Label: TEGSEDI- inotersen injection, solution
- NDC Code(s): 72126-007-01, 72126-007-02
- Packager: Akcea Therapeutics, Inc.
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated January 25, 2024
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Medication Guide: HTML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use TEGSEDI® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TEGSEDI. TEGSEDI (inotersen) injection, for ...
-
Table of ContentsTable of Contents
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: THROMBOCYTOPENIA AND GLOMERULONEPHRITIS
Thrombocytopenia
TEGSEDI causes reductions in platelet count that may result in sudden and unpredictable thrombocytopenia, which can be life-threatening. One clinical trial patient died from intracranial hemorrhage.
TEGSEDI is contraindicated in patients with a platelet count below 100 x 109/L [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Prior to starting TEGSEDI, obtain a platelet count [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. During treatment, monitor platelet counts weekly if values are 75 x 109/L or greater, and more frequently if values are less than 75 x 109/L [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
If a patient develops signs or symptoms of thrombocytopenia, obtain a platelet count as soon as possible. The patient should not receive additional TEGSEDI unless a platelet count is determined to be interpretable and acceptable by a medical professional [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Following discontinuation of treatment for any reason, continue to monitor platelet count for 8 weeks, or longer if platelet counts are less than 100 x 109/L, to verify that platelet counts remain above 75 x 109/L [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Glomerulonephritis
TEGSEDI can cause glomerulonephritis that may require immunosuppressive treatment and may result in dialysis-dependent renal failure. One clinical trial patient who developed glomerulonephritis and did not receive immunosuppressive treatment remained dialysis-dependent. In clinical trials, cases of glomerulonephritis were accompanied by nephrotic syndrome, which can have manifestations of edema, hypercoagulability with venous or arterial thrombosis, and increased susceptibility to infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
TEGSEDI should generally not be initiated in patients with urinary protein to creatinine ratio (UPCR) of 1000 mg/g or higher [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Prior to starting TEGSEDI, measure the serum creatinine, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), urine protein to creatinine ratio (UPCR), and perform a urinalysis [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. During treatment, monitor serum creatinine, eGFR urinalysis, and UPCR every two weeks. TEGSEDI should not be given to patients who develop a UPCR of 1000 mg/g or higher, or eGFR below 45 mL/minute/1.73 m2, pending further evaluation of the cause.
If a dose is held, once eGFR increases to ≥45 mL/minute/1.73 m2, UPCR decreases to below 1000 mg/g, or the underlying cause of the decline in renal function is corrected, weekly dosing may be reinitiated. In patients with UPCR of 2000 mg/g or higher, perform further evaluation for acute glomerulonephritis, as clinically indicated. If acute glomerulonephritis is confirmed, TEGSEDI should be permanently discontinued [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
TEGSEDI REMS Program
Because of the risks of serious bleeding caused by severe thrombocytopenia and because of glomerulonephritis, both of which require frequent monitoring, TEGSEDI is available only through a restricted distribution program under a Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy (REMS) called the TEGSEDI REMS Program [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Close -
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGETEGSEDI is indicated for the treatment of the polyneuropathy of hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis in adults.
-
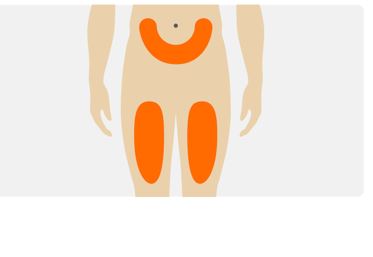
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION2.1 Dosing Information - The recommended dose of TEGSEDI is 284 mg injected subcutaneously once weekly. For consistency of dosing, patients should be instructed to give the injection on the same ...
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSInjection: 284 mg/1.5 mL clear, colorless to pale yellow solution in a single-dose prefilled syringe.
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONSTEGSEDI is contraindicated in patients with: Platelet count below 100 x 109/L [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] History of acute glomerulonephritis caused by TEGSEDI [see Warnings and ...
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS5.1 Thrombocytopenia - TEGSEDI causes reductions in platelet count at any time during treatment that may result in sudden and unpredictable thrombocytopenia that can be life-threatening. In Study ...
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONSThe following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling: Thrombocytopenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] Glomerulonephritis and Renal ...
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS7.1 Antiplatelet Drugs or Anticoagulant Medications - Because of the risk of thrombocytopenia, caution should be used when using antiplatelet drugs (e.g., adenosine, clopidogrel, prasugrel ...
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS8.1 Pregnancy - Pregnancy Exposure Registry - There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to TEGSEDI during pregnancy. Health care providers are ...
-
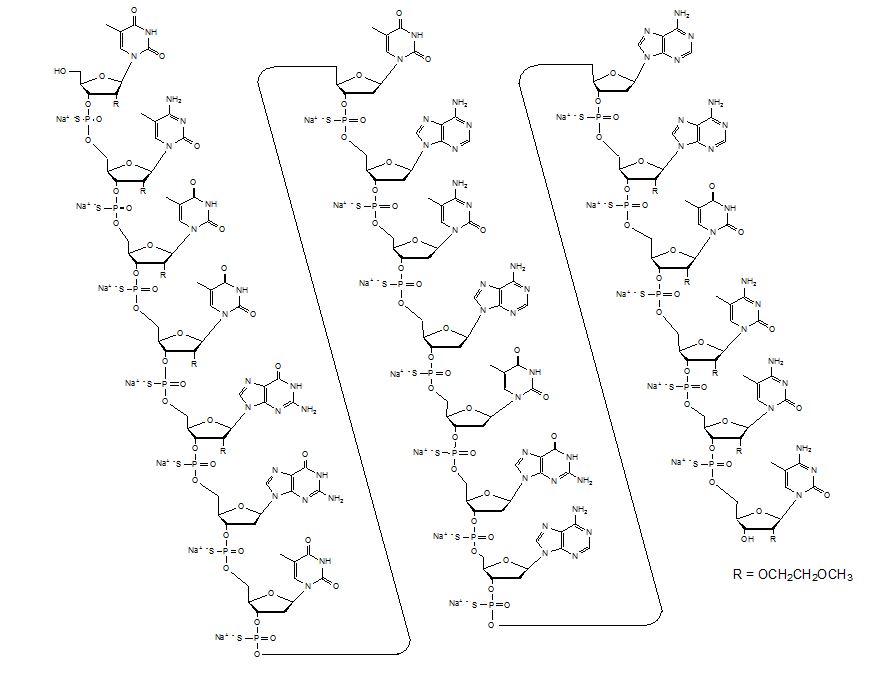
11 DESCRIPTIONInotersen is an antisense oligonucleotide (ASO) inhibitor of human transthyretin (TTR) protein synthesis. TEGSEDI contains inotersen sodium as the active ingredient. Inotersen sodium is a white to ...
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY12.1 Mechanism of Action - Inotersen is an antisense oligonucleotide that causes degradation of mutant and wild-type TTR mRNA through binding to the TTR mRNA, which results in a reduction of ...
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility - Carcinogenesis - In a 26-week carcinogenicity study in transgenic (TgRasH2) mice, weekly subcutaneous administration of inotersen (0 ...
-
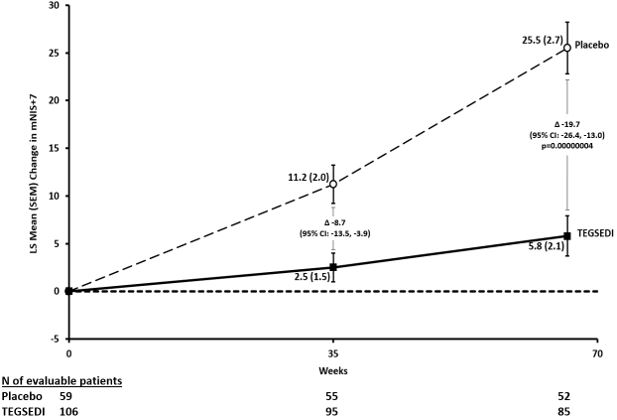
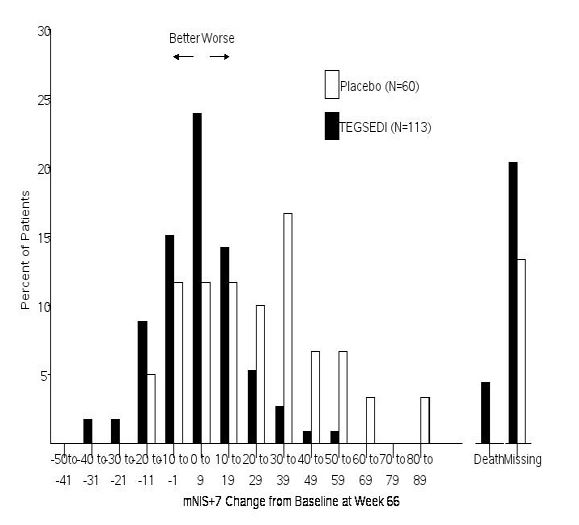
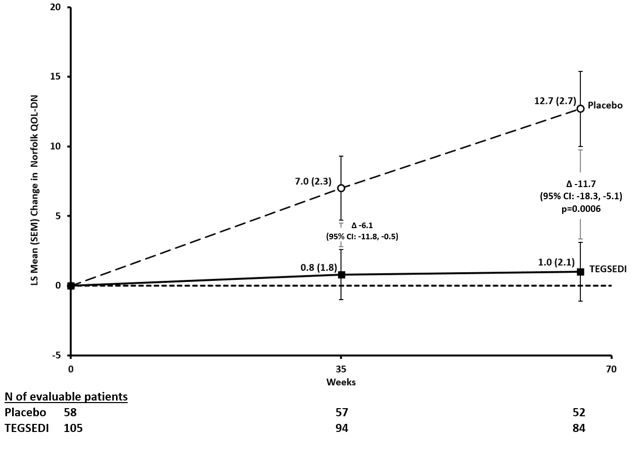
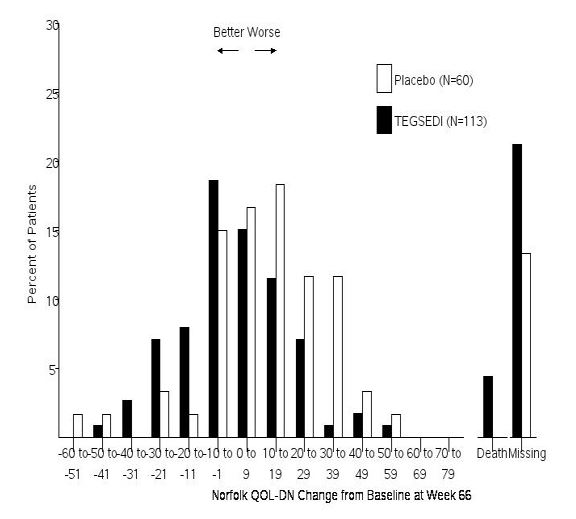
14 CLINICAL STUDIESThe efficacy of TEGSEDI was demonstrated in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical trial in adult patients with polyneuropathy caused by hATTR amyloidosis (Study 1 ...
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLINGTEGSEDI is a clear, colorless to pale yellow solution supplied in a single-dose, prefilled syringe with a SSD. Each prefilled syringe of TEGSEDI is filled to deliver 1.5 mL of solution containing ...
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATIONAdvise the patient and caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use). Thrombocytopenia - Inform patients that TEGSEDI can cause reductions in ...
-
MEDICATION GUIDEThis Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.Issued: 01/2024 - MEDICATION GUIDE - TEGSEDI (Teg-SED-ee) (inotersen) injection ...
-
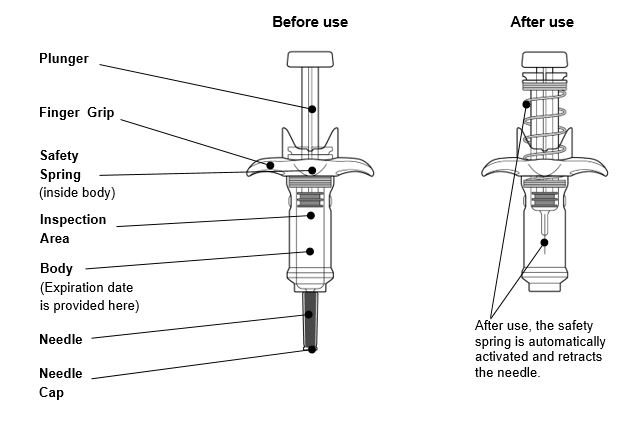
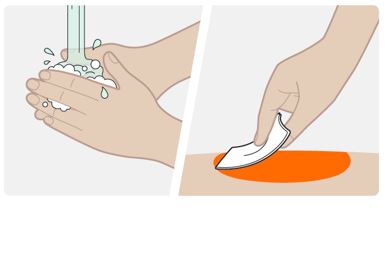
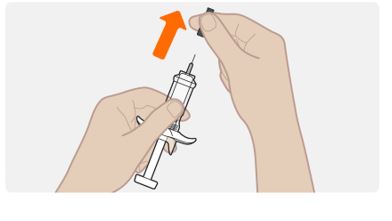
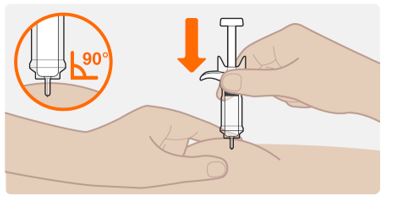
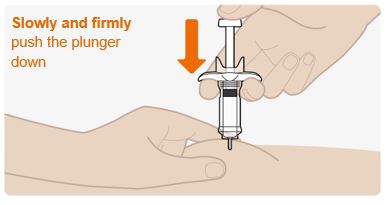
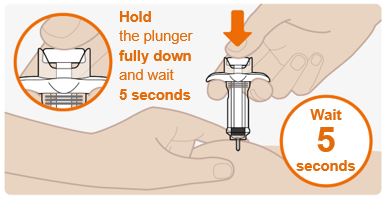
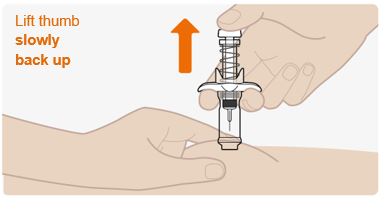
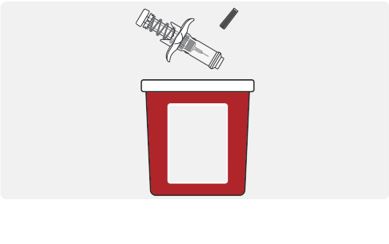
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USEThis Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug AdministrationIssued:10/2018 - TEGSEDI (Teg-SED-ee) (inotersen) injection - for subcutaneous use ...
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - NDC: 72126-007-02 - Syringe Label

-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - NDC: 72126-007-02 - 1-count Tray Label

-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - NDC: 72126-007-01 - 4-count Carton Label

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCEProduct Information