Label: ISOLYTE P IN DEXTROSE- dextrose, sodium acetate, potassium chloride, magnesium chloride, and potassium phosphate, dibasic injection, solution
- NDC Code(s): 0264-7730-10
- Packager: B. Braun Medical Inc.
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated October 17, 2022
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
DESCRIPTION
Each 100 mL of Isolyte® P (Multi-Electrolyte Injection) in 5% Dextrose contains:
Hydrous Dextrose USP 5 g; Sodium Acetate Trihydrate USP 0.32 g
Potassium Chloride USP 0.13 g; Magnesium Chloride Hexahydrate USP 0.031 g
Dibasic Potassium Phosphate USP 0.026 g; Water for Injection USP qspH adjusted with Hydrochloric Acid NF
pH: 5.0 (4.0–6.0) Calories per liter: 170
Calculated Osmolarity: 340 mOsmol/literConcentration of Electrolytes (mEq/liter): Sodium 23; Chloride 29
Acetate (CH3COO-) 23; Potassium 20; Magnesium 3; 1Phosphate (HPO ) 3
) 3 Isolyte® P in 5% Dextrose is sterile, nonpyrogenic, and contains no bacteriostatic or antimicrobial agents or added buffers. This product is intended for intravenous administration.
The formulas of the active ingredients are:
Ingredients Molecular
FormulaMolecular
WeightSodium Acetate Trihydrate USP CH3COONa•3H2O 136.08 Potassium Chloride USP KCl 74.55 Magnesium Chloride Hexahydrate USP MgCl2•6H2O 203.30 Dibasic Potassium Phosphate USP K2HPO4 174.18 Hydrous Dextrose USP
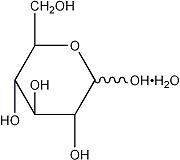
198.17 Not made with natural rubber latex, PVC or DEHP.
The plastic container is made from a multilayered film specifically developed for parenteral drugs. It contains no plasticizers. The solution contact layer is a rubberized copolymer of ethylene and propylene. Solutions in contact with the plastic container may leach out certain chemical components from the plastic in very small amounts; however, biological testing was supportive of the safety of the plastic container materials. The container-solution unit is a closed system and is not dependent upon entry of external air during administration. The container is overwrapped to provide protection from the physical environment and to provide an additional moisture barrier when necessary. Exposure to temperatures above 25°C/77°F during transport and storage will lead to minor losses in moisture content. Higher temperatures lead to greater losses. It is unlikely that these minor losses will lead to clinically significant changes within the expiration period.
Addition of medication should be accomplished using complete aseptic technique.
The closure system has two ports; the one for the administration set has a tamper evident plastic protector and the other is a medication site. Refer to the Directions for Use of the container.
- 1
- 1.5 mmole P/liter
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Isolyte® P in 5% Dextrose provides electrolytes and calories, and is a source of water for hydration. It is capable of inducing diuresis depending on the clinical condition of the patient.
Sodium, the major cation of the extracellular fluid, functions primarily in the control of water distribution, fluid balance, and osmotic pressure of body fluids. Sodium is also associated with chloride and bicarbonate in the regulation of the acid-base equilibrium of body fluid.
Potassium, the principal cation of intracellular fluid, participates in carbohydrate utilization and protein synthesis, and is critical in the regulation of nerve conduction and muscle contraction, particularly in the heart.
Chloride, the major extracellular anion, closely follows the metabolism of sodium, and changes in the acid-base balance of the body are reflected by changes in the chloride concentration.
Magnesium, a principal cation of soft tissue, is primarily involved in enzyme activity associated with the metabolism of carbohydrates and protein. Magnesium is also involved in neuromuscular irritability.
Phosphate is a major intracellular anion which participates in providing energy for metabolism of substrates and contributes to significant metabolic and enzymatic reactions in almost all organs and tissues. It exerts a modifying influence on calcium levels, a buffering effect on acid-base equilibrium and has a primary role in the renal excretion of hydrogen ions.
Acetate is an organic ion which is a hydrogen ion acceptor and contributes bicarbonate during its metabolism to carbon dioxide and water, and in sufficient quantities may serve as an alkalinizing agent.
Dextrose provides a source of calories. Dextrose is readily metabolized, may decrease losses of body protein and nitrogen, promotes glycogen deposition and decreases or prevents ketosis if sufficient doses are provided.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
The administration of intravenous solutions can cause fluid and/or solute overload resulting in dilution of serum electrolyte concentrations, overhydration, congested states or pulmonary edema. The risk of dilutional states is inversely proportional to the electrolyte concentration. The risk of solute overload causing congested states with peripheral and pulmonary edema is directly proportional to the electrolyte concentration.
Solutions containing sodium ions should be used with great care, if at all, in patients with congestive heart failure, severe renal insufficiency, and in clinical states in which there is sodium retention with edema.
Solutions containing potassium ions should be used with great care, if at all, in patients with hyperkalemia, severe renal failure, and in conditions in which potassium retention is present.
In patients with diminished renal function, administration of solutions containing sodium or potassium ions may result in sodium or potassium retention.
Infuse solutions containing phosphate slowly to avoid phosphate intoxication. Infusing high concentrations of phosphate may cause hypocalcemia and tetany. Serum phosphorus and calcium levels should be monitored frequently.
Solutions containing acetate should be used with great care in patients with metabolic or respiratory alkalosis. The administration of acetate should be done with great care in those conditions in which there is an increased level or an impaired utilization of acetate, such as severe hepatic insufficiency.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
This solution should be used with care in patients with hypervolemia, renal insufficiency, urinary tract obstruction, impending or frank cardiac decompensation.
Extraordinary electrolyte losses such as may occur during protracted nasogastric suction, vomiting, diarrhea or gastrointestinal fistula drainage may necessitate additional electrolyte supplementation.
Additional essential electrolytes, minerals, and vitamins should be supplied as needed.
Care should be exercised in administering solutions containing sodium or potassium to patients with renal or cardiovascular insufficiency, with or without congestive heart failure, particularly if they are postoperative or elderly.
Potassium therapy should be guided primarily by serial electrocardiograms, especially in patients receiving digitalis. Serum potassium levels are not necessarily indicative of tissue potassium levels.
Solutions containing potassium or magnesium should be used with caution in the presence of cardiac disease, particularly in the presence of renal disease.
Solutions containing acetate should be used with caution. Excess administration may result in metabolic alkalosis.
Solutions containing dextrose should be used with caution in patients with overt or known subclinical diabetes mellitus, or carbohydrate intolerance for any reason.
To minimize the risk of possible incompatibilities arising from mixing this solution with other additives that may be prescribed, the final infusate should be inspected for cloudiness or precipitation immediately after mixing, prior to administration, and periodically during administration.
Do not use plastic containers in series connection.
If administration is controlled by a pumping device, care must be taken to discontinue pumping action before the container runs dry or air embolism may result. If administration is not controlled by a pumping device, refrain from applying excessive pressure (>300mmHg) causing distortion to the container such as wringing or twisting. Such handling could result in breakage of the container.
This solution is intended for intravenous administration using sterile equipment.
Use only if solution is clear and container and seals are intact.
Laboratory Tests
Clinical evaluation and periodic laboratory determinations are necessary to monitor changes in fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations, and acid-base balance during prolonged parenteral therapy or whenever the condition of the patient warrants such evaluation. Significant deviations from normal concentrations may require the use of additional electrolyte supplements, or the use of electrolyte-free dextrose solutions to which individualized electrolyte supplements may be added.
Drug Interactions
Sodium-containing solutions should be administered with caution to patients receiving corticosteroids or corticotropin, or to other salt-retaining patients.
Administration of barbiturates, narcotics, hypnotics, or systemic anesthetics should be adjusted with caution in patients also receiving magnesium-containing solutions because of an additive central depressive effect.
Parenteral magnesium should be administered with extreme caution to patients receiving digitalis preparations.
Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, impairment of fertility
Long term animal studies with Isolyte® P (Multi-Electrolyte Injection) in 5% Dextrose have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential, mutagenic potential, or effects on fertility.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Isolyte® P in 5% Dextrose. It is also not known whether Isolyte® P in 5% Dextrose can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Isolyte® P in 5% Dextrose should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Labor and Delivery
As reported in the literature, Dextrose and electrolyte solutions have been administered during labor and delivery. Caution should be exercised, and the fluid balance, glucose and electrolyte concentrations, and acid-base balance, of both mother and fetus should be evaluated periodically or whenever warranted by the condition of the patient or fetus.
Nursing Mothers
Caution should be exercised when Isolyte® P in 5% Dextrose is administered to a nursing woman.
Geriatric Use
In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
See WARNINGS.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Reactions which may occur because of the solution or the technique of administration include febrile response, infection at the site of injection, venous thrombosis or phlebitis extending from the site of injection, extravasation and hypervolemia.
Too rapid infusion of hypertonic solutions may cause local pain and venous irritation. Rate of administration should be adjusted according to tolerance. Use of the largest peripheral vein and a small bore needle is recommended. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Symptoms may result from an excess or deficit of one or more of the ions present in the solution; therefore, frequent monitoring of electrolyte levels is essential.
Hypernatremia may be associated with edema and exacerbation of congestive heart failure due to the retention of water, resulting in an expanded extracellular fluid volume.
Reactions reported with the use of potassium-containing solutions include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhea. The signs and symptoms of potassium intoxication include paresthesias of the extremities, areflexia, muscular or respiratory paralysis, mental confusion, weakness, hypotension, cardiac arrhythmias, heart block, electrocardiographic abnormalities and cardiac arrest. Potassium deficits result in disruption of neuromuscular function, and intestinal ileus and dilatation.
If infused in large amounts, chloride ions may cause a loss of bicarbonate ions, resulting in an acidifying effect.
Abnormally high plasma levels of magnesium can result in flushing, sweating, hypotension, circulatory collapse, and depression of cardiac and central nervous system function. Respiratory depression is the most immediate threat to life. Magnesium deficits can result in tachycardia, hypertension, hyperirritability and psychotic behavior.
Phosphorus deficiency may lead to impaired tissue oxygenation and acute hemolytic anemia. Relative to calcium, excessive phosphorus intake can precipitate hypocalcemia with cramps, tetany and muscular hyperexcitability.
The physician should also be alert to the possibility of adverse reactions to drug additives. Prescribing information for drug additives to be administered in this manner should be consulted.
If an adverse reaction does occur, discontinue the infusion, evaluate the patient, institute appropriate therapeutic countermeasures and save the remainder of the fluid for examination if deemed necessary.
-
OVERDOSAGE
In the event of a fluid or solute overload during parenteral therapy, reevaluate the patient's condition, and institute appropriate corrective treatment.
In the event of overdosage with potassium-containing solutions, discontinue the infusion immediately and institute corrective therapy to reduce serum potassium levels.
Treatment of hyperkalemia includes the following:
- Dextrose Injection USP, 10% or 25% containing 10 units of crystalline insulin per 20 grams of dextrose administered intravenously, 300 to 500 mL per hour.
- Absorption and exchange of potassium using sodium or ammonium cycle cation exchange resin, orally and as retention enema.
- Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis. The use of potassium-containing foods or medications must be eliminated. However, in cases of digitalization, too rapid a lowering of plasma potassium concentration can cause digitalis toxicity.
Over-aggressive phosphate replacement may precipitate hypocalcemic tetany. To prevent hypocalcemia, calcium supplementation should always accompany phosphate administration.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
This solution is for intravenous use only.
Dosage is to be directed by a physician and is dependent upon age, weight, clinical condition of the patient and laboratory determinations. Frequent laboratory determinations and clinical evaluation are essential to monitor changes in blood glucose and electrolyte concentrations, and fluid and electrolyte balance during prolonged parenteral therapy.
When a hypertonic solution is to be administered peripherally, it should be slowly infused through a small bore needle, placed well within the lumen of a large vein to minimize venous irritation. Carefully avoid infiltration.
Fluid administration should be based on calculated maintenance or replacement fluid requirements for each patient.
Some additives may be incompatible. Consult with pharmacist. When introducing additives, use aseptic techniques. Mix thoroughly. Do not store.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
-
Directions for Use of EXCEL® Container
To Open
Tear overwrap down at notch and remove solution container. Check for minute leaks by squeezing solution container firmly. If leaks are found, discard solution as sterility may be impaired. If supplemental medication is desired, follow directions below before preparing for administration.
Before use, perform the following checks:
- Inspect each container. Read the label. Ensure solution is the one ordered and is within the expiration date.
- Invert container and carefully inspect the solution in good light for cloudiness, haze, or particulate matter. Any container which is suspect should not be used.
- Use only if solution is clear and container and seals are intact.
Preparation for Administration
- Remove plastic protector from sterile set port at bottom of container.
- Attach administration set. Refer to complete directions accompanying set.
To Add Medication Before Solution Administration
- Prepare medication site.
- Using syringe with 18–22 gauge needle, puncture medication port and inner diaphragm and inject.
- Squeeze and tap ports while ports are upright and mix solution and medication thoroughly.
To Add Medication During Solution Administration
- Close clamp on the set.
- Prepare medication site.
- Using syringe with 18–22 gauge needle of appropriate length (at least 5/8 inch), puncture resealable medication port and inner diaphragm and inject.
- Remove container from IV pole and/or turn to an upright position.
- Evacuate both ports by tapping and squeezing them while container is in the upright position.
- Mix solution and medication thoroughly.
- Return container to in use position and continue administration.
- HOW SUPPLIED
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 500 mL Container Label
Isolyte® P in 5% Dextrose
(Multi-Electrolyte Injection)REF L7301
NDC 0264-7730-10
HK 22411500 mL
EXCEL® CONTAINERElectrolytes (mEq/liter):
Na+ 23
K+ 20
Mg++ 3
Cl– 29
Acetate 23
Phosphate
(HPO ) 3
) 3
(1.5 mmole P/L)Each 100 mL contains: Hydrous Dextrose USP 5 g; Sodium Acetate•3H2O USP
0.32 g; Potassium Chloride USP 0.13 g; Magnesium Chloride•6H2O USP 0.031 g;
Dibasic Potassium Phosphate USP 0.026 g; Water for Injection USP qs
pH adjusted with HCl NF
pH: 5.0 (4.0-6.0) Calc Osmolarity: 340 mOsmol/literSterile, nonpyrogenic. Single dose container. Do not use in series connection. For
intravenous use only.Use only if solution is clear and container and seals are intact.WARNINGS: Some additives may be incompatible. Consult with pharmacist. When
introducing additives, use aseptic techniques. Mix thoroughly. Do not store.Recommended Storage: Room temperature (25°C). Avoid excessive heat. Protect
from freezing. See Package Insert.Do not remove overwrap until ready for use. After removing the overwrap, check for minute leaks by squeezing container firmly. If leaks are found, discard solution as sterility may be impaired.
Not made with natural rubber latex, PVC or DEHP.Rx only

EXCEL and Isolyte are registered trademarks of B. Braun Medical Inc.
B. Braun Medical Inc.
Bethlehem, PA 18018 3524 USA
1-800-227-2862Y94-003-244
LD-145-4EXP
LOT
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ISOLYTE P IN DEXTROSE
dextrose, sodium acetate, potassium chloride, magnesium chloride, and potassium phosphate, dibasic injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:0264-7730 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DEXTROSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: LX22YL083G) (ANHYDROUS DEXTROSE - UNII:5SL0G7R0OK) DEXTROSE MONOHYDRATE 5 g in 100 mL SODIUM ACETATE (UNII: 4550K0SC9B) (SODIUM CATION - UNII:LYR4M0NH37, ACETATE ION - UNII:569DQM74SC) SODIUM ACETATE 0.32 g in 100 mL POTASSIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 660YQ98I10) (POTASSIUM CATION - UNII:295O53K152, CHLORIDE ION - UNII:Q32ZN48698) POTASSIUM CHLORIDE 0.13 g in 100 mL MAGNESIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 02F3473H9O) (MAGNESIUM CATION - UNII:T6V3LHY838, CHLORIDE ION - UNII:Q32ZN48698) MAGNESIUM CHLORIDE 0.031 g in 100 mL POTASSIUM PHOSPHATE, DIBASIC (UNII: CI71S98N1Z) (POTASSIUM CATION - UNII:295O53K152, PHOSPHATE ION - UNII:NK08V8K8HR) POTASSIUM PHOSPHATE, DIBASIC 0.026 g in 100 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:0264-7730-10 24 in 1 CASE 06/10/1993 1 500 mL in 1 CONTAINER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA019873 06/10/1993 Labeler - B. Braun Medical Inc. (002397347)



