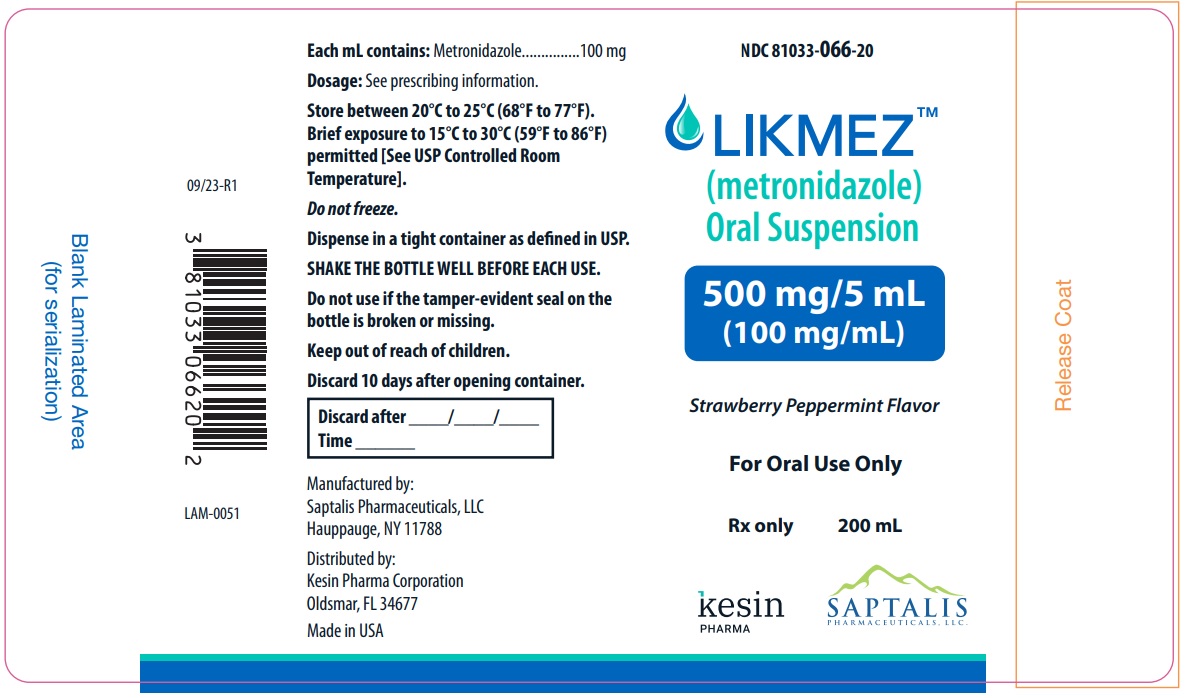
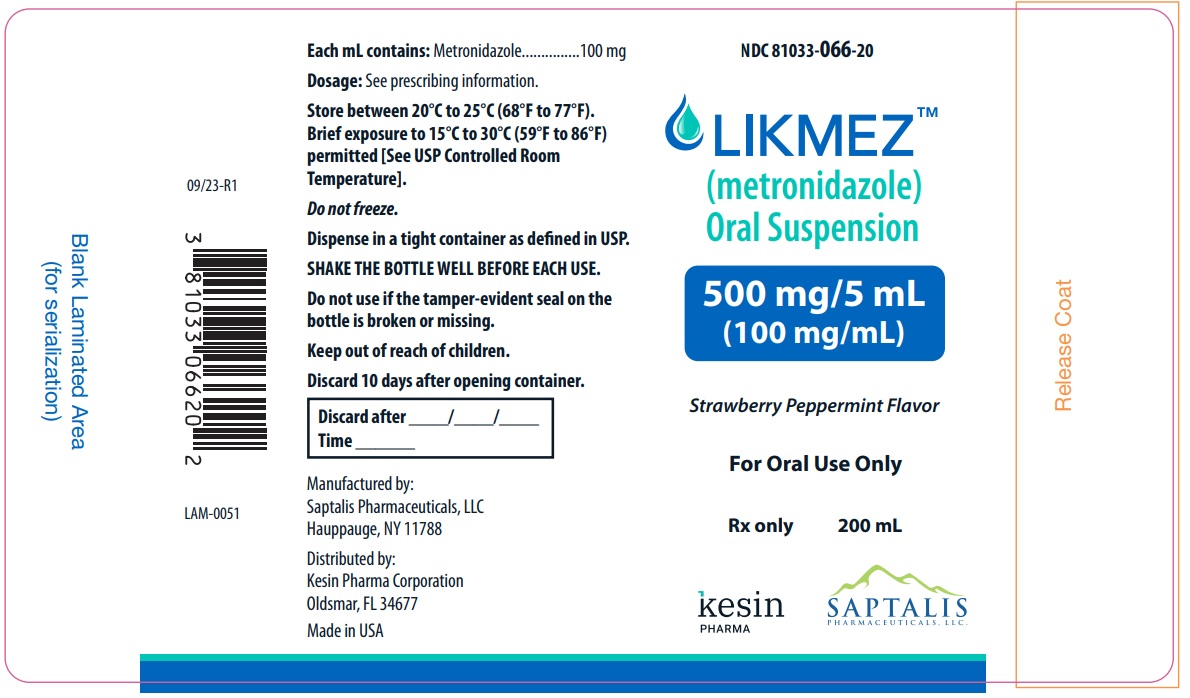
Label: LIKMEZ- metronidazole oral suspension
- NDC Code(s): 81033-066-20
- Packager: Kesin Pharma Corporation
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated March 6, 2024
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use LIKMEZ safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for LIKMEZ.
LIKMEZ™ (metronidazole) oral suspension
Initial U.S. Approval: 1963WARNING: POTENTIAL FOR CARCINOGENICITY
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Metronidazole has been shown to be carcinogenic in mice and rats ( 5.1). Avoid unnecessary use of LIKMEZ. Reserve LIKMEZ for use in the following indications: trichomoniasis ( 1.1), amebiasis ( 1.2) and anaerobic bacterial infections ( 1.3).
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
LIKMEZ is a nitroimidazole antimicrobial indicated for
- Trichomoniasis in adults ( 1.1)
- Amebiasis in adults and pediatric patients ( 1.2)
- Anaerobic Bacterial Infections in adults ( 1.3)
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of LIKMEZ and other antibacterial drugs, LIKMEZ should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria ( 1.4).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Trichomoniasis:
Adult Female and Male Patients:
- One-day treatment: 2 g (20 mL) of LIKMEZ, given either as a single oral dose or in 2 divided oral doses of 1 g (10 mL) each, given on the same day. ( 2.1)
- Seven-day course of treatment: 250 mg (2.5 mL) of LIKMEZ given three times daily for 7 consecutive days. ( 2.1)
- Individualize the dosing regimen. ( 2.1)
Amebiasis:
Adult Patients:
- For acute intestinal amebiasis (acute amebic dysentery):750 mg (7.5 mL) orally three times daily for 5 days to 10 days. ( 2.2)
- For amebic liver abscess:500 mg (5 mL) or 750 mg (7.5 mL) orally three times daily for 5 days to 10 days. ( 2.2)
Pediatric Patients:35 mg/kg/24 hours to 50 mg/kg/24 hours, divided into three doses, to a maximum dose of 2,250 mg/24 hours (maximum dose 750 mg/dose or 7.5 mL/dose),orally for 10 days. ( 2.2)
Anaerobic Bacterial Infections:
- In the treatment of most serious anaerobic infections, intravenous metronidazole is usually administered initially. ( 2.3)
- Adult Patients:7.5 mg/kg every six hours (approx. 500 mg (5 mL) for a 70-kg adult) to a maximum dose of 4 g (40 mL) during a 24-hour period, orally for 7 to 10 days. ( 2.3)
- Infections of the bone and joint, lower respiratory tract, and endocardium may require longer treatment. ( 2.3)
Patients with Severe Hepatic Impairment (Child-Pugh C)
- Reduce the dose of LIKMEZ by 50%. ( 2.4)
Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis:
Consider a supplemental dose of LIKMEZ following the hemodialysis session, depending on the patient’s clinical situation. ( 2.5)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Oral Suspension:500 mg/5 mL ( 3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Prior history of hypersensitivity to metronidazole or other nitroimidazole derivatives ( 4.1)
- Patients who have used disulfiram within the last two weeks. ( 4.2, 7.1)
- Patients who consume alcohol or products containing propylene glycol during and for at least three days after LIKMEZ therapy. ( 4.3, 7.2)
- Patients with Cockayne syndrome ( 4.4, 6.2)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Central and Peripheral Nervous System Effects:Encephalopathy, convulsive seizures, aseptic meningitis and peripheral neuropathy have been reported with metronidazole. Promptly evaluate the benefit/risk of continuation of LIKMEZ if abnormal neurological signs develop. ( 5.2)
- Blood Dyscrasias: Use LIKMEZ with care in patients with a history of blood dyscrasias. LIKMEZ may cause mild transient leukopenia. ( 5.4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Common adverse reactions include nausea, headache, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramping, epigastric distress, and constipation. ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contactSaptalis Pharmaceuticals, LLCat 1-833-727-8254 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or http://www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Disulfiram:Psychotic reactions can occur in patients who are using LIKMEZ and disulfiram concurrently. ( 4.2, 7.1)
- Alcohol or Other Products Containing Propylene Glycol:Abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, headaches, and flushing can occur in patients who are using LIKMEZ and alcohol or other products containing propylene glycol concurrently. ( 4.3, 7.2)
- Warfarin and Other Oral Anticoagulants: LIKMEZ can potentiate the anticoagulant effect. Carefully monitor prothrombin time and International Normalized Ratio (INR). ( 7.3)
- Lithium:Increased lithium serum concentrations; measure serum lithium and serum creatinine concentrations during therapy. ( 7.4)
- Busulfan: Increased busulfan serum concentrations; avoid concomitant use, monitor for plasma concentrations and adjust the busulfan dose accordingly. ( 7.5)
- CYP Inducers and CYP Inhibitors: Prolonged or accelerated half-life of metronidazole or concomitant medications. ( 7.6, 7.7)
- Drugs with the Potential for Prolonging the QT Interval:QT prolongation when used with LIKMEZ ( 7.8)
- Interference with Laboratory Tests:Metronidazole may interfere with certain serum chemistry laboratory values ( 7.9)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Lactation: A lactating woman may choose to pump and discard human milk for the duration of LIKMEZ therapy and for 48 hours after the last dose and feed her infant stored human milk or formula. ( 8.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 9/2023
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: POTENTIAL FOR CARCINOGENICITY
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Trichomoniasis
1.2 Amebiasis
1.3 Anaerobic Bacterial Infections
1.4 Usage
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage for Trichomoniasis
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Amebiasis
2.3 Recommended Dosage for Anaerobic Bacterial Infections
2.4 Recommended Dosage in Patients with Severe Hepatic Impairment
2.5 Recommended Dosage in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis
2.6 Important Administration Instructions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
4.2 Psychotic Reactions with Disulfiram
4.3 Interaction with Alcohol
4.4 Cockayne Syndrome
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Potential for Carcinogenicity
5.2 Central and Peripheral Nervous System Effects
5.3 Fungal Superinfections
5.4 Blood Dyscrasias
5.5 Drug-Resistant Bacteria
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Disulfiram
7.2 Alcoholic Beverages
7.3 Warfarin and other Oral Anticoagulants
7.4 Lithium
7.5 Busulfan
7.6 Inhibitors of CYP450 Liver Enzymes
7.7 Inducers of CYP450 Liver Enzymes
7.8 Drugs that Prolong the QT Interval
7.9 Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.4 Microbiology
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: POTENTIAL FOR CARCINOGENICITY
Metronidazole has been shown to be carcinogenic in mice and rats [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] . Avoid unnecessary use of LIKMEZ. Reserve LIKMEZ for use in the following indications: trichomoniasis [see Indications and Usage (1.1)] , amebiasis [see Indications and Usage (1.2)] and anaerobic bacterial infections [see Indications and Usage (1.3)].
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Trichomoniasis
LIKMEZ is indicated for the treatment of:
- Symptomatic trichomoniasis caused by Trichomonas vaginalisin adult females and males when the diagnosis is confirmed by appropriate laboratory procedures.
- Asymptomatic trichomoniasis caused by Trichomonas vaginalisin adult females when the organism is associated with endocervicitis, cervicitis, or cervical erosion.
Because trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted disease with potentially serious sequelae, treat sexual partners of patients simultaneously to prevent re-infection.
1.2 Amebiasis
LIKMEZ is indicated for the treatment of acute intestinal amebiasis (amoebic dysentery) and amebic liver abscess in adults and pediatric patients. In amebic liver abscess, treatment with LIKMEZ does not obviate the need for aspiration or drainage of pus.
1.3 Anaerobic Bacterial Infections
LIKMEZ is indicated in the treatment of the following serious infections caused by susceptible anaerobic bacteria in adults:
- Intra-abdominal infections, including peritonitis, intra-abdominal abscess, and liver abscess, caused by Bacteroidesspecies including the B. fragilisgroup ( B. fragilis, B. ovatus, B. thetaiotaomicron, B. vulgatus), Parabacteroides distasonis, Clostridiumspecies, Eubacteriumspecies, Peptococcusspecies ,and Peptostreptococcusspecies.
- Skin and skin structure infections caused by Bacteroidesspecies including the B. fragilisgroup, Clostridiumspecies, Peptococcusspecies , Peptostreptococcusspecies, and Fusobacteriumspecies.
- Gynecologic infections, including endometritis, endomyometritis, tubo-ovarian abscess, and postsurgical vaginal cuff infection, caused by Bacteroidesspecies including the B. fragilisgroup, Clostridiumspecies, Peptococcusspecies , Peptostreptococcusspecies, and Fusobacteriumspecies.
- Bacterial septicemia caused by Bacteroidesspecies including the B. fragilisgroup and Clostridiumspecies.
- Bone and joint infections, (as adjunctive therapy), caused by Bacteroidesspecies including the B. fragilisgroup.
- Central nervous system (CNS) infections, including meningitis and brain abscess, caused by Bacteroidesspecies including the B. fragilisgroup.
- Lower respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia, empyema, and lung abscess, caused by Bacteroidesspecies including the B. fragilisgroup.
- Endocarditis caused by Bacteroidesspecies including the B. fragilisgroup.
Indicated surgical procedures should be performed in conjunction with LIKMEZ therapy. In a mixed aerobic and anaerobic infection, antimicrobials appropriate for the treatment of aerobic infection should be used in addition to LIKMEZ.
1.4 Usage
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of LIKMEZ and other antibacterial drugs, LIKMEZ should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage for Trichomoniasis
Adult Female and Male Patients:
- One-day Treatment–Administer 2 g (20 mL) of LIKMEZ, either as a single oral dose or in 2 divided oral doses of 1 g (10 mL) each, given on the same day.
- Seven-day Course of Treatment−Administer 250 mg (2.5 mL) of LIKMEZ orally 3 times daily for 7 consecutive days.
The dosage regimen should be individualized. Single-dose treatment may help improve compliance, especially if administered under supervision, in those patients who cannot be relied on to continue the seven-day regimen.
A seven-day course of treatment may minimize reinfection by protecting the patient long enough for the sexual contacts to obtain appropriate treatment. There are some data from controlled comparative studies that cure rates as determined by vaginal smears and signs and symptoms, may be higher after a seven-day course of treatment than after a one-day treatment regimen. Further, some patients may tolerate one treatment regimen better than the other.
When repeat courses of LIKMEZ are required, it is recommended that an interval of four to six weeks elapse between courses and that the presence of the trichomonad be reconfirmed by appropriate laboratory measures. Total and differential leukocyte counts should be made before and after re-treatment.
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Amebiasis
Adult Patients:
- For acute intestinal amebiasis (acute amebic dysentery):Administer 750 mg (7.5 mL) of LIKMEZ orally three times daily for 5 days to 10 days.
- For amebic liver abscess:Administer 500 mg (5 mL) or 750 mg (7.5 mL) of LIKMEZ orally three times daily for 5 days to 10 days.
Pediatric Patients:
- Administer 35 mg/kg/24 hours to 50 mg/kg/24 hours of LIKMEZ, divided into three doses, to a maximum dose of 2250 mg/24 hours (maximum dose 750 mg/dose or 7.5 mL/dose), orally for 10 days.
2.3 Recommended Dosage for Anaerobic Bacterial Infections
In the treatment of most serious anaerobic infections, intravenous metronidazole is usually administered initially.
Adult Patients: Administer 7.5 mg/kg of LIKMEZ orally every six hours (approx. 500 mg (5 mL) for a 70 kg adult) for 7 days to 10 days. Infections of the bone and joint, lower respiratory tract, and endocardium may require longer treatment.
Do notexceed a maximum of 4 g (40 mL) during a 24-hour period.
2.4 Recommended Dosage in Patients with Severe Hepatic Impairment
For patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C), reduce the dose of LIKMEZ by 50% [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.5 Recommended Dosage in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis removes significant amounts of metronidazole and its metabolites from systemic circulation. The clearance of metronidazole will depend on the type of dialysis membrane used, the duration of the dialysis session, and other factors. If the administration of LIKMEZ cannot be separated from the hemodialysis session, consider a supplemental dose of LIKMEZ following the hemodialysis session, depending on the patient’s clinical situation [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
No adjustment in LIKMEZ dose is needed in patients undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
2.6 Important Administration Instructions
Shake the bottle well before administering the recommended dosage.
Use a calibrated oral dosing device to correctly measure the prescribed dose of medication. Do not use household teaspoons or tablespoons to measure doses. Calibrated oral dosing devices may be obtained from the pharmacy.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
LIKMEZ is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to metronidazole or other nitroimidazole derivatives [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .
4.2 Psychotic Reactions with Disulfiram
LIKMEZ is contraindicated in patients who have used disulfiram within the last two weeks. Use of oral metronidazole is associated with psychotic reactions in alcoholic patients who were using disulfiram concurrently [see Drug Interactions (7.1)] .
4.3 Interaction with Alcohol
LIKMEZ is contraindicated in patients who consume alcohol or products containing propylene glycol during and for at least three days after LIKMEZ therapy. Use of oral metronidazole is associated with a disulfiram-like reaction to alcohol, including abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, headaches, and flushing [see Drug Interactions (7.2)] .
4.4 Cockayne Syndrome
LIKMEZ is contraindicated in patients with Cockayne syndrome. Severe irreversible hepatotoxicity/acute liver failure with fatal outcomes have been reported after initiation of metronidazole in patients with Cockayne syndrome [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)] .
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Potential for Carcinogenicity
Metronidazole has been shown to be carcinogenic in mice and rats. Tumors affecting the liver, lungs, mammary, and lymphatic tissues have been detected in several studies of metronidazole in rats and mice, but not hamsters [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)] . Avoid unnecessary use of LIKMEZ. Reserve LIKMEZ for use in the following indications: trichomoniasis [see Indications and Usage (1.1)] , amebiasis [see Indications and Usage (1.2)] and anaerobic bacterial infections [see Indications and Usage (1.3)].
5.2 Central and Peripheral Nervous System Effects
Encephalopathy, aseptic meningitis, peripheral neuropathy (including optic neuropathy) and convulsive seizures have been reported with metronidazole. Encephalopathy has been reported in association with cerebellar toxicity characterized by ataxia, dizziness, and dysarthria. CNS lesions seen on MRI have been described in reports of encephalopathy. CNS symptoms are generally reversible within days to weeks upon discontinuation of metronidazole. CNS lesions seen on MRI have also been described as reversible. Peripheral neuropathy, mainly of sensory type has been reported and is characterized by numbness or paresthesia of an extremity. Cases of aseptic meningitis have been reported with metronidazole [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] . Symptoms may occur within hours of dose administration and generally resolve after metronidazole therapy is discontinued. The appearance of abnormal neurological signs and symptoms demands the prompt evaluation of the benefit/risk ratio of the continuation of therapy.
5.3 Fungal Superinfections
Known or previously unrecognized candidiasis may present more prominent symptoms during therapy with LIKMEZ and requires treatment with an antifungal agent.
5.4 Blood Dyscrasias
LIKMEZ is a nitroimidazole and should be used with care in patients with evidence of or history of blood dyscrasia. A mild leukopenia has been observed during metronidazole administration; however, no persistent hematologic abnormalities attributable to metronidazole have been observed in clinical studies. Total and differential leukocyte counts are recommended before and after therapy [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] .
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Central and Peripheral Nervous System Effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Blood Dyscrasias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The following reactions have been reported during treatment with metronidazole:
Central and Peripheral Nervous System:The most serious adverse reactions reported in patients treated with metronidazole have been convulsive seizures, encephalopathy, aseptic meningitis, optic and peripheral neuropathy, the latter characterized mainly by numbness or paresthesia of an extremity. Persistent peripheral neuropathy has been reported in some patients receiving prolonged administration of metronidazole. In addition, headache, syncope, dizziness, vertigo, incoordination, ataxia, confusion, dysarthria, irritability, depression, weakness, and insomnia have been reported.
Gastrointestinal:The most common adverse reactions reported have been referable to the gastrointestinal tract, particularly nausea, sometimes accompanied by headache, anorexia, and occasionally vomiting; diarrhea; epigastric distress; and abdominal cramping and constipation.
Mouth:A sharp, unpleasant metallic taste is not unusual. Furry tongue, glossitis, and stomatitis have occurred; these may be associated with a sudden overgrowth of Candidawhich may occur during therapy.
Dermatologic:Erythematous rash and pruritus.
Hematopoietic:Reversible neutropenia (leukopenia); reversible thrombocytopenia.
Cardiovascular:QT prolongation has been reported, particularly when metronidazole was administered with drugs with the potential for prolonging the QT interval. Flattening of the T‑wave may be seen in electrocardiographic tracings.
Hypersensitivity:Urticaria, erythematous rash, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, flushing, nasal congestion, dryness of the mouth (or vagina or vulva), and fever.
Renal:Dysuria, cystitis, polyuria, incontinence, and a sense of pelvic pressure. Instances of darkened urine have been reported by approximately one patient in 100,000. Although the pigment which is probably responsible for this phenomenon has not been positively identified, it is almost certainly a metabolite of metronidazole and seems to have no clinical significance.
Other:Proliferation of Candidain the vagina, dyspareunia, decrease of libido, proctitis, and fleeting joint pains sometimes resembling “serum sickness". Cases of pancreatitis, which generally abated on withdrawal of the drug, have been reported.
Patients with Crohn’s disease are known to have an increased incidence of gastrointestinal and certain extraintestinal cancers. There have been some reports in the medical literature of breast and colon cancer in Crohn’s disease patients who have been treated with metronidazole at high doses for extended periods of time. A cause-and-effect relationship has not been established. Crohn’s disease is not an approved indication for LIKMEZ.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of metronidazole. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
The cases of severe irreversible hepatotoxicity/acute liver failure, including cases with fatal outcomes with very rapid onset after initiation of systemic use of metronidazole have been reported in patients with Cockayne syndrome (latency from drug start to signs of liver failure as short as 2 days) [see Contraindications (4.4)] .
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Disulfiram
Psychotic reactions have been reported in alcoholic patients who are using metronidazole and disulfiram concurrently. LIKMEZ is contraindicated in patients who have taken disulfiram within the last two weeks [see Contraindications (4.2)] .
7.2 Alcoholic Beverages
LIKMEZ is contraindicated in patients who consume alcohol or products containing propylene glycol during and for at least 3 days after therapy with LIKMEZ. Use of LIKMEZ with alcohol or other products containing propylene glycol is associated with a disulfiram-like reaction (abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, headaches, and flushing) [see Contraindications (4.3)] .
7.3 Warfarin and other Oral Anticoagulants
Metronidazole has been reported to potentiate the anticoagulant effect of warfarin and other oral coumarin anticoagulants, resulting in a prolongation of prothrombin time. When LIKMEZ is prescribed for patients on this type of anticoagulant therapy, prothrombin time and INR should be carefully monitored.
7.4 Lithium
In patients stabilized on relatively high doses of lithium, short-term use of LIKMEZ has been associated with elevation of serum lithium concentrations and signs of lithium toxicity due to the interaction between metronidazole and lithium. Monitor serum lithium and serum creatinine concentrations for several days after beginning treatment with LIKMEZ to detect any increase that may precede clinical symptoms of lithium toxicity.
7.5 Busulfan
Metronidazole has been reported to increase plasma concentrations of busulfan, which can result in an increased risk for serious busulfan toxicity. Do not administer LIKMEZ concomitantly with busulfan unless the benefit outweighs the risk. If no therapeutic alternatives to LIKMEZ are available, and concomitant administration with busulfan is medically needed, monitor for busulfan plasma concentrations and adjust the busulfan dose accordingly.
7.6 Inhibitors of CYP450 Liver Enzymes
The simultaneous administration of LIKMEZ and drugs that decrease microsomal liver enzymes, such as cimetidine, may prolong the half-life and decrease plasma clearance of metronidazole.
7.7 Inducers of CYP450 Liver Enzymes
The simultaneous administration of LIKMEZ and drugs that induce microsomal liver enzymes, such as phenytoin or phenobarbital, may accelerate the elimination of metronidazole, resulting in reduced plasma concentrations of metronidazole. Impaired clearance of phenytoin has also been reported.
7.8 Drugs that Prolong the QT Interval
QT prolongation has been reported, particularly when metronidazole was administered with drugs with the potential for prolonging the QT interval.
7.9 Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Metronidazole may interfere with certain types of determinations of serum chemistry values, such as aspartate aminotransferase (AST, SGOT), alanine aminotransferase (ALT, SGPT), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), triglycerides, and glucose hexokinase. Values of zero may be observed. All of the assays in which interference has been reported involve enzymatic coupling of the assay to oxidation-reduction of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD +⇌ NADH). Interference is due to the similarity in absorbance peaks of NADH (340 nm) and metronidazole (322 nm) at pH 7.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
While available studies cannot definitively establish the absence of risk, published data from case-control studies, cohort studies and meta-analyses have not established an association with metronidazole use during pregnancy and major birth defects, miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
There are published data from case-control studies, cohort studies, and 2 meta-analyses that include more than 5,000 pregnant women who used metronidazole during pregnancy. Many studies included first trimester exposures. One study showed an increased risk of cleft lip, with or without cleft palate, in infants exposed to metronidazole in-utero; however, these findings were not confirmed. In addition, more than ten randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials enrolled more than 5,000 pregnant women to assess the use of antibiotic treatment (including metronidazole) for bacterial vaginosis on the incidence of preterm delivery. Most studies did not show an increased risk for congenital anomalies or other adverse fetal outcomes following metronidazole exposure during pregnancy. Three studies conducted to assess the risk of infant cancer following metronidazole exposure during pregnancy did not show an increased risk; however, the ability of these studies to detect such a signal was limited.
Animal Data
Metronidazole crosses the placental barrier. Reproduction studies have been performed in rats, rabbits, and mice at doses similar to the maximum recommended human dose based on body surface area comparisons. There was no evidence of harm to the fetus due to metronidazole.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Metronidazole is present in human milk at concentrations similar to maternal serum levels, and infant serum levels can be close to or comparable to infant therapeutic levels. There are no data on the effects of metronidazole on milk production. Animal studies have shown the potential for tumorigenicity after oral metronidazole was administered chronically to rats and mice [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. This drug is not intended to be administered chronically; therefore, the clinical relevance of the findings of the animal studies is unclear.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for LIKMEZ and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from LIKMEZ or from the underlying maternal condition. Alternatively, a lactating woman may choose to pump and discard human milk for the duration of LIKMEZ therapy, and for 48 hours after the last dose and feed her infant stored human milk or formula.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of LIKMEZ for the treatment of amebiasis have been established in pediatric patients.
The safety and effectiveness of LIKMEZ for the treatment of trichomoniasis and anaerobic bacterial infections have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In elderly geriatric patients, monitoring for LIKMEZ associated adverse reactions is recommended [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . Decreased liver function in geriatric patients can result in increased concentrations of metronidazole that may necessitate adjustment of metronidazole dosage [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Patients with end-stage renal disease may excrete metronidazole and metabolites slowly in the urine, resulting in significant accumulation of metronidazole metabolites. Monitor for LIKMEZ associated adverse reactions [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
Patients with hepatic impairment metabolize metronidazole slowly, with resultant accumulation of metronidazole in the plasma. For patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C), reduce the dose of LIKMEZ by 50%. For patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment, no dosage adjustment is needed but these patients should be monitored for LIKMEZ associated adverse reactions [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)and Dosage and Administration (2.4)] .
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
General
Single oral doses of metronidazole, up to 15 g (7.5 times the maximum recommended single dose), have been reported in suicide attempts and accidental overdoses. Symptoms reported include nausea, vomiting, and ataxia. Metronidazole is dialyzable.
Neurotoxic effects, including seizures and peripheral neuropathy, have been reported after 5 days to 7 days of doses of 6 g to 10.4 g every other day (3 times to 5.2 times the maximum recommended single dose).
Treatment of Overdosage
There is no specific antidote for metronidazole overdose; therefore, management of the patient should consist of symptomatic and supportive therapy.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
LIKMEZ (metronidazole) oral suspension is a nitroimidazole antimicrobial. The chemical name of metronidazole is 2-methyl-5-nitro-1H-imidazole-1-ethanol. The structural formula is shown as:
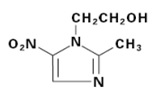
Metronidazole is a white to pale yellow crystalline powder with a molecular formula of C 6H 9N 3O 3and a molecular weight of 171.2 g/mole. The pKa of metronidazole is 14.44 ± 0.10. The pH of a 1% aqueous solution of metronidazole is 5.5-7.5. It is slightly soluble in water, acetone, alcohol, and methylene chloride.
LIKMEZ is an oral suspension containing 500 mg of metronidazole per 5 mL, and the following inactive ingredients: Glycerin, magnesium aluminum silicate, methylparaben, microcrystalline cellulose, natural peppermint flavor, natural strawberry flavor, propylparaben, purified water, sodium phosphate dibasic, sodium phosphate monobasic, sucralose, and sucrose.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Metronidazole is a nitroimidazole antimicrobial drug [see Microbiology (12.4)] .
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Metronidazole pharmacokinetics are similar for both oral and intravenous dosage forms. The C maxis dose proportional between 250 mg, 500 mg, and 2,000 mg for metronidazole oral tablets, producing peak plasma concentrations of 6 mcg/mL, 12 mcg/mL, and 40 mcg/mL, respectively.
Absorption
Following oral administration, LIKMEZ is well absorbed, with peak plasma concentrations occurring between 0.25 and 6 hours after administration.
Two pharmacokinetic studies (Study 1 and Study 2) performed in healthy adult volunteers evaluated the bioavailability of LIKMEZ under fasting and fed conditions.
Effect of Food
Food delays T maxand lowers C maxwhen compared to fasted conditions, but systemic exposure (AUC) is similar in fed and fasted state (see Table 1).
Table 1: Mean (± S.D.) Pharmacokinetic Parameters Following Single Oral Doses of 500 mg LIKMEZ in Healthy Adults Under Fed and Fasting Conditions Formulation C max
(mcg/mL)AUC 0-∞
(mcg.h/mL)Tmax *
(h)Study 1- Fasting state (n = 44) LIKMEZ 13 ± 3 146 ± 36 0.75
(0.25 to 6)Study 2- Fed State † (n = 46) LIKMEZ 10 ± 1 144 ± 30 2.33
(0.25 to 4)Distribution
Metronidazole is the major component appearing in the plasma, with lesser quantities of metabolites also being present. Less than 20% of the circulating metronidazole is bound to plasma proteins. Metronidazole appears in cerebrospinal fluid, saliva, and breast milk in concentrations similar to those found in plasma. Bactericidal concentrations of metronidazole have also been detected in pus from hepatic abscesses.
Elimination
Metabolism
The metabolites of metronidazole that appear in the urine result primarily from side-chain oxidation [1-(-hydroxyethyl)-2-hydroxymethyl-5-nitroimidazole and 2-methyl-5-nitroimidazole-1-ylacetic acid] and glucuronide conjugation, with unchanged metronidazole accounting for approximately 20% of the total. Both the parent compound and the hydroxyl metabolite possess in vitroantimicrobial activity.
Excretion
The major route of elimination of metronidazole and its metabolites is via the urine (60% to 80% of the dose), with fecal excretion accounting for 6% to 15% of the dose.
Renal clearance of metronidazole is approximately 10 mL/min/1.73 m 2. The average elimination half-life of LIKMEZ in healthy adult subjects is nine hours.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients
Following a single 500 mg oral or IV dose of metronidazole, subjects >70 years old with no apparent renal or hepatic dysfunction had a 40% to 80% higher mean AUC of hydroxy‑metronidazole (active metabolite), with no apparent increase in the mean AUC of metronidazole (parent compound), compared to young healthy controls <40 years old [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)] .
Pediatric Patients
In one study, newborn infants appeared to demonstrate diminished capacity to eliminate metronidazole. The elimination half-life, measured during the first 3 days of life, was inversely related to gestational age. In infants whose gestational ages were between 28 weeks and 40 weeks, the corresponding elimination half-lives ranged from 109 hours to 22.5 hours.
Male and Female Patients
Studies reveal no significant bioavailability differences between males and females; however, because of weight differences, the resulting plasma levels in males are generally lower.
Patients with Renal Impairment
Decreased renal function does not alter the single-dose pharmacokinetics of metronidazole.
Subjects with end-stage renal disease (ESRD; CL CR= 8.1±9.1 mL/min) and who received a single intravenous infusion of metronidazole 500 mg had no significant change in metronidazole pharmacokinetics but had 2-fold higher C maxof hydroxy-metronidazole and 5‑fold higher C maxof metronidazole acetate, compared to healthy subjects with normal renal function (CL CR= 126±16 mL/min). Thus, on account of the potential accumulation of metronidazole metabolites in ESRD patients, monitoring for metronidazole associated adverse reactions are recommended [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)] .
Following a single intravenous infusion or oral dose of metronidazole 500 mg, the clearance of metronidazole was investigated in ESRD subjects undergoing hemodialysis or continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD). A hemodialysis session lasting for 4 hours to 8 hours removed 40% to 65% of the administered metronidazole dose, depending on the type of dialyzer membrane used and the duration of the dialysis session. If the administration of metronidazole cannot be separated from the dialysis session, supplementation of metronidazole dose following hemodialysis should be considered [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. A peritoneal dialysis session lasting for 7.5 hours removed approximately 10% of the administered metronidazole dose. No adjustment in metronidazole dose is needed in ESRD patients undergoing CAPD.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Following a single intravenous infusion of 500 mg metronidazole, the mean AUC 24of metronidazole was higher by 114% in patients with severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment, and by 54% and 53% in patients with mild (Child-Pugh A) and moderate (Child-Pugh B) hepatic impairment, respectively, compared to healthy control subjects. There were no significant changes in the AUC 24of hydroxyl-metronidazole in these hepatically impaired patients. A reduction in metronidazole dosage by 50% is recommended in patients with severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment. No dosage adjustment is needed for patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. Patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment should be monitored for metronidazole associated adverse reactions [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)and Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Metronidazole, a nitroimidazole, exerts antibacterial effects in an anaerobic environment against most obligate anaerobes. Once metronidazole enters the organism by passive diffusion and activated in the cytoplasm of susceptible anaerobic bacteria, it is reduced; this process includes intracellular electron transport proteins such as ferredoxin, transfer of an electron to the nitro group of the metronidazole, and formation of a short-lived nitroso free radical. Because of this alteration of the metronidazole molecule, a concentration gradient is created and maintained which promotes the drug’s intracellular transport. The reduced form of metronidazole and free radicals can interact with DNA leading to inhibition of DNA synthesis and DNA degradation leading to death of the bacteria. The precise mechanism of action of metronidazole is unclear.
Resistance
A potential for development of resistance exists against metronidazole.
Resistance may be due to multiple mechanisms that include decreased uptake of the drug, altered reduction efficiency, overexpression of the efflux pumps, inactivation of the drug, and/or increased DNA damage repair.
Metronidazole does not possess any clinically relevant activity against facultative anaerobes or obligate aerobes.
Antimicrobial Activity
Metronidazole has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following microorganisms, both in vitroand in clinical infections [see Indications and Usage(1)].
Gram-positive anaerobes
Clostridiumspecies
Eubacteriumspecies
Peptococcusspecies
Peptostreptococcusspecies
Gram-negative anaerobes
Bacteroides fragilisgroup (B. fragilis, B. ovatus, B. thetaiotaomicron, B. vulgatus)
Parabacteroides distasonis
Fusobacteriumspecies
Protozoal parasites
Entamoeba histolytica
Trichomonas vaginalis
The following in vitrodata are available, but their clinical significance is unknown. At least 90 percent of the following bacteria exhibit an in vitrominimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) less than or equal to the susceptible breakpoint for metronidazole against isolates of similar genus or organism group. However, the efficacy of metronidazole in treating clinical infections caused by these bacteria has not been established in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials.
Gram-negative anaerobes
Bacteroides fragilisgroup (B. caccae, B. uniformis)
Prevotellaspecies (P. bivia, P. buccae, P. disiens)
Susceptibility Testing
For specific information regarding susceptibility test interpretive criteria and associated test methods and quality control standards recognized by FDA for this drug, please see: https://www.fda.gov/STIC.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Tumors affecting the liver, lungs, mammary, and lymphatic tissues have been detected in several studies of metronidazole in rats and mice, but not hamsters. Pulmonary tumors have been observed in all six reported studies in the mouse, including one study in which the animals were dosed on an intermittent schedule (administration during every fourth week only). Malignant liver tumors were increased in male mice treated at approximately 1,500 mg/m 2(similar to the maximum recommended daily dose, based on body surface area comparisons). Malignant lymphomas and pulmonary neoplasms were also increased with lifetime feeding of the drug to mice. Mammary and hepatic tumors were increased among female rats administered oral metronidazole compared to concurrent controls. Two lifetime tumorigenicity studies in hamsters have been performed and reported to be negative.
Mutagenesis
Metronidazole has shown mutagenic activity in in vitroassay systems including the Ames test. Studies in mammals in vivohave failed to demonstrate a potential for genetic damage.
Impairment of Fertility
Metronidazole failed to produce any adverse effects on fertility or testicular function in male rats at doses up at 400 mg/kg/day (similar to the maximum recommended clinical dose, based on body surface area comparisons) for 28 days. However, rats treated at the same dose for 6 weeks or longer were infertile and showed severe degeneration of the seminiferous epithelium in the testes as well as marked decreases in testicular spermatid counts and epididymal sperm counts. Fertility was restored in most rats after an eight-week, drug-free recovery period.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
LIKMEZ 500 mg/5 mL is supplied as 200 mL of white to slightly brown suspension with characteristic strawberry peppermint flavor packed in white HDPE round bottle with a child‑resistant cap (NDC 81033-066-20).
Storage
Store between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Brief exposure to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) permitted [See USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Do not freeze.
Dispense in a tight container as defined in USP. Discard 10 days after opening container.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Administration Instructions
Instruct the patients and caregivers to:
- Ensure the prescribed dose of LIKMEZ oral suspension is taken as directed [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
- Use a calibrated oral dosing device to correctly measure the prescribed dose of medication. Do not use a household teaspoon or tablespoon to measure doses. Calibrated oral dosing devices may be obtained from the pharmacy.
- Shake LIKMEZ oral suspension well before use each time.
Alcohol or Products Containing Propylene Glycol
Advise patients to avoid consumption of alcoholic beverages and preparations containing ethanol or propylene glycol during LIKMEZ therapy and for 3 days afterward because abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, headaches, and flushing may occur [see Contraindications (4.3)and Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Lactation
Advise lactating women that they may choose to pump and discard human milk for the duration of LIKMEZ therapy and for 48 hours after the last dose and feed her infant stored human milk or formula [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Central and Peripheral Nervous System Effects
Inform patients of the risk of central and peripheral nervous system effects while taking LIKMEZ. Advise patients to stop taking LIKMEZ and report immediately to their healthcare provider if any neurological symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Drug Interactions
Advise patients to report the use of any other medications while taking LIKMEZ. The administration of any of the following drugs with LIKMEZ may result in clinically significant adverse reactions or reduced effectiveness of the drug [see Contraindications (4.2)and Drug Interactions (7.1to 7.7)]:
- Disulfiram
- Warfarin and other oral Anticoagulants
- Lithium
- Busulfan
- Cimetidine
- Phenytoin and Phenobarbital
Antibacterial Resistance
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including LIKMEZ should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When LIKMEZ is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by LIKMEZ or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Manufactured by:
Saptalis Pharmaceuticals LLC
Hauppauge, NY 11788
Distributed by:
Kesin Pharma Corporation
Oldsmar, FL 34677
Made in USA
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Issued: 09/2023
PATIENT INFORMATION
LIKMEZ™ (lik mez)
(metronidazole)
oral suspension
What is LIKMEZ?
LIKMEZ is an antibiotic medicine used to treat:
- trichomoniasis (a sexually transmitted infection) in adults
- amebiasis (an infection caused by a parasite) in adults and children
- anaerobic bacterial infections (infections caused by bacteria that do not need oxygen to survive) in adults
Do not take LIKMEZ if you:
- are allergic to metronidazole or other nitroimidazole medicines.
- have taken disulfiram (medicine used to help people stop drinking alcohol) in the last 2 weeks. Taking LIKMEZ with disulfiram can cause psychotic symptoms (seeing or hearing things that are not really there) in people who drink alcohol.
- drink alcohol or use products with propylene glycol during treatment with LIKMEZ and for at least 3 days after you stop taking LIKMEZ, because this can cause side effects including abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, headaches, and flushing.
- have Cockayne Syndrome (a rare genetic disorder that affects growth and development).
Before taking LIKMEZ, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have liver problems.
- have kidney problems.
- have medical problems that affect the brain.
- have a yeast infection.
- have a history of blood problems.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. LIKMEZ can pass into your breastmilk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby while taking LIKMEZ. If you are breastfeeding, you may consider pumping and throwing away your breast milk during treatment with LIKMEZ and for 48 hours after your last dose of LIKMEZ and feeding your infant stored human milk or formula.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. LIKMEZ and other medicines can affect each other causing side effects.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
- warfarin or other blood thinners (anticoagulants)
- lithium
- busulfan
- cimetidine
- phenytoin and phenobarbital
You can ask your pharmacist for a list of medicines that interact with LIKMEZ.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.How should I take LIKMEZ?
- Take LIKMEZ exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Shake LIKMEZ oral suspension well before each use.
- Always use an accurate measuring device to measure the correct amount of LIKMEZ. Do notuse a household teaspoon or tablespoon to measure your medicine. You can ask your pharmacist for the measuring device you should use and how to measure the correct dose.
- Do not skip any doses of LIKMEZ or stop taking it, even if you begin to feel better, until you have finished your prescribed treatment. Taking all of your LIKMEZ doses will help make sure that all of the bacteria are killed. Taking all of your LIKMEZ doses will help lower the chance that the bacteria will become resistant to LIKMEZ. If you become resistant to LIKMEZ, LIKMEZ and other antibacterial medicines may not work for you in the future.
What are the possible side effects of LIKMEZ?
LIKMEZ may cause serious side effects including:
- Nervous system problems, including brain disorder (encephalopathy), inflammation of the brain and spinal cord membranes (aseptic meningitis), numbness or tingling in the hands or feet (peripheral neuropathy) and seizures (convulsions). Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any nervous system problems while taking LIKMEZ.
- Worsening yeast infection (candidiasis) symptomsin people with a known yeast infection or a yeast infection they were not aware of.
- Low white blood cell count (leukopenia) in people with a history of blood problems. This can affect how well the body fights infection.
The most common side effects of LIKMEZ include: nausea, headache, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, pain in the upper abdomen, abdominal cramping, and constipation.
Other side effects of LIKMEZ include:
- allergic reactions: such as itching, hives (urticaria), flushing of the skin, red skin rash that can be widespread, blisters and separation of skin layers, nasal congestion, dryness of the mouth and vagina, and fever
- abnormal heart rhythm (QT prolongation)
How should I store LIKMEZ?
- Store LIKMEZ oral suspension at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Do not freeze.
- Throw away (discard) any unused LIKMEZ 10 days after opening the container.
General information about the safe and effective use of LIKMEZ.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use LIKMEZ for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give LIKMEZ to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about LIKMEZ that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in LIKMEZ?
Active ingredient:metronidazole
Inactive ingredients:glycerin, magnesium aluminum silicate, methylparaben, microcrystalline cellulose, natural peppermint flavor, natural strawberry flavor, propylparaben, purified water, sodium phosphate dibasic, sodium phosphate monobasic, sucralose, and sucrose.Manufactured by:
Saptalis Pharmaceuticals LLC
Hauppauge, NY 11788
Distributed by:
Kesin Pharma Corporation
Oldsmar, FL 34677Made in USA
For more information, call 1-833-727-8254. - Princial Display Panel
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
LIKMEZ
metronidazole oral suspensionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:81033-066 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength METRONIDAZOLE (UNII: 140QMO216E) (METRONIDAZOLE - UNII:140QMO216E) METRONIDAZOLE 100 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) MAGNESIUM ALUMINUM SILICATE (UNII: 6M3P64V0NC) METHYLPARABEN (UNII: A2I8C7HI9T) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) PEPPERMINT (UNII: V95R5KMY2B) PROPYLPARABEN (UNII: Z8IX2SC1OH) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) SODIUM PHOSPHATE DIBASIC DIHYDRATE (UNII: 94255I6E2T) SODIUM PHOSPHATE, MONOBASIC (UNII: 3980JIH2SW) STRAWBERRY (UNII: 4J2TY8Y81V) SUCRALOSE (UNII: 96K6UQ3ZD4) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) Product Characteristics Color white (white to slightly brown) Score Shape Size Flavor PEPPERMINT, STRAWBERRY Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:81033-066-20 200 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/13/2023 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA216755 10/13/2023 Labeler - Kesin Pharma Corporation (117447816) Registrant - Saptalis Pharmaceuticals, LLC (081154447) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Saptalis Pharmaceuticals, LLC 081154447 manufacture(81033-066)