Label: PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE- phenylephrine hydrochloride injection
- NDC Code(s): 63323-751-00, 63323-751-01
- Packager: Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Abbreviated New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated September 7, 2023
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE.
PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2012RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Dosage and Administration (2.1) 03/2023 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Phenylephrine Hydrochloride Injection 10 mg/mL is alpha-1 adrenergic receptor agonist indicated for increasing blood pressure in adults with clinically important hypotension resulting primarily from vasodilation in the settings of anesthesia and septic shock. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- MUST BE DILUTED before administration. (2.1)
Dosing for Perioperative Hypotension
- -
- Intravenous bolus administration: 50 mcg to 250 mcg (2.2)
- -
- Intravenous continuous infusion: 0.5 mcg/kg/minute to 1.4 mcg/kg/minute titrated to effect (2.2)
Dosing for Patients with Vasodilatory Shock
- -
- Intravenous continuous infusion: 0.5 mcg/kg/minute to 6 mcg/kg/minute titrated to effect (2.2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Phenylephrine Hydrochloride Injection:
- 10 mg per mL supplied as a 1 mL single dose vial (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Hypersensitivity to the products or any of its components (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions: nausea and vomiting, headache, nervousness (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC at 1-800-551-7176 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Agonistic effects with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI), β-adrenergic blocking agents, α-2 adrenergic agonists, steroids, tricyclic antidepressants, norepinephrine transport inhibitors, ergot alkaloids, centrally-acting sympatholytic agents and atropine sulfate (7.1)
- Antagonistic effects on and by α-adrenergic blocking agents (7.2)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 7/2023
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Administration Instructions
2.2 Preparation of Phenylephrine Hydrochloride Injection
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Exacerbation of Angina, Heart Failure, or Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
5.2 Bradycardia
5.3 Risk in Patients with Autonomic Dysfunction
5.4 Skin and Subcutaneous Necrosis
5.5 Pressor Effect with Concomitant Oxytocic Drugs
5.7 Peripheral and Visceral Ischemia
5.8 Renal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Agonists
7.2 Antagonists
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
8.7 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Administration Instructions
- Phenylephrine Hydrochloride Injection 10 mg/mL MUST BE DILUTED before administration as an intravenous bolus or for continuous intravenous infusion. The diluted solution should not be held for more than 4 hours at room temperature or for more than 24 hours under refrigerated conditions (2°C – 8°C).
Parenteral drug products should be inspected for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration.
Discard any unused portion.
During Phenylephrine Hydrochloride Injection 10 mg/mL administration:
- Correct intravascular volume depletion.
- Correct acidosis. Acidosis may reduce the effectiveness of phenylephrine.
2.2 Preparation of Phenylephrine Hydrochloride Injection
Preparing a 100 mcg/mL Solution for Intravenous Bolus Administration
For intravenous bolus administration, withdraw 10 mg (1 mL of a 10 mg/mL concentration) of Phenylephrine Hydrochloride Injection 10 mg/mL and dilute with 99 mL of 5% Dextrose Injection, USP or 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP. This will yield a final concentration of 100 mcg/mL. Withdraw an appropriate dose from the 100 mcg/mL solution prior to intravenous bolus administration.
Preparing a 20 mcg/mL Solution for Continuous Intravenous Infusion
For continuous intravenous infusion, withdraw 10 mg (1 mL of 10 mg/mL concentration) of phenylephrine hydrochloride injection 10 mg/mL and add to 500 mL of 5% Dextrose Injection, USP or 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP (providing a final concentration of 20 mcg/mL).
Dosing for Perioperative Setting
In adult patients undergoing surgical procedures with either neuraxial anesthesia or general anesthesia:
- Phenylephrine Hydrochloride Injection 10 mg/mL (diluted to 20 mcg/mL): 0.5 mcg/kg/min to 1.4 mcg/kg/min by intravenous continuous infusion, titrated to blood pressure goal.
Dosing for Septic or Other Vasodilatory Shock
In adult patients with septic or other vasodilatory shock:
- No bolus.
- 0.5 mcg/kg/min to 6 mcg/kg/min by intravenous continuous infusion, titrated to blood pressure goal. Doses above 6 mcg/kg/min do not show significant incremental increase in blood pressure.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Exacerbation of Angina, Heart Failure, or Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Because of its pressor effects, phenylephrine hydrochloride can precipitate angina in patients with severe arteriosclerosis or history of angina, exacerbate underlying heart failure, and increase pulmonary arterial pressure.
5.2 Bradycardia
Phenylephrine Hydrochloride Injection 10 mg/mL can cause severe bradycardia and decreased cardiac output.
5.3 Risk in Patients with Autonomic Dysfunction
The pressor response to adrenergic drugs, including phenylephrine, can be increased in patients with autonomic dysfunction, as may occur with spinal cord injuries.
5.4 Skin and Subcutaneous Necrosis
Extravasation of phenylephrine can cause necrosis or sloughing of tissue.
5.5 Pressor Effect with Concomitant Oxytocic Drugs
Oxytocic drugs potentiate the pressor effect of sympathomimetic pressor amines including Phenylephrine Hydrochloride Injection 10 mg/mL [see Drug Interactions (7.1)], with the potential for hemorrhagic stroke.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of phenylephrine hydrochloride were identified in the literature. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to estimate their frequency reliably or to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiac disorders: Bradycardia, AV block, ventricular extrasystoles, myocardial ischemia
Gastrointestinal disorders: Nausea, vomiting
General disorders and administrative site conditions: Chest pain, extravasation
Immune system disorders: Sulfite sensitivity
Nervous system disorders: Headache, nervousness, paresthesia, tremor
Psychiatric disorders: Excitability
Respiratory: Pulmonary edema, rales
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Diaphoresis, pallor, piloerection, skin blanching, skin necrosis with extravasation
Vascular disorders: Hypertensive crisis
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Agonists
The pressor effect of phenylephrine hydrochloride is increased in patients receiving:
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI), such as selegiline.
- β-adrenergic blockers
- α-2 adrenergic agonists, such as clonidine
- Steroids
- Tricyclic antidepressants
- Norepinephrine transport inhibitors, such as atomoxetine
- Ergot alkaloids, such as methylergonovine maleate
- Centrally-acting sympatholytic agents, such as guanfacine or reserpine
- Atropine sulfate
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
In animal reproductive and developmental studies, decreased fetal body weights were noted at 0.4 times the human daily dose (HDD) of 10 mg. No malformations were reported, however, an increased incidence of agenesis of the intermediate lobe of the lung, a visceral variation, was reported at levels as low as 0.08 times the HDD.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
No malformations were noted when normotensive pregnant rats were treated with a single daily intravenous bolus dose of 50 mcg, 150 mcg, or 300/200 mcg/kg phenylephrine hydrochloride from Gestation Day 6 to 17 (high dose is 0.3/0.2 times the human daily dose (HDD) of 10 mg/day based on body surface area). Evidence of maternal toxicity, including mortality, was noted at the highest tested dose of 300/200 mcg/kg.
Decreased fetal body weights but no clear treatment-related malformations were reported when normotensive pregnant rabbits were treated with a single daily intravenous bolus dose of 40 mcg, 100 mcg and 200 mcg/kg (0.08, 0.2, and 0.4 times the HDD based on body surface area) phenylephrine hydrochloride from Gestation Day 7 to 19. Maternal toxicity, as manifested by decreased food consumption and body weight gain at all doses. An increased incidence of agenesis of the intermediate lobe of the lung, a visceral variation, was noted in all treatment groups compared to controls.
No adverse effects on the offspring were reported when pregnant rats were treated via a single daily intravenous bolus dose of up to 200 mcg/day phenylephrine hydrochloride (0.2 times the HDD based on body surface area) from Gestation Day 6 to Lactation Day 20.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of phenylephrine did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdose of phenylephrine hydrochloride injection 10 mg/mL can cause a rapid rise in blood pressure. Symptoms of overdose include headache, vomiting, hypertension, reflex bradycardia, and cardiac arrhythmias including ventricular extrasystoles and ventricular tachycardia, and may cause a sensation of fullness in the head and tingling of the extremities. Consider using an α-adrenergic antagonist.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
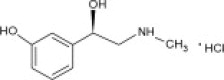
Phenylephrine Hydrochloride Injection contain active pharmaceutical ingredient phenylephrine in the form of hydrochloride salt. Phenylephrine is a synthetic sympathomimetic agent in sterile form for parenteral injection. Chemically, phenylephrine hydrochloride is (-)-m-Hydroxy-α-[(methylamino)methyl]benzyl alcohol hydrochloride and has the following structural formula:
Phenylephrine hydrochloride is very soluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol, and insoluble in chloroform and ethyl ether. Phenylephrine hydrochloride is sensitive to light.
Phenylephrine Hydrochloride Injection, USP is a clear, colorless, aqueous solution that is essentially free of visible foreign matter. It MUST BE DILUTED before administration as bolus intravenous infusion or continuous intravenous infusion.
Each mL contains: Phenylephrine Hydrochloride 10 mg; Sodium Chloride 3.5 mg; Sodium Citrate Dihydrate 4 mg; and Citric Acid 1 mg in water for injection. The pH may be adjusted in the range of 3.5 to 5.5 with Sodium Hydroxide and/or Hydrochloric Acid, if necessary.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Phenylephrine is the active moiety. Metabolites are inactive at both the α-1and α-2 adrenergic receptors. Following parenteral administration of phenylephrine hydrochloride, increases in systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, mean arterial blood pressure, and total peripheral vascular resistance are observed. The onset of blood pressure increase following an intravenous bolus phenylephrine hydrochloride administration is rapid and the effect may persist for up to 20 minutes. As mean arterial pressure increases following parenteral doses, vagal activity also increases, resulting in reflex bradycardia.
Most vascular beds are constricted, including renal, splanchnic, and hepatic.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following an intravenous infusion of phenylephrine hydrochloride, the effective half-life was approximately 5 minutes. The steady-state volume of distribution (340 L) exceeded the body volume by a factor of 5, suggesting a high distribution into certain organ compartments. The average total serum clearance (2095 mL/min) was close to one-third of the cardiac output.
A mass balance study showed that phenylephrine is extensively metabolized by the liver with only 12% of the dose excreted unchanged in the urine. Deamination by monoamino oxidase is the primary metabolic pathway resulting in the formation of the major metabolite (m-hydroxymandelic acid) which accounts for 57% of the total administered dose.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis:
Long-term animal studies that evaluated the carcinogenic potential of orally administered phenylephrine hydrochloride in F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice were completed by the National Toxicology Program using the dietary route of administration. There was no evidence of carcinogenicity in mice administered approximately 270 mg/kg/day (131-times the human daily dose (HDD) of 10 mg/day based on body surface area) or rats administered approximately 50 mg/kg/day (48-times the HDD based on body surface area comparisons).
Mutagenesis:
Phenylephrine hydrochloride tested negative in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay (S. typhimurium strains TA98, TA100, TA1535 and TA1537), the in vitro chromosomal aberrations assay, the in vitro sister chromatid exchange assay, and the in vivo rat micronucleus assay. Positive results were reported in only one of two replicates of the in vitro mouse lymphoma assay.
Impairment of Fertility:
No adverse effects on fertility or early embryonic development were noted when phenylephrine hydrochloride was administered at doses of 50 mcg, 100 mcg, or 200 mcg/kg/day (up to 0.2 times HDD of 10 mg/60 kg/day based on body surface area) via single daily bolus injection for 28 days prior to mating to male rats or for 14 days prior to mating through Gestation Day 7 to female rats.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Increases in systolic and mean blood pressure following administration of phenylephrine were observed in 42 literature-based studies in the perioperative setting, including 26 studies where phenylephrine was used in low- risk (ASA 1 and 2) pregnant women undergoing neuraxial anesthesia during cesarean delivery, 3 studies in non- obstetric surgery under neuraxial anesthesia, and 13 studies in patients undergoing surgery under general anesthesia. Mean arterial blood pressure increases were also observed in two double-blind, active-controlled studies in patients with septic shock.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Phenylephrine Hydrochloride Injection, USP, is supplied as follows:
Product
CodeUnit of Sale Strength Each 751101 NDC 63323-751-01
Unit of 25
10 mg per mL
NDC 63323-751-00
1 mL Single Dose Vial
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F), excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from light. Keep covered in carton until time of use. For single use only. Discard unused portion.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Inform patients, families, or caregivers that the primary side effect of phenylephrine is hypertension and, rarely, hypertensive crisis. Patients may experience bradycardia (slow heart rate), which in some cases may produce heart block or other cardiac arrhythmias, extra ventricular beats, myocardial ischemia in patients with underlying cardiac disease, and pulmonary edema (fluid in the lungs) or rales. Common, less serious symptoms include the following:
- chest pain
- skin or tissue damage if the drug leaks out of the venous catheter into the surrounding tissue
- headache, nervousness, tremor, numbness/tingling (paresthesias) in hands or feet
- nausea, vomiting
- excitability, dizziness, sweating, flushing
Lake Zurich, IL 60047
www.fresenius-kabi.com/us451579B
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PHENYLEPHRINE HYDROCHLORIDE
phenylephrine hydrochloride injectionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:63323-751 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Phenylephrine Hydrochloride (UNII: 04JA59TNSJ) (Phenylephrine - UNII:1WS297W6MV) Phenylephrine Hydrochloride 10 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Sodium Chloride (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) Trisodium Citrate Dihydrate (UNII: B22547B95K) Citric Acid Monohydrate (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Sodium Hydroxide (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Hydrochloric Acid (UNII: QTT17582CB) Nitrogen (UNII: N762921K75) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:63323-751-01 25 in 1 CARTON 05/25/2019 1 NDC:63323-751-00 1 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA210665 05/25/2019 Labeler - Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC (608775388) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Fresenius Kabi USA, LLC 023648251 ANALYSIS(63323-751) , MANUFACTURE(63323-751)