CLARITHROMYCIN- clarithromycin tablet, film coated, extended release
Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATIONThese highlights do not include all the information needed to use CLARITHROMYCIN EXTENDED-RELEASE TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CLARITHROMYCIN EXTENDED-RELEASE TABLETS.
CLARITHROMYCIN extended-release tablets, for oral use. Initial U.S. Approval: 1991 RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
INDICATIONS AND USAGEClarithromycin is a macrolide antimicrobial indicated for mild to moderate infections caused by designated, susceptible bacteria in the following:
Limitations of Use Clarithromycin extended-release tablets are indicated only for acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, acute maxillary sinusitis, and community-acquired pneumonia in adults. (1.9) To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of clarithromycin and other antibacterial drugs, clarithromycin should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. (1.9) DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONDOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSExtended-release Tablets: 500 mg (3) CONTRAINDICATIONSWARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONSMost frequent adverse reactions for both adult and pediatric populations in clinical trials: abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, dysgeusia (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact TEVA USA, PHARMACOVIGILANCE at 1-866-832-8537 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. DRUG INTERACTIONSUSE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONSGeriatric: Increased risk of torsades de pointes (8.5) See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION. Revised: 12/2016 |
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Acute Bacterial Exacerbation of Chronic Bronchitis
Clarithromycin extended-release tablets are indicated in adults for the treatment of mild to moderate infections caused by susceptible isolates due to Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, or Streptococcus pneumoniae [see Indications and Usage (1.9)].
1.2 Acute Maxillary Sinusitis
Clarithromycin extended-release tablets (in adults) are indicated for the treatment of mild to moderate infections caused by susceptible isolates due to Haemophilus influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis, or Streptococcus pneumoniae [see Indications and Usage (1.9)].
1.3 Community-Acquired Pneumonia
Clarithromycin extended-release tablets are indicated [see Indications and Usage (1.9)] for the treatment of mild to moderate infections caused by susceptible isolates due to:
- •
- Haemophilus influenzae (in adults)
- •
- Haemophilus parainfluenzae (in adults)
- •
- Moraxella catarrhalis (in adults)
- •
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Chlamydophila pneumoniae (in adults).
1.9 Limitations of Use
Clarithromycin extended-release tablets are indicated only for acute maxillary sinusitis, acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, and community-acquired pneumonia in adults. The efficacy and safety of clarithromycin extended-release tablets in treating other infections for which clarithromycin immediate-release tablets and clarithromycin granules are approved have not been established.
There is resistance to macrolides in certain bacterial infections caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus. Susceptibility testing should be performed when clinically indicated.
1.10 Usage
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of clarithromycin and other antibacterial drugs, clarithromycin should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
Clarithromycin extended-release tablets should be taken with food. Swallow clarithromycin extended-release tablets whole; do not chew, break or crush clarithromycin extended-release tablets.
2.2 Adult Dosage
The recommended dosage of clarithromycin extended-release tablets for the treatment of mild to moderate infections in adults are listed in Table 1.
|
Clarithromycin Extended-Release Tablets |
||
|
Infection |
Dosage (every 24 hours) |
Duration (days) |
|
Acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis |
1 gram |
7 |
|
Acute maxillary sinusitis |
1 gram |
14 |
|
Community-acquired pneumonia |
1 gram |
7 |
2.6 Dosage Adjustment in Patients with Renal Impairment
See Table 2 for dosage adjustment in patients with moderate or severe renal impairment with or without concomitant atazanavir or ritonavir-containing regimens [see Drug Interactions (7)].
|
Recommended Clarithromycin Dosage Reduction |
|
|
Patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr of < 30 mL/min) |
Reduce the dosage of clarithromycin by 50% |
|
Patients with moderate renal impairment (CLcr of 30 to 60 mL/min) taking concomitant atazanavir or ritonavir-containing regimens |
Reduce the dosage of clarithromycin by 50% |
|
Patients with severe renal impairment (CLcr of < 30 mL/min) taking concomitant atazanavir or ritonavir-containing regimens |
Reduce the dosage of clarithromycin by 75% |
2.7 Dosage Adjustment Due to Drug Interactions
Decrease the dose of clarithromycin by 50 % when coadministered with atazanavir [see Drug Interactions (7)]. Dosage adjustments for other drugs when coadministered with clarithromycin may be recommended due to drug interactions [see Drug Interactions (7)].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Clarithromycin Extended-Release Tablets are available as:
- •
- 500 mg: debossed with “93” on one side and “7244” on the other side
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Hypersensitivity
Clarithromycin is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to clarithromycin, erythromycin, or any of the macrolide antibacterial drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
4.2 Cardiac Arrhythmias
Concomitant administration of clarithromycin with cisapride and pimozide is contraindicated [see Drug Interactions (7)].
There have been postmarketing reports of drug interactions when clarithromycin is coadministered with cisapride or pimozide, resulting in cardiac arrhythmias (QT prolongation, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and torsades de pointes) most likely due to inhibition of metabolism of these drugs by clarithromycin. Fatalities have been reported.
4.3 Cholestatic Jaundice/Hepatic Dysfunction
Clarithromycin is contraindicated in patients with a history of cholestatic jaundice or hepatic dysfunction associated with prior use of clarithromycin.
4.4 Colchicine
Concomitant administration of clarithromycin and colchicine is contraindicated in patients with renal or hepatic impairment.
4.5 HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors
Do not use clarithromycin concomitantly with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) that are extensively metabolized by CYP3A4 (lovastatin or simvastatin), due to the increased risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Drug Interactions (7)].
4.6 Ergot Alkaloids
Concomitant administration of clarithromycin and ergotamine or dihydroergotamine is contraindicated [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Acute Hypersensitivity Reactions
In the event of severe acute hypersensitivity reactions, such as anaphylaxis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), and Henoch-Schonlein purpura, discontinue clarithromycin therapy immediately and institute appropriate treatment.
5.2 QT Prolongation
Clarithromycin has been associated with prolongation of the QT interval and infrequent cases of arrhythmia. Cases of torsades de pointes have been spontaneously reported during postmarketing surveillance in patients receiving clarithromycin. Fatalities have been reported.
Avoid clarithromycin in the following patients:
- •
- patients with known prolongation of the QT interval, ventricular cardiac arrhythmia, including torsades de pointes
- •
- patients receiving drugs known to prolong the QT interval [see also Contraindications (4.2)]
- •
- patients with ongoing proarrhythmic conditions such as uncorrected hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia, clinically significant bradycardia and in patients receiving Class IA (quinidine, procainamide) or Class III (dofetilide, amiodarone, sotalol) antiarrhythmic agents.
Elderly patients may be more susceptible to drug-associated effects on the QT interval [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
5.3 Hepatotoxicity
Hepatic dysfunction, including increased liver enzymes, and hepatocellular and/or cholestatic hepatitis, with or without jaundice, has been reported with clarithromycin. This hepatic dysfunction may be severe and is usually reversible. In some instances, hepatic failure with fatal outcome has been reported and generally has been associated with serious underlying diseases and/or concomitant medications. Symptoms of hepatitis can include anorexia, jaundice, dark urine, pruritus, or tender abdomen. Discontinue clarithromycin immediately if signs and symptoms of hepatitis occur.
5.4 Serious Adverse Reactions Due to Concomitant Use with Other Drugs
Drugs metabolized by CYP3A4: Serious adverse reactions have been reported in patients taking clarithromycin concomitantly with CYP3A4 substrates. These include colchicine toxicity with colchicine; rhabdomyolysis with simvastatin, lovastatin, and atorvastatin; hypoglycemia with disopyramide; hypotension and acute kidney injury with calcium channel blockers metabolized by CYP3A4 (e.g., verapamil, amlodipine, diltiazem, nifedipine). Most reports of acute kidney injury with calcium channel blockers metabolized by CYP3A4 involved elderly patients 65 years of age or older. Use clarithromycin with caution when administered concurrently with medications that induce the cytochrome CYP3A4 enzyme. The use of clarithromycin with simvastatin, lovastatin, ergotamine, or dihydroergotamine is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4.5, 4.6) and Drug Interactions (7)].
Colchicine: Life-threatening and fatal drug interactions have been reported in patients treated with clarithromycin and colchicine. Clarithromycin is a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor and this interaction may occur while using both drugs at their recommended doses. If coadministration of clarithromycin and colchicine is necessary in patients with normal renal and hepatic function, reduce the dose of colchicine. Monitor patients for clinical symptoms of colchicine toxicity. Concomitant administration of clarithromycin and colchicine is contraindicated in patients with renal or hepatic impairment [see Contraindications (4.4) and Drug Interactions (7)].
HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors (statins): Concomitant use of clarithromycin with lovastatin or simvastatin is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4.5)] as these statins are extensively metabolized by CYP3A4, and concomitant treatment with clarithromycin increases their plasma concentration, which increases the risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis. Cases of rhabdomyolysis have been reported in patients taking clarithromycin concomitantly with these statins. If treatment with clarithromycin cannot be avoided, therapy with lovastatin or simvastatin must be suspended during the course of treatment.
Exercise caution when prescribing clarithromycin with atorvastatin or pravastatin. In situations where the concomitant use of clarithromycin with atorvastatin or pravastatin cannot be avoided, atorvastatin dose should not exceed 20 mg daily and pravastatin dose should not exceed 40 mg daily. Use of a statin that is not dependent on CYP3A metabolism (e.g. fluvastatin) can be considered. It is recommended to prescribe the lowest registered dose if concomitant use cannot be avoided.
Oral Hypoglycemic Agents/Insulin: The concomitant use of clarithromycin and oral hypoglycemic agents and/or insulin can result in significant hypoglycemia. With certain hypoglycemic drugs such as nateglinide, pioglitazone, repaglinide and rosiglitazone, inhibition of CYP3A enzyme by clarithromycin may be involved and could cause hypoglycemia when used concomitantly. Careful monitoring of glucose is recommended [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Quetiapine: Use quetiapine and clarithromycin concomitantly with caution. Coadministration could result in increased quetiapine exposure and quetiapine related toxicities such as somnolence, orthostatic hypotension, altered state of consciousness, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, and QT prolongation. Refer to quetiapine prescribing information for recommendations on dose reduction if coadministered with CYP3A4 inhibitors such as clarithromycin [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Oral Anticoagulants: There is a risk of serious hemorrhage and significant elevations in INR and prothrombin time when clarithromycin is coadministered with warfarin. Monitor INR and prothrombin times frequently while patients are receiving clarithromycin and oral anticoagulants concurrently [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Benzodiazepines: Increased sedation and prolongation of sedation have been reported with concomitant administration of clarithromycin and triazolobenzodiazepines, such as triazolam and midazolam [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.5 Clostridium difficile Associated Diarrhea
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including clarithromycin, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibacterial use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibacterial use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibacterial treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
5.6 Embryofetal Toxicity
Clarithromycin should not be used in pregnant women except in clinical circumstances where no alternative therapy is appropriate. If clarithromycin is used during pregnancy, or if pregnancy occurs while the patient is taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus. Clarithromycin has demonstrated adverse effects on pregnancy outcome and/or embryo-fetal development in monkeys, rats, mice, and rabbits at doses that produced plasma levels 2 times to 17 times the serum levels achieved in humans treated at the maximum recommended human doses [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- •
- Acute Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- •
- QT Prolongation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- •
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- •
- Serious Adverse Reactions Due to Concomitant Use with Other Drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- •
- Clostridium difficile Associated Diarrhea [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- •
- Exacerbation of Myasthenia Gravis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Based on pooled data across all indications, the most frequent adverse reactions for both adult and pediatric populations observed in clinical trials are abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting and dysgeusia. Also reported were dyspepsia, liver function test abnormal, anaphylactic reaction, candidiasis, headache, insomnia, and rash.
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
In the acute exacerbation of chronic bronchitis and acute maxillary sinusitis studies overall gastrointestinal adverse reactions were reported by a similar proportion of patients taking either clarithromycin immediate-release tablets or clarithromycin extended-release tablets; however, patients taking clarithromycin extended-release tablets reported significantly less severe gastrointestinal symptoms compared to patients taking clarithromycin immediate-release tablets. In addition, patients taking clarithromycin extended-release tablets had significantly fewer premature discontinuations for drug-related gastrointestinal or abnormal taste adverse reactions compared to clarithromycin immediate-release tablets.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of clarithromycin. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Blood and Lymphatic System: Thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis
Cardiac: Ventricular arrhythmia, ventricular tachycardia, torsades de pointes
Ear and Labyrinth: Deafness was reported chiefly in elderly women and was usually reversible.
Gastrointestinal: Pancreatitis acute, tongue discoloration, tooth discoloration was reported and was usually reversible with professional cleaning upon discontinuation of the drug.
There have been reports of clarithromycin extended-release tablets in the stool, many of which have occurred in patients with anatomic (including ileostomy or colostomy) or functional gastrointestinal disorders with shortened GI transit times. In several reports, tablet residues have occurred in the context of diarrhea. It is recommended that patients who experience tablet residue in the stool and no improvement in their condition should be switched to a different clarithromycin formulation (e.g. suspension) or another antibacterial drug.
Hepatobiliary: Hepatic failure, jaundice hepatocellular. Adverse reactions related to hepatic dysfunction have been reported with clarithromycin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Infections and Infestations: Pseudomembranous colitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
Immune System: Anaphylactic reactions, angioedema
Investigations: Prothrombin time prolonged, white blood cell count decreased, international normalized ratio increased. Abnormal urine color has been reported, associated with hepatic failure.
Metabolism and Nutrition: Hypoglycemia has been reported in patients taking oral hypoglycemic agents or insulin.
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue: Myopathy rhabdomyolysis was reported and in some of the reports, clarithromycin was administered concomitantly with statins, fibrates, colchicine or allopurinol [see Contraindications (4.5) and Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Nervous System: Parosmia, anosmia, ageusia, paresthesia and convulsions
Psychiatric: Abnormal behavior, confusional state, depersonalization, disorientation, hallucination, depression, manic behavior, abnormal dream, psychotic disorder. These disorders usually resolve upon discontinuation of the drug.
Renal and Urinary: Nephritis interstitial, renal failure
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue: Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), Henoch-Schonlein purpura, acne
Vascular: Hemorrhage
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Coadministration of clarithromycin is known to inhibit CYP3A, and a drug primarily metabolized by CYP3A may be associated with elevations in drug concentrations that could increase or prolong both therapeutic and adverse effects of the concomitant drug.
Clarithromycin should be used with caution in patients receiving treatment with other drugs known to be CYP3A enzyme substrates, especially if the CYP3A substrate has a narrow safety margin (e.g., carbamazepine) and/or the substrate is extensively metabolized by this enzyme. Adjust dosage when appropriate and monitor serum concentrations of drugs primarily metabolized by CYP3A closely in patients concurrently receiving clarithromycin.
|
Table 8: Clinically Significant Drug Interactions with Clarithromycin |
||
|
Drugs That Are Affected By Clarithromycin |
||
|
Drug(s) with Pharmacokinetics Affected by Clarithromycin |
Recommendation |
Comments |
|
Antiarrhythmics: Disopyramide Quinidine Dofetilide Amiodarone Sotalol Procainamide Digoxin |
Not Recommended Use With Caution |
Disopyramide, Quinidine: There have been postmarketing reports of torsades de pointes occurring with concurrent use of clarithromycin and quinidine or disopyramide. Electrocardiograms should be monitored for QTc prolongation during coadministration of clarithromycin with these drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Serum concentrations of these medications should also be monitored. There have been spontaneous or published reports of CYP3A based interactions of clarithromycin with disopyramide and quinidine. There have been postmarketing reports of hypoglycemia with the concomitant administration of clarithromycin and disopyramide. Therefore, blood glucose levels should be monitored during concomitant administration of clarithromycin and disopyramide. Digoxin: Digoxin is a substrate for P-glycoprotein (Pgp) and clarithromycin is known to inhibit Pgp. When clarithromycin and digoxin are coadministered, inhibition of Pgp by clarithromycin may lead to increased exposure of digoxin. Elevated digoxin serum concentrations in patients receiving clarithromycin and digoxin concomitantly have been reported in postmarketing surveillance. Some patients have shown clinical signs consistent with digoxin toxicity, including potentially fatal arrhythmias. Monitoring of serum digoxin concentrations should be considered, especially for patients with digoxin concentrations in the upper therapeutic range. |
|
Oral Anticoagulants: Warfarin |
Use With Caution |
Oral anticoagulants: Spontaneous reports in the postmarketing period suggest that concomitant administration of clarithromycin and oral anticoagulants may potentiate the effects of the oral anticoagulants. Prothrombin times should be carefully monitored while patients are receiving clarithromycin and oral anticoagulants simultaneously [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. |
|
Antiepileptics: Carbamazepine |
Use With Caution |
Carbamazepine: Concomitant administration of single doses of clarithromycin and carbamazepine has been shown to result in increased plasma concentrations of carbamazepine. Blood level monitoring of carbamazepine may be considered. Increased serum concentrations of carbamazepine were observed in clinical trials with clarithromycin. There have been spontaneous or published reports of CYP3A based interactions of clarithromycin with carbamazepine. |
|
Antifungals: Itraconazole Fluconazole |
Use With Caution No Dose Adjustment |
Itraconazole: Both clarithromycin and itraconazole are substrates and inhibitors of CYP3A, potentially leading to a bi-directional drug interaction when administered concomitantly (see also Itraconazole under “Drugs That Affect Clarithromycin” in the table below). Clarithromycin may increase the plasma concentrations of itraconazole. Patients taking itraconazole and clarithromycin concomitantly should be monitored closely for signs or symptoms of increased or prolonged adverse reactions. Fluconazole:[see Pharmacokinetics (12.3)] |
|
Anti-Gout Agents: Colchicine (in patients with renal or hepatic impairment) Colchicine (in patients with normal renal and hepatic function) |
Contraindicated Use With Caution |
Colchicine: Colchicine is a substrate for both CYP3A and the efflux transporter, P-glycoprotein (Pgp). Clarithromycin and other macrolides are known to inhibit CYP3A and Pgp. The dose of colchicine should be reduced when coadministered with clarithromycin in patients with normal renal and hepatic function [see Contraindications (4.4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. |
|
Antipsychotics: Pimozide Quetiapine |
Contraindicated |
Pimozide:[see Contraindications (4.2)] Quetiapine: Quetiapine is a substrate for CYP3A4, which is inhibited by clarithromycin. Coadministration with clarithromycin could result in increased quetiapine exposure and possible quetiapine related toxicities. There have been postmarketing reports of somnolence, orthostatic hypotension, altered state of consciousness, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, and QT prolongation during concomitant administration. Refer to quetiapine prescribing information for recommendations on dose reduction if coadministered with CYP3A4 inhibitors such as clarithromycin. |
|
Antispasmodics: Tolterodine (patients deficient in CYP2D6 activity) |
Use With Caution |
Tolterodine: The primary route of metabolism for tolterodine is via CYP2D6. However, in a subset of the population devoid of CYP2D6, the identified pathway of metabolism is via CYP3A. In this population subset, inhibition of CYP3A results in significantly higher serum concentrations of tolterodine. Tolterodine 1 mg twice daily is recommended in patients deficient in CYP2D6 activity (poor metabolizers) when coadministered with clarithromycin. |
|
Antivirals: Atazanavir Saquinavir (in patients with decreased renal function) Ritonavir Etravirine Maraviroc Boceprevir (in patients with normal renal function) Didanosine Zidovudine |
Use With Caution No Dose Adjustment |
Atazanavir: Both clarithromycin and atazanavir are substrates and inhibitors of CYP3A, and there is evidence of a bi-directional drug interaction (see Atazanavir under “Drugs That Affect Clarithromycin” in the table below) [see Pharmacokinetics (12.3)]. Saquinavir: Both clarithromycin and saquinavir are substrates and inhibitors of CYP3A and there is evidence of a bi-directional drug interaction (see Saquinavir under “Drugs That Affect Clarithromycin” in the table below) [see Pharmacokinetics (12.3)]. Ritonavir, Etravirine: (see Ritonavir and Etravirine under “Drugs That Affect Clarithromycin” in the table below) [see Pharmacokinetics (12.3)]. Maraviroc: Clarithromycin may result in increases in maraviroc exposures by inhibition of CYP3A metabolism. See Selzentry® prescribing information for dose recommendation when given with strong CYP3A inhibitors such as clarithromycin. Boceprevir: Both clarithromycin and boceprevir are substrates and inhibitors of CYP3A, potentially leading to a bi-directional drug interaction when coadministered. No dose adjustments are necessary for patients with normal renal function (see Victrelis® prescribing information).
Zidovudine: Simultaneous oral administration of clarithromycin immediate-release tablets and zidovudine to HIV-infected adult patients may result in decreased steady-state zidovudine concentrations. Administration of clarithromycin and zidovudine should be separated by at least two hours [see Pharmacokinetics (12.3)]. |
|
Calcium Channel Blockers: Verapamil Amlodipine Diltiazem Nifedipine |
Use With Caution |
Verapamil: Hypotension, bradyarrhythmias, and lactic acidosis have been observed in patients receiving concurrent verapamil, [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. Amlodipine, Diltiazem:[see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] Nifedipine: Nifedipine is a substrate for CYP3A. Clarithromycin and other macrolides are known to inhibit CYP3A. There is potential of CYP3A-mediated interaction between nifedipine and clarithromycin. Hypotension and peripheral edema were observed when clarithromycin was taken concomitantly with nifedipine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. |
|
Ergot Alkaloids: Ergotamine Dihydroergotamine |
Contraindicated |
Ergotamine, Dihydroergotamine: Postmarketing reports indicate that coadministration of clarithromycin with ergotamine or dihydroergotamine has been associated with acute ergot toxicity characterized by vasospasm and ischemia of the extremities and other tissues including the central nervous system [see Contraindications (4.6)]. |
|
Gastroprokinetic Agents: Cisapride |
Contraindicated |
Cisapride:[see Contraindications (4.2)] |
|
HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitors: Lovastatin Simvastatin Atorvastatin Pravastatin Fluvastatin |
Contraindicated Use With Caution No Dose Adjustment |
Lovastatin, Simvastatin, Atorvastatin, Pravastatin, Fluvastatin:[see Contraindications (4.5) and Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] |
|
Hypoglycemic Agents: Nateglinide Pioglitazone Repaglinide Rosiglitazone Insulin |
Use With Caution |
Nateglinide, Pioglitazone, Repaglinide, Rosiglitazone:[see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Adverse Reactions (6.2)] Insulin:[see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Adverse Reactions (6.2)] |
|
Immunosuppressants: Cyclosporine Tacrolimus |
Use With Caution |
Cyclosporine: There have been spontaneous or published reports of CYP3A based interactions of clarithromycin with cyclosporine. Tacrolimus: There have been spontaneous or published reports of CYP3A based interactions of clarithromycin with tacrolimus. |
|
Phosphodiesterase inhibitors: Sildenafil Tadalafil Vardenafil |
Use With Caution |
Sildenafil, Tadalafil, Vardenafil: Each of these phosphodiesterase inhibitors is primarily metabolized by CYP3A, and CYP3A will be inhibited by concomitant administration of clarithromycin. Coadministration of clarithromycin with sildenafil, tadalafil, or vardenafil will result in increased exposure of these phosphodiesterase inhibitors. Coadministration of these phosphodiesterase inhibitors with clarithromycin is not recommended. Increased systemic exposure of these drugs may occur with clarithromycin; reduction of dosage for phosphodiesterase inhibitors should be considered (see their respective prescribing information). |
|
Proton Pump Inhibitors: Omeprazole |
No Dose Adjustment |
Omeprazole: The mean 24-hour gastric pH value was 5.2 when omeprazole was administered alone and 5.7 when coadministered with clarithromycin as a result of increased omeprazole exposures [see Pharmacokinetics (12.3)] (see also Omeprazole under “Drugs That Affect Clarithromycin” in the table below). |
|
Xanthine Derivatives: Theophylline |
Use With Caution |
Theophylline: Clarithromycin use in patients who are receiving theophylline may be associated with an increase of serum theophylline concentrations [see Pharmacokinetics (12.3)]. Monitoring of serum theophylline concentrations should be considered for patients receiving high doses of theophylline or with baseline concentrations in the upper therapeutic range. |
|
Triazolobenzodiazepines and Other Related Benzodiazepines: Midazolam Alprazolam Triazolam Temazepam Nitrazepam Lorazepam |
Use With Caution No Dose Adjustment |
Midazolam: When oral midazolam is coadministered with clarithromycin, dose adjustments may be necessary and possible prolongation and intensity of effect should be anticipated [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Pharmacokinetics (12.3)]. Triazolam, Alprazolam: Caution and appropriate dose adjustments should be considered when triazolam or alprazolam is coadministered with clarithromycin. There have been postmarketing reports of drug interactions and central nervous system (CNS) effects (e.g., somnolence and confusion) with the concomitant use of clarithromycin and triazolam. Monitoring the patient for increased CNS pharmacological effects is suggested. In postmarketing experience, erythromycin has been reported to decrease the clearance of triazolam and midazolam, and thus, may increase the pharmacologic effect of these benzodiazepines. Temazepam, Nitrazepam, Lorazepam: For benzodiazepines which are not metabolized by CYP3A (e.g., temazepam, nitrazepam, lorazepam), a clinically important interaction with clarithromycin is unlikely. |
|
Cytochrome P450 Inducers: Rifabutin |
Use With Caution |
Rifabutin: Concomitant administration of rifabutin and clarithromycin resulted in an increase in rifabutin, and decrease in clarithromycin serum levels together with an increased risk of uveitis (see Rifabutin under “Drugs That Affect Clarithromycin” in the table below). |
|
Other Drugs Metabolized by CYP3A: Alfentanil Bromocriptine Cilostazol Methylprednisole Vinblastine Phenobarbital St. John’s Wort |
Use With Caution |
There have been spontaneous or published reports of CYP3A based interactions of clarithromycin with alfentanil, methylprednisolone, cilostazol, bromocriptine, vinblastine, phenobarbital, and St. John’s Wort. |
|
Other Drugs Metabolized by CYP450 Isoforms Other than CYP3A: Hexobarbital Phenytoin Valproate |
Use With Caution |
There have been postmarketing reports of interactions of clarithromycin with drugs not thought to be metabolized by CYP3A, including hexobarbital, phenytoin, and valproate. |
|
Drugs that Affect Clarithromycin |
||
|
Drug(s) that Affect the Pharmacokinetics of Clarithromycin |
Recommendation |
Comments |
|
Antifungals: Itraconazole |
Use With Caution |
Itraconazole: Itraconazole may increase the plasma concentrations of clarithromycin. Patients taking itraconazole and clarithromycin concomitantly should be monitored closely for signs or symptoms of increased or prolonged adverse reactions (see also Itraconazole under “Drugs That Are Affected By Clarithromycin” in the table above). |
|
Antivirals: Atazanavir Ritonavir (in patients with decreased renal function) Saquinavir (in patients with decreased renal function) Etravirine Saquinavir (in patients with normal renal function) Ritonavir (in patients with normal renal function) |
Use With Caution No Dose Adjustments |
Atazanavir: When clarithromycin is coadministered with atazanavir, the dose of clarithromycin should be decreased by 50% [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Since concentrations of 14-OH clarithromycin are significantly reduced when clarithromycin is coadministered with atazanavir, alternative antibacterial therapy should be considered for indications other than infections due to Mycobacterium avium complex. Doses of clarithromycin greater than 1000 mg per day should not be coadministered with protease inhibitors. Ritonavir: Since concentrations of 14-OH clarithromycin are significantly reduced when clarithromycin is coadministered with ritonavir, alternative antibacterial therapy should be considered for indications other than infections due to Mycobacterium avium[see Pharmacokinetics (12.3)]. Doses of clarithromycin greater than 1000 mg per day should not be coadministered with protease inhibitors. Saquinavir: When saquinavir is coadministered with ritonavir, consideration should be given to the potential effects of ritonavir on clarithromycin (refer to ritonavir above) [see Pharmacokinetics (12.3)]. Etravirine: Clarithromycin exposure was decreased by etravirine; however, concentrations of the active metabolite, 14-OH-clarithromycin, were increased. Because 14-OH-clarithromycin has reduced activity against Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC), overall activity against this pathogen may be altered; therefore alternatives to clarithromycin should be considered for the treatment of MAC. |
|
Proton Pump Inhibitors: Omeprazole |
Use With Caution |
Omeprazole: Clarithromycin concentrations in the gastric tissue and mucus were also increased by concomitant administration of omeprazole [see Pharmacokinetics (12.3)]. |
|
Miscellaneous Cytochrome P450 Inducers: Efavirenz Nevirapine Rifampicin Rifabutin Rifapentine |
Use With Caution |
Inducers of CYP3A enzymes, such as efavirenz, nevirapine, rifampicin, rifabutin, and rifapentine will increase the metabolism of clarithromycin, thus decreasing plasma concentrations of clarithromycin, while increasing those of 14-OH-clarithromycin. Since the microbiological activities of clarithromycin and 14-OH-clarithromycin are different for different bacteria, the intended therapeutic effect could be impaired during concomitant administration of clarithromycin and enzyme inducers. Alternative antibacterial treatment should be considered when treating patients receiving inducers of CYP3A. There have been spontaneous or published reports of CYP3A based interactions of clarithromycin with rifabutin (see Rifabutin under “Drugs That Are Affected By Clarithromycin” in the table above). |
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C
Clarithromycin should not be used in pregnant women except in clinical circumstances where no alternative therapy is appropriate. If pregnancy occurs while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Four teratogenicity studies in rats (three with oral doses and one with intravenous doses up to 160 mg/kg/day administered during the period of major organogenesis) and two in rabbits at oral doses up to 125 mg/kg/day (approximately twice the recommended maximum human dose based on mg/m2) or intravenous doses of 30 mg/kg/day administered during gestation days 6 to 18 failed to demonstrate any teratogenicity from clarithromycin. Two additional oral studies in a different rat strain at similar doses and similar conditions demonstrated a low incidence of cardiovascular anomalies at doses of 150 mg/kg/day administered during gestation days 6 to 15. Plasma levels after 150 mg/kg/day were twice the human serum levels. Four studies in mice revealed a variable incidence of cleft palate following oral doses of 1000 mg/kg/day (2 and 4 times the recommended maximum human dose based on mg/m2, respectively) during gestation days 6 to 15. Cleft palate was also seen at 500 mg/kg/day. The 1000 mg/kg/day exposure resulted in plasma levels 17 times the human serum levels. In monkeys, an oral dose of 70 mg/kg/day produced fetal growth retardation at plasma levels that were twice the human serum levels.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Caution should be exercised when clarithromycin is administered to nursing women. The development and health benefits of human milk feeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for clarithromycin and any potential adverse effects on the human milk fed child from the drug or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clarithromycin and its active metabolite 14-hydroxy clarithromycin are excreted in human milk. Serum and milk samples were obtained after 3 days of treatment, at steady state, from one published study of 12 lactating women who were taking clarithromycin 250 mg orally twice daily. Based on the limited data from this study, and assuming milk consumption of 150 mL/kg/day, an exclusively human milk fed infant would receive an estimated average of 136 mcg/kg/day of clarithromycin and its active metabolite, with this maternal dosage regimen. This is less than 2% of the maternal weight-adjusted dose (7.8 mg/kg/day, based on the average maternal weight of 64 kg), and less than 1% of the pediatric dose (15 mg/kg/day) for children greater than 6 months of age.
A prospective observational study of 55 breastfed infants of mothers taking a macrolide antibacterial (6 were exposed to clarithromycin) were compared to 36 breastfed infants of mothers taking amoxicillin. Adverse reactions were comparable in both groups. Adverse reactions occurred in 12.7% of infants exposed to macrolides and included rash, diarrhea, loss of appetite, and somnolence.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of clarithromycin extended-release tablets in the treatment of pediatric patients has not been established.
Safety and effectiveness of clarithromycin in pediatric patients under 6 months of age have not been established. The safety of clarithromycin has not been studied in MAC patients under the age of 20 months.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In a steady-state study in which healthy elderly subjects (65 years to 81 years of age) were given 500 mg of clarithromycin every 12 hours, the maximum serum concentrations and area under the curves of clarithromycin and 14-OH clarithromycin were increased compared to those achieved in healthy young adults. These changes in pharmacokinetics parallel known age-related decreases in renal function. In clinical trials, elderly patients did not have an increased incidence of adverse reactions when compared to younger patients. Consider dosage adjustment in elderly patients with severe renal impairment. Elderly patients may be more susceptible to development of torsades de pointes arrhythmias than younger patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Most reports of acute kidney injury with calcium channel blockers metabolized by CYP3A4 (e.g., verapamil, amlodipine, diltiazem, nifedipine) involved elderly patients 65 years of age or older [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Especially in elderly patients, there have been reports of colchicine toxicity with concomitant use of clarithromycin and colchicine, some of which occurred in patients with renal insufficiency. Deaths have been reported in some patients [see Contraindications (4.4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
8.6 Renal and Hepatic Impairment
Clarithromycin is principally excreted via the liver and kidney. Clarithromycin may be administered without dosage adjustment to patients with hepatic impairment and normal renal function. However, in the presence of severe renal impairment with or without coexisting hepatic impairment, decreased dosage or prolonged dosing intervals may be appropriate [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage of clarithromycin can cause gastrointestinal symptoms such as abdominal pain, vomiting, nausea, and diarrhea.
Treat adverse reactions accompanying overdosage by the prompt elimination of unabsorbed drug and supportive measures. As with other macrolides, clarithromycin serum concentrations are not expected to be appreciably affected by hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.
11 DESCRIPTION
Clarithromycin, USP is a semi-synthetic macrolide antibiotic. Chemically, it is 6-O-methylerythromycin. The structural formula is:
C38H69NO13 M.W. 747.96
Figure 1: Structure of Clarithromycin
Clarithromycin, USP is a white to off-white crystalline powder. It is soluble in acetone, slightly soluble in methanol, ethanol, and acetonitrile, and practically insoluble in water.
Clarithromycin is available as extended-release tablets.
Each yellow, film-coated, oval-shaped clarithromycin extended-release tablet USP for oral administration contains 500 mg of clarithromycin, USP and the following inactive ingredients: citric acid anhydrous, ethylcellulose, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, iron oxide black, iron oxide red, iron oxide yellow, lactose monohydrate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene oxide, polyethylene glycol, pregelatinized starch, silicon dioxide, sodium starch glycolate, sodium stearyl fumarate, titanium dioxide, vanillin.
Clarithromycin extended-release tablets USP, 500 mg meet USP Dissolution Test 4.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Clarithromycin is a macrolide antimicrobial drug [see Microbiology (12.4)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Clarithromycin Extended-Release Tablets
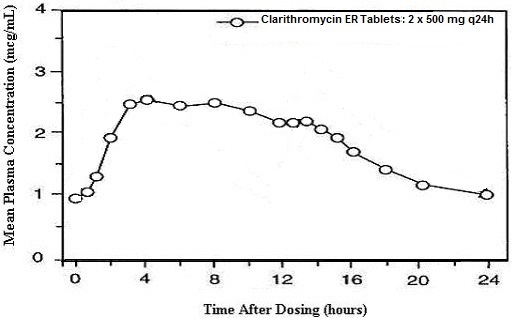
Clarithromycin extended-release tablets provide extended absorption of clarithromycin from the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration. Relative to an equal total daily dose of immediate-release clarithromycin tablets, clarithromycin extended-release tablets provide lower and later steady-state peak plasma concentrations but equivalent 24-hour AUCs for both clarithromycin and its microbiologically-active metabolite, 14-OH clarithromycin. While the extent of formation of 14-OH clarithromycin following administration of clarithromycin extended-release tablets (2 x 500 mg tablets once daily) is not affected by food, administration under fasting conditions is associated with approximately 30% lower clarithromycin AUC relative to administration with food. Therefore, clarithromycin extended-release tablets should be taken with food.
Figure 2: Steady-State Clarithromycin Plasma Concentration-Time Profiles
Distribution
Clarithromycin and the 14-OH clarithromycin metabolite distribute readily into body tissues and fluids. There are no data available on cerebrospinal fluid penetration. Because of high intracellular concentrations, tissue concentrations are higher than serum concentrations. Examples of tissue and serum concentrations are presented below.
|
Table 9. Tissue and Serum Concentrations of Clarithromycin |
||
|
CONCENTRATION (after 250 mg every 12 hours) |
||
|
Tissue Type |
Tissue (mcg/g) |
Serum (mcg/mL) |
|
Tonsil |
1.6 |
0.8 |
|
Lung |
8.8 |
1.7 |
Metabolism and Elimination
Clarithromycin Extended-Release Tablets
In healthy human subjects, steady-state peak plasma clarithromycin concentrations of approximately 2 mcg/mL to 3 mcg/mL were achieved about 5 hours to 8 hours after oral administration of 1000 mg clarithromycin extended-release tablets once daily; for 14-OH clarithromycin, steady-state peak plasma concentrations of approximately 0.8 mcg/mL were attained about 6 hours to 9 hours after dosing. Steady-state peak plasma clarithromycin concentrations of approximately 1 mcg/mL to 2 mcg/mL were achieved about 5 hours to 6 hours after oral administration of a single 500 mg clarithromycin extended-release tablets once daily; for 14-OH clarithromycin, steady-state peak plasma concentrations of approximately 0.6 mcg/mL were attained about 6 hours after dosing.
Specific Populations for clarithromycin extended-release tablets
HIV Infection
Steady-state concentrations of clarithromycin and 14-OH clarithromycin observed following administration of 500 mg doses of clarithromycin every 12 hours to adult patients with HIV infection were similar to those observed in healthy volunteers. In adult HIV-infected patients taking 500-mg or 1000-mg doses of clarithromycin every 12 hours, steady-state clarithromycin Cmax values ranged from 2 mcg/mL to 4 mcg/mL and 5 mcg/mL to 10 mcg/mL, respectively.
Hepatic Impairment
The steady-state concentrations of clarithromycin in subjects with impaired hepatic function did not differ from those in normal subjects; however, the 14-OH clarithromycin concentrations were lower in the hepatically impaired subjects. The decreased formation of 14-OH clarithromycin was at least partially offset by an increase in renal clearance of clarithromycin in the subjects with impaired hepatic function when compared to healthy subjects.
Renal Impairment
The pharmacokinetics of clarithromycin was also altered in subjects with impaired renal function [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6) and Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
Drug Interactions
Fluconazole
Following administration of fluconazole 200 mg daily and clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily to 21 healthy volunteers, the steady-state clarithromycin Cmin and AUC increased 33% and 18%, respectively. Clarithromycin exposures were increased and steady-state concentrations of 14-OH clarithromycin were not significantly affected by concomitant administration of fluconazole.
Colchicine
When a single dose of colchicine 0.6 mg was administered with clarithromycin 250 mg BID for 7 days, the colchicine Cmax increased 197% and the AUC0-∞ increased 239% compared to administration of colchicine alone.
Atazanavir
Following administration of clarithromycin (500 mg twice daily) with atazanavir (400 mg once daily), the clarithromycin AUC increased 94%, the 14-OH clarithromycin AUC decreased 70% and the atazanavir AUC increased 28%.
Ritonavir
Concomitant administration of clarithromycin and ritonavir (n = 22) resulted in a 77% increase in clarithromycin AUC and a 100% decrease in the AUC of 14-OH clarithromycin.
Saquinavir
Following administration of clarithromycin (500 mg bid) and saquinavir (soft gelatin capsules, 1200 mg tid) to 12 healthy volunteers, the steady-state saquinavir AUC and Cmax increased 177% and 187% respectively compared to administration of saquinavir alone. Clarithromycin AUC and Cmax increased 45% and 39% respectively, whereas the 14–OH clarithromycin AUC and Cmax decreased 24% and 34% respectively, compared to administration with clarithromycin alone.
Didanosine
Simultaneous administration of clarithromycin tablets and didanosine to 12 HIV-infected adult patients resulted in no statistically significant change in didanosine pharmacokinetics.
Zidovudine
Following administration of clarithromycin 500 mg tablets twice daily with zidovudine 100 mg every 4 hours, the steady-state zidovudine AUC decreased 12% compared to administration of zidovudine alone (n = 4). Individual values ranged from a decrease of 34% to an increase of 14%. When clarithromycin tablets were administered two to four hours prior to zidovudine, the steady-state zidovudine Cmax increased 100% whereas the AUC was unaffected (n = 24).
Omeprazole
Clarithromycin 500 mg every 8 hours was given in combination with omeprazole 40 mg daily to healthy adult subjects. The steady-state plasma concentrations of omeprazole were increased (Cmax, AUC0-24, and t½ increases of 30%, 89%, and 34%, respectively), by the concomitant administration of clarithromycin.
The plasma levels of clarithromycin and 14–OH clarithromycin were increased by the concomitant administration of omeprazole. For clarithromycin, the mean Cmax was 10% greater, the mean Cmin was 27% greater, and the mean AUC0-8 was 15% greater when clarithromycin was administered with omeprazole than when clarithromycin was administered alone. Similar results were seen for 14–OH clarithromycin, the mean Cmax was 45% greater, the mean Cmin was 57% greater, and the mean AUC0-8 was 45% greater. Clarithromycin concentrations in the gastric tissue and mucus were also increased by concomitant administration of omeprazole.
|
Clarithromycin Tissue Concentrations 2 hours after Dose (mcg/mL)/(mcg/g) |
|||||
|
Treatment |
N |
antrum |
fundus |
N |
Mucus |
|
Clarithromycin |
5 |
10.48 ± 2.01 |
20.81 ± 7.64 |
4 |
4.15 ± 7.74 |
|
Clarithromycin + Omeprazole |
5 |
19.96 ± 4.71 |
24.25 ± 6.37 |
4 |
39.29 ± 32.79 |
Theophylline
In two studies in which theophylline was administered with clarithromycin (a theophylline sustained-release formulation was dosed at either 6.5 mg/kg or 12 mg/kg together with 250 or 500 mg q12h clarithromycin), the steady-state levels of Cmax, Cmin, and the area under the serum concentration time curve (AUC) of theophylline increased about 20%.
Midazolam
When a single dose of midazolam was coadministered with clarithromycin tablets (500 mg twice daily for 7 days), midazolam AUC increased 174% after intravenous administration of midazolam and 600% after oral administration.
For information about other drugs indicated in combination with clarithromycin, refer to their full prescribing information, CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY section.
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Clarithromycin exerts its antibacterial action by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit of susceptible bacteria resulting in inhibition of protein synthesis.
Resistance
The major routes of resistance are modification of the 23S rRNA in the 50S ribosomal subunit to insensitivity or drug efflux pumps. Beta-lactamase production should have no effect on clarithromycin activity.
Most isolates of methicillin-resistant and oxacillin-resistant staphylococci are resistant to clarithromycin.
Antimicrobial Activity
Clarithromycin has been shown to be active against most of the isolates of the following microorganisms both in vitro and in clinical infections [see Indications and Usage (1)].
Gram-Positive Bacteria
- •
- Staphylococcus aureus
- •
- Streptococcus pneumoniae
- •
- Streptococcus pyogenes
Gram-Negative Bacteria
- •
- Haemophilus influenzae
- •
- Haemophilus parainfluenzae
- •
- Moraxella catarrhalis
Other Microorganisms
- •
- Chlamydophila pneumoniae
- •
- Helicobacter pylori
- •
- Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) consisting of M. avium and M. intracellulare
- •
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae
At least 90 percent of the microorganisms listed below exhibit in vitro minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) less than or equal to the clarithromycin susceptible MIC breakpoint for organisms of similar type to those shown in Table 11. However, the efficacy of clarithromycin in treating clinical infections due to these microorganisms has not been established in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials.
Gram-Positive Bacteria
- •
- Streptococcus agalactiae
- •
- Streptococci (Groups C, F, G)
- •
- Viridans group streptococci
Gram-Negative Bacteria
- •
- Legionella pneumophila
- •
- Pasteurella multocida
Anaerobic Bacteria
- •
- Clostridium perfringens
- •
- Peptococcus niger
- •
- Prevotella melaninogenica
- •
- Propionibacterium acnes
Susceptibility Testing Methods (Excluding Mycobacteria and Helicobacter)
When available, the clinical microbiology laboratory should provide the results of in vitro susceptibility test results for antimicrobial drugs used in local hospitals and practice areas to the physician as periodic reports that describe the susceptibility profile of nosocomial and community-acquired pathogens. These reports should aid the physician in selecting an antimicrobial drug for treatment.
Dilution Techniques
Quantitative methods are used to determine antimicrobial minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs). These MICs provide estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. The MICs should be determined using a standardized test method1,2 (broth and/or agar). The MIC values should be interpreted according to the criteria provided in Table 11.
Diffusion Techniques
Quantitative methods that require measurement of zone diameters can also provide reproducible estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. The zone size should be determined using a standardized test method.2,3 This procedure uses paper disks impregnated with 15 mcg of clarithromycin to test the susceptibility of bacteria to clarithromycin. The disk diffusion interpretive criteria are provided in Table 11.
|
||||||
|
Table 11. Susceptibility Test Interpretive Criteria for Clarithromycin |
||||||
|
Minimum Inhibitory Concentrations (mcg/mL) |
Disk Diffusion (zone diameters in mm) |
|||||
|
Pathogen |
S |
I |
R |
S |
I |
R |
|
Staphylococcus aureus |
≤ 2 |
4 |
≥ 8 |
≥ 18 |
14 to 17 |
≤ 13 |
|
Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus pneumoniae |
≤ 0.25* |
0.5* |
≥ 1* |
≥ 21† |
17 to 20† |
≤ 16† |
|
Haemophilus influenzae |
≤ 8‡ |
16‡ |
≥ 32‡ |
≥ 13§ |
11 to 12§ |
≤ 10§ |
Note: When testing Streptococcus pyogenes and Streptococcus pneumoniae, susceptibility and resistance to clarithromycin can be predicted using erythromycin.
A report of Susceptible (S) indicates that the antimicrobial drug is likely to inhibit growth of the pathogen if the antimicrobial drug reaches the concentration usually achievable at the site of infection. A report of Intermediate (I) indicates that the result should be considered equivocal, and, if the microorganism is not fully susceptible to alternative, clinically feasible drugs, the test should be repeated. This category implies possible clinical applicability in body sites where the drug is physiologically concentrated or in situations where high dosage of drug can be used. This category also provides a buffer zone which prevents small uncontrolled technical factors from causing major discrepancies in interpretation. A report of Resistant (R) indicates that the antimicrobial drug is not likely to inhibit growth of the pathogen if the antimicrobial drug reaches the concentration usually achievable at the infection site; other therapy should be selected.
Quality Control
Standardized susceptibility test procedures require the use of laboratory control bacteria to monitor and ensure the accuracy and precision of supplies and reagents in the assay, and the techniques of the individual performing the test.1-3 Standard clarithromycin powder should provide the following range of MIC values as noted in Table 12. For the diffusion technique using the 15 mcg disk, the criteria in Table 12 should be achieved.
|
||
|
Table 12. Acceptable Quality Control Ranges for Clarithromycin |
||
|
QC Strain |
MIC (mcg/mL) |
Zone diameter (mm) |
|
Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 29213* |
0.12 to 0.5 |
- |
|
Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 |
- |
26 to 32 |
|
Streptococcus pneumoniae ATCC 49619 |
0.03 to 0.12† |
25 to 31‡ |
|
Haemophilus influenzae ATCC 49247 |
4 to 16§ |
11 to 17¶ |
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
The following in vitro mutagenicity tests have been conducted with clarithromycin:
- •
- Salmonella/Mammalian Microsomes Test
- •
- Bacterial Induced Mutation Frequency Test
- •
- In Vitro Chromosome Aberration Test
- •
- Rat Hepatocyte DNA Synthesis Assay
- •
- Mouse Lymphoma Assay
- •
- Mouse Dominant Lethal Study
- •
- Mouse Micronucleus Test
All tests had negative results except the in vitro chromosome aberration test which was positive in one test and negative in another. In addition, a bacterial reverse-mutation test (Ames test) has been performed on clarithromycin metabolites with negative results.
Impairment of Fertility
Fertility and reproduction studies have shown that daily doses of up to 160 mg/kg/ to male and female rats caused no adverse effects on the estrous cycle, fertility, parturition, or number and viability of offspring. Plasma levels in rats after 150 mg/kg/day were twice the human serum levels.
Testicular atrophy occurred in rats at doses 7 times, in dogs at doses 3 times, and in monkeys at doses 8 times greater than the maximum human daily dose (on a body surface area basis).
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Corneal opacity occurred in dogs at doses 12 times and in monkeys at doses 8 times greater than the maximum human daily dose (on a body surface area basis). Lymphoid depletion occurred in dogs at doses 3 times greater than and in monkeys at doses 2 times greater than the maximum human daily dose (on a body surface area basis).
15 REFERENCES
1 Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically; Approved Standard—Tenth edition. CLSI Document M07-A10, Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 950 West Valley Rd, Suite 2500, Wayne, Pennsylvania 19087, USA, 2015.
2 Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twenty-fifth Informational Supplement. CLSI document M100-S25, Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 950 West Valley Road, Suite 2500, Wayne, Pennsylvania 19087, USA, 2015.
3 Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Tests; Approved Standard—Twelfth Edition. CLSI document M02-A12, Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 950 West Valley Road, Suite 2500, Wayne, Pennsylvania 19087, USA, 2015.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Clarithromycin extended-release tablets USP are available as follows:
500 mg – yellow, film-coated, oval-shaped tablets, debossed with “93” on one side and “7244” on the other side, in bottles of 60 (NDC 0093-7244-06).
Store at 20º to 25ºC (68º to 77ºF) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP, with a child-resistant closure (as required).
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATIONS OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Provide the following instructions or information about clarithromycin extended-release tablets to patients:
- •
- Counsel patients that antibacterial drugs including clarithromycin extended-release tablets should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When clarithromycin extended-release tablets are prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by clarithromycin or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
- •
- Advise patients that diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibacterials including clarithromycin extended-release tablets which usually ends when the antibacterial is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibacterials, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibacterial. If this occurs, instruct patients to contact their healthcare provider as soon as possible.
- •
- Advise patients that clarithromycin extended-release tablets may interact with some drugs; therefore, advise patients to report to their healthcare provider the use of any other medications.
- •
- Advise patients that clarithromycin extended-release tablets should be taken with food.
- •
- There are no data on the effect of clarithromycin extended-release tablets on the ability to drive or use machines. However, counsel patients regarding the potential for dizziness, vertigo, confusion and disorientation, which may occur with the medication. The potential for these adverse reactions should be taken into account before patients drive or use machines.
- •
- Advise patients that if pregnancy occurs while taking this drug, there is a potential hazard to the fetus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
All brand names listed are the registered trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc.
Manufactured In Israel By:
Teva Pharmaceutical Ind. Ltd.
Jerusalem, 9777402, Israel
Manufactured For:
Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc.
North Wales, PA 19454
Rev. R 6/2016
| CLARITHROMYCIN
clarithromycin tablet, film coated, extended release |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc. (001627975) |