Label: COMBIPATCH (ESTRADIOL/NORETHINDRONE ACETATE TRANSDERMAL SYSTEM)- estradiol/norethindrone acetate transdermal system patc...view full title
- NDC Code(s): 68968-0514-8, 68968-0525-8
- Packager: Noven Therapeutics, LLC
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated February 21, 2024
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING:
CARDIOVASCULAR DISORDERS, BREAST CANCER, ENDOMETRIAL CANCER, AND PROBABLE DEMENTIAEstrogen Plus Progestin Therapy
Cardiovascular Disorders and Probable Dementia
Estrogen plus progestin therapy should not be used for the prevention of cardiovascular disease or dementia. (See CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS, Cardiovascular Disorders and Probable Dementia).
The Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) estrogen plus progestin substudy reported an increased risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism (PE), stroke and myocardial infarction (MI) in postmenopausal women (50 to 79 years of age) during 5.6 years of treatment with daily oral conjugated estrogens (CE) [0.625 mg] combined with medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA) [2.5 mg], relative to placebo. (See CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS, Cardiovascular Disorders).
The WHI Memory Study (WHIMS) estrogen plus progestin ancillary study of the WHI reported an increased risk of developing probable dementia in postmenopausal women 65 years of age or older during 4 years of treatment with daily CE (0.625 mg) combined with MPA (2.5 mg), relative to placebo. It is unknown whether this finding applies to younger postmenopausal women. (See CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS, Probable Dementia and PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use).
Breast Cancer
The WHI estrogen plus progestin substudy demonstrated an increased risk of invasive breast cancer. (See CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS, Malignant Neoplasms, Breast Cancer).
In the absence of comparable data, these risks should be assumed to be similar for other doses of CE and MPA, and other combinations and dosage forms of estrogens and progestins. Estrogens with or without progestins should be prescribed at the lowest effective doses and for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for the individual woman.
Estrogen-Alone Therapy
Endometrial Cancer
There is an increased risk of endometrial cancer in a woman with a uterus who uses unopposed estrogens. Adding a progestin to estrogen therapy has been shown to reduce the risk of endometrial hyperplasia, which may be a precursor to endometrial cancer. Adequate diagnostic measures, including directed or random endometrial sampling when indicated, should be undertaken to rule out malignancy in postmenopausal women with undiagnosed persistent or recurring abnormal genital bleeding. (SeeWARNINGS, Malignant Neoplasms, Endometrial Cancer).
Cardiovascular Disorders and Probable Dementia
Estrogen-alone therapy should not be used for the prevention of cardiovascular disease or dementia (See CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS, Cardiovascular Disorders and Probable Dementia).
The WHI estrogen-alone substudy reported increased risks of stroke and DVT in postmenopausal women (50 to 79 years of age) during 7.1 years of treatment with daily oral CE (0.625 mg)-alone, relative to placebo. (See CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS, Cardiovascular Disorders).
The WHIMS estrogen-alone ancillary study of the WHI reported an increased risk of developing probable dementia in postmenopausal women 65 years of age or older during 5.2 years of treatment with daily CE (0.625 mg)-alone, relative to placebo. It is unknown whether this finding applies to younger postmenopausal women. (See CLINICAL STUDIES and WARNINGS, Probable Dementia and PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use).
In the absence of comparable data, these risks should be assumed to be similar for other doses of CE and other dosage forms of estrogens. Estrogens with or without progestins should be prescribed at the lowest effective doses and for the shortest duration consistent with treatment goals and risks for the individual woman.
Close -
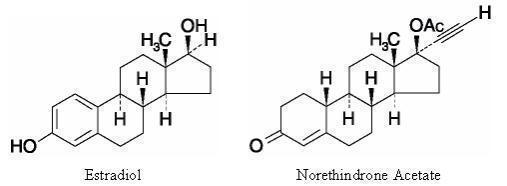
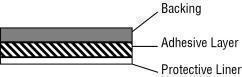
DESCRIPTIONCombiPatch® (estradiol/norethindrone acetate transdermal system) is an adhesive-based matrix transdermal patch designed to release both estradiol, an estrogen, and norethindrone acetate (NETA), a ...
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYEndogenous estrogens are largely responsible for the development and maintenance of the female reproductive system and secondary sexual characteristics. Although circulating estrogens exist in a ...
-
Drug InteractionsNo drug interaction studies have been conducted with CombiPatch. In vitro and in vivo studies have shown that estrogens are metabolized partially by cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4). Therefore ...
-
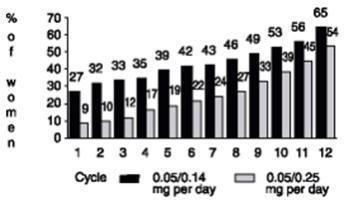
CLINICAL STUDIESEffects on Vasomotor Symptoms - In 2 clinical trials designed to assess the degree of relief of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms in postmenopausal women (n=332), CombiPatch was administered ...
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGECombiPatch is indicated in a woman with a uterus for: Treatment of moderate to severe vasomotor symptoms due to menopause. Treatment of moderate to severe symptoms of vulvar and vaginal atrophy ...
-
CONTRAINDICATIONSCombiPatch is contraindicated in women with any of the following conditions: Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding. Known, suspected, or history of breast cancer. Known or suspected ...
-
WARNINGSSee BOXED WARNING. 1. Cardiovascular Disorders - An increased risk of PE, DVT, stroke and MI has been reported with estrogen plus progestin therapy. An increased risk of stroke and DVT has been ...
-
PRECAUTIONSA. General - 1. Addition of a Progestin when a Woman has not had a Hysterectomy - Studies of the addition of a progestin for 10 or more days of a cycle of estrogen administration, or daily with ...
-
ADVERSE REACTIONSSee BOXED WARNING, WARNINGS, and PRECAUTIONS. Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be ...
-
OVERDOSAGEOverdosage of estrogen or estrogen plus progestin may cause nausea, vomiting, breast tenderness, abdominal pain, drowsiness and fatigue, and withdrawal bleeding may occur in women. Treatment of ...
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONGenerally, when estrogen therapy is prescribed for a postmenopausal woman with a uterus, a progestin should be considered to reduce the risk of endometrial cancer. A woman without a uterus ...
-
HOW SUPPLIEDCombiPatch estradiol/NETA transdermal delivery system is available in: SystemNominal Delivery Rate * SizeEstradiol/NETAPresentationNDCMarkings - 9 cm 20.05/0.14 mg per day8 systems per ...
-
REFERENCESRossouw JE, et al. Postmenopausal Hormone Therapy and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease by Age and Years Since Menopause. JAMA. 2007;297:1465-1477. Hsia J, et al. Conjugated Equine Estrogens and ...
-
Patient InformationCombiPatch - (käm-bē `pach) (estradiol/norethindrone acetate transdermal system) Read this Patient Information before you start using CombiPatch and each time you get a refill. There may be new ...
-
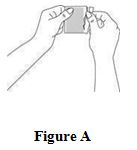
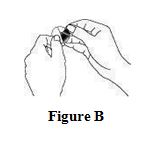
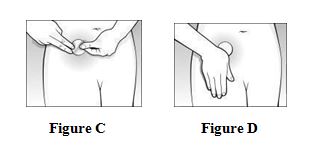
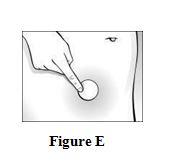
Instructions for UseCombiPatch - (käm-bē `pach) (estradiol/norethindrone acetate transdermal system) Step 1. Pick the days you will change your CombiPatch. You will need to change your patch every 3 to 4 days ...
-
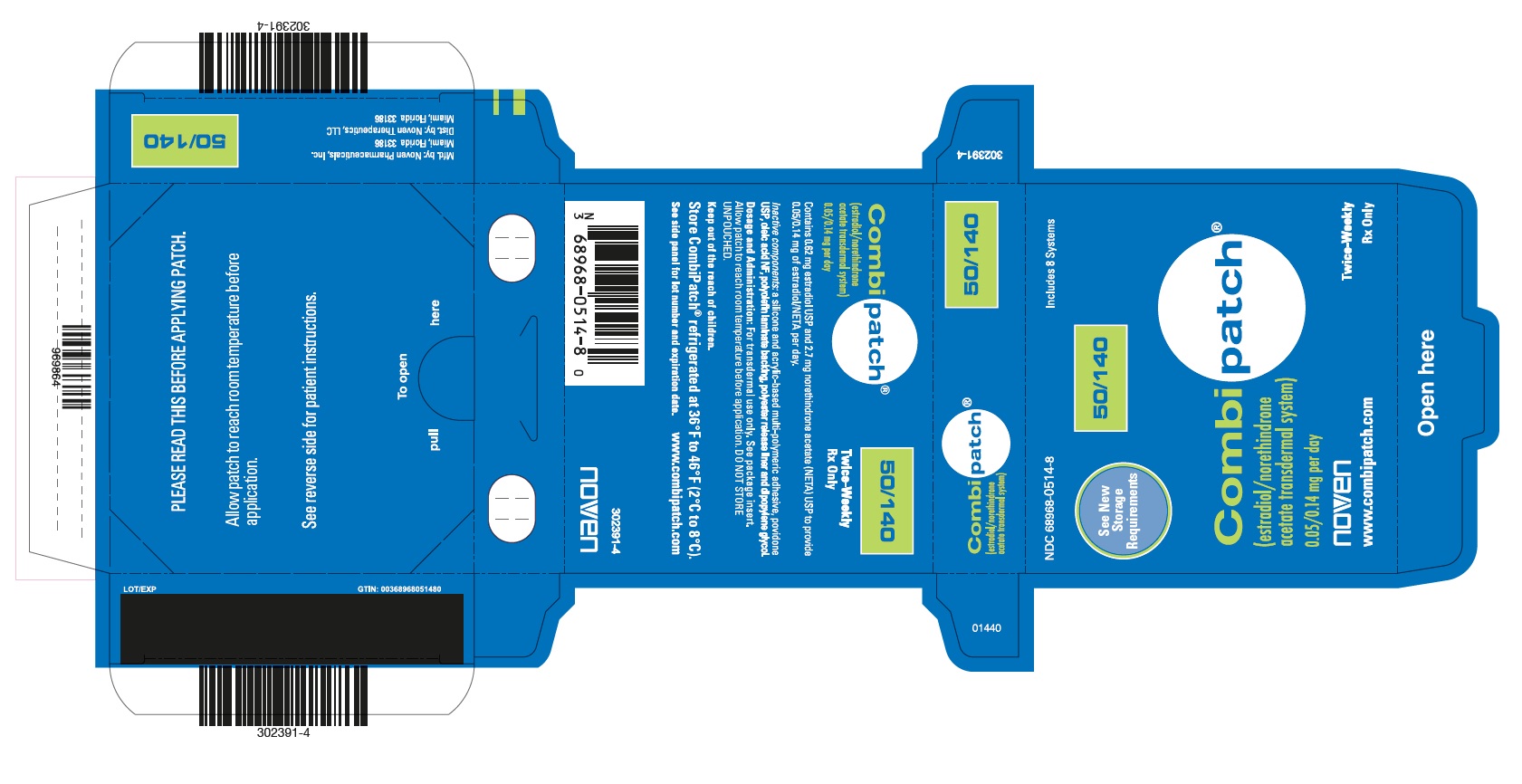
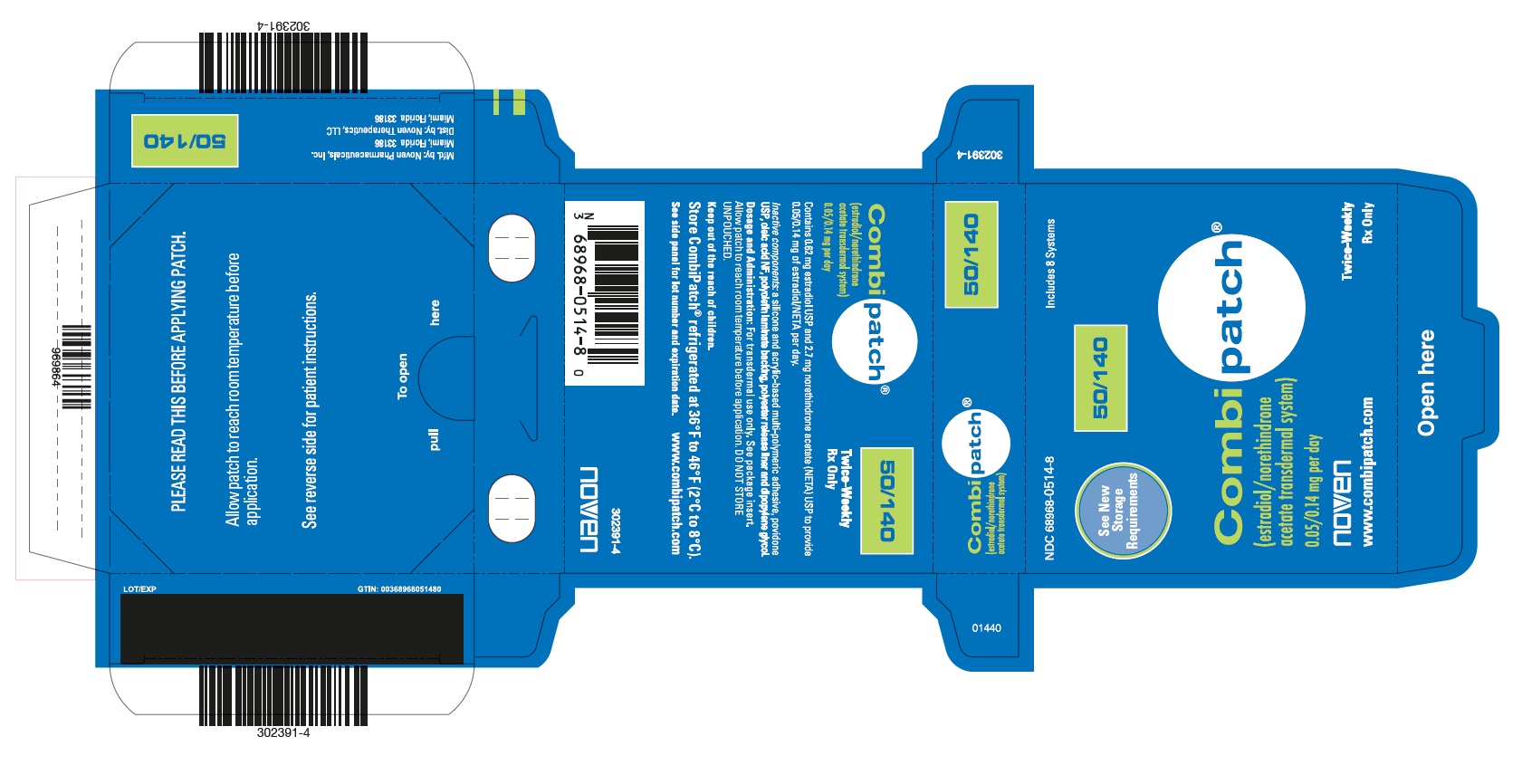
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANELPRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - NDC - 68968-0514-8 CombiPatch Count - 50/140 - NDC 68968-0514-8 - Includes 8 Systems - See New Storage Requirements - Combipatch® 50/140 - (estradiol/norethindrone acetate ...
-
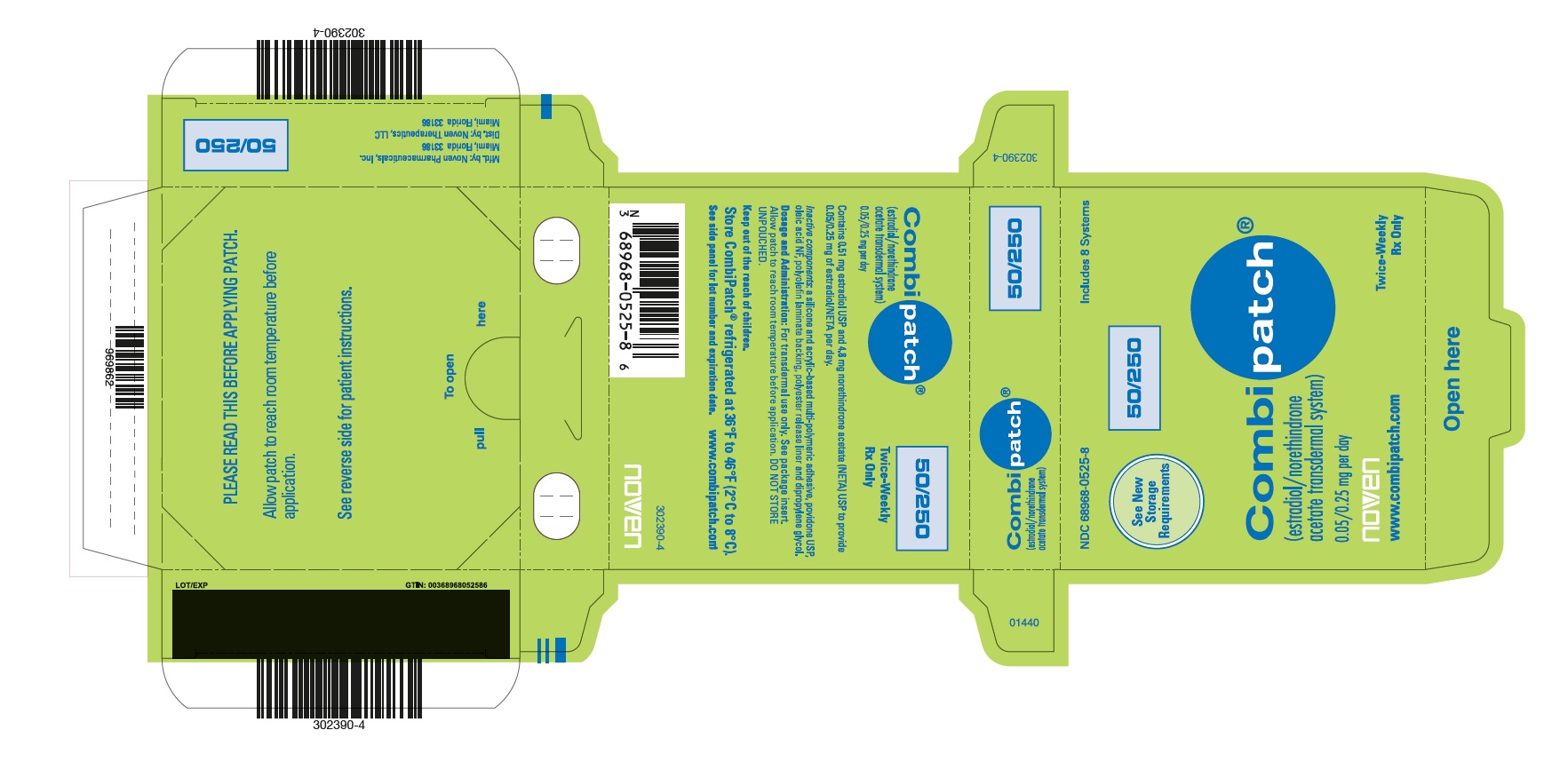
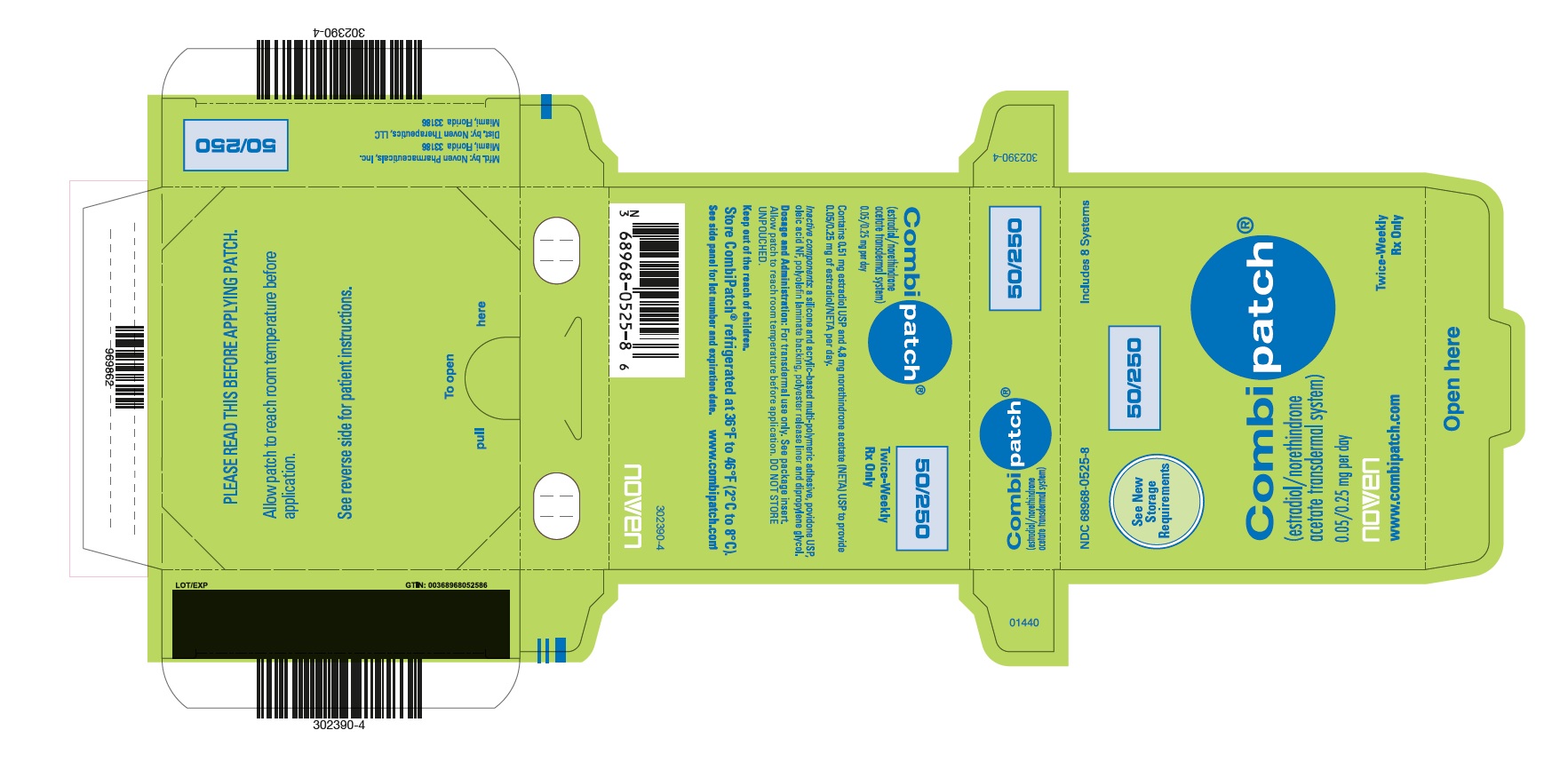
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANELPRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - NDC - 68968-0525-8 CombiPatch Count - 50/250 - NDC 68968-0525-8 - Includes 8 Systems - See New Storage Requirements - Combipatch® 50/250 - (estradiol/norethindrone acetate ...
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCEProduct Information