FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Solifenacin succinate is indicated for the treatment of adults with overactive bladder with symptoms of urge urinary incontinence, urgency, and urinary frequency.
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing Information
The recommended oral dose of solifenacin succinate is 5 mg once daily. If the 5 mg dose is well tolerated, the dose may be increased to 10 mg once daily.
Solifenacin succinate should be taken with water and swallowed whole. Solifenacin succinate can be administered with or without food.
2.2 Dosing Recommendations in Patients with Renal Impairment
Do not exceed 5 mg once daily in patients with severe renal impairment (CL cr < 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)] .
2.3 Dosing Recommendations in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Do not exceed 5 mg once daily in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B). Do not use solifenacin succinate in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
2.4 Dosing Recommendations in Patients Taking CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Do not exceed 5 mg once daily when solifenacin succinate is administered with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors such as ketoconazole [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
The 5 mg tablets are light yellow, round, film coated tablets debossed with 'SG' on one side and '427' on other side.
The 10 mg tablets are light pink, round, film coated tablets debossed with 'SG' on one side and '428' on other side.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Solifenacin succinate is contraindicated in patients:
- With urinary retention [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)],
- With gastric retention [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)],
- With uncontrolled narrow-angle glaucoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] , and
- Who have demonstrated hypersensitivity to solifenacin succinate or the inactive ingredients in solifenacin succinate tablets. Reported adverse reactions have included anaphylaxis and angioedema [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Angioedema and Anaphylactic Reactions
Angioedema of the face, lips, tongue, and/or larynx have been reported with solifenacin succinate. In some cases, angioedema occurred after the first dose, however, cases have been reported to occur hours after the first dose or after multiple doses. Anaphylactic reactions have also been reported in patients treated with solifenacin succinate. Angioedema associated with upper airway swelling and anaphylactic reactions may be life-threatening.
Solifenacin succinate is contraindicated in patients with a known or suspected hypersensitivity to solifenacin succinate [see Contraindications (4)]. If involvement of the tongue, hypopharynx, or larynx occurs, promptly discontinue solifenacin succinate tablets and provide appropriate therapy and/or measures necessary to ensure a patent airway.
5.2 Urinary Retention
The use of solifenacin succinate, like other antimuscarinic drugs, in patients with clinically significant bladder outlet obstruction including patients with urinary retention, may result in further urinary retention and kidney injury. The use of solifenacin succinate is not recommended in patients with clinically significant bladder outlet obstruction and is contraindicated in patients with urinary retention [see Contraindications (4)].
5.3 Gastrointestinal Disorders
The use of solifenacin succinate, like other antimuscarinic drugs, in patients with conditions associated with decreased gastrointestinal motility may result in further decreased gastrointestinal motility. Solifenacin succinate is contraindicated in patients with gastric retention [see Contraindications (4)]. The use of solifenacin succinate is not recommended in patients with conditions associated with decreased gastrointestinal motility.
5.4 Central Nervous System Effects
Solifenacin succinate is associated with antimuscarinic central nervous system (CNS) adverse reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. A variety of CNS antimuscarinic adverse reactions have been reported, including headache, confusion, hallucinations, and somnolence. Monitor patients for signs of antimuscarinic CNS adverse reactions, particularly after beginning treatment or increasing the dose. Advise patients not to drive or operate heavy machinery until they know how solifenacin succinate affects them. If a patient experiences antimuscarinic CNS adverse reactions, consider dose reduction or drug discontinuation.
5.5 Controlled Narrow-Angle Glaucoma
Solifenacin succinate should be used with caution in patients being treated for narrow-angle glaucoma [see Contraindications (4)].
5.6 QT Prolongation in Patients at High Risk of QT Prolongation
In a study of the effect of solifenacin succinate on the QT interval conducted in 76 healthy women [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)] , solifenacin succinate 30 mg (three times the largest maximum recommended dose in adult patients) was associated with a mean increase in the Fridericia-corrected QT interval of 8 msec (90% CI, 4, 13). The QT prolonging effect appeared less with solifenacin succinate 10 mg than with solifenacin succinate 30 mg, and the effect of solifenacin succinate 30 mg did not appear as large as that of the positive control moxifloxacin at its therapeutic dose.
The use of solifenacin succinate is not recommended in patients at high risk of QT prolongation, including patients with a known history of QT prolongation and patients who are taking medications known to prolong the QT interval.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Solifenacin succinate has been evaluated for safety in 1811 adult patients in four randomized, placebo-controlled trials (Studies 1-4) [see Clinical Studies (14)] . Expected adverse reactions of antimuscarinic agents are dry mouth, constipation, blurred vision (accommodation abnormalities), urinary retention, and dry eyes. The incidence of dry mouth and constipation in patients treated with solifenacin succinate was higher in the 10 mg dose group compared to the 5 mg dose group.
In the four 12-week double-blind clinical trials, severe fecal impaction, colonic obstruction, and intestinal obstruction were reported in one patient each, all in the solifenacin succinate 10 mg group. Angioneurotic edema was reported in one patient taking solifenacin succinate 5 mg. Compared to 12 weeks of treatment with solifenacin succinate, the incidence and severity of adverse reactions were similar in patients who remained on drug for up to 12 months in Study 5 [see Clinical Studies (14)] .
The most frequent adverse reaction leading to study discontinuation was dry mouth (1.5%). Table 1 lists the rates of identified adverse reactions, in the four randomized, placebo-controlled trials at an incidence greater than placebo and in 1% or more of patients treated with solifenacin succinate 5 mg or 10 mg once daily for up to 12 weeks.
| Placebo (%) | Solifenacin succinate
5 mg (%) | Solifenacin succinate
10 mg (%) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Name of Patients |
1216 |
578 |
1233 |
|
GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS | |||
|
Dry Mouth |
4.2 |
10.9 |
27.6 |
|
Constipation |
2.9 |
5.4 |
13.4 |
|
Nausea |
2.0 |
1.7 |
3.3 |
|
Dyspepsia |
1.0 |
1.4 |
3.9 |
|
Abdominal Pain Upper |
1.0 |
1.9 |
1.2 |
|
Vomiting NOS |
0.9 |
0.2 |
1.1 |
|
INFECTIONS AND INFESTATIONS | |||
|
Unrinary Track Infection NOS |
2.8 |
2.8 |
4.8 |
|
Influenza |
1.3 |
2.2 |
0.9 |
|
Pharyngitis NOS |
1.0 |
0.3 |
1.1 |
|
NERVOUS SYSTEM DISORDERS | |||
|
Dizziness |
1.8 |
1.9 |
1.8 |
|
EYE DISORDERS | |||
|
Vision Blurred |
1.8 |
3.8 |
4.8 |
|
Dry Eyes NOS |
0.6 |
0.3 |
1.6 |
|
RENAL AND URINARY DISORDERS | |||
|
Urinary Retention |
0.6 |
0 |
1.4 |
|
GENERAL DISORDERS AND ADMINISTRATION SITE CONDITIONS | |||
|
Edema Lower Limb |
0.7 |
0.3 |
1.1 |
|
Fatigue |
1.1 |
1.0 |
2.1 |
|
PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS | |||
|
Depression NOS |
0.8 |
1.2 |
0.8 |
|
RESPIRATORY, THORACIC AND MEDIASTINAL DISORDERS | |||
|
Cough |
0.2 |
0.2 |
1.1 |
|
VASCULAR DISORDERS | |||
|
Hypertension NOS |
0.6 |
1.4 |
0.5 |
6.2 Post-Marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of solifenacin succinate in the U.S. and/or outside of the U.S. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
General disorders and administration site conditions: peripheral edema, hypersensitivity reactions (including angioedema with airway obstruction, rash, pruritus, urticaria, anaphylactic reaction);
Nervous system disorders: dizziness, headache, confusion, hallucinations, delirium, somnolence;
Cardiac disorders: QT prolongation, Torsade de Pointes, atrial fibrillation, tachycardia, palpitations;
Hepatobiliary disorders: liver disorders mostly characterized by abnormal liver function tests, AST (aspartate aminotransferase), ALT (alanine aminotransferase), GGT (gamma-glutamyl transferase);
Renal and urinary disorders: renal impairment, urinary retention;
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: decreased appetite, hyperkalemia;
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme, dry skin;
Eye disorders: glaucoma;
Gastrointestinal disorders: gastroesophageal reflux disease, ileus, vomiting, abdominal pain, dysgeusia, sialadenitis;
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: dysphonia, nasal dryness;
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders: muscular weakness.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Solifenacin is a substrate of CYP3A4. Concomitant use of ketoconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, significantly increased the exposure of solifenacin [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] . The dosage of solifenacin succinate greater than 5 mg once daily is not recommended when concomitantly used with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)] .
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no studies with the use of solifenacin succinate in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriages, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. No adverse developmental outcomes were observed in animal reproduction studies with oral administration of solifenacin succinate to pregnant mice during the period of organogenesis at a dose resulting in 1.2 times the systemic exposure at the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 10 mg/day. However, administration of doses 3.6 times and greater than the MRHD during organogenesis produced maternal toxicity in the pregnant mice and resulted in developmental toxicity and reduced fetal body weights in offspring [see Data].
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects or miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Oral administration of 14C-solifenacin succinate to pregnant mice resulted in the recovery of radiolabel in the fetus indicating that solifenacin-related product can cross the placental barrier. In pregnant mice, administration of solifenacin succinate at a dose of 250 mg/kg/day (7.9 times the systemic exposure at the MRHD of 10 mg), resulted in an increased incidence of cleft palate and increased maternal lethality. Administration of solifenacin succinate to pregnant mice during organogenesis at greater than or equal to 3.6 times (100 mg/kg/day and greater) the systemic exposure at the MRHD, resulted in reduced fetal body weights and reduced maternal body weight gain. No embryo-fetal toxicity or teratogenicity was observed in fetuses from pregnant mice treated with solifenacin succinate at a dose of 30 mg/kg/day (1.2 times the systemic exposure at the MRHD). Administration of solifenacin succinate to pregnant rats and rabbits at a dose of 50 mg/kg/day (< 1 times and 1.8 times the systemic exposure at the MRHD, respectively), resulted in no findings of embryo-fetal toxicity. Oral pre- and post-natal administration of solifenacin succinate at 100 mg/kg/day (3.6 times the systemic exposure at the MRHD) during the period of organogenesis through weaning, resulted in reduced peripartum and postnatal survival, reduced body weight gain by the pups, and delayed physical development (eye opening and vaginal patency). An increase in the percentage of male offspring was also observed in litters from offspring (F2 generation) exposed to maternal doses of 250 mg/kg/day. There were no effects on natural delivery in mice treated with 1.2 times (30 mg/kg/day) the expected systemic exposure at the MRHD.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information on the presence of solifenacin in human milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. Solifenacin is present in mouse milk [see Data]. When a drug is present in animal milk, it is likely that the drug will be present in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for solifenacin succinate and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from solifenacin succinate or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
Animal Data
Oral administration of 14C-solifenacin succinate to lactating mice resulted in the recovery of radioactivity in maternal milk. Lactating female mice orally administered solifenacin succinate at a maternally toxic dose of 100 mg/kg/day (3.6 times the systemic exposure at the MRHD) had increased postpartum pup mortality, pups with reduced body weights, or delays in the onset of reflex and physical development. Pups from lactating dams orally administered solifenacin succinate at a dose of 30 mg/kg/day (1.2 times the systemic exposure at the MRHD) had no discernible adverse findings. The concentrations of solifenacin in animal milk does not necessarily predict the concentration of drug in human milk.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of solifenacin succinate tablets have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In placebo-controlled clinical studies, similar safety and effectiveness were observed between geriatric patients (623 patients ≥ 65 years and 189 patients ≥ 75 years) and younger adult patients (1188 patients < 65 years) treated with solifenacin succinate [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Solifenacin plasma concentrations are greater in patients with severe renal impairment compared to subjects with normal renal function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Because increased solifenacin plasma concentrations increase the risk of antimuscarinic adverse reactions, the maximum recommended dose of solifenacin succinate in patients with severe renal impairment (CL cr < 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2) is 5 mg once daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. The recommended dose in patients with mild or moderate renal impairment is the same as in patients with normal renal function.
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
Solifenacin plasma concentrations are greater in patients with moderate hepatic impairment compared to subjects with normal hepatic function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Because increased solifenacin plasma concentrations increase the risk of antimuscarinic adverse reactions, the maximum recommended dose of solifenacin succinate in patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B) is 5 mg once daily [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] and solifenacin succinate is not recommended for use in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C).
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage with solifenacin succinate can potentially result in severe antimuscarinic effects and should be treated accordingly. The highest dose ingested in an accidental overdose of solifenacin succinate was 280 mg (28 times the maximum dosage) in a 5-hour period. This case was associated with mental status changes. Some cases reported a decrease in the level of consciousness.
Intolerable antimuscarinic adverse reactions (fixed and dilated pupils, blurred vision, failure of heel-to-toe exam, tremors, and dry skin) occurred on day 3 in normal volunteers taking 50 mg daily (5 times the maximum recommended therapeutic dose) and resolved within 7 days following discontinuation of drug.
In the event of overdose with solifenacin succinate, treat with gastric lavage and appropriate supportive measures. ECG monitoring is also recommended.
11 DESCRIPTION
Solifenacin succinate is a muscarinic receptor antagonist. Chemically, solifenacin succinate is butanedioic acid, compounded with (1 S)-(3 R)-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]oct-3-yl 3,4-dihydro-1-phenyl-2(1 H)-iso-quinolinecarboxylate (1:1) having an empirical formula of C 23H 26N 2O 2•C 4H 6O 4, and a molecular weight of 480.55. The structural formula of solifenacin succinate is:
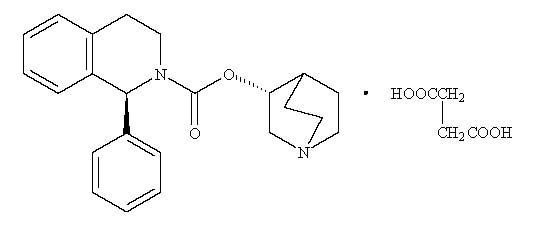
Solifenacin succinate is a white to light yellow powder. It is freely soluble at room temperature in water, and ethanol.
Each solifenacin succinate tablet contains 5 mg or 10 mg of solifenacin succinate and is for oral administration. In addition to the active ingredient solifenacin succinate, each solifenacin succinate tablet also contains the following inactive ingredients: corn starch, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, and titanium dioxide with yellow ferric oxide (5 mg solifenacin succinate tablet) or red ferric oxide (10 mg solifenacin succinate tablet).
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Solifenacin is a competitive muscarinic receptor antagonist. Muscarinic receptors play an important role in several major cholinergically mediated functions, including contractions of urinary bladder smooth muscle.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of 10 mg and 30 mg solifenacin succinate (three times the maximum recommended dose) on the QT interval was evaluated at the time of peak plasma concentration of solifenacin in a multi-dose, randomized, double-blind, placebo and positive-controlled (moxifloxacin 400 mg) trial [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]. After receiving placebo and moxifloxacin sequentially, subjects were randomized to one of two treatment groups. One group (n=51) completed 3 additional sequential periods of dosing with solifenacin succinate 10 mg, 20 mg, and 30 mg while the second group (n=25) in parallel completed a sequence of placebo and moxifloxacin. Study subjects were female volunteers aged 19 to 79 years. The 30 mg dose of solifenacin succinate (three times the highest recommended dose) was chosen for use in this study because this dose results in a solifenacin exposure that covers those observed upon coadministration of 10 mg solifenacin succinate with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, 400 mg). Due to the sequential dose escalating nature of the study, baseline ECG measurements were separated from the final QT assessment (of the 30 mg dose level) by 33 days.
The median difference from baseline in heart rate associated with the 10 and 30 mg doses of solifenacin succinate compared to placebo was -2 and 0 beats/minute, respectively. Because a significant period effect on QTc was observed, the QTc effects were analyzed utilizing the parallel placebo control arm rather than the pre-specified intra-patient analysis. Representative results are shown in Table 2.
| Drug/Dose | Fridericia method
(using mean difference) |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Results displayed are those derived from the parallel design portion of the study and represent the comparison of Group 1 to time-matched placebo effects in Group 2. | |||||||||
|
Solifenacin succinate 10 mg |
2 (-3,6) |
||||||||
|
Solifenacin succinate 30 mg |
8 (4,13) |
||||||||
Moxifloxacin was included as a positive control in this study and, given the length of the study, its effect on the QT interval was evaluated in 3 different sessions. The placebo-subtracted mean changes (90% CI) in QTcF for moxifloxacin in the three sessions were 11 (7, 14), 12 (8, 17), and 16 (12, 21), respectively.
The QT interval prolonging effect of the highest solifenacin succinate dose (three times the maximum therapeutic dose) studied was not as large as that of the positive control moxifloxacin at its recommended dose. However, the confidence intervals overlapped, and this study was not designed to draw direct statistical conclusions between the drugs or the dose levels.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
After oral administration of solifenacin succinate in healthy volunteers, peak plasma concentrations (C
max) of solifenacin were reached within 3 to 8 hours after administration and, at steady-state, ranged from 32.3 ng/mL to 62.9 ng/mL for the 5 mg and 10 mg solifenacin succinate tablets, respectively. The absolute bioavailability of solifenacin is approximately 90%, with plasma concentrations of solifenacin proportional to the dose administered.
Effect of Food
Solifenacin succinate may be administered without regard to meals. A single 10 mg dose administration of solifenacin succinate with food increased C
max and AUC of solifenacin by 4% and 3%, respectively.
Distribution
Solifenacin is approximately 98% (
in vivo) bound to human plasma proteins, principally to ∝
1-acid glycoprotein. Solifenacin is highly distributed to non-CNS tissues, having a mean steady-state volume of distribution of 600 L.
Elimination
The elimination half-life (t
1/2) of solifenacin following chronic dosing is approximately 45 to 68 hours.
Metabolism
Solifenacin is extensively metabolized in the liver. The primary pathway for elimination is by way of CYP3A4; however, alternate metabolic pathways exist. The primary metabolic routes of solifenacin are through N-oxidation of the quinuclidin ring and 4R-hydroxylation of the tetrahydroisoquinoline ring. One pharmacologically active metabolite (4R-hydroxy solifenacin), occurring at low concentrations and unlikely to contribute significantly to clinical activity, and three pharmacologically inactive metabolites (N-glucuronide and the N-oxide and 4R-hydroxy-N-oxide of solifenacin) have been found in human plasma after oral dosing.
Excretion
Following the administration of 10 mg of
14C-solifenacin succinate to healthy volunteers, 69% of the radioactivity was recovered in the urine and 23% in the feces over 26 days. Less than 15% (as mean value) of the dose was recovered in the urine as intact solifenacin. The major metabolites identified in urine were N-oxide of solifenacin, 4R-hydroxy solifenacin, and 4R-hydroxy-N-oxide of solifenacin and, in feces, 4R-hydroxy solifenacin.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients
Multiple dose studies of solifenacin succinate in geriatric volunteers (65 to 80 years) showed that C
max, AUC and t
1/2 values of solifenacin were 20 to 25% higher compared to the younger adult volunteers (18 to 55 years).
[see
Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Patients with Renal Impairment
In studies with solifenacin succinate 10 mg, there was a 2.1-fold increase in AUC and a 1.6-fold increase in t
1/2 of solifenacin in patients with severe renal impairment compared to subjects with normal renal function
[see
Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
In studies with solifenacin succinate 10 mg, there was a 2-fold increase in the t
1/2 and a 35% increase in AUC of solifenacin in patients with moderate hepatic impairment compared to subjects with normal hepatic function
[see
Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
Solifenacin succinate has not been studied in patients with severe hepatic impairment.
Drug Interaction Studies
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
In a crossover study, following blockade of CYP3A4 by coadministration of the strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, ketoconazole 400 mg once daily for 21 days, the mean C
max and AUC of solifenacin increased by 1.5 and 2.7-fold, respectively
[see
Dosage and Administration (2.4) and
Drug Interactions (7.1)].
CYP3A4 Inducers
Because solifenacin is a substrate of CYP3A4, inducers of CYP3A4 may decrease the concentration of solifenacin.
Warfarin
In a crossover study, subjects received a single oral dose of warfarin 25 mg on the 10 th day of dosing with either solifenacin succinate 10 mg or matching placebo once daily for 16 days. For R-warfarin, when it was coadministered with solifenacin succinate, the mean C max increased by 3% and AUC decreased by 2%. For S-warfarin, when it was coadministered with solifenacin succinate, the mean C max and AUC increased by 5% and 1%, respectively.
Oral Contraceptives
In a crossover study, subjects received 2 cycles of 21 days of oral contraceptives containing 30 mcg ethinyl estradiol and 150 mcg levonorgestrel. During the second cycle, subjects received additional solifenacin succinate 10 mg or matching placebo once daily for 10 days starting from the 12 th day of receipt of oral contraceptives. For ethinyl estradiol, when it was administered with solifenacin succinate, the mean C max and AUC increased by 2% and 3%, respectively. For levonorgestrel, when it was administered with solifenacin succinate, the mean C max and AUC decreased by 1%.
Digoxin
In a crossover study, subjects received digoxin (loading dose of 0.25 mg on day 1, followed by 0.125 mg from days 2 to 8) for 8 days. Consecutively, they received solifenacin succinate 10 mg or matching placebo with digoxin 0.125 mg for an additional 10 days. When digoxin was coadministered with solifenacin succinate, the mean C max and AUC increased by 13% and 4%, respectively.
Drugs Metabolized by Cytochrome P450 Enzymes
In vitro studies demonstrated that, at therapeutic concentrations, solifenacin does not inhibit CYP1A1/2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6, or 3A4 derived from human liver microsomes.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No increase in tumors was found following the administration of solifenacin succinate to male and female mice for 104 weeks at doses up to 200 mg/kg/day (5 and 9 times, respectively, of the exposure at the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] of 10 mg), and male and female rats for 104 weeks at doses up to 20 and 15 mg/kg/day, respectively (< 1 times the exposure at the MRHD).
Solifenacin succinate was not mutagenic in the in vitro Salmonella typhimurium or Escherichia coli microbial mutagenicity test or chromosomal aberration test in human peripheral blood lymphocytes with or without metabolic activation or in the in vivo micronucleus test in rats.
Solifenacin succinate had no effect on reproductive function, fertility, or early embryonic development of the fetus in male and female mice treated with 250 mg/kg/day (13 times the exposure at the MRHD) of solifenacin succinate, and in male rats treated with 50 mg/kg/day (< 1 times the exposure at the MRHD) and female rats treated with 100 mg/kg/day (1.7 times the exposure at the MRHD) of solifenacin succinate.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Juvenile Animal Toxicology Data
Dose-related increased mortality without preceding clinical signs occurred in juvenile mice treated before weaning for a duration of 12 weeks, from day 10 after birth, with doses that achieved a pharmacological effect. Animals dosed from postnatal day 10 onwards had higher mortality compared to the mortality in adult mice. No increased frequency in mortality was observed in juvenile mice that were treated after weaning for a duration of 4 weeks, from day 21 after birth onwards. Plasma exposure at postnatal day 10 was higher than in adult mice; the systemic exposure at postnatal day 21 was comparable to the systemic exposure in adult mice.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Solifenacin succinate was evaluated in four twelve-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel group, multicenter clinical trials for the treatment of overactive bladder in adult patients having symptoms of urinary frequency, urgency, and/or urge or mixed incontinence (with a predominance of urge). Entry criteria required that patients have symptoms of overactive bladder for ≥ 3 months duration. These studies involved 3027 patients (1811 on solifenacin succinate and 1216 on placebo), and approximately 90% of these patients completed the 12-week studies. Two of the four studies evaluated the 5 mg and 10 mg solifenacin succinate doses (Studies 1 and 2) and the other two evaluated only the 10 mg dose (Studies 3 and 4). All patients completing the 12-week studies were eligible to enter an open-label, long-term extension study (Study 5) and 81% of patients enrolling completed the additional 40-week treatment period. The majority of patients were Caucasian (93%) and female (80%) with a mean age of 58 years.
The primary endpoint in all four trials was the mean change from baseline to 12 weeks in number of micturitions/24 hours. Secondary endpoints included mean change from baseline to 12 weeks in number of incontinence episodes/24 hours, and mean volume voided per micturition.
The efficacy of solifenacin succinate was similar across patient age groups and gender. The mean reduction in the number of micturitions per 24 hours was significantly greater with solifenacin succinate 5 mg (2.3; p < 0.001) and solifenacin succinate 10 mg (2.7; p < 0.001) compared to placebo (1.4). The mean reduction in the number of incontinence episodes per 24 hours was significantly greater with solifenacin succinate 5 mg (1.5; p < 0.001) and solifenacin succinate 10 mg (1.8; p < 0.001) treatment groups compared to the placebo treatment group (1.1). The mean increase in the volume voided per micturition was significantly greater with solifenacin succinate 5 mg (32.3 mL; p < 0.001) and solifenacin succinate 10 mg (42.5 mL; p < 0.001) compared with placebo (8.5 mL).
The results for the primary and secondary endpoints in the four individual 12-week clinical studies of solifenacin succinate are reported in Tables 3 through 6.
| Parameter | Placebo
(N=253) Mean (SE) | Solifenacin
succinate 5 mg (N=266) Mean (SE) | Solifenacin
succinate 10 mg (N=264) Mean (SE) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Primary endpoint | |||||||||
| 2. Secondary endpoint | |||||||||
|
Urinary Frequency (Number of
| |||||||||
|
Baseline Reduction P value vs. placebo |
12.2 (0.26) 1.2 (0.21) |
12.1 (0.24) 2.2 (0.18) < 0.001 |
12.3 (0.24) 2.6 (0.20) < 0.001 |
||||||
|
Number of Incontinence
| |||||||||
|
Baseline Reduction P value vs. placebo |
2.7 (0.23) 0.8 (0.18) |
2.6 (0.22) 1.4 (0.15) < 0.01 |
2.6 (0.23) 1.5 (0.18) < 0.01 |
||||||
|
Volume Voided per Micturition [mL] 2 | |||||||||
|
Baseline Increase P value vs. placebo |
143.8 (3.37) 7.4 (2.28) |
149.6 (3.35) 32.9 (2.92) < 0.001 |
147.2 (3.15) 39.2 (3.11) < 0.001 |
||||||
| Parameter | Placebo
(N=281) Mean (SE) | Solifenacin
succinate 5 mg (N=286) Mean (SE) | Solifenacin
succinate 10 mg (N=290) Mean (SE) |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Primary endpoint | |||||||||
| 2. Secondary endpoint | |||||||||
|
Urinary Frequency (Number of
| |||||||||
|
Baseline Reduction P value vs. placebo |
12.3 (0.23) 1.7 (0.19) |
12.1 (0.23) 2.4 (0.17) < 0.001 |
12.1 (0.21) 2.9 (0.18) < 0.001 |
||||||
|
Number of Incontinence Episodes/24 hours 2 | |||||||||
|
Baseline Reduction P value vs. placebo |
3.2 (0.24) 1.3 (0.19) |
2.6 (0.18) 1.6 (0.16) < 0.01 |
2.8 (0.20) 1.6 (0.18) 0.016 |
||||||
|
Volume Voided per Micturition [mL] 2 | |||||||||
|
Baseline Increase P value vs. placebo |
147.2 (3.18) 11.3 (2.52) |
148.5 (3.16) 31.8 (2.94) < 0.001 |
145.9 (3.42) 36.6 (3.04) < 0.001 |
||||||
| Parameter | Placebo
(N=309) Mean (SE) | Solifenacin succinate
10 mg (N=306) Mean (SE) |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Primary endpoint | |||||||||
| 2. Secondary endpoint | |||||||||
|
Urinary Frequency (Number of Micturitions/24 hours) 1 | |||||||||
|
Baseline Reduction P Value vs. placebo |
11.5 (0.18) 1.5 (0.15) |
11.7 (0.18) 3.0 (0.15) < 0. 001 |
|||||||
|
Number of Incontinence Episodes/24 hours 2 | |||||||||
|
Baseline Reduction P value vs. placebo |
3.0 (0.20) 1.1 (0.16) |
3.1 (0.22) 2.0 (0.19) < 0.001 |
|||||||
|
Volume Voided per Micturition [mL] 2 | |||||||||
|
Baseline Increase P value vs. placebo |
190.3 (5.48) 2.7 (3.15) |
183.5 (4.97) 47.2 (3.79) < 0.001 |
|||||||
| Parameter | Placebo
(N=295) Mean (SE) | Solifenacin
succinate 10 mg (N=298) Mean (SE) |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Primary endpoint | |||||||||
| 2. Secondary endpoint | |||||||||
|
Urinary Frequency (Number of Micturitions/24 hours) 1 | |||||||||
|
Baseline Reduction P value vs. placebo |
11.8 (0.18) 1.3 (0.16) |
11.5 (0.18) 2.4 (0.15) < 0. 001 |
|||||||
|
Number of Incontinence Episodes/24 hours 2 | |||||||||
|
Baseline Reduction P value vs. placebo |
2.9 (0.18) 1.2 (0.15) |
2.9 (0.17) 2.0 (0.15) < 0.001 |
|||||||
|
Volume Voided per Micturition [mL] 2 | |||||||||
|
Baseline Increase P value vs. placebo |
175.7 (4.44) 13.0 (3.45) |
174.1 (4.15) 46.4 (3.73) < 0.001 |
|||||||
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
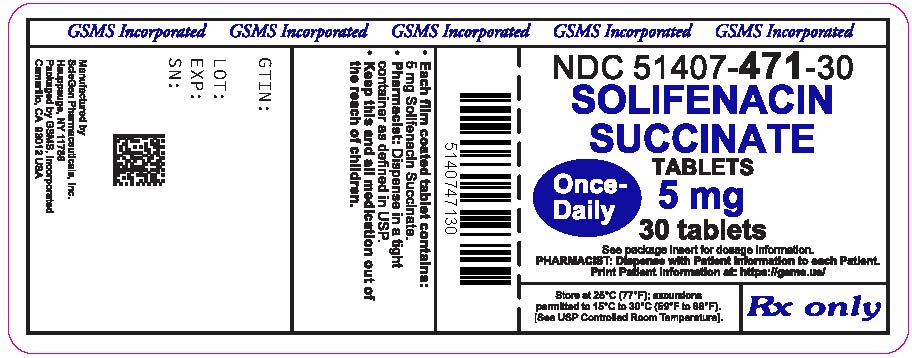
Solifenacin succinate tablets, 5 mg, are light yellow, round, film coated tablets debossed with 'SG' on one side and '427' on other side. They are supplied as follows:
NDC 51407-471-30 bottles of 30
NDC 51407-471-90 bottles of 90
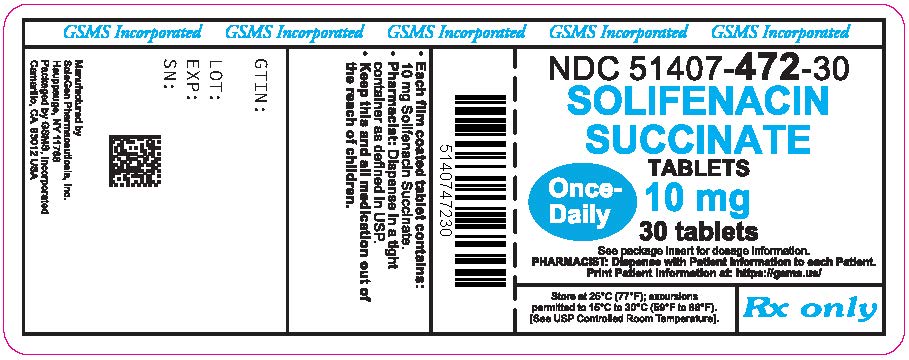
Solifenacin succinate tablets, 10 mg, are light pink, round, film coated tablets debossed with 'SG' on one side and '428' on other side. They are supplied as follows:
NDC 51407-472-30 bottles of 30
NDC 51407-472-90 bottles of 90
Store at 25°C (77°F) with excursions permitted from 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Angioedema and Anaphylactic Reactions
Inform patients that angioedema and anaphylactic reactions have been reported in patients treated with solifenacin succinate. Angioedema and anaphylactic reactions may be life-threatening. Advise patients to promptly discontinue solifenacin succinate therapy and seek immediate attention if they experience edema of the tongue or laryngopharynx, or difficulty breathing [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Urinary Retention
Inform patients that solifenacin succinate may cause urinary retention in patients with conditions associated with bladder outlet obstruction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Gastrointestinal Disorders
Inform patients that solifenacin succinate may cause further decrease in gastrointestinal motility in patients with conditions associated with decreased gastrointestinal motility. Solifenacin succinate has been associated with constipation and dry mouth. Advise patients to contact their health care providers if they experience severe abdominal pain or become constipated for 3 or more days [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Central Nervous System Effects
Because solifenacin succinate, like other antimuscarinic agents, may cause central nervous system effects or blurred vision, advise patients to exercise caution in decisions to engage in potentially dangerous activities until the drug’s effect on the patient has been determined [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Narrow-Angle Glaucoma
Inform patients that solifenacin succinate, like other antimuscarinics, may cause worsening of the glaucoma condition in patients with narrow-angle glaucoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Dry Skin
Inform patients that solifenacin succinate, like other antimuscarinics, may cause dry skin due to decreased sweating. Heat prostration due to decreased sweating can occur when solifenacin succinate is used in a hot environment [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Manufactured by:
ScieGen Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Hauppauge, NY 11788
Rev. 1/2021
Marketed/Packaged by:
GSMS, Inc.
Camarillo, CA USA 93012
| Patient Information
Solifenacin succinate tablet (SOE-li-FEN-a-sin SUX-i-nate) |
|
| Read the Patient Information that comes with solifenacin succinate before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This leaflet does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or treatment. | |
| What is solifenacin succinate?
Solifenacin succinate is a prescription medicine for adults used to treat the following symptoms due to a condition called overactive bladder:
Solifenacin succinate 5 mg and 10 mg tablets are not approved for use in children. |
|
| Who should not take solifenacin succinate?
Do nottake solifenacin succinate if you:
|
|
| What should I tell my doctor before taking solifenacin succinate?
Before you take solifenacin succinate, tell your doctor if you:
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Solifenacin succinate may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how solifenacin succinate works. |
|
How should I take solifenacin succinate?
|
|
| What should I avoid while taking solifenacin succinate?
Solifenacin succinate can cause blurred vision or drowsiness. Do not drive or operate heavy machinery until you know how solifenacin succinate affects you. |
|
| What are the possible side effects of solifenacin succinate?
The most common side effects of solifenacin succinate include:
Other side effects have been observed with anticholinergic drugs such as solifenacin succinate and may include: dry skin due to decreased sweating. Heat exhaustion or heat stroke can happen due to decreased sweating when solifenacin succinate is used in hot environments. Symptoms may include:
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all the possible side effects of solifenacin succinate. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
|
|
How should I store solifenacin succinate?
Keep solifenacin succinate and all medicines out of the reach of children. |
|
|
General information about the safe and effective use of solifenacin succinate Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in Patient Information leaflets. Do not use solifenacin succinate for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give solifenacin succinate to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
|
|
|
What are the ingredients in solifenacin succinate? Active ingredient: solifenacin succinate Inactive ingredients: corn starch, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, polyethylene glycol, and titanium dioxide with yellow ferric oxide (5 mg solifenacin succinate tablet) or red ferric oxide (10 mg solifenacin succinate tablet). |
|
| What is overactive bladder?
Overactive bladder occurs when you cannot control your bladder contractions. When these muscle contractions happen too often or cannot be controlled you can get symptoms of overactive bladder, which are urinary frequency, urinary urgency, and urinary incontinence (leakage).
Manufactured by:
Marketed/Packaged by:
Camarillo, CA USA 93012 |