FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: CIGARETTE SMOKING AND SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR EVENTS
Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular events from combined hormonal contraceptive (CHC) use. This risk increases with age, particularly in females over 35 years of age, and with the number of cigarettes smoked. For this reason, CHCs, including NEXTSTELLIS, are contraindicated in females who are over 35 years of age and smoke. [See Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
NEXTSTELLIS is indicated for use by females of reproductive potential to prevent pregnancy.
Limitations of Use
NEXTSTELLIS may be less effective in females with a BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2. In females with BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2, decreasing effectiveness may be associated with increasing BMI [see Clinical Studies (14)].
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage and Administration
Start NEXTSTELLIS using a Day 1 start. Take one tablet by mouth at the same time every day with or without food.
2.2 Additional Administration Information
To achieve maximum contraceptive effectiveness, take one tablet every day at about the same time each day. The recommended dosage of NEXTSTELLIS is one tablet daily for 28 consecutive days: one pink active tablet daily during the first 24 days followed by one white inactive tablet daily during the 4 following days (see Table 1).
| Starting NEXTSTELLIS in females with no current use of hormonal contraception | Important:
|
| Switching to NEXTSTELLIS from another contraceptive method | Start NEXTSTELLIS on the day: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Starting NEXTSTELLIS after delivery (>20 weeks gestation) | Must not start earlier than 4 weeks after delivery (due to the increased risk of thromboembolism [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
If menstrual cycles have returned, follow instructions for "Starting NEXTSTELLIS in females with no current use of hormonal contraception". If menstrual cycles have not resumed, consider the possibility of ovulation and pregnancy. If not pregnant, use additional nonhormonal contraception for the first 7 days of NEXTSTELLIS use. |
Starting NEXTSTELLIS after Abortion or Miscarriage
| Within the first 7 days of complete first trimester abortion or miscarriage, use additional nonhormonal contraception for the next 7 days. After the first 7 days, follow instructions for "Starting NEXTSTELLIS in females with no current use of hormonal contraception". |
| After 4 weeks following second trimester abortion or miscarriage. Consider duration of pregnancy and increased risk of thromboembolism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
If menstrual cycles have returned, follow instructions for "Starting NEXTSTELLIS in females with no current use of hormonal contraception." If menstrual cycles have not resumed, consider the possibility of ovulation and pregnancy. If not pregnant, use additional nonhormonal contraception for the first 7 days of NEXTSTELLIS use. |
2.3 Missed Doses
| Take the missed tablet as soon as possible and take the next tablet at the scheduled time, even if two active tablets are taken in one day. Continue taking one tablet a day until the pack is finished. |
| Take one missed tablet as soon as possible and take the tablet for the current day (that means taking two tablets in one day) and discard the other missed tablets. Continue taking one tablet a day until the pack is finished. Use additional non-hormonal contraception as back-up until pink tablets have been taken for 7 consecutive days. |
| Take one missed tablet as soon as possible and take the tablet for the current day (that means taking two tablets in one day) and discard the other missed tablets. Finish the active tablets and discard the inactive tablets in the pack. Start a new pack of tablets the next day. Use additional non-hormonal contraception as back-up until pink tablets have been taken for 7 consecutive days. |
| Skip the missed pill days and continue taking one tablet a day until the pack is finished. |
2.4 Administration Recommendations after Vomiting or Acute Diarrhea
If vomiting or acute diarrhea occurs within 3 to 4 hours after taking an active tablet, take the new active tablet (scheduled for the next day) as soon as possible. Take the new tablet within 12 hours of the usual time of tablet-taking if possible. If more than two tablets are missed, follow the advice concerning missed tablets, including using backup non-hormonal contraception. For additional recommendations, refer to the table above [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
NEXTSTELLIS (drospirenone and estetrol tablets) is available in a blister card, with 28 6-mm round, bi-convex film-coated tablets in the following order:
- 24 pink active tablets containing 3 mg drospirenone and 14.2 mg estetrol embossed with a drop-shaped logo on one side.
- 4 white inert tablets embossed with a drop-shaped logo on one side.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
NEXTSTELLIS is contraindicated in females who are known to have or develop the following conditions:
- A history of, increased risk for, or current arterial or venous thrombotic/thromboembolic diseases. Examples include females who are known to:
- -
- Smoke, if 35 years of age and older [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- -
- Have current or history of deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- -
- Have cerebrovascular disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- -
- Have coronary artery disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- -
- Have thrombogenic valvular or thrombogenic rhythm diseases of the heart (for example, subacute bacterial endocarditis with valvular disease, or atrial fibrillation) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- -
- Have inherited or acquired hypercoagulopathies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- -
- Have uncontrolled hypertension or hypertension with vascular disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- -
- Have diabetes mellitus with hypertension or end-organ damage; or diabetes mellitus of > 20 years duration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- -
- Have migraine headaches with aura [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Current diagnosis of, or history of, breast cancer, which may be hormone-sensitive [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Hepatic adenoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, acute hepatitis, or severe (decompensated) cirrhosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Use of hepatitis C drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, due to the potential for ALT elevations [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Abnormal uterine bleeding that has an undiagnosed etiology [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Renal Impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Adrenal insufficiency [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Thromboembolic Disorders and Other Vascular Problems
- Stop NEXTSTELLIS if an arterial or venous thrombotic/thromboembolic event occurs.
- Stop NEXTSTELLIS if there is unexplained loss of vision, proptosis, diplopia, papilledema, or retinal vascular lesions and evaluate for retinal vein thrombosis immediately.
- Discontinue NEXTSTELLIS during prolonged immobilization.
- Start NEXTSTELLIS no earlier than four weeks after delivery in females who are not breast feeding. The risk of postpartum thromboembolism decreases after the third postpartum week, whereas the likelihood of ovulation increases after the third postpartum week.
Before starting NEXTSTELLIS, evaluate any past medical history or family history of thrombotic or thromboembolic disorders and consider whether the history suggests an inherited or acquired hypercoagulopathy. NEXTSTELLIS is contraindicated in females with a high risk of arterial or venous thrombotic/thromboembolic diseases [see Contraindications (4)].
Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Events
Use of CHCs increases the risk of cardiovascular events and cerebrovascular events, such as myocardial infarction and stroke. The risk is greater among females over age 40, smokers, and females with hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, or obesity. The risk increases with age, particularly in females 35 years of age and older, and with the number of cigarettes smoked. In addition to cigarettes, use of other nicotine-containing products – including cigars, smokeless tobacco, hookah tobacco, e-cigarettes, and nicotine replacement therapy – may also increase the risk of serious cardiovascular events from CHC use.
Venous Thromboembolism
Use of CHCs also increases the risk of venous thromboembolic events (VTEs), such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. The rate of VTE in females using COCs has been estimated to be 3 to 9 cases per 10,000 woman-years and should be considered in the context of other female of reproductive potential subpopulations who are not taking CHCs [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Risk factors for VTEs include smoking, obesity, family history of VTE, and prolonged immobilization in addition to other factors that contraindicate use of CHCs [see Contraindications (4)]. The presence of multiple risk factors for VTE may increase the risk synergistically. The risk of VTE is highest during the first year of CHC use and when restarting hormonal contraception after a break of four weeks or longer. The risk of VTE returns to baseline approximately 3 months after CHC use is discontinued.
Postpartum Venous Thromboembolism
The risk of VTE is increased during the first six weeks postpartum compared to the risk in non-pregnant, non-postpartum females. The risk is highest in the first three weeks postpartum, but remains higher than baseline until at least six weeks postpartum. The presence of multiple risk factors for VTE may further increase the risk. Obstetric complications may extend the elevated risk up to 12 weeks postpartum.
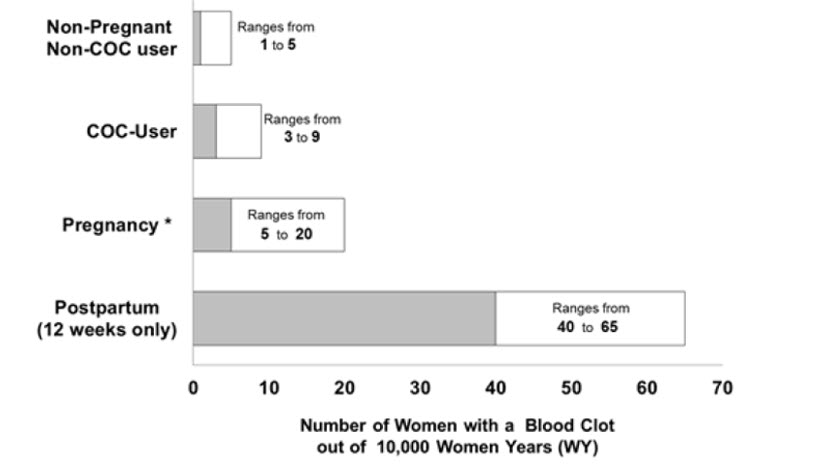
Figure 1 shows the risk of developing a VTE for females who are not pregnant and do not use COCs, for females who use COCs, for pregnant females, and for females in the postpartum period. To put the risk of developing a VTE into perspective: if 10,000 females who are not pregnant and do not use oral contraceptives are followed for one year, between 1 and 5 of these females will develop a VTE.
Figure 1 Likelihood of Developing a VTE
Two prospective studies of NEXTSTELLIS have been conducted, one in Europe/Russia (NCT02817828; C301) and one in North America (NCT02817841; C302) (N=3,632), for the prevention of pregnancy in females 16-50 years of age. There was one reported VTE in the Europe/Russia study [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.2 Hyperkalemia
NEXTSTELLIS is contraindicated in females with conditions that predispose to hyperkalemia (e.g., renal impairment, hepatic impairment, and adrenal insufficiency). Females receiving daily, long-term treatment for chronic conditions or diseases with medications that may increase serum potassium concentration should have their serum potassium concentration checked during the first treatment cycle. Monitor serum potassium concentration in females at increased risk for hyperkalemia (i.e., those females who take a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor long-term and concomitantly with NEXTSTELLIS). [see Drug interactions (7)]. Monitor females taking NEXTSTELLIS who later develop medical conditions and/or begin medication that put them at an increased risk for hyperkalemia.
NEXTSTELLIS contains drospirenone, a progestin, which has anti-mineralocorticoid activity, including the potential for hyperkalemia in high-risk females, comparable to a 25 mg dose of spironolactone. In two Phase 3 trials of NEXTSTELLIS (N = 3,632) for the prevention of pregnancy in females 16-50 years of age, seven subjects were noted to have hyperkalemia and one subject discontinued due to elevated potassium levels. Most females who developed hyperkalemia in the clinical development studies of NEXTSTELLIS had only mild potassium elevations and/or isolated increases that returned to normal while still on study medication.
5.3 Hypertension
NEXTSTELLIS is contraindicated in females with uncontrolled hypertension or hypertension with vascular disease [see Contraindications (4)]. For all females, including those with well-controlled hypertension, monitor blood pressure periodically and stop NEXTSTELLIS if blood pressure rises significantly.
An increase in blood pressure has been reported in females using COCs. This increase is more likely in older females with extended duration of use.
5.4 Migraine
NEXTSTELLIS is contraindicated in females who have migraines with aura [see Contraindications (4)]. Discontinue NEXTSTELLIS in females using NEXTSTELLIS who develop new migraines that are recurrent, persistent, or severe. Discontinue NEXTSTELLIS if there is an increased frequency or severity of migraines during CHC use (which may be prodromal of a cerebrovascular event).
Migraines with aura increase the risk for stroke. This stroke risk is further increased in females who have migraines with aura with use of CHCs.
5.5 Malignant Neoplasms
Breast Cancer
NEXTSTELLIS is contraindicated in females who currently have or have had breast cancer because breast cancer may be hormonally sensitive [see Contraindications (4)].
Epidemiology studies have not found a consistent association between use of combined oral contraceptives (COCs) and breast cancer risk. Studies do not show an association between ever (current or past) use of COCs and risk of breast cancer. However, some studies report a small increase in the risk of breast cancer among current or recent users (<6 months since last use) and current users with longer duration of COC use [see Postmarketing Experience (6.2)].
Cervical Cancer
A causal relationship between the use of CHCs and the development of cervical cancer and intraepithelial neoplasia has not been clearly established. In observational studies, the use of oral hormonal contraceptives in females for five years or more, compared to females who did not use oral hormonal contraceptives, was associated with an increased risk of cervical cancer and intraepithelial neoplasia. In these studies, the use of oral hormonal contraceptives in females for 10 years or more, compared to females who received oral hormonal contraceptives for 5-9 years, was associated with an increased risk of cervical cancer and intraepithelial neoplasia. Limitations in these epidemiologic studies include potential recall bias, differences in sexual behavior, and other factors such as establishing whether there were data on persistent high-risk Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) infection.
5.6 Liver Disease
Elevated Liver Enzymes
NEXTSTELLIS is contraindicated in females with acute hepatitis or severe (decompensated) cirrhosis [see Contraindications (4)]. Withhold or permanently discontinue NEXTSTELLIS for persistent or significant elevation of liver enzymes. NEXTSTELLIS can cause elevated liver enzymes.
Liver Tumors
NEXTSTELLIS is contraindicated in females with hepatic adenomas and malignant liver tumors [see Contraindications (4)]. CHCs increase the risk of hepatic tumors, particularly hepatic adenomas. Rupture of hepatic adenomas may cause death from abdominal hemorrhage.
5.7 Risk of Liver Enzyme Elevations with Concomitant Hepatitis C Treatment
CHCs, such as NEXTSTELLIS, are contraindicated for use with Hepatitis C drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir (with or without dasabuvir) [see Contraindications (4)]. Discontinue NEXTSTELLIS prior to starting therapy with the combination drug regimen ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir (with or without dasabuvir). NEXTSTELLIS can be restarted approximately 2 weeks following completion of treatment with this hepatitis C combination drug regimen.
During clinical trials with the above-mentioned Hepatitis C combination drug regimen, ALT elevations greater than 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN), including some cases greater than 20 times the ULN, were significantly more frequent in females using ethinyl estradiol (EE)-containing drugs, such as CHCs. Females using medications containing estrogens other than EE had a rate of ALT elevation similar to those not receiving any estrogens. NEXTSTELLIS contains E4 rather than EE, but as no data are available for co-administration with this Hepatitis C combination drug regimen, caution is warranted.
5.8 Glucose Tolerance and Hypertriglyceridemia
Glucose Tolerance
Carefully monitor females with prediabetes and diabetes who are using NEXSTELLIS. NEXTSTELLIS may decrease glucose tolerance [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
5.9 Gallbladder Disease and Cholestasis
Consider discontinuing NEXTSTELLIS in females with symptomatic gallbladder disease or cholestatic disease. Studies suggest an increased risk of developing gallbladder disease among CHC users. Use of CHCs may also worsen existing gallbladder disease.
A past history of CHC-related cholestasis predicts an increased risk with subsequent CHC use. Females with a history of pregnancy-related cholestasis may be at an increased risk for CHC-related cholestasis.
5.10 Effect on Binding Globulins
Increase the dosage of thyroid hormone replacement therapy as needed in females taking NEXTSTELLIS [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. The estrogen component of NEXTSTELLIS may increase the serum concentrations of thyroxine-binding globulin, sex hormone-binding globulin, and cortisol-binding globulin.
5.11 Bleeding Irregularities and Amenorrhea
Unscheduled Bleeding and Spotting
Females using NEXTSTELLIS may experience unscheduled (breakthrough or intracyclic) bleeding and spotting, especially during the first 4 months of use. Bleeding irregularities may resolve over time or by changing to a different contraceptive product. If bleeding persists or occurs after previously regular cycles, evaluate for causes such as pregnancy or malignancy.
Unscheduled bleeding was defined as bleeding or spotting that occurred on Day 4 through Day 24 of a 28-day cycle. Based on subject diaries from C302 (US/CA), the proportion of subjects reporting unscheduled bleeding or spotting per 28-day cycle decreased over time: 30.3% at Cycle 1 versus 17.4% at Cycle 12. The mean number of unscheduled bleeding/spotting days per cycle also gradually decreased over time, with a mean of 0.4 (± 1.42) bleeding days at Cycle 1, versus a mean of 0.2 (± 0.98) bleeding days at Cycle 12.
Absence of Scheduled Bleeding
Females who use NEXTSTELLIS may experience absence of scheduled (withdrawal) bleeding, even if they are not pregnant [See Adverse Reactions (6)]. The proportion of subjects reporting absence of scheduled bleeding remained constant overall, with on average 15.5% of subjects reporting absence of scheduled bleeding from Cycles 1 through 12.
If scheduled bleeding does not occur, consider the possibility of pregnancy. If the patient has not adhered to the prescribed dosing schedule (missed one or two active tablets or started taking them on a day later than prescribed), consider the possibility of pregnancy at the time of the first missed period and perform appropriate diagnostic measures.
After discontinuation of NEXTSTELLIS, amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea may occur, especially if these conditions were pre-existent.
5.12 Depression
Monitor females with a history of depression and discontinue NEXTSTELLIS if depression recurs to a serious degree. Data on the association of COCs with onset of depression or exacerbation of existing depression are limited.
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions with the use of COCs are discussed elsewhere in labeling:
- Serious cardiovascular events including venous and arterial thromboembolism [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hyperkalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Liver disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of one drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data provided reflect the experience with the use of NEXTSTELLIS in two large prospective studies, one in Europe/Russia (C301) and one in North America (C302) (N = 3,632) of NEXTSTELLIS for the prevention of pregnancy in females 16-50 years of age. The mean duration of NEXTSTELLIS exposure was 317 and 257 days for the respective studies. The study population was 27 years of age on average, with a mean BMI of 25 kg/m2. The racial distribution was 83% White; 11% Black; 3% Asian; and 3% Other.
| Preferred Term (PT) | Participants with Adverse Reaction – US/Canada Phase 3 trial (n [%]) (N = 2073)* | Participants with Adverse Reaction – Two Phase 3 trials (n [%]) (N=3632)† |
|---|---|---|
|
||
| Any adverse reaction‡ | 1205 (58.1) | 2126 (58.5) |
| Mood disturbance§ | 226 (10.9) | 329 (9.1) |
| Bleeding irregularities¶ | 201 (9.7) | 393 (10.8) |
| Breast symptoms# | 110 (5.3) | 197 (5.4) |
| HeadacheÞ | 100 (4.8) | 227 (6.3) |
| Dysmenorrheaß | 84 (4.1) | 133 (3.7) |
| Weight increasedà | 68 (3.3) | 108 (3.0) |
| Acneè | 66 (3.2) | 136 (3.7) |
| Libido decreased/lostð | 27 (1.3) | 72 (2.0) |
Adverse Reactions Leading to Study Discontinuation (> 1%)
Of 3,632 females in two clinical studies for prevention of pregnancy in females 16-50 years of age, 9.6% discontinued due to an adverse reaction; the most frequent adverse reaction leading to discontinuation was bleeding irregularity (2.8%). Six subjects (0.17%) discontinued study participation due to new onset of migraine with aura; two subjects (0.05%) discontinued due to severe migraine.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
Five studies that compared breast cancer risk between ever-users (current or past use) of COCs and never-users of COCs reported no association between ever use of COCs and breast cancer risk, with effect estimates ranging from 0.90 - 1.12 (Figure 2).
Three studies compared breast cancer risk between current or recent COC users (<6 months since last use) and never users of COCs (Figure 2). One of these studies reported no association between breast cancer risk and COC use. The other two studies found an increased relative risk of 1.19 - 1.33 with current or recent use. Both of these studies found an increased risk of breast cancer with current use of longer duration, with relative risks ranging from 1.03 with less than one year of COC use to approximately 1.4 with more than 8-10 years of COC use.
Figure 2 Relevant Studies of Risk of Breast Cancer with Combined Oral Contraceptives
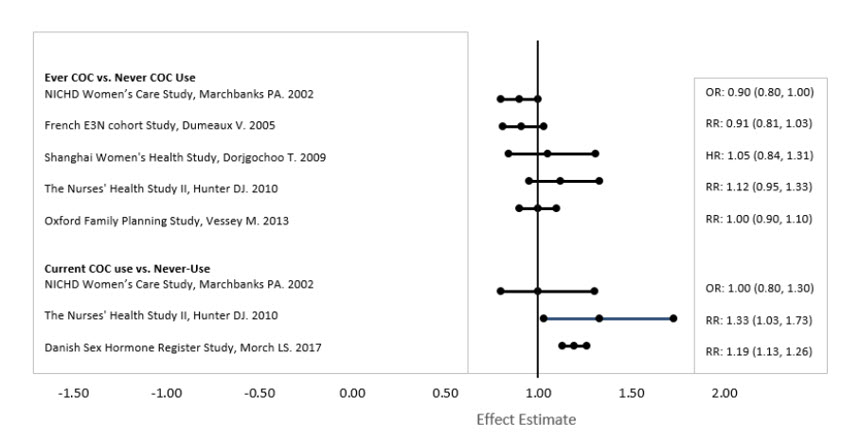
RR = relative risk; OR = odds ratio; HR = hazard ratio. "ever COC" are females with current or past COC use; "never COC use" are females that never used COCs.
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on Hormonal Contraceptives
Clinically significant drug interactions with other drugs that affect NEXTSTELLIS are presented in Table 5.
| CYP3A Inducers | ||
| Clinical Effect | DRSP is a CYP3A4 substrate. Concomitant use with strong CYP3A inducers or certain moderate or weak CYP3A inducers may decrease DRSP exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may lead to contraceptive failure. | |
| Prevention or Management | Strong CYP3A Inducers | Avoid concomitant use. If concomitant use is unavoidable, use an alternative contraceptive method (e.g., intrauterine system) or backup non-hormonal contraceptive method during coadministration and up to 28 days after discontinuation of the strong CYP3A inducer. |
| Moderate and Weak CYP3A Inducers | Use an alternative or backup contraceptive method during coadministration and up to 28 days after discontinuation of the CYP3A inducer, unless the Prescribing Information of the specific moderate or weak CYP3A inducer indicates there is no clinically significant interaction with NEXTSTELLIS. | |
| Strong CYP3A Inhibitors | ||
| Clinical Effect | DRSP is a CYP3A4 substrate. Concomitant use with a strong CYP3A inhibitor may increase DRSP exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may increase the risk of adverse reactions of NEXTSTELLIS, including hyperkalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. | |
| Prevention or Management | Consider monitoring serum potassium concentration in patients who take a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor long-term and concomitantly with NEXTSTELLIS. | |
| Drugs that May Reduce the Absorption of NEXTSTELLIS | ||
| Clinical Effect | Concomitant use with drugs such as bile acid sequestrants may decrease the E4 and DRSP exposure, which may lead to contraceptive failure and/or an increase in breakthrough bleeding. | |
| Prevention or Management | Separate time of administration of NEXTSTELLIS and the concomitant drug. Refer to the concomitant drug's Prescribing Information for additional information. | |
7.2 Effects of NEXTSTELLIS on Other Drugs
Table 6 includes clinically significant drug interactions with NEXTSTELLIS that affect other drugs.
| Anti-Diabetic Drugs | |
| Clinical Effect | Concomitant use of NEXTSTELLIS may reduce the blood glucose lowering effect of anti-diabetic drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2). |
| Prevention or Management | Increase frequency of glucose monitoring and increase anti-diabetic drug dosage, as needed, based on glucose levels. |
| Drugs that may increase serum potassium concentration | |
| Clinical Effect | There is a potential for an increase in serum potassium concentration in females taking NEXTSTELLIS with other drugs that may increase serum potassium concentration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. |
| Prevention or Management | Monitor serum potassium concentration in females at increased risk for hyperkalemia. |
| Lamotrigine | |
| Clinical Effect | Concomitant use of NEXTSTELLIS may decrease lamotrigine exposure [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], which may reduce efficacy of lamotrigine. |
| Prevention or Management | Adjust lamotrigine dosage as recommended in its Prescribing Information based on NEXTSTELLIS initiation or discontinuation. |
| Systemic Corticosteroids | |
| Clinical Effect | Concomitant use of NEXTSTELLIS may increase the exposure of certain systemic corticosteroids, which may increase the risk of corticosteroid-related adverse reactions [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2). |
| Prevention or Management | Follow the recommendation for the corticosteroid in accordance with its Prescribing Information. Consider more frequent monitoring for corticosteroid adverse reactions when used concomitantly with NEXTSTELLIS. |
| Thyroid Hormone Replacement Therapy | |
| Clinical Effect | Concomitant use of NEXTSTELLIS may increase thyroid-binding globulin concentration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. |
| Prevention or Management | Monitor thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) level and follow the recommendation for thyroid hormone replacement in accordance with its Prescribing Information. |
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Discontinue NEXTSTELLIS if pregnancy occurs, because there is no reason to use hormonal contraceptives during pregnancy [see Contraindications (4)]. Epidemiologic studies and meta-analyses have not found an increased risk of genital or nongenital birth defects (including cardiac anomalies and limb-reduction defects) following exposure to COCs before conception or during early pregnancy. Reproductive toxicity studies performed with E4 alone have shown expected pharmacologic effects in animals, which are considered consistent with estrogen exposure.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4 percent and 15 to 20 percent, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Contraceptive hormones and/or metabolites are present in human milk. COCs can reduce milk production in breast-feeding females. This reduction can occur at any time but is less likely to occur once breast-feeding is well established. When possible, advise the nursing woman to use other methods of contraception until she discontinues breast-feeding [see also Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. The developmental and health benefits of breast-feeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for NEXTSTELLIS and any potential adverse effects on the breast-fed child from NEXTSTELLIS or from the underlying maternal condition.
After oral administration of DRSP 3 mg/EE 30 µg, about 0.02% of the DRSP dose was excreted into the breast milk of postpartum females within 24 hours. This results in a potential maximal daily dose of less than 1 µg DRSP in an infant.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of NEXTSTELLIS have been established in females of reproductive potential. The study population of C302 [see Clinical Studies (14)] was in females of reproduction age 16-50 years of age. Use of NEXTSTELLIS before menarche is not indicated.
8.5 Geriatric Use
NEXTSTELLIS has not been studied in postmenopausal females and is not indicated in this population.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
NEXTSTELLIS is contraindicated in females with hepatic impairment [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3)]. The mean exposure to drospirenone (DRSP) in females with moderate liver impairment is approximately three times higher than the exposure in females with normal liver function. NEXTSTELLIS has not been studied in females with severe hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
NEXTSTELLIS is contraindicated in females with renal impairment [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
In subjects with creatinine clearance (CLcr) of 50–79 mL/min, serum DRSP levels were comparable to those in a control group with CLcr ≥ 80 mL/min. In subjects with CLcr of 30–49 mL/min, serum DRSP concentrations were on average 37% higher than those in the control group. In addition, there is a potential to develop hyperkalemia in subjects with renal impairment whose serum potassium is in the upper reference range, and who are concomitantly using potassium sparing drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Drug Interactions (7.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.8 Race/Ethnicity
No clinically significant difference was observed between the pharmacokinetics of E4 or DRSP depending on race [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage of CHCs may cause nausea, vomiting, and severe headaches. Individual reports of thromboembolic complications and vaginal bleeding have occurred from overdosage. Pediatric patients with unintended CHC ingestion have reported nausea and vomiting and some developed irritability and drowsiness; rare reports described vaginal bleeding.
11 DESCRIPTION
NEXTSTELLIS® (drospirenone and estetrol tablets) is an oral contraceptive. It is supplied in a transparent PVC/aluminum blister card containing 28 tablets:
- 24 pink active tablets contain 3 mg drospirenone and 14.2 mg of estetrol on the anhydrous basis. Drospirenone is a synthetic progestin and estetrol is a synthetic estrogen.
- 4 white inert tablets.
The chemical name for estetrol is estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,15α,16α,17α-tetrol monohydrate. It has a molecular formula of C18H24O4∙H2O and a molecular weight of 322.4 g/mol, equivalent to 304.4 g/mol (anhydrous). Estetrol has the following chemical structure:
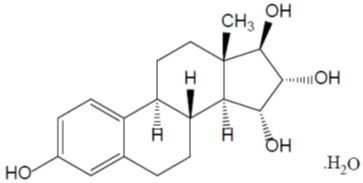
Estetrol (monohydrate) is a white to off-white crystalline solid that is poorly soluble in water and aqueous solutions. It is soluble in methanol, ethanol, sparingly soluble in acetone, and slightly soluble in ethyl acetate and acetonitrile.
Drospirenone is chemically described as (6R,7R,8R,9S,10R,13S,14S,15S,16S,17S)-1,3',4',6,6a,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,15a,16-hexadecahydro10,13-dimethylspiro-[17H-dicyclopropa-[6,7:15,16]cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene-17,2'(5H)-furan]-3,5'(2H)-dione). It has a molecular weight of 366.5 g/mol, a molecular formula of C24H30O3, and the structural formula below:
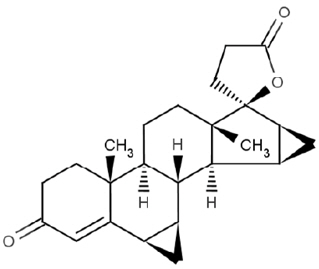
Drospirenone is a white to almost white or slightly yellow crystalline powder. It is a neutral molecule with slight solubility in water.
The active tablet is a 6 mm, round pink film-coated tablet which contains 3 mg of drospirenone and 15 mg of estetrol as the monohydrate, equivalent to 14.2 mg of estetrol on the anhydrous basis, and the following inactive ingredients: corn starch, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, povidone, and sodium starch glycolate. Each tablet is embossed on one side with a drop-shaped logo. The pink film-coating has the following inactive ingredients: hydrogenated cottonseed oil, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, iron oxide red, talc, and titanium dioxide.
The inert tablet is a 6 mm, round white film-coated tablet which contains the inactive ingredients corn starch, lactose monohydrate, and magnesium stearate. Each tablet is embossed on one side with a drop-shaped logo. The film-coating has the following inactive ingredients: hydrogenated cottonseed oil, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, talc, and titanium dioxide.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Drospirenone is a spironolactone analogue with anti-mineralocorticoid and antiandrogenic activity. The estrogen in NEXTSTELLIS is estetrol, a synthetic analogue of a native estrogen present during pregnancy, that is selective for nuclear estrogen receptor-α (ER-α) and ER-β.
Effect of NEXTSTELLIS on ovarian function
A clinical study evaluated the effect of NEXTSTELLIS on the suppression of ovarian activity as assessed by measurement of follicle size via transvaginal ultrasound and serum hormone (progesterone and estradiol) analyses in two of the three treatment cycles (24-day active tablet period plus 4-day pill-free period). No ovulations were observed during the study.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At a dose 5 times the maximum recommended dose (i.e., supra-therapeutic dose of 15 mg DRSP /71 mg E4), NEXTSTELLIS does not prolong the QT interval to any clinically relevant extent.
Drugs That Have the Potential to Increase Serum Potassium Concentration
There is a potential for an increase in serum potassium concentration in females taking NEXTSTELLIS with other drugs that may increase serum potassium concentration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
A drug-drug interaction study of DRSP 3 mg /E2 1 mg versus placebo was performed in 24 mildly hypertensive postmenopausal females taking enalapril maleate 10 mg twice daily. Potassium concentrations were obtained every other day for a total of 2 weeks in all subjects. Mean serum potassium concentrations in DRSP/E2 treatment group relative to baseline were 0.22 mEq/L higher than those in the placebo group. Serum potassium concentrations also were measured at multiple time points over 24 hours at baseline and on Day 14. On Day 14, the ratios for serum potassium Cmax and AUC in the DRSP/E2 group to those in the placebo group were 0.955 (90% CI: 0.914, 0.999) and 1.010 (90% CI: 0.944, 1.08), respectively. No patient in either treatment group developed hyperkalemia (serum potassium concentrations > 5.5 mEq/L).
Other PD effects of NEXTSTELLIS
Table 7 displays pharmacodynamic effects of CHCs on hemostatic, metabolic, and endocrine parameters.
| Category | Direction of Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Increase | Decrease | No change | |
| Coagulation Factors | ↑ Platelet count; factors II, VII antigen, VIII coagulant activity, IX, X, XII, VII-X complex, and beta-thromboglobulin; fibrinogen and fibrinogen activity; plasminogen antigen and activity | ↓(Accelerated) Prothrombin time, partial thromboplastin time, and platelet aggregation time ↓ Anti-factor Xa and antithrombin III, antithrombin III activity | |
| Corticosteroids | ↑ Corticosteroid-binding globulin (CBG), total circulating corticosteroids | - | - |
| Glucose | - | ↓ Glucose tolerance | - |
| Lipids | ↑ | ↓ Low-density lipoprotein concentration | Plasma high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and HDL2 cholesterol subfraction concentration, triglyceride levels |
| Mineralocorticoids | ↑ Aldosterone | ||
| Plasma proteins | ↑ Concentrations of angiotensinogen/renin substrate, alpha-1 antitrypsin, ceruloplasmin | - | - |
| Sex hormones | ↑ Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) | ↓ Possible decreased free testosterone concentrations ↓ Androstenedione, progesterone, free testosterone, estradiol | DHEA-S, FSH, LH,Dihydrotestosterone |
| Thyroid hormones | ↑ Thyroxin-binding globulin (TBG), total thyroid hormone levels, total T4 and T3 levels | ↓ T3 resin uptake | ↔ TSH, Free T4 and free T3 concentrations in females with normal thyroid function |
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion
The pharmacokinetic properties of E4 and DRSP following administration of NEXTSTELLIS are provided in TABLE 8.
| E4 | DRSP | |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax= Maximum plasma concentration; AUC0-t= Area under the plasma concentration-time curve integrated from time of administration (0) to time of last quantifiable observation (t); AUC0-INF= Area under the plasma concentration-time curve from time of administration extrapolated to infinity from AUC0-t; CI= Confidence interval; Tmax= Time to maximum concentration | ||
| Multiple-dose pharmacokinetics parameters | ||
| Mean (CV%) Cmax, ng/mL | 17.9 (68.1) | 48.7 (24.6) |
| Mean (CV%) AUC0-24h, ng*hr/mL | 59.1 (24.3) | 519.0 (27.7) |
| Dose Proportionality | 15 mg to 75 mg | 1-10 mg |
| Time to Steady State, days | 4 | 10 |
| Accumulation Ratio | 1.6 | 2.3 |
| Absorption | ||
| Median (range) Tmax, hours | 0.5 (0.5 to 2) | 1.0 (1.0 to 3.0) |
| Effect of high-fat meal (relative to fasting) | ||
| Geometric Mean (90% CI) Cmax, Ratio | 0.51 (0.37, 0.70) | 0.75 (0.66, 0.84) |
| Geometric Mean (90% CI) AUC0-INF, Ratio | 1.01 (0.86, 1.19) | 1.08 (1.02, 1.14) |
| Distribution | ||
| Plasma Protein Binding | 46% to 50% | 95% to 97%* |
| Elimination | ||
| Elimination Half-life, hours | 27† | 34 |
| Metabolism | ||
| Primary Pathways | Phase 2 metabolism to form glucuronide and sulphate conjugates which have negligible in-vitro estrogenic activity. In vitro studies show that UGT2B7 is the dominant UGT isoform that catalyzes the formation of E4-16-glucuronide | CYP3A4; two main metabolites: acid form of DRSP generated by opening of lactone ring and the 4,5-dihydrodrospirenone formed by reduction followed by sulfation. Both metabolites are not pharmacologically active. |
| Excretion | ||
| Primary Pathways | ||
| % Dose in Urine | 69% (0% unchanged) | 38% |
| % Dose in Feces | 22% (100% unchanged) | 44% |
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of E4 or DRSP in females were observed based on race/ethnicity (Japanese and Caucasian).
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of E4 is unknown.
The mean exposure to DRSP is approximately three times higher in females with moderate liver impairment than the exposure in females with normal liver function. The effect of severe hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of DRSP is unknown.
Patients with Renal Impairment
The effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of E4 is unknown. The mean serum DRSP concentrations increased by 37% in subjects with CLcr of 30 to 49 mL/min on a low potassium diet using potassium-sparing drugs. No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of DRSP were observed based on CLcr of 50 to 79 mL/min. DRSP treatment did not show any clinically significant effect on serum potassium concentration. Although hyperkalemia was not observed in the study, in five of the seven subjects who continued use of potassium-sparing drugs during the study, mean serum potassium concentrations increased by up to 0.33 mEq/L.
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitor: Concomitant use of a COC containing DRSP 3 mg/EE 20 µg with ketoconazole (strong CYP3A4 inhibitor) increased the AUC0-24h and Cmax of DRSP by 2.68-fold (90% CI: 2.44, 2.95) and 1.97-fold (90% CI: 1.79, 2.17), respectively.
CYP3A4 Inducer: Concomitant use of a COC containing DRSP 3 mg/EE 20 µg with high dose (strong CYP3A induction) and low dose of rifampin (weak CYP3A4 induction) decreased the AUC0-24h of DRSP by 86% (90% CI: 85%, 87%) and 30% (90% CI: 25%, 34%), respectively.
UGT2B7 Inhibitor: No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of NEXTSTELLIS were observed when used concomitantly with valproic acid (UGT2B7 inhibitor).
In Vitro Studies
E4 is not a substrate of CYP1A1, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2D6, CYP3A4, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT1, OAT3, OCT2, MATE1, MATE2-K. E4 is unlikely to induce CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP3A4 or inhibit CYP3A4, CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, UGT1A9, UGT2B7, drug transporters P-pg, BCRP, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OAT1, OAT3, OCT2, MATE1 and MATE2-K or at clinically relevant dose.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 24-month oral carcinogenicity study in mice with doses up to 10 mg/kg/day DRSP, equating to 2 times the maximum clinical exposure (based on AUC), there was an increase in carcinomas of the harderian gland in the high dose DRSP group. In a similar study in rats given doses up to 10 mg/kg/day DRSP, 10 times the maximum clinical exposure (based on AUC), there was an increased incidence of benign and total (benign and malignant) adrenal gland pheochromocytomas in the high dose DRSP group.
Mutagenesis studies for DRSP were conducted in vivo and in vitro and no evidence of mutagenic activity was observed. E4 is not considered to be genotoxic based on weight of evidence from in vivo and in vitro mutagenesis studies.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Pregnancy Prevention
The efficacy of NEXTSTELLIS was evaluated in a prospective, multicenter, open-label, single-arm study in North America (NCT02817841; C302) of one-year duration that enrolled 1,674 females 16 to 35 years of age. The mean age was 25.8 years and mean BMI was 25.8 kg/m2. Females with a BMI between 30 and 35 kg/m2 accounted for 22.3% of the study population. Females with a BMI greater than 35 kg/m2 were not enrolled in the study. The racial distribution was 70.1% Caucasian, 19.5% Black or African American, 4.8% Asian, 0.9% American Indian or Alaska native, 0.4% Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander and 4.2% other.
A total of 26 on-treatment pregnancies occurred in 1,524 females contributing 12,763 at-risk cycles. The overall Pearl Index was 2.65 (95% CI: 1.73-3.88) per 100 woman-years of use. Table 9 lists the Pearl Index by BMI subgroup. A trend of decreasing effectiveness with increasing BMI was observed in the study.
| Subgroup | N* | On-treatment pregnancies | At-risk cycles | Pearl Index (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study C302 | 1524 | 26 | 12,763 | 2.65 (1.73, 3.88) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | ||||
| < 30 | 1,187 | 20 | 10,113 | 2.57 (1.57, 3.97) |
| ≥ 30 to < 35† | 337 | 6 | 2,650 | 2.94 (1.08, 6.41) |
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
NEXTSTELLIS® (drospirenone and estetrol tablets) is available in a blister card, with 28 6-mm round, bi-convex film-coated tablets in the following order:
- 24 pink active film-coated tablets containing 3 mg drospirenone and 14.2 mg estetrol embossed with a drop-shaped logo on one side.
- 4 white inert film-coated tablets embossed with a drop-shaped logo on one side.
NEXTSTELLIS® is supplied in cartons containing 1 blister card of 28 tablets: NDC 51862-258-01.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-Approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions of Use).
Sexually Transmitted Infections
Advise females that NEXTSTELLIS does not protect against HIV infection or other sexually transmitted infections.
Important Administration Instructions and Instructions for Missed Doses
Instruct females to take one tablet daily by mouth at the same time every day. Advise patients about what to do in the event that pills are missed [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- Advise females starting NEXTSTELLIS to use additional nonhormonal contraception for 7 days after the first dose unless NEXTSTELLIS is started on the first day (Day 1) of menses [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]
- Advise females who miss more than two consecutive days of NEXTSTELLIS or experience vomiting or diarrhea for > 48 hours consecutively to use additional nonhormonal contraception for 7 days [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4)]
Thromboembolic Disorders and Other Vascular Problems [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Advise females that there is an increased risk of arterial and/or venous thrombotic/thromboembolic events with NEXTSTELLIS and the risk of arterial and/or venous thrombotic/thromboembolism is greater in smokers and females with preexisting medical conditions including hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, and obesity.
- Advise patients of the pertinent factors that further increase their risk and ways to diminish the risk, e.g., to stop smoking (if applicable).
- Advise patients to contact their healthcare professional for any signs or symptoms of arterial and/or VTE
- Advise patients to contact their healthcare professional if they will be immobilized for a prolonged period of time.
Hyperkalemia
Advise females to contact their healthcare professional if signs or symptoms of hyperkalemia develop [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Hypertension
Advise females that NEXTSTELLIS can cause an increase in blood pressure over time. Instruct patients to contact their healthcare professional if blood pressure increases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Liver Disease
Advise females that use of NEXTSTELLIS can cause elevated liver enzymes and can increase the risk of liver tumors. Instruct females to contact their healthcare professional for any signs or symptoms of liver disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Glucose Tolerance
Advise females that NEXTSTELLIS may decrease glucose tolerance. Instruct females with diabetes and prediabetes to contact their healthcare professional for any signs or symptoms of hyperglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Gallbladder Disease and Cholestasis
Advise females that use of NEXTSTELLIS is associated with an increased risk of developing and/or worsening gallbladder disease. Instruct patients to contact their healthcare professional for any signs or symptoms of gallbladder disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Bleeding Irregularities, Amenorrhea, and Pregnancy
Advise females that NEXTSTELLIS can cause unscheduled bleeding and spotting, as well as amenorrhea and oligomenorrhea. Advise females to contact their health care professional if amenorrhea occurs in two or more consecutive cycles or symptoms of pregnancy occur, e.g., morning sickness or unusual breast tenderness. Instruct females to stop NEXTSTELLIS if pregnancy is confirmed during use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Chloasma
Advise females that NEXTSTELLIS can cause chloasma and the risk is highest in females with a history of chloasma, especially chloasma gravidarum. Instruct females to take precautions to limit UVA and UVB exposure while using NEXTSTELLIS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)].
Lactation
Advise postpartum females that NEXTSTELLIS may reduce breast milk production. Advise females that this reduction is less likely to occur if breast-feeding is well established [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Drug Interactions
NEXTSTELLIS may interact with many drugs, foods, and dietary supplements. Therefore, advise females to report to their healthcare professional the use of any other prescription or nonprescription drugs or dietary supplements [see Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2)].
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
NEXTSTELLIS® (NEXT ste LIS)
(drospirenone and estetrol tablets)
for oral use
Important Information about taking NEXTSTELLIS
- Take 1 pill every day at the same time. Take the pills in the order directed on your blister pack.
- Swallow both the pink pills and white pills whole. You may take NEXTSTELLIS with or without food.
- Do not skip your pills, even if you do not have sex often. If you miss pills (including starting the pack late) you could get pregnant. The more pills you miss, the more likely you are to get pregnant.
- If you have trouble remembering to take NEXTSTELLIS, talk to your healthcare provider. When you first start taking NEXTSTELLIS, spotting or light bleeding in between your periods may occur. Contact your healthcare provider if this does not go away after a few months.
- Some females miss periods on hormonal birth control, even when they are not pregnant. However, if you miss a period and have not taken NEXTSTELLIS according to the directions, or miss 2 periods in a row, or feel like you may be pregnant, call your healthcare provider. If you have a positive pregnancy test, you should stop taking NEXTSTELLIS.
- If you have vomiting or diarrhea (within 3 to 4 hours after you take a pink active pill), take a new pink active pill that was scheduled for the next day as soon as possible. If possible, take the new pink active pill within 12 hours of the time you usually take it. If you miss more than 2 pink active pills, follow the instructions for "What Should I do if I miss any NEXTSTELLIS pills?"
- If you have vomiting or diarrhea for more than 2 days (48 hours) in a row, or if you take certain medicines, including some antibiotics and some herbal products such as St. John's Wort, your pills may not work as well. Use an additional non-hormonal birth control method, such as condoms or spermicide, until you talk to your healthcare provider.
- Talk to your healthcare provider before you have major surgery. Be sure to use another form of non-hormonal birth control (such as condoms or spermicide) if your healthcare provider tells you to stop NEXTSTELLIS before your surgery.
Before you start taking NEXTSTELLIS
- Decide what time of day you want to take your pill. It is important to take it at the same time every day and in the order as directed on your blister pack.
- Have backup non-hormonal birth control (such as condoms or spermicide) available and an extra full pack of pills if possible.
When should I start taking NEXTSTELLIS?
If you start taking NEXTSTELLIS and you have not used a hormonal birth control method before:
- Start on the first day (Day 1) of your natural menstrual period (Day 1 Start).
You do not need a back-up non-hormonal birth control method.
- If you start taking NEXTSTELLIS on any day other than the first day of your natural menstrual period, use a back-up non-hormonal birth control method (such as condoms or spermicide) until you have taken one (1) active (pink) pill every day for seven (7) days.
If you start taking NEXTSTELLIS and you are switching from another birth control pill:
- Start your new NEXTSTELLIS pack on the same day that you would start the next pack of your previous birth control method.
- Do not continue taking the pills from your previous birth control pack.
If you start taking NEXTSTELLIS and previously used a vaginal ring or transdermal patch:
- Start using NEXTSTELLIS on the day you would have reapplied the patch or inserted the vaginal ring.
If you start taking NEXTSTELLIS and you are switching from a progestin-only method such as an implant or injection:
- Start taking NEXTSTELLIS on the day of removal of your implant or on the day when you would have had your next injection.
If you start taking NEXTSTELLIS and you are switching from an intrauterine device or system (IUD or IUS):
- Start taking NEXTSTELLIS on the day of removal of your IUD or IUS.
- You do not need a non-hormonal back-up birth control method if your IUD or IUS is removed on the first day (Day 1) of your period. If your IUD or IUS is removed on any other day, use a non-hormonal back-up birth control method such as condoms or spermicide for the first 7 days that you take NEXTSTELLIS.
If you start taking NEXTSTELLIS after you have given birth and you were more than 20 weeks pregnant:
- Do not start NEXTSTELLIS earlier than 4 weeks after you have given birth.
- If your menstrual cycles have returned, see "If you start taking NEXTSTELLIS and you have not used a hormonal birth control method before".
- If your menstrual cycles have not returned, use additional non-hormonal birth control (such as condoms or spermicide) for the first 7 days that you take NEXTSTELLIS.
If you start taking NEXTSTELLIS after an abortion or miscarriage and you were 14 weeks pregnant or less:
- If within the first 7 days of abortion or miscarriage:
- Use additional non-hormonal birth control such as condoms or spermicide for the first 7 days you take NEXTSTELLIS.
- After the first 7 days following an abortion or miscarriage:
If you start taking NEXTSTELLIS after an abortion or miscarriage and you were more than 14 weeks pregnant but 20 weeks pregnant or less:
- Start NEXTSTELLIS after 4 weeks following the abortion or miscarriage.
- If your menstrual cycles have returned, see "If you start taking NEXTSTELLIS and you have not used a hormonal birth control method before".
- If your menstrual cycles have not returned, use additional non-hormonal birth control (such as condoms or spermicide) for the first 7 days you take NEXTSTELLIS.
Keep a calendar to track your menstrual period. If this is the first time you are taking birth control pills, read, "When should I start taking NEXTSTELLIS?" above and follow these instructions.
Before you start taking your pills
- Decide what time of day you want to take your pill. It is important to take it at about the same time every day.
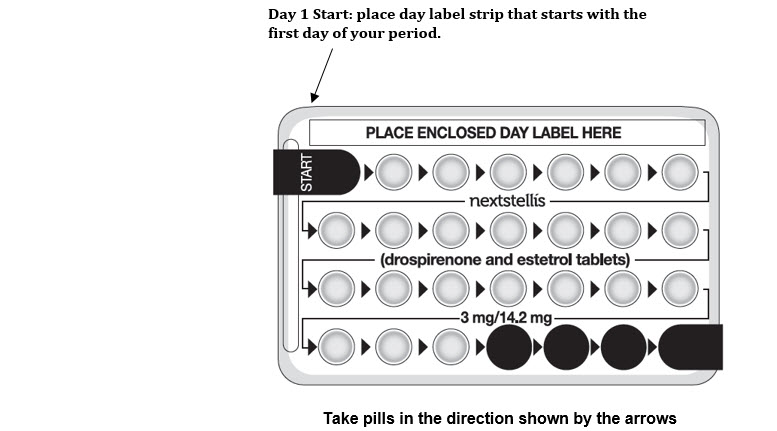
- Look at your NEXTSTELLIS pill pack. See the Figure below. The pill pack has 24 "active" pink pills (with hormone) to take for 3 weeks and 3 days, followed by 4 "inactive" white pills (without hormone).
When to start the first pack of pills
Start on the first day (Day 1) of your natural menstrual period (Day 1 start). Pick a time of day which will be easy to remember.
Day 1 Start:
- Pick the day label strip that starts with the first day of your period.
- Place this day label strip on the pill dispenser over the area that says: "Place enclosed day label here".
- Take the first active pink pill of the first pack during the first 24 hours of your period. Take 1 pill every day in the order of the blister pack, at the same time each day, for 28 days.
- The day after taking the last pill on Day 28 from the blister pack, start taking the first pill from the new pack, on the same day of the week as the first pack. Take the first pill in the new pack whether or not you are having your period.
What should I do if I miss any NEXTSTELLIS pills?
If you miss 1 pink active pill in Weeks 1, 2 or 3, follow these steps:
- Take it as soon as you remember. Take the next pill at your regular time. This means you may take 2 pills in 1 day.
- Then continue taking 1 pill every day until you finish the pack.
- You do not need to use a back-up non-hormonal birth control method if you have sex.
If you miss 2 or more pink active pills in Week 1 or Week 2 of your pack, follow these steps:
- Take 1 missed pill as soon as possible and take the pill scheduled for the current day (which means you will take 2 pills in 1 day).
- Throw away the other missed pills.
- Then continue taking 1 pill a day until the pack is finished.
- Use a back-up non-hormonal birth control method (such as condoms or spermicide) if you have sex during the first 7 days after missing your pills.
If you miss 2 pink active pills in a row in week 3 of your pack, follow these steps:
- Take 1 missed pill as soon as possible and take the pill scheduled for the current day (which means you will take 2 pills in 1 day).
- Throw away the other missed pills.
- Continue taking 1 pill a day until you finish the pink active pills in the pack. Then throw away the inactive white pills in the pack.
- Start a new pack of pills the next day.
- If you miss your period this month, call your healthcare provider because you might be pregnant.
- You could become pregnant if you have sex during the first 7 days after you restart your pills. You should use a back-up non-hormonal birth control method (such as condoms or spermicide) if you have sex during the first 7 days after you restart your pills.
If you miss 1 or more white inactive pills, follow these steps:
- Skip the missed pill days.
- Continue taking 1 pill a day until the pack is finished.
If you have any questions or are unsure about the information in this leaflet, call your healthcare provider. They have a more technical leaflet called the Professional Labeling which you may read.
This Patient Information and Instructions for Use have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
Mayne Pharma
Raleigh, NC 27609
Approved: 02/2023
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - Kit Carton
NDC 51862-258-01
nextstellis®
(drospirenone and
estetrol tablets)
3 mg/14.2 mg
This product (like all oral contraceptives)
is intended to prevent pregnancy.
It does not protect against HIV infection
(AIDS) and other sexually transmitted
diseases.
Rx Only
1 Blister Card Containing 28 Tablets
mayne pharma