3.0] nonadec-11-yl]carbamoyl]phenoxazine-1,9-dicarboxamide. The molecular formula is C62H86N12O16 and the molecular weight is 1255.42 daltons. The structural formula of dactinomycin is shown below:
Dactinomycin for Injection, USP for intravenous use is a sterile, amorphous yellow to orange, lyophilized powder in a single-dose vial. Each vial contains 500 mcg of dactinomycin and 20 mg of mannitol.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Dactinomycin is a cytotoxic actinomycin that binds DNA and inhibits RNA synthesis. The cytotoxic activity of dactinomycin has been demonstrated in animal models of different human cancers.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Dactinomycin exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamics response are unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The distribution and excretion of radiolabeled dactinomycin (3H actinomycin D) were assessed in three adult patients with malignant melanoma.
Distribution
3H actinomycin D is concentrated in nucleated cells and does not penetrate the blood-brain barrier.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Dactinomycin is a carcinogen in animals. Local sarcomas were produced in mice and rats after repeated subcutaneous or intraperitoneal injections. Mesenchymal tumors occurred in male rats given intraperitoneal injections of 50 mcg/kg, 2 to 5 times per week, for 18 weeks, at doses (based on body surface area) 0.5 times the clinical dose of 1,250 mcg/m2.
Dactinomycin was mutagenic in several in vitro and in vivo test systems including human fibroblasts and leukocytes, and HeLa cells. DNA damage and cytogenetic effects have been demonstrated in the mouse and the rat.
- 15 REFERENCES
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Dactinomycin for Injection, USP for intravenous use is an amorphous yellow to orange powder. Each vial contains 500 mcg (0.5 mg) of dactinomycin and 20 mg of mannitol. It is supplied as follows:
NDC Dactinomycin for Injection, USP (500 mcg per vial) Package Factor 71288-129-02 500 mcg Single-Dose Vial 1 vial per carton Storage Conditions
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Protect from light and humidity.
Store the reconstituted Dactinomycin for Injection, USP at room temperature for no more than 4 hours from reconstitution to completion of administration [see Dosage and Administration (2.7)].
Dactinomycin for Injection, USP is a cytotoxic drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures.1
Discard unused portion.
Lyophilized.
Sterile, Nonpyrogenic, Preservative-free.
The container closure is not made with natural rubber latex. -
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Secondary Malignancy or Leukemia
Advise patients of the increased risk of secondary malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Veno-occlusive Disease
Advise patients about the symptoms of VOD and to seek medical attention if they develop new onset jaundice, abdominal distention, or right upper quadrant pain [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Myelosuppression
Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider for any signs or symptoms of myelosuppression or infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Severe Mucocutaneous Reactions
Advise patients of the risk of severe mucocutaneous reactions and to contact their health care provided for new skin lesions, mouth sores or oropharyngeal lesions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Renal Toxicity or Hepatotoxicity
Advise patients of the need for periodic laboratory testing to monitor for renal toxicity and hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.8)].
Potentiation of Radiation Toxicity and Radiation Recall
Advise patients of the risk of increased radiation-induced gastrointestinal, myelosuppression and skin toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with dactinomycin and for 6 months after final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with dactinomycin and for 3 months after final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation
Advise females not to breastfeed during treatment with dactinomycin and for 14 days after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
meitheal®
Mfd. for Meitheal Pharmaceuticals
Chicago, IL 60631 (USA)
©2020 Meitheal Pharmaceuticals Inc.August 2020
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
DACTINOMYCIN
dactinomycin injection, powder, lyophilized, for solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:71288-129 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength dactinomycin (UNII: 1CC1JFE158) (dactinomycin - UNII:1CC1JFE158) dactinomycin 0.5 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength mannitol (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:71288-129-02 1 in 1 CARTON 11/13/2020 1 1 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA213463 11/13/2020 Labeler - Meitheal Pharmaceuticals Inc. (080548348) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Kindos Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd. 529111185 MANUFACTURE(71288-129)