DESCRIPTION
Leucovorin Calcium Tablets contain either 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg or 25 mg leucovorin as the calcium salt of N-[4-[[(2-amino-5-formyl-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-4-oxo-6-pteridinyl)methyl]amino]benzoyl]-L- glutamic acid and the inactive ingredients Colloidal Silicon Dioxide, Croscarmellose Sodium, Magnesium Stearate, Microcrystalline Cellulose and Pregelatinized Starch. This is equivalent to 5.4 mg, 10.8 mg, 16.21 mg or 27.01 mg of anhydrous leucovorin calcium.
Leucovorin is a water soluble form of reduced folate in the folate group; it is useful as an antidote to drugs which act as folic acid antagonists. These tablets are intended for oral administration only. The structural formula of leucovorin calcium is:
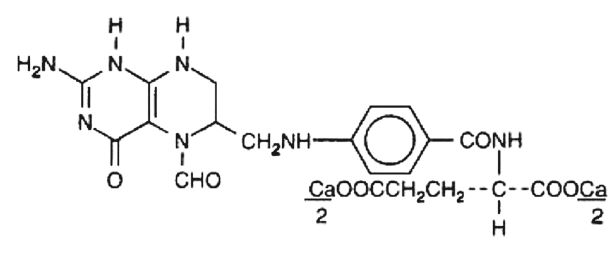
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Leucovorin is a racemic mixture of the diastereoisomers of the 5-formyl derivative of tetrahydrofolic acid. The biologically active compound of the mixture is the (-)-L-isomer, known as Citrovorum factor, or (-)-folinic acid. Leucovorin does not require reduction by the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase in order to participate in reactions utilizing folates as a source of “one-carbon” moieties. Following oral administration, leucovorin is rapidly absorbed and enters the general body pool of reduced folates. The increase in plasma and serum folate activity (determined microbiologically with Lactobacillus casei) seen after oral administration of leucovorin is predominantly due to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate.
Twenty normal men were given a single, oral 15-mg dose (7.5 mg/m2) of leucovorin calcium and serum folate concentrations were assayed with L. casei. Mean values observed (± one standard error) were:
a) Time to peak serum folate concentration: 1.72 ± 0.08 hours,
b) Peak serum folate concentration achieved: 268 ± 18 ng/mL,
c) Serum folate half-disappearance time: 3.5 hours.
Oral tablets yielded areas under the serum folate concentration-time curves (AUCs) that were 12% greater than equal amounts of leucovorin given intramuscularly and equal to the same amounts given intravenously.
Oral absorption of leucovorin is saturable at doses above 25 mg. The apparent bioavailability of leucovorin was 97% for 25 mg, 75% for 50 mg and 37% for 100 mg.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Leucovorin Calcium Tablets are indicated to diminish the toxicity and counteract the effects of impaired methotrexate elimination and of inadvertent overdosages of folic acid antagonists.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Leucovorin is improper therapy for pernicious anemia and other megaloblastic anemias secondary to the lack of vitamin B12. A hematologic remission may occur while neurologic manifestations continue to progress.
WARNINGS
In the treatment of accidental overdosage of folic acid antagonists, leucovorin should be administered as promptly as possible. As the time interval between antifolate administration (e.g., methotrexate [MTX]) and leucovorin rescue increases, leucovorin’s effectiveness in counteracting hematologic toxicity decreases.
Monitoring of the serum MTX concentration is essential in determining the optimal dose and duration of treatment with leucovorin.
Delayed MTX excretion may be caused by a third space fluid accumulation (i.e., ascites, pleural effusion), renal insufficiency, or inadequate hydration. Under such circumstances, higher doses of leucovorin or prolonged administration may be indicated. Doses higher than those recommended for oral use must be given intravenously.
Leucovorin may enhance the toxicity of fluorouracil. Deaths from severe enterocolitis, diarrhea, and dehydration have been reported in elderly patients receiving weekly leucovorin and fluorouracil.1 Concomitant granulocytopenia and fever were present in some but not all of the patients.
The concomitant use of leucovorin with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for the acute treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in patients with HIV infection was associated with increased rates of treatment failure and mortality in a placebo-controlled study.
PRECAUTIONS
General
Parenteral administration is preferable to oral dosing if there is a possibility that the patient may vomit or not absorb the leucovorin. Leucovorin has no effect on other established toxicities of MTX, such as the nephrotoxicity resulting from drug and/or metabolite precipitation in the kidney.
Drug Interactions
Folic acid in large amounts may counteract the antiepileptic effect of phenobarbital, phenytoin, and primidone, and increase the frequency of seizures in susceptible pediatric patients.
Preliminary animal and human studies have shown that small quantities of systemically administered leucovorin enter the CSF primarily as 5-methyltetrahydrofolate and, in humans, remain one to three orders of magnitude lower than the usual MTX concentrations following intrathecal administration.
However, high doses of leucovorin may reduce the efficacy of intrathecally administered MTX.
Leucovorin may enhance the toxicity of fluorouracil (see WARNINGS).
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with leucovorin. It is also not known whether leucovorin can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Leucovorin should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
CALL YOUR DOCTOR FOR MEDICAL ADVICE ABOUT SIDE EFFECTS. YOU MAY REPORT SIDE EFFECTS TO THE FDA AT 1-800-FDA-1088 OR LEADING PHARMA, LLC AT 1-844-740-7500.
Allergic sensitization has been reported following both oral and parenteral administration of folic acid.
OVERDOSAGE
Excessive amounts of leucovorin may nullify the chemotherapeutic effect of folic acid antagonists.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Leucovorin calcium tablets are intended for oral administration. Because absorption is saturable, oral administration of doses greater than 25 mg is not recommended.
Impaired Methotrexate Elimination or Inadvertent Overdosage
Leucovorin rescue should begin as soon as possible after an inadvertent overdosage and within 24 hours of methotrexate administration when there is delayed excretion (see WARNINGS). Leucovorin 15 mg (10 mg/m2) should be administered I.M., I.V., or P.O. every 6 hours until the serum methotrexate level is less than 10-8M. In the presence of gastrointestinal toxicity, nausea, or vomiting, leucovorin should be administered parenterally.
Serum creatinine and methotrexate levels should be determined at 24-hour intervals. If the 24-hour serum creatinine has increased 50% over baseline or if the 24-hour methotrexate level is greater than 5 x 10-6M or the 48-hour level is greater than 9 x 10-7M, the dose of leucovorin should be increased to 150 mg (100 mg/m2) I.V. every 3 hours until the methotrexate level is less than 10-8M. Doses greater than 25 mg should be given parenterally (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Hydration (3 L/d) and urinary alkalinization with sodium bicarbonate should be employed concomitantly. The bicarbonate dose should be adjusted to maintain the urine pH at 7.0 or greater.
The recommended dose of leucovorin to counteract hematologic toxicity from folic acid antagonists with less affinity for mammalian dihydrofolate reductase than methotrexate (i.e., trimethoprim, pyrimethamine) is substantially less, and 5 to 15 mg of leucovorin per day has been recommended by some investigators.
Patients who experience delayed early methotrexate elimination are likely to develop reversible non-oliguric renal failure. In addition to appropriate leucovorin therapy, these patients require continuing hydration and urinary alkalinization, and close monitoring of fluid and electrolyte status, until the serum methotrexate level has fallen below 0.05 micromolar and the renal failure has resolved.
Some patients will have abnormalities in methotrexate elimination or renal function following methotrexate administration, which are significant but less severe. These abnormalities may or may not be associated with significant clinical toxicity. If significant clinical toxicity is observed, leucovorin rescue should be extended for an additional 24 hours (total 14 doses over 84 hours) in subsequent courses of therapy. The possibility that the patient is taking other medications which interact with methotrexate (e.g., medications which may interfere with methotrexate elimination or binding to serum albumin) should always be reconsidered when laboratory abnormalities or clinical toxicities are observed.
HOW SUPPLIED
Leucovorin Calcium Tablets USP
5 mg tablets are supplied as a white to off-white to pale yellow, round tablet; scored on one side and "LP" over "184" debossed on the other side; bottles of 30 (NDC 69315-184-03) and 100 (NDC 69315-184-01).
10 mg tablets are supplied as a white to off-white to pale yellow, round tablet; scored on one side and "LP" over "185" debossed on the other side; bottles of 12 (NDC 69315-185-12) and 24 (NDC 69315-185-24).
15 mg tablets are supplied as a white to off-white to pale yellow, round tablet; scored on one side and "LP" over " 186" debossed on the other side; bottles of 24 (NDC 69315-186-24).
25 mg tablets are supplied as a white to off-white to pale yellow, round tablet; scored on one side and "LP" over " 187" debossed on the other side; bottles of 25 (NDC 69315-187-25).
Store at 15° to 25°C (59° to 77°F). Protect from light and moisture.
REFERENCES
- Grem JL, Shoemaker DD, Petrelli NJ, Douglas HO Jr. Severe and fatal toxic effects observed in treatment with high- and low-dose leucovorin plus 5-fluorouracil for colorectal carcinoma. Cancer Treat Rep.1987;71:1122.
- Link MP, Goorin AM, Miser AW et al. The effect of adjuvant chemotherapy on relapse-free survival in patients with osteosarcoma of the extremity. N Engl J Med.1986;314:1600-1606.
Rx only
Manufactured and Distributed by:
Leading Pharma, LLC
Fairfield, NJ 07004, USA
Rev.02 11/21





