FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
APONVIE is indicated for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) in adults.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended dose in adults of APONVIE is 32 mg administered as a 30 second intravenous injection prior to induction of anesthesia.
2.2 Preparation and Administration
- Inspect the vial for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration; discard if present. APONVIE is opaque and off-white to amber in color.
- Aseptically withdraw 4.4 mL from the vial.
- Flush the infusion line with normal saline before and after administration of APONVIE.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injectable emulsion: 32 mg/4.4 mL (7.2 mg/mL) aprepitant as an opaque, off-white to amber emulsion, in a single-dose vial.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
APONVIE is contraindicated in patients:
- with a history of hypersensitivity to aprepitant or any component of the product [see Description (11)]. Hypersensitivity reactions have included anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- taking pimozide. Inhibition of CYP3A4 by aprepitant could result in elevated plasma concentrations of pimozide, which is a CYP3A4 substrate, potentially causing serious or life-threatening reactions, such as QT prolongation, a known adverse reaction of pimozide [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, during or soon after administration of aprepitant have occurred. Symptoms including dyspnea, eye swelling, flushing, pruritus, and wheezing have been reported [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Monitor patients during and after administration. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, administer appropriate medical therapy. Do not administer APONVIE in patients who experience these symptoms with previous use of aprepitant.
5.2 Clinically Significant CYP3A4 Drug Interactions
Aprepitant is a substrate, a weak-to-moderate (dose-dependent) inhibitor, and an inducer of CYP3A4.
- Use of pimozide, a CYP3A4 substrate, with APONVIE is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)].
- Use of APONVIE with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole) may increase plasma concentrations of aprepitant and result in an increased risk of adverse reactions related to APONVIE [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
- Use of APONVIE with strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin) may result in a reduction in aprepitant plasma concentrations and decreased efficacy of APONVIE [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
5.3 Decrease in INR with Concomitant Warfarin
Use of aprepitant with warfarin, a CYP2C9 substrate, may result in a clinically significant decrease in the International Normalized Ratio (INR) of prothrombin time [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Monitor the INR in patients on chronic warfarin therapy in the 2-week period, particularly at 7 to 10 days, following administration of APONVIE [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.4 Risk of Reduced Efficacy of Hormonal Contraceptives
The efficacy of hormonal contraceptives may be reduced for 28 days following administration of APONVIE [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Advise patients to use effective alternative or back-up methods of non-hormonal contraception for 1 month following administration of APONVIE [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The safety of APONVIE for prevention of PONV was evaluated as a single dose in healthy subjects and established from adequate and well-controlled studies of oral aprepitant [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Adverse reactions observed in these studies are described below.
Safety of APONVIE
A total of 51 healthy subjects received a single 32 mg dose of APONVIE as a 30 second intravenous injection. Adverse reactions reported in at least 3% of subjects were constipation (8%), fatigue (6%), and headache (4%).
Safety of Oral Aprepitant
In 2 active-controlled, double-blind clinical studies in patients receiving general anesthesia (Studies 1 and 2), 40 mg oral aprepitant was compared to 4 mg intravenous ondansetron [see Clinical Studies (14)].
There were 564 patients treated with oral aprepitant and 538 patients treated with ondansetron.
The most common adverse reactions reported in patients treated with oral aprepitant for PONV in pooled Studies 1 and 2 are listed in Table 1.
| Oral Aprepitant 40 mg (N = 564) | Ondansetron (N = 538) |
|
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Constipation | 9% | 8% |
| hypotension | 6% | 5% |
In a pooled analysis of PONV studies, less common adverse reactions reported in more than 0.5% of patients treated with oral aprepitant and at a greater incidence than ondansetron were dizziness and urticaria.
In addition, two serious adverse reactions were reported in PONV clinical studies of oral aprepitant in patients taking a higher than recommended dose: one case of constipation, and one case of sub-ileus.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of aprepitant. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: pruritus, rash, urticaria, Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Immune system disorders: hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis and anaphylactic shock [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Nervous system disorders: ifosfamide-induced neurotoxicity reported after aprepitant and ifosfamide coadministration.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effect of Aprepitant on the Pharmacokinetics of Other Drugs
Aprepitant is a substrate, a weak-to-moderate (dose-dependent) inhibitor, and an inducer of CYP3A4. Aprepitant is also an inducer of CYP2C9 [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Table 2 includes drug interactions affecting drugs co-administered with APONVIE and instructions for preventing or managing them.
| Pimozide | |
| Clinical Impact | Increased pimozide exposure. |
| Intervention | APONVIE is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)]. |
| Hormonal Contraceptives | |
| Clinical Impact | Decreased hormonal exposure for 28 days after administration of APONVIE [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Use in Specific Populations (8.3), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention | Effective alternative or back-up methods of contraception (such as condoms and spermicides) should be used for 1 month following administration of APONVIE. |
| Examples | birth control pills, transdermal systems, implants, and certain intrauterine systems |
| CYP2C9 Substrates | |
| Warfarin | |
| Clinical Impact | Decreased warfarin exposure and decreased prothrombin time (INR) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention | In patients on chronic warfarin therapy, monitor prothrombin time (INR) in the 2-week period, particularly at 7 to 10 days, following administration of APONVIE. |
| Other Antiemetic Agents | |
| 5-HT3 Antagonists | |
| Clinical Impact | No change in the exposure of the 5-HT3 antagonist [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention | No dosage adjustment needed. |
| Examples | ondansetron, granisetron, dolasetron |
| Corticosteroids | |
| Clinical Impact | No clinically significant change in the exposure of dexamethasone or methylprednisolone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention | No dosage adjustment needed. |
7.2 Effect of Other Drugs on the Pharmacokinetics of Aprepitant
Aprepitant is a CYP3A4 substrate [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Table 3 includes drug interactions affecting APONVIE when co-administered with other drugs and instructions for preventing them.
| Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors | |
| Clinical Impact | Significantly increased exposure of aprepitant may increase the risk of adverse reactions associated with APONVIE [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention | Avoid concomitant use of APONVIE. |
| Examples | ketoconazole, itraconazole, nefazodone, troleandomycin, clarithromycin, ritonavir, nelfinavir |
| Strong CYP3A4 Inducers | |
| Clinical Impact | Substantially decreased exposure of aprepitant in patients chronically taking a strong CYP3A4 inducer may decrease the efficacy of APONVIE [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Intervention | Avoid concomitant use of APONVIE. |
| Examples | rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin |
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are insufficient data on aprepitant use in pregnant women to identify a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Avoid use of APONVIE in pregnant women due to the alcohol content (see Clinical Considerations). In animal reproduction studies, no adverse developmental effects were observed in rats or rabbits exposed during the period of organogenesis to systemic drug concentrations (area under the plasma-concentration time curve [AUC]) of oral aprepitant approximately 4.8 times the exposure at the recommended human dose of APONVIE (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reactions
APONVIE contains alcohol. Published studies have demonstrated that alcohol is associated with fetal harm including central nervous system abnormalities, behavioral disorders, and impaired intellectual development. There is no safe level of alcohol exposure in pregnancy; therefore, avoid use of APONVIE in pregnant women.
Data
Animal Data
In embryofetal development studies in rats and rabbits, aprepitant was administered during the period of organogenesis at oral doses up to 1000 mg/kg twice daily (rats) and up to the maximum tolerated dose of 125 mg/kg/day (rabbits). No embryofetal lethality or malformations were observed at any dose level in either species. The exposures (AUC) in pregnant rats at 1000 mg/kg twice daily and in pregnant rabbits at 125 mg/kg/day were approximately 4.8 times the exposure at the recommended human dose of APONVIE. Aprepitant crosses the placenta in rats and rabbits.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of aprepitant in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Aprepitant is present in rat milk. When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that the drug will be present in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for APONVIE and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from APONVIE or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Upon administration of APONVIE, the efficacy of hormonal contraceptives may be reduced. Advise females of reproductive potential using hormonal contraceptives to use an effective alternative or back-up non-hormonal contraceptive (such as condoms or spermicides) for 1 month following administration of APONVIE [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Drug Interactions (7.1), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of APONVIE have not been established in pediatric patients.
Juvenile Animal Study
A study was conducted in young rats to evaluate the effects of aprepitant on growth and on neurobehavioral and sexual development. Rats were treated at oral doses up to the maximum feasible dose of 1000 mg/kg twice daily from the early postnatal period (Postnatal Day 10) through Postnatal Day 58. Slight changes in the onset of sexual maturation were observed in female and male rats; however, there were no effects on mating, fertility, embryonic-fetal survival, or histomorphology of the reproductive organs. There were no effects in neurobehavioral tests of sensory function, motor function, and learning and memory.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 1120 adult patients treated with oral aprepitant in PONV clinical studies, 7% were aged 65 and over, while 2% were aged 75 and over. Clinical studies of aprepitant did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they responded differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. No clinically meaningful differences in the pharmacokinetics of oral aprepitant were observed in healthy geriatric subjects compared to younger adult subjects [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
Headache, fatigue, and dizziness were reported in healthy subjects receiving a single dose of 100 or 130 mg aprepitant injectable emulsion (3.1 to 4 times the recommended dose).
Drowsiness and headache were reported in one patient who ingested 1440 mg of oral aprepitant.
In the event of overdose, general supportive treatment and monitoring should be provided.
Aprepitant is not removed by hemodialysis.
11 DESCRIPTION
APONVIE injectable emulsion contains the active ingredient, aprepitant. Aprepitant is a substance P/neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptor antagonist, an antiemetic agent, and chemically described as 5-[[(2R,3S)-2-[(1R)-1-[3,5bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]ethoxy]-3-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-morpholinyl]methyl]-1,2-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazol-3-one.
Its empirical formula is C23H21F7N4O3, and its structural formula is:
Aprepitant is a white to off-white crystalline solid, with a molecular weight of 534.43. It is practically insoluble in water. Aprepitant is sparingly soluble in ethanol and isopropyl acetate and slightly soluble in acetonitrile.
APONVIE (aprepitant) injectable emulsion is a sterile, opaque, off-white to amber liquid in a single-dose vial for intravenous use. Each vial contains 32 mg aprepitant in 4.4 mL of emulsion. The emulsion also contains the following inactive ingredients: dehydrated alcohol (125 mg), egg lecithin (636 mg), sodium oleate (21 mg), soybean oil (424 mg), sucrose (238 mg), and water for injection (2968 mg).
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Aprepitant is a selective high-affinity antagonist of human substance P/neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptors. Aprepitant has little or no affinity for serotonin (5-HT3), dopamine, and corticosteroid receptors, the targets of existing therapies for postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV). Aprepitant has been shown in animal models to inhibit emesis via central actions. Animal and human Positron Emission Tomography (PET) studies with aprepitant have shown that it crosses the blood brain barrier and occupies brain NK1 receptors.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
NK1 Receptor Occupancy
In two single-blind, multiple-dose, randomized, and placebo-controlled studies, healthy young men received oral aprepitant doses of 10 mg (N=2), 30 mg (N=3), 100 mg (N=3), or 300 mg (N=5) once daily (0.08, 0.24, 0.8, and 2.4 times a single 125 mg dose of oral aprepitant, respectively) for 14 days with 2 or 3 subjects on placebo. Both plasma aprepitant concentration and NK1 receptor occupancy in the corpus striatum by PET were evaluated, at predose and 24 hours after the last dose. At aprepitant plasma concentrations of approximately 10 ng/mL and 100 ng/mL, the NK1 receptor occupancies were approximately 50% and 90%, respectively. The oral aprepitant regimen produced mean trough plasma aprepitant concentrations greater than 500 ng/mL in adults, which would be expected to, based on the fitted curve with the Hill equation, result in greater than 95% brain NK1 receptor occupancy. However, the receptor occupancy for the PONV dosing regimen has not been determined. In addition, the relationship between NK1 receptor occupancy and the clinical efficacy of aprepitant has not been established.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Following administration of a single intravenous 32 mg dose of APONVIE administered as a 30 second injection to healthy subjects, mean (CV%) area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC0-∞) was 7.8 (27.4%) mcg∙hr/mL and mean plasma concentration at 5 minutes post-dose was 2.1 (19%) mcg/mL.
In healthy subjects, a single dose of 32 mg of APONVIE administered as a 30 second intravenous injection resulted in a 13% higher AUC0-∞ of aprepitant compared to a single oral dose of 40 mg aprepitant, which was not considered clinically meaningful.
Distribution
Aprepitant was greater than 99% bound to plasma proteins. The mean volume of distribution following APONVIE administration was approximately 72 L in healthy subjects.
Aprepitant crossed the blood-brain barrier in humans [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)].
Elimination
Metabolism
Aprepitant underwent extensive metabolism. In vitro studies using human liver microsomes indicated that aprepitant was metabolized primarily by CYP3A4 with minor metabolism by CYP1A2 and CYP2C19. Metabolism was largely via oxidation at the morpholine ring and its side chains. No metabolism by CYP2D6, CYP2C9, or CYP2E1 was detected.
In healthy young adults, aprepitant accounted for approximately 24% of the radioactivity in plasma over 72 hours following a single oral 300 mg dose of [14C]-aprepitant, indicating a substantial presence of metabolites in the plasma. Seven metabolites of aprepitant, which were only weakly active, had been identified in human plasma.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients
Following oral administration of a single 125 mg dose of aprepitant on Day 1 and 80 mg once daily on Days 2 through 5, the AUC0-24hr of aprepitant was 21% higher on Day 1 and 36% higher on Day 5 in healthy elderly subjects (65 years and older) relative to younger adult subject. The Cmax was 10% higher on Day 1 and 24% higher on Day 5 in healthy elderly subjects relative to younger adult subjects. These differences are not considered clinically meaningful [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Male and Female Patients
Following oral administration of a single dose of aprepitant ranging from 40 mg to 375 mg, the AUC0-24hr and Cmax are 9% and 17% higher in females as compared with males. The half-life of aprepitant was approximately 25% lower in females as compared with males. These differences are not considered clinically meaningful.
Racial or Ethnic Groups
Following oral administration of a single dose of aprepitant, ranging from 40 mg to 375 mg, the AUC0-24hr and Cmax were approximately 27% and 19% higher in Hispanics as compared with Caucasians. The AUC0-24hr and Cmax were 74% and 47% higher in Asians as compared to Caucasians. There was no difference in AUC0-24hr or Cmax between Caucasians and Blacks. These differences are not considered clinically meaningful.
Patients with Renal Impairment
A single 240 mg oral dose of aprepitant was administered to patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 as measured by 24-hour urinary creatinine clearance) and to patients with end stage renal disease (ESRD) requiring hemodialysis. In patients with severe renal impairment, the AUC0-∞ of total aprepitant (unbound and protein bound) decreased by 21% and Cmax decreased by 32%, relative to healthy subjects (creatinine clearance greater than 80 mL/min estimated by Cockcroft-Gault method). In patients with ESRD undergoing hemodialysis, the AUC0-∞ of total aprepitant decreased by 42% and Cmax decreased by 32%. Due to modest decreases in protein binding of aprepitant in patients with renal disease, the AUC of pharmacologically active unbound drug was not significantly affected in patients with renal impairment compared with healthy subjects. Hemodialysis conducted 4 or 48 hours after dosing had no significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of aprepitant; less than 0.2% of the dose was recovered in the dialysate.
No clinically meaningful changes in the pharmacokinetics of aprepitant are expected in patients with any degree of renal impairment following administration of a single dose of APONVIE 32 mg as an intravenous injection.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Following administration of a single 125 mg oral dose of aprepitant on Day 1 and 80 mg once daily on Days 2 and 3 to patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 5 to 6), the AUC0-24hr of aprepitant was 11% lower on Day 1 and 36% lower on Day 3, as compared with healthy subjects given the same regimen. In patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child Pugh score 7 to 9), the AUC0-24hr of aprepitant was 10% higher on Day 1 and 18% higher on Day 3, as compared with healthy subjects given the same regimen. These differences in AUC0-24hr are not considered clinically meaningful.
No clinically meaningful changes in the pharmacokinetics of aprepitant are expected in patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment following administration of a single dose of APONVIE 32 mg as an intravenous injection. There are no clinical or pharmacokinetic data in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score greater than 9).
Drug Interactions Studies
Aprepitant is a substrate, a weak-to-moderate (dose-dependent) inhibitor, and an inducer of CYP3A4. Aprepitant is also an inducer of CYP2C9. Aprepitant is unlikely to interact with drugs that are substrates for the P-glycoprotein transporter.
Aprepitant acts as a weak inhibitor of CYP3A4 when administered as a single intravenous 32 mg dose of APONVIE.
Effects of Aprepitant on the Pharmacokinetics of Other Drugs
Corticosteroids:
Dexamethasone: A single dose of oral aprepitant 40 mg when coadministered with a single dose of dexamethasone 20 mg, increased the AUC of dexamethasone by 1.45-fold, which is not considered clinically meaningful.
Methylprednisolone: Although the concomitant administration of methylprednisolone with the single 40 mg dose of oral aprepitant has not been studied, a single 40 mg dose of oral aprepitant produces a weak inhibition of CYP3A4 (based on midazolam interaction study) and it is not expected to alter the plasma concentrations of methylprednisolone to a clinically meaningful degree.
CYP2C9 substrates:
Warfarin: A single 125 mg dose of oral aprepitant was administered on Day 1 and 80 mg/day on Days 2 and 3 to subjects who were stabilized on chronic warfarin therapy. Although there was no effect of oral aprepitant on the plasma AUC of R(+) or S(-) warfarin determined on Day 3, there was a 34% decrease in S(-) warfarin trough concentration accompanied by a 14% decrease in the prothrombin time (reported as International Normalized Ratio or INR) 5 days after completion of dosing with oral aprepitant [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Tolbutamide: Oral aprepitant, when given as a 40 mg single dose on Day 1, decreased the AUC of tolbutamide by 8% on Day 2, 16% on Day 4, 15% on Day 8, and 10% on Day 15, when a single dose of tolbutamide 500 mg was administered prior to the administration of oral aprepitant 40 mg and on Days 2, 4, 8, and 15. This effect was not considered clinically meaningful.
Other Drugs:
Oral contraceptives: When a daily dosage of an oral contraceptive containing ethinyl estradiol and norgestimate was administered on Days 1 through 21, and oral aprepitant 40 mg was given on Day 8, the AUC of ethinyl estradiol decreased by 4% and by 29% on Day 8 and Day 12, respectively, while the AUC of norelgestromin increased by 18% on Day 8 and decreased by 10% on Day 12. In addition, the trough concentrations of ethinyl estradiol and norelgestromin on Days 8 through 21 were generally lower following coadministration of the oral contraceptive with oral aprepitant 40 mg on Day 8 compared to the trough levels following administration of the oral contraceptive alone [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Effect of Other Drugs on the Pharmacokinetics of Aprepitant
Rifampin: When a single 375 mg dose of oral aprepitant was administered on Day 9 of a 14-day regimen of 600 mg/day of rifampin, a strong CYP3A4 inducer, the AUC of aprepitant decreased approximately 11-fold and the mean terminal half-life decreased approximately 3-fold [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Ketoconazole: When a single 125 mg dose of oral aprepitant was administered on Day 5 of a 10-day regimen of 400 mg/day of ketoconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, the AUC of aprepitant increased approximately 5-fold and the mean terminal half-life of aprepitant increased approximately 3-fold [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
Diltiazem: In a study in 10 subjects with mild to moderate hypertension, administration of 100 mg of fosaprepitant, a prodrug of aprepitant, as an intravenous infusion with 120 mg of diltiazem, a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor administered three times daily, resulted in a 1.5-fold increase in the aprepitant AUC and a 1.4-fold increase in the diltiazem AUC. This effect was not considered clinically meaningful.
When fosaprepitant was administered with diltiazem, the mean maximum decrease in diastolic blood pressure was greater than that observed with diltiazem alone (24.3 ± 10.2 mm Hg with fosaprepitant versus 15.6 ± 4.1 mm Hg without fosaprepitant). The mean maximum decrease in systolic blood pressure was also greater after co-administration of diltiazem with fosaprepitant than administration of diltiazem alone (29.5 ± 7.9 mm Hg with fosaprepitant versus 23.8 ± 4.8 mm Hg without fosaprepitant). Co-administration of fosaprepitant and diltiazem, however, did not result in any additional clinically meaningful changes in heart rate or PR interval, beyond those changes observed with diltiazem alone.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Carcinogenicity studies were conducted in Sprague-Dawley rats and in CD-1 mice for 2 years. In the rat carcinogenicity studies, animals were treated with oral doses ranging from 0.05 to 1000 mg/kg twice daily. The highest dose produced systemic exposures to aprepitant (AUC) approximately 5.1 times the human exposure from APONVIE 32 mg. Treatment with aprepitant at doses of 5 to 1000 mg/kg twice daily caused an increase in the incidences of thyroid follicular cell adenomas and carcinomas in male rats. In female rats, it produced hepatocellular adenomas at 5 to 1000 mg/kg twice daily and hepatocellular carcinomas and thyroid follicular cell adenomas at 125 to 1000 mg/kg twice daily. In the mouse carcinogenicity studies, the animals were treated with oral doses ranging from 2.5 to 2000 mg/kg/day. The highest dose produced a systemic exposure approximately 11.5 times the human exposure at the recommended human dose of APONVIE. Treatment with aprepitant produced skin fibrosarcomas at 125 and 500 mg/kg/day doses in male mice.
Mutagenesis
Aprepitant was not genotoxic in the Ames test, the human lymphoblastoid cell (TK6) mutagenesis test, the rat hepatocyte DNA strand break test, the Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell chromosome aberration test, and the mouse micronucleus test.
Impairment of Fertility
Oral aprepitant did not affect the fertility or general reproductive performance of male or female rats at doses up to the maximum feasible dose of 1000 mg/kg twice daily (providing exposure in male and female rats higher than the exposure at the recommended human dose of APONVIE).
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and efficacy of APONVIE have been established based on adequate and well-controlled studies of a single-dose of oral aprepitant in adults. Below is a description of the results of these adequate and well-controlled studies of oral aprepitant for the prevention of PONV.
In two multicenter, randomized, double-blind, active comparator-controlled, parallel-group clinical studies (Studies 1 and 2), oral aprepitant was compared with ondansetron for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting in 1658 patients undergoing open abdominal surgery. These two studies were of similar design; however, they differed in terms of study hypothesis, efficacy analyses, and geographic location. Study 1 was a multinational study including the U.S., whereas, Study 2 was conducted entirely in the U.S.
In the two studies, patients were randomized to receive 40 mg oral aprepitant, 125 mg oral aprepitant, or 4 mg intravenous ondansetron as a single dose. Aprepitant was given orally with 50 mL of water 1 to 3 hours before anesthesia. Ondansetron was given intravenously immediately before induction of anesthesia. A comparison between the oral aprepitant 125 mg dose did not demonstrate any additional clinical benefit over the oral 40 mg dose.
Of the 564 patients who received 40 mg oral aprepitant, 92% were women and 8% were men; of these, 58% were White, 13% Hispanic American, 7% Multi-Racial, 14% Black, 6% Asian, and 2% Other. The age of patients treated with 40 mg oral aprepitant ranged from 19 to 84 years, with a mean age of 46.1 years. 46 patients were 65 years or older, with 13 patients being 75 years or older.
The antiemetic activity of oral aprepitant was evaluated during the 0 to 48 hour period following the end of surgery.
Efficacy measures in Study 1 included:
- no emesis (defined as no emetic episodes regardless of use of rescue therapy) in the 0 to 24 hours following the end of surgery (primary)
- complete response (defined as no emetic episodes and no use of rescue therapy) in the 0 to 24 hours following the end of surgery (primary)
- no emesis (defined as no emetic episodes regardless of use of rescue therapy) in the 0 to 48 hours following the end of surgery (secondary)
- time to first use of rescue medication in the 0 to 24 hours following the end of surgery (exploratory)
- time to first emesis in the 0 to 48 hours following the end of surgery (exploratory)
A closed testing procedure was applied to control the type I error for the primary endpoints.
The results of the primary and secondary endpoints for 40 mg oral aprepitant and 4 mg ondansetron are described in Table 4.
| Treatment | n/N (%) | Oral Aprepitant vs. Ondansetron |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Difference* | Odds Ratio† | Analysis | ||
| PRIMARY ENDPOINTS | ||||
| n/N = Number of responders/number of patients in analysis. | ||||
|
||||
| No Vomiting 0 to 24 hours (Superiority) (no emetic episodes) |
||||
| Oral aprepitant 40 mg | 246/293 (84.0) | 12.6% | 2.1 | P<0.001‡ |
| Ondansetron | 200/280 (71.4) | |||
| Complete Response (Non-inferiority: If LB§ >0.65) (no emesis and no rescue therapy, 0 to 24 hours) |
||||
| Oral aprepitant 40 mg | 187/293 (63.8) | 8.8% | 1.4 | LB=1.02 |
| Ondansetron | 154/280 (55.0) | |||
| Complete Response (Superiority: If LB >1.0) (no emesis and no rescue therapy, 0 to 24 hours) |
||||
| Oral aprepitant 40 mg | 187/293 (63.8) | 8.8% | 1.4 | LB=1.02§ |
| Ondansetron | 154/280 (55.0) | |||
| SECONDARY ENDPOINT | ||||
| No Vomiting 0 to 48 hours (Superiority) (no emetic episodes) | ||||
| Oral aprepitant 40 mg | 238/292 (81.5) | 15.2% | 2.3 | P<0.001¶ |
| Ondansetron | 185/279 (66.3) | |||
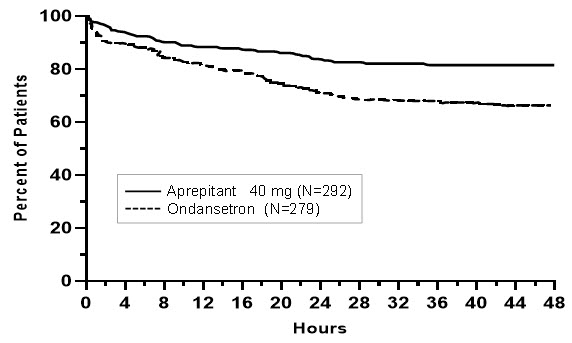
In Study 1, the use of oral aprepitant did not affect the time to first use of rescue medication when compared to ondansetron. However, compared to the ondansetron group, use of oral aprepitant delayed the time to first vomiting, as depicted in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Percent of Patients Who Remain Emesis Free During the 48 Hours Following End of Surgery in Study 1
Efficacy measures in Study 2 included:
- complete response (defined as no emetic episodes and no use of rescue therapy) in the 0 to 24 hours following the end of surgery (primary)
- no emesis (defined as no emetic episodes regardless of use of rescue therapy) in the 0 to 24 hours following the end of surgery (secondary)
- no use of rescue therapy in the 0 to 24 hours following the end of surgery (secondary)
- no emesis (defined as no emetic episodes regardless of use of rescue therapy) in the 0 to 48 hours following the end of surgery (secondary)
Study 2 failed to satisfy its primary hypothesis that oral aprepitant is superior to ondansetron in the prevention of PONV as measured by the proportion of patients with complete response in the 24 hours following end of surgery.
The study demonstrated that 40 mg oral aprepitant had a clinically meaningful effect with respect to the secondary endpoint "no vomiting" during the first 24 hours after surgery and was associated with a 16% improvement over ondansetron for the no vomiting endpoint (Table 5).
| Treatment | n/N (%) | Oral Aprepitant vs. Ondansetron | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Difference* | Odds Ratio† | Analysis | ||
| PRIMARY ENDPOINT | ||||
| n/N = Number of responders/number of patients in analysis. | ||||
| Complete Response
(no emesis and no rescue therapy, 0 to 24 hours) |
||||
| Oral aprepitant 40 mg | 111/248 (44.8) | 2.5% | 1.1 | 0.61 |
| Ondansetron | 104/246 (42.3) | |||
| SECONDARY ENDPOINTS | ||||
| No Vomiting
(no emetic episodes, 0 to 24 hours) |
||||
| Oral aprepitant 40 mg | 223/248 (89.9) | 16.3% | 3.2 | <0.001‡ |
| Ondansetron | 181/246 (73.6) | |||
| No Use of Rescue Medication
(for established emesis or nausea, 0 to 24 hours) |
||||
| Oral aprepitant 40 mg | 112/248 (45.2) | -0.7% | 1.0 | 0.83 |
| Ondansetron | 113/246 (45.9) | |||
| No Vomiting 0 to 48 hours (Superiority) (no emetic episodes, 0 to 48 hours) |
||||
| Oral aprepitant 40 mg | 209/247 (84.6) | 17.7% | 2.7 | <0.001‡ |
| Ondansetron | 164/245 (66.9) | |||
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
APONVIE injectable emulsion is supplied as an opaque, off-white to amber emulsion in a single-dose glass vial containing 32 mg/4.4 mL (7.2 mg/mL) aprepitant:
| NDC 47426-401-10 | 10 single-dose vials (NDC 47426-401-01) per carton |
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Hypersensitivity
Advise patients that hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported with aprepitant [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Advise patients to seek immediate medical attention if they experience signs or symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction, such as hives, rash and itching, skin peeling or sores, or difficulty in breathing or swallowing, or dizziness, rapid or weak heartbeat or feeling faint.
Drug Interactions
Advise patients to discuss all medications they are taking, including other prescription, non- prescription medication or herbal products [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Warfarin: Instruct patients on chronic warfarin therapy to follow instructions from their healthcare provider regarding blood draws to monitor their INR during the 2-week period, particularly at 7 to 10 days, following administration of APONVIE [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Hormonal Contraceptives: Advise patients that administration of APONVIE may reduce the efficacy of hormonal contraceptives. Instruct patients to use effective alternative or back-up methods of non-hormonal contraception (such as condoms or spermicides) for 1 month following administration of APONVIE [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Pregnancy
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus and to avoid use of APONVIE during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Manufactured for: Heron Therapeutics, Inc., San Diego, CA, 92121, USA
Patent: https://www.herontx.com/patents/
APONVIE® is a registered trademark of Heron Therapeutics, Inc.
Copyright © 2022-2024 Heron Therapeutics, Inc.
All rights reserved.
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 Vial Carton
NDC 47426-401-10
How Supplied:
APONVIE injectable emulsion
is supplied in a carton
containing 10 sterile,
single-dose glass vials of
32 mg aprepitant per 4.4 mL for
intravenous administration.
Recommended Dosage:
See Prescribing Information.
APONVIE®
(aprepitant) injectible emulsion
32 mg per 4.4 mL
(7.2 mg/mL)
For Intravenous Use Only
10 x 5 mL single-dose vials -
Discard unused portion
of vial.
Storage:
Must be refrigerated,
2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F).
Do not freeze.
Rx Only
