| This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration | Revised: March 2023 |
| MEDICATION GUIDE | |
| PROMACTA® (pro-MAC-ta) (eltrombopag) tablets | PROMACTA® (pro-MAC-ta) (eltrombopag) for oral suspension |
| What is the most important information I should know about PROMACTA?
PROMACTA can cause serious side effects, including: Liver problems:
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any of these signs and symptoms of liver problems: |
|
|
|
| See “What are the possible side effects of PROMACTA?” for other side effects of PROMACTA. | |
| What is PROMACTA?
PROMACTA is a prescription medicine used to treat adults and children 1 year of age and older with low blood platelet counts due to persistent or chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP), when other medicines to treat ITP or surgery to remove the spleen have not worked well enough. PROMACTA is also used to treat people with:
PROMACTA is used to try to raise platelet counts in order to lower your risk for bleeding. PROMACTA is not used to make platelet counts normal. PROMACTA is not for use in people with a pre-cancerous condition called myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), or in people with low platelet counts caused by certain other medical conditions or diseases. It is not known if PROMACTA is safe and effective when used with other antiviral medicines to treat chronic hepatitis C. It is not known if PROMACTA is safe and effective in children:
|
|
Before you take PROMACTA, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
Certain medicines may keep PROMACTA from working correctly. Take PROMACTA at least 2 hours before or 4 hours after taking these products:
Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure if your medicine is one that is listed above. |
|
How should I take PROMACTA?
|
|
| What should I avoid while taking PROMACTA?
Avoid situations and medicines that may increase your risk of bleeding. |
|
| What are the possible side effects of PROMACTA?
PROMACTA may cause serious side effects, including:
The most common side effects of PROMACTA in adults and children include: |
|
|
|
| Laboratory tests may show abnormal changes to the cells in your bone marrow. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all of the possible side effects of PROMACTA. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
| How should I store PROMACTA tablets and PROMACTA for oral suspension?
Tablets:
For oral suspension:
Keep PROMACTA and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
|
| General information about the safe and effective use of PROMACTA
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use PROMACTA for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give PROMACTA to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about PROMACTA that is written for health professionals. |
|
| What are the ingredients in PROMACTA?
Tablets Active ingredient: eltrombopag olamine Inactive ingredients:
For oral suspension Active ingredient: eltrombopag olamine Inactive ingredients: mannitol, sucralose, and xanthan gum Distributed by: Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, East Hanover, New Jersey 07936 © Novartis For more information about PROMACTA, go to www.PROMACTA.com or call 1-888-669-6682. |
|
T2023-14
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
PROMACTA® [pro-MAC-ta]
(eltrombopag)
for oral suspension
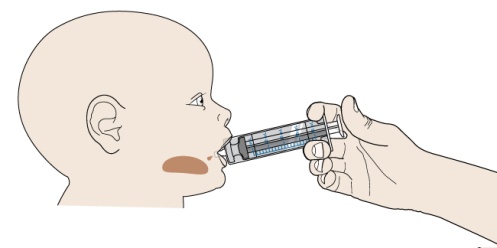
Read all the Instructions for Use and follow the steps below to mix and give a dose of PROMACTA for oral suspension.
Important information you need to know before taking PROMACTA for oral suspension:
- Do not take PROMACTA for oral suspension or give it to someone else until you have been shown how to properly mix and give a dose of PROMACTA for oral suspension. Your healthcare provider or nurse will show you how to mix and give a dose of PROMACTA for oral suspension properly.
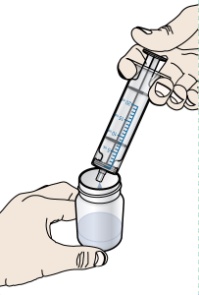
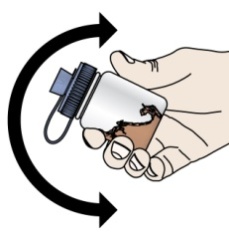
- PROMACTA for oral suspension must be mixed with cool or cold water only. Do not use hot water to prepare the oral suspension.
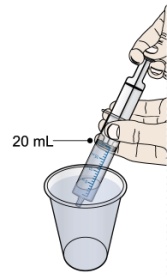
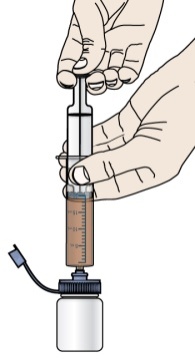
- Give the dose of suspension right away after mixing with water. If the medicine is not given within 30 minutes, you will have to mix a new dose. Throw away (discard) the unused mixture into the trash. Do not pour it down the drain.
- If PROMACTA for oral suspension comes in contact with your skin, wash the skin right away with soap and water. Call your healthcare provider if you have a skin reaction or if you have any questions. If you spill any powder or liquid, follow the clean-up instructions in Step 12.
- Contact your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you have any questions about how to mix or give PROMACTA to your child, or if you damage or lose any of the supplies in your kit.
- Do not re-use the oral dosing syringe. Use a new single-use oral dosing syringe to prepare each dose of PROMACTA for oral suspension.
- After you have used all 30 packets, throw all the remaining supplies (mixing bottle, lid with cap, and oral dosing syringe) away in the trash.
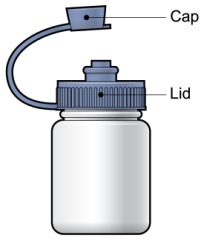
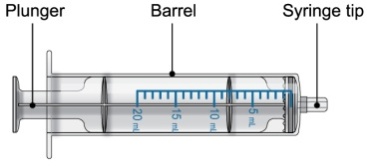
Each PROMACTA for oral suspension kit contains the following supplies:
You will need the following to give a dose of PROMACTA for oral suspension.
From the kit:
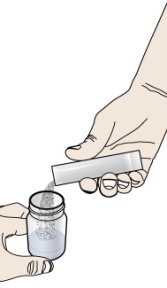
- prescribed number of packets
- 1 reusable mixing bottle with lid and cap. Note: Due to its small size, the cap may pose a danger of choking to small children.
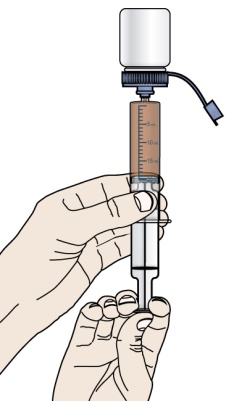
- 1 single-use 20-mL oral dosing syringe (Use a new (single-use) oral dosing syringe to prepare each dose of PROMACTA for oral suspension)
Not included in the kit:
- 1 clean glass or cup filled with drinking water
- scissors to cut packet
- paper towels or disposable cloth
- disposable gloves (optional)
T2020-61