FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Information
Veregen is to be applied three times per day to all external genital and perianal warts.
Apply about an 0.5 cm strand of the Veregen to each wart using the finger(s), dabbing it on to ensure complete coverage and leaving a thin layer of the ointment on the warts. Patients should wash their hands before and after application of Veregen.
It is not necessary to wash off the ointment from the treated area prior to the next application.
Veregen® is not for ophthalmic, oral, intravaginal, or intra-anal use.
2.2 Treatment Period
Treatment with Veregen should be continued until complete clearance of all warts, however no longer than 16 weeks.
Local skin reactions (e.g. erythema) at the treatment site are frequent. Nevertheless, treatment should be continued when the severity of the local skin reaction is acceptable.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Ointment, 15% w/w. Each gram of Veregen Ointment, 15% contains 150 mg of sinecatechins in a brown ointment base.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Veregen has not been evaluated for the treatment of urethral, intra-vaginal, cervical, rectal, or intra-anal human papilloma viral disease and should not be used for the treatment of these conditions.
Use of Veregen on open wounds should be avoided.
Patients should be advised to avoid exposure of the genital and perianal area to sun/UV-light as Veregen has not been tested under these circumstances.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In Phase 3 clinical trials, a total of 397 subjects received Veregen three times per day topical application for the treatment of external genital and perianal warts for up to 16 weeks.
Serious local adverse events of pain and inflammation were reported in two subjects (0.5%), both women.
In clinical trials, the incidence of patients with local adverse events leading to discontinuation or dose interruption (reduction) was 5% (19/397). These included the following events: application site reactions (local pain, erythema, vesicles, skin erosion/ulceration), phimosis, inguinal lymphadenitis, urethral meatal stenosis, dysuria, genital herpes simplex, vulvitis, hypersensitivity, pruritus, pyodermitis, skin ulcer, erosions in the urethral meatus, and superinfection of warts and ulcers.
Local and regional reactions (including adenopathy) occurring at >1% in the treated groups are presented in Table 1.
|
Veregen®
|
Vehicle |
|
|
Erythema |
70 |
32 |
|
Pruritus |
69 |
45 |
|
Burning |
67 |
31 |
|
Pain/discomfort |
56 |
14 |
|
Erosion/Ulceration |
49 |
10 |
|
Edema |
45 |
11 |
|
Induration |
35 |
11 |
|
Rash vesicular |
20 |
6 |
|
Regional Lymphadenitis |
3 |
1 |
|
Desquamation |
5 |
<1 |
|
Discharge |
3 |
<1 |
|
Bleeding |
2 |
<1 |
|
Reaction |
2 |
0 |
|
Scar |
1 |
0 |
|
Irritation |
1 |
0 |
|
Rash |
1 |
0 |
A total of 266/397 (67%) of subjects in the Veregen group had either a moderate or a severe reaction that was considered probably related to the drug, of which 120 (30%) subjects had a severe reaction. Severe reactions occurred in 37% (71/192) of women and in 24% (49/205) of men. The percentage of subjects with at least one severe, related adverse event was 26% (86/328) for subjects with genital warts only, 42% (19/45) in subjects with both genital and perianal warts and 48% (11/23) of subjects with perianal warts only.
Phimosis occurred in 3% of uncircumcised male subjects (5/174) treated with Veregen and in 1% (1/99) in vehicle.
The maximum mean severity of erythema, erosion, edema, and induration was observed by week 2 of treatment.
Less common local adverse events included urethritis, perianal infection, pigmentation changes, dryness, eczema, hyperesthesia, necrosis, papules, and discoloration. Other less common adverse events included cervical dysplasia, pelvic pain, cutaneous facial rash, and staphylococcemia.
In a dermal sensitization study of Veregen in healthy volunteers, hypersensitivity (type IV) was observed in 5 out of 209 subjects (2.4%) under occlusive conditions.
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on Veregen use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. In animal reproduction studies, sinecatechins did not cause malformations, but did affect the developing fetus in the presence of maternal toxicity when given to pregnant rabbits and rats by intravaginal or systemic routes of administration during the period of organogenesis (see Data). The available data do not allow the calculation of relevant comparisons between the systemic exposure of sinecatechins observed in the animal studies to the systemic exposure that would be expected in humans after topical use of Veregen.
Data
Embryo-fetal development studies were conducted in rats and rabbits using intravaginal and systemic routes of administration, respectively. Oral administration of sinecatechins during the period of organogenesis (gestational Days 6 to 15 in rats or 6 to 18 in rabbits) did not cause treatment-related malformations or effects on embryo-fetal development at doses of up to 1,000 mg/kg/day.
In the presence of maternal toxicity (characterized by marked local irritation at the administration sites and decreased body weight and food consumption) in pregnant female rabbits, subcutaneous doses of 12 and 36 mg/kg/day of sinecatechins during the period of organogenesis (gestational Days 6 to 19) resulted in corresponding influences on fetal development including reduced fetal body weights and delays in skeletal ossification. No treatment-related effects on embryo-fetal development were noted at 4 mg/kg/day. No malformations were noted at any of the doses evaluated in this study.
A combined fertility and embryo-fetal development study using daily vaginal administration of Veregen to rats from Day 4 before mating and throughout mating until Day 17 of gestation did not show treatment-related effects on fertility, malformations, or embryo-fetal development at doses up to 0.15 mL/rat/day. This dose corresponds to approximately 150 mg/rat/day.
A pre- and post-natal development study was conducted in rats using vaginal administration of Veregen at doses of 0.05, 0.10 and 0.15 mL/rat/day from Day 6 of gestation through parturition and lactation. The high and intermediate dose levels of 0.15 and 0.10 mL/rat/day resulted in an increased mortality of the F0 dams, associated with indications of parturition complications. The high dose level of 0.15 mL/rat/day also resulted in an increased incidence of stillbirths. There were no other treatment-related effects on pre- and post-natal development, growth, reproduction and fertility at any dose tested.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of sinecatechins in human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. After topical application, Veregen concentrations in plasma are low and therefore concentrations in human breast milk are likely to be low [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Veregenand any potential adverse effects on the breast-fed child from Veregenor from the underlying maternal condition.
11 DESCRIPTION
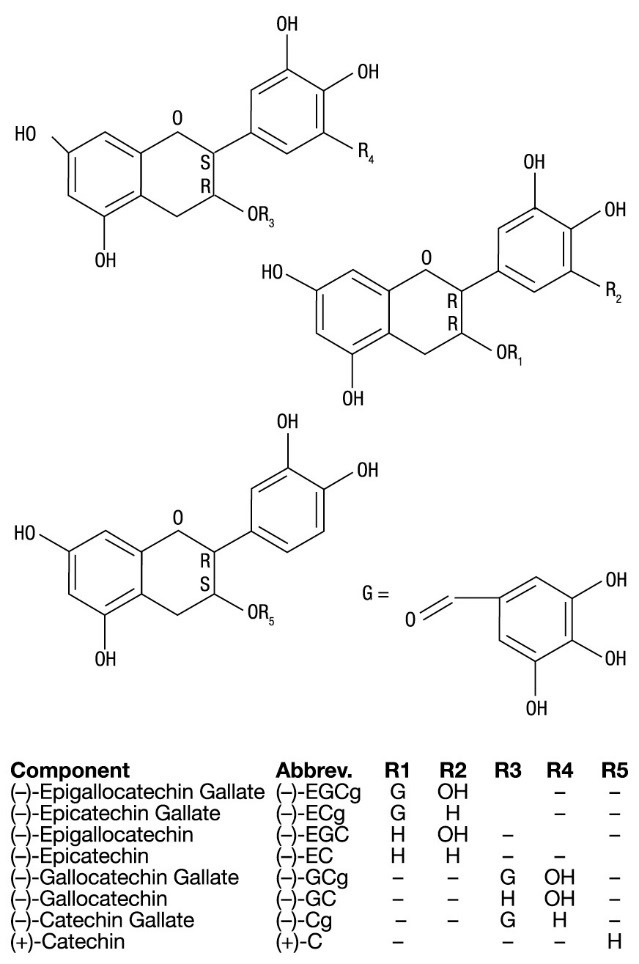
Veregen (sinecatechins) Ointment, 15% is a botanical drug product for topical use. The drug substance in Veregen is sinecatechins, which is a partially purified fraction of the water extract of green tea leaves from Camellia sinensis (L.) O Kuntze, and is a mixture of catechins and other green tea components. Catechins constitute 85 to 95% (by weight) of the total drug substance which includes more than 55% of Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCg), other catechin derivatives such as Epicatechin (EC), Epigallocatechin (EGC), Epicatechin gallate (ECg), and some additional minor catechin derivatives i.e. Gallocatechin gallate (GCg), Gallocatechin (GC), Catechin gallate (Cg), and Catechin (C). In addition to the known catechin components, it also contains gallic acid, caffeine, and theobromine which together constitute about 2.5% of the drug substance. The remaining amount of the drug substance contains undefined botanical constituents derived from green tea leaves.
The structural formulae of catechins are shown below.
General Structure of Catechins
Each gram of the ointment contains 150 mg of sinecatechins in a water free ointment base consisting of isopropyl myristate, white petrolatum, cera alba (white wax), propylene glycol palmitostearate, and oleyl alcohol.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mode of action of Veregen involved in the clearance of genital and perianal warts is unknown. In vitro, sinecatechins had anti-oxidative activity; the clinical significance of this finding is unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
- Systemic exposure to EGCg, EGC, ECg, and EC were evaluated following either topical application of Veregen to subjects with external genital and perianal warts (250 mg applied 3 times a day for 7 days) or following oral ingestion of green tea beverage (500 mL ingested 3 times a day for 7 days). Following topical application of Veregen, plasma concentration of all 4 catechins were below the limit of quantification (<5 ng/mL) on Day 1. After application of Veregen for 7 days, plasma EGC, ECg, and EC concentrations were below the limit of quantification while plasma concentration of EGCg were measurable in 2 out of 20 subjects. The mean maximal plasma concentration (Cmax) of EGCg was 10.1 ng/mL and the mean area under the concentration versus time curve (AUC) of EGCg was 52.2 ng*h/mL in these 2 subjects. Oral ingestion of green tea beverage resulted in measurable concentration of EGCg in all subjects on both Day 1 and Day 7, with mean (SD) Cmax of 23.0 (12.0) ng/mL and AUC of 104.6 (39.0) ng*h/mL on Day 7.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In an oral (gavage) carcinogenicity study, sinecatechins was administered daily for 26 weeks to p53 transgenic mice at doses up to 500 mg/kg/day. Treatment with sinecatechins was not associated with an increased incidence of either neoplastic or non-neoplastic lesions in the organs and tissues examined. Veregen has not been evaluated in a dermal carcinogenicity study.
Sinecatechins was negative in the Ames test, in vivo rat micronucleus assay, UDS test, and transgenic mouse mutation assay, but positive in the mouse lymphoma mutation assay.
Daily vaginal administration of Veregen to rats from Day 4 before mating and throughout mating until Day 17 of gestation did not cause adverse effects on mating performance and fertility at doses up to 0.15 mL/rat/day.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Two randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trials were performed to investigate the safety and efficacy of Veregen in the treatment of immunocompetent subjects 18 years of age and older with external genital and perianal warts. The subjects applied the ointment 3 times daily for up to 16 weeks or until complete clearance of all warts (baseline and new warts occurring during treatment).
Over both trials the median baseline wart area was 51 mm2 (range 12 to 585 mm2), and the median baseline number of warts was 6 (range 2 to 30).
The primary efficacy outcome measure was the response rate defined as the proportion of subjects with complete clinical (visual) clearance of all external genital and perianal warts (baseline and new) by week 16, presented in Tables 2 and 3 for all randomized subjects dispensed medication.
|
Complete Clearance |
|
|
All Countries
| |
|
Veregen® 15% (N = 397) |
213 (53.6%) |
|
Vehicle (N = 207) |
73 (35.3%) |
|
United States | |
|
Veregen® 15% (N = 21) |
5 (23.8%) |
|
Vehicle (N = 9) |
0 (0.0%) |
|
Complete Clearance |
|
|
Males | |
|
Veregen® 15% (N = 205) |
97 (47.3%) |
|
Vehicle (N = 118) |
34 (28.8%) |
|
Females | |
|
Veregen® 15% (N = 192) |
116 (60.4%) |
|
Vehicle (N = 89) |
39 (43.8%) |
Median time to complete wart clearance was 16 weeks and 10 weeks, respectively, in the two phase 3 clinical trials.
The rate of recurrence of external genital and perianal warts 12 weeks after completion of treatment in subjects with complete clearance is 6.8% (14/206) for those treated with Veregen and 5.8% (4/69) for those treated with vehicle.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Veregen is a brown ointment and is supplied in an aluminum tube containing 30 grams (NDC 62559-385-30) of ointment per tube.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information)
Patients using Veregen should receive the following information and instructions:
- •
- This medication is only to be used as directed by a physician. It is for external use only. Eye contact should be avoided as well as application into the vagina or anus.
- •
- It is not necessary to wash off Veregen prior to the next application. When the treatment area is washed or a bath is taken, the ointment should be applied afterwards.
- •
- It is common for patients to experience local skin reactions such as erythema, erosion, edema, itching, and burning at the site of application. Severe skin reactions can occur and should be promptly reported to the healthcare provider. Should severe local skin reaction occur, the ointment should be removed by washing the treatment area with mild soap and water, and further doses withheld.
- •
- Sexual (genital, anal or oral) contact should be avoided while the ointment is on the skin, or the ointment should be washed off prior to these activities. Veregen may weaken condoms and vaginal diaphragms. Therefore, the use in combination with Veregen is not recommended.
- •
- Female patients using tampons should insert the tampon before applying the ointment. If the tampon is changed while the ointment is on the skin, accidental application of the ointment into the vagina must be avoided.
- •
- Veregen may stain clothing and bedding.
- •
- Veregen is not a cure and new warts might develop during or after a course of therapy. If new warts develop during the 16-week treatment period, these should also be treated with Veregen.
- •
- The effect of Veregen on the transmission of genital/perianal warts is unknown.
- •
- Patients should be advised to avoid exposure of the genital and perianal area to sun/UV light as Veregen has not been tested under these circumstances.
- •
- The treatment area should not be bandaged or otherwise covered or wrapped as to be occlusive.
- •
- Uncircumcised males treating warts under the foreskin should retract the foreskin and clean the area daily.
Patient Package Insert
PATIENT INFORMATION
Veregen®
(sinecatechins)
Ointment, 15%
Read this leaflet carefully before you start using Veregen Ointment and each time you refill your prescription. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of your doctor’s advice. If you have any questions about Veregen Ointment or your condition ask your doctor or pharmacist. Only your doctor can prescribe Veregen and determine if it is right for you.
What is Veregen Ointment?
Veregen Ointment is a medicine for skin use only (topical) for the treatment of warts on the outside of the genitals and around the outside of the anus. It is not a treatment for warts in the vagina, cervix, or inside the anus. Your doctor may recommend examination and screening tests (such as a Pap smear) to evaluate these areas.
Who should not use Veregen Ointment?
Do not use Veregen Ointment if you are allergic to an ingredient in Veregen Ointment. The list of ingredients is at the end of this leaflet.
What should I tell my doctor before using Veregen Ointment?
Tell your doctor about all your health conditions and all the medicines you take including prescription, over-the-counter medicine, vitamins, supplements, and herbals. Be sure to tell your doctor if you are:
- •
- pregnant or planning to become pregnant, as it is not known if Veregen Ointment can harm your unborn baby. Your doctor will determine whether the benefit outweighs the risk.
- •
- breastfeeding, as it is not known if Veregen Ointment can pass into your milk and if it can harm your baby.
- •
- using any other type of skin product or have open wounds on the area to be treated. Veregen Ointment should not be used until your skin has healed from other treatments applied to the same area.
- •
- immunocompromised. This means that your immune system cannot fight infections as well as it should.
How should I use Veregen Ointment?
- •
- Use Veregen Ointment only on the area affected exactly as prescribed by your doctor.
- •
- Wash your hands before and after application of Veregen Ointment. A small amount of the ointment should be applied to all warts using your finger(s), dabbing it on to ensure complete coverage and leaving a thin layer of the ointment on the warts as directed by your doctor.
- •
- Apply Veregen Ointment three times per day — in the morning, at noontime and in the evening. Do not wash off the ointment from the treated area before the next application. When you wash the treatment area or bathe, apply the ointment afterwards.
- •
- Treatment with Veregen Ointment should be continued until complete clearance of all warts, however no longer than 16 weeks. If your warts do not go away, or if they come back after treatment call your doctor.
- •
- Veregen Ointment is not a cure for warts on your genitals or around your anus with certainty. New warts may develop during or after treatment, and may need treatment.
What should I avoid while using Veregen Ointment?
- •
- Do not apply Veregen Ointment on open wounds or into the vagina or into the anus.
- •
- Genital warts are a sexually transmitted disease, and you may infect your partner.
- •
- Avoid sexual contact (genital, anal or oral) when Veregen Ointment is on your genital or perianal skin. If you do choose to have sexual contact, you must wash off the ointment carefully before having protected sexual contact as the ointment may weaken condoms and vaginal diaphragms. Talk to your doctor about safe sex practices.
- •
- Avoid contact with your eyes, nostrils and mouth while ointment is on your finger(s).
- •
- Women using tampons: insert the tampon before applying the ointment. If you need to change your tampon while the ointment is on your skin, avoid getting the ointment into the vagina.
- •
- Uncircumcised men treating warts under the foreskin should retract the foreskin and clean the area daily.
- •
- Do not expose the genital area treated with Veregen Ointment to sunlight, sunlamps or tanning beds.
- •
- Do not cover the treated area. Loose-fitting undergarments can be worn after applying Veregen Ointment.
- •
- Veregen Ointment may stain your light colored clothes and bedding.
What are the possible side effects of Veregen Ointment?
The most common side effects with Veregen Ointment are local skin and application site reactions including:
- •
- redness
- •
- swelling
- •
- sores or blisters
- •
- burning
- •
- itching
- •
- pain
Many patients experience itching, reddening or swelling on or around the application site during the course of treatment. Some of these side effects could be a sign of an allergic reaction. If you experience open sores or other severe reactions at the locations you applied Veregen Ointment, stop treatment and call your doctor right away.
You may experience other side effects of Veregen Ointment which are not mentioned here. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
Patients should be aware that new warts may develop during treatment as Veregen Ointment is not a cure.
How should I store Veregen Ointment?
- •
- Store Veregen Ointment refrigerated or up to 77°F (25°C).
- •
- Do not freeze.
- •
- Make sure the cap on the tube is tightly closed.
- •
- Safely throw away Veregen Ointment tubes that are out of date or are empty.
Keep Veregen Ointment and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General advice about prescription medicines
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are not mentioned in patient information leaflets. Do not use Veregen Ointment for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Veregen Ointment to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
Do not use Veregen Ointment after the expiration date on the tube.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about Veregen Ointment. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about Veregen Ointment that is written for the doctor.
For more information, go to www.anipharmaceuticals.com or call 1-800-308-6755.
What are the ingredients in Veregen Ointment?
Active ingredient:
A defined green tea extract named sinecatechins.
Inactive ingredients:
Isopropyl myristate, white petrolatum, cera alba (white wax), propylene glycol palmitostearate, and oleyl alcohol.
Manufactured by:
C.P.M. ContractPharma GmbH.
Frühlingstrasse 7 D-83620
Feldkirchen-Westerham, Germany
Distributed by:
ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Baudette, MN 56623

U.S. Patent Nos. 5795911 and 5968973
0-20720-00 Rev 01/22
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.