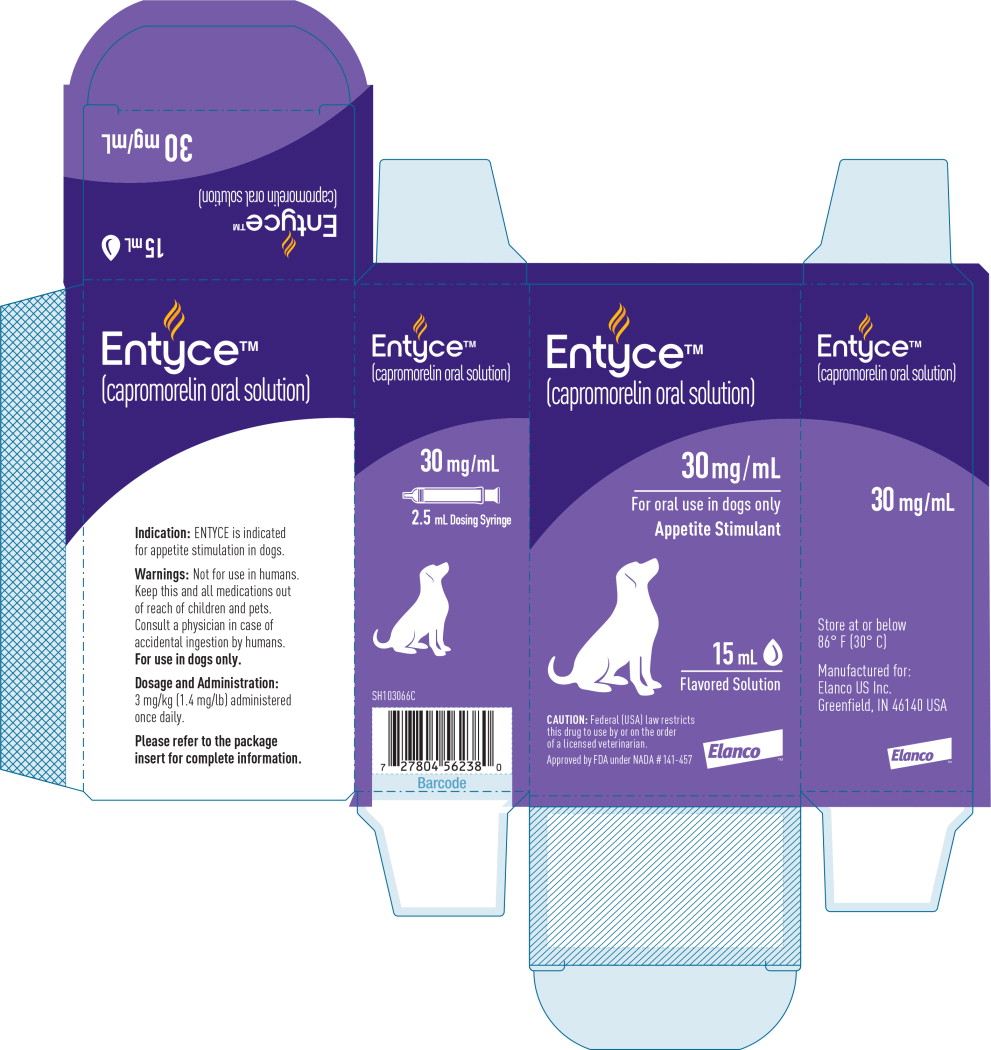
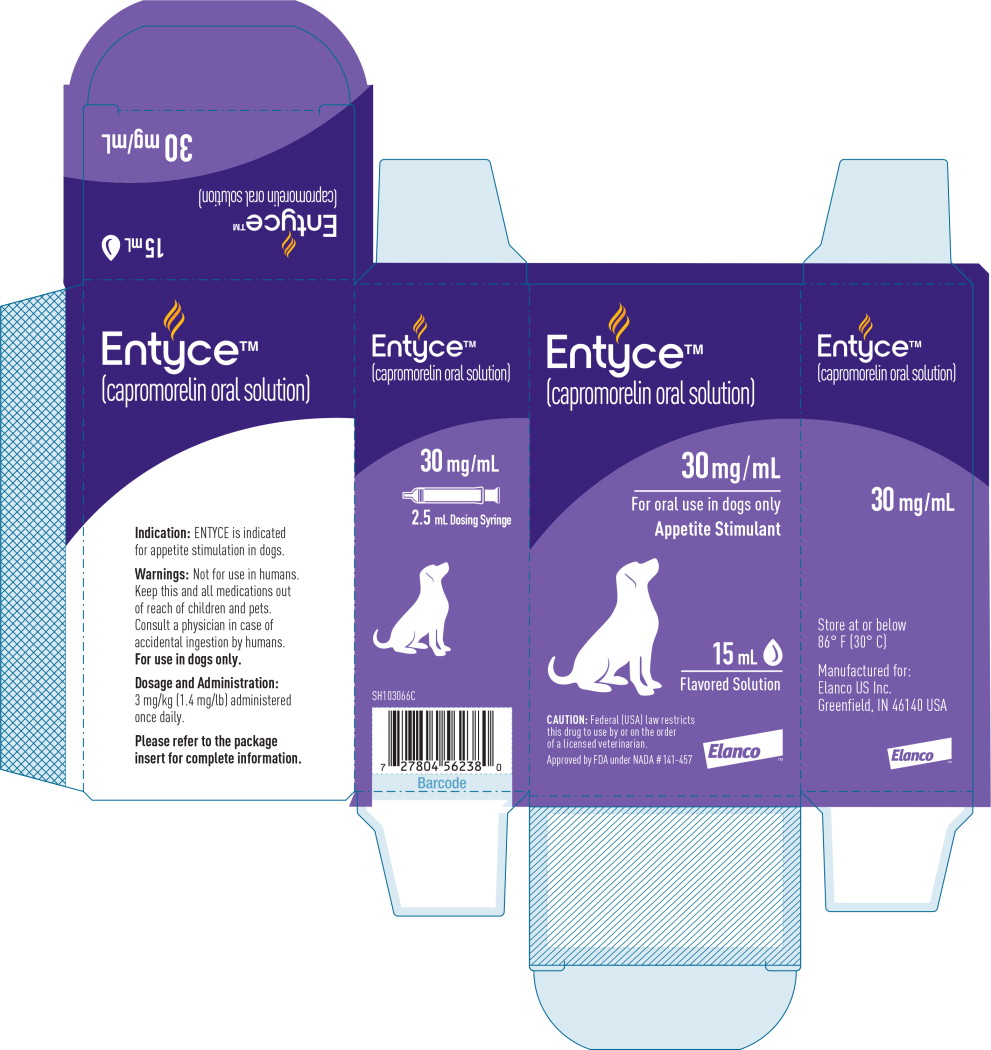
Label: ENTYCE- capromorelin tartrate solution
- NDC Code(s): 58198-5535-1, 58198-5535-2, 58198-5535-3
- Packager: Elanco US Inc.
- Category: PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG LABEL
Drug Label Information
Updated August 4, 2021
If you are a healthcare professional or from the pharmaceutical industry please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
Description:
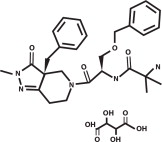
ENTYCE (capromorelin oral solution) is a selective ghrelin receptor agonist that binds to receptors and affects signaling in the hypothalamus to cause appetite stimulation and binds to the growth hormone secretagogue receptor in the pituitary gland to increase growth hormone secretion. The empirical formula is C28H35N5O4·C4H6O6 and the molecular weight 655.70. The chemical name is 2-amino-N-[2-(3aR-benzyl-2-methyl-3-oxo-2,3,3a,4,6,7-hexahydro-pyrazolo[4,3-c]pyridin-5-yl)1R-benzyloxymethyl-2-oxo-ethyl]-isobutyramide L-tartrate.
The chemical structure of capromorelin tartrate is:
- Indication:
-
Dosage and Administration:
Administer ENTYCE orally at a dose of 3 mg/kg (1.4 mg/lb) body weight once daily.
To administer ENTYCE, gently shake the bottle, and then withdraw the appropriate amount of solution using the provided syringe. Rinse syringe between treatment doses.
The effectiveness of ENTYCE has not been evaluated beyond 4 days of treatment in the clinical field study (See Effectiveness).
- Contraindications:
- Warnings:
-
Precautions:
Use with caution in dogs with hepatic dysfunction. ENTYCE is metabolized by CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 enzymes (See Clinical Pharmacology). Use with caution in dogs with renal insufficiency. ENTYCE is excreted approximately 37% in urine and 62% in feces (See Adverse Reactions and Clinical Pharmacology).
The safe use of ENTYCE has not been evaluated in dogs used for breeding or pregnant or lactating bitches.
-
Adverse Reactions:
In a controlled field study, 244 dogs were evaluated for safety when administered either ENTYCE or a vehicle control (solution minus capromorelin) at a dose of 3 mg/kg once daily for 4 days. Enrolled dogs had a reduced or absent appetite for a minimum of 2 days prior to day 0 and had various medical conditions: arthritis (40); gastrointestinal disease (24); allergy (22); dental disease (22); cardiovascular disease (16); renal disease (13); and others. Some dogs may have experienced more than one of the adverse reactions during the study.
The following adverse reactions were observed:
Table 1: Adverse Reactions reported in dogs administered ENTYCE oral solution compared to vehicle control Adverse Reactions ENTYCE (n = 171)
n (%)Vehicle Control (n = 73)
n (%)GASTROINTESTINAL Diarrhea 12 (7.0 %) 5 (6.8 %) Vomiting 11 (6.4 %) 4 (5.5 %) Hypersalivation 4 (2.3 %) 0 (0.0 %) Abdominal discomfort 2 (1.2 %) 0 (0.0 %) Flatulence 2 (1.2 %) 0 (0.0 %) Nausea 2 (1.2 %) 0 (0.0 %) CLINICAL PATHOLOGY Elevated blood urea nitrogen 7 (4.1 %) 2 (2.7 %) Elevated phosphorus 4 (2.3 %) 1 (1.4 %) Elevated creatinine 1 (0.6 %) 1 (1.4 %) OTHER Polydipsia 7 (4.1 %) 1 (1.4 %) Lethargy/depression 2 (1.2 %) 0 (0.0 %) The following adverse reactions were reported in < 1% of dogs administered ENTYCE: hyperactivity, increase fecal volume, increase gut sounds, and polyuria.
To report suspected adverse events, for technical assistance or to obtain a copy of the Safety Data Sheet (SDS), contact Elanco US Inc. at 1-888-545-5973. For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or http://www.fda.gov/reportanimalae.
-
Clinical Pharmacology:
Following oral administration of ENTYCE at a dose of 3 mg/kg to 12 Beagle dogs, absorption of capromorelin was rapid with the maximum concentration (Cmax) reached within 0.83 hr (Tmax). After Cmax, the plasma concentrations declined mono-exponentially with a short terminal half-life (T½) of approximately 1.19 hrs. There were no gender differences in capromorelin pharmacokinetics. The exposure (Cmax and AUC) of capromorelin increased with dose, but the increases were not dose proportional following single and repeat once daily administrations of capromorelin. There was no drug accumulation following repeat oral administration.
Table 2. Plasma PK parameters following oral administration of 3 mg/kg of ENTYCE Parameter Mean SD Tmax (hr) 0.83 0.58 Cmax (ng/mL) 330 143 AUCt (ng*hr/mL) 655 276 AUCinf (ng*hr/mL) 695 262 T½ (hr) 1.19 0.17 The mean absolute oral bioavailability of capromorelin was 44%. The mean total plasma clearance and volume of distribution was 18.9 mL/min/kg and 2.0 L/kg, respectively. Capromorelin was not highly bound (unbound fraction 51%) to plasma protein. The protein binding was concentration-independent over the range of 10 to 1000 ng/mL. In vitro (human liver microsomes) and in vivo (rats) metabolism studies suggest that capromorelin is metabolized by hepatic enzymes, mainly CYP3A4 and CYP3A5. Therefore, drugs that inhibit CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 activity may affect capromorelin metabolism. Following oral administration of radio-labelled capromorelin to dogs, capromorelin was excreted in urine (37%) and in feces (62%) within 72 hours.
-
Effectiveness:
Laboratory Effectiveness Study: Twenty four healthy Beagle dogs (6 dogs per sex in each group) with normal appetite were randomized into two groups and dosed daily with ENTYCE (capromorelin oral solution) at 3 mg/kg/day or vehicle control (solution minus capromorelin) to compare food intake over a 4-day period. The dogs were 13 months of age and weighed between 6.5 and 12.5 kg at the time of randomization. Six dogs administered ENTYCE repeatedly exhibited salivation post dosing and two dogs administered vehicle control exhibited salivation only one time on study day 0. Emesis was observed in one dog administered ENTYCE on study day 1. Dogs administered ENTYCE at a dose of 3 mg/kg/day for 4 consecutive days had statistically significantly increased food consumption compared to the vehicle control group (p < 0.001).
Clinical Field Study: Effectiveness was evaluated in 177 dogs (121 dogs in the ENTYCE group and 56 dogs in the vehicle control group) in a double-masked, vehicle controlled field study. Dogs with a reduced appetite or no appetite, with various medical conditions, for a minimum of 2 days prior to day 0 were enrolled in the study. The dogs ranged in age from 4 months to 18 years. Dogs were randomized to treatment group and dosed once daily for 4 days with ENTYCE at 3 mg/kg or vehicle control. Dogs were assessed for appetite by owners on day 0 and day 3 ± 1 using an “increased”, “no change” or “decreased” scoring system. Dogs were classified as a treatment success if the owner scored their dog's appetite as “increased” on day 3 ± 1. The success rates of the two groups were significantly different (p = 0.0078); 68.6% (n = 83) of dogs administered ENTYCE were successes, compared to 44.6% (n = 25) of the dogs in the vehicle control group.
-
Animal Safety:
In a 12-month laboratory safety study, 32 healthy Beagle dogs (4 dogs per sex per group) approximately 11-12 months of age and weighing 9-13.6 kg were dosed orally with capromorelin in deionized water daily at 0X (placebo), 0.3 (0.13X), 7 (3.07X), and 40 (17.5X) mg/kg/day. Administration of capromorelin was associated with increased salivation and reddening/swollen paws, increased liver weights and hepatocellular cytoplasmic vacuolation. Treatment related decreases were seen in red blood cell count, hemoglobin and hematocrit in the 40 mg/kg group.
Pale skin, pale gums, and decreased red blood cell count, hemoglobin and hematocrit were observed in one dog administered 40 mg/kg/day.
Increases were seen in cholesterol, high density lipoproteins, and the liver specific isozyme of serum alkaline phosphatase in the 40 mg/kg group. Growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1 plasma levels were increased in all groups administered capromorelin. There were no effects noted on gross necropsy. Capromorelin levels were similar in plasma collected on days 90, 181, and 349 indicating no accumulation of drug.
- Storage Conditions:
-
How Supplied:
30 mg/mL flavored solution in 10 mL, 15 mL and 30 mL bottles with measuring syringe
Approved by FDA under NADA # 141-457
Manufactured for:
Elanco US Inc.
Greenfield, IN 46140, USA
Revised: September 2020ENTYCE, Elanco and the diagonal bar logo are trademarks of Elanco or its affiliates.
ElancoTM
PA103066X - Principal Display Panel - 10 mL Carton Label
- Principal Display Panel - 10 mL Bottle Label
- Principal Display Panel - 15 mL Carton Label
- Principal Display Panel - 15 mL Bottle Label
- Principal Display Panel - 30 mL Carton Label
- Principal Display Panel - 30 mL Bottle Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ENTYCE
capromorelin tartrate solutionProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:58198-5535 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Capromorelin tartrate (UNII: 4150VMF5EP) (Capromorelin - UNII:0MQ44VUN84) Capromorelin tartrate 30 mg in 1 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:58198-5535-1 1 in 1 CARTON 1 10 mL in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 2 NDC:58198-5535-2 1 in 1 CARTON 2 15 mL in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 3 NDC:58198-5535-3 1 in 1 CARTON 3 30 mL in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NADA NADA141457 02/08/2017 Labeler - Elanco US Inc. (966985624) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Halo Pharmaceutical Canada, Inc 250928632 MANUFACTURE, PACK, LABEL Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Cambrex Charles City 782974257 API MANUFACTURE Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Sterling Wisconsin, LLC 054452136 API MANUFACTURE