Label: CILOXAN- ciprofloxacin hydrochloride solution
-
Contains inactivated NDC Code(s)
NDC Code(s): 54868-2782-0 - Packager: Physicians Total Care, Inc.
- This is a repackaged label.
- Source NDC Code(s): 0065-0656
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated December 13, 2010
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
DESCRIPTION
CILOXAN® (ciprofloxacin HCl ophthalmic solution) is a synthetic, sterile, multiple dose, antimicrobial for topical ophthalmic use. Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibacterial active against a broad spectrum of gram-positive and gram-negative ocular pathogens. It is available as the monohydrochloride monohydrate salt of 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinoline-carboxylic acid. It is a faint to light yellow crystalline powder with a molecular weight of 385.8. Its empirical formula is C17H18FN3O3•HCl•H2O and its chemical structure is as follows:
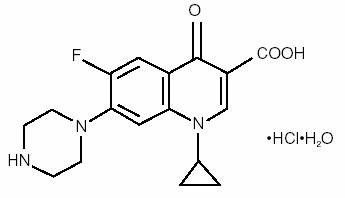
Ciprofloxacin differs from other quinolones in that it has a fluorine atom at the 6-position, a piperazine moiety at the 7-position, and a cyclopropyl ring at the 1-position.
Each mL of CILOXAN Ophthalmic Solution contains: Active: ciprofloxacin HCl 3.5 mg equivalent to 3 mg base. Preservative: benzalkonium chloride 0.006%. Inactive: sodium acetate, acetic acid, mannitol 4.6%, edetate disodium 0.05%, hydrochloric acid and/or sodium hydroxide (to adjust pH) and purified water. The pH is approximately 4.5 and the osmolality is approximately 300 mOsm.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Systemic Absorption
A systemic absorption study was performed in which CILOXAN Ophthalmic Solution was administered in each eye every two hours while awake for two days followed by every four hours while awake for an additional 5 days. The maximum reported plasma concentration of ciprofloxacin was less than 5 ng/mL. The mean concentration was usually less than 2.5 ng/mL.
MicrobiologyCiprofloxacin hasin vitro activity against a wide range of gram-negative and gram-positive organisms. The bactericidal action of ciprofloxacin results from interference with the enzyme DNA gyrase which is needed for the synthesis of bacterial DNA.
Ciprofloxacin has been shown to be active against most strains of the following organisms both in vitro and in clinical infections. (See INDICATIONS AND USAGE section).
Gram-PositiveStaphylococcus aureus
Gram-Negative
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus (Viridans Group)Haemophilus influenzae
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Serratia marcescensCiprofloxacin has been shown to be active in vitro against most strains of the following organisms, however, the clinical significance of these data is unknown:
Gram-PositiveEnterococcus faecalis (Many strains are only moderately susceptible)
Gram-Negative
Staphylococcus haemolyticus
Staphylococcus hominis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Streptococcus pyogenesAcinetobacter calcoaceticus
Other Organisms
subsp. anitratus
Aeromonas caviae
Aeromonas hydrophila
Brucella melitensis
Campylobacter coli
Campylobacter jejuni
Citrobacter diversus
Citrobacter freundii
Edwardsiella tarda
Enterobacter aerogenes
Enterobacter cloacae
Escherichia coli
Haemophilus ducreyi
Haemophilus parainfluenzae
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Klebsiella oxytoca
Legionella pneumophila
Moraxella (Branhamella)
catarrhalis
Morganella morganii
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Neisseria meningitidis
Pasteurella multocida
Proteus mirabilis
Proteus vulgaris
Providencia rettgeri
Providencia stuartii
Salmonella enteritidis
Salmonella typhi
Shigella sonneii
Shigella flexneri
Vibrio cholerae
Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Vibrio vulnificus
Yersinia enterocoliticaChlamydia trachomatis (only moderately susceptible) and Mycobacterium tuberculosis (only moderately susceptible).
Most strains of Pseudomonas cepacia and some strains of Pseudomonas maltophilia are resistant to ciprofloxacin as are most anaerobic bacteria, including Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium difficile.
The minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) generally does not exceed the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) by more than a factor of 2. Resistance to ciprofloxacin in vitro usually develops slowly (multiple-step mutation).
Ciprofloxacin does not cross-react with other antimicrobial agents such as beta-lactams or aminoglycosides; therefore, organisms resistant to these drugs may be susceptible to ciprofloxacin.
Clinical StudiesFollowing therapy with CILOXAN Ophthalmic Solution, 76% of the patients with corneal ulcers and positive bacterial cultures were clinically cured and complete re-epithelialization occurred in about 92% of the ulcers.
In 3 and 7 day multicenter clinical trials, 52% of the patients with conjunctivitis and positive conjunctival cultures were clinically cured and 70-80% had all causative pathogens eradicated by the end of treatment.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
CILOXAN Ophthalmic Solution is indicated for the treatment of infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in the conditions listed below:
Corneal Ulcers:
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Serratia marcescens *
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus (Viridans Group)*
Conjunctivitis:
Haemophilus influenzae
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Streptococcus pneumoniae*Efficacy for this organism was studied in fewer than 10 infections.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
NOT FOR INJECTION INTO THE EYE.
Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions, some following the first dose, have been reported in patients receiving systemic quinolone therapy. Some reactions were accompanied by cardiovascular collapse, loss of consciousness, tingling, pharyngeal or facial edema, dyspnea, urticaria, and itching. Only a few patients had a history of hypersensitivity reactions. Serious anaphylactic reactions require immediate emergency treatment with epinephrine and other resuscitation measures, including oxygen, intravenous fluids, intravenous antihistamines, corticosteroids, pressor amines and airway management, as clinically indicated.
Remove contact lenses before using.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
As with other antibacterial preparations, prolonged use of ciprofloxacin may result in overgrowth of nonsusceptible organisms, including fungi. If superinfection occurs, appropriate therapy should be initiated. Whenever clinical judgment dictates, the patient should be examined with the aid of magnification, such as slit lamp biomicroscopy and, where appropriate, fluorescein staining.
Ciprofloxacin should be discontinued at the first appearance of a skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity reaction.
In clinical studies of patients with bacterial corneal ulcer, a white crystalline precipitate located in the superficial portion of the corneal defect was observed in 35 (16.6%) of 210 patients. The onset of the precipitate was within 24 hours to 7 days after starting therapy. In one patient, the precipitate was immediately irrigated out upon its appearance. In 17 patients, resolution of the precipitate was seen in 1 to 8 days (seven within the first 24-72 hours), in five patients, resolution was noted in 10-13 days. In nine patients, exact resolution days were unavailable; however, at follow-up examinations, 18-44 days after onset of the event, complete resolution of the precipitate was noted. In three patients, outcome information was unavailable. The precipitate did not preclude continued use of ciprofloxacin, nor did it adversely affect the clinical course of the ulcer or visual outcome. (SEE ADVERSE REACTIONS).
Information for patientsDo not touch dropper tip to any surface, as this may contaminate the solution.
Drug InteractionsSpecific drug interaction studies have not been conducted with ophthalmic ciprofloxacin. However, the systemic administration of some quinolones has been shown to elevate plasma concentrations of theophylline, interfere with the metabolism of caffeine, enhance the effects of the oral anticoagulant, warfarin, and its derivatives and has been associated with transient elevations in serum creatinine in patients receiving cyclosporine concomitantly.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of FertilityEight in vitro mutagenicity tests have been conducted with ciprofloxacin and the test results are listed below:
Salmonella/Microsome Test (Negative)
E. coli DNA Repair Assay (Negative)
Mouse Lymphoma Cell Forward Mutation Assay (Positive)
Chinese Hamster V79 Cell HGPRT Test (Negative)
Syrian Hamster Embryo Cell Transformation Assay (Negative)
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Point Mutation Assay (Negative)
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mitotic Crossover and Gene Conversion Assay (Negative)
Rat Hepatocyte DNA Repair Assay (Positive)Thus, two of the eight tests were positive, but the results of the following three in vivo test systems gave negative results:
Rat Hepatocyte DNA Repair Assay
Micronucleus Test (Mice)
Dominant Lethal Test (Mice)Long term carcinogenicity studies in mice and rats have been completed. After daily oral dosing for up to two years, there is no evidence that ciprofloxacin had any carcinogenic or tumorigenic effects in these species.
PregnancyPregnancy Category CReproduction studies have been performed in rats and mice at doses up to six times the usual daily human oral dose and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to ciprofloxacin. In rabbits, as with most antimicrobial agents, ciprofloxacin (30 and 100 mg/kg orally) produced gastrointestinal disturbances resulting in maternal weight loss and an increased incidence of abortion. No teratogenicity was observed at either dose. After intravenous administration, at doses up to 20 mg/kg, no maternal toxicity was produced and no embryotoxicity or teratogenicity was observed. There are no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women. CILOXAN® Ophthalmic Solution should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing MothersIt is not known whether topically applied ciprofloxacin is excreted in human milk; however, it is known that orally administered ciprofloxacin is excreted in the milk of lactating rats and oral ciprofloxacin has been reported in human breast milk after a single 500 mg dose. Caution should be exercised when CILOXAN Ophthalmic Solution is administered to a nursing mother.
Pediatric UseSafety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 1 year have not been established. Although ciprofloxacin and other quinolones cause arthropathy in immature animals after oral administration, topical ocular administration of ciprofloxacin to immature animals did not cause any arthropathy and there is no evidence that the ophthalmic dosage form has any effect on the weight bearing joints.
Geriatric UseNo overall differences in safety or effectiveness have been observed between elderly and younger patients.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequently reported drug related adverse reaction was local burning or discomfort. In corneal ulcer studies with frequent administration of the drug, white crystalline precipitates were seen in approximately 17% of patients (SEE PRECAUTIONS). Other reactions occurring in less than 10% of patients included lid margin crusting, crystals/scales, foreign body sensation, itching, conjunctival hyperemia and a bad taste following instillation. Additional events occurring in less than 1% of patients included corneal staining, keratopathy/keratitis, allergic reactions, lid edema, tearing, photophobia, corneal infiltrates, nausea and decreased vision.
- OVERDOSAGE
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Corneal Ulcers
The recommended dosage regimen for the treatment of corneal ulcers is two drops into the affected eye every 15 minutes for the first six hours and then two drops into the affected eye every 30 minutes for the remainder of the first day. On the second day, instill two drops in the affected eye hourly. On the third through the fourteenth day, place two drops in the affected eye every four hours. Treatment may be continued after 14 days if corneal re-epithelialization has not occurred.
Bacterial ConjunctivitisThe recommended dosage regimen for the treatment of bacterial conjunctivitis is one or two drops instilled into the conjunctival sac(s) every two hours while awake for two days and one or two drops every four hours while awake for the next five days.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
As a sterile ophthalmic solution in Alcon's DROP-TAINER® dispensing system consisting of a natural low density polyethylene bottle and dispensing plug and tan polypropylene closure. Tamper evidence is provided with a shrink band around the closure and neck area of the package.
5 mL in 8mL bottle – NDC 54868-2782-0
STORAGE: Store at 2° to 25°C (36° to 77°F). Protect from light.
-
ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY
Ciprofloxacin and related drugs have been shown to cause arthropathy in immature animals of most species tested following oral administration. However, a one-month topical ocular study using immature Beagle dogs did not demonstrate any articular lesions.
Rx Only
Rev: March 2006
©2003, 2004, 2006 Alcon, Inc.ALCON LABORATORIES, INC.
Fort Worth, Texas 76134 USAPrinted in USA
9001529-0306
Relabeling of "Additional Barcode Label" by:
Physicians Total Care, Inc.
Tulsa, OK 74146
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CILOXAN
ciprofloxacin hydrochloride solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:54868-2782(NDC:0065-0656) Route of Administration OPHTHALMIC Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CIPROFLOXACIN HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 4BA73M5E37) (CIPROFLOXACIN - UNII:5E8K9I0O4U) CIPROFLOXACIN HYDROCHLORIDE 3.5 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength BENZALKONIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: F5UM2KM3W7) SODIUM ACETATE (UNII: 4550K0SC9B) ACETIC ACID (UNII: Q40Q9N063P) MANNITOL (UNII: 3OWL53L36A) EDETATE DISODIUM (UNII: 7FLD91C86K) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:54868-2782-0 1 in 1 CARTON 1 5 mL in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA019992 07/10/1995 Labeler - Physicians Total Care, Inc. (194123980) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Physicians Total Care, Inc. 194123980 relabel


