Label: CYPROHEPTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE tablet
-
Contains inactivated NDC Code(s)
NDC Code(s): 54868-1332-3, 54868-1332-4, 54868-1332-5, 54868-1332-6, view more54868-1332-7 - Packager: Physicians Total Care, Inc.
- This is a repackaged label.
- Source NDC Code(s): 64980-123
- Category: HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
- DEA Schedule: None
- Marketing Status: Abbreviated New Drug Application
Drug Label Information
Updated December 30, 2010
If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version.
- Download DRUG LABEL INFO: PDF XML
- Official Label (Printer Friendly)
-
DESCRIPTION
Cyproheptadine HCI, is an antihistaminic and antiserotonergic agent. Cyproheptadine hydrochloride is a white to slightly yellowish crystalline solid, with a molecular weight of 350.89, which is soluble in water, freely soluble in methanol, sparingly soluble in ethanol, soluble in chloroform, and practically insoluble in ether. It is the sesquihydrate of 4-(5H-dibenzo[a,d]cyclohepten-5-ylidene)-1-methylpiperidine hydrochloride. The molecular formula of the anhydrous salt is C21H21N•HCl and the structural formula of the anhydrous salt is:
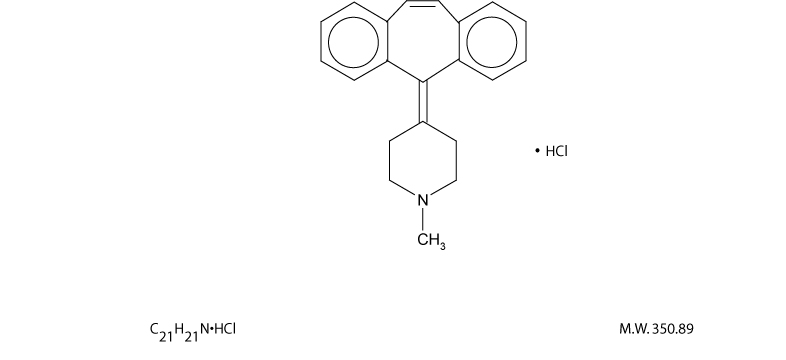
Cyproheptadine hydrochloride is available for oral administration in 4 mg tablets. Inactive ingredients include: lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and pregelatinized starch.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Cyproheptadine is a serotonin and histamine antagonist with anticholinergic and sedative effects. Antiserotonin and antihistamine drugs appear to compete with serotonin and histamine, respectively, for receptor sites.
Pharmacokinetics and MetabolismAfter a single 4 mg oral dose of 14C-labelled cyproheptadine HCl in normal subjects, given as tablets, 2-20% of the radioactivity was excreted in the stools. Only about 34% of the stool radioactivity was unchanged drug, corresponding to less than 5.7% of the dose. At least 40% of the administered radioactivity was excreted in the urine. No detectable amounts of unchanged drug were present in the urine of patients on chronic 12-20 mg daily doses. The principal metabolite found in human urine has been identified as a quaternary ammonium glucuronide conjugate of cyproheptadine. Elimination is diminished in renal insufficiency.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Perennial and seasonal allergic rhinitis
Vasomotor rhinitis
Allergic conjunctivitis due to inhalant allergens and foods
Mild, uncomplicated allergic skin manifestations of urticaria and angioedema.
Amelioration of allergic reactions to blood or plasma
Cold urticaria
Dermatographism
As therapy for anaphylactic reactions adjunctive to epinephrine and other standard measures after the acute manifestations have been controlled. -
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Newborn or Premature Infants
This drug should not be used in newborn or premature infants.
Nursing MothersBecause of the higher risk of antihistamines for infants generally and for newborns and prematures in particular, antihistamine therapy is contraindicated in nursing mothers.
Other ConditionsHypersensitivity to cyproheptadine and other drugs of similar chemical structure.
Monoamine oxidase inhibitor therapy (see DRUG INTERACTIONS.)
Angle-closure glaucoma
Stenosing peptic ulcer
Symptomatic prostatic hypertrophy
Bladder neck obstruction
Pyloroduodenal obstruction
Elderly, debilitated patients -
WARNINGS
Pediatric Patients
Overdosage of antihistamines, particularly in infants and young children, may produce hallucinations, central nervous system depression, convulsions, respiratory and cardiac arrest, and death.
Antihistamines may diminish mental alertness; conversely, particularly, in the young child, they may occasionally produce excitation.
CNS DepressantsAntihistamines may have additive effects with alcohol and other CNS depressants, e.g., hypnotics, sedatives, tranquilizers, antianxiety agents.
Activities Requiring Mental AlertnessPatients should be warned about engaging in activities requiring mental alertness and motor coordination, such as driving a car or operating machinery.
Antihistamines are more likely to cause dizziness, sedation, and hypotension in elderly patients. (see PRECAUTIONS, Geriatric Use).
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Cyproheptadine has an atropine-like action and, therefore, should be used with caution in patients with:
Information for Patients
History of bronchial asthma
Increased intraocular pressure
Hyperthyroidism
Cardiovascular disease
HypertensionAntihistamines may diminish mental alertness; conversely, particularly, in the young child, they may occasionally produce excitation. Patients should be warned about engaging in activities requiring mental alertness and motor coordination, such as driving a car or operating machinery.
Drug InteractionsMAO inhibitors prolong and intensify the anticholinergic effects of antihistamines.
Antihistamines may have additive effects with alcohol and other CNS depressants, e.g., hypnotics, sedatives, tranquilizers, antianxiety agents.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of FertilityLong-term carcinogenic studies have not been done with cyproheptadine.
Cyproheptadine had no effect on fertility in a two-litter study in rats or a two generation study in mice at about 10 times the human dose.
Cyproheptadine did not produce chromosome damage in human lymphocytes or fibroblasts in vitro; high doses (10-4M) were cytotoxic. Cyproheptadine did not have any mutagenic effect in the Ames microbial mutagen test; concentrations of above 500 mcg/plate inhibited bacterial growth.
PREGNANCYPregnancy Category BReproduction studies have been performed in rabbits, mice, and rats at oral or subcutaneous doses up to 32 times the maximum recommended human oral dose and have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to cyproheptadine. Cyproheptadine has been shown to be fetotoxic in rats when given by intraperitoneal injection in doses four times the maximum recommended human oral dose. Two studies in pregnant women, however, have not shown that cyproheptadine increases the risk of abnormalities when administered during the first, second and third trimesters of pregnancy. No teratogenic effects were observed in any of the newborns. Nevertheless, because the studies in humans cannot rule out the possibility of harm, cyproheptadine should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing MothersIt is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from cyproheptadine, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Pediatric UseSafety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of two have not been established. (see CONTRAINDICATIONS, Newborn or Premature Infants, and WARNINGS, Pediatric Patients).
Geriatric UseClinical studies of cyproheptadine HCI tablets did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy (see WARNINGS, Activities Requiring Mental Alertness).
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse reactions which have been reported with the use of antihistamines are as follows:
Central Nervous SystemSedation and sleepiness (often transient), dizziness, disturbed coordination, confusion, restlessness, excitation, nervousness, tremor, irritability, insomnia, paresthesias, neuritis, convulsions, euphoria, hallucinations, hysteria, faintness.
IntegumentaryAllergic manifestation of rash and edema, excessive perspiration, urticaria, photosensitivity.
Special SensesAcute labyrinthitis, blurred vision, diplopia, vertigo, tinnitus.
CardiovascularHypotension, palpitation, tachycardia, extrasystoles, anaphylactic shock.
HematologicHemolytic anemia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia.
Digestive SystemCholestasis, hepatic failure, hepatitis, hepatic function abnormality, dryness of mouth, epigastric distress, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, jaundice.
GenitourinaryUrinary frequency, difficult urination, urinary retention, early menses.
RespiratoryDryness of nose and throat, thickening of bronchial secretions, tightness of chest and wheezing, nasal stuffiness.
MiscellaneousFatigue, chills, headache, increased appetite/weight gain.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Antihistamine overdosage reactions may vary from central nervous system depression to stimulation especially in pediatric patients. Also, atropine-like signs and symptoms (dry mouth; fixed, dilated pupils; flushing, etc.) as well as gastrointestinal symptoms may occur.
If vomiting has not occurred spontaneously, the patient should be induced to vomit with syrup of ipecac.
If patient is unable to vomit, perform gastric lavage followed by activated charcoal. Isotonic or 1⁄2 isotonic saline is the lavage of choice. Precautions against aspiration must be taken especially in infants and children.
When life threatening CNS signs and symptoms are present, intravenous physostigmine salicylate may be considered. Dosage and frequency of administration are dependent on age, clinical response, and recurrence after response. (See package circulars for physostigmine products.)
Saline cathartics, as milk of magnesia, by osmosis draw water into the bowel and, therefore, are valuable for their action in rapid dilution of bowel content.
Stimulants should not be used.
Vasopressors may be used to treat hypotension.
The oral LD50 of cyproheptadine is 123 mg/kg, and 295 mg/kg in the mouse and rat, respectively.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE SHOULD BE INDIVIDUALIZED ACCORDING TO THE NEEDS AND THE RESPONSE OF THE PATIENT.
Each tablet contains 4 mg of cyproheptadine hydrochloride.
Pediatric PatientsAge 2 to 6 years: The total daily dosage for pediatric patients may be calculated on the basis of body weight or body area using approximately 0.25 mg/kg/day or 8 mg per square meter of body surface (8 mg/m2).
The usual dose is 2 mg (½ tablet) two or three times a day, adjusted as necessary to the size and response of the patient. The dose is not to exceed 12 mg a day.
Age 7 to 14 yearsThe usual dose is 4 mg (1 tablet) two or three times a day adjusted as necessary to the size and response of the patient. The dose is not to exceed 16 mg a day.
AdultsThe total daily dose for adults should not exceed 0.5 mg/kg/day. The therapeutic range is 4 to 20 mg a day, with the majority of patients requiring 12 to 16 mg a day. An occasional patient may require as much as 32 mg a day for adequate relief. It is suggested that dosage be initiated with 4 mg (1 tablet) three times a day and adjusted according to the size and response of the patient.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Cyproheptadine hydrochloride tablets USP 4 mg are supplied as white, round, compressed tablets, debossed “cor” above the bisect and “150” below the bisect and the other side is plain.
They are supplied as follows:
Bottles of 20
NDC 54868-1332-7
Bottles of 30
NDC 54868-1332-4
Bottles of 50
NDC 54868-1332-5
Bottles of 90
NDC 54868-1332-3
Bottles of 100
NDC 54868-1332-6
Dispense in a well-closed container as defined in the USP. Use child-resistant closure (as required).
Store at controlled room temperature 15° - 30°C (59° - 86°F) (see USP).
KEEP THIS AND ALL DRUGS OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
Manufactured by:
Corepharma LLC
Middlesex, NJ 08846Manufactured for:
Rising Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Allendale, NJ 07401MF # 309-04
January 2007
Relabeling and Repackaging by:
Physicians Total Care, Inc.
Tulsa, OK 74146
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CYPROHEPTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE
cyproheptadine hydrochloride tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC:54868-1332(NDC:64980-123) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CYPROHEPTADINE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: NJ82J0F8QC) (CYPROHEPTADINE - UNII:2YHB6175DO) CYPROHEPTADINE 4 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) Product Characteristics Color white (White) Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND (round) Size 7mm Flavor Imprint Code cor;150 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC:54868-1332-3 90 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 2 NDC:54868-1332-4 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 3 NDC:54868-1332-5 50 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 4 NDC:54868-1332-6 100 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 5 NDC:54868-1332-7 20 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA040537 05/21/2003 Labeler - Physicians Total Care, Inc. (194123980) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Physicians Total Care, Inc. 194123980 relabel, repack


