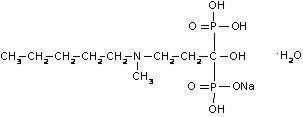17.2 FDA-Approved Patient Labeling
Read this patient information carefully before you start taking
BONIVA. Read this patient information each time you get a refill for BONIVA.
There may be new information. This information is not everything you need to
know about BONIVA. It does not take the place of talking with your health care
provider about your condition or your treatment. Talk about BONIVA with your
health care provider before you start taking it, and at your regular
check-ups.
What is the most important information I should
know about BONIVA?
BONIVA may cause serious problems in the stomach and the esophagus (the tube
that connects your mouth and stomach) such as trouble swallowing, heartburn, and
ulcers (see "What are the possible side
effects of BONIVA?").
You must take BONIVA exactly as prescribed for BONIVA to
work for you and to lower the chance of serious side effects (see "How should I take BONIVA?").
What is BONIVA?
BONIVA is a prescription medicine used to treat or prevent osteoporosis in
women after menopause (see the end of this leaflet for "What is osteoporosis?").
BONIVA may reverse bone loss by stopping more loss of bone and increasing
bone mass in most women who take it, even though they won't be able to see or
feel a difference. BONIVA may help lower the chances of breaking bones
(fractures).
For BONIVA to treat or prevent osteoporosis, you have to take it as
prescribed. BONIVA will not work if you stop taking it.
Who should not take BONIVA?
Do not take BONIVA if you:
- have certain problems with your esophagus, the tube that connects your mouth
and stomach
- cannot sit or stand up for at least 60 minutes
- have low blood calcium (hypocalcemia)
- are allergic to ibandronate sodium or any of the other ingredients of BONIVA
(see the end of this leaflet for a list of all the ingredients in BONIVA)
- have kidneys that work very poorly
Tell your health care provider before using BONIVA:
- if you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if
BONIVA can harm your unborn baby.
- if you are breast-feeding. It is not known if BONIVA passes into your milk
and if it can harm your baby.
- have swallowing problems or other problems with your esophagus (the tube
that connects your mouth and stomach)
- if you have kidney problems
- if you are planning a dental procedure such as tooth extraction
Tell your health care provider (including your dentist)
about all the medicines you take including prescription and
non-prescription medicines, vitamins and supplements. Some medicines, especially
certain vitamins, supplements, and antacids can stop BONIVA from getting to your
bones. This can happen if you take other medicines too close to the time that
you take BONIVA (see "How should I take
BONIVA?").
How should I take BONIVA?
- Take BONIVA exactly as instructed by your health care provider.
- Take BONIVA first thing in the morning at least 60 minutes before you eat,
drink anything other than plain water, or take any other oral medicine.
- Take BONIVA with 6 to 8 ounces (about 1 full cup) of plain water. Do not
take it with any drink other than plain water. Do not take it with other drinks,
such as mineral water, sparkling water, coffee, tea, dairy drinks (such as
milk), or juice.
- Swallow BONIVA whole. Do not chew or suck the tablet or keep it in your
mouth to melt or dissolve.
- After taking BONIVA you must wait at least 60 minutes before:
–Lying down. You may sit, stand, or do normal activities like read the
newspaper or take a walk.–Eating or drinking anything except for plain water.–Taking other oral medicines including vitamins, calcium, or antacids. Take
your vitamins, calcium, and antacids at a different time of the day from the
time when you take BONIVA.
- If you take too much BONIVA, drink a full glass of milk and call your local
poison control center or emergency room right away. Do not make yourself vomit.
Do not lie down.
- Keep taking BONIVA for as long as your health care provider tells you.
BONIVA will not work if you stop taking it.
- Your health care provider may tell you to exercise and take calcium and
vitamin supplements to help your osteoporosis.
- Your health care provider may do a test to measure the thickness (density)
of your bones or do other tests to check your progress.
What is my BONIVA schedule?
Schedule for taking BONIVA 2.5 mg once-daily:
- Take one BONIVA 2.5 mg tablet once a day first thing in the morning at least
60 minutes before you eat, drink anything other than plain water, or take any
other oral medicine (see "How should I take
BONIVA?").
What to do if I miss a daily dose:
- If you forget to take your BONIVA 2.5 mg tablet in the morning, do not take it later in the day. Just return to your normal
schedule and take 1 tablet the next morning. Do not take
two tablets on the same day.
-
If you are not sure what to do if you miss a dose, contact
your health care provider who will be able to advise you.
Schedule for taking BONIVA 150 mg once-monthly:
- Take one BONIVA 150 mg tablet once a month.
- Choose one date of the month (your BONIVA day) that you will remember and
that best fits your schedule to take your BONIVA 150 mg tablet.
- Take one BONIVA 150 mg tablet in the morning of your chosen day (see "How should I take BONIVA?").
What to do if I miss a monthly dose:
- If your next scheduled BONIVA day is more than 7 days away, take one BONIVA
150 mg tablet in the morning following the day that you remember (see "How should I take BONIVA?"). Then return
to taking one BONIVA 150 mg tablet every month in the morning of your chosen
day, according to your original schedule.
-
Do not take two 150 mg tablets within the same week.
If your next scheduled BONIVA day is only 1 to 7 days away, wait until your next scheduled BONIVA day to take your tablet.
Then return to taking one BONIVA 150 mg tablet every month in the morning of
your chosen day, according to your original schedule.
-
If you are not sure what to do if you miss a dose, contact
your health care provider who will be able to advise you.
What should I avoid while taking BONIVA?
- Do not take other medicines, or eat or drink anything but plain water before
you take BONIVA and for at least 60 minutes after you take it.
- Do not lie down for at least 60 minutes after you take BONIVA.
What are the possible side effects of
BONIVA?
Stop taking BONIVA and call your health care provider right
away if you have:
-
pain or trouble with swallowing
-
chest pain
-
very bad heartburn or heartburn that does not get
better
BONIVA MAY CAUSE:
- pain or trouble swallowing (dysphagia)
- heartburn (esophagitis)
- ulcers in your stomach or esophagus (the tube that connects your mouth and
stomach)
Common side effects with BONIVA are:
- diarrhea
- pain in extremities (arms or legs)
- dyspepsia (upset stomach)
Less common side effects with BONIVA are short-lasting, mild flu-like
symptoms (which usually improve after the first dose). These are not all the
possible side effects of BONIVA. For more information ask your health care
provider or pharmacist.
Rarely, patients have reported allergic and skin reactions. Contact your
health care provider if you develop any symptoms of an allergic reaction
including skin rash (with or without blisters), hives, wheezing, or swelling of
the face, lips, tongue or throat. Get medical help right away if you have
trouble breathing, swallowing or feel light-headed.
Rarely, patients have reported severe bone, joint, and/or muscle pain
starting within one day to several months after beginning to take, by mouth,
bisphosphonate drugs to treat osteoporosis (thin bones). This group of drugs
includes BONIVA. Most patients experienced relief after stopping the drug.
Contact your health care provider if you develop these symptoms after starting
BONIVA.
Rarely, patients taking bisphosphonates have reported serious jaw problems
associated with delayed healing and infection, often following dental procedures
such as tooth extraction. If you experience jaw problems, contact your health
care provider and dentist.
What is osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis is a disease that causes bones to become thinner. Thin bones can
break easily. Most people think of their bones as being solid like a rock.
Actually, bone is living tissue, just like other parts of the body, such as your
heart, brain, or skin. Bone just happens to be a harder type of tissue. Bone is
always changing. Your body keeps your bones strong and healthy by replacing old
bone with new bone.
Osteoporosis causes the body to remove more bone than it replaces. This means
that bones get weaker. Weak bones are more likely to break. Osteoporosis is a
bone disease that is quite common in women after menopause. At first,
osteoporosis has no symptoms, but people with osteoporosis may develop loss of
height and are more likely to break (fracture) their bones, especially the back
(spine), wrist, and hip bones.
Osteoporosis can be prevented, and with proper therapy it can be treated.
Who is at risk for osteoporosis?
Talk to your health care provider about your chances for getting
osteoporosis.
Many things put people at risk for osteoporosis. The following people have a
higher chance of getting osteoporosis:
Women who:
- are going through or who are past menopause ("the change")
- are white (Caucasian) or Asian
People who:
- are thin
- have a family member with osteoporosis
- do not get enough calcium or vitamin D
- do not exercise
- smoke
- drink alcohol often
- take bone thinning medicines (like prednisone) for a long time
General information about BONIVA
Do not use BONIVA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not
give BONIVA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It
may harm them.
Store BONIVA at 77°F (25°C) or at room temperature between 59°F and 86°F
(15°C and 30°C).
Keep BONIVA and all medicines out of the reach of children.
This summarizes the most important information about BONIVA. If you would
like more information, talk with your health care provider. You can ask your
health care provider or pharmacist for information about BONIVA that is written
for health professionals.
For more information about BONIVA, call 1-888-MY-BONIVA or visit
www.myboniva.com.
What are the ingredients of
BONIVA?
BONIVA (active ingredient): ibandronate sodium
BONIVA (inactive ingredients): lactose monohydrate, povidone,
microcrystalline cellulose, crospovidone, purified stearic acid, colloidal
silicon dioxide, and purified water. The tablet film coating contains
hypromellose, titanium dioxide, talc, polyethylene glycol 6000 and purified
water.
BONIVA is a registered trademark of Roche Therapeutics Inc.
Distributed by:
Genentech USA, Inc.
A Member
of the Roche Group
1 DNA Way
South San Francisco, CA 94080-4990
BAT_2005450_PI_AR2010_K(1)
Revised: January 2010
© 2010 Genentech, Inc. All rights reserved.
(see the HOW SUPPLIED section for complete
listing)