Label: ISOFLURANE liquid
- NDC Code(s): 11695-6777-1, 11695-6777-2
- Packager: Butler Animal Health Supply, LLC
- Category: PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Abbreviated New Animal Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated March 29, 2023
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Isoflurane, USP is a nonflammable, nonexplosive general inhalation anesthetic agent. Its chemical name is l-chloro-2,2,2-trifluoroethyl difluoromethyl ether, and its structural formula is:
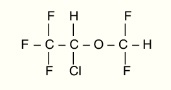
Each mL contains 99.9% isoflurane.
Some physical constants are:
Molecular weight
184.5
Boiling point at 760 mm Hg
48.5° C (uncorr.)
Refractive index n 20
D
1.2990 to 1.3005
Specific gravity 25°/25° C
1.496
Vapor pressure in mm Hg**
20° C
238
25° C
295
30° C
367
35° C
450
**Equation for vapor pressure calculation:
log10Pvap= A + B/T where: A = 8.056
B = -1664.58
T = °C + 273.16 (Kelvin)
Partition coefficients at 37° C:
Water/gas
0.61
Blood/gas
1.43
Oil/gas
90.8
Partition coefficients at 25° C - rubber and plastic
Conductive rubber/gas
62.0
Butyl rubber/gas
75.0
Polyvinyl chloride/gas
110.0
Polyethylene/gas
~2.0
Polyurethane/gas
~1.4
Polyolefin/gas
~1.1
Butyl acetate/gas
~2.5
Purity by gas chromatography
>99.9%
Lower limit of flammability in oxygen or
nitrous oxide at 9 joules/sec. and 23° C
None
Lower limit of flammability in oxygen or nitrous oxide at 900 joules/sec. and 23° C
Greater than useful concentration in anesthesia.
MAC (Minimum Alveolar Concentration) is 1.31% in horses1 and 1.28% in dogs.6
Isoflurane is a clear, colorless, stable liquid containing no additives or chemical stabilizers. Isoflurane has a mildly pungent, musty, ethereal odor. Samples stored in indirect sunlight in clear, colorless glass for five years, as well as samples directly exposed for 30 hours to a 2 amp, 115 volt, 60 cycle long wave U.V. light were unchanged in composition as determined by gas chromatography. Isoflurane in one normal sodium methoxide-methanol solution, a strong base, for over six months consumed essentially no alkali, indicative of strong base stability. Isoflurane does not decompose in the presence of soda lime (at normal operating temperatures), and does not attack aluminum, tin, brass, iron or copper.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Isoflurane is an inhalation anesthetic. Induction and recovery from anesthesia with isoflurane are rapid.2,5 The level of anesthesia may be changed rapidly with isoflurane. Isoflurane is a profound respiratory depressant. RESPIRATION MUST BE MONITORED CLOSELY IN THE HORSE AND DOG AND SUPPORTED WHEN NECESSARY. As anesthetic dose is increased, both tidal volume and respiratory rate decrease.3,6 This depression is partially reversed by surgical stimulation, even at deeper levels of anesthesia.
Blood pressure decreases with induction of anesthesia but returns toward normal with surgical stimulation. Progressive increases in depth of anesthesia produce corresponding decreases in blood pressure; however, heart rhythm is stable and cardiac output is maintained with controlled ventilation and normal PaCO2 despite increasing depth of anesthesia. The hypercapnia which attends spontaneous ventilation during isoflurane anesthesia increases heart rate and raises cardiac output above levels observed with controlled ventilation.3 Isoflurane does not sensitize the myocardium to exogenously administered epinephrine in the dog.
Muscle relaxation may be adequate for intra-abdominal operations at normal levels of anesthesia. However, if muscle relaxants are used to achieve greater relaxation, it should be noted that: ALL COMMONLY USED MUSCLE RELAXANTS ARE MARKEDLY POTENTIATED WITH ISOFLURANE, THE EFFECT BEING MOST PROFOUND WITH THE NONDEPOLARIZING TYPE. Neostigmine reverses the effect of nondepolarizing muscle relaxants in the presence of isoflurane but does not reverse the direct neuromuscular depression of isoflurane.
- INDICATIONS
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
Increasing depth of anesthesia with isoflurane may increase hypotension and respiratory depression. The electroencephalographic pattern associated with deep anesthesia is characterized by burst suppression, spiking, and isoelectric periods.4
Since levels of anesthesia may be altered easily and rapidly, only vaporizers producing predictable percentage concentrations of isoflurane should be used. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
The action of nondepolarizing relaxants is augmented by isoflurane. Less than the usual amounts of these drugs should be used. If the usual amounts of nondepolarizing relaxants are given, the time for recovery from myoneural blockade will be longer in the presence of isoflurane than in the presence of other commonly used anesthetics.
Not for use in horses intended for food.
Keep out of reach of children.
-
PRECAUTIONS
Isoflurane, like other inhalational anesthetics, can react with desiccated carbon dioxide (CO2) absorbents to produce carbon monoxide which may result in elevated carboxyhemoglobin levels in some patients. Case reports suggest that barium hydroxide lime and soda lime become desiccated when fresh gases are passed through the CO2 absorber canister at high flow rates over many hours or days. When a clinician suspects that CO2 absorbent may be desiccated, it should be replaced before the administration of isoflurane.
Usage in pregnancy: Reproduction studies have been performed in mice and rats with no evidence of fetal malformation attributable to isoflurane. Adequate data concerning the safe use of isoflurane in pregnant and breeding horses and dogs have not been obtained.
- ADVERSE REACTIONS
- OVERDOSAGE
-
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
Caution: Operating rooms should be provided with adequate ventilation to prevent the accumulation of anesthetic vapors.
Premedication: A premedication regimen, which may be employed depending upon the patient status, to avert excitement during induction, might include an anticholinergic, a tranquilizer, a muscle relaxant, and a short-acting barbiturate.
Inspired concentration: The delivered concentration of isoflurane should be known. Isoflurane may be vaporized using a flow-through vaporizer specifically calibrated for isoflurane. Vaporizers delivering a saturated vapor which is then diluted (e.g. Vernitrol® vaporizer) also may be used. The delivered concentration from such a vaporizer may be calculated using the formula:
% Isoflurane = 100 PVFV
FT (PA – PV)
where:
PA = Pressure of atmosphere
PV = Vapor pressure of isoflurane
FV = Flow of gas through vaporizer (mL/min)
FT = Total gas flow (mL/min)
Isoflurane contains no stabilizer. Nothing in the drug product alters calibration or operation of these vaporizers.
Induction:
Horses: Inspired concentrations of 3.0% to 5.0% isoflurane alone with oxygen following a barbiturate anesthetic induction are usually employed to induce surgical anesthesia in the horse.
Dogs: Inspired concentrations of 2.0% to 2.5% isoflurane alone with oxygen following a barbiturate anesthetic induction are usually employed to induce surgical anesthesia in the dog.
These concentrations can be expected to product surgical anesthesia in 5 to 10 minutes.
Maintenance: The concentration of vapor necessary to maintain anesthesia is much less than that required to induce it.
Horses: Surgical levels of anesthesia in the horse may be sustained with a 1.5% to 1.8% concentration of isoflurane in oxygen.
Dogs: Surgical levels of anesthesia in the dog may be sustained with a 1.5% to 1.8% concentration of isoflurane in oxygen.
The level of blood pressure during maintenance is an inverse function of isoflurane concentration in the absence of other complicating problems. Excessive decreases, unless related to hypovolemia, may be due to depth of anesthesia and in such instances may be corrected by lightening the level of anesthesia.
Recovery from isoflurane anesthesia is typically uneventful.2
- HOW SUPPLIED
-
REFERENCES
- Steffey, E.P., Howland, D. Jr., Giri, S. and Eger, E.I. II.: Enflurane, halothane and isoflurane potency in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1977; 38(7): 1037-1039.
- Auer, J.A., Garner, H.E., Amend, J.F., Hutcheson, D.P. and Salem, C.A., Recovery from anesthesia in ponies: A comparative study of the effects of isoflurane, enflurane, methoxyflurane and halothane. Equine Vet. J. 1978; 10(1): 18-23.
- Steffey, E.P. and Howland, D. Jr., Comparison of circulatory and respiratory effects of isoflurane and halothane anesthesia in horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1980; 41(5): 821-825.
- Auer, J.A., Amend, J.F., Garner, H.E., Hutcheson, D.P. and Salem, C.A., Electroencephalographic responses during volatile anesthesia in domestic ponies: A comparative study of isoflurane, enflurane, methoxyflurane, and halothane. Equine Practice. 1979:3:130-134.
- Klide, A.M., Cardiopulmonary effects of enflurane and isoflurane in the dog. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1976; 37(2): 127-131.
- Steffey, E.P., and Howland, D. Jr., Isoflurane potency in the dog and cat. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1977; 38(11): 1833-1936.
Text revised: January 2023
Distributed by:
Covetrus® North America
400 Metro Place North
Dublin, OH 43017
covetrus.com
Product of India
To report suspected adverse drug events, for technical assistance or to obtain a copy of the Safety Data Sheet, contact Covetrus® at
1-855-724-3461. For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS, or online at http://www.fda.gov/reportanimalae.
Approved by FDA under ANADA # 200-237 - PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ISOFLURANE
isoflurane liquidProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:11695-6777 Route of Administration RESPIRATORY (INHALATION) Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Isoflurane (UNII: CYS9AKD70P) (Isoflurane - UNII:CYS9AKD70P) Isoflurane 99.9 mL in 100 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:11695-6777-1 100 mL in 1 BOTTLE 2 NDC:11695-6777-2 250 mL in 1 BOTTLE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANADA ANADA200237 08/20/2019 Labeler - Butler Animal Health Supply, LLC (603750329) Registrant - Butler Animal Health Supply LLC, dba Covetrus North America (603750329) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Piramal Pharma Limited 919067108 ANALYSIS, API MANUFACTURE, LABEL, MANUFACTURE, PACK