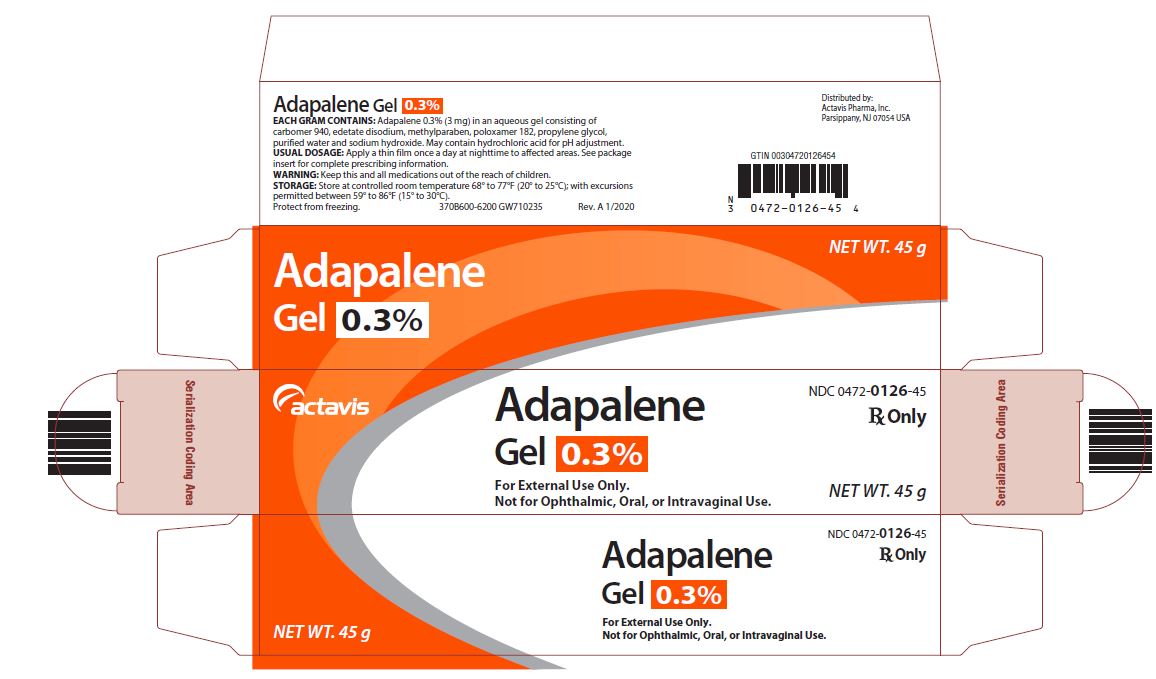
Label: ADAPALENE gel
- NDC Code(s): 0472-0126-45
- Packager: Actavis Pharma, Inc.
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Abbreviated New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated October 18, 2022
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ADAPALENE GEL safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ADAPALENE GEL.
ADAPALENE gel, for topical use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1996INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Adapalene Gel is a retinoid, indicated for the topical treatment of acne vulgaris in patients 12 years of age and older. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Gel, 0.3% (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Contraindicated in patients who have known hypersensitivity to adapalene or any excipient of adapalene gel. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Allergic/ Hypersensitivity Reactions: Allergy/hypersensitivity reactions include anaphylaxis, angioedema, urticaria, and pruritis. Discontinue adapalene gel in the event of an allergic/hypersensitivity reaction. (5.1)
- Ultraviolet Light and Environmental Exposure: Avoid exposure to sunlight and sunlamps. Wear sunscreen when sun exposure cannot be avoided (5.2).
-
Local Cutaneous Reactions: Erythema, scaling, dryness, and stinging/burning were reported with use of adapalene gel.
Concomitant use of other potentially irritating topical products (medicated or abrasive soaps and cleansers, soaps and cosmetics that have a strong drying effect and products with high concentrations of alcohol, astringents, spices, or lime) should be approached with caution. (5.3).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequently reported (≥ 1%) adverse reactions were dry skin, skin discomfort, pruritus, desquamation, and sunburn. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Actavis at 1-888-838-2872 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 10/2022
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Allergic/ Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.2 Ultraviolet Light and Environmental Exposure
5.3 Local Cutaneous Reactions
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- *
- Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Wash affected areas gently with a non-medicated soap. Apply a thin film of adapalene gel to the entire face and any other affected areas of the skin once daily in the evening. Avoid application to the areas of skin around eyes, lips, and mucous membranes. A mild transitory sensation of warmth or slight stinging may occur shortly after the application of adapalene gel. Instruct patients to minimize sun exposure and to use moisturizers for relief of dry skin or irritation.
If therapeutic results are not noticed after 12 weeks of treatment, therapy should be reevaluated.
For topical use only. Not for ophthalmic, oral or intravaginal use.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Allergic/ Hypersensitivity Reactions
Adverse reactions including anaphylaxis angioedema, face edema, eyelid edema, lip swelling, and pruritus that sometimes required medical treatment have been reported during postmarketing use of adapalene. Advise a patient to stop using adapalene gel and seek medical attention if experiencing allergic or anaphylactoid/anaphylactic reactions during treatment.
5.2 Ultraviolet Light and Environmental Exposure
Exposure to sunlight, including sunlamps, should be minimized during use of adapalene gel. Patients who normally experience high levels of sun exposure, and those with inherent sensitivity to sun, should be warned to exercise caution. Use of sunscreen products and protective clothing over treated areas is recommended when exposure cannot be avoided. Weather extremes, such as wind or cold, also may be irritating to patients under treatment with adapalene gel.
5.3 Local Cutaneous Reactions
Cutaneous signs and symptoms such as erythema, scaling, dryness, and stinging/burning were reported with use of adapalene gel. These were most likely to occur during the first four weeks of treatment, were mostly mild to moderate in intensity, and usually lessened with continued use of the medication. Depending upon the severity of these side effects, patients should be instructed to either use a moisturizer, reduce the frequency of application of adapalene gel or discontinue use.
Avoid application to cuts, abrasions, eczematous or sunburned skin. As with other retinoids, use of “waxing” as a depilatory method should be avoided on skin treated with adapalene.
As adapalene gel has the potential to induce local irritation in some patients, concomitant use of other potentially irritating topical products (medicated or abrasive soaps and cleansers, soaps and cosmetics that have a strong drying effect and products with high concentrations of alcohol, astringents, spices, or lime) should be approached with caution.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reactions rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In the multi-center, controlled clinical trial, signs and symptoms of local cutaneous irritation were monitored in 258 acne subjects who used adapalene gel once daily for 12 weeks. Of the subjects who experienced cutaneous irritation (erythema, scaling, dryness, and/or burning/stinging), the majority of cases were mild to moderate in severity, occurred early in treatment and decreased thereafter. The incidence of local cutaneous irritation with adapalene gel from the controlled clinical trial is provided in the following table:
Table 1: Physician assessed local cutaneous irritation with Adapalene Gel Incidence of Local Cutaneous Irritation with Adapalene Gel from Controlled Clinical Study
(N = 253*)
Maximum Severity Scores Higher Than BaselineMild Moderate Severe * Total number of subjects with local cutaneous data for at least one post-Baseline evaluation. Erythema 66 (26.1%) 33 (13.0%) 1 (0.4%) Scaling 110 (43.5%) 47 (18.6%) 3 (1.2%) Dryness 113 (44.7%) 43 (17.0%) 2 (0.8%) Burning/Stinging 72 (28.5%) 36 (14.2%) 9 (3.6%) Table 2: Patient reported local cutaneous adverse reactions with Adapalene Gel Adapalene Gel
N=258Vehicle Gel
N=134* Selected adverse reactions defined by investigator as Possibly, Probably or Definitely Related Related* Adverse Reactions 57 (22.1%) 6 (4.5%) Dry Skin 36 (14%) 2 (1.5%) Skin Discomfort 15 (5.8%) 0 (0.0%) Desquamation 4 (1.6%) 0 (0.0%) The following adverse reactions occurred in less than 1% of subjects: acne flare, contact dermatitis, eyelid edema, conjunctivitis, erythema, pruritus, skin discoloration, rash, and eczema.
In a one-year, open-label safety trial of 551 patients with acne who received adapalene gel the pattern of adverse reactions was similar to the 12-week controlled study.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of adapalene:
Immune system disorders: angioedema, face edema, lip swelling
Skin disorders: application site pain
Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate the frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from clinical trials with adapalene gel use in pregnant women are insufficient to establish a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In animal reproduction studies, oral administration of adapalene to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis at dose exposures 40 and 81 times, respectively, the human exposure at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 2 g resulted in fetal skeletal and visceral malformations (see Data).The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defects, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies are 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
No malformations were observed in rats treated with oral adapalene doses of 0.15 mg/kg/day to 5.0 mg/kg/day, up to 8 times the MRHD based on a mg/m² comparison. However, malformations were observed in rats and rabbits when treated with oral doses of ≥ 25 mg/kg/day adapalene (40 and 81 times the MRHD, respectively, based on a mg/m² comparison). Findings included cleft palate, microphthalmia, encephalocele, and skeletal abnormalities in rats and umbilical hernia, exophthalmos, and kidney and skeletal abnormalities in rabbits.Dermal adapalene embryofetal development studies in rats and rabbits at doses up to 6.0 mg/kg/day (9.7 and 19.5 times the MRHD, respectively, based on a mg/m2 comparison) exhibited no fetotoxicity and only minimal increases in skeletal variations (supernumerary ribs in both species and delayed ossification in rabbits).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of topical adapalene gel or its metabolite in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. In animal studies, adapalene is present in rat milk with oral administration of the drug. When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that the drug will be present in human milk. It is possible that topical administration of large amounts of adapalene could result in sufficient systemic absorption to produce detectable quantities in human milk (see Clinical Considerations). The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for adapalene gel and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from adapalene gel, or from the underlying maternal condition.Clinical Considerations
To minimize potential exposure to the breastfed infant via breastmilk, use adapalene gel on the smallest area of skin and for the shortest duration possible while breastfeeding. Avoid application of adapalene gel to areas with increased risk for potential ingestion by or ocular exposure to the breastfeeding child. - 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Adapalene gel, 0.3% contains adapalene (3 mg/g) in a topical aqueous gel for use in the treatment of acne vulgaris, consisting of carbomer 940, edetate disodium, methylparaben, poloxamer 182, propylene glycol, purified water, and sodium hydroxide. May contain hydrochloric acid for pH adjustment.
The chemical name of adapalene is 6-[3-(1-adamantyl)-4-methoxyphenyl]-2-naphthoic acid. It is a white to off-white powder, which is soluble in tetrahydrofuran, very slightly soluble in ethanol, and practically insoluble in water. The molecular formula is C28H28O3 and molecular weight is 412.53. Adapalene is represented by the following structural formula.
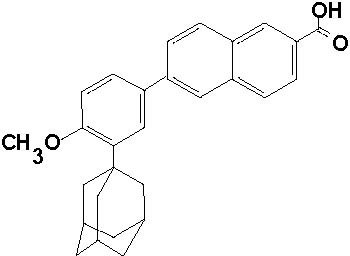
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Adapalene binds to specific retinoic acid nuclear receptors but does not bind to cytosolic receptor protein. Biochemical and pharmacological profile studies have demonstrated that adapalene is a modulator of cellular differentiation, keratinization, and inflammatory processes. However, the significance of these findings with regard to the mechanism of action of adapalene for the treatment of acne is unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Systemic exposure of adapalene following topical application of adapalene gel was evaluated in a clinical trial. Sixteen acne subjects were treated once daily for 10 days with 2 grams of adapalene gel applied to the face, chest and back, corresponding to approximately 2 mg/cm2. Fifteen subjects had quantifiable (LOQ = 0.1 ng/mL) adapalene levels resulting in a mean Cmax of 0.553 ± 0.466 ng/mL on Day 10 of treatment. The mean AUC0-24hr was 8.37 ± 8.46 ng.h/mL as determined in 15 of the 16 subjects on Day 10. The terminal apparent half-life, determined in 15 of 16 subjects, ranged from 7 to 51 hours, with a mean of 17.2 ± 10.2 hours. Adapalene was rapidly cleared from plasma and was not detected 72 hours after the last application for all but one subject. Exposure of potential circulating metabolites of adapalene was not measured. Excretion of adapalene appears to be primarily by the biliary route.
In another clinical trial in subjects with moderate to moderately severe acne, adapalene gel, 0.3% or Adapalene Gel, 0.1% was applied to the face and optionally to the trunk, once daily for 12 weeks. Seventy-eight (78) subjects had plasma adapalene levels evaluated at Weeks 2, 8, and 12. Of the 209 plasma samples analyzed, adapalene concentrations were below the limit of detection (LOD = 0.15 ng/mL) of the method in all samples but three. For the three samples, traces of adapalene below the limit of quantification (LOQ = 0.25 ng/mL) of the method were found. One of these samples was taken at Week 12 from a male patient treated with adapalene gel who treated the face and the trunk for eight weeks (thereafter, only the face was treated). The second and third samples were from the Week 2 and 12 visits of a female subject treated with adapalene gel, 0.1% who treated only the face for 12 weeks. In this study, the average daily usage of product was 1 g/day.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No carcinogenicity, genotoxicity, or impairment of fertility studies were conducted with adapalene gel.
Carcinogenicity studies with adapalene were conducted in mice at topical doses of 0.4 mg/kg/day,
1.3 mg/kg/day, and 4.0 mg/kg/day (1.2, 3.9, and 12 mg/m2/day) and in rats at oral doses of 0.15 mg/kg/day, 0.5 mg/kg/day, and 1.5 mg/kg/day (0.9, 3.0, and 9.0 mg/m2/day). The highest dose levels are 3.2 (mice) and 2.4 (rats) times the MRHD based on a mg/m2 comparison. In the rat study, an increased incidence of benign and malignant pheochromocytomas reported in the adrenal medulla of male rats was observed.Adapalene was not mutagenic or genotoxic in vitro (Ames test, Chinese hamster ovary cell assay, or mouse lymphoma TK assay) or in vivo (mouse micronucleus test).
In rat oral studies, 20 mg/kg/day adapalene (32 times the MRHD based on a mg/m2 comparison) did not affect the reproductive performance and fertility of F0 males and females or the growth, development, or reproductive function of F1 offspring.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and efficacy of once daily use of adapalene gel for treatment of acne vulgaris were assessed in one 12 week, multi-center, controlled, clinical trial, conducted in a total of 653 subjects 12 years to 52 years of age with acne vulgaris of mild to moderate severity. All female subjects of child-bearing potential enrolled in the trial were required to have a negative urine pregnancy test at the beginning of the trial and were required to practice a highly effective method of contraception during the trial. Female subjects who were pregnant, nursing or planning to become pregnant were excluded from the trial.
Subjects enrolled in the trial were Caucasian (72%), Hispanic (12%), African-American (10%), Asian (3%), and other (2%). An equal number of males (49.5%) and females (50.5%) enrolled. Success was defined as “Clear” or “Almost Clear” in the Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA). The success rate, mean reduction, and percent reduction in acne lesion counts from Baseline after 12 weeks of treatment are presented in the following table:
Table 3: Clinical study primary efficacy results at Week 12 Adapalene Gel, 0.3% Adapalene Gel, 0.1% Vehicle Gel N=258 N=261 N=134 IGA Success Rate 53 (21%) 41 (16%) 12 (9%) Inflammatory Lesions Mean Baseline Count 27.7 28.1 27.2 Mean Absolute (%) Reduction 14.4 (51.6%) 13.9 (49.7%) 11.2 (40.7%) Non-inflammatory Lesions Mean Baseline Count 39.4 41.0 40.0 Mean Absolute (%) Reduction 16.3 (39.7%) 15.2 (35.2%) 10.3 (27.2%) Total Lesions Mean Baseline Count 67.1 69.1 67.2 Mean Absolute (%) Reduction 30.6 (45.3%) 29.0 (41.8%) 21.4 (33.7%) - 16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information)
Information for Patients
Patients using adapalene gel, should receive the following information and instructions:
- Apply a thin film of adapalene gel to the entire face and any other affected areas of the skin once daily in the evening. Apply a thin film of adapalene gel to the entire face and any other affected areas of the skin once daily in the evening, after washing gently with a non-medicated soap.
- Avoid contact with the eyes, lips, angles of the nose, and mucous membranes.
- Moisturizers may be used if necessary; however, products containing alpha hydroxy or glycolic acids should be avoided.
- This medication should not be applied to cuts, abrasions, eczematous, or sunburned skin.
- Wax depilation should not be performed on treated skin due to the potential for skin erosions.
- Minimize exposure to sunlight including sunlamps. Recommend the use of sunscreen products and protective apparel (e.g., hat) when exposure cannot be avoided.
- Contact the doctor if skin rash, pruritus, hives, chest pain, edema, and shortness of breath occurs, as these may be signs of allergy or hypersensitivity.
- This product is for external use only.
- Lactation: Use adapalene gel on the smallest area of skin and for the shortest duration possible while breastfeeding. Avoid application of adapalene gel to areas with increased risk for potential ingestion by or ocular exposure to the breastfeeding child. [See Use in Specific Populations, Lactation (8.2)]
Distributed by:
Actavis Pharma, Inc.
Parsippany, NJ 07054 USARev. B 10/2022
-
PATIENT INFORMATION
Adapalene (a dap' a leen) Gel
Important: For use on the skin only (topical). Do not use adapalene gel in or on your mouth, eyes, or vagina.
Read this Patient Information that comes with adapalene gel before you start using it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your treatment or your medical condition. If you have any questions about adapalene gel talk with your doctor or pharmacist.
What is adapalene gel?
Adapalene gel is a prescription medicine for skin use only (topical) used to treat acne vulgaris in people 12 years of age and older.
Acne vulgaris is a condition in which the skin has blackheads, whiteheads and pimples.
It is not known if adapalene gel is safe and effective in children younger than 12 years of age or in people 65 years of age and older.
Who should not use adapalene gel?
Do not use adapalene gel if you:
- are allergic to adapalene or any of the ingredients in adapalene gel. See the end of this Patient Information for a complete list of ingredients in adapalene gel.
What should I tell my doctor before using adapalene gel?
Before you use adapalene gel, tell your doctor if you:
- have other skin problems, including cuts or sunburn
- have any other medical conditions
- are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if adapalene gel can harm your unborn baby. Talk to your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if adapalene passes into your breast milk and if it can harm your baby. Talk to your doctor about the best way to feed your baby if you use adapalene gel.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements.
Especially tell your doctor if you use any other medicine for acne. Using adapalene gel with topical medicines that contain sulfur, resorcinol or salicylic acid may cause skin irritation.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I use adapalene gel?
- Use adapalene gel exactly as your doctor tells you to use it. Adapalene gel is for skin use only. Do not use adapalene gel in or on your mouth, eyes, or vagina.
- Apply adapalene gel 1 time a day. Do not use more adapalene gel than you need to cover the treatment area. Using too much adapalene gel or using it more than 1 time a day may increase your chance of skin irritation.
Applying adapalene gel:
- Wash the area where adapalene gel will be applied with a soap that does not contain a medicine and pat dry.
- Adapalene gel comes in a tube. If you have been prescribed the:
- Squeeze a small amount onto your fingertips and spread a thin layer over the entire face and any other affected areas.
What should I avoid while using adapalene gel?
- You should avoid spending time in sunlight or artificial sunlight, such as tanning beds or sunlamps. Adapalene gel can make your skin sensitive to sun and the light from tanning beds and sunlamps. You should wear sunscreen and wear hat and clothes that cover the areas treated with adapalene gel if you have to be in sunlight.
- You should avoid weather extremes such as wind and cold as this may cause irritation to your skin.
- You should avoid applying adapalene gel to cuts, abrasions and sunburned skin.
- You should avoid skin products that may dry or irritate your skin such as harsh soaps, astringents, cosmetics that have strong skin drying effects and products containing high levels of alcohol.
- You should avoid the use of “waxing” as a hair removal method on skin treated with adapalene gel.
What are the possible side effects of adapalene gel?
Adapalene gel may cause serious side effects including:
-
Local skin reactions. Local skin reactions are most likely to happen during the first 4 weeks of treatment and usually lessen with continued use of adapalene gel. Signs and symptoms of local skin reaction include:
- Redness
- Dryness
- Scaling
- Stinging or burning
-
Allergic reactions. Adapalene gel may cause an allergic reaction that may require medical treatment. Stop using adapalene gel and tell your doctor right away if you have any of these symptoms of an allergic reaction:
- skin rash, itching or hives
- trouble breathing or chest pain
- swelling of your face, eyes, lips, tongue or throat
You may use a moisturizer for relief of dry skin or irritation, however you should avoid products that contain alpha hydroxy or glycolic acid.
The most common side effects of adapalene gel are:
- skin pain
- skin peeling
- sunburn
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of adapalene gel. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
You may also report side effects to Actavis at 1-888-838-2872.
How should I store adapalene gel?
- Store adapalene gel at room temperature between 68° F to 77° F (20° C to 25° C).
- Do not freeze adapalene gel.
Keep adapalene gel and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about adapalene gel
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information Leaflet. Do not use adapalene gel for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give adapalene gel to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about adapalene gel. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can also ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about adapalene gel that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in adapalene gel?
Active ingredient: adapalene
Inactive ingredients: carbomer 940, edetate disodium, methylparaben, poloxamer 182, propylene glycol, purified water and sodium hydroxide. May contain hydrochloric acid for pH adjustment.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
Actavis Pharma, Inc.
Parsippany, NJ 07054 USARev. B 10/2022
- PACKAGE LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ADAPALENE
adapalene gelProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:0472-0126 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ADAPALENE (UNII: 1L4806J2QF) (ADAPALENE - UNII:1L4806J2QF) ADAPALENE 3 mg in 1 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CARBOMER HOMOPOLYMER TYPE C (UNII: 4Q93RCW27E) EDETATE SODIUM (UNII: MP1J8420LU) METHYLPARABEN (UNII: A2I8C7HI9T) POLOXAMER 182 (UNII: JX0HIX6OAG) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:0472-0126-45 1 in 1 CARTON 10/27/2014 1 45 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA201000 10/27/2014 Labeler - Actavis Pharma, Inc. (119723554)