Label: FLUCELVAX (influenza a virus a/georgia/12/2022 cvr-167 (h1n1) antigen (mdck cell derived, propiolactone inactivated), influenza a virus a/sydney/1304/2022 (h3n2) antigen (mdck cell derived, propiolactone inactivated), influenza b virus b/singapore/wuh4618/2021 antigen- mdck cell derived, propiolactone inactivated injection, suspension
FLUCELVAX (influenza a virus a/georgia/12/2022 crv-167 (h1n1) antigen (mdck cell derived, propiolactone inactivated), influenza a virus a/sydney/1304/2022 (h3n2) antigen (mdck cell derived, propiolactone inactivated), influenza b virus b/singapore/wuh4618/2021 antigen- mdck cell derived, propiolactone inactivated injection, suspension
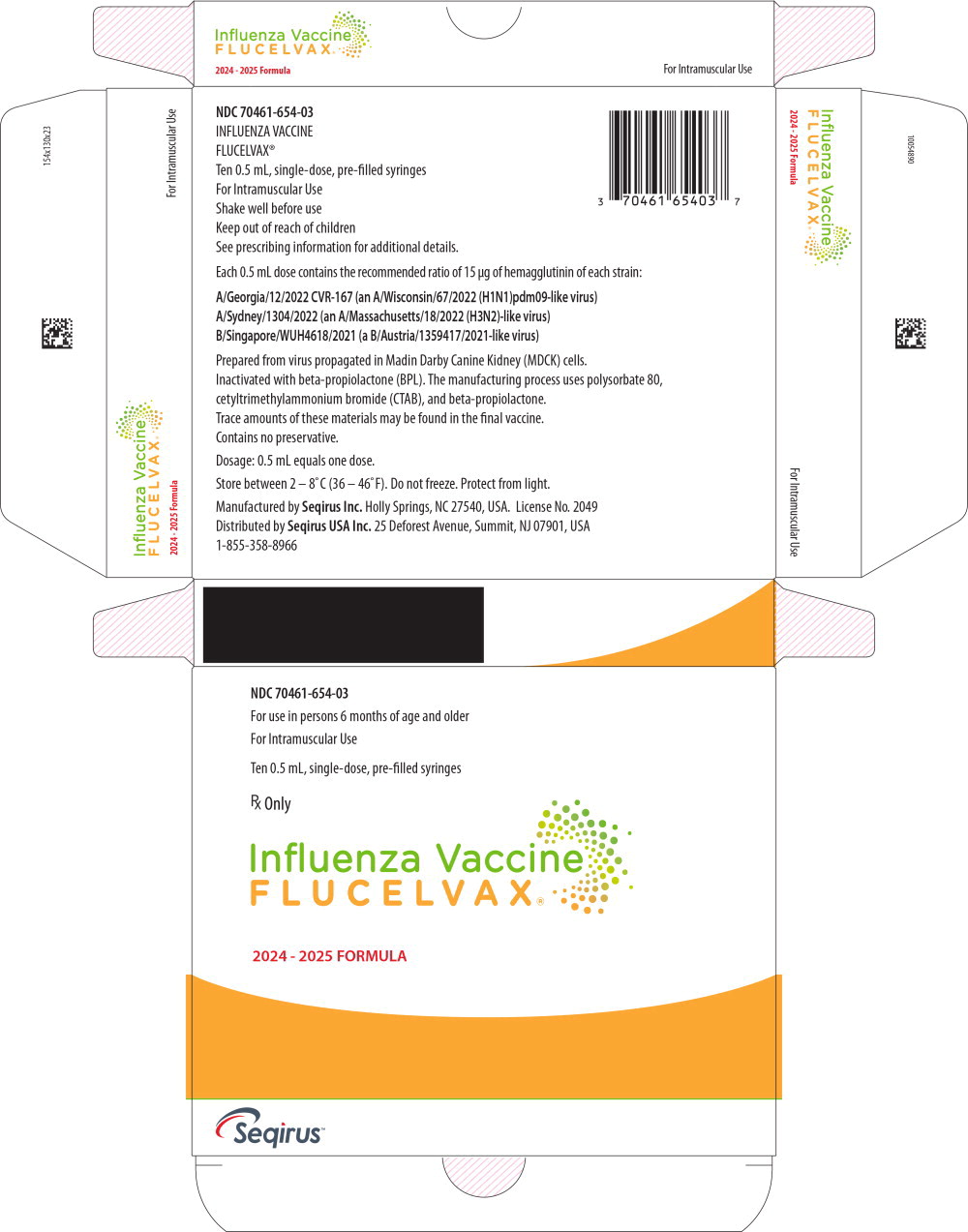
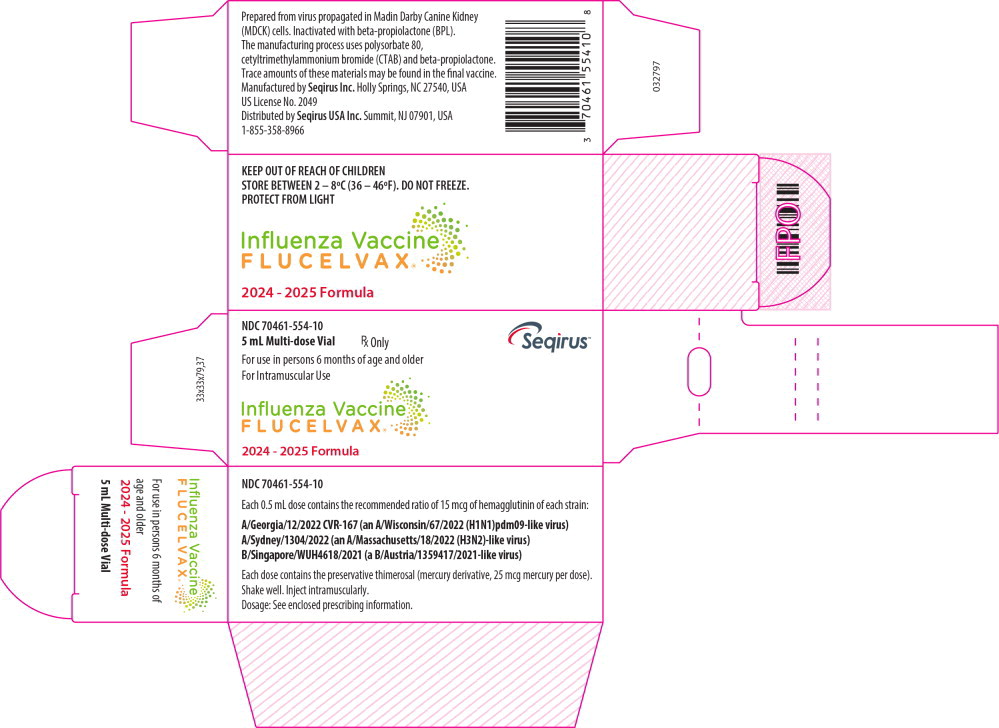
- NDC Code(s): 70461-554-10, 70461-554-11, 70461-654-03, 70461-654-04
- Packager: Seqirus Inc.
- Category: VACCINE LABEL
Drug Label Information
Updated July 1, 2024
If you are a healthcare professional or from the pharmaceutical industry please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use FLUCELVAX® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for FLUCELVAX.
FLUCELVAX (Influenza Vaccine)
Injectable Suspension, for Intramuscular Use
2024-2025 Formula
Initial U.S. Approval: 2012INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For intramuscular use. (2)
a 1 or 2 doses depends on vaccination history as per Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices annual recommendations on prevention and control of influenza with vaccines. (2)
Age Dose Schedule 6 months through 8 years of age One or two dosesa, 0.5 mL each If 2 doses, administer at least 4 weeks apart 9 years of age and older One dose, 0.5 mL Not Applicable DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
FLUCELVAX is an injectable suspension. A single dose is 0.5 mL (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- If Guillain-Barré syndrome has occurred within 6 weeks of receipt of a prior influenza vaccine, the decision to give FLUCELVAX should be based on careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks. (5.1)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Data for FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT are relevant to FLUCELVAX because both vaccines are manufactured using the same process and have overlapping compositions.
- In children 6 months through 3 years of age who received FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT, the most commonly reported injection-site adverse reactions were tenderness (28%), erythema (26%), induration (17%) and ecchymosis (11%). The most common systemic adverse reactions were irritability (28%), sleepiness (27%), diarrhea (18%) and change of eating habits (17%). (6)
- In children 4 through 8 years of age who received FLUCELVAX, the most commonly reported local injection-site adverse reactions were pain (29%) and erythema (11%). The most common systemic adverse reaction was fatigue (10%). (6)
- In children and adolescents 9 through 17 years of age who received FLUCELVAX, the most commonly reported injection-site adverse reactions were pain (34%) and erythema (14%). The most common systemic adverse reactions were myalgia (15%) and headache (14%). (6)
- In adults 18 through 64 years of age who received FLUCELVAX, the most commonly reported injection-site adverse reactions were pain (28%) and erythema (13%). The most common systemic adverse reactions were headache (16%), fatigue (12%), myalgia (11%) and malaise (10%). (6)
- In adults ≥65 years who received FLUCELVAX the most commonly reported injection-site reaction was erythema (10%). The most common systemic adverse reactions were fatigue (11%), headache (10%) and malaise (10%). (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Seqirus at 1-855-358-8966 or VAERS at 1-800-822-7967 or www.vaers.hhs.gov.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Geriatric Use: Antibody responses were lower in adults 65 years and older than in younger adults. (8.5)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 7/2024
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosage and Schedule
2.2 Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Guillain-Barré Syndrome
5.2 Preventing and Managing Allergic Reactions
5.3 Syncope
5.4 Altered Immunocompetence
5.5 Limitations of Vaccine Effectiveness
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Efficacy in Adults
14.2 Efficacy in Children and Adolescents
14.3 Immunogenicity in Adults
14.4 Immunogenicity in Children
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
FLUCELVAX is an inactivated vaccine indicated for active immunization for the prevention of influenza disease caused by influenza virus subtypes A and type B contained in the vaccine. FLUCELVAX is approved for use in persons 6 months of age and older. [see Clinical Studies (14)]
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For intramuscular use.
2.1 Dosage and Schedule
Administer FLUCELVAX as a single 0.5 mL dose.
Table 1: Dosage and Schedule 1 1 or 2 doses depends on vaccination history as per Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices annual recommendations on prevention and control of influenza with vaccines.
Age Dose Schedule 6 months through 8 years
of ageOne or two doses1, 0.5 mL each If 2 doses, administer at least
4 weeks apart9 years of age and older One dose, 0.5 mL Not Applicable 2.2 Administration
Shake the syringe vigorously before administering and shake the multi-dose vial preparation each time before withdrawing a dose of vaccine. FLUCELVAX is a slightly opalescent suspension. Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. If either condition exists, do not administer the vaccine. Between uses, return the multi-dose vial to the recommended storage conditions between 2º and 8ºC (36º and 46ºF). Do not freeze. Discard if the vaccine has been frozen.
Administer FLUCELVAX intramuscularly.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Do not administer FLUCELVAX to anyone with a history of a severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) to any component of the vaccine [see Description (11)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Guillain-Barré Syndrome
If Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) has occurred after receipt of a prior influenza vaccine, the decision to give FLUCELVAX should be based on careful consideration of the potential benefits and risks.
The 1976 swine influenza vaccine was associated with an elevated risk of GBS. Evidence for a causal relation of GBS with other influenza vaccines is inconclusive; if an excess risk exists, it is probably slightly more than 1 additional case per 1 million persons vaccinated.1
5.2 Preventing and Managing Allergic Reactions
Appropriate medical treatment must be immediately available to manage potential anaphylactic reactions following administration of FLUCELVAX.
5.3 Syncope
Syncope (fainting) has been reported following vaccination with FLUCELVAX. Procedures should be in place to avoid injury from fainting.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Data for FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT are relevant to FLUCELVAX because both vaccines are manufactured using the same process and have overlapping compositions.
In children 6 months through 3 years of age who received FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT, the most commonly reported (≥10%) injection-site adverse reactions were tenderness (28%), erythema (26%), induration (17%) and ecchymosis (11%). The most common systemic adverse reactions were irritability (28%), sleepiness (27%), diarrhea (18%) and change of eating habits (17%).
In children 4 through 8 years of age who received FLUCELVAX, the most commonly reported (≥10%) local injection-site adverse reactions were pain (29%) and erythema (11%). The most common systemic adverse reaction was fatigue (10%).
In children and adolescents 9 through 17 years of age who received FLUCELVAX, the most commonly reported (≥10%) injection-site adverse reactions were pain (34%) and erythema (14%). The most common systemic adverse reactions were myalgia (15%) and headache (14%).
In adults 18 through 64 years of age who received FLUCELVAX, the most commonly reported (≥10%) injection-site adverse reactions were pain (28%) and erythema (13%). The most common systemic adverse reactions were headache (16%), fatigue (12%), myalgia (11%) and malaise (10%).
In adults 65 years of age and older who received FLUCELVAX the most commonly reported (≥10%) injection-site reaction was erythema (10%). The most common systemic adverse reactions were fatigue (11%), headache (10%) and malaise (10%).
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a vaccine cannot be directly compared to rates in clinical studies of another vaccine and may not reflect rates observed in clinical practice.
Children and Adolescents 6 months through 17 years of age:
Study 1 (NCT 04074928) was a randomized, observer-blind, multicenter study in children 6 months through 3 years of age. The safety population included a total of 2402 children 6 months through 3 years of age who received FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT (N=1597) or a US-licensed quadrivalent influenza vaccine comparator, AFLURIA QUADRIVALENT (N=805). In the safety population, 894 subjects (37.2%) were 6 months through 23 months of age, and 1508 subjects (62.8%) were 24 months through 47 months of age. The solicited safety set consisted of 2348 subjects who received FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT (N=1564) or a US-licensed quadrivalent influenza vaccine comparator (N=784). Study subjects received one or two doses (separated by 4 weeks) of FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT or the comparator vaccine depending on the subject's prior influenza vaccination history. Data for FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT are relevant to FLUCELVAX because both vaccines are manufactured using the same process and have overlapping compositions.
In this study, solicited local injection site and systemic adverse reactions were collected on a symptom diary card for 7 days following vaccination.
In children 6 months through 3 years of age, the incidence of local and systemic solicited adverse reactions reported by children who received FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT and comparator are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2: Incidence of Solicited Adverse Reactions in the Safety Population1 (6 months through 3 years of age) Reported Within 7 Days of Any Dose of Vaccination (Study 1) Percentage (%)2 of participants Reporting a Reaction Participants 6 through 23 months Participants 24 through 47 months FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT
N=581Comparator3
N=292FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT
N=983Comparator3
N=492Any Gr 3 Any Gr 3 Any Gr 3 Any Gr 3 Abbreviations: Gr 3, Grade 3.
N = number of participants in the Safety Population for each study vaccine group.
1 Solicited Safety Population: participants who were vaccinated and provided any solicited local or systemic adverse reaction safety data on subject diary cards from Day 1 through Day 7 after vaccination.
2 Proportion of participants reporting each solicited local adverse reaction or systemic adverse event by study vaccine group based on the number of participants contributing any follow up safety information for at least one data value of an individual sign/symptom.
3 Comparator: US-Licensed Quadrivalent Influenza vaccine
4 Local adverse reactions: Grade 3 tenderness defined as, “Cried when limb was moved/spontaneously painful” in subjects 6 through 23 months, and “Prevents daily activity” in subjects 24 months and older; Erythema, induration and ecchymosis: any = ≥1mm diameter, Grade 3 => 50 mm diameter.
5 Systemic adverse reactions: Fever: any = ≥ 100.4°F , Grade 3 = ≥ 104.0°F (either rectal, oral, axillary, or tympanic membrane); Grade 3 change of eating habits: Missed more than 2 feeds/meals; Grade 3 sleepiness: Sleeps most of the time and is hard to arouse him/her; Grade 3 vomiting: 6 or more times in 24 hours or requires intravenous hydration; Grade 3 diarrhea: 6 or more loose stools in 24 hours or requires intravenous hydration; Grade 3 irritability: unable to console. Grade 3 for all other adverse reactions is that which prevents daily activity.
The rates of antipyretic or analgesic use reported on the diary card for prophylaxis or treatment of high temperature or pain were as follows: 6 through 23 months of age FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT 20.3%, Comparator 23.6%; 24 through 47 months of age FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT 12.4%, Comparator 13.6%.
Study 1: NCT 04074928
Local Adverse Reactions4 Tenderness 25.5 2.1 23.3 1.4 29.3 2.2 33.9 1.4 Erythema 25.3 0 18.2 0 26.0 0.7 28.5 0 Induration 16.5 0.5 12.0 0 17.7 0.3 18.3 0 Ecchymosis 11.2 0.2 7.5 0 10.5 0.1 12.8 0 Systemic Adverse Reactions5 Irritability 35.1 5.2 35.6 2.1 23.6 1.8 26.0 3.0 Sleepiness 35.5 2.4 30.5 1.7 21.8 1.9 22.6 1.2 Diarrhea 23.2 2.4 20.2 0.7 14.8 1.1 14.0 1.2 Change of eating habits 21.0 1.7 21.9 2.4 15.3 1.4 15.0 1.2 Fever 9.3 0.7 10.3 0 5.4 0.6 4.8 0.2 Vomiting 10.5 0.7 6.8 0.7 4.6 0.5 5.9 0.4 Shivering 3.1 0.2 3.1 0 3.3 0.2 3.7 0 In children who received two doses, the rates of solicited local and systemic adverse reactions were generally similar or lower after the second dose compared to the first dose.
All unsolicited adverse events were collected for 28 days after last vaccination. In children 6 months through 3 years of age, unsolicited adverse events were reported in 26.2% of subjects who received FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT and 25.7% of subjects who received the US-licensed quadrivalent influenza vaccine comparator within 28 days after last vaccination.
In children 6 months through 3 years of age, serious adverse events (SAEs) were collected throughout the study duration (until 6 months after last vaccination) and were reported by 0.9% of the subjects who received FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT and 0.9% of subjects who received the US-licensed quadrivalent influenza vaccine comparator. None of the SAEs were assessed as being related to study vaccine.
Information on the safety of FLUCELVAX administered to 3346 children and adolescents 4 through 17 years of age is available from two multinational, randomized, controlled clinical studies (Studies 2- NCT 00645411 and 3- NCT 01857206). In both studies, children 9 through 17 years of age received a single dose of FLUCELVAX or a US-licensed trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine (FLUVIRIN). In study 2, all children 4 through 8 years of age received two doses of study vaccine separated by 4 weeks. In study 3, children 4 through 8 years of age received one or two doses (separated by 4 weeks) of study vaccine based on determination of the subject's prior influenza vaccination history. Among subjects enrolled in these two studies, the mean age was 8.5 years, 49% were female, and 59% were Caucasian.
Solicited adverse reactions for FLUCELVAX and the comparator trivalent influenza vaccine (FLUVIRIN) for study 2 are summarized in Table 3. In children who received a second dose of FLUCELVAX or the comparator trivalent influenza vaccine (FLUVIRIN), the incidence of adverse reactions following the second dose of vaccine were similar to those observed with the first dose.
Table 3: Solicited Adverse Reactions in the Safety Population1 Reported Within 7 Days of Vaccination with FLUCELVAX (Study 22) 1 Safety population: all subjects in the exposed population who provided post-vaccination safety data.
2 NCT 00645411
3 For children 4 through 8 years of age, data shown are after first dose of vaccination
4 FLUVIRIN (Influenza Virus Vaccine)
5 Severity gradings: For erythema, induration, ecchymosis and swelling: Moderate= 51-≤100 mm; Severe= >100 mm; For pain and systemic adverse reactions: Moderate = some limitation to perform daily activity; Severe = unable to perform daily activity; For fever: Moderate = 39-<40°C; Severe = ≥40°C
Children 4 through 8 Years Adverse Reaction Percentages (%)3 FLUCELVAX
N=1324Comparator4
N=831Any Moderate5 Severe5 Any Moderate5 Severe5 Local adverse reactions Injection site pain 29 4 <1 26 3 1 Erythema 11 <1 0 14 0 0 Induration 6 <1 0 4 0 0 Swelling 4 0 0 5 <1 0 Ecchymosis 6 0 0 6 0 0 Systemic adverse reactions Headache 9 2 1 11 3 <1 Fatigue 10 2 <1 12 2 1 Myalgia 9 2 <1 8 2 <1 Malaise 7 2 1 8 2 1 Chills 3 <1 <1 5 1 <1 Arthralgia 3 <1 0 1 <1 0 Sweating 2 <1 <1 2 1 <1 Fever ≥38°C 2 1 <1 4 1 0 Adverse Reaction Children and Adolescents 9 through 17 Years Percentages (%) FLUCELVAX
N=652Comparator4
N=316Any Moderate5 Severe5 Any Moderate5 Severe5 Local adverse reactions Injection site pain 34 5 <1 38 9 1 Erythema 14 0 0 14 <1 0 Induration 7 <1 0 9 0 0 Swelling 5 <1 0 5 <1 0 Ecchymosis 5 0 0 3 0 0 Systemic adverse reactions Headache 14 3 <1 14 5 1 Fatigue 9 2 1 13 3 1 Myalgia 15 3 <1 19 4 1 Malaise 9 2 1 11 3 1 Chills 4 1 <1 4 <1 <1 Arthralgia 4 <1 <1 5 1 0 Sweating 2 0 0 1 0 <1 Fever ≥38°C 1 <1 0 1 0 0 In studies 2 and 3 combined, the frequencies of unsolicited non-serious adverse events occurring within 28 days of vaccination were present in 32% of subjects who received FLUCELVAX and in 35% of subjects who received a comparator trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine.
One case of erythema multiforme considered related to vaccination with FLUCELVAX occurred in a 5 year old male.
In the two controlled studies in children and adolescents 4 through 17 years of age, serious adverse events were monitored for 6 months after last vaccination. Serious adverse events occurring within 28 days of any vaccination were reported in <1% of subjects (8 of 3345) who received FLUCELVAX, and in <1% of subjects (5 of 1828) who received a comparator trivalent influenza vaccine . No serious adverse events occurring within 6 months post-vaccination were considered related to the study vaccine.
Additional safety data are available from Study 4 (NCT 03165617). Study 4 was a multi-season, multi-national (Australia, Estonia, Finland, Lithuania, Philippines, Poland, Spain, Thailand), randomized, observer-blind study in children and adolescents 2 through 17 years of age. The solicited safety population included a total of 4509 children and adolescents 2 through 17 years of age who received FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT (N=2255) or a non-influenza (meningococcal (Groups A, C, Y, and W-135) oligosaccharide diphtheria CRM197 conjugate) comparator vaccine (N=2254).
Children 2 through 8 years of age received one or two doses (separated by 4 weeks) of FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT or comparator vaccine depending on the subject's prior influenza vaccination history. Children in the 2-dose comparator group received non-influenza comparator as the first dose and saline placebo as the second dose. Children and adolescents 9 through 17 years of age received a single dose of FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT or non-influenza comparator vaccine.
In this study, serious adverse events (SAEs) were collected throughout the study duration (until 6 months after last vaccination) and were reported by 1.1% of the children and adolescents who received FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT. None of the SAEs were assessed as being related to study vaccine.
Adults 18 years of age and older:
The safety of FLUCELVAX was evaluated in seven randomized, controlled studies conducted in the US, Europe and New Zealand (Study 5: NCT 00630331, Study 6: NCT 00492063, Study 7: NCT 00306527, Study 8: NCT 00264576, Study 9: NCT 00310804, Study 10: NCT number not assigned, Study 11: NCT number not assigned). The safety population includes 5709 adults 18 through 64 years of age and 572 adults 65 years of age and older administered FLUCELVAX.
In all studies, solicited local injection site and systemic adverse reactions were collected from subjects who completed a symptom diary card for 7 days following vaccination.
One of the seven clinical trials, Study 5 (NCT 00630331) was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study that evaluated three vaccines including: FLUCELVAX (N=3813), placebo (N=3894) and another influenza vaccine. The population was 18 through 49 years of age (mean 32.8 years), 55% were female and 84% were Caucasian. Solicited adverse reactions for FLUCELVAX and placebo are summarized in Table 4.
Table 4: Solicited Adverse Reactions in the Safety Population2 Reported Within 7 Days of Vaccination with FLUCELVAX (Study 51) 1 NCT 00630331
2 Safety population: all subjects in the exposed population who provided post vaccination safety data.
3 Placebo: 0.5 mL Phosphate Buffered Saline
Adults 18 through 49 Years Percentages (%) FLUCELVAX
N=3813Placebo3
N=3894Local adverse reactions Injection site pain 30 10 Erythema 13 10 Induration 6 3 Swelling 6 3 Ecchymosis 4 4 Systemic adverse reactions Headache 15 15 Fatigue 10 10 Myalgia 12 7 Malaise 8 6 Chills 6 6 Arthralgia 3 3 Sweating 3 3 Fever (≥38o C) 1 <1 Study 6 (NCT 00492063) was a randomized, double-blind study comparing FLUCELVAX (N=1330) to AGRIFLU, a US-licensed trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine (N=1324) in adults 18 years of age or older. The mean age was 43.7 years of age for adults 18 through 64 years of age and 71.3 years of age for adults 65 years of age and older; 57% of subjects were female and 100% were Caucasian. The safety data observed are summarized in Table 5.
Table 5: Solicited Adverse Reactions in the Safety Population1 Reported Within 7 Days of Vaccination with FLUCELVAX (Study 62) 1 Safety population: all subjects in the exposed population who provided post-vaccination safety data.
2 NCT 00492063
3 AGRIFLU (Influenza Virus Vaccine)
Adults 18 through 64 Years Adults 65 Years of Age and Older Percentages (%) FLUCELVAX
N=821Comparator3
N=841FLUCELVAX
N=509Comparator3
N=483Local adverse reactions Injection site pain 20 15 8 4 Erythema 14 15 10 11 Induration 6 6 5 4 Swelling 4 4 4 2 Ecchymosis 3 3 4 4 Systemic adverse reactions Headache 12 11 10 11 Fatigue 11 11 11 13 Myalgia 7 8 6 8 Malaise 11 11 10 11 Chills 4 4 3 4 Arthralgia 5 5 6 7 Sweating 5 4 7 8 Fever (≥38o C) 1 1 <1 1 Unsolicited adverse events, including serious adverse events (SAEs), were collected for 21 days after vaccination in five studies. In adults 18 through 64 years of age (N=4038), 13% (284 out of 2266) of subjects who received FLUCELVAX and 13% (224 out of 1772) of subjects who received the comparator trivalent influenza vaccine (AGRIFLU) reported at least one unsolicited adverse event within 21 days after vaccination. The most commonly reported unsolicited adverse events after FLUCELVAX vaccination were rhinitis (3%), headache (2%) and oropharyngeal pain (2%). In adults 65 years of age and older (N=2013), 11% (110 out of 997) of subjects who received FLUCELVAX and 9% (95 out of 1016) of subjects who received the comparator trivalent influenza vaccine (AGRIFLU) reported at least one unsolicited adverse event within 21 days after vaccination. Within this age group, the most commonly reported unsolicited adverse events after FLUCELVAX vaccination were rhinitis (3%) and cough (2%). In both age groups, all other unsolicited adverse events were reported in 1% or fewer subjects.
In the seven controlled studies of FLUCELVAX, serious adverse events were collected for a duration of 21 days in two studies and for a duration of 6 to 9 months in five studies. Participants in Study 6 were revaccinated with FLUCELVAX or AGRIFLU in Study 7. Across the seven controlled studies, the rates per dose of serious adverse events among adults 18 through 64 years of age were 1% (84 out of 6388 doses) for FLUCELVAX, 1% (55 out of 5745 doses) for the comparator trivalent influenza vaccine (AGRIFLU) and 1% (37 out of 3894 doses) for placebo. The rates per dose of serious adverse events among adults 65 years of age and older were 4% (36 out of 997 doses) for FLUCELVAX and 4% (44 out of 1016 doses) for the comparator trivalent influenza vaccine (AGRIFLU).
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse events have been identified during post-approval use of FLUCELVAX or FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to the vaccine.
Immune system disorders: Allergic or immediate hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic shock.
Nervous systems disorders: Syncope, presyncope, paresthesia, Guillain-Barré syndrome.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: Generalized skin reactions including pruritus, urticaria or non-specific rash.
General disorders and administration site conditions: Extensive swelling of injected limb.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
All pregnancies have a risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the US general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively. Data collected in a prospective Pregnancy Exposure Registry from 665 women vaccinated with FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT showed no evidence of a vaccine-associated increase in the risk of major birth defects and miscarriages when FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT is administered during any trimester of pregnancy (see Data). Data for FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT are relevant to FLUCELVAX because both vaccines are manufactured using the same process and have overlapping compositions.
A developmental toxicity study has been performed in female rabbits administered FLUCELVAX prior to mating and during gestation. The dose was 0.5 mL on each occasion (a single human dose is 0.5 mL). This study revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus due to FLUCELVAX.
Disease-associated Maternal and/or Embryo-Fetal Risk
Pregnant women are at increased risk for severe illness due to influenza compared to non-pregnant women. Pregnant women with influenza may be at increased risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes, including preterm labor and delivery.
Human Data
Data from a prospective Pregnancy Exposure Registry in the US were collected from women vaccinated with FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT during 3 Northern Hemisphere influenza seasons (2017-18 through 2019-20) and there was no evidence of a vaccine-associated increase in the risk of major birth defects and miscarriages. A total of 665 pregnancy outcomes were reported, of which 27%, 42%, and 31% of the pregnancies were exposed to FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT during the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd trimester, respectively; 659 resulted in live births, 4 resulted in spontaneous pregnancy loss, 1 resulted in ectopic pregnancy, 1 resulted in elective pregnancy termination and there were no stillbirths. The prevalence rates for miscarriage and major birth defects assessed at time of birth were each 1.9% from the study. These rates of assessed outcomes in the prospective population were consistent with estimated background rates.
Animal Data
In a developmental toxicity study, female rabbits were administered FLUCELVAX by intramuscular injection 1, 3, and 5 weeks prior to mating, and on gestation days 7 and 20. The dose was 0.5 mL on each occasion (a single human dose is 0.5 mL). No vaccine-related fetal malformations or variations and no adverse effects on pre-weaning development or on female fertility were observed in the study.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
It is not known whether FLUCELVAX is excreted in human milk. Data are not available to assess the effects of FLUCELVAX on the breastfed infant or on milk production/excretion.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for FLUCELVAX and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from FLUCELVAX or from the underlying maternal condition. For preventive vaccines, the underlying maternal condition is susceptibility to disease prevented by the vaccine or the effects on milk production.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness have not been established in children less than 6 months of age.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the total number of subjects who received one dose of FLUCELVAX in clinical studies and included in the safety population (6281), 9% (572) were 65 years of age and older and 2% (140) were 75 years of age or older.
Antibody responses to FLUCELVAX were lower in the geriatric (adults 65 years and older) population than in younger adults.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
FLUCELVAX (Influenza Vaccine) is a trivalent subunit influenza vaccine manufactured using cell derived candidate vaccine viruses (CVV) that are propagated in Madin Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) cells, a continuous cell line. These cells were adapted to grow freely in suspension in culture medium. The virus is inactivated with β-propiolactone, disrupted by the detergent cetyltrimethylammonium bromide and purified through several process steps. Each of the virus strains are produced and purified separately then pooled to formulate the vaccine.
FLUCELVAX is a sterile, slightly opalescent injectable suspension in phosphate buffered saline. FLUCELVAX is standardized according to United States Public Health Service requirements for the 2024-2025 influenza season and is formulated to contain a total of 45 micrograms (mcg) hemagglutinin (HA) per 0.5 mL dose in the recommended ratio of 15 mcg HA of each of the following influenza strains:
A/Georgia/12/2022 CVR-167 (an A/Wisconsin/67/2022 (H1N1)pdm09-like virus);
A/Sydney/1304/2022 (an A/Massachusetts/18/2022 (H3N2)-like virus);
B/Singapore/WUH4618/2021 (a B/Austria/1359417/2021-like virus).
Each dose of FLUCELVAX may contain residual amounts of MDCK cell protein (≤ 21.6 mcg), protein other than HA (≤ 225 mcg), MDCK cell DNA (≤ 10 ng), polysorbate 80 (≤ 1125 mcg), cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (≤ 13.5 mcg), and β-propiolactone (< 0.5 mcg), which are used in the manufacturing process.
FLUCELVAX contains no egg protein or antibiotics.
FLUCELVAX 0.5 mL pre-filled syringes contain no preservative.
FLUCELVAX 5 mL multi-dose vials contain thimerosal, a mercury derivative, added as a preservative. Each 0.5 mL dose from the multi-dose vial contains 25 mcg mercury.
The tip caps and plungers of the pre-filled syringes and the multi-dose vial stopper are not made with natural rubber latex.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Specific levels of hemagglutination inhibition (HI) antibody titers induced by vaccination with inactivated influenza virus vaccine have not been correlated with protection from influenza illness. In some studies, HI antibody titers of ≥ 1:40 have been associated with protection from influenza illness in up to 50% of adults.2,3
Antibody against one influenza virus type or subtype confers little or no protection against another. Furthermore, antibody to one antigenic variant of influenza virus might not protect against a new antigenic variant of the same type or subtype. Frequent development of antigenic variants through antigenic drift is the virologic basis for seasonal epidemics and the reason for the usual change of one or more strains in each year's influenza vaccine.
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Efficacy in Adults
A multinational (US, Finland, and Poland), randomized, observer-blind, placebo-controlled trial was performed to assess clinical efficacy and safety of FLUCELVAX during the 2007-2008 influenza season in adults aged 18 through 49 years (Study 5). A total of 11,404 adults were enrolled to receive FLUCELVAX (N=3828), AGRIFLU (N=3676) or placebo (N=3900) in a 1:1:1 ratio. Among the overall study population enrolled, the mean age was 33 years, 55% were female, 84% were Caucasian, 7% were Black, 7% were Hispanic, and 2% were of other ethnic origin.
FLUCELVAX efficacy was assessed by the prevention of culture-confirmed symptomatic influenza illness caused by viruses antigenically matched to those in the vaccine and prevention of influenza illness caused by all influenza viruses compared to placebo. Influenza cases were identified by active and passive surveillance of influenza-like illness (ILI). ILI was defined as a fever (oral temperature ≥ 100.0°F / 38°C) and cough or sore throat. Nose and throat swab samples were collected for analysis within 120 hours of onset of an influenza-like illness in the period from 21 days to 6 months after vaccination. Overall vaccine efficacy against all influenza viral subtypes and vaccine efficacy against individual influenza viral subtypes were calculated (Tables 6 and 7, respectively).
Table 6: Vaccine Efficacy against Culture-Confirmed Influenza in Participants aged 18 through 49 years (Study 5) 1 Efficacy against influenza was evaluated over a 9-month period in 2007/2008
2 Simultaneous one-sided 97.5% confidence intervals for the vaccine efficacy (VE) of FLUCELVAX relative to placebo based on the Sidak-corrected score confidence intervals for the relative risk. Vaccine Efficacy = (1 - Relative Risk) x 100 %
3 VE success criterion: the lower limit of the one-sided 97.5% CI for the estimate of the VE relative to placebo is > 40%
Study 5: NCT00630331
Number of participants per protocol Number of participants with influenza Attack Rate
(%)Vaccine Efficacy (VE)1,2 % Lower Limit of One-
Sided 97.5% CI of VE2,3Antigenically Matched Strains FLUCELVAX 3776 7 0.19 83.8 61.0 Placebo 3843 44 1.14 -- -- All Culture-Confirmed Influenza FLUCELVAX 3776 42 1.11 69.5 55.0 Placebo 3843 140 3.64 -- -- Table 7: Efficacy of FLUCELVAX against Culture-Confirmed Influenza by Influenza Viral Subtype in Participants aged 18 through 49 years (Study 5) 1 No VE success criterion was prespecified in the protocol for each individual influenza virus subtype.
2 Simultaneous one-sided 97.5% confidence intervals for the vaccine efficacy (VE) of FLUCELVAX relative to placebo based on the Sidak-corrected score confidence intervals for the relative risk. Vaccine Efficacy = (1 - Relative Risk) x 100 %.
3 There were too few cases of influenza due to vaccine-matched influenza A/H3N2 or B to adequately assess vaccine efficacy.
Study 5: NCT00630331
FLUCELVAX
(N=3776)Placebo
(N=3843)Vaccine Efficacy (VE)2 Attack Rate
(%)Number of Participants with Influenza Attack Rate
(%)Number of Participants with Influenza % Lower Limit of One-Sided 97.5% CI of VE1,2 Antigenically Matched Strains A/H3N23 0. 05 2 0 0 -- -- A/H1N1 0.13 5 1.12 43 88.2 67.4 B3 0 0 0.03 1 -- -- All Culture-Confirmed Influenza A/H3N2 0.16 6 0.65 25 75.6 35.1 A/H1N1 0.16 6 1.48 57 89.3 73.0 B 0.79 30 1.59 61 49.9 18.2 14.2 Efficacy in Children and Adolescents
Absolute efficacy of FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT was evaluated in children and adolescents 2 through 17 years of age in Study 4. This was a multinational, randomized, non-influenza vaccine comparator-controlled efficacy, immunogenicity and safety study conducted in 8 countries during the following 3 influenza seasons: Southern Hemisphere 2017, Northern Hemisphere 2017/2018 and Northern Hemisphere 2018/2019. The study enrolled 4514 children and adolescents. Out of the 4514 enrolled, 4513 received either FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT (N=2258) or a non-influenza (meningococcal (Groups A, C, Y, and W-135) oligosaccharide diphtheria CRM197 conjugate) comparator vaccine (N=2255). The full analysis set (FAS) for efficacy consisted of 4509 children and adolescents. Data for FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT are relevant to FLUCELVAX because both vaccines are manufactured using the same process and have overlapping compositions.
Children 2 through 8 years of age received either one or two doses (separated by 4 weeks) of FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT or comparator vaccine depending on the subject's prior influenza vaccination history. Children in the 2-dose comparator group received non-influenza comparator as the first dose and saline placebo as the second dose. Children and adolescents 9 through 17 years of age received a single dose of FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT or non-influenza comparator vaccine. Among all enrolled children and adolescents (N=4514), the mean age was 8.8 years, 48% were female, 51% were 2 through 8 years of age, 50% were Caucasian and 49% were Asian. There were no notable differences in the distribution of demographic and baseline characteristics between the two treatment groups.
FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT efficacy was assessed by the prevention of confirmed influenza illness caused by any influenza Type A or B strain. Influenza cases were identified by active and passive surveillance of influenza-like illness (ILI) and confirmed by cell culture and/or real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). ILI was defined as a fever (oral temperature ≥ 100.0°F / 37.8°C) along with any of the following: cough, sore throat, nasal congestion, or rhinorrhea. The overall vaccine efficacy for the entire study population (2 through 17 years) was 54.6% (95% CI 45.7 – 62.1), which met predefined success criteria. In addition, vaccine efficacy was 50.5% (95% CI 38.4 – 60.2) in children 2 through 8 years of age and 61.9% (95% CI 47.4 – 72.3) in those 9 through 17 years of age. Vaccine efficacy against all influenza viral subtypes and against individual influenza viral subtypes antigenically similar to the subtypes in the vaccine were calculated (Table 8).
Table 8: Efficacy of FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT Against First Occurrence RT-PCR Confirmed or Culture Confirmed Influenza in Participants 2 through 17 years of age – FAS Efficacy1 (Study 4). Number of participants per protocol1 Number of cases of influenza Attack Rate
(%)Vaccine Efficacy (VE)2 VE % 95% Confidence Interval3 1 Number of participants in the Full-Analysis Set (FAS) – Efficacy, which included all participants randomized, received a study vaccination and provided efficacy data
2 Efficacy against influenza was evaluated over three influenza seasons, SH 2017, NH 2017-18 and NH 2018-19
3 FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT met the pre-defined success criterion defined as the lower limit of the two-sided 95% CI of absolute vaccine efficacy greater than 20%
4 Non-Influenza Comparator: (MENVEO, meningococcal (Groups A, C, Y, and W-135) oligosaccharide diphtheria CRM197 conjugate vaccine, GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals SA); children assigned to 2 doses received saline placebo as the second dose.
Study 4: NCT03165617
RT-PCR or Culture Confirmed Influenza FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT 2257 175 7.8 54.6 45.7 - 62.1 Non-Influenza Comparator4 2252 364 16.2 - - Culture Confirmed Influenza FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT 2257 115 5.1 60.8 51.3 - 68.5 Non-Influenza Comparator4 2252 279 12.4 - - Antigenically Matched Culture-Confirmed Influenza FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT 2257 90 4.0 63.6 53.6 - 71.5 Non-Influenza Comparator4 2252 236 10.5 - - 14.3 Immunogenicity in Adults
Immunogenicity in adults 18 years of age and older was evaluated in clinical Study 6, a randomized, active controlled, multicenter study conducted in Poland during the 2004-05 Northern Hemisphere influenza season. In this study, immunogenicity was assessed 3 weeks after vaccination in 2640 subjects who received either FLUCELVAX (N=1322) or the egg-based trivalent influenza comparator, AGRIFLU (N=1318). Among the overall study population enrolled, 59% were female, 100% of subjects were Caucasian, and the mean age was 43.6 years.
In study 6, non-inferiority of FLUCELVAX to AGRIFLU was demonstrated for HI antibody responses to all three strains for both post-vaccination geometric mean titre (GMT) ratios and seroconversion rates. Success for non-inferiority of the GMT ratio was defined as the lower limit of the two-sided 95% CI for GMT ratio (FLUCELVAX / AGRIFLU) was >0.67; and success for non-inferiority of seroconversion rate was defined as the lower limit of the two-sided 95% CI for the difference between the seroconversion rates (FLUCELVAX – AGRIFLU) was >-10%) (Table 9).
Table 9: Non-inferiority Analysis of FLUCELVAX to a US-Licensed Comparator in Adults 18 through 49 Years and 50 through 64 Years of Age (Study 61) 1 NCT00492063
2 AGRIFLU (Influenza Virus Vaccine)
3 Non inferiority was demonstrated if the lower limit of the two-sided 95% confidence interval (CI) for geometric mean titer (GMT) ratio (FLUCELVAX/AGRIFLU) was >0.67.
4 Egg derived antigen hemagglutination inhibition (HI) assay results
5 Rates of seroconversion = percentage of subjects with either a pre-vaccination HI titer < 1:10 and a post-vaccination HI titer ≥ 1:40 or a pre-vaccination HI titer ≥ 1:10 and at least a four-fold rise in post-vaccination HI antibody titer
6 Non inferiority was demonstrated if the lower limit of two-sided 95% confidence interval (CI) for difference in percentages of subjects with seroconversion (FLUCELVAX – AGRIFLU) was >-10%.
Ratio or Difference
(95% CI)
FLUCELVAX Versus Comparator2A/H1N1 A/H3N2 B Subjects 18 through 49 Years: N FLUCELVAX=478; N comparator=472 GMTs ratio3,4
(FLUCELVAX / AGRIFLU)0.96
(0.81, 1.13)0.98
(0.87, 1.11)1.07
(0.93, 1.23)Difference in Seroconversion Rates4,5,6
(FLUCELVAX – AGRIFLU)2%
(-4, 8)2%
(-5, 8)5%
(1, 10)Subjects 50 through 64 Years: N FLUCELVAX=340; N comparator=365 GMTs ratio3,4
(FLUCELVAX / AGRIFLU)0.96
(0.79, 1.16)0.87
(0.74, 1.02)1.23
(1.02, 1.48)Difference in Seroconversion Rates4,5,6
(FLUCELVAX – AGRIFLU)1%
(-6, 8)-2%
(-9, 5)3%
(-4, 9)Non-inferiority of FLUCELVAX to AGRIFLU was demonstrated for HI antibody responses to all three strains for both post-vaccination GMT ratios and seroconversion rates. Success for non-inferiority of the GMT ratio was defined as the lower limit of the two-sided 95% CI for the GMT ratio (FLUCELVAX / AGRIFLU) >0.67; and success for non-inferiority of seroconversion rate was defined as the lower limit of the two-sided 95% CI for the difference between the seroconversion rates (FLUCELVAX – AGRIFLU) >-10%) (Table 10).
Table 10: Non-inferiority Analysis of FLUCELVAX to a US-Licensed Comparator in Adults 65 Years of Age and Older (Study 61) 1 NCT 00492063
2 AGRIFLU (Influenza Virus Vaccine)
3 Non inferiority was demonstrated if the lower limit of the two-sided 95% confidence interval (CI) for geometric mean titer (GMT) ratio (FLUCELVAX/AGRIFLU) was >0.67.
4 Egg derived antigen hemagglutination inhibition (HI) assay results
5 Rates of seroconversion = percentage of subjects with either a pre-vaccination HI titer < 1:10 and a post-vaccination HI titer ≥ 1:40 or a pre-vaccination HI titer ≥ 1:10 and at least a four-fold rise in post-vaccination HI antibody titer
6 Non inferiority was demonstrated if the lower limit of the two-sided 95% confidence interval (CI) for difference in percentages of subjects with seroconversion (FLUCELVAX – AGRIFLU) was >-10%.
Ratio or Difference (95% CI)
FLUCELVAX Versus Comparator2
(N FLUCELVAX=504; N comparator=481)A/H1N1 A/H3N2 B GMTs ratio3,4
(FLUCELVAX / AGRIFLU)1.06
(0.92, 1.22)0.97
(0.84, 1.12)1.28
(1.1, 1.48)Difference in Seroconversion Rates4,5,6
(FLUCELVAX – AGRIFLU)-1%
(-7, 6)3%
(-2, 9)7%
(1, 12)14.4 Immunogenicity in Children
Immunogenicity in children 6 months through 3 years of age was evaluated in a randomized, observer-blind, multicenter study conducted in the US (Study 1). In this study, subjects received FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT or a US-licensed comparator quadrivalent influenza vaccine (FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT N=1597, Comparator QUADRIVALENT (QIV) N=805). In the per protocol set, the mean age of subjects who received FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT was 29 months; 49% of subjects were female and 67% of subjects were Caucasian, 27% were Black and < 1% were Asian, Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander and American Indian or Alaska Native. Twenty six percent of subjects were of Hispanic origin. The immune response to each of the vaccine antigens was assessed 28 days after last vaccination.
The immunogenicity endpoints were geometric mean antibody titers (GMTs) and percentage of subjects who achieved seroconversion, defined as a pre-vaccination HI or microneutralization (MN) titer of < 1:10 with a post-vaccination titer ≥ 1:40 or with a pre-vaccination HI or MN titer ≥ 1:10 and a minimum 4-fold increase in serum antibody titer. GMTs and seroconversion rates were measured by hemagglutination inhibition (HI) assay for A/H1N1, B/Yamagata and B/Victoria strains and by microneutralization (MN) assay for the A/H3N2 strain.
FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT was noninferior to the Comparator QIV. Noninferiority was established for all 4 influenza strains as assessed by ratios of GMTs and the differences in the percentages of subjects achieving seroconversion at 4 weeks following vaccination.
The noninferiority data observed are summarized in Table 11.
Table 11: Noninferiority1 of FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT Relative to Comparator QIV in Children 6 Months through 3 Years of Age – Per-Protocol Analysis Set2 (Study 1) Abbreviations: GMT = geometric mean titer. CI = confidence interval.
Assays: GMTs and seroconversion rates were measured by hemagglutination inhibition (HI)* assay for A/H1N1, B/Yamagata and B/Victoria strains and by microneutralization (MN)# assay for the A/H3N2 strain, using cell-derived target viruses. The MN assay was used for A/H3N2 as circulating strains indicated a reduced ability to agglutinate red blood cells. FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT was noninferior to the Comparator QIV irrespective of the assay used. HI assay data for A/H3N2: GMT (95%CI) for FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT (N=1089) = 288.1 (261.46, 317.54), Comparator QIV (N=575) = 227.6 (201.87, 256.58), Vaccine group ratio (95%CI) = 0.79 (0.69, 0.90), Seroconversion rate (95%CI) for FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT (N=1089) = 72.27% (69.51,74.91), Comparator QIV (N=575) = 64.52% (60.46, 68.44), Vaccine Group Difference (95%CI) = -7.75% (-12.51, -3.06).
Success criteria: The upper bound of the two-sided 95% confidence interval (CI) on the ratio of the GMTs (calculated as GMT US-licensed comparator QIV divided by GMT FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT) does not exceed 1.5. The upper bound of the two-sided 95% CI on the difference between the seroconversion rates (calculated as Seroconversion rate US-licensed comparator QIV minus Seroconversion rate FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT) does not exceed 10%.
1 Analyses are performed on data for Day 29 for previously vaccinated subjects and Day 57 for not previously vaccinated subjects.
2 Per protocol set: All participants in Full Analysis Set, immunogenicity population, who have correctly received the assigned vaccine, have no major protocol deviations leading to exclusion as defined prior to unblinding/ analysis and are not excluded due to other reasons defined prior to unblinding or analysis.
3 Seroconversion rate = percentage of subjects with either a pre-vaccination titer < 1:10 and post-vaccination titer ≥ 1:40 or with a pre-vaccination titer ≥ 1:10 and a minimum 4-fold increase in post-vaccination antibody titer
Study 1: NCT 04074928
FLUCELVAX
QUADRIVALENTComparator
QIVVaccine Group Ratio Vaccine Group Difference A/H1N1* N=1092 N=575 GMT (95% CI) 78.0
(70.75, 86.03)57.3
(50.76, 64.63)0.73
(0.65, 0.84)- Seroconversion Rate3 (95% CI) 58.24%
(55.25, 61.19)46.78%
(42.64, 50.96)- -11.46
(-16.45, -6.42)A/H3N2# N = 1078 N = 572 GMT (95% CI) 23.1
(21.21, 25.12)23.9
(21.57, 26.57)1.04
(0.93, 1.16)- Seroconversion Rate3 (95% CI) 27.64%
(24.99, 30.42)30.77%
(27.01, 34.73)- 3.13
(-1.44, 7.81)B/Yamagata* N = 1092 N = 575 GMT (95% CI) 35.6
(32.93, 38.58)26.0
(23.54, 28.63)0.73
(0.66, 0.81)- Seroconversion Rate3 (95% CI) 46.52%
(43.53, 49.53)31.65%
(27.87, 35.63)- -14.87
(-19.61, -9.98)B/Victoria* N = 1092 N = 575 GMT (95% CI) 22.4
(20.70, 24.19)19.6
(17.81, 21.58)0.88
(0.79, 0.97)- Seroconversion Rate3 (95% CI) 30.31%
(27.60, 33.13)24.35%
(20.89, 28.07)- -5.96
(-10.33, -1.44) -
15 REFERENCES
- Lasky T, Terracciano GJ, Magder L, et al. The Guillain-Barré syndrome and the 1992-1993 and 1993-1994 influenza vaccines. N Engl J Med 1998; 339(25):1797-1802.
- Hannoun C, Megas F, Piercy J. Immunogenicity and protective efficacy of influenza vaccination. Virus Res 2004; 103:133-138.
- Hobson D, Curry RL, Beare A, et al. The role of serum hemagglutinin-inhibiting antibody in protection against challenge infection with influenza A2 and B viruses. J Hyg Camb 1972; 767-777.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
FLUCELVAX product presentations are listed in Table 12 below:
Table 12: FLUCELVAX Product Presentations Presentation Carton NDC Number Components Pre-filled Syringe 70461-654-03 0.5 mL single dose pre-filled syringe, package of 10 syringes per carton [NDC 70461-654-04] Multi-dose Vial 70461-554-10 5 mL multi-dose vial, individually packaged in a carton [NDC 70461-554-11] Store this product refrigerated at 2°C to 8°C (36ºF to 46ºF). Between uses, return the multi-dose vial to the recommended storage conditions. Do not freeze. Protect from light. Do not use after the expiration date.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Inform vaccine recipients of the potential benefits and risks of immunization with FLUCELVAX.
Educate vaccine recipients regarding the potential side effects; clinicians should emphasize that (1) FLUCELVAX contains non-infectious particles and cannot cause influenza and (2) FLUCELVAX is intended to provide protection against illness due to influenza viruses only and cannot provide protection against other respiratory illnesses.
Instruct vaccine recipients to report adverse reactions to their healthcare provider.
Provide vaccine recipients with the Vaccine Information Statements which are required by the National Childhood Vaccine Injury Act of 1986. These materials are available free of charge at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website (www.cdc.gov/vaccines).
Inform vaccine recipients that annual vaccination is recommended.
FLUCELVAX and FLUCELVAX QUADRIVALENT are registered trademarks of Seqirus UK Limited or its affiliates.
Manufactured by: Seqirus Inc. Holly Springs, NC 27540, USA
US License No. 2049
Distributed by: Seqirus USA Inc. 25 Deforest Avenue, Summit, NJ 07901, USA
1-855-358-8966
- Principal Display Panel – 0.5 mL Carton Label
- Principal Display Panel – 0.5 mL Syringe Label
- Principal Display Panel – 5 mL Carton Label
- Principal Display Panel – 0.5 mL Vial Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
FLUCELVAX
influenza a virus a/georgia/12/2022 cvr-167 (h1n1) antigen (mdck cell derived, propiolactone inactivated), influenza a virus a/sydney/1304/2022 (h3n2) antigen (mdck cell derived, propiolactone inactivated), influenza b virus b/singapore/wuh4618/2021 antigen (mdck cell derived, propiolactone inactivated) injection, suspensionProduct Information Product Type VACCINE Item Code (Source) NDC:70461-654 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength INFLUENZA A VIRUS A/Georgia/12/2022 CVR-167 (H1N1) ANTIGEN (MDCK CELL DERIVED, PROPIOLACTONE INACTIVATED) (UNII: B8P3XN76W4) (INFLUENZA A VIRUS A/Georgia/12/2022 CVR-167 (H1N1) HEMAGGLUTININ ANTIGEN (MDCK CELL DERIVED, PROPIOLACTONE INACTIVATED) - UNII:N8JKS3VK2A) INFLUENZA A VIRUS A/Georgia/12/2022 CVR-167 (H1N1) HEMAGGLUTININ ANTIGEN (MDCK CELL DERIVED, PROPIOLACTONE INACTIVATED) 15 ug in 0.5 mL INFLUENZA A VIRUS A/Sydney/1304/2022 (H3N2) ANTIGEN (MDCK CELL DERIVED, PROPIOLACTONE INACTIVATED) (UNII: 2DVY566JY6) (INFLUENZA A VIRUS A/SYDNEY/1304/2022 HEMAGGLUTININ ANTIGEN (MDCK CELL DERIVED, PROPIOLACTONE INACTIVATED) - UNII:5CH2Y25VXX) INFLUENZA A VIRUS A/SYDNEY/1304/2022 HEMAGGLUTININ ANTIGEN (MDCK CELL DERIVED, PROPIOLACTONE INACTIVATED) 15 ug in 0.5 mL INFLUENZA B VIRUS B/Singapore/WUH4618/2021 ANTIGEN (MDCK CELL DERIVED, PROPIOLACTONE INACTIVATED) (UNII: TUE3AGP9ME) (INFLUENZA B VIRUS B/Singapore/WUH4618/2021 HEMAGGLUTININ ANTIGEN (MDCK CELL DERIVED, PROPIOLACTONE INACTIVATED) - UNII:C76JLA4DM6) INFLUENZA B VIRUS B/Singapore/WUH4618/2021 HEMAGGLUTININ ANTIGEN (MDCK CELL DERIVED, PROPIOLACTONE INACTIVATED) 15 ug in 0.5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength POTASSIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 660YQ98I10) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) MAGNESIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 02F3473H9O) SODIUM PHOSPHATE, DIBASIC, DIHYDRATE (UNII: 94255I6E2T) POTASSIUM PHOSPHATE, MONOBASIC (UNII: 4J9FJ0HL51) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:70461-654-03 10 in 1 CARTON 1 NDC:70461-654-04 0.5 mL in 1 SYRINGE, GLASS; Type 3: Prefilled Biologic Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA125408 07/01/2024 07/31/2025 FLUCELVAX
influenza a virus a/georgia/12/2022 crv-167 (h1n1) antigen (mdck cell derived, propiolactone inactivated), influenza a virus a/sydney/1304/2022 (h3n2) antigen (mdck cell derived, propiolactone inactivated), influenza b virus b/singapore/wuh4618/2021 antigen (mdck cell derived, propiolactone inactivated) injection, suspensionProduct Information Product Type VACCINE Item Code (Source) NDC:70461-554 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength INFLUENZA A VIRUS A/Georgia/12/2022 CVR-167 (H1N1) ANTIGEN (MDCK CELL DERIVED, PROPIOLACTONE INACTIVATED) (UNII: B8P3XN76W4) (INFLUENZA A VIRUS A/Georgia/12/2022 CVR-167 (H1N1) HEMAGGLUTININ ANTIGEN (MDCK CELL DERIVED, PROPIOLACTONE INACTIVATED) - UNII:N8JKS3VK2A) INFLUENZA A VIRUS A/Georgia/12/2022 CVR-167 (H1N1) HEMAGGLUTININ ANTIGEN (MDCK CELL DERIVED, PROPIOLACTONE INACTIVATED) 15 ug in 0.5 mL INFLUENZA A VIRUS A/Sydney/1304/2022 (H3N2) ANTIGEN (MDCK CELL DERIVED, PROPIOLACTONE INACTIVATED) (UNII: 2DVY566JY6) (INFLUENZA A VIRUS A/SYDNEY/1304/2022 HEMAGGLUTININ ANTIGEN (MDCK CELL DERIVED, PROPIOLACTONE INACTIVATED) - UNII:5CH2Y25VXX) INFLUENZA A VIRUS A/SYDNEY/1304/2022 HEMAGGLUTININ ANTIGEN (MDCK CELL DERIVED, PROPIOLACTONE INACTIVATED) 15 ug in 0.5 mL INFLUENZA B VIRUS B/Singapore/WUH4618/2021 ANTIGEN (MDCK CELL DERIVED, PROPIOLACTONE INACTIVATED) (UNII: TUE3AGP9ME) (INFLUENZA B VIRUS B/Singapore/WUH4618/2021 HEMAGGLUTININ ANTIGEN (MDCK CELL DERIVED, PROPIOLACTONE INACTIVATED) - UNII:C76JLA4DM6) INFLUENZA B VIRUS B/Singapore/WUH4618/2021 HEMAGGLUTININ ANTIGEN (MDCK CELL DERIVED, PROPIOLACTONE INACTIVATED) 15 ug in 0.5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength POTASSIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 660YQ98I10) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) MAGNESIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 02F3473H9O) SODIUM PHOSPHATE, DIBASIC, DIHYDRATE (UNII: 94255I6E2T) POTASSIUM PHOSPHATE, MONOBASIC (UNII: 4J9FJ0HL51) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) THIMEROSAL (UNII: 2225PI3MOV) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:70461-554-10 1 in 1 CARTON 1 NDC:70461-554-11 5 mL in 1 VIAL, MULTI-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date BLA BLA125408 07/01/2024 07/31/2025 Labeler - Seqirus Inc. (080102141) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Seqirus Inc. 080102141 MANUFACTURE, LABEL, PACK, ANALYSIS