FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING
THROMBOSIS, RENAL DYSFUNCTION AND ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
Thrombosis may occur with immune globulin intravenous (IGIV) products, including Octagam 5% liquid. Risk factors may include: advanced age, prolonged immobilization, hypercoagulable conditions, history of venous or arterial thrombosis, use of estrogens, indwelling central vascular catheters, hyperviscosity, and cardiovascular risk factors. Thrombosis may occur in the absence of known risk factors. (See WARNING and PRECAUTIONS [ 5.5 ], PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION [ 17 ])
Renal dysfunction, acute renal failure, osmotic nephrosis, and death may occur in predisposed patients who receive IGIV products, including Octagam 5% liquid. Patients predisposed to renal dysfunction include those with a degree of pre-existing renal insufficiency, diabetes mellitus, age greater than 65, volume depletion, sepsis, paraproteinemia, or patients receiving known nephrotoxic drugs. Renal dysfunction and acute renal failure occur more commonly in patients receiving IGIV product containing sucrose. Octagam 5% liquid does not contain sucrose.
For patients at risk of thrombosis, renal dysfunction or acute renal failure, administer Octagam 5% liquid at the minimum dose and infusion rate practicable. Ensure adequate hydration in patients before administration. Monitor for signs and symptoms of thrombosis and assess blood viscosity in patients at risk for hyperviscosity. (See DOSAGE and ADMINISTRATION [ 2 ], WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS [ 5.5 ])
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Primary Humoral Immunodeficiency Diseases (PI)
Octagam is an immune globulin intravenous (human) 5% liquid indicated for treatment of primary humoral immunodeficiency (PI), such as congenital agammaglobulinemia, common variable immunodeficiency, X-linked agammaglobulinemia, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome and severe combined immunodeficiencies.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For intravenous use only
2.1 Dose
As there are significant differences in the half-life of IgG among patients with primary humoral immunodeficiencies, the frequency and amount of immunoglobulin therapy may vary from patient to patient. The proper amount can be determined by monitoring clinical response.
The dose of Octagam 5% liquid for replacement therapy in primary humoral immunodeficiency diseases is 300 to 600 mg/kg body weight (6-12 mL/kg) administered every 3 to 4 weeks. Adjust the dosage over time to achieve the desired trough levels and clinical responses. If a patient on regular treatment missed a dose, administer the missed dose as soon as possible, and then continue treatment as before.
Measles Exposure
If a patient with primary humoral immunodeficiency has been exposed to measles, it may be prudent to administer an extra dose of IGIV as soon as possible and within 6 days of exposure. A dose of 400 mg/kg should provide a serum level > 240 mIU/mL of measles antibodies for at least two weeks.
If a patient with primary humoral immunodeficiency is at risk of future measles exposure and receives a dose of less than 530 mg/kg every 3-4 weeks, the dose should be increased to at least 530 mg/kg. This should provide a serum level of 240 mIU/mL of measles antibodies for at least 22 days after infusion.
2.2 Preparation
- Inspect each vial of Octagam 5% liquid visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Do not use if the solution is turbid and/or a discoloration is observed.
- Do not freeze. Do not use solutions that have been frozen.
- Octagam 5% liquid contains no preservative. The Octagam 5% liquid bottle is for single use only. Promptly use any bottle that has been entered.
- Prior to use, allow the solution to reach ambient room temperature.
- Do not use after expiration date.
- The content of Octagam 5% liquid bottles may be pooled under aseptic conditions into sterile infusion bags and infused within 8 hours after pooling.
- Do not dilute Octagam 5% liquid. Do not mix Octagam 5% liquid with other medicinal products.
- Do not mix with immune globulin intravenous (IGIV) products from other manufacturers.
2.3 Administration
Octagam 5% liquid is for intravenous use only.
- The infusion line may be flushed before and after administration of Octagam 5% liquid with either normal saline or 5% dextrose in water.
- Administer Octagam 5% liquid at room temperature.
- Do not administer Octagam 5% liquid simultaneously with other intravenous preparations in the same infusion set.
- Octagam 5% liquid is not supplied with an infusion set. If using an in-line filter, choose a filter with a pore size of 0.2 – 200 microns.
- Do not use a needle of larger than 16 gauge to prevent the possibility of coring. Insert needle only once within the stopper area delineated (by the raised ring for penetration). Penetrate the stopper within the ring and perpendicularly to the plane of the stopper.
- Monitor the patient carefully throughout the infusion. Certain adverse drug reactions may be related to the rate of infusion. Slowing or stopping the infusion usually allows the symptoms to [subside or] disappear promptly. Once the symptoms subside, the infusion may then be resumed at a lower rate.
- Ensure that patients with pre-existing renal insufficiency are not volume depleted. For patients at risk of renal dysfunction or thromboembolic events, administer Octagam 5% at the minimum infusion rate practicable, not to exceed 3.3mg/kg/min (0.07 mL/kg/min). Discontinue Octagam 5% if renal function deteriorates.
Rate of Administration
Initially infuse Octagam 5% liquid at infusion rates stated below, at least until the physician has had adequate experience with a given patient.
Infusion rates (see also Table 1): 0.5 mg/kg/min (30 mg/kg/hr) for the first 30 minutes; if tolerated, advance to 1 mg/kg/min (60 mg/kg/hr) for the second 30 minutes; and if still tolerated, advance to 2 mg/kg/min (120 mg/kg/hr) for the third 30 minutes. If tolerated the infusion rate can be increased to and maintained at a maximum rate of 3.33 mg/kg/min (200 mg/kg/hr)
For patients judged to be at risk for developing renal dysfunction, administer Octagam 5% liquid at the minimum infusion rate practicable, not to exceed 0.07 mL/kg (3.3 mg/kg)/min (200 mg/kg/hr).
Table 1: Infusion Rates
| Rate of Administration | mg/kg/min (mg/kg/hr) | mL/kg/min |
| first 30 min | 0.5 (30) | 0.01 |
| next 30 min | 1.0 (60) | 0.02 |
| next 30 min | 2.0 (120) | 0.04 |
| Maximum | < 3.33 (< 200) | less than 0.07 |
- Certain severe adverse drug reactions may be related to the rate of infusion. Slowing or stopping the infusion usually allows the symptoms to disappear promptly.
- Ensure that patients with pre-existing renal insufficiency are not volume depleted; discontinue Octagam 5% liquid if renal function deteriorates.
- For patients at risk of renal dysfunction or thromboembolic events, administer Octagam 5% liquid at the minimum infusion rate practicable.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Octagam 5% liquid is supplied in 1.0 g, 2.5 g, 5 g, 10 g, or 25 g single use bottles (See How Supplied/Storage and Handling [ 16 ]).
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Octagam 5% liquid is contraindicated
- in patients who have acute severe hypersensitivity reactions to human immunoglobulin.
- in IgA deficient patients with antibodies against IgA and history of hypersensitivity. Octagam 5% liquid contains trace amounts of IgA (not more than 0.2 mg/mL in a 5% solution). (See Description [ 11 ])
- in patients with acute hypersensitivity reaction to corn. Octagam 5% liquid contains maltose, a disaccharide sugar that is derived from corn. Patients known to have corn allergies should avoid using Octagam 5% liquid.
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Severe hypersensitivity reactions may occur [ 1 ] (See Contraindications [ 4 ] ) . In case of hypersensitivity, discontinue Octagam 5% liquid infusion immediately and institute appropriate treatment. Always have medications such as epinephrine available for immediate treatment of acute severe hypersensitivity reactions.
IgA deficient patients with antibodies against IgA are at greater risk of developing severe hypersensitivity and anaphylactoid reactions when administered Octagam 5% liquid (See Contraindications [ 4 ]) .
Patients known to have corn allergies should avoid using Octagam 5% liquid (See Contraindications [ 4 ]).
5.2 Renal Failure
Renal dysfunction, acute renal failure, osmotic nephropathy, and death may occur upon use of IGIV products in predisposed patients.
Assure that patients are not volume depleted prior to the initiation of the infusion of Octagam 5% liquid.
Assess renal function, including a measurement of blood urea nitrogen (BUN)/serum creatinine, prior to the initial infusion of Octagam 5% liquid and again at appropriate intervals thereafter. It is particularly important to do periodic monitoring of renal function tests and urine output in patients judged to have a potential increased risk of developing acute renal failure. Consider discontinuation of the infusion if renal function deteriorates. (See Patient Counseling Information [ 17 ].)
For patients judged to be at risk for developing renal dysfunction and/or at risk of developing thrombotic events (such as those with diabetes mellitus or hypovolemia, those who are obese, those who use concomitant nephrotoxic medicinal products, or those who are over 65 years of age), administer Octagam 5% liquid at the minimum rate of infusion practicable (less than 0.07 mL/kg/min (3.3 mg/kg/min) (See Boxed Warning, and Dosage and Administration [ 2.3 ]).
5.3 Blood Glucose Monitoring
Some types of blood glucose testing systems (for example, those based on the glucose dehydrogenase pyrroloquinolinequinone (GDH-PQQ) or glucose-dye-oxidoreductase methods) falsely interpret the maltose contained in Octagam 5% liquid as glucose. This has resulted in falsely elevated glucose readings and, consequently, in the inappropriate administration of insulin, resulting in life-threatening hypoglycemia. Further, cases of true hypoglycemia may go untreated if the hypoglycemic state is masked by falsely elevated glucose readings. Therefore, always use a glucose-specific method for the measurement of blood glucose, when administering Octagam 5% liquid. Carefully review the product information of the blood glucose testing system, including that of the test strips, to determine if the system is appropriate for use with maltose-containing parenteral products. If any uncertainty exists, contact the manufacturer of the testing system to determine if the system is appropriate for use with maltose-containing parenteral products. [ 2 ]
5.4 Hyperproteinemia
Hyperproteinemia, increased serum viscosity and hyponatremia may occur in patients receiving IGIV therapy, including Octagam 5% liquid. The hyponatremia is likely to be a pseudohyponatremia as demonstrated by a decreased calculated serum osmolality or elevated osmolar gap. Distinguishing true hyponatremia from pseudohyponatremia is clinically critical, as treatment aimed at decreasing serum free water in patients with pseudohyponatremia may lead to volume depletion, a further increase in serum viscosity and a disposition to thromboembolic events [ 3 ].
5.5 Thrombotic events
Thrombosis may occur following treatment with immune globulin products, including Octagam 5% liquid. Risk factors may include advanced age, prolonged immobilization, hypercoagulable conditions, history of venous or arterial thrombosis, use of estrogens, indwelling central vascular catheters, hyperviscosity, and cardiovascular risk factors. Thrombosis may occur in the absence of known risk factors.
Consider baseline assessment of blood viscosity in patients at risk for hyperviscosity, including those with cryoglobulins, fasting chylomicronemia/markedly high triacylglycerols (triglycerides), or monoclonal gammopathies. For patients at risk of thrombosis, administer Octagam 5% liquid at the minimum dose and infusion rate practicable. Ensure adequate hydration in patients before administration. Monitor for signs and symptoms of thrombosis and assess blood viscosity in patients at risk for hyperviscosity. [ 4 ], [ 5 ], [ 6 ]. (See Boxed Warning, Dosage and Administration [ 2 ], Patient Counseling Information [ 17 ])
5.6 Aseptic meningitis syndrome
Aseptic meningitis syndrome (AMS) has been reported to occur infrequently in association with IGIV treatment, including Octagam 5% liquid. Discontinuation of IGIV treatment has resulted in remission of AMS within several days without sequelae. The syndrome usually begins within several hours to two days following IGIV treatment and rapid infusion. It is characterized by symptoms and signs including severe headache, nuchal rigidity, drowsiness, fever, photophobia, painful eye movements, nausea and vomiting. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) studies are frequently positive with pleocytosis up to several thousand cells per cu mm, predominantly from the granulocytic series, and elevated protein levels up to several hundred mg/dl. Conduct a thorough neurological examination on patients exhibiting such signs and symptoms, including CSF studies, to rule out other causes of meningitis. AMS may occur more frequently in association with high doses (2 g/kg) and/or rapid infusion of IGIV. It appears that patients with a history of migraine may be more susceptible. [ 7 ] (See Patient Counseling Information [ 17 ]).
5.7 Hemolysis
Octagam 5% liquid may contain blood group antibodies, which may act as hemolysins and induce in vivo coating of red blood cells with immunoglobulin, causing a positive direct antiglobulin reaction and, rarely, hemolysis [ 8 ]. Delayed hemolytic anemia can develop subsequent to IGIV therapy due to enhanced RBC sequestration and acute hemolysis, consistent with intravascular hemolysis, has been reported. Cases of severe hemolysis-related renal dysfunction/failure or disseminated intravascular coagulation have occurred following infusion of IGIV (See Adverse Reactions [ 6 ]) [ 9 ].
The following risk factors may be associated with the development of hemolysis following IGIV administration: high doses (e.g. ≥ 2 g/kg), given either as a single administration or divided over several days, and non-O blood group. Other individual patient factors, such as an underlying inflammatory state (as may be reflected by, for example, elevated C-reactive protein or erythrocyte sedimentation rate), have been hypothesized to increase the risk of hemolysis following administration of IGIV but their role is uncertain. Hemolysis has been reported following administration of IGIV for a variety of indications.
Closely monitor patients for clinical signs and symptoms of hemolysis, particularly patients with risk factors noted above. Consider appropriate laboratory testing in higher risk patients, including measurement of hemoglobin or hematocrit prior to infusion and within approximately 36 to 96 hours post infusion. If clinical signs and symptoms of hemolysis or a significant drop in hemoglobin or hematocrit have been observed, perform confirmatory laboratory testing. If transfusion is indicated for patients who develop hemolysis with clinically compromising anemia after receiving IGIV, perform adequate cross-matching to avoid exacerbating on-going hemolysis. (See Patient Counseling Information [ 17 ]) .
5.8 Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI)
Noncardiogenic pulmonary edema [Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury (TRALI)] may occur in patients treated with IGIV products, including Octagam 5% liquid [ 10 ]. TRALI is characterized by severe respiratory distress, pulmonary edema, hypoxemia, normal left ventricular function, and fever and typically occurs within 1-6 hours after transfusion.
Monitor patients for pulmonary adverse reactions (See Patient Counseling Information [ 17 ]) . If TRALI is suspected, perform appropriate tests for the presence of anti-neutrophil antibodies in both the product and patient serum. Patients with TRALI may be managed using oxygen therapy with adequate ventilatory support.
5.9 Transmissible Infectious Agents
Because Octagam 5% liquid is made from human blood, it may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, e.g., viruses and theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent. The risk of infectious agent transmission has been reduced by screening plasma donors for prior exposure to certain viruses, testing for the presence of certain current virus infections, and including virus inactivation/removal steps in the manufacturing process for Octagam 5% liquid.
Report all infections thought to possibly be transmitted by Octagam 5% liquid to Octapharma USA Inc. at 1-866-766-4860 . Always discuss the risks and benefits of this product with the patient, before prescribing or administering it to the patient (See Patient Counseling Information [ 17 ]).
5.10 Laboratory Tests
- Periodic monitoring of renal function and urine output is particularly important in patients judged to be at increased risk of developing acute renal failure. Assess renal function, including measurement of BUN and serum creatinine, before the initial infusion of Octagam 5% liquid and at appropriate intervals thereafter.
- Consider baseline assessment of blood viscosity in patients at risk for hyperviscosity, including those with cryoglobulins, fasting chylomicronemia/markedly high triacylglycerols (triglycerides), or monoclonal gammopathies, because of the potentially increased risk of thrombosis.
- If signs and/or symptoms of hemolysis are present after an infusion of Octagam 5% liquid, perform appropriate laboratory testing for confirmation.
- If TRALI is suspected, perform appropriate tests for the presence of anti-neutrophil antibodies and anti-HLA antibodies in both the product and patient’s serum.
5.11 Interference with Laboratory Tests
After infusion of IgG, the transitory rise of the various passively transferred antibodies in the patient’s blood may yield positive serological testing results, with the potential for misleading interpretation. Passive transmission of antibodies to erythrocyte antigens (e.g., A, B, and D) may cause a positive direct or indirect antiglobulin (Coombs) test.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions observed with Octagam 5% liquid treatment during clinical trial (> 5%) were headache and nausea.
The most serious adverse reactions observed with Octagam 5% liquid treatment have been immediate anaphylactic reactions (see Warning and Precautions [ 5.1 ]), thromboembolic events ( Warning and Precautions [ 5.5 ]), aseptic meningitis ( Warnings and Precautions [ 5.6 ]), and hemolytic anemia ( Warnings and Precautions [ 5.7 ]).
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a product cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another product and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The clinical trial database includes a multi-center, study in 46 children and adults with PI. Subjects participated in the study for a mean of 346 days and received 300 to 450 mg/kg every 21 days or 400 to 600 mg/kg every 28 days. Infusions were initiated at a rate of 30 mg/kg/hr for the first 30 minutes, and, if tolerated, could be advanced to a maximum tolerated rate not exceeding 200 mg/kg/hr. Over half of the subjects were male (n=28; 61%), and more than half were on the 28-day infusion schedule (n=27; 59%). The mean age of subjects was 31.5 years.
Pre-medications were used in 165 (25.2%) out of 654 infusions and in 14 (30.4%) out of 46 patients. Infusions were slowed or interrupted in 9 out of 489 infusions (1.84%) without pre-medication and in 10 out of 165 infusions (6.06%) with pre-medication. Five out of 32 (15.63%) patients who never received any pre-medication had at least one slowed or interrupted infusion, whereas 9 out of 14 (64.29%) patients who received pre-medication at least once also had a slowed or interrupted infusion.
During the described trial 12 serious adverse events were reported in 6 patients. Eleven SAEs were assessed as being not related. One serious adverse event (Calculus renal NOS) war reported just before the next infusion, and was not temporarily related to the previous infusion. No subject withdrew from the study due to an adverse event or adverse reaction.
The adverse reactions (= adverse events that were assessed as treatment related) reported by at least 5% of subjects during the 12-month treatment are given in Table 2 below.
Table 2: Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥ 5% of Subjects Receiving Octagam 5%
| No. of subjects (%) | No. of events (%) | |
| Total | 46 (100%) | 71 (100%) |
| Headache NOS | 7 (15%) | 18 (25%) |
| Nausea | 3 (7%) | 4 (6%) |
Laboratory Abnormalities
Standard clinical laboratory evaluations were performed in the study. Three subjects (7%) had incidences of AST (>2.5 x ULN) which were all assessed as clinically non-significant. No subject had a positive Coombs test or other signs of hemolysis (such as drop of hemoglobin of ≥ 2 g/dL) during the study.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Because postmarketing reporting of adverse reactions is voluntary and from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate the frequency of these reactions or establish a causal relationship to product exposure.
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of Octagam 5% liquid.
|
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Leukopenia, hemolytic anemia |
|
Immune system disorders
Hypersensitivity, anaphylactic shock, anaphylactic reaction, anaphylactoid reaction, angioedema, face oedema |
|
Metabolic and nutritional disorders
Fluid overload, (pseudo)hyponatremia |
|
Psychiatric disorders
Agitation, confusional state, anxiety, nervousness |
|
Nervous system disorders
Cerebrovascular accident, loss of consciousness, speech disorder, meningitis aseptic, migraine, dizziness, paresthesia, hypoesthesia, tremor, photophobia |
|
Eye disorders
Visual impairment |
|
Cardiac disorders
Myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, bradycardia, tachycardia, palpitations, cyanosis |
|
Vascular disorders
Hypotension, thrombosis, circulatory collapse, peripheral circulatory failure, hypertension, phlebitis, pallor |
|
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
Respiratory failure, pulmonary embolism, pulmonary oedema, bronchospasm, dyspnea, cough, hypoxia |
|
Gastrointestinal disorders
Vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain |
|
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Eczema, skin exfoliation, urticaria, rash, rash erythematous, dermatitis, erythema, pruritus, alopecia |
|
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Back pain, arthralgia, myalgia, pain in extremity, neck pain, muscle spasm, muscular weakness, musculoskeletal stiffness |
|
Renal and urinary disorders
Renal failure acute, renal pain |
|
General disorders and administration site conditions
Fatigue, oedema, injection site reaction, pyrexia, influenza-like illness, chills, chest pain, chest discomfort, hot flush, flushing, feeling hot, feeling cold, hyperhidrosis, malaise, lethargy, asthenia, burning sensation |
|
Investigations
Hepatic enzymes increased, blood glucose false positive |
|
Injury, poisoning and procedural complications
Transfusion-related acute lung injury |
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
It is recommended that Octagam 5% liquid be administered separately from other drugs or medications which the patient may be receiving.
Antibodies in Octagam 5% liquid may interfere with the response to live viral vaccines, such as measles, mumps, and rubella. Inform the immunizing physician of recent therapy with Octagam 5% liquid, so that administration of live viral vaccines, if indicated, can be appropriately delayed 3 or more months from the time of IGIV administration .
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
No human data are available to indicate the presence or absence of drug-associated risk. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Octagam 5% liquid. It is not known whether Octagam 5% liquid can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Immune globulins cross the placenta from maternal circulation increasingly after 30 weeks of gestation. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
No human data are available to assess the presence or absence of Octagam 5% in human milk, the effects of Octagam 5% on the breastfed child, and the effects of Octagam 5% on milk production/excretion. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Octagam 5% liquid and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Octagam 5% liquid or from the underlying maternal condition. Immunoglobulins are excreted into the milk and may contribute to the transfer of protective antibodies to the neonate.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Octagam 5% liquid was evaluated in 11 pediatric subjects (age range 6 – 16 years). There were no obvious differences observed between adults and pediatric subjects with respect to pharmacokinetics, efficacy and safety. No pediatric specific dose requirements were necessary to achieve the desired serum IgG levels.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Patients > 65 years of age may be at increased risk for developing certain adverse reactions such as thromboembolic events and acute renal failure (See Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions [ 5 ]).
Clinical studies of Octagam 5% liquid did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdose may lead to fluid overload and hyperviscosity, particularly in the elderly and in patients with impaired renal function.
11 DESCRIPTION
Immune Globulin Intravenous (Human), Octagam 5% liquid, is a solvent/detergent (S/D)-treated, sterile preparation of highly purified immunoglobulin G (IgG) derived from large pools of human plasma. Octagam 5% liquid is a solution for infusion which must be administered intravenously.
All units of human plasma used in the manufacture of Octagam 5% liquid are provided by FDA-approved blood establishments only, and are tested by FDA-licensed serological tests for HBsAg, antibodies to HCV and HIV and Nucleic Acid Test (NAT) for HCV and HIV-1 and found to be non-reactive (negative).
The product is manufactured by the cold ethanol fractionation process followed by ultrafiltration and chromatography. The manufacturing process includes treatment with an organic S/D mixture composed of tri-n-butyl phosphate (TNBP) and Triton X-100 (Octoxynol). The Octagam 5% liquid manufacturing process provides a significant viral reduction in in vitro studies (Table 3). These reductions are achieved through a combination of process steps including cold ethanol fractionation, S/D treatment and pH 4 treatment.
Table 3: In vitro reduction factor during Octagam 5% liquid manufacturing
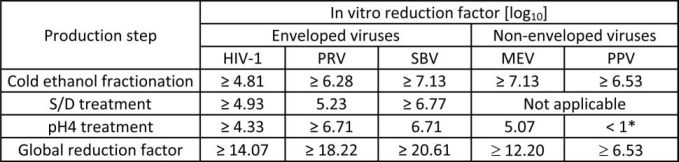
*not calculated for global LRF
HIV-1: Human Immunodeficiency Virus - 1
PRV: Pseudorabies Virus
SBV: Sindbis Virus
MEV: Mouse Encephalomyelitis Virus
PPV: Porcine Parvovirus
11.1 Composition
The composition of Octagam 5% liquid is shown in Table 4 as follows:
Table 4: Composition.
| Component | Quantity/mL |
| Protein, of which not less than 96% is human normal immunoglobulin G | 50 mg |
| Maltose | 100 mg |
| Triton X-100 | not more than 5 mcg |
| TNBP | not more than 1 mcg |
| IgA | not more than 0.2 mg |
| IgM | not more than 0.1 mg |
| Water for Injection | ad. |
This preparation contains approximately 50 mg of protein per mL (5%) of which not less than 96% is human normal immunoglobulin G. Octagam 5% liquid contains not more than 3% aggregates, not less than 90% monomers and dimers and not more than 3% fragments.
The sodium content of the final solution is not more than 30 mmol/l and the pH is between 5.1 and 6.0. The osmolality is 310 - 380 mosmol/kg.
The manufacturing process for Octagam 5% liquid isolates IgG without additional chemical or enzymatic modification, and the Fc portion is maintained intact. Octagam 5% liquid contains the IgG antibody activities present in the donor population. IgG subclasses are fully represented with the following approximate percents of total IgG: IgG 1 is 65%, IgG 2 is 30%, IgG 3 is 3% and IgG 4 is 2%.
Octagam 5% liquid contains a broad spectrum of IgG antibodies against bacterial and viral agents that are capable of opsonization and neutralization of microbes and toxins.
Octagam 5% liquid contains no preservative and no sucrose.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Octagam 5% liquid supplies a broad spectrum of opsonic and neutralizing IgG antibodies against bacteria or their toxins. The mechanism of action in PI has not been fully elucidated.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Octagam 5% liquid contains mainly immunoglobulin G (IgG) with a broad spectrum of antibodies against various infectious agents reflecting the IgG activity found in the donor population. Octagam 5% liquid which is prepared from pooled material from not less than 1000 donors, has an IgG subclass distribution similar to that of native human plasma. Adequate doses of IGIV can restore abnormally low IgG level to the normal range. Standard pharmacodynamic studies were not performed.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Peak levels of IgG are reached immediately after infusion of Octagam 5% liquid . It has been shown that after infusion, exogenous IgG is distributed relatively rapidly between plasma and extravascular fluid until approximately half is partitioned in the extravascular space. Therefore a rapid initial drop in serum IgG is expected [ 11 ].
Studies show that the apparent half-life of Octagam 5% liquid is approximately 40 days in immunodeficient patients.
The main pharmacokinetic parameters of Octagam 5% liquid measured as total IgG in the clinical study are displayed in Table 5 below:
In the pharmacokinetic study, a subset of 14 patients aged between 10 and 70 years with PI underwent pharmacokinetic assessments. Patients received infusions of Octagam 5% liquid (300 to 600 mg/kg) every 3 (n=6) to 4 (n=8) weeks for 12 months. Pharmacokinetic samples were collected at baseline and after the 5 th month of treatment. After the infusion, blood samples were taken until day 28 (for patients on a 21 day schedule, the interval was extended to 4 weeks for the pharmacokinetic study).
Table 5: PK Parameters of Octagam 5% liquid in the clinical study
| Octagam | 5% liquid | |||
| N | Mean | SD | Median | |
| Cmax (mg/mL) | 14 | 16.7 | 3.2 | 16.4 |
| AUC (mg*h/mL) | 14 | 7022 | 1179 | 7103 |
| T1/2 (days) | 14 | 40.7 | 17.0 | 36.3 |
|
Trough IgG Level 21 Day Infusion Schedule (mg/dL) | 19 | 881.6 | 151.5 | 859 |
|
Trough IgG Level 28 Day Infusion Schedule (mg/dL) | 25 | 763.5 | 156.8 | 760 |
The half-life of IgG can vary considerably from person to person. In particular, high concentrations of IgG and hypermetabolism associated with fever and infection have been seen to coincide with a shortened half-life of IgG. Longer half-lives are often seen with immunodeficient patients [ 12 ].
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No studies were conducted on carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, or impairment of fertility with Octagam 5% liquid.
Repeated-dose toxicity studies and the genotoxic studies gave no evidence of carcinogenic properties of TNBP and Octoxynol [ 13 ], [ 14 ].
The results of in vitro and in vivo genotoxicity studies for TNBP and Octoxynol were negative. The results of studies on the embryotoxic and teratogenic properties of TNBP and Octoxynol in rats and rabbits at a wide range of i.v. doses were also negative.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
No studies were conducted on non-clinical pharmacology, toxicology, local tolerance or pharmacokinetics with Octagam 5% liquid.
A variety of single-dose toxicity studies were performed for TNBP and Octoxynol alone or in combination. The lowest toxic dose of TNBP + Octoxynol (1+5) was 10,000 mcg/kg BM in rats after intravenous administration. Studies on 13-week toxicity were performed for combinations of TNBP + Octoxynol in a broad dose range intravenously in dogs and rats. In these studies the lowest toxic dose for rats was local 60 mcg TNBP/kg +300 mcg Octoxynol/kg BM i.v. (concentration: 0.0006% and 0.003%, respectively) and systemic 300 mcg TNBP/kg + 1,500 mcg Octoxynol/kg BM i.v. (concentration: 0.003% and 0.015%, respectively). The lowest toxic dose for dogs was local 50 mcg TNBP/kg + 250 mcg Octoxynol/kg BM i.v. (concentration: 0.005% and 0.025%, respectively) and systemic 500 mcg TNBP/kg + 2,500 mcg Octoxynol/kg BM i.v. (concentration: 0.05% and 0.25%, respectively).
Local tolerance of TNBP and Octoxynol was evaluated from the experiments on repeat-dose toxicity (rats, dogs) and on developmental toxicity (rats, rabbits). In these animal studies the lowest dose exerting local adverse reactions was 50 + 250 mcg/kg BM (TNBP + Octoxynol; daily injections) in dogs. At this dose 4 out of 6 dogs were affected starting in week 7 of treatment.
A pharmacokinetic study was carried out in rats given 300 mcg of TNBP/kg and 1,500 mcg Octoxynol/kg BM i.v. The plasma half-life for TNBP was approximately 20 minutes. Octoxynol was not detected.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
In an open-label, multicenter study, 46 patients (including 10 patients between the ages of 6 and 12, and one 15 years old) with primary humoral immunodeficiency (PI) received Octagam 5% liquid in individualized doses of 300 - 600 mg/kg every 3 or 4 weeks for 12 months. More than half of the patients (n=27; 59%) were on a 4-week treatment schedule, the remainder received the study drug every 3 weeks. Six patients discontinued the study prematurely.
The study examined the number of episodes of serious infections (pneumonia, bacteremia, sepsis, osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, visceral abscesses, bacterial or viral meningitis) per patient in a year, as well as the number of other infections, number of school or work days missed, the number and length of hospitalizations, and the number of visits to a physician or the emergency department for acute problems.
The rate of serious infections per patient per year was 0.1 (5 infections over 43.5 patient-years). There were no other infections documented by positive radiograph or fever during the study period. Table 6 summarizes the other efficacy data such as work/school days missed, days in hospital and visits to physician/ER.
Table 6: Summary of Secondary Efficacy Variables.
| Variable | Subjects N | Subjects % | Total Days or Visits | Total Subject Years | Days or Visits/Subj./YearEstimate |
| Work/School Days Missed | 30 | 65 | 241 | 43.5 | 5.5 |
| Days in Hospital | 4 | 9 | 16 | 43.5 | 0.4 |
| Visits to Physician/ER | 27 | 59 | 92 | 43.5 | 2.1 |
15 REFERENCES
- Duhem, C., Dicato, M. A. and Ries, F. Side-effects of intravenous immune globulins. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 97 Suppl 1, 79-83 (1994).
- Kannan, S., Rowland, C. H., Hockings, G. I. and Tauchmann, P. M. Intragam can interfere with blood glucose monitoring. Med. J. Aust. 180, 251-252 (2004).
- Steinberger, B. A., Ford, S. M., Coleman, T. A. Intravenous Immunoglobulin Therapy Results in Post-infusional Hyperproteinemia, Increased Serum Viscosity, and Pseudohyponatremia. Am J Hematol 73:97-100 (2003)
- Dalakas, M. C. High-dose intravenous immunoglobulin and serum viscosity: risk of precipitating thromboembolic events. Neurology 44, 223-226 (1994).
- Wolberg, A. S., Kon, R. H., Monroe, D. M. and Hoffman, M. Coagulation factor XI is a contaminant in intravenous immunoglobulin preparations. Am. J Hematol. 65, 30-34 (2000).
- Go RS, Call TG: Deep venous thrombosis of the arm after intravenous immunoglobulin infusion: case report and literature review of intravenous immunoglobulin-related thrombotic complications. Mayo Clin Proc75:83-85 (2000)
- Sekul, E. A., Cupler, E. J. and Dalakas, M. C. Aseptic meningitis associated with high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin therapy: frequency and risk factors. Ann Intern. Med. 121, 259-262 (1994).
- Pierce LR, Jain N: Risks associated with the use of intravenous immunoglobulin. Transfus Med Rev 17:241-251 (2003)
- Kessary-Shoham H., Levy, Y., Shoenfeld, Y., Lorber, M. and Gershon, H. In vivo administration of intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) can lead to enhanced erythrocyte sequestration. Journal of Autoimmunity. 13, 129-135 (1999).
- Rizk, A., Gorson, K. C., Kenney, L. and Weinstein, R. Transfusion-related acute lung injury after the infusion of IVIG. Transfusion 41, 264-268 (2001).
- Koleba T, Ensom MH: Pharmacokinetics of intravenous immunoglobulin: a systematic review. Pharmacotherapy 26:813-827 (2006)
- Lever, A. M., Yap, P. L., Cuthbertson, B., Wootton, R. and Webster, A. D. Increased half-life of gammaglobulin after prolonged intravenous replacement therapy. Clin Exp. Immunol 67, 441-446 (1987).
- Auletta, CS., Kotkoskie, LA., Saulog, T., Richter, WR. A dietary oncogenicity study of tributyl phosphate in the CD-1 mouse. Toxicology 128, 135-141 (1998a).
- Auletta CS., Weiner ML., Richter WR. A dietary toxicity/oncogenicity study of tributyl phosphate in the rat. Toxicology 128: 125-134 (1998b).
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Octagam 5% liquid is supplied in 1.0 g, 2.5 g, 5 g, 10 g or 25 g single use bottles.
| NDC Number | Size | Grams Protein |
| 68982 – 840 – 01 | 20 mL | 1.0 |
| 68982 – 840 – 02 | 50 mL | 2.5 |
| 68982 – 840 – 03 | 100 mL | 5.0 |
| 68982 – 840 – 04 | 200 mL | 10.0 |
| 68982 – 840 – 05* | 500 mL | 25.0 |
- Octagam 5% liquid is not supplied with an infusion set. If a filtered infusion set is used (not mandatory), the filter size must be 0.2 – 200 microns.
- Components used in the packaging of Octagam 5% liquid are not made with natural rubber latex.
- Octagam 5% liquid may be stored for 36 months at +2°C to + 8°C (36°F to 46°F) from the date of manufacture. Within the first 24 months of this shelf life, the product may be stored at ≤ +25°C (77°F). After storage at ≤ +25°C (77°F) the product must be used or discarded.
- Do not use after expiration date.
- Do not freeze. Do not use product that has been frozen.
- Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local requirements.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Information for Patients
( See also Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions [ 5 ] )
Inform patients of the early signs of hypersensitivity reactions including hives, generalized urticaria, tightness of the chest, wheezing, hypotension, and anaphylaxis. Instruct patients that they should contact their physicians immediately if such symptoms occur. ( See Warnings and Precautions [ 5.1 ])
Instruct patients to immediately report the following signs and symptoms to their health care provider:
- symptoms of thrombosis which may include pain and/or swelling of an arm or leg with warmth over the affected area; discoloration of an arm or leg; unexplained shortness of breath; chest pain or discomfort that worsens on deep breathing; unexplained rapid pulse; numbness or weakness on one side of the body. (see Warnings and Precautions [ 5.5 ])
- decreased urine output, sudden weight gain, fluid retention/edema, and/or shortness of breath ( see Warnings and Precautions [ 5.2 ])
- severe headache, neck stiffness, drowsiness, fever, sensitivity to light, painful eye movements, nausea, and vomiting ( see Warnings and Precautions [ 5.6 ])
- fatigue, increased heart rate, yellowing of the skin or eyes, and dark-colored urine ( see Warning and Precautions [ 5.7 ] )
- trouble breathing, chest pain, blue lips or extremities, lightheadedness and fever These may be signs for TRALI which typically occurs within 1 to 6 hours following transfusion ( see Warning and Precautions [ 5.8 ])
Inform patients that Octagam 5% liquid is made from human plasma and may contain infectious agents that can cause disease (e.g., viruses, and, theoretically, the CJD agent). Inform patients that the risk Octagam 5% liquid may transmit an infectious agent has been reduced by screening plasma donors for prior exposure to certain viruses, by testing the donated plasma for certain virus infections and by inactivating and/or removing certain viruses during manufacturing. Nevertheless, instruct patients that they should report any symptoms that concern them ( see Warning and Precautions ([ 5.9 ]).
Inform patients that administration of IgG may interfere with the response to live viral vaccines such as measles, mumps and rubella. Inform patients to notify their immunizing physician of therapy with Octagam 5% liquid ( see Drug Interactions [ 7 ]).
Manufactured by:
Octapharma Pharmazeutika Produktionsges.m.b.H.
Oberlaaer Strasse 235
A-1100 Vienna, Austria
Octapharma AB
Lars Forssells gata 23
SE- 112 75, Sweden
Distributed by:
Octapharma USA Inc.Paramus, NJ 07652

