Label: NOREPINEPHRINE BITARTRATE injection, solution
- NDC Code(s): 25021-316-04
- Packager: Sagent Pharmaceuticals
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Abbreviated New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated February 17, 2021
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use NOREPINEPHRINE BITARTRATE INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for NOREPINEPHRINE BITARTRATE INJECTION.
NOREPINEPHRINE BITARTRATE injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1950INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Norepinephrine Bitartrate Injection is a catecholamine indicated for restoration of blood pressure in adult patients with acute hypotensive states. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Initial dose of 0.25 mL to 0.375 mL (from 8 mcg to 12 mcg of base) per minute, adjust the rate of flow to establish and maintain a low to normal blood pressure (usually 80 mm Hg to 100 mm Hg systolic) sufficient to maintain the circulation of vital organs. (2.2)
- The average maintenance dose ranges from 0.0625 mL to 0.125 mL per minute (from 2 mcg to 4 mcg of base). (2.2)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 4 mg per 4 mL (1 mg per mL) norepinephrine base in single-dose glass vial. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Tissue Ischemia: Avoid extravasation of norepinephrine bitartrate into the tissues, as local necrosis might ensue due to the vasoconstrictive action of the drug. Infuse norepinephrine bitartrate into a large vein. To prevent sloughing and necrosis in areas in which extravasation has taken place, the area should be infiltrated as soon as possible with 10 mL to 15 mL of saline solution containing from 5 mg to 10 mg of an adrenergic blocking agent. (5.1)
- Hypotension After Abrupt Discontinuation: Sudden cessation of the infusion rate may result in marked hypotension. Reduce the norepinephrine bitartrate infusion rate gradually. (5.2)
- Cardiac Arrhythmias: Norepinephrine Bitartrate may cause arrhythmias. Monitor cardiac function in patients with underlying heart disease. (5.3)
- Allergic Reactions with Sulfite: Norepinephrine Bitartrate contains sodium metabisulfite. Sulfite may cause allergic-type-reactions. (5.4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions are ischemic injury, bradycardia, anxiety, transient headache, respiratory difficulty, and extravasation necrosis at injection site. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Sagent Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-866-625-1618 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Elderly patients may be at greater risk of developing adverse reactions. (8.5)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 2/2021
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Instructions
2.2 Dosage
2.3 Preparation of Diluted Solution
2.4 Drug Incompatibilities
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Tissue Ischemia
5.2 Hypotension after Abrupt Discontinuation
5.3 Cardiac Arrhythmias
5.4 Allergic Reactions Associated with Sulfite
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 MAO-Inhibiting Drugs
7.2 Tricyclic Antidepressants
7.3 Antidiabetics
7.4 Halogenated Anesthetics
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Instructions
Correct Hypovolemia
Address hypovolemia before initiation of norepinephrine bitartrate injection therapy. If the patient does not respond to therapy, suspect occult hypovolemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Administration
Dilute norepinephrine bitartrate injection prior to use [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Infuse norepinephrine bitartrate injection into a large vein. Avoid infusions into the veins of the leg in the elderly or in patients with occlusive vascular disease of the legs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Avoid using a catheter-tie-in technique.
2.2 Dosage
After an initial dosage of 8 to 12 mcg per minute via intravenous infusion, assess patient response and adjust dosage to maintain desired hemodynamic effect. Monitor blood pressure every two minutes until the desired hemodynamic effect is achieved, and then monitor blood pressure every five minutes for the duration of the infusion.
Typical maintenance intravenous dosage is 2 to 4 mcg per minute.
2.3 Preparation of Diluted Solution
Visually inspect norepinephrine bitartrate injection for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration (the solution is colorless). Do not use the solution if its color is pinkish or darker than slightly yellow or if it contains a precipitate.
Add the content of one norepinephrine bitartrate injection vial (4 mg in 4 mL) to 1,000 mL of 5% Dextrose Injection, USP or Sodium Chloride Injection solutions that contain 5% dextrose to produce a 4 mcg per mL dilution. Dextrose reduces loss of potency due to oxidation. Administration in saline solution alone is not recommended.
Use higher concentration solutions in patients requiring fluid restriction. Prior to use, store the diluted norepinephrine bitartrate injection solution for up to 24 hours at room temperature [20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F)] and protect from light.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Tissue Ischemia
Administration of norepinephrine bitartrate to patients who are hypotensive from hypovolemia can result in severe peripheral and visceral vasoconstriction, decreased renal perfusion and reduced urine output, tissue hypoxia, lactic acidosis, and reduced systemic blood flow despite “normal” blood pressure. Address hypovolemia prior to initiating norepinephrine bitartrate [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. Avoid norepinephrine bitartrate in patients with mesenteric or peripheral vascular thrombosis, as this may increase ischemia and extend the area of infarction.
Gangrene of the extremities has occurred in patients with occlusive or thrombotic vascular disease or who received prolonged or high dose infusions. Monitor for changes to the skin of the extremities in susceptible patients.
Extravasation of norepinephrine bitartrate may cause necrosis and sloughing of surrounding tissue. To reduce the risk of extravasation, infuse into a large vein, check the infusion site frequently for free flow, and monitor for signs of extravasation [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Emergency Treatment of Extravasation
To prevent sloughing and necrosis in areas in which extravasation has occurred, infiltrate the ischemic area as soon as possible, using a syringe with a fine hypodermic needle with 5 to 10 mg of phentolamine mesylate in 10 to 15 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection in adults.
Sympathetic blockade with phentolamine causes immediate and conspicuous local hyperemic changes if the area is infiltrated within 12 hours.
5.2 Hypotension after Abrupt Discontinuation
Sudden cessation of the infusion rate may result in marked hypotension. When discontinuing the infusion, gradually reduce the norepinephrine bitartrate infusion rate while expanding blood volume with intravenous fluids.
5.3 Cardiac Arrhythmias
Norepinephrine Bitartrate elevates intracellular calcium concentrations and may cause arrhythmias, particularly in the setting of hypoxia or hypercarbia. Perform continuous cardiac monitoring of patients with arrhythmias.
5.4 Allergic Reactions Associated with Sulfite
Norepinephrine Bitartrate Injection contains sodium metabisulfite, a sulfite that may cause allergic-type reactions including anaphylactic symptoms and life-threatening or less severe asthmatic episodes in certain susceptible people. The overall prevalence of sulfite sensitivity in the general population is unknown. Sulfite sensitivity is seen more frequently in asthmatic than in non-asthmatic people.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described in greater detail in other sections:
- Tissue Ischemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hypotension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Cardiac Arrhythmias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
The most common adverse reactions are hypertension and bradycardia.
The following adverse reactions can occur:
Nervous system disorders: Anxiety, headache
Respiratory disorders: Respiratory difficulty, pulmonary edema
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 MAO-Inhibiting Drugs
Co-administration of norepinephrine bitartrate with monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors or other drugs with MAO-inhibiting properties (e.g., linezolid) can cause severe, prolonged hypertension.
If administration of norepinephrine bitartrate cannot be avoided in patients who recently have received any of these drugs and in whom, after discontinuation, MAO activity has not yet sufficiently recovered, monitor for hypertension.
7.2 Tricyclic Antidepressants
Co-administration of norepinephrine bitartrate with tricyclic antidepressants (including amitriptyline, nortriptyline, protriptyline, clomipramine, desipramine, imipramine) can cause severe, prolonged hypertension. If administration of norepinephrine bitartrate cannot be avoided in these patients, monitor for hypertension.
7.3 Antidiabetics
Norepinephrine Bitartrate can decrease insulin sensitivity and raise blood glucose. Monitor glucose and consider dosage adjustment of antidiabetic drugs.
7.4 Halogenated Anesthetics
Concomitant use of norepinephrine bitartrate with halogenated anesthetics (e.g., cyclopropane, desflurane, enflurane, isoflurane, and sevoflurane) may lead to ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. Monitor cardiac rhythm in patients receiving concomitant halogenated anesthetics.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Limited published data consisting of a small number of case reports and multiple small trials involving the use of norepinephrine in pregnant women at the time of delivery have not identified an increased risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. There are risks to the mother and fetus from hypotension associated with septic shock, myocardial infarction and stroke which are medical emergencies in pregnancy and can be fatal if left untreated. (see Clinical Considerations). In animal reproduction studies, using high doses of intravenous norepinephrine resulted in lowered maternal placental blood flow. Clinical relevance to changes in the human fetus is unknown since the average maintenance dose is ten times lower (see Data). Increased fetal reabsorptions were observed in pregnant hamsters after receiving daily injections at approximately 2 times the maximum recommended dose on a mg/m3 basis for four days during organogenesis (see Data).
The estimated background risk for major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in the clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
Hypotension associated with septic shock, myocardial infarction, and stroke are medical emergencies in pregnancy which can be fatal if left untreated. Delaying treatment in pregnant women with hypotension associated with septic shock, myocardial infarction and stroke may increase the risk of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality. Life-sustaining therapy for the pregnant woman should not be withheld due to potential concerns regarding the effects of norepinephrine on the fetus.
Animal Data
A study in pregnant sheep receiving high doses of intravenous norepinephrine (40 mcg/min, at approximately 10 times the average maintenance dose of 2 to 4 mcg/min in human, on a mg/kg basis) exhibited a significant decrease in maternal placental blood flow. Decreases in fetal oxygenation, urine and lung liquid flow were also observed.
Norepinephrine administration to pregnant rats on Gestation Day 16 or 17 resulted in cataract production in rat fetuses.
In hamsters, an increased number of resorptions (29.1% in study group vs. 3.4% in control group), fetal microscopic liver abnormalities and delayed skeletal ossification were observed at approximately 2 times the maximum recommended intramuscular or subcutaneous dose (on a mg/m2 basis at a maternal subcutaneous dose of 0.5 mg/kg/day from Gestation Day 7 to 10).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of norepinephrine in either human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Clinically relevant exposure to the infant is not expected based on the short half-life and poor oral bioavailability of norepinephrine.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of norepinephrine bitartrate did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
Avoid administration of norepinephrine bitartrate into the veins in the leg in elderly patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Norepinephrine (sometimes referred to as l-arterenol/Levarterenol or l-norepinephrine) is a sympathomimetic amine which differs from epinephrine by the absence of a methyl group on the nitrogen atom.
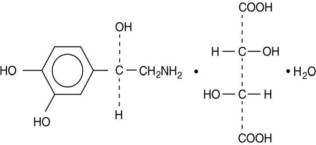
Norepinephrine Bitartrate is (-)-α-(aminomethyl)-3,4-dihydroxybenzyl alcohol tartrate (1:1) (salt) monohydrate (molecular weight 337.3 g/mol) and has the following structural formula:
Norepinephrine Bitartrate Injection, USP is supplied in a sterile aqueous solution in the form of the bitartrate salt to be administered by intravenous infusion. Norepinephrine is sparingly soluble in water, very slightly soluble in alcohol and ether, and readily soluble in acids. Each mL contains 1 mg of norepinephrine base (equivalent to 1.89 mg of norepinephrine bitartrate, anhydrous basis), sodium chloride for isotonicity, not more than 0.2 mg (vials) of sodium metabisulfite as an antioxidant. It has a pH of 3.0 to 4.5. The air in the containers has been displaced by nitrogen gas.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Norepinephrine is a peripheral vasoconstrictor (alpha-adrenergic action) and an inotropic stimulator of the heart and dilator of coronary arteries (beta-adrenergic action).
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The primary pharmacodynamic effects of norepinephrine are cardiac stimulation and vasoconstriction. Cardiac output is generally unaffected, although it can be decreased, and total peripheral resistance is also elevated. The elevation in resistance and pressure result in reflex vagal activity, which slows the heart rate and increases stroke volume. The elevation in vascular tone or resistance reduces blood flow to the major abdominal organs as well as to skeletal muscle. Coronary blood flow is substantially increased secondary to the indirect effects of alpha stimulation. After intravenous administration, a pressor response occurs rapidly and reaches steady state within 5 minutes. The pharmacologic actions of norepinephrine are terminated primarily by uptake and metabolism in sympathetic nerve endings. The pressor action stops within 1 to 2 minutes after the infusion is discontinued.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following initiation of intravenous infusion, the steady state plasma concentration is achieved in 5 min.
Distribution
Plasma protein binding of norepinephrine is approximately 25%. It is mainly bound to plasma albumin and to a smaller extent to prealbumin and alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. The volume of distribution is 8.8 L. Norepinephrine localizes mainly in sympathetic nervous tissue. It crosses the placenta but not the blood-brain barrier.
Elimination
The mean half-life of norepinephrine is approximately 2.4 min. The average metabolic clearance is 3.1 L/min.
Metabolism
Norepinephrine is metabolized in the liver and other tissues by a combination of reactions involving the enzymes catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) and MAO. The major metabolites are normetanephrine and 3-methoxyl-4-hydroxy mandelic acid (vanillylmandelic acid, VMA), both of which are inactive. Other inactive metabolites include 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol, 3,4-dihydroxymandelic acid, and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycol.
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Norepinephrine Bitartrate Injection, USP, is a sterile, colorless to pale yellow solution for injection intended for intravenous use. It contains the equivalent of 1 mg of norepinephrine base per 1 mL (4 mg per 4 mL). It is supplied in amber glass vials as follows:
NDC Norepinephrine Bitartrate Injection, USP
(1 mg per mL)Package Factor 25021-316-04 4 mg per 4 mL Single-Dose Vial 10 vials per carton Storage Conditions
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° and 30°C (59° and 86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Protect from light. Retain in carton until time of use.
Discard unused portion.
Sterile, Nonpyrogenic, Preservative-free.
The container closure is not made with natural rubber latex. -
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Risk of Tissue Damage
Advise the patient, family, or caregiver to report signs of extravasation urgently [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
SAGENT®
Mfd. for SAGENT Pharmaceuticals
Schaumburg, IL 60195 (USA)
Made in India
©2021 Sagent Pharmaceuticals, Inc.February 2021
SAGENT Pharmaceuticals ®
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
NOREPINEPHRINE BITARTRATE
norepinephrine bitartrate injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:25021-316 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Norepinephrine Bitartrate (UNII: IFY5PE3ZRW) (Norepinephrine - UNII:X4W3ENH1CV) Norepinephrine 1 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Sodium Chloride (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) Sodium Metabisulfite (UNII: 4VON5FNS3C) Nitrogen (UNII: N762921K75) Water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:25021-316-04 10 in 1 CARTON 07/01/2021 1 4 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA214323 07/01/2021 Labeler - Sagent Pharmaceuticals (796852890)