FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Patients with Cancer Receiving Myelosuppressive Chemotherapy
Neulasta is indicated to decrease the incidence of infection, as manifested by febrile neutropenia, in patients with non-myeloid malignancies receiving myelosuppressive anti-cancer drugs associated with a clinically significant incidence of febrile neutropenia [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
1.2 Patients with Hematopoietic Subsyndrome of Acute Radiation Syndrome
Neulasta is indicated to increase survival in patients acutely exposed to myelosuppressive doses of radiation [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Clinical Studies (14.2)].
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Patients with Cancer Receiving Myelosuppressive Chemotherapy
The recommended dosage of Neulasta is a single subcutaneous injection of 6 mg administered once per chemotherapy cycle. For dosing in pediatric patients weighing less than 45 kg, refer to Table 1. Do not administer Neulasta between 14 days before and 24 hours after administration of cytotoxic chemotherapy.
2.2 Patients with Hematopoietic Subsyndrome of Acute Radiation Syndrome
The recommended dose of Neulasta is two doses, 6 mg each, administered subcutaneously one week apart. For dosing in pediatric patients weighing less than 45 kg, refer to Table 1. Administer the first dose as soon as possible after suspected or confirmed exposure to radiation levels greater than 2 gray (Gy). Administer the second dose one week after the first dose.
Obtain a baseline complete blood count (CBC). Do not delay administration of Neulasta if a CBC is not readily available. Estimate a patient's absorbed radiation dose (i.e., level of radiation exposure) based on information from public health authorities, biodosimetry if available, or clinical findings such as time to onset of vomiting or lymphocyte depletion kinetics.
2.3 Administration
Neulasta is administered subcutaneously via a single-dose prefilled syringe for manual use or for use with the on-body injector (OBI) for Neulasta, which is co-packaged with a single-dose prefilled syringe. Use of the OBI for Neulasta is not recommended for patients with Hematopoietic Subsyndrome of Acute Radiation Syndrome. Use of the OBI for Neulasta has not been studied in pediatric patients.
Prior to use‚ remove the carton from the refrigerator and allow the Neulasta prefilled syringe to reach room temperature for a minimum of 30 minutes. Discard any prefilled syringe left at room temperature for greater than 48 hours.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Do not administer Neulasta if discoloration or particulates are observed.
The needle cap on the prefilled syringes contains dry natural rubber (derived from latex); persons with latex allergies should not administer these products.
Pediatric Patients weighing less than 45 kg
The Neulasta prefilled syringe is not designed to allow for direct administration of doses less than 0.6 mL (6 mg). The syringe does not bear graduation marks, which are necessary to accurately measure doses of Neulasta less than 0.6 mL (6 mg) for direct administration to patients. Thus, the direct administration to patients requiring dosing of less than 0.6 mL (6 mg) is not recommended due to the potential for dosing errors. Refer to Table 1.
| Body Weight | Neulasta Dose | Volume to Administer |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Less than 10 kg* | See below* | See below* |
| 10 - 20 kg | 1.5 mg | 0.15 mL |
| 21 - 30 kg | 2.5 mg | 0.25 mL |
| 31 - 44 kg | 4 mg | 0.4 mL |
2.4 Special Healthcare Provider Instructions for the On-body Injector for Neulasta
A healthcare provider must fill the on-body injector (OBI) with Neulasta using the prefilled syringe and then apply the OBI for Neulasta to the patient's skin (abdomen or back of arm). The back of the arm may only be used if there is a caregiver available to monitor the status of the OBI for Neulasta. Approximately 27 hours after the OBI for Neulasta is applied to the patient's skin, Neulasta will be delivered over approximately 45 minutes. A healthcare provider may initiate administration with the OBI for Neulasta on the same day as the administration of cytotoxic chemotherapy, as long as the OBI for Neulasta delivers Neulasta no less than 24 hours after administration of cytotoxic chemotherapy.
The prefilled syringe co-packaged in Neulasta Onpro® kit must only be used with the OBI for Neulasta. The prefilled syringe contains additional solution to compensate for liquid loss during delivery through the OBI for Neulasta. If the prefilled syringe co-packaged in Neulasta Onpro kit is used for manual subcutaneous injection, the patient will receive an overdose. If the single-dose prefilled syringe for manual use is used with the OBI for Neulasta, the patient may receive less than the recommended dose.
Do not use the OBI for Neulasta to deliver any other drug product except the Neulasta prefilled syringe co-packaged with the OBI for Neulasta.
The OBI for Neulasta should be applied to intact, non-irritated skin on the arm or abdomen.
A missed dose could occur due to an OBI for Neulasta failure or leakage. If the patient misses a dose, a new dose should be administered by single-dose prefilled syringe for manual use, as soon as possible after detection.
Refer to the Healthcare Provider Instructions for Use for the OBI for Neulasta for full administration information.
2.5 Advice to Give to Patients Regarding Administration via the On-body Injector for Neulasta
Advise patients to avoid activities such as traveling, driving, or operating heavy machinery during hours 26-29 following application of the on-body injector (OBI) for Neulasta (this includes the 45-minute delivery period plus an hour post-delivery). Patients should have a caregiver nearby for the first use.
Refer the patient to the dose delivery information written on the Patient Instructions for Use. Provide training to patients to ensure they understand when the dose delivery of Neulasta will begin and how to monitor the OBI for Neulasta for completed delivery. Ensure patients understand how to identify signs of malfunction of OBI for Neulasta [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) and Patient Counseling Information (17)]. Instruct patients using the OBI to notify their healthcare professional immediately in order to determine the need for a replacement dose of Neulasta if they suspect that the device may not have performed as intended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Neulasta is a clear, colorless, preservative-free solution available as:
- Injection: 6 mg/0.6 mL in a single-dose prefilled syringe for manual use only.
- Injection: 6 mg/0.6 mL in a single-dose prefilled syringe co-packaged with the on-body injector (OBI) for Neulasta (Neulasta Onpro kit).
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Neulasta is contraindicated in patients with a history of serious allergic reactions to pegfilgrastim or filgrastim. Reactions have included anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Splenic Rupture
Splenic rupture, including fatal cases, can occur following the administration of Neulasta. Evaluate for an enlarged spleen or splenic rupture in patients who report left upper abdominal or shoulder pain after receiving Neulasta.
5.2 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) can occur in patients receiving Neulasta. Evaluate patients who develop fever and lung infiltrates or respiratory distress after receiving Neulasta, for ARDS. Discontinue Neulasta in patients with ARDS.
5.3 Serious Allergic Reactions
Serious allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, can occur in patients receiving Neulasta. The majority of reported events occurred upon initial exposure. Allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, can recur within days after the discontinuation of initial anti-allergic treatment. Permanently discontinue Neulasta in patients with serious allergic reactions. Do not administer Neulasta to patients with a history of serious allergic reactions to pegfilgrastim or filgrastim.
5.4 Allergies to Acrylics
The on-body injector (OBI) for Neulasta uses acrylic adhesive. For patients who have reactions to acrylic adhesives, use of this product may result in a significant reaction.
5.5 Use in Patients with Sickle Cell Disorders
Severe and sometimes fatal sickle cell crises can occur in patients with sickle cell disorders receiving pegfilgrastim products. Discontinue Neulasta if sickle cell crisis occurs.
5.6 Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis has occurred in patients receiving Neulasta. The diagnoses were based upon azotemia, hematuria (microscopic and macroscopic), proteinuria, and renal biopsy. Generally, events of glomerulonephritis resolved after dose-reduction or discontinuation of Neulasta. If glomerulonephritis is suspected, evaluate for cause. If causality is likely, consider dose-reduction or interruption of Neulasta.
5.7 Leukocytosis
White blood cell (WBC) counts of 100 × 109/L or greater have been observed in patients receiving pegfilgrastim. Monitoring of complete blood count (CBC) during pegfilgrastim therapy is recommended.
5.8 Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytopenia has been reported in patients receiving pegfilgrastim. Monitor platelet counts.
5.9 Capillary Leak Syndrome
Capillary leak syndrome has been reported after G-CSF administration, including Neulasta, and is characterized by hypotension, hypoalbuminemia, edema and hemoconcentration. Episodes vary in frequency, severity and may be life-threatening if treatment is delayed. Patients who develop symptoms of capillary leak syndrome should be closely monitored and receive standard symptomatic treatment, which may include a need for intensive care.
5.10 Potential for Tumor Growth Stimulatory Effects on Malignant Cells
The granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) receptor through which pegfilgrastim and filgrastim act has been found on tumor cell lines. The possibility that pegfilgrastim acts as a growth factor for any tumor type, including myeloid malignancies and myelodysplasia, diseases for which pegfilgrastim is not approved, cannot be excluded.
5.11 Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) and Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) in Patients with Breast and Lung Cancer
MDS and AML have been associated with the use of Neulasta in conjunction with chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy in patients with breast and lung cancer. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of MDS/AML in these settings.
5.12 Potential Device Failures
Missed or partial doses have been reported in patients receiving Neulasta via the on-body injector (OBI) due to the device not performing as intended. In the event of a missed or partial dose, patients may be at increased risk of events such as neutropenia, febrile neutropenia and/or infection than if the dose had been correctly delivered. Instruct patients using the OBI to notify their healthcare professional immediately in order to determine the need for a replacement dose of Neulasta if they suspect that the device may not have performed as intended.
5.13 Aortitis
Aortitis has been reported in patients receiving Neulasta. It may occur as early as the first week after start of therapy. Manifestations may include generalized signs and symptoms such as fever, abdominal pain, malaise, back pain, and increased inflammatory markers (e.g., c-reactive protein and white blood cell count). Consider aortitis in patients who develop these signs and symptoms without known etiology. Discontinue Neulasta if aortitis is suspected.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Splenic Rupture [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Serious Allergic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Allergies to Acrylics [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Use in Patients with Sickle Cell Disorders [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Glomerulonephritis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Leukocytosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Thrombocytopenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Capillary Leak Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Potential for Tumor Growth Stimulatory Effects on Malignant Cells [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Myelodysplastic syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Acute myeloid leukemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Aortitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared with rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Neulasta clinical trials safety data are based upon 932 patients receiving Neulasta in seven randomized clinical trials. The population was 21 to 88 years of age and 92% female. The ethnicity was 75% Caucasian, 18% Hispanic, 5% Black, and 1% Asian. Patients with breast (n = 823), lung and thoracic tumors (n = 53) and lymphoma (n = 56) received Neulasta after nonmyeloablative cytotoxic chemotherapy. Most patients received a single 100 mcg/kg (n = 259) or a single 6 mg (n = 546) dose per chemotherapy cycle over 4 cycles.
The following adverse reaction data in Table 2 are from a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in patients with metastatic or non-metastatic breast cancer receiving docetaxel 100 mg/m2 every 21 days (Study 3). A total of 928 patients were randomized to receive either 6 mg Neulasta (n = 467) or placebo (n = 461). The patients were 21 to 88 years of age and 99% female. The ethnicity was 66% Caucasian, 31% Hispanic, 2% Black, and < 1% Asian, Native American, or other.
The most common adverse reactions occurring in ≥ 5% of patients and with a between-group difference of ≥ 5% higher in the pegfilgrastim arm in placebo-controlled clinical trials are bone pain and pain in extremity.
| Body System Adverse Reaction | Placebo (N = 461) | Neulasta 6 mg SC on Day 2 (N = 467) |
|---|---|---|
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | ||
| Bone pain | 26% | 31% |
| Pain in extremity | 4% | 9% |
6.2 Immunogenicity
As with all therapeutic proteins, there is a potential for immunogenicity. The detection of antibody formation is highly dependent on the sensitivity and specificity of the assay. Additionally, the observed incidence of antibody (including neutralizing antibody) positivity in an assay may be influenced by several factors, including assay methodology, sample handling, timing of sample collection, concomitant medications, and underlying disease. For these reasons, comparison of the incidence of antibodies to pegfilgrastim in the studies described below with the incidence of antibodies in other studies or to other products may be misleading.
Binding antibodies to pegfilgrastim were detected using a BIAcore assay. The approximate limit of detection for this assay is 500 ng/mL. Pre-existing binding antibodies were detected in approximately 6% (51/849) of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Four of 521 pegfilgrastim-treated subjects who were negative at baseline developed binding antibodies to pegfilgrastim following treatment. None of these 4 patients had evidence of neutralizing antibodies detected using a cell-based bioassay.
6.3 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of Neulasta. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Splenic rupture and splenomegaly (enlarged spleen) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Allergic reactions/hypersensitivity, including anaphylaxis, skin rash, urticaria, generalized erythema, and flushing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Sickle cell crisis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Glomerulonephritis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Leukocytosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Thrombocytopenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Capillary Leak Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Injection site reactions
- Sweet's syndrome (acute febrile neutrophilic dermatosis), cutaneous vasculitis
- Application site reactions (including events such as application site hemorrhage, application site pain, application site discomfort, application site bruise, and application site erythema) have been reported with the use of the on-body injector for Neulasta.
- Contact dermatitis and local skin reactions such as rash, pruritus, and urticaria have been reported with the use of the on-body injector for Neulasta, possibly indicating a hypersensitivity reaction to the adhesive.
- Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in patients with breast and lung cancer receiving chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Aortitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Alveolar hemorrhage
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Although available data with Neulasta use in pregnant women are insufficient to establish whether there is a drug associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes, there are available data from published studies in pregnant women exposed to filgrastim products. These studies have not established an association of filgrastim product use during pregnancy with major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
In animal studies, no evidence of reproductive/developmental toxicity occurred in the offspring of pregnant rats that received cumulative doses of pegfilgrastim approximately 10 times the recommended human dose (based on body surface area). In pregnant rabbits, increased embryolethality and spontaneous abortions occurred at 4 times the maximum recommended human dose simultaneously with signs of maternal toxicity (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risks of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Pregnant rabbits were dosed with pegfilgrastim subcutaneously every other day during the period of organogenesis. At cumulative doses ranging from the approximate human dose to approximately 4 times the recommended human dose (based on body surface area), the treated rabbits exhibited decreased maternal food consumption, maternal weight loss, as well as reduced fetal body weights and delayed ossification of the fetal skull; however, no structural anomalies were observed in the offspring from either study. Increased incidences of post-implantation losses and spontaneous abortions (more than half the pregnancies) were observed at cumulative doses approximately 4 times the recommended human dose, which were not seen when pregnant rabbits were exposed to the recommended human dose.
Three studies were conducted in pregnant rats dosed with pegfilgrastim at cumulative doses up to approximately 10 times the recommended human dose at the following stages of gestation: during the period of organogenesis, from mating through the first half of pregnancy, and from the first trimester through delivery and lactation. No evidence of fetal loss or structural malformations was observed in any study. Cumulative doses equivalent to approximately 3 and 10 times the recommended human dose resulted in transient evidence of wavy ribs in fetuses of treated mothers (detected at the end of gestation but no longer present in pups evaluated at the end of lactation).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of pegfilgrastim in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Other filgrastim products are secreted poorly into breast milk, and filgrastim products are not absorbed orally by neonates. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for Neulasta and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from Neulasta or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Neulasta have been established in pediatric patients. No overall differences in safety were identified between adult and pediatric patients based on postmarketing surveillance and review of the scientific literature.
Use of Neulasta in pediatric patients for chemotherapy-induced neutropenia is based on adequate and well-controlled studies in adults with additional pharmacokinetic and safety data in pediatric patients with sarcoma [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14.1)].
The use of Neulasta to increase survival in pediatric patients acutely exposed to myelosuppressive doses of radiation is based on efficacy studies conducted in animals and clinical data supporting the use of Neulasta in patients with cancer receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy. Efficacy studies of Neulasta could not be conducted in humans with acute radiation syndrome for ethical and feasibility reasons. Results from population modeling and simulation indicate that two doses of Neulasta (Table 1), administered one week apart provide pediatric patients with exposures comparable to that in adults receiving two 6 mg doses one week apart [see Dosage and Administration (2.3), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14.2)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage of Neulasta may result in leukocytosis and bone pain. Events of edema, dyspnea, and pleural effusion have been reported in a single patient who administered Neulasta on 8 consecutive days in error. In the event of overdose, the patient should be monitored for adverse reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
11 DESCRIPTION
Pegfilgrastim is a covalent conjugate of recombinant methionyl human G-CSF (filgrastim) and monomethoxypolyethylene glycol. Filgrastim is a water-soluble 175 amino acid protein with a molecular weight of approximately 19 kilodaltons (kD). Filgrastim is obtained from the bacterial fermentation of a strain of E coli transformed with a genetically engineered plasmid containing the human G-CSF gene. To produce pegfilgrastim, a 20 kD monomethoxypolyethylene glycol molecule is covalently bound to the N-terminal methionyl residue of filgrastim. The average molecular weight of pegfilgrastim is approximately 39 kD.
Neulasta is provided in two presentations:
- Neulasta for manual subcutaneous injection is supplied in 0.6 mL prefilled syringes. The prefilled syringe does not bear graduation marks and is designed to deliver the entire contents of the syringe (6 mg/0.6 mL).
- On-body injector (OBI) for Neulasta is supplied with a prefilled syringe containing 0.64 mL of Neulasta in solution that delivers 0.6 mL of Neulasta in solution when used with the OBI for Neulasta. The syringe does not bear graduation marks and is only to be used with the OBI for Neulasta.
The delivered 0.6 mL dose from either the prefilled syringe for manual subcutaneous injection or the OBI for Neulasta contains 6 mg pegfilgrastim (based on protein weight) in a sterile, clear, colorless, preservative-free solution (pH 4.0) containing acetate (0.35 mg), polysorbate 20 (0.02 mg), sodium (0.02 mg), and sorbitol (30 mg) in Water for Injection, USP.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Pegfilgrastim is a colony-stimulating factor that acts on hematopoietic cells by binding to specific cell surface receptors, thereby stimulating proliferation, differentiation, commitment, and end cell functional activation.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Animal data and clinical data in humans suggest a correlation between pegfilgrastim exposure and the duration of severe neutropenia as a predictor of efficacy. Selection of the dosing regimen of Neulasta is based on reducing the duration of severe neutropenia.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim was studied in 379 patients with cancer. The pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim was nonlinear, and clearance decreased with increases in dose. Neutrophil receptor binding is an important component of the clearance of pegfilgrastim, and serum clearance is directly related to the number of neutrophils. In addition to numbers of neutrophils, body weight appeared to be a factor. Patients with higher body weights experienced higher systemic exposure to pegfilgrastim after receiving a dose normalized for body weight. A large variability in the pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim was observed. The half-life of Neulasta ranged from 15 to 80 hours after subcutaneous injection. In healthy volunteers, the pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim were comparable when delivered subcutaneously via a manual prefilled syringe versus via the on-body injector (OBI) for Neulasta.
Specific Populations
No gender-related differences were observed in the pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim, and no differences were observed in the pharmacokinetics of geriatric patients (≥ 65 years of age) compared with younger patients (< 65 years of age) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Renal Impairment
In a study of 30 subjects with varying degrees of renal dysfunction, including end stage renal disease, renal dysfunction had no effect on the pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim.
Pediatric Patients with Cancer Receiving Myelosuppressive Chemotherapy
The pharmacokinetics and safety of pegfilgrastim were studied in 37 pediatric patients with sarcoma in Study 4 [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. The mean (± standard deviation [SD]) systemic exposure (AUC0-inf) of Neulasta after subcutaneous administration at 100 mcg/kg was 47.9 (± 22.5) mcg∙hr/mL in the youngest age group (0 to 5 years, n = 11), 22.0 (± 13.1) mcg∙hr/mL in the 6 to 11 years age group (n = 10), and 29.3 (± 23.2) mcg∙hr/mL in the 12 to 21 years age group (n = 13). The terminal elimination half-lives of the corresponding age groups were 30.1 (± 38.2) hours, 20.2 (± 11.3) hours, and 21.2 (± 16.0) hours, respectively.
Patients Acutely Exposed to Myelosuppressive Doses of Radiation
The pharmacokinetics of pegfilgrastim is not available in patients acutely exposed to myelosuppressive doses of radiation. Based on limited pharmacokinetic data in irradiated non-human primates, the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC), reflecting the exposure to pegfilgrastim in non-human primates following a 300 mcg/kg dose of Neulasta, appears to be greater than in humans receiving a 6 mg dose. Results from population modeling and simulation indicate that two 6 mg doses of Neulasta administered one week apart in adults result in clinically relevant effects on duration of grade 3 and 4 neutropenia. In addition, weight based dosing in pediatric patients weighing less than 45 kg [see Dosage and Administration, Section 2.3, Table 1] provides exposures comparable to those in adults receiving two 6 mg doses one week apart.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No carcinogenicity or mutagenesis studies have been performed with pegfilgrastim.
Pegfilgrastim did not affect reproductive performance or fertility in male or female rats at cumulative weekly doses approximately 6 to 9 times higher than the recommended human dose (based on body surface area).
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Patients with Cancer Receiving Myelosuppressive Chemotherapy
Neulasta was evaluated in three randomized, double-blind, controlled studies. Studies 1 and 2 were active-controlled studies that employed doxorubicin 60 mg/m2 and docetaxel 75 mg/m2 administered every 21 days for up to 4 cycles for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Study 1 investigated the utility of a fixed dose of Neulasta. Study 2 employed a weight-adjusted dose. In the absence of growth factor support, similar chemotherapy regimens have been reported to result in a 100% incidence of severe neutropenia (ANC < 0.5 × 109/L) with a mean duration of 5 to 7 days and a 30% to 40% incidence of febrile neutropenia. Based on the correlation between the duration of severe neutropenia and the incidence of febrile neutropenia found in studies with filgrastim, duration of severe neutropenia was chosen as the primary endpoint in both studies, and the efficacy of Neulasta was demonstrated by establishing comparability to filgrastim-treated patients in the mean days of severe neutropenia.
In Study 1, 157 patients were randomized to receive a single subcutaneous injection of Neulasta (6 mg) on day 2 of each chemotherapy cycle or daily subcutaneous filgrastim (5 mcg/kg/day) beginning on day 2 of each chemotherapy cycle. In Study 2, 310 patients were randomized to receive a single subcutaneous injection of Neulasta (100 mcg/kg) on day 2 or daily subcutaneous filgrastim (5 mcg/kg/day) beginning on day 2 of each chemotherapy cycle.
Both studies met the major efficacy outcome measure of demonstrating that the mean days of severe neutropenia of Neulasta-treated patients did not exceed that of filgrastim-treated patients by more than 1 day in cycle 1 of chemotherapy. The mean days of cycle 1 severe neutropenia in Study 1 were 1.8 days in the Neulasta arm compared to 1.6 days in the filgrastim arm [difference in means 0.2 (95% CI - 0.2, 0.6)] and in Study 2 were 1.7 days in the Neulasta arm compared to 1.6 days in the filgrastim arm [difference in means 0.1 (95% CI - 0.2, 0.4)].
A secondary endpoint in both studies was days of severe neutropenia in cycles 2 through 4 with results similar to those for cycle 1.
Study 3 was a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study that employed docetaxel 100 mg/m2 administered every 21 days for up to 4 cycles for the treatment of metastatic or non-metastatic breast cancer. In this study, 928 patients were randomized to receive a single subcutaneous injection of Neulasta (6 mg) or placebo on day 2 of each chemotherapy cycle. Study 3 met the major trial outcome measure of demonstrating that the incidence of febrile neutropenia (defined as temperature ≥ 38.2°C and ANC ≤ 0.5 × 109/L) was lower for Neulasta-treated patients as compared to placebo-treated patients (1% versus 17%, respectively, p < 0.001). The incidence of hospitalizations (1% versus 14%) and IV anti-infective use (2% versus 10%) for the treatment of febrile neutropenia was also lower in the Neulasta-treated patients compared to the placebo-treated patients.
Study 4 was a multicenter, randomized, open-label study to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] of Neulasta in pediatric and young adult patients with sarcoma. Patients with sarcoma receiving chemotherapy age 0 to 21 years were eligible. Patients were randomized to receive subcutaneous Neulasta as a single-dose of 100 mcg/kg (n = 37) or subcutaneous filgrastim at a dose 5 mcg/kg/day (n = 6) following myelosuppressive chemotherapy. Recovery of neutrophil counts was similar in the Neulasta and filgrastim groups. The most common adverse reaction reported was bone pain.
14.2 Patients with Hematopoietic Subsyndrome of Acute Radiation Syndrome
Efficacy studies of Neulasta could not be conducted in humans with acute radiation syndrome for ethical and feasibility reasons. Approval of this indication was based on efficacy studies conducted in animals and data supporting Neulasta's effect on severe neutropenia in patients with cancer receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
The recommended dose of Neulasta is two doses, 6 mg each, administered one week apart for humans exposed to myelosuppressive doses of radiation. For pediatric patients weighing less than 45 kg, dosing of Neulasta is weight based and is provided in Table 1 [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. This dosing regimen is based on population modeling and simulation analyses. The exposure associated with this dosing regimen is expected to provide sufficient pharmacodynamic activity to treat humans exposed to myelosuppressive doses of radiation [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The safety of Neulasta at a dose of 6 mg has been assessed on the basis of clinical experience in patients with cancer receiving myelosuppressive chemotherapy.
The efficacy of Neulasta for the acute radiation syndrome setting was studied in a randomized, placebo-controlled non-human primate model of radiation injury. Rhesus macaques were randomized to either a control (n = 23) or treated (n = 23) cohort. On study day 0, animals (n = 6 to 8 per irradiation day) were exposed to total body irradiation (TBI) of 7.50 ± 0.15 Gy delivered at 0.8 ± 0.03 Gy/min, representing a dose that would be lethal in 50% of animals by 60 days of follow-up (LD50/60). Animals were administered subcutaneous injections of a blinded treatment (control article [5% dextrose in water] or pegfilgrastim [300-319 mcg/kg/day]) on study day 1 and on study day 8. The primary endpoint was survival. Animals received medical management consisting of intravenous fluids, antibiotics, blood transfusions, and other support as required.
Pegfilgrastim significantly (at 0.0014 level of significance) increased 60-day survival in irradiated non-human primates: 91% survival (21/23) in the pegfilgrastim group compared to 48% survival (11/23) in the control group.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Neulasta single-dose prefilled syringe for manual use
Neulasta injection is a clear, colorless solution supplied in a prefilled single-dose syringe for manual use containing 6 mg pegfilgrastim, supplied with a 27-gauge, 1/2-inch needle with an UltraSafe® Needle Guard.
The needle cap of the prefilled syringe contains dry natural rubber (a derivative of latex).
Neulasta is provided in a dispensing pack containing one sterile 6 mg/0.6 mL prefilled syringe (NDC 55513-190-01).
Neulasta prefilled syringe does not bear graduation marks and is intended only to deliver the entire contents of the syringe (6 mg/0.6 mL) for direct administration. Use of the prefilled syringe is not recommended for direct administration for pediatric patients weighing less than 45 kg who require doses that are less than the full contents of the syringe.
Neulasta Onpro® kit
Neulasta Onpro kit is provided in a carton containing one sterile prefilled syringe and one sterile on-body injector (OBI) for Neulasta (NDC 55513-192-01).
The Neulasta injection single-dose prefilled syringe contains 0.64 mL of a clear, colorless solution that delivers 6 mg/0.6 mL of pegfilgrastim when used with the OBI for Neulasta. The prefilled syringe is supplied with a 27-gauge, 1/2-inch needle. The syringe does not bear graduation marks and is only to be used with the OBI for Neulasta.
The needle cap of the prefilled syringe contains dry natural rubber (a derivative of latex).
Store Neulasta Onpro kit in the refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) until 30 minutes prior to use. Because the OBI for Neulasta is at room temperature during the period of use, Neulasta Onpro kit should not be held at room temperature longer than 12 hours prior to use. Discard Neulasta Onpro kit if stored at room temperature for more than 12 hours.
Do not use the OBI for Neulasta if its packaging has been previously opened.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Advise patients of the following risks and potential risks with Neulasta:
- Splenic rupture and splenomegaly
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome
- Serious allergic reactions
- Sickle cell crisis
- Glomerulonephritis
- Increased risk of Myelodysplastic Syndrome and/or Acute Myeloid Leukemia in patients with breast and lung cancer who receive Neulasta in conjunction with chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy
- Capillary Leak Syndrome
- Aortitis
Advise patients acutely exposed to myelosuppressive doses of radiation (Hematopoietic Subsyndrome of Acute Radiation Syndrome) that efficacy studies of Neulasta for this indication could not be conducted in humans for ethical and feasibility reasons and that, therefore, approval of this use was based on efficacy studies conducted in animals [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
Instruct patients who self-administer Neulasta using the single-dose prefilled syringe of the:
- Importance of following the Instructions for Use.
- Dangers of reusing syringes.
- Importance of following local requirements for proper disposal of used syringes.
Advise patients on the use of the on-body injector (OBI) for Neulasta:
- Review the Patient Information and Patient Instructions for Use with the patient and provide the instructions to the patient.
- Refer the patient to the dose delivery information written on the Patient Instructions for Use.
- Tell the patient when their dose delivery of Neulasta will begin and when their dose delivery should be completed.
- Advise the patient that serious allergic reactions can happen with Neulasta. Patients should have a caregiver nearby for the first use. Patients should plan to be in a place where they can appropriately monitor the OBI for Neulasta during the approximately 45 minute Neulasta delivery and for an hour after the delivery. Advise the patient to avoid traveling, driving, or operating heavy machinery during hours 26-29 following application of the OBI for Neulasta.
- If the OBI for Neulasta is placed on the back of the arm, remind the patient that a caregiver must be available to monitor the OBI for Neulasta.
- If a patient calls the healthcare provider regarding any OBI for Neulasta problems, the healthcare provider is advised to call Amgen at 1-800-772-6436.
- Advise the patient:
- to call their healthcare provider immediately if the status light on the OBI for Neulasta is flashing red (see the Patient Instructions for Use).
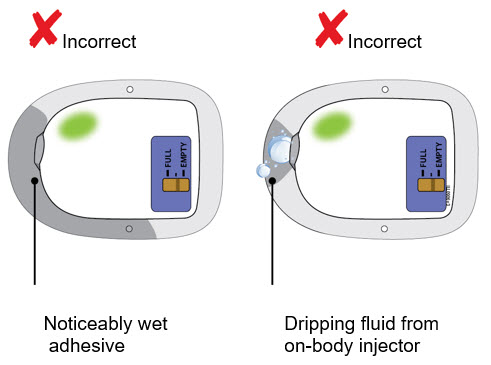
- to inform their healthcare provider if the adhesive on the OBI for Neulasta becomes saturated with fluid, or there is dripping, as this may be evidence of significant product leakage, resulting in inadequate or missed dose (see the Patient Instructions for Use).
- to keep the OBI for Neulasta dry for approximately the last 3 hours prior to the dose delivery start to better enable potential leak detection.
- that the OBI for Neulasta should only be exposed to temperatures between 41°F and 104°F (5°C-40°C).
- to keep the OBI for Neulasta at least 4 inches away from electrical equipment such as cell phones, cordless telephones, microwaves, and other common appliances. Failure to keep the OBI for Neulasta at least this recommended distance may interfere with operation and can lead to a missed or incomplete dose of Neulasta.
- that if the needle is exposed after OBI for Neulasta removal, place the used OBI for Neulasta in a sharps disposal container to avoid accidental needle stick and call their healthcare provider immediately.
- to remove the OBI for Neulasta after the green light shines continuously and to place the used OBI for Neulasta in a sharps disposal container (see the Patient Instructions for Use).
- Advise the patient:
- do not reapply the OBI for Neulasta if the OBI for Neulasta comes off before full dose is delivered and instead call their healthcare provider immediately, as they may need a replacement dose.
- avoid bumping the OBI for Neulasta or knocking the OBI for Neulasta off the body.
- do not use other materials to hold the on-body injector in place that could cover audio/visual indicators or compress the on-body injector against the patient's skin, as this could dislodge the cannula and lead to a missed dose or incomplete dose of Neulasta.
- do not expose the OBI for Neulasta to medical imaging studies (e.g., X-ray scan, MRI, CT scan and ultrasound), radiation treatment, and oxygen rich environments such as hyperbaric chambers to avoid OBI for Neulasta damage and patient injury.
- Advise the patient to avoid:
- airport X-ray scans and request a manual pat down instead; remind patients who elect to request a manual pat down to exercise care to avoid having the OBI for Neulasta dislodged during the pat down process.
- sleeping on the OBI for Neulasta or applying pressure on the OBI for Neulasta as this may affect OBI for Neulasta performance.
- getting body lotions, creams, oils, and cleaning agents near the OBI for Neulasta as these products may loosen the adhesive.
- use of lotions, creams, or oils on their arms and abdomen prior to their next scheduled OBI for Neulasta dose (to help with device adherence to the skin).
- using bath tubs, hot tubs, whirlpools, or saunas and avoid exposing the OBI for Neulasta to direct sunlight as these may affect the drug.
- peeling off or disturbing the OBI for Neulasta adhesive before delivery of full dose is complete.
Neulasta® (pegfilgrastim)
Manufactured by:
Amgen Inc.
One Amgen Center Drive
Thousand Oaks, California 91320-1799
U.S. License No. 1080
Patent: http://pat.amgen.com/onpro/
© 2002-2021 Amgen Inc. All rights reserved.
www.neulasta.com
1-800-77-AMGEN (1-800-772-6436)
v27
| Patient Information Neulasta® (nu-las-tah) (pegfilgrastim) injection Single-Dose Prefilled Syringe |
|
|---|---|
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: 01/2021 |
| What is Neulasta?
Neulasta is a man-made form of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF). G-CSF is a substance produced by the body. It stimulates the growth of neutrophils, a type of white blood cell important in the body's fight against infection. Acute Radiation Syndrome: The effectiveness of Neulasta for this use was only studied in animals, because it could not be studied in people. |
|
| Do not take Neulasta if you have had a serious allergic reaction to pegfilgrastim or filgrastim. | |
Before you receive Neulasta, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
|
How will I receive Neulasta?
|
|
| What are possible side effects of Neulasta? Neulasta may cause serious side effects, including:
These are not all the possible side effects of Neulasta. Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
How should I store Neulasta?
|
|
| General information about the safe and effective use of Neulasta.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Neulasta for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Neulasta to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Neulasta that is written for health professionals. |
|
| What are the ingredients in Neulasta?
Active ingredient: pegfilgrastim Inactive ingredients: acetate, polysorbate 20, sodium and sorbitol in water for injection. Manufactured by: Amgen Inc., One Amgen Center Drive, Thousand Oaks, California 91320-1799 U.S. License No. 1080 Patent: http://pat.amgen.com/onpro/ ©2002- 2021 Amgen Inc. All rights reserved. For more information go to www.neulasta.com, or call 1-800-77-AMGEN (1-800-772-6436). 1xxxxx v16 |
|
| Patient Information Neulasta® (nu-las-tah) (pegfilgrastim) injection On-body injector for Neulasta |
|
|---|---|
| This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. | Revised: 01/2021 |
| What is the most important information I need to know about receiving Neulasta with the on-body injector for Neulasta? | |
|
|
| What is Neulasta?
Neulasta is a prescription medicine used to help reduce the chance of infection due to a low white blood cell count, in people with certain types of cancer (non-myeloid), who receive anti-cancer medicines (chemotherapy) that can cause fever and low blood cell count. |
|
| Do not take Neulasta if you have had a serious allergic reaction to pegfilgrastim or filgrastim. | |
Before you receive Neulasta, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
|
|
| How will I receive Neulasta? See the Instructions for Use for detailed information about how you will receive a dose of Neulasta with the on-body injector for Neulasta, and how to remove and dispose of the on-body injector for Neulasta.
|
|
While the on-body injector for Neulasta is in place you should avoid:
|
|
| What are the possible side effects of Neulasta? Neulasta may cause serious side effects, including:
These are not all the possible side effects of Neulasta. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist. Call your healthcare provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
|
| General information about the safe and effective use of Neulasta
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. If you would like more information about Neulasta, talk with your healthcare provider or pharmacist. You can ask your pharmacist for information about Neulasta that is written for health professionals. |
|
| What are the ingredients in Neulasta?
Active ingredient: pegfilgrastim Inactive ingredients: acetate, polysorbate 20, sodium and sorbitol in Water for Injection Manufactured by: Amgen Inc., One Amgen Center Drive, Thousand Oaks, California 91320-1799 US License No. 1080 Patent: http://pat.amgen.com/onpro/ © 2002 to 2021 Amgen Inc. All rights reserved. For more information, go to www.neulasta.com or call 1-844-696-3852 (1-844-MYNEULASTA). v7 |
|
Neulasta® (pegfilgrastim) Onpro® kit
Healthcare Provider INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
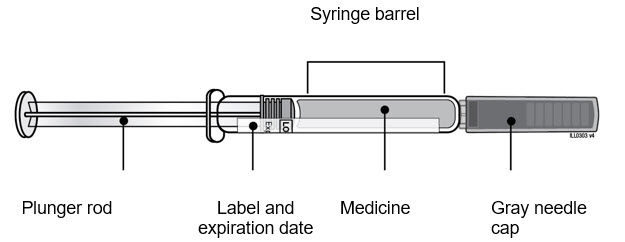
| Guide to Parts Neulasta Prefilled Syringe |
 |
| On-body Injector for Neulasta |
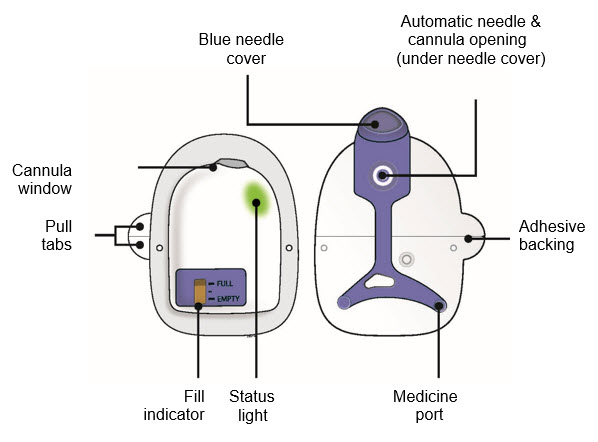 |
Important
READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE USING NEULASTA ONPRO KIT
Prescribing Information
- See Prescribing Information for information on Neulasta.
- The on-body injector is for adult patients only.
- The on-body injector is not recommended for patients with Hematopoietic Subsyndrome of Acute Radiation Syndrome.
- Neulasta prefilled syringe gray needle cap contains dry natural rubber, which is derived from latex.
- For patients who have had severe skin reactions to acrylic adhesives, consider the benefit:risk profile before administering pegfilgrastim via the on-body injector for Neulasta.
Application Information
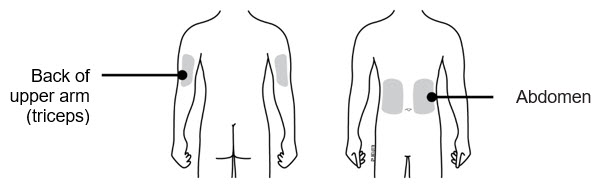
- The on-body injector should be applied to intact, non-irritated skin on the abdomen or back of the arm. The back of the arm may only be used if there is a caregiver available to monitor the status of the on-body injector.
- The on-body injector has a self-adhesive backing to attach it to the skin, do not use additional materials to hold it in place as this could dislodge the cannula and lead to a missed or incomplete dose of Neulasta.
Environmental Information
-
Do not expose the on-body injector for Neulasta to the following environments as the on-body injector may be damaged and the patient could be injured:
- Diagnostic imaging (e.g., CT Scan, MRI, Ultrasound, X-ray)
- Radiation treatment
- Oxygen rich environments such as hyperbaric chambers
Cautions
- Do not use Neulasta Onpro kit to deliver any other drug product
- Do not use the on-body injector if its packaging has been previously opened, or the expiration date on the carton or any components has passed.
- Do not use if the name Neulasta does not appear on Neulasta Onpro kit carton.
- Do not modify the on-body injector.
- Do not attempt to reapply the on-body injector.
- Do not use if either the on-body injector or prefilled syringe is dropped. Start again with a new kit
Storage Information
- Store the kit in the refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C) until ready for use. If the kit is stored at room temperature for more than 12 hours, do not use. Start again with a new kit.
- Keep the prefilled syringe in the kit carton until use to protect from light.
- Do not freeze the kit.
- Do not separate the components of Neulasta Onpro kit until ready for use.
For all questions, or if a patient calls you regarding any injector problems, call Amgen at 1-800-772-6436.
Step 1: Prepare
| A | Place the syringe tray and the on-body injector tray on a clean, well-lit work surface.
Allow the syringe and on-body injector to come naturally to room temperature for 30 minutes prior to activating. Do not warm the kit components using a heat source. |
|
| B | Choose the patient's injection site.
 Ask the patient about their ability to monitor and remove the on-body injector.
|
|
| C | Clean an area on the injection site larger than the on-body injector adhesive backing. | |
Thoroughly clean the site with alcohol to enhance on-body adherence to the skin.
|  |
|
| Remove Neulasta prefilled syringe from tray.
| ||
| D | ||
For safety reasons:
| ||
| E | Inspect Neulasta prefilled syringe. Neulasta liquid should always be clear and colorless.
|
|
Step 2: Fill
| A | Remove air bubbles in prefilled syringe.
Injecting air bubbles could interfere with proper operation of the on-body injector.
| 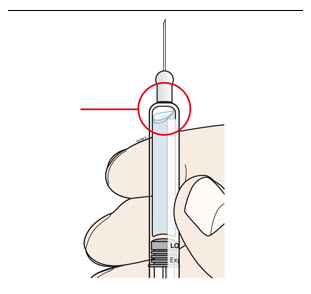 |
||
| B | Center the needle directly over the medicine port and insert all the way into the port, avoiding sides. | |||
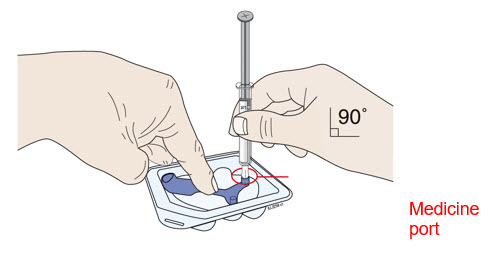 | ||||
Insert needle into medicine port at a 90 degree angle only.
- Do not remove the blue needle cover before filling the on-body injector.
- Do not insert the needle more than once.
- Do not bend the needle. Avoid spilling the medicine.
| C | Push the plunger rod to empty entire syringe contents into the on-body injector. | |
| 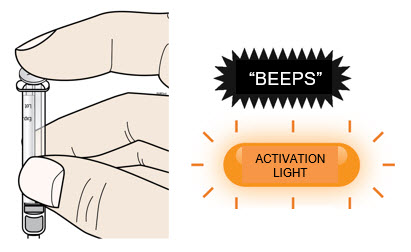 |
|
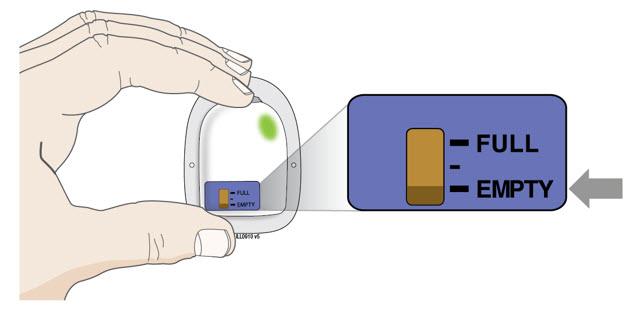
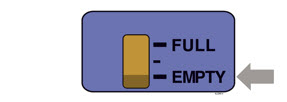
| D | Check to see if the on-body injector is full and the amber light is flashing. You should see a black line next to FULL on the fill indicator.
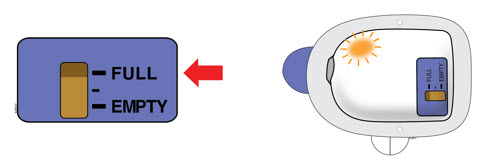 If this is not the case, do not use. Start again with a new Neulasta Onpro kit. |
|
| E | Firmly lift and remove the blue needle cover away from the on-body injector.
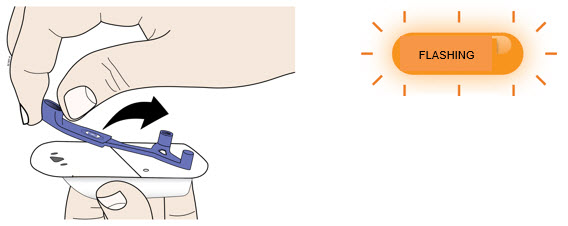 |
|
Step 3: Apply
| A | Peel away both pull tabs to show the adhesive. Never touch hands or gloves to the adhesive.
Make sure skin is dry prior to applying the on-body injector. 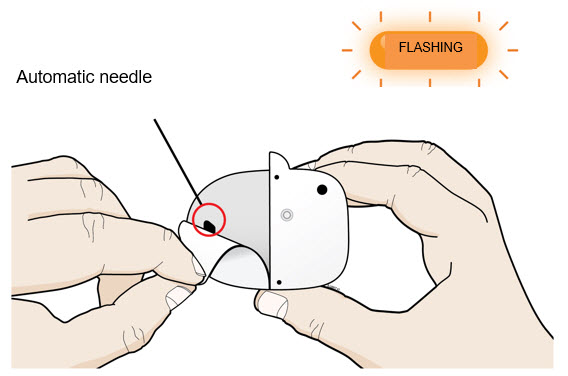
|
||
| B | Before the cannula inserts, securely apply the on-body injector so it is visible and can be monitored by the patient or caregiver. You now have time to carefully apply the on-body injector without folding or wrinkling the adhesive. |
||
|  |
||
| Back of upper arm (triceps)
Vertical with the light facing down toward the elbow | 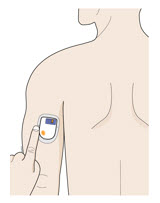 |
||
| Abdomen
Horizontal with the light facing up and visible to the patient | 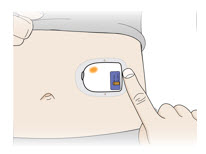 |
||
 | Do not worry if the on-body injector is quiet. When 3 minutes are up, the on-body injector will beep telling you the cannula is about to insert. |
Step 4: Finish
| A | Wait for the status light to turn green. This means the cannula has been inserted. Do not remove the on-body injector during cannula insertion to avoid needle stick injury to you or to the patient. |

|
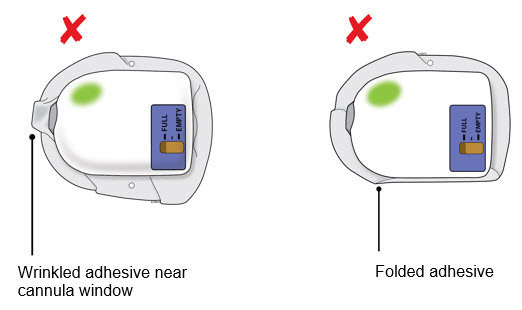
| Check the quality of adhesion before sending the patient home. |
If the adhesive is wrinkled in front of the cannula window or has folds anywhere that prevent the on-body injector from securely adhering, remove the on-body injector. Start again with a new kit and call Amgen at 1-800-772-6436.
 |
|
| B | Provide the Patient IFU Booklet for the patient to take home. Fill in the Dose Delivery information on the booklet, and review the following instructions with your patient:
|
| Attention! What to do if you hear beeping or when you look at status light and it is flashing red. 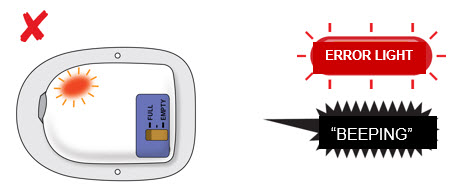 If at any time the on-body injector beeps continuously for 5 minutes, and the status light is flashing red, take the on-body injector off of the patient.
|
|
| What to do if your patient reports the status light is flashing red.
If the patient reports the status light is flashing red, they may not have received the full dose. Schedule a follow-up appointment with your patient. |
|
What to do if your patient reports the adhesive is saturated with fluid or the on-body injector is dripping.
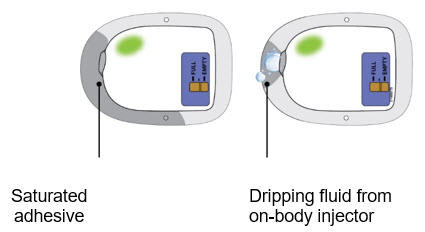 If the patient reports an on-body injector leak, they may not have received the full dose. Schedule a follow-up appointment with your patient. |
|
In all cases report the incident to Amgen at 1-800-772-6436.
Neulasta® (pegfilgrastim)
Manufactured by:
Amgen Inc.
One Amgen Center Drive
Thousand Oaks, California 91320-1799
US License No. 1080
Patent: http://pat.amgen.com/onpro/
© 2002 to 2021 Amgen Inc. All rights reserved.
http://www.neulasta.com/
1-844-MYNEULASTA (1-844-696-3852)
Issued: 03/2021
V12
Before You Begin
 | The following is an overview of on-body injector preparation steps. Read this section first
To prepare and apply the on-body injector, you will use a pre-filled syringe to fill and activate it. As part of this process, the on-body injector uses lights and sounds as signals to help guide you through the preparation and application process. As you fill the on-body injector, the status light flashes amber and the on-body injector beeps 3 times. When the status light flashes amber and the on-body injector beeps, this means it has been properly filled and activated. | |
After the on-body injector activates, you will have 3 full minutes to remove the blue needle guard and adhesive backing, and then apply the on-body injector to your patient.
|  |
|
| When the status light flashes green, this means the on-body injector has successfully inserted the cannula. |  |
|
| For all questions, or if a patient calls you regarding any on-body injector problems, call Amgen at 1-800-772-6436. ← Turn over to continue with the Instructions for Use |
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
 | Do not reuse this on-body injector. Single-use only |
 | Refer to Instructions for Use |
 | Do not use if packaging is damaged |
 | Temperature limitation |
 | Humidity limitation |
 | Expiration date (use by date) |
 | Reference/model number |
 | Lot number |
 | Type BF medical device (protection from electrical shock) |
 | Sterilized by ethylene oxide |
 | Waterproof up to 8 feet for 1 hour |
 | Prescription use only |
 | MR Unsafe |
 | On-body injector for Neulasta® (pegfilgrastim) |
 | Neulasta® (pegfilgrastim) prefilled syringe |
 | Pressure Limitation |
Do not expose the on-body injector for Neulasta to the following environments as the on-body injector may be damaged and the patient could be injured:
- Diagnostic imaging (e.g., CT Scan, MRI, Ultrasound, X-ray)
- Radiation treatment
- Oxygen rich environments such as hyperbaric chambers
Electromagnetic Compatibility
The information contained in this section (such as separation distances) is, in general, specifically written in regard to the on-body injector for Neulasta. The numbers provided will not guarantee faultless operation but should provide reasonable assurance of such. This information may not be applicable to other medical electrical equipment; older equipment may be particularly susceptible to interference.
General Notes:
Medical electrical equipment requires special precautions regarding electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), and needs to be installed and put into service according to the EMC information provided in this document.
Portable and mobile RF communications equipment can affect medical electrical equipment.
Cables and accessories not specified within the instructions for use are not authorized. Using cables and/or accessories may adversely impact safety, performance, and electromagnetic compatibility (increased emission and decreased immunity).
Care should be taken if the on-body injector for Neulasta is used adjacent to other electrical equipment; if adjacent use is inevitable, the on-body injector for Neulasta should be observed to verify normal operation in this setting.
| Electromagnetic Emissions | ||
|---|---|---|
| The on-body injector for Neulasta is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The user of the on-body injector for Neulasta should ensure that it is used in such an environment. | ||
| Emissions | Compliance according to | Electromagnetic environment |
| RF Emissions (CISPR 11) | Group 1 | The on-body injector for Neulasta uses RF energy only for its internal function. Therefore, its RF emissions are very low and are not likely to cause any interference in nearby equipment. |
| CISPR B Emissions Classification | Class B | |
| Electromagnetic Immunity | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| The on-body injector for Neulasta is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment specified below. The user of this equipment should ensure that it is used in such an environment. | |||
| Immunity Test | IEC 60601 Test Level | Compliance Level | Electromagnetic Environment-Guidance |
| ESD IEC 61000-4-2 | ±8 kV Contact ±15 kV Air | ±8 kV Contact ±15 kV Air | Floors should be wood, concrete or ceramic tile. If floors are synthetic, the r/h should be at least 30%. |
| Power Frequency 50/60 Hz Magnetic Field IEC 61000-4-8 | 30 A/m | 30 A/m | Power frequency magnetic fields should be that of typical commercial or hospital environment. |
| Radiated RF Fields 61000-4-3 | 3 V/m 80 MHz to 2.7 GHz | (E1)=3 V/m | Portable and mobile communications equipment should be separated from the on-body injector for Neulasta by no less than the distances calculated/listed below: D=(3.5/V1)(√P)150 kHz to 80 MHz D=(3.5/E1)(√P)80 to 800 MHz D=(7/E1)(√P)800 MHz to 2.5 GHz Where P is the max power in watts and D is the recommended separation distance in meters. Field strengths from fixed transmitters, as determined by an electromagnetic site survey, should be less than the compliance levels (V1 and E1). Interference may occur in the vicinity of equipment containing a transmitter. |
| Test specifications for ENCLOSURE PORT IMMUNITY to RF wireless communications equipment | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The on-body injector for Neulasta is intended for use in the radio frequency environment specified below. The user of this equipment should ensure that it is used in such an environment. | ||||||
| Test Frequency | Band* | Service * | Modulation† | Maximum Power | Distance | Immunity Test Level |
| (MHz) | (MHz) | (W) | (m) | (V/m) | ||
| NOTE If necessary to achieve the IMMUNITY TEST LEVEL, the distance between the transmitting antenna and the ME EQUIPMENT OF ME SYSTEM may be reduced to 1 m. The 1 m test distance is permitted by IEC 61000-4-3. | ||||||
| 385 | 380-390 | TETRA 400 | Pulse modulation†
18 Hz | 1.8 | 0.3 | 27 |
| 450 | 430-470 | GMRS 460, FRS 460 | FM ‡
± 5 kHz deviation 1 kHz sine | 2 | 0.3 | 28 |
| 710 | 704-787 | LTE Band 13, 17 | Pulse modulation †
217 Hz | 0.2 | 0.3 | 9 |
| 745 | ||||||
| 780 | ||||||
| 810 | 800-960 | GSM 800/900, TETRA 800, iDEN 820, CDMA 850, LTE Band 5 | Pulse modulation †
18 Hz | 2 | 0.3 | 28 |
| 870 | ||||||
| 930 | ||||||
| 1720 | 1700-1990 | GSM 1800; CDMA 1900; GSM 1900; DECT; LTE Band 1, 3, 4, 25; UMTS | Pulse modulation†
217 Hz | 2 | 0.3 | 28 |
| 1845 | ||||||
| 1970 | ||||||
| 2450 | 2400-2570 | Bluetooth, WLAN, 802.11 b/g/n, RFID 2450, LTE Band 7 | Pulse modulation†
217 Hz | 2 | 0.3 | 28 |
| 5240 | 5100-5800 | WLAN 802.11 a/n | Pulse modulation†
217 Hz | 0.2 | 0.3 | 9 |
| 5500 | ||||||
| 5785 | ||||||
| Recommended separation distances between portable and mobile RF communications equipment and the on-body injector for Neulasta | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| You can help prevent electromagnetic interference by maintaining a minimum distance between portable and mobile RF communications equipment (transmitters) and the on-body injector for Neulasta, as recommended below, according to the maximum power of the communication equipment. | |||
| Rated maximum output power of transmitter, in watts | Separation distance according to frequency of transmitter, in meters | ||
| 150 kHz to 80 MHz | 80 MHz to 800 MHz | 800 MHz to 2.5 GHz | |
| D=(3.5/V1)(√P) | D=(3.5/E1)(√P) | D=(7/E1)(√P) | |
| 0.01 | 0.11667 | 0.11667 | 0.23333 |
| 0.1 | 0.36894 | 0.36894 | 0.73785 |
| 1 | 1.1667 | 1.1667 | 2.3333 |
| 10 | 3.6894 | 3.6894 | 7.3785 |
| 100 | 11.667 | 11.667 | 23.333 |
Instructions for Use
Neulasta (nu-las-tah)
(pegfilgrastim)
Injection, for subcutaneous use
Single-Dose Prefilled Syringe
Guide to parts
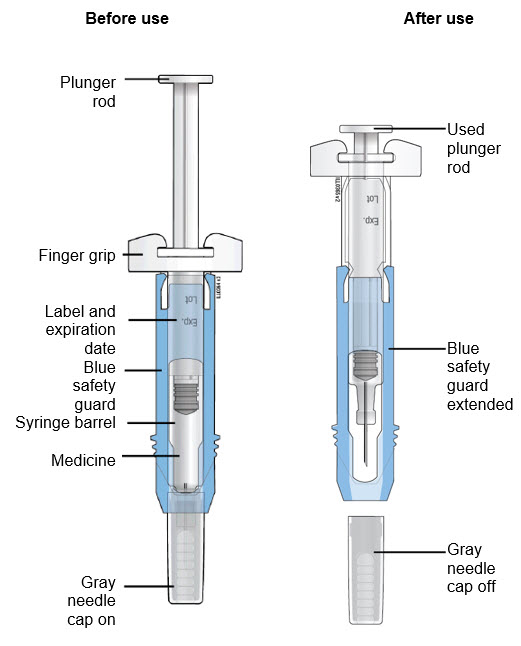
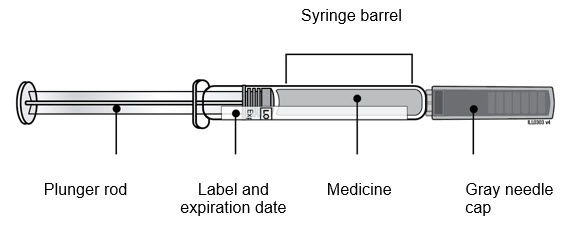
Important: The needle is covered by the gray needle cap before use.
Important
Read the Patient Information for important information you need to know about Neulasta before using these Instructions for Use.
Before you use a Neulasta prefilled syringe, read this important information.
Storing the prefilled syringe
- Store Neulasta in the refrigerator between 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C).
- Do not freeze.
- Keep the prefilled syringe in the original carton to protect from light or physical damage.
- Take the prefilled syringe out of the refrigerator 30 minutes before use and allow it to reach room temperature before preparing an injection.
- Throw away (dispose of) any Neulasta that has been left at room temperature, 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C), for more than 48 hours.
- Keep the Neulasta prefilled syringe out of the reach of children.
Using the prefilled syringe
- It is important that you do not try to give the injection unless you or your caregiver has received training from your healthcare provider.
- Make sure the name Neulasta appears on the carton and prefilled syringe label.
- Check the carton and prefilled syringe label to make sure the dose strength is 6 mg.
- You should not inject a dose of Neulasta to children weighing less than 45 kg from a Neulasta prefilled syringe. A dose less than 0.6 mL (6 mg) cannot be accurately measured using the Neulasta prefilled syringe.
- Do not use a prefilled syringe after the expiration date on the label.
- Do not shake the prefilled syringe.
- Do not remove the gray needle cap from the prefilled syringe until you are ready to inject.
- Do not use the prefilled syringe if the carton is open or damaged.
- Do not use a prefilled syringe if it has been dropped on a hard surface. The prefilled syringe may be broken even if you cannot see the break. Use a new prefilled syringe.
- Do not slide the blue safety guard over the needle before you give the injection. This will "activate" or lock the blue safety guard. Use another prefilled syringe that has not been activated and is ready to use.
- The gray needle cap on the prefilled syringe contains dry natural rubber (made from latex). Tell your healthcare provider if you are allergic to latex. You should not give Neulasta using the prefilled syringe if you have latex allergies.
Call your healthcare provider if you have any questions.
Step 1: Prepare
A Remove the prefilled syringe carton from the refrigerator.
Put the original carton with any unused prefilled syringes back in the refrigerator.
Remove the syringe tray from the carton. On a clean, well-lit surface, place the syringe tray at room temperature for 30 minutes before you give an injection.
- Do not use the prefilled syringe if the carton is damaged.
- Do not try to warm the prefilled syringe by using a heat source such as hot water or microwave.
- Do not leave the prefilled syringe in direct sunlight.
- Do not shake the prefilled syringe.
Open the tray by peeling away the cover. Grab the blue safety guard to remove the prefilled syringe from the tray.
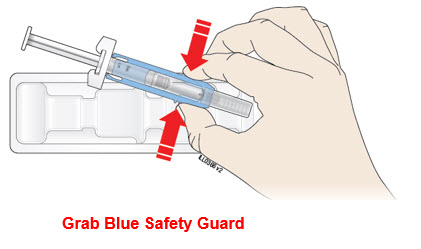
For safety reasons:
- Do not grab the plunger rod.
- Do not grab the gray needle cap.
B Inspect the medicine and prefilled syringe.
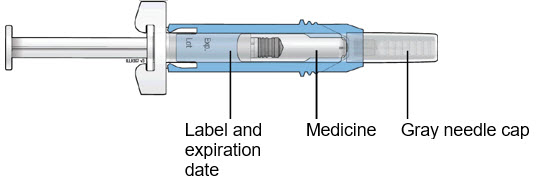
Make sure the medicine in the prefilled syringe is clear and colorless.
-
Do not use the prefilled syringe if:
- The medicine is cloudy or discolored or contains flakes or particles.
- Any part appears cracked or broken.
- The prefilled syringe has been dropped.
- The gray needle cap is missing or not securely attached.
- The expiration date printed on the label has passed.
In all cases, use a new prefilled syringe and call your healthcare provider.
C Gather all materials needed for the injection.
Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water.
On a clean, well-lit work surface, place the:
- Prefilled syringe
- Alcohol wipe
- Cotton ball or gauze pad
- Adhesive bandage
- Sharps disposal container

Step 2: Get ready
D Prepare and clean the injection site(s).
You can use:
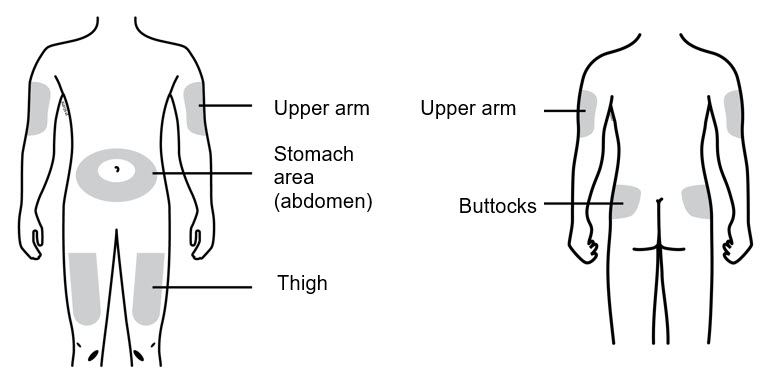
- Thigh
- Stomach area (abdomen), except for a 2-inch area right around the navel (belly button)
- Upper outer area of the buttocks (only if someone else is giving you the injection)
- Outer area of upper arm (only if someone else is giving you the injection)
Clean the injection site with an alcohol wipe. Let the skin dry.
- Do not touch this area again before injecting.
- If you want to use the same injection site, make sure it is not the same spot on the injection site you used for a previous injection.
- Do not inject into areas where the skin is tender, bruised, red, or hard. Avoid injecting into areas with scars or stretch marks.
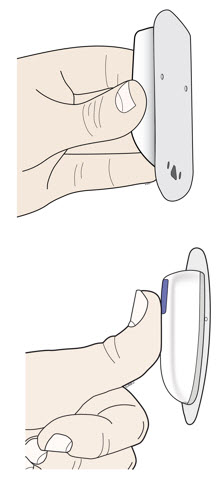
E Hold the prefilled syringe by the syringe barrel. Carefully pull the gray needle cap straight off and away from the body.
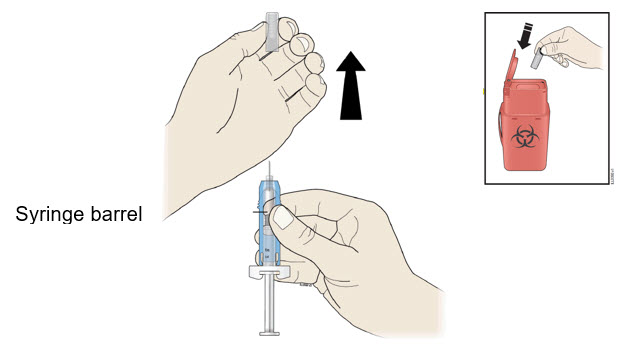
- Do not remove the gray needle cap from the prefilled syringe until you are ready to inject.
- Do not twist or bend the gray needle cap.
- Do not hold the prefilled syringe by the plunger rod.
- Do not put the gray needle cap back onto the prefilled syringe.
Important: Throw the gray needle cap into the sharps disposal container.
Step 3: Subcutaneous (under the skin) injection
F Pinch the injection site to create a firm surface.
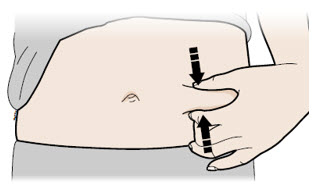
Important: Keep skin pinched while injecting.
G Hold the pinch. Insert the needle into the skin at 45 to 90 degrees.
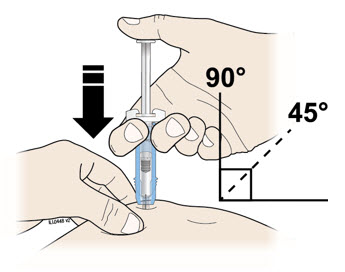
H Using slow and constant pressure, push the plunger rod until it reaches the bottom.
When done, gently pull the syringe off of the skin.
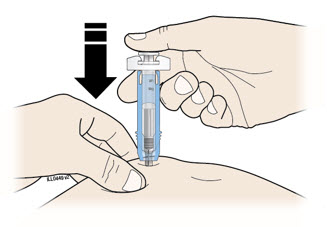
Important: When you remove the syringe, if it looks like the medicine is still in the syringe barrel, this means you have not received a full dose. Call your healthcare provider right away.
Step 4: Finish
| I |
|
For your safety, pull the blue safety guard until it clicks and covers the needle.
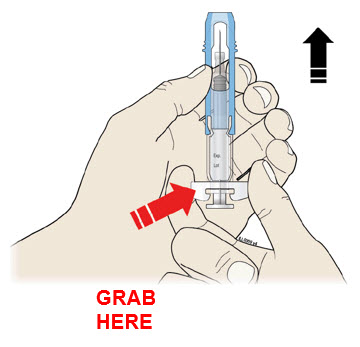
Once extended, the blue safety guard will lock into position and will not slide back over the needle.
Keep your hands away from the needle at all times.
J Discard (throw away) the used prefilled syringe.
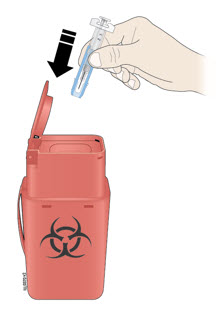
- Put the used prefilled syringe in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) the syringe in the household trash.
- If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
- made of a heavy-duty plastic,
- can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
- upright and stable during use,
- leak-resistant, and
- properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal
- Do not reuse the prefilled syringe.
- Do not recycle the prefilled syringe or sharps disposal container or throw them into household trash.
Important: Always keep the sharps disposal container out of the reach of children.
K Examine the injection site.
If there is blood, press a cotton ball or gauze pad on the injection site. Do not rub the injection site. Apply an adhesive bandage if needed.
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
Amgen Inc.
One Amgen Center Drive
Thousand Oaks, California 91320-1799
U.S. License No. 1080
Patent: http://pat.amgen.com/onpro/
© 2002-2016 Amgen Inc. All rights reserved.
1xxxxxx
Revised: 12/2016 v2
Patient INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Neulasta® Onpro® (nu-las-tah)
(pegfilgrastim) injection
Single-Use On-body Injector
| Your On-body injector was applied: | |||
 | AM | ||
| Day | Time | PM | |
| Injection of your dose (delivery) will start around: | |||
| AM | |||
| Day | Time | PM | |
| Healthcare Provider name: | |||
| Healthcare Provider contact number: | |||
| On-body Injector lot number: | |||
AMGEN®
Neulasta®
(pegfilgrastim)
Onpro®
kit
| Parts and Signals | ||
| Status Light | ||
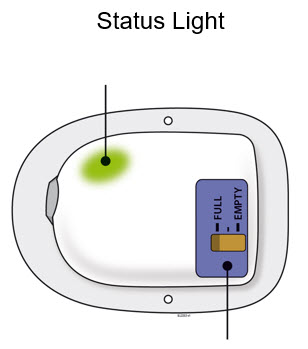 |  | Flashing Green:
The on-body injector is working properly. Do not remove the on-body injector if the status light is flashing green. |
 | Solid Green (or off):
Signals dose delivery is complete. Check to see if fill indicator reads empty. |
|
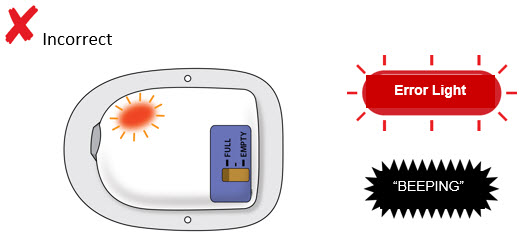
 | Flashing Red:
On-body injector error. If you hear beeping at any time, check the status light. If it is flashing red, call your healthcare provider right away as you may need a replacement dose. |
|
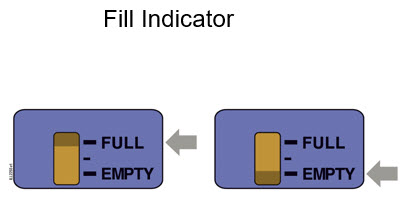 | Fill Indicator:
Black line shows how much Neulasta is in the on-body injector. |
Contents
| IMPORTANT INFORMATION
Learn about your Neulasta On-body Injector. | INFO |
| STEP 1: MONITOR
What to expect from your device for most of the day. | |
| STEP 2: OBSERVE
What to watch for during dose delivery and what to do if there is an issue. | |
| STEP 3: VERIFY
Understand when delivery is complete and when you may remove the device. | |
| STEP 4: FINISH
Confirm the dose was delivered and dispose of the device. | |
| FAQ
When it is safe to remove your on-body injector and answers to frequently asked questions. |
| Important Information | |
| On-body Injector for Neulasta Description | |
| INFO |
|
Warnings
|
|
|
|
| Important Information Wearing the On-body Injector
|
|
| Environmental Precautions | ||
| 1 | |
|
A healthcare provider who is familiar with Neulasta should answer your questions. For general questions or support call 1-844-MYNEULASTA (1-844-696-3852) or visit www.neulasta.com.
Step 1: Monitor On-body Injector
| A | For the next 27 hours, occasionally check the status light for at least 10 seconds. If the status light is flashing green, it is okay. | ||
| 1 | 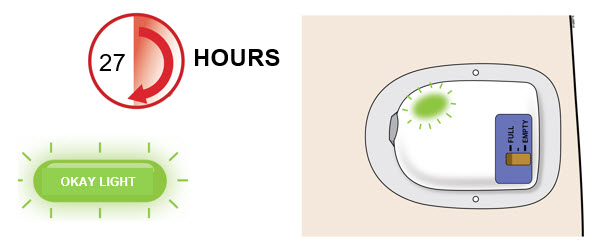 |
||
|
|||
| 2 | ||
Step 2: Observe Dose Delivery
| A | After about 27 hours, your on-body injector will begin to deliver your dose of Neulasta. | ||
|
|||
| 2 | 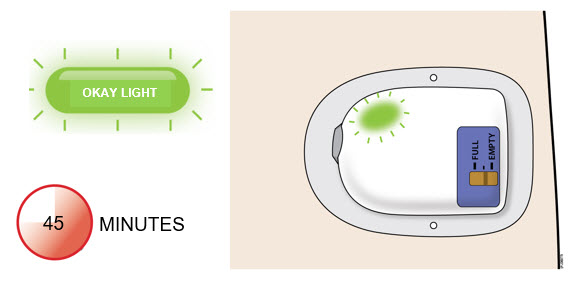 |
||
|
|||
 | Check your on-body injector often for leaks during the 45-minute dose delivery. If the on-body injector was placed on the back of your arm, a caregiver must be available to check your on-body injector. | ||
| 3 | ||
Step 3: Verify Dose Complete
| A | After the beep, check the color of the status light. | |||
| 3 | 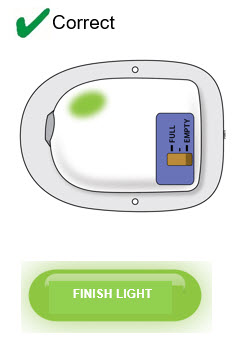 Check to see if the status light is SOLID GREEN or has switched off. This means the dose is complete. If the dose is complete, go to the next step. Do not remove the on-body injector if the status light is flashing green. |  If you see the status light is FLASHING RED, and your on-body injector is beeping, your on-body injector is not functioning properly. Call your healthcare provider right away, as you may need a replacement dose. |
||
| B | Grab the edge of the adhesive pad. Slowly peel off the on-body injector. | |||
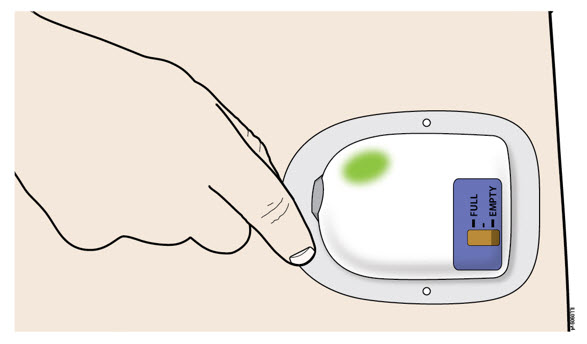 | 4 | |||
| ||||
Step 4: Finish
 | Check to see if your on-body injector is empty. | |||
| 4 |
|
|||
| A | Check off the box below to record how your on-body injector looks after use. | |||
| ⃞ | Status light is solid green or the status light has switched off. This means that the delivery is complete. |
|||
| ⃞ | On-body injector leaked, call your healthcare provider right away, as you may need a replacement dose. | |||
| ⃞ | Status light is red, call your healthcare provider right away, as you may need a replacement dose. | |||
| B | Properly dispose of the on-body injector. | |||
|  | |||
| FAQ | |||
|
||||
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I know it is safe to remove the on-body injector?
It is safe to remove the on-body injector after checking the following:
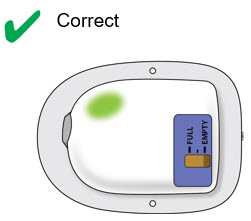 |
|
 |
|
FAQ
What to do if you hear beeping or when you look at the status light and it is flashing red?
- If the status light is flashing red, you may not have received your full dose and may need a replacement dose. Call your healthcare provider right away.
What do I do if the on-body injector comes off before the full dose is delivered?
- Call your healthcare provider right away if the on-body injector at any time comes away from your skin before your full dose delivery, as you may need a replacement dose. Do not reapply it.
What if there is blood at my application site after the on-body injector has been removed?
- If there is blood, press a clean cotton ball or gauze pad on the application site. Apply an adhesive bandage if needed.
What if my application site is red or tender after on-body injector removal?
- Call your healthcare provider right away if you experience persistent or worsening redness or tenderness at the application site, as this can be a sign of infection.
Notes
Neulasta® Onpro®
Patient INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Neulasta® (pegfilgrastim)
Manufactured by:
Amgen Inc.
One Amgen Center Drive
Thousand Oaks, California 91320-1799
US License No. 1080
Patent: http://pat.amgen.com/onpro/
© 2002 to 2020 Amgen Inc. All rights reserved.
http://www.neulasta.com
1-844-MYNEULASTA (1-844-696-3852)
Revised: 11/2020
V9
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Kit Carton
1 - Single Dose Neulasta Prefilled Syringe
1 - Sterile On-body Injector for Neulasta
NDC 55513-192-01
AMGEN®
Neulasta®
(pegfilgrastim) injection
Onpro®
kit
Pegylated Recombinant Methionyl Human Granulocyte
Colony-Stimulating Factor (PEG-r-metHuG-CSF) derived from E. Coli
6 mg/
0.6 mL*
6 mg/0.6 mL*
* Prefilled syringe contains 0.64 mL to deliver
6 mg/0.6 mL when used with on-body injector
For Subcutaneous Use Only
Carton Contents (intended to be dispensed as a unit):
- 1 sterile On-body Injector for Neulasta
- 1 Neulasta prefilled syringe labeled for use with on-body injector only
- 1 patient instructions for use
- 1 healthcare provider instructions for use, 1 package insert
This Product Contains Dry Natural Rubber
Store at 2° to 8°C (36° to 46°F).
Do Not Freeze or Shake.
Keep in Carton to Protect from Light.
See package insert for full prescribing
information and Instructions for Use
Rx Only

Principal Display Panel
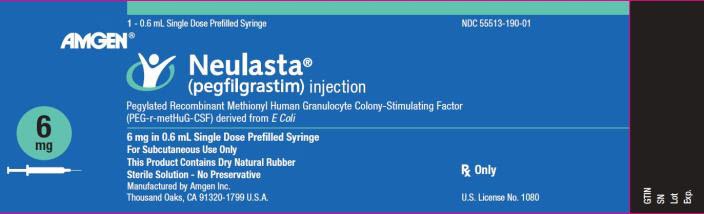
NDC 55513-190-01
1 - 0.6 mL Single Dose Prefilled Syringe
AMGEN®
Neulasta ®
(pegfilgrastim) injection
Pegylated Recombinant Methionyl Human Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor
(PEG-r-metHuG-CSF) derived from E Coli
6 mg
6 mg in 0.6 mL Single Dose Prefilled Syringe
For Subcutaneous Use Only
This Product Contains Dry Natural Rubber
Sterile Solution – No Preservative
Rx Only
Manufactured by Amgen Inc.
Thousand Oaks, CA 91320-1799 U.S.A.
U.S. License No. 1080