WARNING: RISKS FROM CONCOMITANT USE WITH OPIOIDS; ABUSE, MISUSE, AND ADDICTION; and DEPENDENCE AND WITHDRAWAL REACTIONS
-
Concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs for patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate. Limit dosages and durations to the minimum required. Follow patients for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation (see
WARNINGS and
PRECAUTIONS).
- The use of benzodiazepines, including lorazepam tablets, exposes users to risks of abuse, misuse, and addiction, which can lead to overdose or death. Abuse and misuse of benzodiazepines commonly involve concomitant use of other medications, alcohol, and/or illicit substances, which is associated with an increased frequency of serious adverse outcomes. Before prescribing lorazepam tablets and throughout treatment, assess each patient’s risk for abuse, misuse, and addiction (see WARNINGS).
- The continued use of benzodiazepines, including lorazepam tablets may lead to clinically significant physical dependence. The risks of dependence and withdrawal increase with longer treatment duration and higher daily dose. Abrupt discontinuation or rapid dosage reduction of lorazepam tablets after continued use may precipitate acute withdrawal reactions, which can be life-threatening. To reduce the risk of withdrawal reactions, use a gradual taper to discontinue lorazepam tablets or reduce the dosage ( DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION and WARNINGS).
DESCRIPTION
Lorazepam, USP, an antianxiety agent, has the chemical formula, 7-chloro-5-( o-chlorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-2 H-1,4-benzodiazepin-2-one:
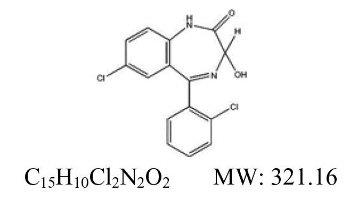
It is a nearly white powder almost insoluble in water. Each lorazepam tablet, to be taken orally, contains 0.5 mg, 1 mg, or 2 mg of lorazepam, USP. The inactive ingredients present are lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and polacrilin potassium.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Studies in healthy volunteers show that in single high doses lorazepam has a tranquilizing action on the central nervous system with no appreciable effect on the respiratory or cardiovascular systems.
Lorazepam is readily absorbed with an absolute bioavailability of 90%. Peak concentrations in plasma occur approximately 2 hours following administration. The peak plasma level of lorazepam from a 2 mg dose is approximately 20 ng/mL.
The mean half-life of unconjugated lorazepam in human plasma is about 12 hours and for its major metabolite, lorazepam glucuronide, about 18 hours. At clinically relevant concentrations, lorazepam is approximately 85% bound to plasma proteins. Lorazepam is rapidly conjugated at its 3-hydroxy group into lorazepam glucuronide which is then excreted in the urine. Lorazepam glucuronide has no demonstrable central nervous system (CNS) activity in animals.
The plasma levels of lorazepam are proportional to the dose given. There is no evidence of accumulation of lorazepam on administration up to 6 months.
Studies comparing young and elderly subjects have shown that advancing age does not have a significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of lorazepam. However, in one study involving single intravenous doses of 1.5 to 3 mg of lorazepam injection, mean total body clearance of lorazepam decreased by 20% in 15 elderly subjects of 60 to 84 years of age compared to that in 15 younger subjects of 19 to 38 years of age.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Lorazepam tablets are indicated for the management of anxiety disorders or for the short-term relief of the symptoms of anxiety or anxiety associated with depressive symptoms. Anxiety or tension associated with the stress of everyday life usually does not require treatment with an anxiolytic.
The effectiveness of lorazepam in long-term use, that is, more than 4 months, has not been assessed by systematic clinical studies. The physician should periodically reassess the usefulness of the drug for the individual patient.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Lorazepam is contraindicated in patients with:
- hypersensitivity to benzodiazepines or to any components of the formulation.
- acute narrow-angle glaucoma.
WARNINGS
Risks from Concomitant Use with Opioids
Concomitant use of benzodiazepines, including lorazepam, and opioids may result in profound sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death. Because of these risks, reserve concomitant prescribing of these drugs in patients for whom alternative treatment options are inadequate.
Observational studies have demonstrated that concomitant use of opioid analgesics and benzodiazepines increases the risk of drug-related mortality compared to use of opioids alone. If a decision is made to prescribe lorazepam concomitantly with opioids, prescribe the lowest effective dosages and minimum durations of concomitant use, and follow patients closely for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation. In patients already receiving an opioid analgesic, prescribe a lower initial dose of lorazepam than indicated in the absence of an opioid and titrate based on clinical response. If an opioid is initiated in a patient already taking lorazepam, prescribe a lower initial dose of the opioid and titrate based upon clinical response.
Advise both patients and caregivers about the risks of respiratory depression and sedation when lorazepam is used with opioids. Advise patients not to drive or operate heavy machinery until the effects of concomitant use with the opioid have been determined (see PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions).
Abuse, Misuse, and Addiction
The use of benzodiazepines, including lorazepam, exposes users to the risks of abuse, misuse, and addiction, which can lead to overdose or death. Abuse and misuse of benzodiazepines often (but not always) involve the use of doses greater than the maximum recommended dosage and commonly involve concomitant use of other medications, alcohol, and/or illicit substances, which is associated with an increased frequency of serious adverse outcomes, including respiratory depression, overdose, or death (see DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE: Abuse).
Before prescribing lorazepam and throughout treatment, assess each patient’s risk for abuse, misuse, and addiction (e.g., using a standardized screening tool). Use of lorazepam, particularly in patients at elevated risk, necessitates counseling about the risks and proper use of lorazepam along with monitoring for signs and symptoms of abuse, misuse, and addiction. Prescribe the lowest effective dosage; avoid or minimize concomitant use of CNS depressants and other substances associated with abuse, misuse, and addiction (e.g., opioid analgesics, stimulants); and advise patients on the proper disposal of unused drug. If a substance use disorder is suspected, evaluate the patient and institute (or refer them for) early treatment, as appropriate.
Dependence and Withdrawal Reactions
To reduce the risk of withdrawal reactions, use a gradual taper to discontinue lorazepam or reduce the dosage (a patient-specific plan should be used to taper the dose) (see DOSAGE AND ADMINSTRATION: Discontinuation or Dosage Reduction of Lorazepam Tablets).
Patients at an increased risk of withdrawal adverse reactions after benzodiazepine discontinuation or rapid dosage reduction include those who take higher dosages, and those who have had longer durations of use.
Acute Withdrawal Reactions
The continued use of benzodiazepines, including lorazepam, may lead to clinically significant physical dependence. Abrupt discontinuation or rapid dosage reduction of lorazepam after continued use, or administration of flumazenil (a benzodiazepine antagonist) may precipitate acute withdrawal reactions, which can be life-threatening (e.g., seizures) (see DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE: Dependence) .
Protracted Withdrawal Syndrome
In some cases, benzodiazepine users have developed a protracted withdrawal syndrome with withdrawal symptoms lasting weeks to more than 12 months (see DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE: Dependence).
Pre-existing depression may emerge or worsen during use of benzodiazepines including lorazepam. Lorazepam is not recommended for use in patients with a primary depressive disorder or psychosis.
Use of benzodiazepines, including lorazepam, both used alone and in combination with other CNS depressants, may lead to potentially fatal respiratory depression (see PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions).
As with all patients on CNS-depressant drugs, patients receiving lorazepam should be warned not to operate dangerous machinery or motor vehicles and that their tolerance for alcohol and other CNS depressants will be diminished.
PRECAUTIONS
In patients with depression, a possibility for suicide should be borne in mind; benzodiazepines should not be used in such patients without adequate antidepressant therapy.
Lorazepam should be used with caution in patients with compromised respiratory function (e.g., COPD, sleep apnea syndrome).
Elderly or debilitated patients may be more susceptible to the sedative effects of lorazepam. Therefore, these patients should be monitored frequently and have their dosage adjusted carefully according to patient response; the initial dosage should not exceed 2 mg.
Paradoxical reactions have been occasionally reported during benzodiazepine use. Such reactions may be more likely to occur in children and the elderly. Should these occur, use of the drug should be discontinued.
The usual precautions for treating patients with impaired renal or hepatic function should be observed. As with all benzodiazepines, the use of lorazepam may worsen hepatic encephalopathy; therefore, lorazepam should be used with caution in patients with severe hepatic insufficiency and/or encephalopathy. Dosage for patients with severe hepatic insufficiency should be adjusted carefully according to patient response; lower doses may be sufficient in such patients.
In patients where gastrointestinal or cardiovascular disorders coexist with anxiety, it should be noted that lorazepam has not been shown to be of significant benefit in treating the gastrointestinal or cardiovascular component.
Esophageal dilation occurred in rats treated with lorazepam for more than 1 year at 6 mg/kg/day. The no- effect dose was 1.25 mg/kg/day (approximately 6 times the maximum human therapeutic dose of 10 mg/day). The effect was reversible only when the treatment was withdrawn within 2 months of first observation of the phenomenon. The clinical significance of this is unknown. However, use of lorazepam for prolonged periods and in geriatric patients requires caution, and there should be frequent monitoring for symptoms of upper GI disease.
Safety and effectiveness of lorazepam in children of less than 12 years have not been established.
Information for Patients
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Risks from Concomitant Use with Opioids
Advise both patients and caregivers about the risks of potentially fatal respiratory depression and sedation when lorazepam is used with opioids and not to use such drugs concomitantly unless supervised by a health care provider. Advise patients not to drive or operate heavy machinery until the effects of concomitant use with the opioid have been determined (see WARNINGS: Risks from Concomitant Use of Opioids and PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions).
Abuse, Misuse, and Addiction
Inform patients that the use of lorazepam even at recommended doses, exposes users to risks of abuse, misuse, and addiction, which can lead to overdose and death, especially when used in combination with other medications (e.g., opioid analgesics), alcohol, and/or illicit substances. Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of benzodiazepine abuse, misuse, and addiction; to seek medical help if they develop these signs and/or symptoms; and on the proper disposal of unused drug (see WARNINGS: Abuse Misuse, and Addiction and DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE).
Withdrawal Reactions
Inform patients that the continued use of lorazepam may lead to clinically significant physical dependence and that abrupt discontinuation or rapid dosage reduction of lorazepam may precipitate acute withdrawal reactions, which can be life-threatening. Inform patients that in some cases, patients taking benzodiazepines have developed a protracted withdrawal syndrome with withdrawal symptoms lasting weeks to more than 12 months. Instruct patients that discontinuation or dosage reduction of lorazepam may require a slow taper (see WARNINGS: Dependence and Withdrawal Reactions and DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE).
Essential Laboratory Tests
Some patients on lorazepam have developed leukopenia, and some have had elevations of LDH. As with other benzodiazepines, periodic blood counts and liver function tests are recommended for patients on long-term therapy.
Drug Interactions
The concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids increases the risk of respiratory depression because of actions at different receptor sites in the CNS that control respiration. Benzodiazepines interact at GABAA sites and opioids interact primarily at mu receptors. When benzodiazepines and opioids are combined, the potential for benzodiazepines to significantly worsen opioid-related respiratory depression exists. Limit dosage and duration of concomitant use of benzodiazepines and opioids, and monitor patients closely for respiratory depression and sedation.
The benzodiazepines, including lorazepam, produce increased CNS-depressant effects when administered with other CNS depressants such as alcohol, barbiturates, antipsychotics, sedative/hypnotics, anxiolytics, antidepressants, narcotic analgesics, sedative antihistamines, anticonvulsants, and anesthetics.
Concomitant use of clozapine and lorazepam may produce marked sedation, excessive salivation, hypotension, ataxia, delirium, and respiratory arrest.
Concurrent administration of lorazepam with valproate results in increased plasma concentrations and reduced clearance of lorazepam. Lorazepam dosage should be reduced to approximately 50% when coadministered with valproate.
Concurrent administration of lorazepam with probenecid may result in a more rapid onset or prolonged effect of lorazepam due to increased half-life and decreased total clearance. Lorazepam dosage needs to be reduced by approximately 50% when coadministered with probenecid.
The effects of probenecid and valproate on lorazepam may be due to inhibition of glucuronidation.
Administration of theophylline or aminophylline may reduce the sedative effects of benzodiazepines, including lorazepam.
Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis
No evidence of carcinogenic potential emerged in rats during an 18-month study with lorazepam. No studies regarding mutagenesis have been performed.
Pregnancy
Reproductive studies in animals were performed in mice, rats, and two strains of rabbits. Occasional anomalies (reduction of tarsals, tibia, metatarsals, malrotated limbs, gastroschisis, malformed skull, and microphthalmia) were seen in drug-treated rabbits without relationship to dosage. Although all of these anomalies were not present in the concurrent control group, they have been reported to occur randomly in historical controls. At doses of 40 mg/kg and higher, there was evidence of fetal resorption and increased fetal loss in rabbits which was not seen at lower doses.
The clinical significance of the above findings is not known. However, an increased risk of congenital malformations associated with the use of minor tranquilizers (chlordiazepoxide, diazepam, and meprobamate) during the first trimester of pregnancy has been suggested in several studies. Because the use of these drugs is rarely a matter of urgency, the use of lorazepam during this period should be avoided. The possibility that a woman of childbearing potential may be pregnant at the time of institution of therapy should be considered. Patients should be advised that if they become pregnant, they should communicate with their physician about the desirability of discontinuing the drug.
In humans, blood levels obtained from umbilical cord blood indicate placental transfer of lorazepam and lorazepam glucuronide. Infants of mothers who ingested benzodiazepines for several weeks or more preceding delivery have been reported to have withdrawal symptoms during the postnatal period. Symptoms such as hypoactivity, hypotonia, hypothermia, respiratory depression, apnea, feeding problems, and impaired metabolic response to cold stress have been reported in neonates born of mothers who have received benzodiazepines during the late phase of pregnancy or at delivery.
Nursing Mothers
Lorazepam has been detected in human breast milk; therefore, it should not be administered to breastfeeding women, unless the expected benefit to the woman outweighs the potential risk to the infant.
Sedation and inability to suckle have occurred in neonates of lactating mothers taking benzodiazepines. Infants of lactating mothers should be observed for pharmacological effects (including sedation and irritability).
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of lorazepam generally were not adequate to determine whether subjects aged 65 and over respond differently than younger subjects; however, the incidence of sedation and unsteadiness was observed to increase with age (see ADVERSE REACTIONS).
Age does not appear to have a significant effect on lorazepam kinetics (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Clinical circumstances, some of which may be more common in the elderly, such as hepatic or renal impairment, should be considered. Greater sensitivity (e.g., sedation) of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, and lower doses may be sufficient in these patients (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most adverse reactions to benzodiazepines, including CNS effects and respiratory depression, are dose dependent, with more severe effects occurring with high doses.
In a sample of about 3500 patients treated for anxiety, the most frequent adverse reaction to lorazepam was sedation (15.9%), followed by dizziness (6.9%), weakness (4.2%), and unsteadiness (3.4%). The incidence of sedation and unsteadiness increased with age.
Other adverse reactions to benzodiazepines, including lorazepam are fatigue, drowsiness, amnesia, memory impairment, confusion, disorientation, depression, unmasking of depression, disinhibition, euphoria, suicidal ideation/attempt, ataxia, asthenia, extrapyramidal symptoms, convulsions/seizures, tremor, vertigo, eye function/visual disturbance (including diplopia and blurred vision), dysarthria/slurred speech, change in libido, impotence, decreased orgasm; headache, coma; respiratory depression, apnea, worsening of sleep apnea, worsening of obstructive pulmonary disease; gastrointestinal symptoms including nausea, change in appetite, constipation, jaundice, increase in bilirubin, increase in liver transaminases, increase in alkaline phosphatase; hypersensitivity reactions, anaphylactoid reactions; dermatological symptoms, allergic skin reactions, alopecia; syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH), hyponatremia; thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis, pancytopenia; hypothermia; and autonomic manifestations.
Paradoxical reactions, including anxiety, excitation, agitation, hostility, aggression, rage, sleep disturbances/insomnia, sexual arousal, and hallucinations may occur. Small decreases in blood pressure and hypotension may occur but are usually not clinically significant, probably being related to the relief of anxiety produced by lorazepam.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE EVENTS, contact Teva at 1-888-838-2872 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or http://www.fda.gov/medwatch for voluntary reporting of adverse reactions.
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Controlled Substance
Lorazepam tablets contain lorazepam, a Schedule IV controlled substance.
Abuse
Lorazepam tablets are a benzodiazepine and a CNS depressant with a potential for abuse and addiction. Abuse is the intentional, non-therapeutic use of a drug, even once, for its desirable psychological or physiological effects. Misuse is the intentional use, for therapeutic purposes, of a drug by an individual in a way other than prescribed by a health care provider or for whom it was not prescribed. Drug addiction is a cluster of behavioral, cognitive, and physiological phenomena that may include a strong desire to take the drug, difficulties in controlling drug use (e.g., continuing drug use despite harmful consequences, giving a higher priority to drug use than other activities and obligations), and possible tolerance or physical dependence. Even taking benzodiazepines as prescribed may put patients at risk for abuse and misuse of their medication. Abuse and misuse of benzodiazepines may lead to addiction.
Abuse and misuse of benzodiazepines often (but not always) involve the use of doses greater than the maximum recommended dosage and commonly involve concomitant use of other medications, alcohol, and/or illicit substances, which is associated with an increased frequency of serious adverse outcomes, including respiratory depression, overdose, or death. Benzodiazepines are often sought by individuals who abuse drugs and other substances, and by individuals with addictive disorders (see WARNINGS: Abuse, Misuse, and Addiction).
The following adverse reactions have occurred with benzodiazepine abuse and/or misuse: abdominal pain, amnesia, anorexia, anxiety, aggression, ataxia, blurred vision, confusion, depression, disinhibition, disorientation, dizziness, euphoria, impaired concentration and memory, indigestion, irritability, muscle pain, slurred speech, tremors, and vertigo.
The following severe adverse reactions have occurred with benzodiazepine abuse and/or misuse: delirium, paranoia, suicidal ideation and behavior, seizures, coma, breathing difficulty, and death. Death is more often associated with polysubstance use (especially benzodiazepines with other CNS depressants such as opioids and alcohol).
Dependence
Physical Dependence
Lorazepam tablets may produce physical dependence from continued therapy. Physical dependence is a state that develops as a result of physiological adaptation in response to repeated drug use, manifested by withdrawal signs and symptoms after abrupt discontinuation or a significant dose reduction of a drug. Abrupt discontinuation or rapid dosage reduction of benzodiazepines or administration of flumazenil, a benzodiazepine antagonist, may precipitate acute withdrawal reactions, including seizures, which can be life-threatening. Patients at an increased risk of withdrawal adverse reactions after benzodiazepine discontinuation or rapid dosage reduction include those who take higher dosages (i.e., higher and/or more frequent doses) and those who have had longer durations of use (see WARNINGS: Dependence and Withdrawal Reactions) .
To reduce the risk of withdrawal reactions, use a gradual taper to discontinue lorazepam tablets or reduce the dosage (see DOSAGE and ADMINISTRATION: Discontinuation or Dosage Reduction of lorazepam tablets and WARNINGS) .
Acute Withdrawal Signs and Symptoms
Acute withdrawal signs and symptoms associated with benzodiazepines have included abnormal involuntary movements, anxiety, blurred vision, depersonalization, depression, derealization, dizziness, fatigue, gastrointestinal adverse reactions (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, weight loss, decreased appetite), headache, hyperacusis, hypertension, irritability, insomnia, memory impairment, muscle pain and stiffness, panic attacks, photophobia, restlessness, tachycardia, and tremor. More severe acute withdrawal signs and symptoms, including life-threatening reactions, have included catatonia, convulsions, delirium tremens, depression, hallucinations, mania, psychosis, seizures and suicidality.
Protracted Withdrawal Syndrome
Protracted withdrawal syndrome associated with benzodiazepines is characterized by anxiety, cognitive impairment, depression, insomnia, formication, motor symptoms (e.g., weakness, tremor, muscle twitches), paresthesia, and tinnitus that persists beyond 4 to 6 weeks after initial benzodiazepine withdrawal. Protracted withdrawal symptoms may last weeks to more than 12 months. As a result, there may be difficulty in differentiating withdrawal symptoms from potential re-emergence or continuation of symptoms for which the benzodiazepine was being used.
Tolerance
Tolerance to lorazepam tablets may develop from continued therapy. Tolerance is a physiological state characterized by a reduced response to a drug after repeated administration (i.e., a higher dose of a drug is required to produce the same effect that was once obtained at a lower dose). Tolerance to the therapeutic effect of lorazepam tablets may develop; however, little tolerance develops to the amnestic reactions and other cognitive impairments caused by benzodiazepines.
OVERDOSAGE
In postmarketing experience, overdose with lorazepam has occurred predominantly in combination with alcohol and/or other drugs. Therefore, in the management of overdosage, it should be borne in mind that multiple agents may have been taken.
Symptoms
Overdosage of benzodiazepines is usually manifested by varying degrees of CNS depression ranging from drowsiness to coma. In mild cases, symptoms include drowsiness, mental confusion, paradoxical reactions, dysarthria, and lethargy. In more serious cases, and especially when other drugs or alcohol were ingested, symptoms may include ataxia, hypotonia, hypotension, cardiovascular depression, respiratory depression, hypnotic state, coma, and death.
Management
General supportive and symptomatic measures are recommended; vital signs must be monitored and the patient closely observed. When there is a risk of aspiration, induction of emesis is not recommended. Gastric lavage may be indicated if performed soon after ingestion or in symptomatic patients. Administration of activated charcoal may also limit drug absorption. Hypotension, though unlikely, usually may be controlled with norepinephrine bitartrate injection. Lorazepam is poorly dialyzable. Lorazepam glucuronide, the inactive metabolite, may be highly dialyzable.
The benzodiazepine antagonist flumazenil may be used in hospitalized patients as an adjunct to, not as a substitute for, proper management of benzodiazepine overdose. The prescriber should be aware of a risk of seizure in association with flumazenil treatment, particularly in long-term benzodiazepine users and in cyclic antidepressant overdose. The complete flumazenil package insert including CONTRAINDICATIONS, WARNINGS, and PRECAUTIONS sections should be consulted prior to use.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Lorazepam tablets are administered orally. For optimal results, dose, frequency of administration, and duration of therapy should be individualized according to patient response. To facilitate this, 0.5 mg, 1 mg, and 2 mg tablets are available.
The usual range is 2 to 6 mg/day given in divided doses, the largest dose being taken before bedtime, but the daily dosage may vary from 1 to 10 mg/day.
For anxiety, most patients require an initial dose of 2 to 3 mg/day given two times a day or three times a day.
For insomnia due to anxiety or transient situational stress, a single daily dose of 2 to 4 mg may be given, usually at bedtime.
For elderly or debilitated patients, an initial dosage of 1 to 2 mg/day in divided doses is recommended, to be adjusted as needed and tolerated.
The dosage of lorazepam tablets should be increased gradually when needed to help avoid adverse effects. When higher dosage is indicated, the evening dose should be increased before the daytime doses.
Discontinuation or Dosage Reduction of Lorazepam Tablets
To reduce the risk of withdrawal reactions, use a gradual taper to discontinue lorazepam tablets or reduce the dosage. If a patient develops withdrawal reactions, consider pausing the taper or increasing the dosage to the previous tapered dosage level. Subsequently decrease the dosage more slowly (see WARNINGS: Dependence and Withdrawal Reactions and DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE: Dependence).
HOW SUPPLIED
Lorazepam Tablets, USP are available in the following dosage strengths:
0.5 mg: white to off-white, unscored, round flat faced beveled edge tablet, debossed with TV over 0.5 on one side and 5R on the other side, supplied in bottles of 4 (NDC 68071-2666-4) and 6 ( NDC 68071-2666-6)
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP.
Dispense with Medication Guide available at: www.tevausa.com/medguides
Manufactured In Czech Republic By:
Teva Czech Industries, s.r.o.
Opava-Komarov, Czech Republic
Manufactured For:
Teva Pharmaceuticals
Parsippany, NJ 07054
Rev. C 8/2021
Dispense with Medication Guide available at: www.tevausa.com/medguides
|
MEDICATION GUIDE
|
|
What is the most important information I should know about lorazepam tablets?
Do not drive or operate heavy machinery until you know how taking lorazepam tablets with opioids affects you.
|
|
What are lorazepam tablets?
|
|
Do not take lorazepam tablets if you:
|
|
Before you take lorazepam tablets, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Taking lorazepam tablets with certain other medicines can cause side effects or affect how well lorazepam tablets or the other medicines work. Do not start or stop other medicines without talking to your healthcare provider.
|
|
How should I take lorazepam tablets?
|
|
What are the possible side effects of lorazepam tablets? Lorazepam tablets may cause serious side effects, including:
The most common side effects of lorazepam tablets include:
These are not all the possible side effects of lorazepam tablets. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. |
How should I store lorazepam tablets?
|
| General information about the safe and effective use of lorazepam tablets
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use lorazepam tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give lorazepam tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about lorazepam tablets that is written for health professionals. |
|
What are the ingredients in lorazepam tablets?
Active ingredient: lorazepam Inactive ingredients: lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and polacrilin potassium |
|
Manufactured In Czech Republic By:
Teva Czech Industries, s.r.o., Opava-Komarov, Czech Republic
|
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Rev. C 8/2021
