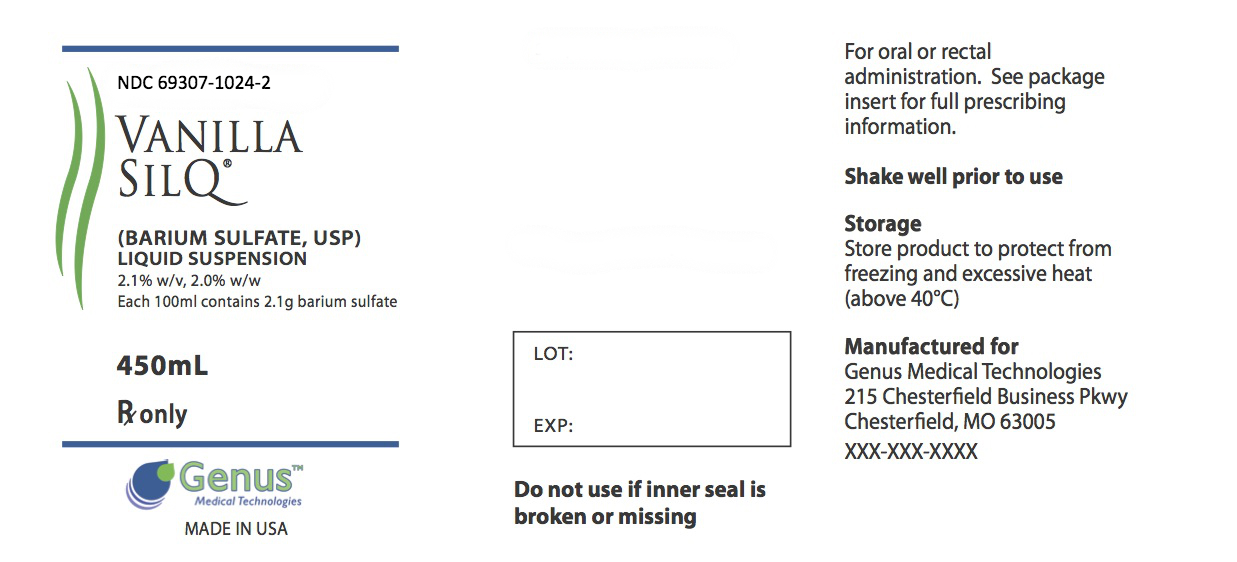
Label: VANILLA SILQ- barium sulfate suspension
-
Contains inactivated NDC Code(s)
NDC Code(s): 69307-1024-2 - Packager: Genus Medical Technologies, LLC
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: unapproved drug other
DISCLAIMER: This drug has not been found by FDA to be safe and effective, and this labeling has not been approved by FDA. For further information about unapproved drugs, click here.
Drug Label Information
Updated January 11, 2021
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION: SILQ™ is a barium sulfate suspension 2.1% w/v, 2.0% w/w for oral and rectal administration. Each 100 mL contains 2.1 g barium sulfate. Barium sulfate, due to its high molecular density is opaque to x-rays and therefore, acts as a positive contrast agent for radiographic studies. The active ingredient is barium sulfate and its structural formula is BaSO 4. Barium sulfate occurs as a fine, white, odorless, tasteless, bulky powder which is free from grittiness. Its aqueous suspensions are neutral to litmus. It is practically insoluble in water solutions of acids and alkalies, and organic solvents.
- INACTIVE INGREDIENT
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Barium sulfate, due to its high molecular density is opaque to x-rays and, therefore, acts as a positive contrast agent for radiographic studies. Barium sulfate is biologically inert and, therefore, is not absorbed or metabolized by the body, and is eliminated from the GI tract unchanged. Excretion rate is a function of gastrointestinal transit time.
- INDICATIONS & USAGE
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS: This product should not be used in patients with known or suspected gastric or intestinal perforation, or hypersensitivity to barium sulfate or any component of this barium sulfate formulation; in patients with known or suspected obstruction of the colon; suspected tracheoesophageal fistula; obstructing lesions of the small intestine; pyloric stenosis; inflammation or neoplastic lesions of the rectum; or in patients who have had a recent rectal biopsy.
Barium sulfate suspensions should not be used for infants with swallowing disorders or for newborns with complete duodenal or jejunal obstruction or when distal small bowel or colon obstruction is suspected. Barium sulfate suspension is not recommended for very small preterm infants and young babies requiring small volumes of contrast media or for infants and young children when there is a possibility of leakage from the gastrointestinal tract, such as nectrotizing enterocolitis, unexplained pneumoperitoneum, gasless abdomen, other bowel perforation, esophageal perforation or post operative anastomosis
- WARNINGS
-
PRECAUTIONS
PRECAUTIONS: General: Procedures which involve the use of radiopaque contrast agents should be carried out under the direction of personnel with the requisite training and with a thorough knowledge of the particular procedure to be performed. A history of bronchial asthma, atopy, as evidenced by hay fever and eczema, or a previous reaction to a contrast agent, warrant special attention. Caution should be exercised with the use of radiopaque media in severly debilitated patients and in those with marked hypertension or advanced cardiac disease. Ingestion of barium is not recommended in patients with a history of food aspiration or in patients in whom the integrity of the swallowing mechanism is unknown. If barium is aspirated into the larynx, further administration should be immediately discontinued. After any barium study of the GI tract, it may be important to rehydrate the patient as quickly as possible to prevent impaction of the barium. To prevent barium impaction in the colon, the use of mild laxatives such as milk of magnesia or lactulose following completion of the examination may also be required. These mild laxatives are recommended on a routine basis and in patients with a history of constipation unless clinically contraindicated.
-
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
Information for Patients: Before using this product patients should be instructed to tell the physician ordering the procedure and the imaging technologist:
- if they are pregnant.
- if they are allergic to any foods or medication, or if they have had any prior reactions to barium sulfate products or other x-ray contrast agents.
- if they are currently taking any medications, have any serious medical condition for which they are being treated or followed, or had any recent surgery.
- Seek immediate medical attention if they experience an allergic
- DRUG INTERACTIONS
- PREGNANCY
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS: Adverse reactions accompanying the use of barium sulfate formulations are infrequent and usually mild, though severe reactions (approximately 1 in 500,000) and fatalities (approximately 1 in 2,000,000) have occurred. Procedural complications are rare, but may include aspiration pneumonitis, barium sulfate impaction, granuloma formation, intravasation, embolization and peritonitis following intestinal perforation, vasovagal and syncopal episodes, and fatalities. EKG changes have been shown to occur following or during barium sulfate suspension enemas. It is of the utmost importance to be completely prepared to treat any such occurrence.
Due to the increased likelihood of allergic reactions in atopic patients, a complete history of known and suspected allergies as well as allergic-like symptoms, e.g. rhinitis, bronchial asthma, eczema and urticaria, must be obtained prior to any medical procedure.
Aspiration of large amounts of barium sulfate suspension may cause pneumonitis or nodular granulomas of interstitial lung tissues and lymph nodes; asphyxiation and death have been reported.
Transient bacteremia, beginning almost immediately and lasting up to 15 minutes, may also occur during rectal administration of barium sulfate suspension, and rarely septicemia has been reported.
A rare mild allergic reaction would most likely be generalized pruritis, erythema or urticaria (approximately 1 in 100,000 reactions). Such reactions will often respond to an antihistamine. More serious reactions (approximately 1 in 500,000) may result in laryngeal edema, bronchospasm or hypotension.
Severe reactions which may require emergency measures are often characterized by peripheral vasodilation, hypotension, reflex tachycardia, dyspnea, bronchospasm, agitation, confusion and cyanosis, progressing to unconsciousness. Treatment should be initiated immediately according to established standard of care.
Apprehensive patients may develop weakness, pallor, tinnitus, diaphoresis and bradycardia following the administration of any diagnostic agent. Such reactions are usually non-allergic in nature.
Allergic reactions to the enema accessories, in particular to retention catheters (tips) with latex cuffs, can occur. Such reactions could occur immediately and result in the previously mentioned acute allergic-like responses or might be delayed in appearance and result in a contact dermatitis. Known atopic patients, particularly those with a history of asthma or eczema, should be evaluated for alternative methods of administration in order to avoid these adverse reactions. These plastic/rubber accessories are disposable, single-use devices that must not be reused or left in the body cavity for an extended period of time.
- OVERDOSAGE
- DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
VANILLA SILQ
barium sulfate suspensionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:69307-1024 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Barium Sulfate (UNII: 25BB7EKE2E) (Barium Sulfate - UNII:25BB7EKE2E) Barium Sulfate 21 mg in 1 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:69307-1024-2 450 mL in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 10/27/2014 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date unapproved drug other 10/27/2014 Labeler - Genus Medical Technologies, LLC (079478547)