Label: LITHOSTAT- acetohydroxamic acid tablet
- NDC Code(s): 0178-0500-01
- Packager: Mission Pharmacal Company
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated January 8, 2024
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
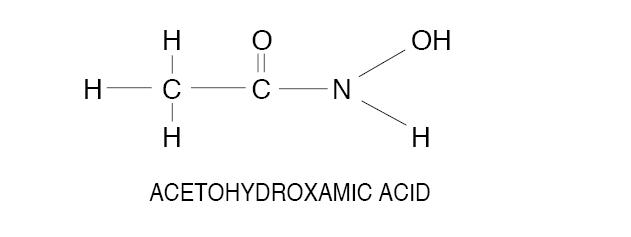
DESCRIPTIONAcetohydroxamic acid (AHA) is a stable, synthetic compound derived from hydroxylamine and ethyl acetate. Its molecular structure is similar to urea: AHA is weakly acidic, highly soluble in ...
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYAHA reversibly inhibits the bacterial enzyme urease, thereby inhibiting the hydrolysis of urea and production of ammonia in urine infected with urea-splitting organisms. The reduced ammonia ...
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGEAcetohydroxamic acid is indicated as adjunctive therapy in patients with chronic urea-splitting urinary infection. AHA is intended to decrease urinary ammonia and alkalinity, but it should not be ...
-
CONTRAINDICATIONSAcetohydroxamic acid - should not be used in: a. patients whose physical state and disease are amenable to definitive surgery and appropriate antimicrobial agents - b. patients whose ...
-
WARNINGSA Coombs negative hemolytic anemia has occurred in patients receiving AHA. Gastrointestinal upset characterized by nausea, vomiting, anorexia and generalized malaise have accompanied the most ...
-
PRECAUTIONSGeneral - Hematologic Effects: Bone marrow depression (leukopenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia) has occurred in experimental animals receiving large doses of AHA, but has not been seen in man ...
-
DRUG INTERACTIONSAHA has been used concomitantly with insulin, oral and parenteral antibiotics, and progestational agents. No clinically significant interactions have been noted, but until wider clinical ...
-
CARCINOGENESIS, MUTAGENESIS, IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITYWell controlled, long-term animal studies that identify the carcinogenic potential of AHA treatment have not been conducted. Acetamide, a metabolite of AHA, has been shown to cause hepatocellular ...
-
PREGNANCY(See Contraindications.)
-
NURSING MOTHERSIt is not known whether AHA is secreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from AHA, a ...
-
PEDIATRIC USEChildren with chronic, recalcitrant, urea-splitting urinary infection may benefit from treatment with AHA. However, detailed studies involving dosage and dose intervals in children have not been ...
-
ADVERSE REACTIONSExperience with AHA is limited. About 150 patients have been treated, most for periods of more than a year. Adverse reactions have occurred in up to thirty percent (30%) of the patients ...
-
OVERDOSAGEAcute deliberate overdosage in man has not occurred, but would be expected to induce the following symptoms: anorexia, malaise, lethargy, diminished sense of well being, tremulousness, anxiety ...
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONAHA should be administered orally, one tablet 3-4 times a day in a total daily dose of 10-15 mg/kg/day. The recommended starting dose is 12 mg/kg/day, administered at 6-8 hour intervals at a time ...
-
HOW SUPPLIEDLITHOSTAT - ®, NDC 0178-0500-01, is available for oral administration as 250 mg white, round tablets, in unit of use packages of 100 tablets. Each LITHOSTAT - ®tablet is debossed MPC 500 on ...
-
PATIENT INFORMATIONPLEASE READ THIS INFORMATION BEFORE USING THIS DRUG. GENERAL INFORMATION:It has been known for many years that urinary infection may cause the formation of urinary stones. As these stones form ...
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANELLithostat 250mg Label - NDC: 0178-0500-01
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCEProduct Information